文章编号:1004-0609(2016)-11-2296-07
放电等离子烧结MoSi2陶瓷的微观结构与力学性能
李 恒1,郝安林2,王雅雷1,熊 翔1,陈招科1,孙 威1,韩欣欣1
(1. 中南大学 粉末冶金国家重点实验室,长沙 410083;2. 安阳工学院,安阳 455000)
摘 要:以微米级MoSi2粉末为原料,利用放电等离子烧结技术制备致密度达99%的MoSi2陶瓷材料。研究烧结温度对MoSi2陶瓷的致密化、微观结构和力学性能的影响。结果表明:SPS烧结技术制备的MoSi2陶瓷由MoSi2、少量的Mo5Si3和SiO2组成;随着烧结温度的升高,材料的致密化效果明显加强;当烧结温度为1600 ℃时,材料的综合性能最优,相对密度和抗弯强度达到98.9%和417 MPa。但当烧结温度达到1800 ℃时,致密度基本保持不变,MoSi2晶粒长大明显,材料抗弯强度降低。
关键词:MoSi2;放电等离子烧结;微观结构;力学性能
中图分类号:TB321 文献标志码:A
随着近代科学技术的发展,航天、航空和先进能源等领域对材料的耐高温和抗氧化性能的要求愈加严苛。MoSi2因其高熔点、低密度、良好的导热性和导电性以及优良的高温抗氧化能力[1],特别是具有在高温下保持屈服强度不变的特性而备受关注[2],是当前高温结构材料的研究热点之一。然而,MoSi2陶瓷在低温环境中(500 ℃)会发生粉化现象[3],严重影响了MoSi2的适用范围。近年来,有学者研究发现[4-5],通过提高MoSi2材料的致密度(大于MoSi2理论密度的98%)可以有效抑制MoSi2陶瓷的低温粉化现象。因此,如何制备出高致密的MoSi2陶瓷成为当下的研究热点。
目前,MoSi2陶瓷常见的制备方法有原位合成法[6]、自蔓延合成法(SHS)[7]、机械合金化法(MA)[8]、微波烧结(WA)[9]、热压烧结(HP)[10]和热喷涂法[11]等。放电等离子烧结(SPS)作为一种新的特种烧结技术,具有烧结温度低、烧结时间短、单件能耗低、晶粒细小和操作简单等优点[12-14]。SPS对于制备高密度的MoSi2陶瓷材料是一种有效的烧结手段。目前,通过放电等离子烧结技术来制备MoSi2材料的研究报道较少,还需要大量的研究工作。在此,本文作者采用放电等离子烧结技术来制备MoSi2陶瓷,研究了不同烧结温度对MoSi2陶瓷微观结构和力学性能的影响,并探讨了其致密化行为。
1 实验
1.1 样品制备
实验所用MoSi2粉末为辽宁德盛特种陶瓷制造公司生产,粒径为3~5 μm,纯度≥99.9%。由于粉末采用真空包装,导致粉末出现软团聚,为排除粉末团聚对烧结造成的影响,将MoSi2粉末进行研磨分散。为了防止粉末在干燥过程中氧化,选择将粉末在50 ℃条件下鼓风干燥4 h以充分去除水分。
将干燥后的MoSi2粉末装填入石墨模具,然后将模具放置于放电等离子快速烧结炉(德国FCT公司生产,型号为HP D 25/3),在真空条件下进行烧结。SPS烧结工艺如下:升温速率为100 ℃/min,烧结温度为1200、1400、1600和1800 ℃,烧结时间为10 min,对试样施加的轴向压力为30 MPa。
1.2 分析与表征
