DOI:10.19476/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2017.12.25
铝电解阳极气泡动力学及分布特性的低温电解实验研究
詹水清1,王贞涛1,杨建红2,郑 俊1,王军锋1
(1. 江苏大学 能源与动力工程学院,镇江212013;
2.江苏大学 绿色材料与冶金研究院,镇江212013)
摘 要:以河南某厂300 kA铝电解槽为原型,基于相似原理,按与原型1:4的几何比例设计和搭建大尺度低温电解实验平台,探讨和分析阳极底掌气泡的成核、长大、聚并、破碎及分离等动力学行为及分布特性规律。结果表明:阳极底掌成核点处首先主要产生尺寸极小且分布比较均匀的气泡,然后这些气泡在扩散和传质引起的生长及碰撞和“吞噬”引起的聚并过程中不断长大,最后在阳极底掌边缘发生一定的分离与破碎过程,同时还伴随着较强烈的液体局部循环扰动。阳极底掌气泡层内气泡的尺寸分布范围比较宽且形状差异较大,数量比较少的大尺寸及中等尺寸气泡的周围存在着数量比较多的小尺寸气泡。改变电流密度和阳极倾斜角均对上述气泡的相关动力学行为和尺寸分布特性有着重要的影响。
关键词:铝电解;阳极气泡动力学;分布特性;低温电解;实验研究
文章编号:1004-0609(2017)-12-2605-10 中图分类号:TF821 文献标志码:A
在铝电解过程中,熔融电解质内的氧化铝与碳阳极发生复杂的电化学反应,主要在阳极底掌析出二氧化碳气体[1]。由于阳极底掌面积较大,阳极底掌产生的阳极气泡逐渐增多并不断地生长,长大后的气泡与相邻气泡间会发生一定的聚并、破碎及分离等现象,产生不同尺寸大小的气泡/气泡群。一方面,气泡搅动电解质的气液两相运动会提高熔体温度与氧化铝浓度分布的均匀性;另一方面,形成的气泡群使极间电场及磁场分布发生变化,引起极间电阻增大、电压升高,影响正常的下料控制策略,会引发阳极效应的发生,甚至会导致电解槽无法正常运行[2]。
由于受工业铝槽内高温及强腐蚀等不利环境的限制,现场难以直接测量槽内的阳极气泡动力学行为及分布特性,因此,物理模型实验方法成为了主要研究手段,主要包括冷态模拟实验、热力模拟实验和实验室电解实验研究。冷态模拟实验一般采用室温水来近似代替熔融电解质进行研究[3-7],主要探讨了阳极底掌典型的气泡成核、长大、聚并及逸出等动力学行为及影响因素,以及气泡逸出引起的气液两相动量及湍流传输等行为。冷态模拟实验的优点在于设备简单、成本较低、装置易于大型化,便于改变多种参数进行测量,但主要缺点是采用压缩空气来模拟实际的阳极气体,这与工业槽内由于电化学反应产生气体的机理是完全不同的,且固定喷射点连续产生气泡与实际电解情况不符。
目前,有关热力模拟实验研究的相关报道比较少,KISS等[8]通过将金属块加热使水汽化沸腾的方法来模拟槽内的阳极气泡行为及其引起的电解质运动;韩莉[9]采用加热合金的实验研究发现,加热体汽化产生气泡的运动速度和尺寸大小均比实际电解槽中的结果大。热力模拟实验中水的运动受温度梯度的影响非常明显,且气泡产生速率与加热温度密切相关,而工业槽内电解质运动受温度梯度的影响非常小,因此,该类型的模型实验难以获得广泛应用。
实验室电解实验研究主要分为高温电解和低温电解实验研究两种类型。高温电解实验直接通过高温电化学反应生成阳极气泡,与工业槽内的气体产生方式一样。目前国内外学者已经开展了诸多高温电解实验研究[10-15],系统性地对阳极气泡在电极表面的成核、长大、聚并及脱离等行为进行了详细分析。高温电解实验能较真实地反映电解条件下阳极气泡的生成机理,获得了许多有关气泡动力学行为及分布的参数信息,能够加深对电解过程的认识;但实验中所使用的阳极形状及尺寸大小受到很大的限制,而实际气泡形态及尺寸分布等行为受其影响非常明显,且实验观察与测量较为困难,也无法合理描述宏观的电解质流场信息,相关的实验设计及测试方法仍有待进一步的改进和完善。
