文章编号: 1004-0609(2006)10-1823-06
铝电解槽内阳极气泡运动的冷态模拟
薛玉卿, 周乃君, 包生重
(中南大学 能源科学与工程学院, 长沙 410083)
摘 要: 采用硫酸铜作电解质、 石墨作阳极的电解实验模拟研究工业铝电解槽的阳极气体运动规律, 以及气泡运动对电解质运动影响的规律。 当阳极倾斜度小于6°时, 倾角的变化对速度影响较大, 阳极倾斜角的增加会加速气泡运动速度但减小气泡尺寸; 阳极倾斜度达到6°以上时, 几乎不存在气泡合并现象, 且倾角变化对气泡速度的影响变小; 气泡运动对电解质的推动作用主要体现在阳极底部气泡所在的薄层内, 同时在电解质的底部存在回流现象, 但流速甚小, 约为5mm/s。
关键词: 铝电解; 阳极气泡; 电解质流动; 冷态模拟
中图分类号: O646.5; TQ151 文献标识码: A
Normal temperature analogue experiment of
anode bubbles behavior in aluminum electrolysis cells
XUE Yu-qing, ZHOU Nai-jun, BAO Sheng-zhong
(Shool of Energy Science and Engineering, Central South University,
Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: A electrolysis experiment using the bluestone solution as electrolyte and graphite as anode was carried out to simulate and research the anode gass law of movement and its influence to the electrolyte flow. When the gradient of anode is below 6°, the change of it has significant influence to the bubbles velocity. The increase of the gradient will speed the bubbles velocity but decrease the bubbles size. When the gradient of anode is above 6°, the phenomenon of bubbles combination hardly exists, and the change of the anodes gradient has little influence on the bubbles velocity. The bubbles impetus function to the electrolyte flow mainly lies in the thin layer of anode bottom where the bubbles are. There are back-flow phenomena in the bottom layer of electrolyte, but the velocity of electrolyte is very small, and the velocity is about 5mm/s.
Key words: aluminum reduction cell; anode gas; electrolyte flow; normal temperature analogue experiment
工业铝电解槽中, 阳极生成的CO2气体以气泡的形式或吸附在阳极的底掌或沿底掌运动。 一方面, 正常生产中覆盖了阳极底掌约50%面积的气泡减小了阳极的有效面积, 增加了槽电压, 降低了电流效率[1, 2]; 另一方面, 运动的阳极气泡, 又促进了电解质的运动和氧化铝的扩散溶解[3, 4]。 因此, 阳极气体对电解槽生产工艺有着重要的影响[5, 6]。 特别是对新型导流型铝电解槽, 阳极具有一定的倾斜度, 气泡的排放具有与在常规槽中不同的规律, 所以对阳极气泡的生成和运动规律的研究显得十分重要。