采用Archimedes排水法测定MoSi2陶瓷试样的体积密度,并计算得出陶瓷试样的相对密度,计算公式如下:
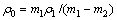 (1)
(1)
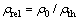 (2)
(2)
式中:ρ0为陶瓷试样的体积密度,g/cm3;ρ1为实验温度下浸渍液体的密度,g/cm3;m1为干燥陶瓷试样的质量,g;m2为液体中饱和试样的表观质量,g;ρrel为陶瓷试样的相对密度,%;ρth为MoSi2的理论密度(6.24 g/cm3)。
利用日本理学D/max2550VB+18K转靶X射线衍射仪(XRD)分析陶瓷材料的物相组成。利用扫描电子显微镜(FEI CO., NOVA Nano230)对陶瓷材料的显微组织结构和断口形貌进行分析。根据GB/T 6569-2006在INSTRON试验机上测定MoSi2陶瓷材料的抗弯强度,试样尺寸为40 mm×5 mm×4 mm,试样跨距为30 mm,加载速率为1 mm/min,每组试样5个。弯曲强度按式(3)计算:
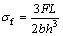 (3)
(3)
式中:σf为弯曲强度,MPa;F为最大破坏载荷,N;L为跨距,mm;h为试样厚度,mm;b为试样宽度,mm。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 MoSi2粉末的烧结行为
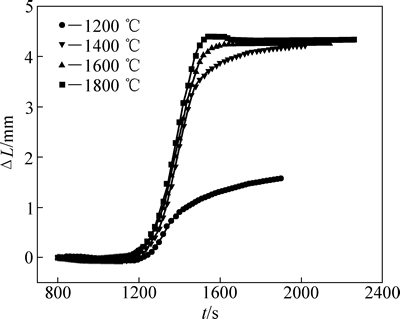
图1 不同烧结温度下MoSi2试样收缩程度与时间的关系
Fig. 1 Relationship between shrinkage and time of sample MoSi2 sintered at different sintering temperatures
图1所示为不同烧结温度条件下模具压头位移随烧结时间的变化曲线。可以看出,在烧结的初始阶段,残余气体和粉末的受热会导致试样发生轻微的膨胀;在烧结过程进行1200 s之后,试样开始出现收缩位移,实现致密化过程。由图1还可以看出,当烧结温度为1200 ℃时,烧结试样的收缩位移及速度均远小于1400、1600和1800 ℃烧结试样的,MoSi2试样的烧结致密化效果较差,这是由于烧结温度偏低导致试样无法完成有效烧结。但当烧结温度≥1400℃时,MoSi2试样的收缩位移及速率迅速提高,MoSi2试样能快速地完成致密化过程,达到较高的致密度。随着烧结温度进一步提高,试样的最大收缩位移逐渐提升。但1600 ℃烧结和1800 ℃烧结相比,致密化效率已无明显差异。
2.2 MoSi2陶瓷的微观结构
图2所示为不同烧结温度条件下MoSi2陶瓷试样的SEM像。可以明显发现,1200 ℃条件下烧结的MoSi2陶瓷材料疏松多孔,材料烧结不充分,整体致密化效果较差(见图2(a))。放大图片显示(见图2(b)),1200 ℃烧结的MoSi2陶瓷内部存在大量孔隙结构,MoSi2晶粒尺寸与原始粉末相近,颗粒间结合较差,烧结效果不明显。当烧结温度升高至1400 ℃以上时,MoSi2材料烧结充分,烧结体内部孔隙的尺寸大大减小,数量明显减少,仅存在少量微小孔洞(见图2(c),(e),(g))。进一步放大观察(见图2(d),(f),(g)),烧结后的MoSi2陶瓷结构主要由灰色和白色两种晶粒构成,随着烧结温度的升高,烧结体内部孔洞的数量、形状发生了明显的变化,尤其是孔洞的形状随着烧结温度的升高逐渐显现出球化特征。
