铜渣煅烧过程中的多相转变
刘慧利,胡建杭,王华,王超,李娟琴
(昆明理工大学 冶金与能源工程学院,冶金节能减排教育部工程研究中心,云南 昆明,650093)
摘要:利用X射线衍射、傅里叶变换红外光谱和扫描电镜等分析测试手段对铜渣在煅烧过程中的多相转变进行研究。结果表明:铜渣原渣从800 ℃开始发生物相转变,由Fe2SiO4转变为Fe3O4和非晶SiO2,Fe2SiO4向Fe3O4的转变在1 000 ℃结束。850 ℃时开始发生Fe3O4向α-Fe2O3的转变,1 050 ℃时转变基本完成,1 000~1 050 ℃是Fe3O4向α-Fe2O3转变的主要温度区间。Fe2SiO4向Fe3O4的转变和Fe3O4向α-Fe2O3的转变在850~1 050 ℃同时发生。Fe2SiO4煅烧生成的非晶SiO2从900 ℃开始析晶,析晶产物为石英晶体,1 000 ℃时开始发生石英向方石英的转变。与煅烧时间的延长相比,煅烧温度的升高对Fe3O4转变为α-Fe2O3更有利,但煅烧时间的延长使生成的α-Fe2O3颗粒大小更均匀,颗粒形状更接近于球形。
关键词:铜渣;煅烧;多相转变;铁橄榄石;磁铁矿;赤铁矿;二氧化硅
中图分类号:TF09;O614.8;O613.7 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2013)08-3159-07
Multiphase transformation during process of copper slag calcination
LIU Huili, HU Jianhang, WANG Hua, WANG Chao, LI Juanqin
(Engineering Research Center of Metallurgical Energy Conservation & Emission Reduction, Ministry of Education,
Faculty of Metallurgical and Energy Engineering, Kunming University of Science and Technology, Kunming 650093, China)
Abstract: Multiphase transformation during the process of copper slag calcination was studied by X-ray diffraction, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and scanning electron microscope. The results show that the transformation of Fe2SiO4 into Fe3O4 and amorphous SiO2 in the initial copper slag takes place when the temperature is about 800 ℃. The transformation of Fe2SiO4 into Fe3O4 is completed at about 1 000 ℃. The transformation of Fe3O4 into α-Fe2O3 occurs within a wide temperature range from 850 to 1 050 ℃. The transformation of Fe2SiO4 into Fe3O4 and Fe3O4 into α-Fe2O3 occurs simultaneously over temperatures between 850~1 050 ℃. Amorphous SiO2 generated from Fe2SiO4 decomposition begins to crystallize at 900 ℃. The product of amorphous SiO2 crystallization is identified as quzrtz. The transformation of quartz into cristobalite takes place at 1 000 ℃. Compared with the prolonging of calcination time, the increase in calcination temperature is benefitial for the transformation of Fe3O4 to α-Fe2O3. The prolonging of calcination time makes the grains of α-Fe2O3 more uniform in size and spherical in shape.