相对于高温电解实验来说,低温电解实验由于也能通过电化学反应产生气体,实验操作简便、易于测量,且实验模型尺度及宏观流场等均不会受到限制,因此受到越来越多研究者的关注[16-18]。QIAN等[16]在低温电解实验中选择氢氧化钠溶液作为电解质,发现阳极和阴极表面均产生了气泡,与实际电解产生气泡的机制并不相同。为了使实验中只在阳极表面产生气泡,薛玉卿等[17]以硫酸铜(CuSO4)溶液代替电解质,研究了阳极气泡逸出及其影响电解质运动的规律,但该实验的主要不足之处在于实验模型尺寸非常小,观察到的实验现象及规律可能与实际情况相差较大。ALAM等[18]基于相似原理,搭建了低温铝电解实验装置对阳极气泡的成核、长大、聚并和分离等过程进行了初步研究,但更多相关阳极气泡动力学行为及分布特性的研究仍有待于进一步探讨。
为更好地对实际槽内阳极气泡的动力学行为及尺寸分布等特性进行系统性描述,本文作者基于相似原理设计和搭建了一套尺度较大的低温电解实验装置。虽然低温电解产生的气体与高温电解不同,但主要研究重点是探讨和分析大尺度阳极底掌下的气泡产生、成核长大、聚并、破碎及分离等行为过程,因此能较好地加深对实际槽阳极底掌气泡动力学行为及分布特性规律的认识,研究结果将为大型工业铝电解槽的设计及研发等提供理论基础和依据。
1 低温电解实验原理及过程
1.1 实验原理
工业铝电解槽为960 ℃左右的高温强腐蚀熔融盐体系,主要在阳极底掌产生二氧化碳气体,槽内总的电解过程反应为:
2Al2O3+3C=4Al+3CO2 (1)
阳极气泡从阳极底掌产生到逸出电解质表面过程中,气泡主要受惯性力、浮力、表面张力和粘性力等作用。根据相似原理理论,必须保证实验模型与工业槽模型的几何相似和动力相似。以国内河南某厂300 kA铝电解槽为原型,确定实验模型与工业槽模型的几何相似比为1:4,具体结构参数如表1所列。
表1 实验模型与原型的主要结构尺寸参数
Table 1 Geometric configurations of physical and prototype models

动力相似要求实验槽内液体的物理性质与工业槽内电解质的物理性质相同或相近。经过大量的实验前期准备及调研工作认为,要使实验原理和现象与实际情况比较接近,CuSO4溶液作为电解质比较合适。利用CuSO4溶液电解时,只有阳极表面会产生气泡,虽然溶液为蓝色,但是实验中选择合适的光源和合适浓度大小的溶液,仍能得到较为合理清晰的气泡图像数据。依据工业电解精炼铜电化学原理,在电解过程中,阳极底掌会产生一定的氧气,而阴极的产物为金属铜,实验中总的电解过程反应为:
CuSO4+2e+H2O=Cu+H2SO4+1/2O2 (2)
本研究建立的冷态实验电解槽能近似地反映工业铝电解槽内的阳极气泡生成机理,虽然产生的O2与实际槽内的CO2不同,但为探讨大尺度阳极底掌下的气泡产生、成核长大、聚并、破碎及分离等行为过程提供理论依据。实验模型中CuSO4溶液和工业槽内熔融电解质的相关物性参数对比如表2所列。
表2 电解实验模型与原型的物性参数[19]
Table 2 Fluid properties of physical and prototype models[19]

动力相似还要求表征不同模型中的相关无量纲准则数均相同或相近。在铝电解槽气-液两相体系内,阳极气泡主要在惯性力和浮力的共同作用下逸出电解质表面,因此弗劳德数Fr对于其引起的宏观流动过程非常重要;同时,为能准确描述槽内阳极气泡的尺寸及分布等特性,奥托数Eo和莫顿数Mo的影响也必须考虑进去,这两个无量纲数是决定气泡尺寸和形状等特性的关键参数[6, 20]。因此,本文作者主要依据Fr、Eo和Mo的相似设计实验,详细的动力学相似准则数核算及表达式参见文献[21]。
