
Oxidation process of low-grade vanadium slag in presence of Na2CO3
LI Xin-sheng, XIE Bing, WANG Guang-en, LI Xiao-jun
College of Materials Science and Engineering, Chongqing University, Chongqing 400044, China
Received 20 October 2010; accepted 20 January 2011
Abstract: The oxidation process of low-grade vanadium slag in the presence of Na2CO3 was investigated by XRD, SEM/EDS and TG-DSC techniques. The results show that the vanadium slag is oxidized in a temperature range from 273 to 700 °C. Olivine phases and spinel phases are completely decomposed at 500 and 600 °C, respectively. Most of water-soluble sodium vanadates are formed between 500 and 600 °C. When roasting temperature reaches above 700 °C, the vanadium-rich phases of sodium vanadates can be obviously observed. However, at temperature above 800 °C, the samples are sintered. Most of the vanadium is enwrapped by glassy phase compounds which lead to the decrease of the leaching rate of vanadium. At the same time, the effect of roasting temperature on extraction of vanadium and characterization of leach residues were discussed.
Key words: low-grade vanadium slag; Na2CO3; roasting; vanadium-rich phases; leaching
1 Introduction
Vanadium is an important metal used almost exclusively in ferrous and non-ferrous alloys due to its physical properties such as high tensile strength, hardness and fatigue resistance [1]. Vanadium-bearing slag is one of the most important sources of vanadium, which accounts for 58% for the production of vanadium [2]. The main processes for production of vanadium slag include shaking ladle process, hot metal ladle process and converter process [3-4]. The representative vanadium extraction route mainly consists of the following procedures: sodium salt roasting, water leaching, solution purification and V precipitation [5]. It is well known that oxidation roasting is a key stage in the whole process of vanadium extraction. The objective of salt roasting is to convert vanadium to water-soluble sodium salt [6]. During slat roasting, the oxidation process of vanadium slag in the presence of Na2CO3 under oxidizing atmosphere is quite complex, which mainly includes oxidation of iron, decomposition of silicate phases and spinel phases, and formation of vanadates, chromates, silicates, titanates, aluminates and ferrates of sodium depending on the quantity of Na2CO3 used [7].
Many studies have focused on the vanadium recovery from vanadium slag through optimizing the process conditions to develop an economical and effective production route. Studies on oxidation process indicate that conversion rate of vanadium is strongly dependent on the roasting temperature, additive content, particle size and roasting time [7-10]. However, to the best of our knowledge, few reports are available on the oxidation process of vanadium slag in the presence of Na2CO3.
Therefore, in this work, it is attempted to investigate the oxidation process of vanadium slag in the presence of Na2CO3 at different temperatures. The change in mineralogy of vanadium slag was studied by XRD, SEM/EDS and TG-DSC techniques, the effect of roasting temperature on vanadium extraction and characterization of leach residues were also discussed.
2 Experimental
2.1 Materials
The vanadium slag used was obtained by a duplex process from Panzhihua Steel & Iron (Group) Corporation, Sichuan, China. After crushing, magnetic separation and grinding, the materials were screened through a 75 μm sieve. Figure 1 depicts the XRD pattern of the vanadium slag, which mainly consists of vanadium-bearing spinel phases (i.e. (Fe, Mn) V2O4) silicate phases (i.e. (Fe, Mn)2SiO4) and minor phase V3O4 (V2O3 and VO) [11-13]. The chemical composition of vanadium slag is given in Table 1. Compared with the normal metallurgical slag with 12%-25% V2O5 [1], the vanadium slag in this study contains lower V, higher Si, Ti and Ca content.
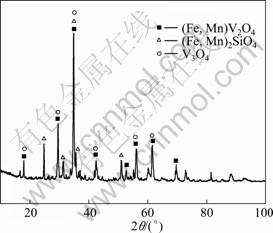
Fig. 1 XRD pattern of vanadium slag
Table 1 Chemical composition of vanadium slag (mass fraction, %)

2.2 Sample preparation
The vanadium slag was thoroughly mixed with analytical reagent Na2CO3 at a mass ratio of 41:9. The mixed samples were put and heated in an electrical resistance furnace at required temperature for 2.5 h. A temperature controller was used to maintain the predetermined furnace temperature, with the furnace door kept open to maintain an oxidizing atmosphere. The samples were stirred to be fully oxidized in order to achieve high conversion rate of vanadium during roasting. Then the samples were removed from the furnace and cooled to room temperature.