Key words: copper slag; calcination; multiphase transformation; fayalite; magnetite; hematite; silica
铜渣是火法炼铜工艺在造锍熔炼和冰铜吹炼工序中产生的废渣。铜渣中含有Fe,Cu,Zn,Co和Ni等有价金属以及SiO2,Al2O3,CaO和MgO等氧化物,其中Fe元素和SiO2的含量(质量分数)一般分别在40%和30%以上。目前我国铜渣资源化利用率较低,大部分铜渣处于堆存状态,既占用土地、污染环境,又造成铜渣中多种矿物资源的浪费。回收铜渣中的矿物资源,特别是含量较高的Fe元素和SiO2,对实现铜渣的资源化利用具有重要意义。铜渣中的Fe元素主要以铁橄榄石(Fe2SiO4)的形式存在,少量存在于磁铁矿(Fe3O4)中。以铁橄榄石形式存在的Fe采用传统矿物加工和冶金方法难以直接回收利用[1],而通过氧化煅烧的方法可使铜渣中的Fe2SiO4转变为Fe3O4, Fe2O3和SiO2[2-4]。通过对煅烧后的铜渣进行磁选、浮选和湿法浸出等操作可有效回收铜渣中的铁氧化物(Fe3O4,Fe2O3)和SiO2[5-7]。目前,对铜渣煅烧过程相转变的研究只限于铜渣中Fe2SiO4转变为Fe3O4[8-9],然后通过磁选回收高炉炼铁原料—铁精矿(Fe3O4),对于铜渣煅烧过程中完整的多相转变,特别是煅烧时Fe3O4转变为Fe2O3和Fe2SiO4热分解产物SiO2在煅烧过程中相转变的研究至今未见报道。因此,本文作者采用X线衍射、傅里叶变换红外光谱和扫描电镜技术对铜渣在750~1 050 ℃范围内煅烧的多相转变过程进行了研究,为认识铜渣煅烧温度提高后的矿相转变情况和后续对铜渣的资源化利用提供理论依据。
1 实验
1.1 原材料
铜渣样品是云南铜业股份有限公司铜精矿艾萨炉熔炼电炉贫化后分离出的工业废渣,经空气缓冷收集所得。铜渣的化学组成(质量分数)为:Fe 40.4%;Cu 0.75%;S 1.15%;CaO 4.33%;Al2O3 4.90%;MgO 2.38%;SiO2 31.1%;其他16.14%,其中Fe含量为铜渣中全铁(TFe)的含量。
1.2 样品制备与表征
铜渣经机械破碎后,筛分出其中粒径为0.425~0.850 mm的颗粒备用。实验过程中每次取100 g铜渣置于刚玉坩埚中,放到马弗炉中加热煅烧,煅烧温度设定为750,800,850,900,950,1 000和1 050 ℃,煅烧时间为5,15和20 h,随后样品随炉温冷却至室温,得到不同煅烧条件下的铜渣样品。
样品物相组成采用日本理学D/Max-3B型X线衍射仪(XRD)测定,Cu Kα射线源,电压35 KV,电流20 mA,扫描速度10 (°)/min,扫描范围2θ为10°~90°。样品红外光谱(FT-IR)采用德国Bruker VERTEX-70测试,光谱扫描范围1 400~400 cm-1。采用Philip公司的XL30ESEM扫描电镜(SEM)对样品的微观形貌进行观测。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 X线衍射分析
铜渣原渣和750~1 050 ℃煅烧5 h铜渣的XRD谱如图1所示。由图1可知:原渣主要由Fe2SiO4和Fe3O4 2种物相组成,其他少量物相(CaO,MgO和Al2O3等)被Fe2SiO4相包裹,而且含量较低,XRD分析技术无法检出。750 ℃煅烧铜渣的XRD谱与原渣基本一致,表明750 ℃时铜渣尚未发生明显的物相转变。800~900 ℃煅烧铜渣的主要物相为Fe2SiO4和Fe3O4,随煅烧温度升高,Fe2SiO4特征峰强度降低,Fe3O4特征峰强度增加。800 ℃时Fe3O4特征峰强度的增加和Fe2SiO4特征峰强度的降低表明铜渣中的Fe2SiO4开始发生物相转变。