由于工业上电解质的温度非常高(950~970℃), 实验室不易实现。 模拟实验是对工业铝电解槽阳极气体研究的主要手段[7, 8]。 文献[9-13]用室温水作电解质, 用树脂玻璃槽作为模型槽, 用底部带筛板的铝盒或钢盒来模拟阳极, 通过筛板通入压缩空气来模拟阳极气气泡的产生。 但是气泡生成的均匀性受到阳极倾斜度的影响(阳极浸没深度不同, 液压随浸没深度变化)。 此外, 工业电解槽的气泡来源于化学反应, 并且会影响电流密度, 从而影响新气泡生成。 所以该类模型不能很好的模拟气泡行为, 根据水模型得出的气泡运动关系式值得商榷[13]。
文献[14-16]采用电解方法对气泡运动进行模拟, 电解质采用氧化铝, 电解温度也与工业电解槽相同, 阳极采用炭阳极或是惰性阳极。 由于阳极的尺寸太小(直径60~70mm), 及阳极形状为圆柱形, 气泡的形状尺寸和阳极的形状及大小有关[17], 并且实验过程中, 对阳极倾斜度和极距调整困难, 所以不能得到不同极距和倾斜度条件下阳极气泡的运动规律。
文献[18]用金属块模拟阳极, 用水模拟电解质, 加热阳极使得水在金属底部气化模拟电解槽的气体产生。 这样使得水的运动受温度梯度的影响, 而工业电解质中温度梯度对电解质运动的影响很小。
本文作者吸取以往经验, 用石墨作为阳极, 紫铜电极板做阴极在常温下电解硫酸铜, 来模拟工业铝电解过程, 避免了以上各种模型的缺陷, 能更好地模拟工业铝电解槽中阳极气泡的产生及运动规律。 通过录像并进行分析得出阳极气泡的生成和运动的规律。
1 原理和装置图
工业电解槽阳极气体的产生过程比较复杂, 并且对于阴极反应还存在争议, 但可以简化为[19]
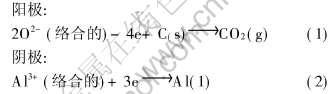
本文中的模拟实验用硫酸铜代替氧化铝作电解质, 电解质中发生的反应有
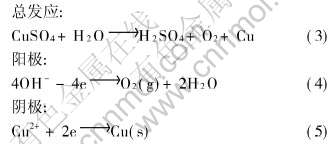
其中式(4)和(5)是模拟实验的析气公式。 分析以上公式, 可以得出: 实验和工业铝电解过程中产生的阳极气体均是由化学反应得到, 并且产生阳极气体的物质的量取决于通过阳极的电量或者说阳极的电流密度。 此外, 实验中阳极气泡也是在阳极底掌上析出。
在实验中, 采用单块阳极, 极距和阳极倾斜度均可调, 阴、 阳极连接整流器, 电流范围是0~100A, 电压范围为0~50V。 电解质为不同浓度的硫酸铜溶液(由分析纯硫酸铜与蒸馏水配制而成)。 为了更好地模拟工业电解槽中阳极气泡的运动规律, 该模拟实验保证了与工业电解槽的几何相似, 以及电解质的粘度和表面张力与工业电解质接近, 如表1所示。 实验装置如图1和2所示。
表1 模拟实验与工业电解槽的对比
Table 1 Comparison between simulation experiment and industry cell

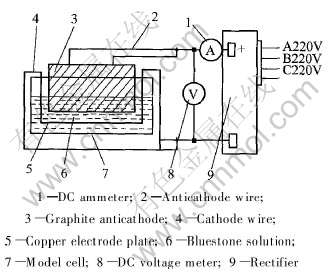
图1 实验装置原理图
Fig.1 Schematic diagram of experiment

图2 冷态模拟电解槽
Fig.2 Model electrolytic cell for normal state experiment
2 结果及讨论
2.1 阳极水平时
实验中, 首先观察了阳极水平时的气泡生成、 生长以及脱离阳极的过程。 当浓度小于0.2mol/L或电解时间太长时, 阴极出现气体, 这是由于电解质浓度过低, 电解中的水也发生电解, 电解方程式为
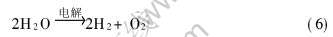
开始通电时, 阳极底部就出现细小、 均匀的气泡, 同时, 阳极的边缘的小气泡脱离阳极向上释放。 阳极底部中心的气泡开始长大并出现合并。 气泡长大或合并到一定尺寸时, 开始向阳极的边部运动并脱离阳极; 在脱离的途中, 大气泡合并沿途的小气泡。 大约1min后, 气泡脱离阳极的频率达到稳定。
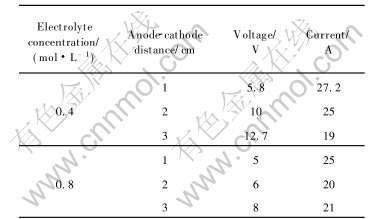