The roasted samples at different temperatures were leached with distilled water under required conditions (leaching temperature of 90 °C, leaching time of 30 min and liquid to solid ratio of 5:1 mL/g). Then the solid residues were separated via filtration from the solution.
2.3 Characterization methods
The mixed samples were measured by thermal gravimetry (TG) and differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) with NETZSCH STA 449C Thermal analyzer at a rate of 10 °C/min in air atmosphere. The crystalline phases of the samples were analyzed by X-ray diffractometer (Rigaku D/max 2500PC) using Cu Ka radiation. The surface morphologies of the samples were observed using scanning electronic microscopy (SEM Tescan VEGA II) and the surface compositions were measured by INCA Energy 350 energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS) attachment.
Vanadium concentration in the leaching solution was analyzed by the ammonium ferrous sulfate titration method.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 XRD analysis
Figure 2 shows the XRD patterns of the roasted samples at different temperatures. It can be observed from Fig. 2 that the diffraction peaks of crystalline structure gradually broaden and weaken from 300 to 600 °C, indicating olivine phases and spinel phases in vanadium slag are increasingly destroyed. Compared with vanadium slag, the roasted sample at 300 °C presents a series of FeOx (4/3<x<3/2) diffraction peaks. It can be inferred that FeOx comes from the oxidation of iron or Fe2+ in fayalite.
When the roasting temperature is 500 °C, the characteristic peaks of olivine phases disappear. Inverse spinel (Fe, Mn)2VO4 is observed, indicating partial Fe2+ is oxidized to Fe3+ in spinel phases. Minor phases, such as Na5V12O32, NaV6O15, NaVO3, Na4V2O7, R2O3 (R= Ti and V or V and Cr), vanadium oxides VnO2n-1 (2≤n≤8) and V6O13 (V2nO5n-2) are generated, which indicates some V3+ in spinel phases has been oxidized to V4+ or V5+. At 600 °C, the characteristic peaks of spinel phases disappear. Whereas, the diffraction peak of Fe2O3 appears, and its relative intensity increases with the increase of roasting temperature. The characteristic peak of qingheiite (Na3Mn3Mg2Al2(PO4)6) is also detected.
When the roasting temperature reaches 700 °C, major phases such as acmite (NaFeSi2O6) and sodium pyroxene (NaTiSi2O6), and minor phases such as sodium iron titanate (NaFeTiO4) and morimotoite (Ca3TiFeSi3O12) are observed. As the roasting temperature increases to 900 °C, the major phases such as Fe2O3 and Ca3TiFeSi3O12 are detected. Formation of these products may be attributable to higher content of Si, Ti and Ca and may have an adverse effect on the diffusion of vanadium, oxygen, sodium, etc. It is well known that high content of silicon and calcium in vanadium slag have an adverse effect on the vanadium extraction, which leads to the loss of vanadium due to the formation of low-melting sodium iron silicates (Na2O·Fe2O3·4SiO2) which retain the vanadium oxides in water-insoluble solid solution and formation of water-insoluble calcium vanadates in oxidation roasting process [6]. SADYKHOV [14] also found that SiO2 combines Na2O to form sodium silicates, which restricts the formation of sodium vanadates when the titanium- vanadium slags are roasted.
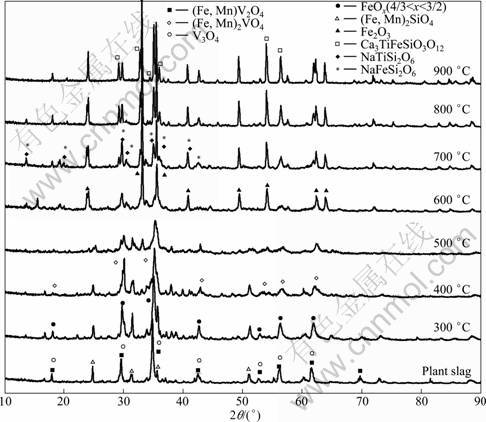
Fig. 2 XRD patterns of roasted samples at different temperatures
3.2 SEM analysis
The SEM micrographs of samples at different temperatures are presented in Fig. 3, and corresponding representative results of SEM/EDS analysis are listed in Table 2. Figure 3 (a) shows the SEM image of vanadium slag after milling. According to the results of SEM/EDS analysis, Ti, V and Cr are mainly concentrated in spinel phases, while Si and Ca mainly in silicate phases. Fe, Mn, O and Mg coexist in both phases.