850 ℃时,在24.1°,33.2°,49.4°,54.1°和62.4°(2θ)处出现强度较弱的Fe2O3特征峰,表明在850 ℃时开始有少量Fe2O3晶体形成,而且其晶体结构为三角晶系、晶胞呈斜方六面体的α-Fe2O3。900 ℃时,在20.8°和26.6°(2θ)处出现强度很弱的石英晶体(SiO2)特征峰,表明900 ℃时开始有少量石英晶体结晶。当煅烧温度由900 ℃升至1 000 ℃时,Fe3O4,α-Fe2O3和石英特征峰强度增加,Fe2SiO4特征峰强度继续降低并在1 000 ℃时完全消失。1 000 ℃时,在21.8°(2θ)处出现强度较弱的方石英特征峰,表明1 000 ℃时开始有方石英晶体形成。当煅烧温度升至1 050 ℃时,Fe3O4特征峰强度明显降低,α-Fe2O3特征峰强度显著增加,石英特征峰强度降低,方石英特征峰强度则明显增加。1 050 ℃煅烧5 h铜渣的主要物相为α-Fe2O3,次要物相为Fe3O4、石英和方石英。

图1 铜渣原渣和750~1 050 ℃煅烧5 h铜渣的XRD谱
Fig. 1 XRD patterns of initial copper slag and copper slag calcined at 750~1 050 ℃ for 5 h
图2所示为1 000 ℃煅烧5~20 h铜渣的XRD谱。由图2所知:1 000 ℃煅烧5 h铜渣的主要物相为Fe3O4,次要物相为α-Fe2O3、石英和方石英。随煅烧时间延长,Fe3O4特征峰强度明显降低,α-Fe2O3特征峰强度显著增加,石英特征峰强度略有降低,方石英特征峰强度增加。1 000 ℃煅烧20 h铜渣的主要物相为α-Fe2O3,次要物相为Fe3O4、石英和方石英。

图2 1 000 ℃煅烧5~20 h铜渣的XRD谱
Fig. 2 XRD patterns of copper slag calcined at 1 000 ℃ for 5~20 h
2.2 红外光谱分析
图3所示为铜渣原渣和800~1 050 ℃煅烧5 h铜渣的FT-IR谱。由图3可知:原渣的FT-IR谱主要表现为Fe2SiO4络阴离子[SiO4]4-中复杂Si—O基团的振动。原渣在1 200~400 cm-1波数范围内存在3个吸收带,位于1 000~850 cm-1之间波数为946.3和871.4cm-1的吸收峰归属于Si—O键的非对称伸缩振动,位于850~600 cm-1之间波数为827.0 cm-1的吸收峰归属于Si—O键的对称伸缩振动,位于600~400 cm-1之间波数为559,501和472 cm-1的吸收峰归属于Si—O键的非对称弯曲振动。
由图3可知:经煅烧处理后,铜渣的FT-IR谱发生明显变化,800 ℃煅烧铜渣在1 069 cm-1处出现新吸收峰,表明此温度下有新物相生成。1 100~1 050 cm-1波数范围内强度较强且形状较宽的吸收峰是非晶SiO2的特征吸收峰[10],该峰由SiO2中Si—O键的不对称伸缩振动引起,而且800 ℃煅烧铜渣的XRD图中未检测到石英晶体,因此新生成的物相为非晶SiO2。由于Fe2SiO4络阴离子[SiO4]4-中4个Si—O键键强不同,800 ℃煅烧铜渣在1 000~850 cm-1范围内出现多峰分裂[11],原渣中946 cm-1处吸收峰向高波数移动、峰宽变宽并分裂出2个峰,分别位于960和949 cm-1,2峰分裂不深;871 cm-1处吸收峰也向高波数移动并分别在916和875 cm-1处分裂出2个峰,2峰分裂明显。当煅烧温度由800 ℃升至900 ℃时,1 069 cm-1附近吸收峰强度增强并且向高波数移动至1076 cm-1,表明随煅烧温度升高,铜渣中非晶SiO2的含量增加[12];960,949,827,564,501和472 cm-1附近吸收峰强度降低;916和875 cm-1处2峰分裂加深、峰强降低;900 ℃时,1 165 cm-1处出现弱肩峰,同时在796和779 cm-1附近出现微弱吸收峰,这3个峰是石英族矿物的特征吸收峰[13],表明此温度下有微量石英晶体析出,与图1中XRD分析结果一致。