由图2(b)可以看到,在1200 ℃烧结时粉末颗粒间已经形成了烧结颈,颗粒相连成片,但粉末颗粒间仍有一定孔隙,大量孔隙连通形成疏松结构。这是因为在放电等离子烧结条件下,MoSi2粉末的烧结过程受到焦耳热和颗粒放电的共同作用,MoSi2颗粒间放电会产生的瞬时高温使颗粒表面熔化和蒸发,颗粒接触处形成烧结颈,热量由中心向四周迅速扩散导致颈部快速冷却,蒸汽压低于其他部位,气相物质凝聚在颈部形成蒸发-凝固传递[15];但是由于烧结温度较低,MoSi2的原子活化度不足,原子扩散与流动速度较低,粉末颗粒之间的烧结颈在较短的烧结过程中不能充分长大,导致材料内部存在大量连通的孔隙网络,使MoSi2烧结体的致密化程度较低。在1400 ℃烧结温度下,大部分连通孔隙消失,进而形成形状不规则的细小闭孔(见图2(d)),陶瓷体已经比较致密,表明试样得到了较为充分的烧结。当烧结温度提高到1600 ℃时,试样内部的孔隙已经全部转化为闭孔,并开始球化,部分小孔消失,孔隙数量明显减少(见图2(f)),这说明在1600 ℃烧结温度下,试样的烧结程度较1400℃时烧结更加充分。而当烧结温度提高到1800 ℃时,试样内部的孔隙已经基本球化,并且平均孔径有所减小(见图2(h)),说明试样烧结程度再次提升。这是因为提升烧结温度可以使粉末颗粒的活性增加,促进原子的扩散流动,加快烧结的进行,提升陶瓷烧结的致密化效率,使陶瓷的致密化程度得到提高。
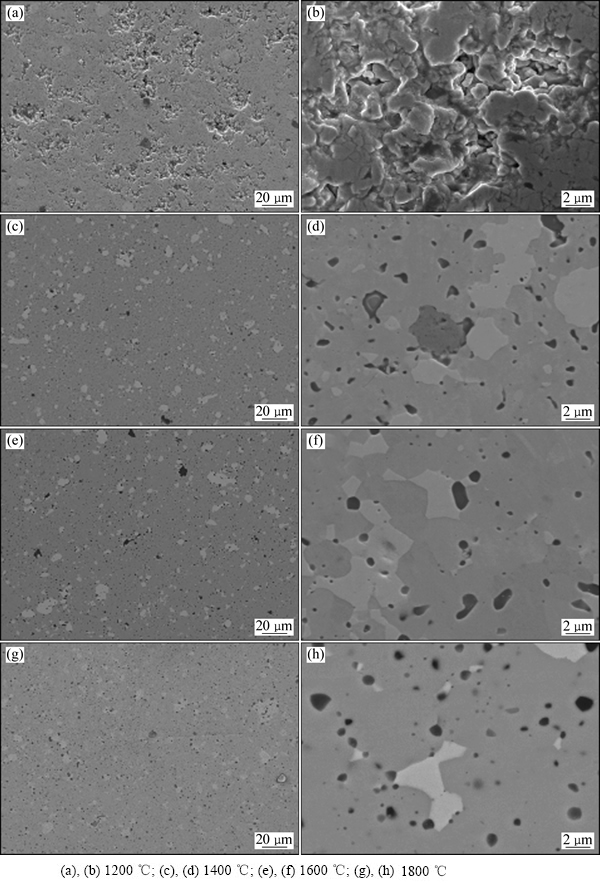
图2 不同温度烧结MoSi2陶瓷的SEM像
Fig. 2 SEM images of MoSi2 ceramics sintered at different temperatures
2.3 MoSi2陶瓷的相组成
图3所示为MoSi2原料粉末的XRD谱。粉末主要由MoSi2和少量的Mo5Si3组成。图4所示为不同烧结温度下MoSi2陶瓷的XRD谱。可以看到,当烧结温度为1200 ℃时,陶瓷的物相成分仍只为MoSi2和少量的Mo5Si3,且各组成物相的衍射峰位置及相对强度与原始粉末基本一致。当烧结温度升高至1400 ℃时,陶瓷试样的XRD谱中出现了微弱的SiO2衍射峰,说明MoSi2粉末在烧结过程中发生了轻微的氧化。同样,当烧结温度上升至1600 ℃和1800 ℃时,陶瓷试样由MoSi2、少量的Mo5Si3和SiO2组成。SiO2的生成是由于MoSi2粉末体在压力的作用下紧密接触,粉末坯体内部存在的少量氧在烧结过程中无法有效排出,在高温条件下将会与MoSi2粉末表面发生反应(见式(4))。因此,SPS烧结MoSi2陶瓷的XRD谱中出现了SiO2衍射峰,MoSi2陶瓷的XRD谱中无明显SiO2衍射峰是由SiO2含量较小所致。
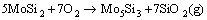 (4)
(4)