同一条件下, 阳极气泡有大体积气泡和小体积气泡之分。 大体积气泡是小体积气泡经过合并后形成的(以后简称为大气泡, 代表合并的作用), 小体积气泡是直接生长长大的(以后简称为小气泡)。 大气泡一般在阳极底部的中心位置附近, 其形状是扁平状的椭球形(图3), 厚度大约为5mm。 当阳极严格水平时, 气泡会一直长大, 直到接近阳极底掌宽度时沿阳极大侧面释放。 表2描述了不同极距和电解质浓度与电解电压和电流的关系。 可以看出, 随着极距的增加, 电解所需电压明显升高, 电流降低。 电解质浓度影响电解过程的电压和电流大小, 电解质浓度增大时, 电解电压减小。
2.2 阳极倾斜时
为了模拟新型导流型铝电解槽中阳极气体释放的影响作用, 重点研究了阳极倾斜、 电解质浓度为0.8mol/L时, 阳极气泡的速度以及大小随极距和阳极倾斜度的关系。

图3 气泡的形状
Fig.3 Shape of bubbles
表2 阳极水平时的平均电解电压与电流
Table 2 Average electrolysis voltage and current in horizontal anticathode state
2.2.1 电解电流和电压
在改变阳极极距和阳极倾斜度过程中, 电解电流和电压都发生变化。 从表3可以看出, 电解过程中, 阳极倾斜角增大, 电解电流增大, 电压减小; 极距的增加, 电解电流减小, 电压增加。
2.2.2 气泡速度
气泡的平均速度随阳极坡度的变化如图4所示, 从图中可以看出, 当极距较小时, 随倾斜角增加, 气泡的速度明显增加, 并且极距对气泡速度的影响较大, 气泡速度随倾斜角的增大改变很快; 当极距较大时, 气泡速度的增长速度先快后慢, 倾斜角对气泡速度的影响逐渐变小, 当阳极的倾斜角达到6°以上, 气泡的速度几乎不再增大; 极距对气泡速度的影响和阳极的倾斜角有关, 当阳极的倾斜角小于3°时, 不同极距的气泡速度很接近, 而随着倾斜角增大, 不同极距的气泡速度开始明显不同; 极距越大, 气泡的速度越小。
表3 阳极倾斜时的电解电流和电压
Table 3 Average electrolysis voltage and current in incline anticathode state
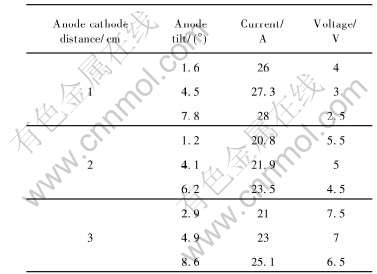
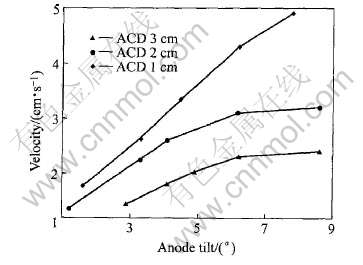
图4 浓度为0.8mol/L的电解液电解时不同状态下的阳极气泡平均速度
Fig.4 Average velocity of bubbles under different states(0.8mol/L CuSO4)
根据观察, 在相同极距和倾斜角时, 气泡运动过程中的运动速度在不断增加。 气泡运动的起始阶段速度很小, 运动中每合并一个气泡, 速度就会有个明显的增加。
2.2.3 气泡的尺寸
阳极倾斜时, 产生的气泡仍然有大小之分。 图5和6显示了气泡大小变化和极距以及倾斜角的关系, 可以看出, 气泡的大小与阳极的倾斜角有很大的关系, 都是随着倾斜角的增大而减小。
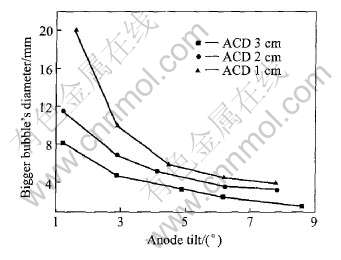
图5 不同状态下的大气泡横向直径
Fig.5 Transverse diameter of bigger bubbles under different states (0.8mol/L)
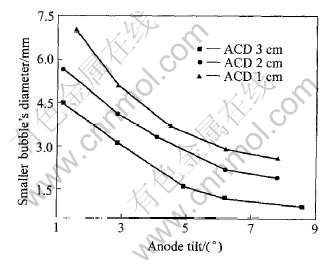
图6 不同状态下小气泡横向直径
Fig.6 Transverse diameter of smaller bubbles under different states (0.8mol/L)
对于大气泡, 极距较大时(2~3cm), 极距对气泡的大小影响很小; 随着阳极倾斜角的增大, 各种极距的气泡尺寸趋于一致, 说明只是在小坡度下, 极距对大气泡尺寸的影响才显著。 同时说明极距对气泡的合并作用不是很明显。
对于小气泡, 极距对气泡大小的影响比对大气泡明显; 极距越大, 气泡的尺寸越小。 但同时电解电流也在改变(表3), 不能得出极距对气泡的尺寸有明显的影响。
大气泡所占比例代表合并的作用强弱, 由图5和6可以看出, 随着阳极倾斜角的增加, 大气泡和小气泡的尺寸逐渐接近, 以至于几乎没有大气泡的产生(图7), 由此可知, 合并作用随阳极倾斜角的增大而减小。

图7 阳极倾斜角度较大时的气泡形状