当煅烧温度由900 ℃升至1 050 ℃时,1 076 cm-1处吸收峰移动至1 088 cm-1,吸收峰强度增强并在1 000 ℃时达到最大值,960,949,916和875 cm-1处吸收峰强度降低并在1 000 ℃时完全消失,表明1 000 ℃时Fe2SiO4完全转变为铁氧化物和SiO2,煅烧铜渣中SiO2的含量在此温度下达到最大值;1 165 cm-1处吸收峰强度增加,796和779 cm-1处2峰分裂加深、峰强增强,表明随温度升高,煅烧铜渣中石英晶体(石英、方石英)的含量增加、结晶度提高;600~400 cm-1波数范围归属于Si—O键的非对称弯曲振动,Fe2SiO4和SiO2在此波数范围内均存在红外吸收并且其吸收峰位置基本相同,472 cm-1处吸收峰是SiO2红外吸收谱的第2个强吸收峰;1 050 ℃煅烧铜渣FT-IR谱呈现出明显的石英晶体的红外特征吸收。

图3 铜渣原渣和800~1 050 ℃煅烧5 h铜渣的FT-IR谱
Fig. 3 FT-IR spectra of initial copper slag and copper slag calcined at 800~1 050 ℃ for 5 h
图4所示为1 000 ℃煅烧5~20 h铜渣的FT-IR谱。由图4可知:1 000 ℃不同煅烧时间铜渣FT-IR谱均表现为石英的特征吸收峰,各吸收峰强度及位置基本一致,1 165 cm-1处吸收峰强度略有增加,1 088 cm-1处吸收峰峰宽变窄,796和779 cm-1 2个峰分裂加深,表明随煅烧时间延长石英的结晶度增加。
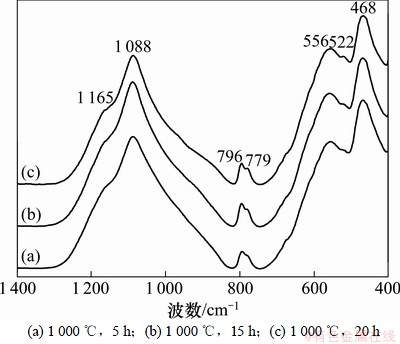
图4 1 000 ℃煅烧5~20 h铜渣的FT-IR谱
Fig. 4 FT-IR spectra of copper slag calcined at 1 000 ℃ for 5~20 h
2.3 显微结构与形貌特征
图5所示为铜渣原渣和不同煅烧条件下铜渣的SEM像。从图5(a)可以看出:原渣中存在典型的Fe2SiO4,Fe3O4和玻璃相结构。玻璃相是原渣的基体物质,Fe2SiO4和Fe3O4等晶体结构嵌入在玻璃相中。Fe2SiO4是原渣中的主要物相,颜色深灰,主要呈现为连续条柱状或树突状晶体[14],少量呈现为板状结构。Fe3O4是渣中最早析出的结晶相,浅灰色,呈现为粒状或不规则状,分布于Fe2SiO4相和玻璃相中,少量Fe3O4颗粒被Fe2SiO4相包裹形成同时含有两种物相的晶体结构。
煅烧温度和煅烧时间对铜渣的微观形貌有很大影响,图5(b)~(h)为不同煅烧条件下铜渣的SEM像。如图5(b)所示,经800 ℃煅烧5 h后,原渣中大部分Fe2SiO4结构遭到破坏,Fe2SiO4晶体溶解于玻璃相中,SEM像中仅余少量呈现为放射状、树枝状和多变状的Fe2SiO4和Fe3O4晶体结构。煅烧后铜渣样品表面分别呈现亮区和暗区,利用EDS对煅烧铜渣表面随机点元素组成进行的分析表明,亮区的主要成分为铁氧化物,暗区为SiO2相。850 ℃煅烧5 h铜渣的形貌如图5(c)所示,除可以观察到零星分布的粒径在2~4 μm的Fe3O4颗粒外,还有大量细小的Fe3O4“晶核”产生,Fe2SiO4完全溶解于玻璃相中。煅烧温度升至900 ℃时,从图5(d)中可观察到更多Fe3O4“晶核”的析出,少量“晶核”已长大;温度为1 000 ℃时(见图5(e)),大量Fe3O4晶体颗粒析出,颗粒大小不均匀,粒径分布范围为1~5 μm,Fe3O4晶体颗粒边缘粗糙,与SiO2相无明显界限;温度为1 050 ℃时(见图5(f)),Fe3O4转变为α-Fe2O3,α-Fe2O3颗粒长得更大,颗粒粒径分布更均匀,平均粒径为3 μm左右,α-Fe2O3晶体与SiO2相边缘界限清晰。由图5(c)~(f)可见:随煅烧温度升高,Fe3O4和α-Fe2O3析出量增加,颗粒尺寸增大,此现象是晶体生长和大颗粒吞并小颗粒的Ostwald熟化效应共同作用的结果。