1.2 实验装置与实验步骤
本研究设计的低温电解实验装置如图1所示,实验采用1.0 mol/L CuSO4与0.2 mol/L硫酸钠(Na2SO4)的混合溶液代替熔融电解质,添加部分Na2SO4溶液的目的是为了增强导电性。采用钢化玻璃槽作为电解槽,其硬度及透明性等均比较好,阳极尺寸为400 mm× 160 mm×400 mm,阳极底部为20 mm厚的铅板,阴极为20 mm厚的紫铜板,阳极与阴极彼此水平放置,且面积相等,极间距离为50 mm,阳极浸入深度为150 mm。实验中设计一个2 mm厚且上下贯穿的不锈钢框架,并将该框架的下端与铅板相连接起来,整体上看起来类似于工业槽内的碳阳极。实验采用400 A-12 V系列的直流电源,可控电流范围为0~400 A,电压范围为0~12 V。进电端和出电端分别采用阳极母线和阴极母线进行连接,阳极母线与铅阳极之间用3根导电性较好的铜棒进行连接,阴极母线直接从紫铜阴极板接到电源的负极。
实验中设计的电流强度变化范围为40~160 A,则对应的电流密度变化范围为0.0625~0.25 A/cm2。由于实验所用的阴极为不透明的紫铜板,难以从阴极底部直接在垂直阳极底掌的方向进行拍照,因此试验中主要从阳极的斜侧面方向对气泡图像进行拍摄。为能较方便地捕捉到清晰的气泡图像,在阴极表面放置一排大功率的荧光钠灯作为加强的光源,因为钠灯所占的体积比较小,基本不影响极间正常的电解过程。通过图像后处理软件将拍摄的视频按一定的帧数截取多个单帧图片,本研究取25帧/s,即每张图像的间隔时间为0.04 s,并将气泡图像进行灰度处理,以便较好地辨别不同的气泡分布形态。
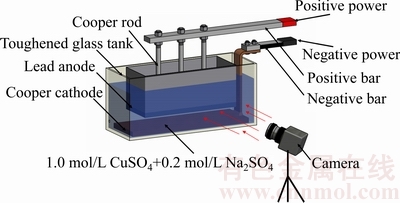
图1 低温电解实验装置示意图
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of low temperature electrolytic apparatus

图2 低温电解实验系统
Fig. 2 Schematic graph of low temperature electrolytic test
2 结果与分析
2.1 初始阶段的气泡成核及生长
本节内容所讨论的均是阳极在水平放置下的气泡分布结果。图3所示为不同电流密度下初始气泡分布特性随时间变化的动态图像,主要考察整个阳极底掌初始气泡的成核及生长过程。可以看出,在电解开始时,阳极底掌均产生尺寸极小的气泡(简称为极小尺寸气泡),且气泡尺寸分布比较均匀。在t=2 s时刻,在不同电流密度下,这些极小尺寸气泡的数量不同,这主要与不同电流密度下阳极表面的气泡成核点数量有关。极小尺寸气泡会继续在成核点处逐渐长大,气泡尺寸也在不断增大,这个过程称为气泡的生长过程。当气泡尺寸增大到一定程度后,气泡便会在阳极表面快速扩张,当促使气泡运动的外力大于束缚于其固定在成核点处的合力时,长大的气泡就会达到一定的固定体积,气泡就会挣脱和离开成核点向周围运动。这种运动机制在不同电流密度下的情况基本类似,但是提高电流密度会加快这种气泡的生长过程,比如在t=5 s时,电流密度为0.25 A/cm2时的气泡便已经开始离开成核点,而电流密度为0.0625 A/cm2时的气泡还仍处于生长阶段。
气泡的生长过程可以理解为硫酸铜溶液(以下均简称为溶液)中的O2分子不断地向成核点处气泡的扩散和传质过程。阳极界面由于电化学反应生成的O2分子首先溶解于溶液中,并不断向溶液主体进行扩散,使某一时刻溶液中的O2分子浓度达到饱和或一定的过饱和状态。若此时阳极界面的成核点上已经形成稳定的极小气泡,在溶液本体中的O2分子浓度与气泡膜内壁面的O2分子浓度差的驱使下,溶液中的O2分子则会不断地向气泡表面进行扩散,由气泡表面的边界逐渐扩散至气泡内部,从而导致成核点处的气泡尺寸、体积及质量等都会有一定程度的增大。