When the roasting temperature is below 500 °C, the samples exist mainly in the form of irregular shape, as shown in Figs. 3(b) and (c). Results from SEM/EDS analysis demonstrate that the samples are mainly composed of spinel phases, silicate phases and unreacted Na2CO3. At 600 °C, strip matters are observed, as shown in Fig. 3(d). When the roasting temperature is 700 °C, it can be clearly seen from Fig. 3(e) that the samples mostly cohere together and present bright areas and dark grey areas. According to SEM/EDS analysis, it should be noted that V, Si and Na are concentrated in dark grey areas, and Mn and Fe are concentrated in bright areas. O and Ti coexist in both areas. This indicates that vanadium-rich phases form.
However, at temperature of 800 °C or higher, the samples are sintered in the experiments. The contrast between the bright areas and dark grey areas becomes more apparent, as observed in Figs. 3(f) and (g). According to SEM/EDS analysis (spots F3 and G2), the dark grey agglomerates contain a relatively high content of sodium, vanadium, silicon and iron. The result is consistent with that of SILITONGA and PROSSER [15], which indicates glassy phase compounds form. This is detrimental to the following water leaching process. In addition, according to SEM/EDS analysis, it should be mentioned that carbon contents in samples are higher, indicating that Na2CO3 can be enwrapped when samples are sintered in a short period at 900 °C.
3.3 TG-DSC analysis
Figure 4 shows the TG-DSC curves of mixed sample. It can be seen from the TG curve that the mass increment is 0.67% from 273 to 504 °C. Combining with XRD analysis, the mass increment is attributable to the oxidation of Fe2+ and Mn2+in olivine phases and partial Fe2+, Mn2+, Cr3+and V3+ in spinel phases. Meanwhile, partial Na2CO3 can react with the above-oxidized products to give sodium salts and carbon dioxides. When the temperature is above 504 °C, the mass loss increases rapidly, indicating Na2CO3 gradually decomposes with the increase of temperature. According to the DSC data, there is an endothermic peak at 583.6 °C with a mass loss of 0.21% due to the decomposition of spinel phases. At 700 °C, the mass loss of the sample is about 2.20%, which is in agreement with the experimental result.
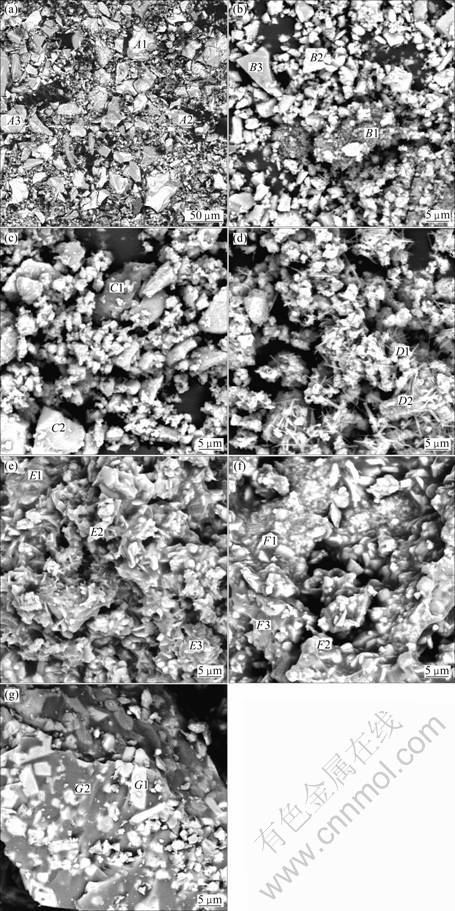
Fig. 3 BSE images of roasted samples at different temperatures: (a) Vanadium slag; (b) 400 °C; (c) 500 °C; (d) 600 °C; (e) 700 °C; (f) 800 °C; (g) 900 °C
Table 2 EDS analysis of roasted samples (mass fraction, %)
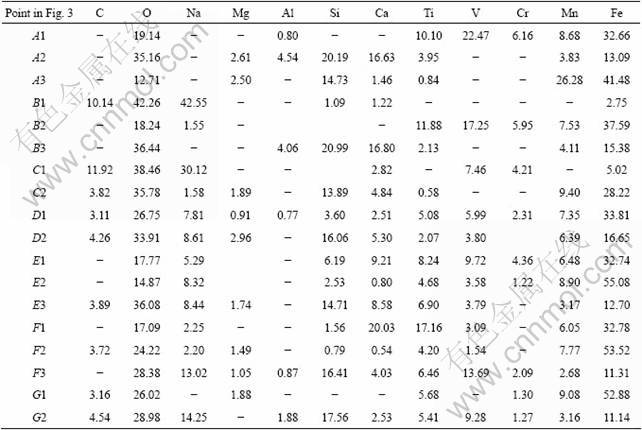

Fig. 4 TG-DSC curves of mixed sample
3.4 Effect of roasting temperature on leaching rate of vanadium
Figure 5 presents the effect of roasting temperature on the leaching rate of vanadium. As can be seen in Fig. 5, the leaching rate of vanadium increases with increasing temperature and reaches a maximum value of 90% at 700 °C, then decreases with higher roasting temperature. It is worth emphasizing that the leaching rate of vanadium has a rapid improvement at temperature between 500 and 600 °C. Combining with XRD analysis, it can be inferred that most spinel phases are oxidized and most water-soluble sodium vanadates are formed in this temperature range. When roasting temperature is above 800 °C, the samples are sintered, and most vanadium is enwrapped by glassy phase compounds, which is the main reason leading to the decrease of leaching rate of vanadium.