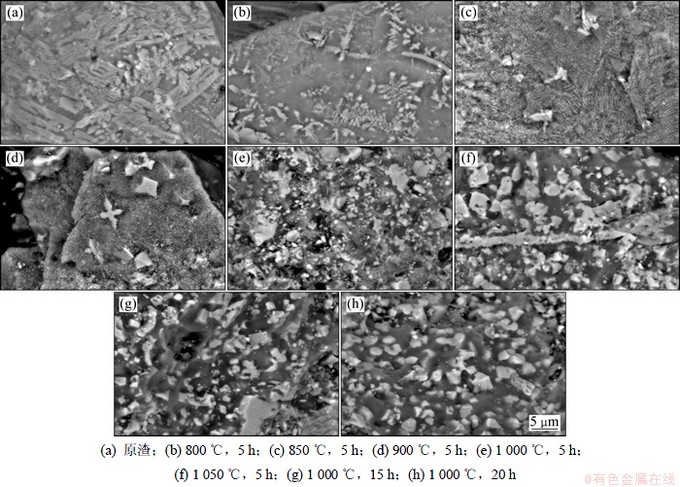
图5 铜渣原渣与煅烧铜渣的SEM像
Fig. 5 SEM images of initial and calcined copper slag under different conditions
1 000 ℃煅烧5~20 h铜渣的SEM像如图5(e),5(g)和5(h)所示。可见:随煅烧时间延长,铁氧化物(Fe3O4和α-Fe2O3)析出量无明显增加,但煅烧时间的延长为铁氧化物颗粒生长提供了良好的动力学条件,促进了颗粒长大,同时使颗粒大小变得更加均匀,1 050 ℃煅烧20 h铜渣中α-Fe2O3颗粒形状呈现为准球形。
在煅烧过程中,铜渣体相内的Fe通过新形成的铁氧化物层迁移到铜渣气固反应界面,发生氧化反应首先生成Fe3O4“晶核”。由于新生成Fe3O4“晶核”之间距离很小,多个“晶核”之间可相互连接并长大,相互连接过程会造成表面能的降低,使得通过扩散作用来完成的物质传递过程成为自发过程,随煅烧温度的升高和煅烧时间的延长,小颗粒不断消失,大颗粒不断形成。
2.4 铜渣煅烧过程多相转变分析
铜渣中Fe2SiO4的含量占铜渣矿物组成的70%以上,Fe3O4只占铜渣矿物组成的5%左右。因此,铜渣煅烧过程主要发生Fe2SiO4的氧化反应。由XRD和FT-IR谱可知:铜渣原渣从800 ℃开始发生物相转变。XRD谱证明Fe3O4是铜渣800 ℃煅烧产物,同时,在FT-IR谱1 069 cm-1处出现宽而钝的非晶SiO2的特征峰,表明非晶SiO2也是铜渣800 ℃煅烧产物。1 000 ℃时,XRD图中Fe2SiO4特征峰消失,说明Fe2SiO4向Fe3O4的转变在1 000 ℃结束,Fe3O4的含量在此温度下达到最大。850 ℃时,XRD谱显示生成少量α-Fe2O3,说明从850 ℃时开始发生Fe3O4向α-Fe2O3的转变,1 050 ℃时转变基本完成,1 000~1 050 ℃是Fe3O4向α-Fe2O3转变的主要温度区间。850~1 050 ℃范围内,Fe2SiO4向Fe3O4的转变和Fe3O4向α-Fe2O3的转变同时发生。当煅烧温度达到1 100 ℃或以上时,铜渣会出现软化和部分熔融现象,本文将铜渣煅烧最高温度控制在1 050 ℃。
900 ℃时,XRD谱中出现石英的特征峰,FT-IR谱在1 165,796和779 cm-1也出现微弱的石英特征峰,表明Fe2SiO4氧化生成的非晶SiO2从900 ℃开始析晶,析晶产物为石英晶体。1 000 ℃时,XRD谱中出现方石英的特征峰并且1 050 ℃煅烧铜渣的XRD谱中石英特征峰强度降低、方石英特征峰强度增加,表明1 000 ℃时开始发生石英向方石英的转变。1 000 ℃出现方石英晶体的现象从相变热力学上来说是异常的,870~1 470 ℃是鳞石英的热力学稳定区,方石英在此温度范围内并不能稳定存在,而且根据文献[15],石英向方石英转变的温度区间为1 470~1 670 ℃。然而,许多非金属矿物类材料在900~1 200 ℃的热处理过程中均可生成方石英,例如稻壳经900 ℃煅烧后可析出方石英[16],长白山硅藻土于1 100 ℃左右开始转变为方石英[17],煤系高岭石在1200℃煅烧时也有方石英生成[18],上述资料说明方石英在热力学亚稳态下形成是一种普遍现象。造成上述现象的原因可能有:(1) 非晶SiO2和石英的微区结构与方石英类似,由非晶SiO2和石英转变为方石英容易进行[19]。(2) 铜渣中的Fe元素以及CaO,MgO和Al2O3等矿化剂能够降低方石英结晶温度、提高析晶速度。Mollah等[20]发现褐煤燃烧飞灰在1 000 ℃热处理时有方石英晶体形成,作者认为飞灰中的碱金属氧化物(Na2O和K2O)和碱土金属氧化物(CaO和MgO)以及Fe2O3等降低了方石英的形成温度。陈美怡等[16]也认为Mg,K和Ca等杂质元素有利于降低方石英的结晶温度。非晶SiO2和石英向方石英转变时会发生Si—O—Si键的断裂与重建,金属离子能使Si—O—Si键断裂数目增多并形成较多晶格缺陷,这些缺陷的存在提高了体系自由能,增加了SiO2反应活性,有利于方石英晶体的成核,从而降低方石英的形成温度。(3) 铜渣煅烧的氧化性气氛有利于方石英晶体形成,空气中的O2能够促使石英颗粒发生表面析晶现象[21],从而促进方石英晶体析出。