图3 不同电流密度下的初始气泡行为
Fig. 3 Initial bubble formation under different current densities
2.2 气泡的聚并过程
阳极气泡在成核点经历一定的生长过程后,在外力的驱动作用下离开成核点,溶液就会穿透和浸入到阳极表面与气泡中间的区域,形成一层液体膜,气泡主要在液体膜上进行移动。气泡在阳极底掌移动过程中,气泡与气泡之间因为碰撞作用会发生一定的聚并过程,气泡尺寸的增大过程比较明显。阳极底掌局部位置的气泡与气泡间的动态聚并行为过程如图4所示,重点分析图中红色标记区域的气泡聚并行为。为叙述方便,把不同尺寸的气泡分别划分为小尺寸气泡、中等尺寸气泡和大尺寸气泡。可以看出,不同尺寸气泡在阳极底掌运动时,由于各个气泡的运动路径及速度不同,大尺寸气泡的运动速度较大,可以较快地追赶运动较慢的小尺寸气泡,导致气泡之间会发生一定的碰撞过程,主要在溶液的局部强湍流涡体的带动作用下,使部分气泡发生明显的聚并,从而使气泡的形状和尺寸发生明显的改变(如t=0.16~0.48 s)。气泡在经历碰撞和聚并后,阳极底掌气泡形态的主要变化趋势是气泡的数量在减少,但是最终的气泡尺寸在增大,气泡尺寸从几毫米增大到几十毫米左右,且这种趋势在t=0.48 s以后的时间内更加明显。
在电解过程中,不同尺寸气泡之间的碰撞引起的聚并行为使整个阳极底掌覆盖着一定厚度的连续气泡层,且该气泡层形态总是动态变化的。图5所示为阳极底掌气泡层内的典型气泡形态特征,包括小尺寸气泡、中等尺寸气泡和大尺寸气泡。可以看出,气泡层内的气泡形状和尺寸与其对应的体积有很大关系,小尺寸气泡主要呈圆球状或半圆球状,大尺寸气泡主要呈扁平状,而中等尺寸气泡经历从圆球状、半圆球状、椭球状到扁平状等形态的改变。从不同尺寸气泡的数量和空间位置上看,数量比较少的大尺寸及中等尺寸气泡的周围存在着数量比较多的小尺寸气泡,即可认为气泡尺寸越大,对应的气泡数量越少,气泡的尺寸大小的分布范围很宽。根据实验中大量的气泡图像数据(未全部列出)对比和分析可知:小尺寸气泡主要为成核、生长及经历聚并程度等较少的气泡,其尺寸大小范围在0.5~5 mm左右;中等尺寸气泡主要为生长及经历聚并程度等较多的气泡,其尺寸大小范围在5~10 mm左右;大尺寸气泡主要为经历多次聚并过程的气泡,其尺寸大小范围在10 mm以上,最大尺寸可能达到几十毫米、甚至上百毫米。
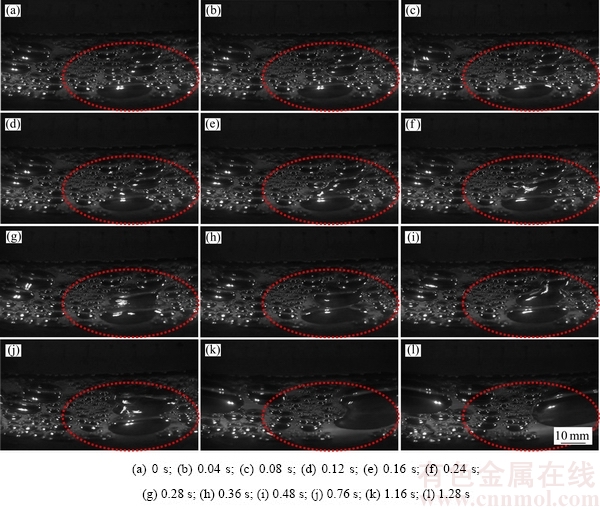
图4 不同时刻下气泡的聚并行为
Fig. 4 Bubble coalescence behaviors at different period of time
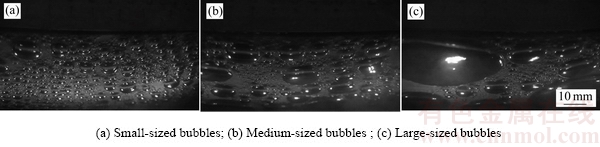
图5 不同尺寸气泡的典型特征
Fig. 5 Typical features of different sizes of bubbles
在分析了气泡的碰撞和聚并规律的基础上,探究电流密度对气泡聚并行为的影响。当电流密度提高时,一方面,气泡在阳极表面成核产生的数量就越多,这样就会有更多的气泡在阳极底掌移动,因此气泡之间的碰撞和聚并机会就会增多,将会产生更多的大尺寸气泡;另一方面,由于大尺寸气泡受到的气-液相间阻力较小,且其所受的浮力随气泡体积增大而增大的程度比较明显,而表面张力却不能增大同样的比例。因此,总的来说,促使大尺寸气泡运动的外力在增大,导致其运动速度加快,能够在短时间内追赶尺寸较小的气泡,也同样增加了不同尺寸气泡间的碰撞和聚并机会。总而言之,当电流密度在一定的合理范围内提高时,能够增加不同尺寸气泡间的碰撞和聚并概率,形成大尺寸气泡的数量会较多。