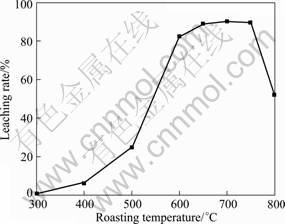
Fig. 5 Effect of roasting temperature on leaching rate of vanadium
3.5 Characterization of leach residues
Figure 6 depicts the XRD patterns of the leach residues at different temperatures. From the XRD analysis, the major mineral matters of leach residues are hardly changed except that sodium salts dissolve in water. Figure 7 shows the SEM images of leach residues at different temperatures. It can be seen from SEM/EDS analysis (Table 3) that the spinel phases still exist in Figs.7 (a) and (b). Comparing Fig. 3 with Fig. 7, there are obvious differences in morphologies between samples before and after leaching at 600 and 700 °C, respectively. This is because the soluble sodium salts in roasted samples dissolve in water in the leaching process. After water leaching, it can be observed that the samples are in the form of strip shape and agglomeration. However, when roasting temperature is higher than 800 °C, the micrographs of the samples present no changes before and after leaching due to the sintering and agglomeration of samples.

Fig. 6 XRD patterns of leach residues at different temperatures
Table 3 EDS analysis of leach residues (mass fraction, %)
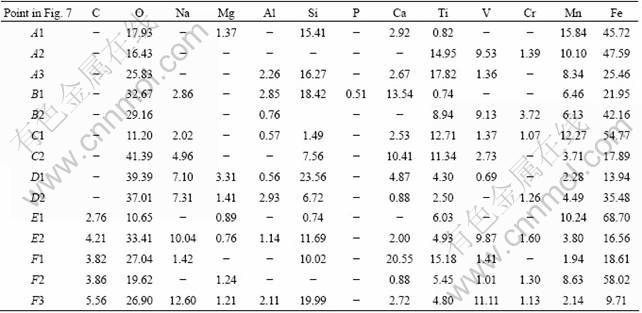

Fig. 7 BSE images of leach residues at different temperatures: (a) 400 °C; (b) 500 °C; (c) 600 °C; (d) 700 °C; (e) 800 °C; (f) 900 °C
4 Conclusions
1) Vanadium slag is oxidized in the temperature range from 273 to 700 °C in the presence of Na2CO3. Olivine phases and spinel phases in vanadium slag gradually decompose and oxidize with increasing temperature in oxidation roasting process. They are completely decomposed at 500 and 600 °C, respectively.
2) The Fe (Fe2+) in vanadium slag is oxidized to Fe2O3 through formation of a series of FeOx (4/3<x<3/2). The diffraction peak of Fe2O3 appears at about 600 °C and its relative intensity increases with the increase of roasting temperature.
3) Most of water-soluble sodium vanadates are formed between 500 and 600 °C. When the roasting temperature reaches above 700 °C, the V-rich phases of sodium vanadates can be obviously observed. However, at temperatures above 800 °C, the samples are sintered and most of the vanadium is enwrapped by glassy phase compounds, which leads to the decrease of the leaching rate of vanadium.
4) Soluble sodium salts dissolve in water during the leaching process, while other mineral matters of leach residues are hardly changed. At temperature above 800 °C, the micrographs of the samples present no changes before and after leaching due to the agglomeration and sintering of samples.