文献[16-18]中方石英形成过程与本研究有所不同,前者方石英是由非晶SiO2直接转变形成,中间无石英晶体存在,而本研究中方石英则由非晶SiO2经历中间产物石英转变形成。本研究中非晶SiO2直接转变为热力学稳定石英晶体的现象可能是由下面2个原因造成的:(1) 非均匀成核作用,非晶SiO2具有的与石英晶体类似的微区结构会增大石英晶体的成核速率;(2) 铜渣中大量存在的Fe元素(Fe2SiO4和Fe3O4)有利于石英晶体的形成,Nanri等[22]探讨了Fe元素对非晶SiO2转变为石英晶体的影响及其机理,认为Fe2SiO4的存在是非晶SiO2直接转变为石英晶体的必备条件。
1 000 ℃煅烧5~20 h铜渣主要发生Fe3O4向α-Fe2O3和石英向方石英的多相转变。与煅烧时间的延长相比,煅烧温度的升高对Fe3O4转变为α-Fe2O3更有利,1 050 ℃煅烧5 h铜渣中α-Fe2O3衍射峰强度比1 000 ℃煅烧20 h铜渣中α-Fe2O3衍射峰强度更强,但是煅烧时间的延长对Fe2O3颗粒形状和颗粒大小均有很大影响,煅烧时间越长,α-Fe2O3颗粒形状越趋近于球形,颗粒大小越均匀。
根据上述分析,铜渣煅烧过程中多相转变反应可总结为:
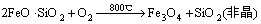 (1)
(1)
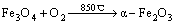 (2)
(2)
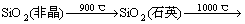
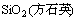 (3)
(3)
3 结论
(1) 铜渣原渣由Fe2SiO4和Fe3O4 2种物相组成,其中Fe2SiO4的含量远大于Fe3O4的含量,铜渣煅烧过程主要发生Fe2SiO4的氧化反应。原渣从800 ℃开始发生物相转变,由Fe2SiO4转变为Fe3O4和非晶SiO2,Fe2SiO4向Fe3O4的转变在1 000 ℃结束。850 ℃时开始发生Fe3O4向α-Fe2O3的转变,1 050 ℃时转变基本完成,1 000~1 050 ℃是Fe3O4向α-Fe2O3转变的主要温度区间。850~1 050 ℃,Fe2SiO4向Fe3O4和Fe3O4向α-Fe2O3的转变同时发生。
(2) 非晶SiO2高温煅烧产物为方石英。方石英由非晶SiO2经历中间产物石英转变形成,石英结晶温度为900 ℃,石英向方石英转变起始温度为1 000 ℃。
(3) 与煅烧时间的延长相比,煅烧温度的升高对Fe3O4转变为α-Fe2O3更有利,但煅烧时间的延长使生成的α-Fe2O3颗粒大小更均匀,颗粒形状更接近于球形。
参考文献:
[1] 杨慧芬, 景丽丽, 党春阁. 铜渣中铁组分的直接还原与磁选回收[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2011, 21(5): 1165-1170.
YANG Huifen, JING Lili, DANG Chunge. Iron recovery from copper-slag with lignite-based direct reduction followed by magnetic separation[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2011, 21(5): 1165-1170.