需要说明的是,与同等面积或体积大小的多个小尺寸气泡相比,阳极底掌的单个大尺寸气泡对气泡层内气-液两相动力学及形态的影响效果比较关键,因此,下面将继续对大尺寸气泡的形态动力学进行介绍。
2.3 大尺寸气泡的横扫效果
由于气泡聚并引起大尺寸气泡的体积越来越大,气泡的运动速度也越大,这样会增加气泡间的聚并机会,并沿途会“吞噬”更多的运动较慢的小尺寸气泡,将会在阳极底掌留下一部分空余的空间,此时的气泡覆盖率会降低很多。以上现象称为大尺寸气泡的横扫现象,如图6中红色框内标记所示。单个大尺寸气泡在阳极底掌几乎以同样的方向移动,其在运动过程中不断地“吞噬”前方数量较多的小尺寸气泡,导致该大尺寸气泡的体积不断增大,但是在较短时间内其沿途流动过的部分区域却没有其他的气泡及时流入和补充,从而在阳极底掌出现面积比较大的空白区域(如t=1.88~3.44 s)。大尺寸气泡的这种横扫效果引起气泡尺寸的继续增大过程与气泡间的聚并行为过程并不相同,主要突出的是单个大尺寸气泡的运动行为特点。因此,可以推测,当阳极尺寸较大时,这种横扫效果可能会产生尺寸更大的气泡,所留下的气泡空白区域将更大,对气泡覆盖率的影响更明显,从而对极间的气泡层形态分布、电流分布、电压降及气泡带动液体的动量及湍流传输等有明显的影响,如气泡层中的小尺寸气泡的数量会减少,被大尺寸气泡横扫区域内的液体运动速度会发生明显的波动等。上述结论可为后续进一步开展更大尺度的实验模型及采用数值模拟方法研究工业大型槽内的气泡动力学行为等奠定理论基础。
2.4 大尺寸气泡的脱离及破碎过程
阳极底掌不同尺寸气泡在经历复杂的成核、生长、聚并及横扫变形等过程后,总会有部分气泡连续地运动到阳极底掌边缘,最后经过阳极不同的缝中而逸出到电解质表面。图7所示为阳极边缘局部位置处单个大尺寸气泡脱离及破碎过程的动态行为过程。可以看出,在单个大尺寸气泡脱离阳极边缘前的极短时间内,如t=0.0~0.20 s内,主要发生气泡的初步变形过程,对液体局部流动过程的影响非常小。从t=0.28 s开始,该气泡开始在紧贴阳极边缘的槽缝逸出和脱离,此时气泡的形态及运动过程发生明显的变化。气泡的收缩和脉动等过程急剧增强,气泡会发生比较严重的变形(如t=0.28~0.40 s),使得气泡的中心薄膜会突然断裂,气泡尺寸会有明显减小的趋势,分裂成一系列的小尺寸气泡,还会伴随着气泡边缘处的液体产生强烈的循环扰动过程,详见红色框内的标记部分(如t=0.60~1.12 s)。气泡发生破碎过程主要是由于气泡前端部分开始自由脱离时,其运动过程由水平方向逐渐突变为垂直方向,运动速度较大,而尾部气泡的运动方向及速度不能和端部气泡的运动方式一样。端部和尾部气泡的运动方向及速度的差异性会导致气泡分布主要分为两个部分,即自由上升的部分和在阳极底掌继续滑移的部分,将不可避免地破碎成不同尺寸分布、数量更多的小尺寸气泡。
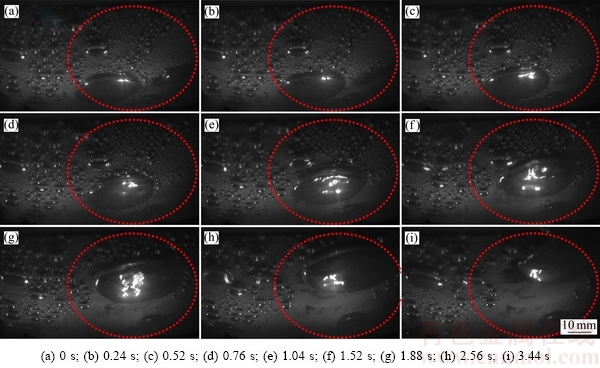
图6 大尺寸气泡横扫小尺寸气泡的过程
Fig. 6 Swallowing process of large bubbles
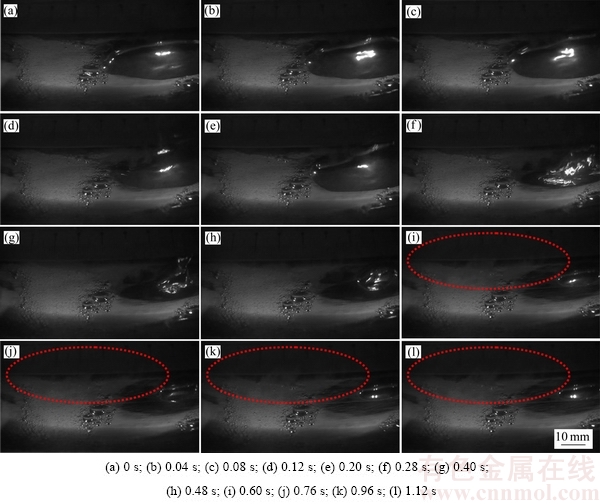
图7 大尺寸气泡的脱离及破碎过程
Fig. 7 Detachment and breakage process of large bubbles
大尺寸气泡的脱离和破碎等过程对槽内局部流动的影响非常重要,此过程将会使更多的液体返回到极间区域以补充大气泡脱离后留下的多余空间,因此在阳极边缘形成一定的回流运动。这种回流现象会带动更多的液体产生非常明显的波动过程,造成局部湍流及流场分布变化较大,气泡覆盖率、电压信号波动等也会产生瞬时的较大变化,有时甚至使阳极底掌的部分气泡暂时停止运动,在有关实验[6,22]及数值模拟[23]研究中均有类似的报道。
2.5 倾斜阳极对气泡分布特性的影响