References
[1] MOSKALYK R R, ALFANTATAZI A M. Processing of vanadium: A review [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2003, 16(9): 793-805.
[2] RAJA B V R. Vanadium market in the world [J]. Steelworld, 2007, 13(2): 19-22.
[3] HUANG D X. Vanadium extraction and steelmaking [M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2000: 55-78. (in Chinese)
[4] ZHOU Jia-cong, CHEN Xiao-ping. Vanadium resource exploitation 40 years in panzhihua [R] Panzhihua: Panzhihua Iron and Steel Corporation, 2005: 45-102. (in Chinese)
[5] BRADBURY D S. The production of vanadium pentoxide [C]//TANER M F, RIVEROS P A, DUTRIZAC J E, GATTRELL M, PERRON L. Vanadium-geology, processing and applications: As held at the 41st Annual Conference of Metallurgists of CIM (COM). Montreal: The Canadian Institute of Mining, Metallurgy and Petroleum, 2002: 115-130.
[6] GUPTA C K, KRISHNAMURTY N. Extractive metallurgy of vanadium [M]. Amsterdam: Elsevier Science Publishers, 1992: 203-380.
[7] GABRA G, MALINSKY I. A comparative study of the extraction of vanadium from titaniferous magnetite and slag [C]// SOHN H Y, CARLSON O N, SMITH J T. Extractive metallurgy of refractory metals. Chicago: The TMS-AIME, 1981: 167-189.
[8] PENG Yi, XIE Tun-liang, ZHOU Zong-quan, PAN Ping, SUN Chao-hui. Preparation V2O5 from low grade vanadium- bearing slag of high calcium and high phosphor [J]. Ferro-alloy, 2007, 195(4): 18-23. (in Chinese)
[9] ZHANG Hui. Determination of the optimum conditions of roasting of vanadium slag by orthogonal test [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2003, 35(3): 29-31. (in Chinese)
[10] JENA B C, DRESLER W, REILLY I G. Extraction of titanium, vanadium and iron from titanomagnetite deposits at pipestone lake [J]. Minerals Engineering, 1995, 8(1-2): 159-168.
[11] CHEN Dong-hui. Theory of chemical formation of vanadium slag [J]. Vanadium Titanium, 1993, 4: 31-39. (in Chinese)
[12] DIAO J, XIE B, JI , GUO X, WANG Y, LI X. Growth of spinel crystals in vanadium slag and their characterization [J]. Crystal Research and Technology, 2009, 44 (7): 707-712.
[13] QING Xue-mei, XIE Bing, LI Dan-ke, HUANG Qing-yun. Study on oxidation of vanadium in molten iron and formation of vanadium-iron spinels [J]. The Chinese Journal of Process Engineering, 2009, 9(s1): 122-126. (in Chinese)
[14] SADYKHOV G B. Oxidation of titanium-vanadium slags with the participation of Na2O and its effect on the behavior of vanadium [J]. Russian Metallurgy, 2008 (6): 449-458.
[15] SILITONGA M, PROSSER A P. The chemistry of vanadium losses in the alkali-roast process [J]. Proceedings of Australasian Institute of Mining and Metallurgy, 1976, 259(9): 13-18.
低品位钒渣在碳酸钠存在下的氧化过程
李新生, 谢 兵, 王广恩, 李晓军
重庆大学 材料科学与工程学院, 重庆 400044
摘 要:利用XRD, SEM/EDS和TG-DSC等手段对低品位钒渣在Na2CO3存在条件下的氧化过程进行检测。结果表明:钒渣的氧化温度范围为273 至 700 °C,橄榄石相与尖晶石相彻底分解的温度分别是500和600 °C,大部分水溶性的钒酸盐在500与600 °C之间形成。当温度达到700 °C以上时,钒酸盐富集相明显可见,但焙烧温度在800 °C以上时,样品发生烧结,并且钒被形成的玻璃相包裹,导致其浸出率下降。同时,研究不同焙烧温度对钒浸出率的影响, 并对浸出残渣进行分析。
关键词:低品位钒渣;碳酸钠;焙烧;钒富集相;浸出
(Edited by FANG Jing-hua)
Foundation item: Project (2008AA031104) supported by the National High-tech Research and Development Program of China; Project (2010063003) supported by the Sharing Fund of Large-scale Equipment of Chongqing University, China
Corresponding author: XIE Bing; Tel: +86-23-65102469; E-mail: bingxie@cqu.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(11)60942-4