[2] Gyurov S, Kostova Y, Klitcheva G, et al. Thermal decomposition of pyrometallurgical copper slag by oxidation in synthetic air[J]. Waste Manage Res, 2011, 29(2): 157-164.
[3] Marghussiana V K, Maghsoodipoorb A. Fabrication of unglazed floor tiles containing Iranian copper slags[J]. Ceramics International, 1999, 25(7): 617-622.
[4] Coruh S, Ergun O N, Cheng T W. Treatment of copper industry waste and production of sintered glass-ceramic[J]. Waste Manage Res, 2006, 24(3): 234-241.
[5] Banza A N, Gock E, Kongolo K. Base metals recovery from copper smelter slag by oxidising leaching and solvent extraction[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2002, 67(1/2/3): 63-69.
[6] Shen H T, Forssberg E. An overview of recovery of metals from slags[J]. Waste Manage, 2003, 23(10): 933-949.
[7] 曹洪杨, 付念新, 王慈公, 等. 铜渣中铁组分的选择性析出与分离[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2009(2): 8-11.
CAO Hongyang, FU Nianxin, WANG Cigong, et al. Selective precipitation and separation of Fe components from copper smelting slags[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2009(2): 8-11.
[8] 曹洪杨, 付念新, 张力, 等. 铜冶炼熔渣中铁组分的迁移与析出行为[J]. 过程工程学报, 2009, 9(2): 284-288.
CAO Hongyang, FU Nianxin, ZHANG Li, et al. Migration and precipitation behavior of Fe components in copper smelting slag[J]. The Chinese Journal of Process Engineering, 2009, 9(2): 284-288.
[9] 杨涛, 胡建杭, 王华. 铜电炉冶炼贫化渣焙烧富集Fe3O4[J]. 过程工程学报, 2011, 11(4): 613-619.
YANG Tao, HU Jianhang, WANG Hua. Concentration of Fe3O4 in roasted slag from copper impoverishment smelting[J]. The Chinese Journal of Process Engineering, 2011, 11(4): 613-619.
