156kA铝电解槽内电解质两相流动的数值模拟
夏小霞1, 2, 周乃君1, 崔大光1, 包生重1
(1. 中南大学 能源科学与工程学院, 长沙 410083;
2. 湘潭大学 机械工程学院, 湘潭 411105)
摘 要: 以商业CFD软件CFX4.3为平台, 采用欧拉-欧拉方法中多流体模型和标准湍流模型, 对156kA铝电解槽内电解质层的气液两相流动流场(半槽)进行数值模拟。 结果表明: 阳极气体的推动对铝电解槽内的电解质运动起主要作用, 电磁力的影响也较显著; 电解质运动主要是以每个阳极周围的小循环为主; 流速较大的区域主要分布在阳极间缝以及中缝和大面正对阳极间缝处; 阳极气体的平均流速为0.199m/s, 最大流速为0.74m/s; 电解质的平均流速为0.079m/s, 最大流速为0.717m/s; 阳极以下以及大面和中缝正对阳极间缝处湍流最强。
关键词: 铝电解槽; 电解质; 两相流动; 数值模拟 中图分类号: TF111.52
文献标识码: A
Numerical simulation on two-phase flow field of electrolyte in 156kA aluminum reduction cells
XIA Xiao-xia1, 2, ZHOU Nai-jun1, CUI Da-guang1, BAO Sheng-zhong1
(1. School of Energy Science and Engineering, Central South University,Changsha 410083, China;
2. Institute of Mechanical Engineering, Xiangtan University, Xiangtan 411105, China)
Abstract: Based on the commercial CFD software CFX-4.3, the two-phase flow of the electrolyte in the 156kA aluminum reduction cells was numerically simulated by multi-fluid model and turbulence model. The results indicate that the electrolyte flow is mainly resulted from anode gas, but the influence of electromagnetic force is also prominent. The electrolyte flow form is mainly a local circulation around each anode. The regions of high velocity are located in the anode slots and the center and the side channel at the mouth of the anode slots. The average velocity of the electrolyte is 0.079m/s, the highest velocity is 0.717m/s. The average and highest velocity of the gas is 0.199m/s and 0.74m/s respectively. The biggest value of turbulence intensity is under anodes and in the center and side channel at the mouth of the anode slots.
Key words: aluminum reduction cells; electrolyte; two-phase flow; numerical simulation
对于铝电解生产而言, 铝电解槽内的熔体(电解质和铝液)运动对铝电解槽的生产稳定性、 电流效率、 槽寿命和能耗有着很重要的影响[1]。 目前对于铝液流动的研究比较多, 而对于电解质的流动, 由于其流动的复杂性, 研究比较困难, 目前研究得比较少。 但是, 电解质运动对铝电解槽中的传质过程和传热过程有着十分重要的影响。 一方面, 电解质运动有助于阳极气体的释放; 有助于加速氧化铝的溶解和扩散, 使氧化铝的浓度分布均匀; 有助于消除电解质的温度梯度, 加强电解质和槽帮之间的传热; 另一方面, 电解质运动也会造成铝液的波动, 使槽子处于不稳定的状态; 会加剧铝的再氧化反应, 降低电流效率。 因此, 对铝电解槽内电解质运动的研究是十分必要的。
1 物理模型和数学模型
铝电解槽内的电解质运动比较复杂, 对电解质流场进行数值模拟时, 为了简化计算, 通常作如下假设:
1) 忽略电解质中氧化铝颗粒的影响, 电解质流动视为气液两相流;
2) 电解质流动视为稳态、 不可压缩流;
3) 电解质视为等温流体, 无热量传递;
4) 铝液上表面与阳极底掌均为水平面, 极距取为实测值4.14cm。
多相模型采用欧拉-欧拉方法中的多流体模型, 对于含离散相的两相流, 一般把离散相指定为层流, 连续相指定为湍流。 因此, 对于本文要计算的电解质区域中的气液两相流动, 把电解质视为湍流, 阳极气体视为层流, 湍流模型采用标准湍流模型, 雷诺方程组可以写成以下统一形式[2-5]:

计算中所用的电解质内电磁力场, 采用与文献[6, 7]类似的方法计算得到。
2 电解质流场的数值模拟
2.1 研究对象及网格划分
本文的研究对象为某厂156kA两端进电铝电解槽。 考虑到对称性, 只对半槽进行计算, 解析区域如图1所示。 其坐标定义为: x方向由A侧指向B侧, y方向由电解质下表面指向上表面, z方向由端部指向中部。 采用多块结构化非均匀网格技术, 整个解析区域共划分为42184个单元、 55413个节点, 在极间和阳极间缝处对网格进行了加密处理。