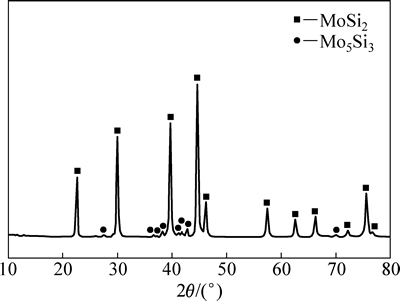
图3 MoSi2原始粉末的XRD谱
Fig. 3 XRD patterns of MoSi2 powder
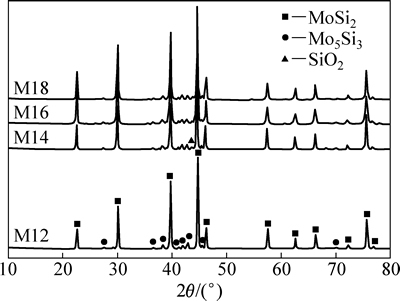
图4 不同烧结温度下MoSi2陶瓷试样的XRD谱
Fig. 4 XRD patterns of MoSi2 samples sintered at different temperatures
图5(a)所示为1600℃烧结制备MoSi2陶瓷材料微观结构的BES像。可以看到,材料主要由灰色相(见图5(a)中1处)、白色相(见图5(a)中2处)和孔洞组成。图5(b)所示为1800 ℃烧结制备MoSi2陶瓷材料微观结构的SEM像。可以发现,陶瓷基体上有不规则环形亮斑。根据EDS元素分析(见图6),灰色组织相由Mo和Si组成,且两者摩尔比约为1:2(见图6(a)),说明此灰色相为MoSi2。不规则块状特征的白色相分布在MoSi2基体内,由Mo和Si组成,两者摩尔比约为5:3(见图6(b)),说明此白色相为Mo5Si3。不规则环形亮斑由Si和O组成,两者摩尔比约为1:2(见图6(c)),说明此亮斑为SiO2。由于SiO2导电性差,所以在二次电子扫描下产生放电现象,形成环形亮斑。
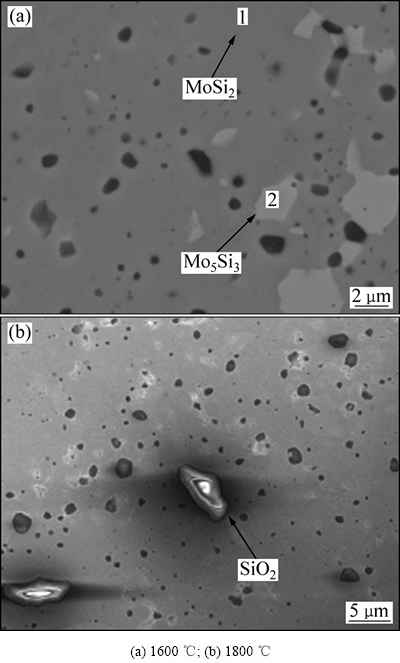
图5 不同温度烧结MoSi2陶瓷内部组织的SEM像
Fig. 5 SEM images of MoSi2 ceramic sintered at different temperatures
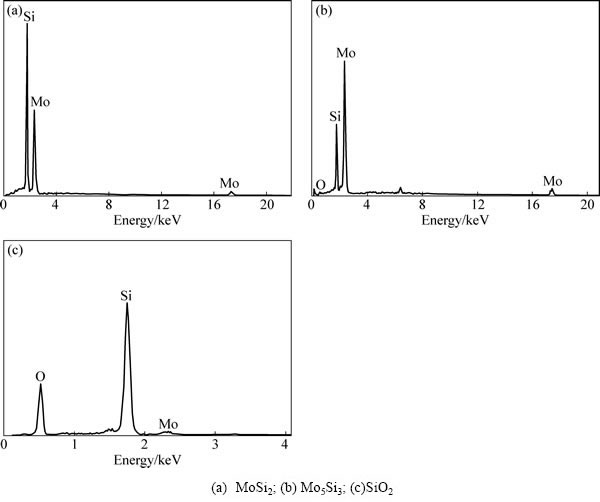
图6 MoSi2陶瓷组织的EDS谱
Fig. 6 EDS patterns of MoSi2 ceramics
2.4 MoSi2陶瓷的力学性能
表1所列为不同烧结温度MoSi2试样的体积密度、相对密度和抗弯强度数据。可以看出,当烧结温度为1200 ℃时,MoSi2试样尚未达到致密化,其体积密度为4.81 g/cm3, 相对密度仅为77.1%。而当烧结温度提升至1400、1600和1800 ℃时,MoSi2试样的体积密度和相对密度明显上升,基本实现致密化,且随着烧结温度的升高,试样的体积密度和相对密度进一步上升,1800 ℃烧结条件下试样的体积密度和相对密度分别可达6.18 g/cm3和99.0%。另外,由表1还可看到,随着烧结温度的升高,MoSi2试样的抗弯强度逐步增加,1800 ℃烧结条件下稍有下降。当烧结温度为1600 ℃时,MoSi2试样的抗弯强度最高,达到417 MPa。
表1 MoSi2陶瓷材料的密度、相对密度及抗弯强度
Table 1 Bulk density, relative density, bending strength of MoSi2 ceramics
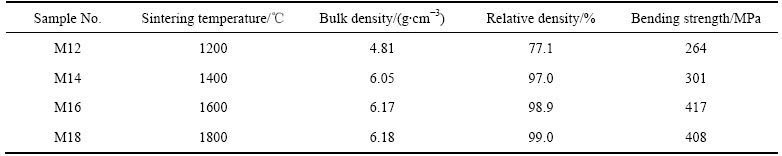
综合上述数据分析表明,在1600℃烧结条件下,MoSi2材料的致密化效果和力学性能最为理想。