Fig.7 Shape of bubbles for bigger incline angle of anticathode
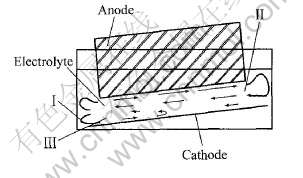
图8 气泡运动引起的电解质运动
Fig.8 Movement of electrolyte driven by bubbles
2.2.4 气泡对电解质运动的影响
为了研究气泡对电解质流动的影响, 在气泡稳定释放时, 往电解质中加入红墨水, 观察电解质的运动。 结果发现, 气泡运动引起了电解质流动; 电解质流动情况如图8所示; 电解质流动速度不大, 主要是阳极底掌下的气泡层随气泡运动, 速度与气泡速度接近; 电解质回流的速度约为几毫米每秒。
电解质在Ⅲ区域出现漩涡, 主要原因可能是气泡的速度在不断增加, 促使紧贴阳极的电解质流速增加, Ⅰ区域的回流小于Ⅱ区域出现的回流。
2.2.5 分析与讨论
阳极倾斜时, 气泡的受力与阳极水平时不同(图9)。 图中FB为气泡所受浮力, FP为阳极底面对气泡的作用力, FG为气泡受的重力, FD为曳拉力。 根据文献[20], 气泡的体积增大和阳极倾斜角的增大都会增大气泡所受到的沿阳极底面向上的合力。 根据对气泡的受力分析得知, 阳极倾斜时, 气泡受同一方向的力(沿阳极底掌向上), 运动方向相同, 与阳极水平相比不易合并, 故气泡的合并现象会随阳极倾斜角的增大而减少, 从而气泡的尺寸减小。 另外, 随着阳极倾斜角的增大, 电解电流在减小, 而气体生成率随电流密度的减小而减小(式(4)), 即电流密度的减小也会导致气泡体积的减小。
考虑到气泡的体积和阳极倾斜度的综合影响, 气泡速度增加的速度随阳极倾斜度的增加是先快后慢。
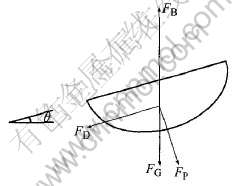
图9 阳极倾斜时气泡受力分析
Fig.9 Dynamics analysis of bubble in incline anticathode state
3 结论
以炭块作阳极, 电解冷态硫酸铜溶液模拟工业铝电解槽的阳极气体的生长、 合并及运动; 研究了阳极气泡的形状、 大小和运动速度及影响它们的因素; 并且研究了气泡运动对电解质运动的影响。 可以得出: 阳极倾斜角是影响气泡速度和尺寸的重要因素; 阳极倾斜角的增加会加速气泡速度但减小气泡尺寸; 阳极倾斜度小于3°时, 不同极距下的气泡速度接近, 阳极极距对气泡速度的影响小; 相同倾角, 极距小的气泡运动速度大, 极距大的气泡运动速度小, 且极距越大, 倾角的变化对气泡速度的影响越小, 气泡的合并现象越少; 阳极倾斜度达到6°以上时, 几乎不存在气泡的合并现象。 气泡运动对电解质的推动作用主要体现在阳极底部气泡所在的薄层内, 同时在电解质的底部存在回流现象, 但电解质的流速甚小。
REFERENCES
[1]陈延禧, 郑平.电化学反应器中气—液混合系有效电导率的研究[J]. 氯碱工业, 1995(2): 18-20.
CHEN Yan-xi, ZHENG Ping. Research on effective conductivity of gas-liquid mixture in electrochemical reactors[J]. Chlor-Alkali Industry, 1995(2): 18-20.
[2]付明录. 铝电解槽提高电流效率的探索[J]. 青海科技, 2004(2): 43-45.
FU Ming-lu. Search for the improvement of current density in aluminum cell[J]. Qinghai Technology, 2004(2): 43-45.
[3]李新海, 陈新民, 莫鼎成, 等. 吸气界面上气泡滑移促进的传热模型探索[J]. 化工冶金, 1994, 25(5): 178-182.
LI Xin-hai, CHEN Xin-min, MO Ding-cheng, et al. Mass transfer induced by bubbles at gas evolving of gas interface[J]. Engineering Chemistry & Metallurgy, 1994, 25(5): 178-182.