[10] 陈和生, 孙振亚, 邵景昌. 八种不同来源二氧化硅的红外光谱特征研究[J]. 硅酸盐通报, 2011, 30(4): 934-937.
CHEN Hesheng, SUN Zhenya, SHAO Jingchang. Investigation on FT-IR spectroscopy for eight different sources of SiO2[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2011, 30(4): 934-937.
[11] Kondratowicz T. Structural changes in sodium-calciun-silicate glass after adding Si3N4[J]. Opt Appl, 2007, 37(1/2): 41-50.
[12] Dalby K N, King P L. A new approach to determine and quantify structural units in silicate glasses using micro Fourier-Transform Infrared spectroscopy[J]. Am Mineral, 2006, 91: 1783-1793.
[13] 闻辂. 矿物红外光谱学[M]. 重庆: 重庆大学出版社, 1988: 116-118.
WEN Lu. The infrared spectroscopy of minerals[M]. Chongqing: Chongqing University Press, 1988: 116-118.
[14] DENG Tong, LING Yunhan. Chemical and mineralogical characterizations of a copper converter slag[J]. Rare Met, 2002, 21(3): 175-181.
[15] 余桂林, 李楠, 许聚良, 等. 方石英的制备及其对磷酸盐包埋料性能的影响[J]. 武汉科技大学学报, 2005, 28(3): 225-227.
YU Guilin, LI Nan, XU Juliang, et al. Preparation of cristobalite and its influence on the properties of phosphate-bonded investment[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Science and Technology, 2005, 28(3): 225-227.
[16] 陈美怡, 李自德. 方石英转变及其在熔模铸造中的意义[J]. 铸造, 1993(4): 9-13.
CHEN Meiyi, LI Zide. Cristobalite transformation and its role in investment casting[J]. Foundry, 1993(4): 9-13.
[17] 肖万生, 陈晋阳, 翁克难, 等. 长白山硅藻土热处理相变及方英石形成机制探讨[J]. 矿物学报, 2005, 25(1): 20-26.
XIAO Wansheng, CHEN Jinyang, WENG Kenan, et al. High-temperature transformation of Changbaishan diatomite and the formation mechanism of cristobalite[J]. Acta Mineralogical Sinica, 2005, 25(1): 20-26.
[18] 魏存弟, 马鸿文, 杨殿范, 等. 煅烧煤系高岭石的相转变[J]. 硅酸盐学报, 2005, 33(1): 77-81.
WEI Cundi, MA Hongwen, YANG Dianfan, et al. Phase transformation for calcined coal measures kaolinite[J]. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2005, 33(1): 77-81.
[19] 邓宗禹, 徐协文, 谢建国, 等. 原料对方石英生成的影响[J]. 现代技术陶瓷, 1999(1): 11-20.
DENG Zongyu, XU Xiewen, XIE Jianguo, et al. Effects of raw materials on formation of cristobalite[J] Advanced Ceramic, 1999(1): 11-20.
[20] Mollah M Y A, Promreuk S, Schennach R, et al. Cristobalite formation from thermal treatment of Texas lignite fly ash[J]. Fuel, 1999, 78(11): 1277-1282.
[21] 徐常明, 王士维, 黄校先, 等. 方石英的析晶与无定形化[J]. 无机材料学报, 2007, 22(4): 577-582.
XU Changming, WANG Shiwei, HUANG Xiaoxian, et al. Crystallization and amorphization of cristobalite[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2007, 22(4): 577-582.
[22] Nanri H, Takeuchi N, Ishida S, et al. Mineralizing action of iron in amorphous silica[J]. J Non-Cryst Solids, 1996, 203: 375-379.
(编辑 陈爱华)
收稿日期:2012-09-13;修回日期:2012-12-24
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(50906035);云南省应用基础研究基金资助项目(2009ZC014M);云南省教育厅科学研究基金资助项目(09Z0015)
通信作者:胡建杭(1976-),男,浙江龙游人,博士,教授,从事工业固废再生资源化利用研究;电话:0871-5153405;E-mail:Hujh51@126.com