图8所示为不同倾斜角下(分别为1°、2°和3°)的气泡分布随时间变化的动态图像,固定电流密度为0.1875 A/cm2。为便于分析,将整个阳极底掌从左至右分为3个区域,分别为左端、中端和右端区域,如图8(a)所示,且阳极倾斜时气泡从左端往右端方向运动。可以看出,倾斜阳极下的气泡成核及生长过程持续时间较短,大概在0.1 s左右,比水平阳极下持续的时间短很多。在不同倾斜角下,由于受沿倾斜方向较大的浮力作用,大多数气泡很容易离开成核点沿倾斜方向运动,气泡运动速度与倾斜角大小密切相关,倾斜角越大,气泡运动越快。因此,相同位置的气泡在较大倾斜角下脱离阳极底掌时所持续的时间变短,气泡间的碰撞和聚并机会减少,最终导致倾斜角越大,气泡尺寸越小,整体的气泡尺寸分布越均匀。在相同的倾斜角下,由于气泡的运动方向是基本确定的,即绝大部分气泡都是沿着其初始位置往右端移动,那么左端的气泡在脱离阳极边缘前的运动时间较长,运动路径也较长,在运动过程中发生的碰撞和聚并会产生一定数量的大尺寸气泡,且这些大尺寸气泡在沿途还会不断“吞噬”运动速度比较慢的小尺寸气泡,导致大尺寸气泡的尺寸越来越大。
图9所示为是倾斜角为1°时阳极底掌不同位置的气泡分布特性。可以看出,左端区域的小尺寸气泡的数量比较多,而右端区域大多是大尺寸气泡,但是气泡数量比较少,中端区域的气泡尺寸及数量等分布规律介于左端与右端之间。倾斜阳极不同部位的气泡尺寸分布规律与相关文献的实验结果一致[6, 22]。
对比水平阳极和倾斜阳极下的气泡分布特性规律可知,倾斜阳极下阳极底掌不同位置处的气泡尺寸及数量分布有明显的不同,而水平阳极下的气泡分布特性在阳极底掌位置上没有一定的规律可言,倾斜阳极下总的气泡数量及各尺寸气泡的数量均大大减少。倾斜阳极下的气泡覆盖率比水平阳极下的气泡覆盖率小很多,阳极倾斜角越大,气泡覆盖率降低的程度更明显。两者的共同之处在于整体的气泡数量分布相似,即气泡尺寸越大,对应的气泡数量越小。实际铝电解过程中,阳极不断被消耗,阳极底掌大多呈复杂的倾斜形状,有关倾斜阳极下的气泡动力学及其分布特性研究非常关键,因此后续研究有必要对该问题进行深入探讨。
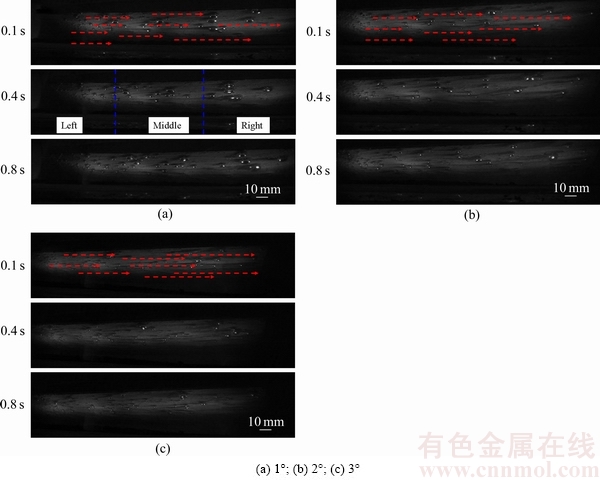
图8 不同倾斜角下气泡移动过程
Fig. 8 Bubble movement under different angles

图9 倾斜角为1°时不同部位气泡分布特性
Fig. 9 Bubble distribution in different parts at 1°
3 结论
1) 在电解初始时刻,阳极底掌的成核点处主要产生尺寸极小的气泡,且气泡尺寸分布比较均匀,气泡成核点的数量与电流密度大小有密切关系,提高电流密度会加快气泡的生长过程。
2) 经历长大过程后的气泡与相邻气泡间会发生一定的碰撞和聚并过程,在阳极底掌生成一定厚度的连续气泡层。该气泡层内的气泡尺寸分布范围比较宽,数量比较少的大尺寸及中等尺寸气泡的周围存在着数量比较多的小尺寸气泡。
3) 由于气泡聚并引起的大尺寸气泡的运动速度越大,进一步增加了气泡间的聚并机会,在沿途会“吞噬”数量多且运动较慢的小尺寸气泡,造成“吞噬”过程中的气泡覆盖率大大降低。
4) 大尺寸气泡在脱离阳极底掌过程中,气泡的体积收缩过程比较明显,还会发生一定的破碎过程,形成数量较多的小尺寸气泡,同时还伴随着较强烈的液体局部循环扰动。
5) 倾斜阳极对气泡运动速度和尺寸分布的影响比较大,增大阳极倾斜角会减少气泡间的碰撞和聚并机会,生成的大尺寸气泡比水平阳极少很多,整体的气泡尺寸分布范围非常窄。
REFERENCES
[1] 刘业翔, 李 劼. 现代铝电解[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2008: 3-6.