图1 156kA铝电解槽的解析区域
Fig.1 Sketch of computational zone in 156kA cell (half of cell)
2.2 边界条件及计算方法
由于模拟的是半槽, 把半槽横断面定义为对称面。 由于电解质与铝液两种流体互不掺混, 且不考虑两者之间的热交换, 电解质/铝液界面可近似处理为对称面。 在对称面上, 垂直于对称面的速度分量为0。 同时, 所有变量沿对称面法向方向的导数都为0。
阳极气体是以气泡的形式释放的, 取气泡的当量直径平均值为1cm。 把阳极底掌作为阳极气体的入口, 单位时间单位阳极面积上的气体生成率为[8]

除了对称面和入口, 其他边界都为壁面。 电解质上表面也定义为壁面, 对气相设为脱气边界条件, 即气泡到达这个边界接触后就终止对气泡的计算, 以此模拟电解质表面阳极气体的自由释放。 壁面上使用无滑移边界条件。
采用CFD商业软件CFX4.3进行求解。 多流体模型采用Spalding的相间滑移算法(IPSA)的改进方法即IPSAC方法求解[3], 速度—压力耦合采用SIMPLEC算法。 为了改善收敛性, 采用了欠松弛因子。
2.3 计算结果及分析
图2所示为半槽的极间水平电磁力场分布。 可以看出, 电磁力的方向指向槽子的中部并偏向B侧, 并且A侧的电磁力大于B侧(这与槽子的母线配置及结构有关)。
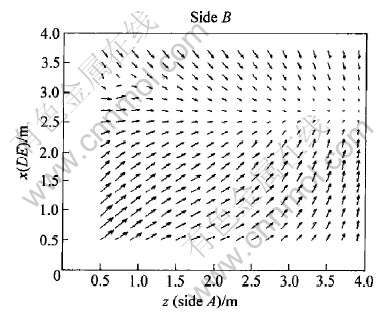
图2 极间水平电磁力的分布
Fig.2 Vector of horizontal electromagnetic force (half of cell)
图3~9所示为阳极气体和电解质流场的计算结果。 为清楚起见, 图中给出了阳极的投影位置。 为了清楚地显示电解质流场, 对矢量图中箭头的大小和疏密进行了处理。
1) 流动趋势
从图3可以看出, 阳极气体主要是流向相邻的阳极间缝, 然后沿阳极边部垂直向上, 从电解质自由表面释放。 造成这种运动的主要原因是由于阳极气体要沿最短的路径释放; 也有一小部分阳极气体从阳极端部释放。

图3 阳极间缝的阳极气体流场
Fig.3 Predicted anode gas flow pattern at anode gap
从流动趋势来看, 电解质运动主要是以每个阳极周围的小循环为主。 从图4和5可以看出, 极间电解质在阳极气体的带动下, 从极间流向相邻的阳极间缝, 并且流向槽中部一侧阳极间缝的电解质明显多于流向端部一侧阳极间缝的电解质。 显然, 这是电磁力的作用使然; 阳极间缝中的电解质然后向上运动, 在阳极间缝上层分成两股分别流向大面和中缝。 流向大面的电解质直接冲刷大面槽壁, 然后分成两部分以相反的方向分别流向槽中部和端部, 在每个阳极附近形成两个方向相反的小涡(图6)。 流向中缝的电解质也分成两部分, 以相反的方向分别流向槽中部和端部, 然后向下回到极间(图7)。 此外, 从阳极端部/边部释放的阳极气体使电解质在大面/小面中形成了沿阳极端部/边部向上、 再沿槽壁向下回到极间的垂直方向的循环(图8, 9)。 本文所得到的电解质流动规律与文献报道结果相一致[9-14], 证明计算模型和算法是可靠的。

图4 极间水平截面的电解质流场
Fig.4 Predicted electrolyte flow pattern on horizontal plane

图5 阳极间缝的电解质流场
Fig.5 Predicted electrolyte flow pattern at anode gap
2) 流速大小
从流速大小来看, 电解质的平均流速为0.079m/s, 最大流速为0.717m/s, 阳极气体的平均流速为0.199m/s, 最大流速为0.74m/s。 虽然最大流速很大, 但流速较大的区域(流速大于0.2m/s)较小, 也比较集中, 主要分布在阳极间缝以及中缝和大面正对阳极间缝处, 这是由于大量的阳极气体和电解质流向阳极间缝, 而阳极间缝的通道较窄所致。

图6 阳极底掌以上水平截面的电解质流场
Fig.6 Predicted electrolyte flow pattern on horizontal plane above anode bottom(y=0.15m)
图7 中缝的电解质流场
Fig.7 Predicted electrolyte flow pattern at central gap