[4]李新海. 吸气界面上气泡聚集促进的传质[J]. 中南矿冶学院学报, 1994, 25(6): 767-770.
LI Xin-hai. Mass transfer induced by coalescence of gas bubbles at gas evolving interface[J]. J Cent South Inst Min Metall, 1994, 25(6): 767-770.
[5]夏小霞. 铝电解槽内电解质流场的数值模拟研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2004.
XIA Xiao-xia. Study on Numerical Simulation of Electrolyte Flow Field in Aluminum Reduction Cells[D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2004.
[6]Cassayre L, Utigard T A, Bouvet S. Visualizing gas evolution on graphite and oxygen-evolving anodes. aluminum production[J]. JOM, 2002: 41-45.
[7]徐君莉, 石忠宁, 高炳亮, 等. 铝电解金属阳极上气泡析出行为[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2004, 14(2): 298-301.
XU Jun-li, SHI Zhong-ning, GAO Bing-liang, et al. Bubble behavior on metal anode of aluminum electrolysis[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2004, 14(2): 298-301.
[8]张建生, 吕 青, 孙传东, 等. 高速摄影技术对水中气泡运动规律的研究[J]. 光子反应工程与工艺, 2000(3): 952-955.
ZHANG Jian-sheng, L Qing, SUN Chuan-dong, et al. The moment of air bubbles in water by use of high speed photography[J]. Acta Photonica Sinica, 2000, 29(10): 952-955.
[9]Dernedde E, Cambridge E L. Gas induced circulation in an aluminum reduction cell[J]. TMS Light Metals, 1957: 111-123.
[10]Fortin S, Gerhardt M, Gesing A J. Physical modeling of bubble behavior and gas release from aluminum reduction cell anodes[J]. TMS Light Metals,1984: 721-741.
[11]Solheim A, Jonansen S T, Rolseth S, et al. Gas driven flow in Hall-Heroult cells[J]. MTS Light Metals, 1989: 245-252.
[12]John J J. Some physical model studies of gas-induced flows in aluminum cells[J]. JOM, 1994, 15/16: 18-20.
[13]Zoric J, Solheim A. On gas bubbe in indystrial aluminum cells with prebaked anodes and their influence on the current distribution[J]. Journal of Applied Electrochemistry, 2000, 30: 787-794.
[14]Hyde T M, Welch B J. The gas under anodes in aluminum smelting cells(Part Ⅰ): Measuring and modlling bubble resistance under horizontally oriented electrodes[J]. TMS Light Metals, 1997: 333-340.
[15]WANG Xiang-wen, Tabereaux A T. Anodic phenomena-servations of anode overvoltage and gas bubbling during aluminum electrolysis[J]. TMS Light Metals, 2000: 239-247.
[16]Alexandre P, László K, Sándor P. Regimes of the movement of bubbles under the anode in an aluminum electrolysis cell[J]. TMS Light Metals, 2005: 565-570.
[17]Richards N, Gudrandsen H, Rolseths S, et al. Characterization of the fluctuation in anode current density and “bubble events” in industrial reduction cells[J]. TMS Light Metals, 2003: 315-322.
[18]László K, Sándor P J. Simulation of the bubble Layer in aluminum electrolysis eells[J]. TMS Light Metals, 2005: 559-564.
[19]邱竹贤. 铝冶金的物理化学[M]. 上海: 上海科学技术出版社, 1985: 144-151.
QIU Zhu-xian. Physical Chemistry in Metallurgy of Aluminum[M]. Shanghai: Shanghai Technology and Science Press, 1985: 144-151.
[20]车得福, 林宗虎, 等. 倾斜下表面上形成气泡的形状及尺寸[J]. 高等化学工程学报, 1994, 8(2): 190-194.
CHE De-fu, LIN Zhong-hu, CHEN Xue-jun, et al. Shape and size of the bubble formed beneath a downward facing inclined surface[J]. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering, 1994, 8(2): 190-194.
(编辑龙怀中)
基金项目: 国家重点基础研究发展计划资助项目(G1999064903)
收稿日期: 2005-10-24; 修订日期: 2006-04-04
通讯作者: 包生重; 电话: 0731-6739942; E-mail: baoszh@yahoo.com.cn; njzhou@mail.csu.edu.cn