LIU Ye-xiang, LI Jie. Modern aluminum electrolysis[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2008: 3-6.
[2] Poncsak S, Kiss L I, Toulouse D, Perron A, Perron S. Size distribution of the bubbles in the Hall-Heroult cells[C]// Hagni A M. Light Metals 2006. San Antonio, TX: TMS, 2006: 457-46.
[3] Fortin S, Gerhardt M, Gesing J A. Physical modeling of bubble behaviour and gas release from aluminum reduction cell anodes[C]// Euel R. Light Metals 1984. Los Angeles, CA: TMS, 1984: 721-741.
[4] Chen J J J. Some physical model studies of gas-induced flows in aluminum cells[J]. Journal of the Minerals, Metals and Materials Society, 1994, 46(11): 15-20.
[5] Cooksey M A, Yang W. PIV measurements on physical models of aluminum reduction cells[C]// Galloway T J. Light Metals 2006.Warrendale, PA: TMS, 2006: 359-365.
[6] Vekony K, Kiss L I. Morphology of two-phase layers with large bubbles[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transaction B, 2010, 41(10): 1006-1017.
[7] 刘 燕, 张延安, 赵秋月, 李 冲, 王洪星, 章 俊, 冯乃祥. 新型阴极结构铝电解槽的物理数学模拟[J]. 过程工程学报, 2011, 11(5): 721-728.
LIU Yan,ZHANG Ting-an,ZHAO Qiu-yue,LI Chong,WANG Hong-xing,ZHANG Jun,FENG Nai-xiang. Mathematical and physical simulation of new cathode structure of aluminum electrolytic cells[J]. The Chinese Journal of Process Engineering, 2011, 11(5): 721-728.
[8] Kiss L I, Ponesak S, Antille J. Simulation of the bubble layer in aluminum electrolysis cell[C]// Kvande H. Light Metals 2005. San Francisco, CA: TMS, 2005: 559-564.
[9] 韩 莉. 新型惰性阳极铝电解槽流场仿真与结构优化[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2012.
HAN Li. Simulation and optimization on the flow field in new type inert anode electrolytic cell[D]. Changsha: CentralSouth University, 2012.
[10] Cassayre L, Plascencia G, Marin T, Fan S, Utigard T. Gas evolution on graphite and oxygen-evolving anodes during aluminium electrolysis[C]// Galloway T J. Light Metals 2006. Warrendale, PA: TMS, 2006: 379-383.
[11] 徐君莉, 石忠宁, 高炳亮, 邱竹贤. 铝电解金属阳极上的气泡析出行为[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2004, 14(2): 298-301.
XU Jun-li, SHI Zhong-ning, GAO Bing-liang, QIU Zhu-xian. Bubble behavior on metal anode of aluminum electrolysis[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2004, 14(2): 298-301.
[12] Xue J, Oye H A. Spectrum analysis of the bubbling acoustic signals through carbon anode[C]// Eckert C E. Light Metals 1999. San Diego, CA: TMS, 1999: 247-253.
[13] 杨少华, 谢宝如, 杨凤丽, 李明周. 铝电解槽阳极气泡行为研究[J]. 有色金属科学与工程, 2013, 4(3): 20-24.
YANG Shao-hua, XIE Bao-ru, YANG Feng-li, LI Ming-zhou. The behavior of anode bubbles in aluminum electrolytic cell[J]. Nonferrous Metals Science and Engineering, 2013, 4(3): 20-24.
[14] ZHAO Z B, WANG Z W, GAO B L, FENG Y Q, SHI Z N, HU X W. Anodic bubble behavior and voltage drop in a laboratory transparent aluminum electrolytic cell[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2016, 47B(6): 1962-1975.