图8 大面的电解质流场
Fig.8 Predicted electrolyte flow pattern in side

图9 小面的电解质流场
Fig.9 Predicted electrolyte flow pattern in side of DE
3) 湍流强度
从图10可知, 阳极以下(以及大面和中缝正对阳极间缝处)湍流最强。 湍动能的平均值为4×10-3m2/s2, 最大值为0.034m2/s2。

图10 水平截面电解质湍动能的分布
Fig.10 Turbulent kinetic energy of electrolyte flow pattern on horizontal plane
3 结论
1) 阳极气体主要是流向相邻的阳极间缝, 然后沿阳极边部垂直向上, 从电解质自由表面释放, 从流动趋势来看, 电解质运动主要是以每个阳极周围的小循环为主。
2) 从流速大小来看, 电解质的平均流速为0.079m/s, 最大流速为0.717m/s, 阳极气体的平均流速为0.199m/s, 最大流速为0.74m/s。
3) 阳极以下(以及大面和中缝正对阳极间缝处)湍流最强。 湍动能的平均值为4×10-3m2/s2, 最大值为0.034m2/s2。
REFERENCES
[1]梅炽. 有色冶金炉窑仿真与优化[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2001: 150-151.
MEI Chi. Simulation and Optimization of the Nonferrous Metallurgy Furnaces[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2001: 150-151.
[2]周力行. 多相湍流反应流体力学[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2002: 78-101.
ZHOU Li-xing. Fluid Mechanics of Multi-Phase Turbulent Reaction[M]. Beijing: National Defence Industry Press, 2002: 78-101.
[3]CFX4.3 Server Manual[M]. AEA Technology Plc. Harwell, 1999: 104-106.
[4]铁军, 邹建成. 铝电解阳极气泡长大过程的计算机模拟[J]. 计算机与应用化学, 2002, 19(2): 172-176.
TIE Jun, ZOU Jian-cheng. The computer simulation for the process of anode gass growing up in aluminum reduction cell[J]. Computer and Application Chemistry, 2002, 19(2): 172-176.
[5]铁军, 邱竹贤. 铝电解中阳极气泡形成的电化学研究[J]. 有色金属, 1996, 8(3): 44-48.
TIE Jun, QIU Zhu-xian. Electrochemistry research on the anode bubble formation in aluminum reduction cell[J]. Nonferrous Metals, 1996, 8(3): 44-48.
[6]姜昌伟, 梅炽, 周乃君, 等. 用标量电位法与双标量磁位法计算铝电解槽三维磁场[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2003, 13(4): 1021-1025.
JIANG Chang-wei, MEI Chi, ZHOU Nai-jun, et al. Computation of 3D magnetic field in pre-baked cells using scalar voltage potential method and two scalar magnetic potentials method[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2003, 13(4): 1021-1025.
[7]ZHOU Nai-jun, MEI Chi, JIANG Chang-wei, et al. Coupled computation method of physics fields in aluminum reduction cells[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2003, 13(2): 431-437.
[8]Solheim A, Johansen S T, Rolseth S, et al. Gas driven flow in Hall-Heroult cells[J]. Light Metals, 1989: 245-252.
[9]Aaberg R J, Ranum V, Williamson K, et al. The gas under anodes in aluminum smelting cells (Part Ⅱ): Gas volume and bubble layer characteristics[J]. Light Metals, 1997: 341-346.
[10]Kobbeltvedt O, Moxnes B P. On the bath flow, alumina distribution and anode gas release in aluminum cells[J]. Light Metals, 1997: 369-376.
[11]Zoric J, Solheim A. On gas bubbles in industrial aluminum cells with prebaked anodes and their influence on the current distribution[J]. Journal of Applied Electrochemistry, 2000, 30: 787-794.
[12]Cassayre L. Visualizing gas evolution on graphite and oxygen-evolving anodes[J]. JOM, 2002, 5: 41-45.
[13]Stein K B, Johansen T, Asbjorn S, et al. Coupled current distribution and convection simulator for electrolysis cells[J]. Light Metals, 2001: 463-468.
[14]Bilek M M, Zhang W D, Stevens F J. Modelling of electrolyte flow and its related transport processes in aluminum reduction cells[J]. Light Metals, 1994: 323-331.
(编辑陈爱华)
基金项目: 国家重点基础研究发展计划资助项目(G1999064903)
收稿日期: 2005-10-27; 修订日期: 2006-04-04
通讯作者: 周乃君, 教授; 电话: 0731-8836920; E-mail: njzhou@mail.csu.edu.cn