[15] 周益文, 周孑民, 陈首慧, 杨建红, 刘志明, 包生重. 垂直惰性阳极铝电解槽内的析气行为[J]. 化工学报, 2017, 68(3): 1185-1190.
ZHOU Yi-wen, ZHOU Jie-min, CHEN Shou-hui, YANG Jian-hong, LIU Zhi-ming, BAO Sheng-zhong. Gas evolution behavior in aluminum electrolysis cell with vertical inert anode[J]. CIESC Journal, 2017, 68(3): 1185-1190.
[16] Qian K, Chen Z D, Chen J J J. Bubble coverage and bubble resistance using cells with horizontal anode[J]. Journal of Applied Electrochemistry, 1998, 28(10): 1141-1145.
[17] 薛玉卿, 周乃君, 包生重. 铝电解槽内阳极气泡运动的冷态模拟[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2006, 16(10): 1823-1828.
XUE Yu-qing, ZHOU Nai-jun, BAO Sheng-zhong. Normal temperature analogue experiment of anode bubbles behavior in aluminum electrolysis cells[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2006, 16(10): 1823-1828.
[18] Alam M, Yang W, Mohanarangam K, BROOKS G, MORSI Y S. Investigation of anodic gas film behavior in Hall-Heroult cell using low temperature electrolyte[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2013, 44(10): 1155-1165.
[19] Djokic S S. Electrodeposition: Theory and practice[M]. New York: Springer, 2010: 143-149.
[20] Perron A, Kiss L I, Poncsák S. Regimes of the movement of bubbles under the anode in an aluminum electrolysis cell[C]// Kvande H. Light Metals 2005. San Francisco, CA: TMS, 2005: 565-570.
[21] 詹水清. 铝电解槽熔体内多相流体动力学行为的数值模拟及应用研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2015.
ZHAN Shui-qing. Numericalsimulation and application of multiphase flow dynamics behavior in melts of aluminum reduction cells[D]. Changsha: CentralSouth University, 2015.
[22] Vekony K, Kiss L I. Experimental study of the morphology and dynamics of gas-laden layers under the anodes in an air-water model of aluminum reduction cells[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2012, 43(10): 1086-1097.
[23] Zhang K Y, Feng Y Q, Schwarz P, Wang Z W, Cooksey M. Computational fluid dynamics(CFD) modeling of bubble dynamics in the aluminum smelting process[J]. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research, 2013, 52(33): 11378-11390.
Experimental research on dynamics and distribution characteristics of anodic bubbles in aluminum electrolysis cells with low temperature electrolysis
ZHAN Shui-qing1, WANG Zhen-tao1, YANG Jian-hong2, ZHENG Jun1, WANG Jun-feng1
(1. School of Energy and Power Engineering, Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang 212013, China;
2. Institute of Green Materials and Metallurgy, Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang 212013, China)
Abstract: Taken a 300 kA aluminum electrolysis cell in some aluminum company in Henan province, a novel low temperature electrolytic model with a geometric similarity ratio of 1:4 to its prototype was designed and constructed based on the principles of geometric and dynamic similarities. In addition, the bubble nucleation, growth, coalescence, breakup and detachment underneath the anode were recorded. The results show that electrolytic bubbles are first nucleated uniformly under the entire anode surface with small size. Then these bubbles grow up uncreasingly through the growth process caused by gas diffusion and mass transfer and the coalescence process caused by collision and swallowing. And finally some large bubbles escape from the edge of the anode bottom and break up into more smaller bubbles with a large amount of liquid flow. The bubble layer underneath the anode has a broad bubble size distribution and differs greatly in shape. The whole anode is covered by a few large and medium-sized bubbles and a large number of small bubbles. Changing current density and anode inclination angle has an important influence on some dynamical behavior mechanisms and distribution characteristics of the bubbles above.
Key words: aluminum electrolysis; anodic bubble dynamics; distribution characteristic; low temperature electrolysis; experimental research
Foundation item: Project(11502097) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project (2016M591781) supported by the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation, China; Project (2015JDG158) supported by the Foundation of Senior Talent of Jiangsu University, China; Project (PAPD) supported by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions, China
Received date: 2017-03-28; Accepted date: 2017-07-23
Corresponding author: ZHAN Shui-qing; Tel: +86-18852869020; E-mail: zhanshuiqing@ujs.edu.cn
(编辑 王 超)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金青年项目(11502097);中国博士后科学基金资助项目(2016M591781);江苏大学高级人才基金资助项目(2015JDG158);江苏省高校优势学科建设工程项目(PAPD)
收稿日期:2017-03-28;修订日期:2017-07-23
通信作者:詹水清,讲师,博士;电话:18852869020;E-mail: zhanshuiqing@ujs.edu.cn