图7所示为不同烧结温度下MoSi2试样断口的SEM像。不同烧结温度条件下MoSi2试样均呈脆性断裂特征。当烧结温度为1200 ℃时,材料断口可以明显看到大量的MoSi2粉末颗粒,其尺寸大小与原始粉末差异不大(见图7(a))。这说明在1200 ℃烧结条件下,MoSi2粉末颗粒未发生有效烧结,材料内部存在大量孔隙,这是此温度条件下烧结试样抗弯强度较低的主要原因。当烧结温度为1400 ℃时,MoSi2粉末颗粒发生了充分的烧结长大,形成较大的晶粒,且材料内部孔隙减少,材料致密化效果明显提高。试样断口以岩石形貌为主(见图7(b)),表明断裂的主要模式为沿晶断裂[16],说明MoSi2晶粒间的结合较弱,因而其弯曲强度提高幅度较小,提高至301 MPa。当烧结温度为1600 ℃时,材料内部孔隙数量减少,材料相对密度明显提高,但MoSi2晶粒尺寸增大,材料内部闭孔数量增加,连通孔隙消失,断口上出现明显的台阶形貌(见图7(c)),表明断裂模式由沿晶断裂转变为穿晶断裂 [16],晶粒结合强度高,因此抗弯性能较1400 ℃时有了较大提升(见表1)。而当烧结温度提高到1800 ℃时,材料内部晶粒进一步长大,孔隙呈明显的球形特征,且主要分布在晶界和晶粒内部(见图7(d))。但由于材料内部晶粒明显长大,力学性能稍有下降。总之,随着烧结温度的升高,MoSi2的烧结越充分,材料内部缺陷减少,结构更加致密,断裂时需要的能量增大,裂纹扩展所需要的临界应力也相应增大,因此试样的抗弯强度明显上升。
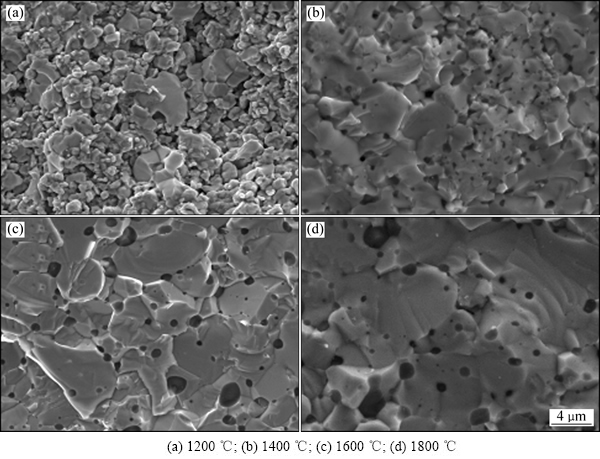
图7 不同温度烧结温度试样的断口形貌
Fig. 7 Fractograghs of MoSi2 ceramics sintered at different temperatures
3 结论
1) 采用放电等离子烧结技术(SPS)可大大促进MoSi2陶瓷材料的烧结致密化,在1400 ℃的条件下即可达到97%以上的高致密度,在1600 ℃可达到98.9%,接近全致密状态。
2) 在1600 ℃烧结温度和30 MPa压力条件下,MoSi2陶瓷的烧结密度为6.17 g/cm3,抗弯强度可达417 MPa,材料的致密化效果和抗弯性能最为理想。材料的抗弯性能主要由材料的致密度和晶粒尺寸所影响,随着烧结温度的升高,材料致密化程度增加,材料抗弯强度增加,同时,材料的晶粒尺寸也伴随着烧结温度的升高而增大,从而使材料抗弯性能下降。
REFERENCES
[1] 张来启, 高 强, 林均品. MoSi2超高温结构材料的研究进展[J]. 中国材料进展, 2015, 34(2): 126-134.
ZHANG Lai-qi, GAO Qiang, LIN Jun-pin. The state-of-art of ultra-high-temperature structural MoSi2[J]. Materials China, 2015, 34(2): 126-134.
[2] 韩 超. MoSi2基耐高温涂层的制备及性能研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2014: 5-6.
HAN Chao. Preparation and properties of MoSi2-based high temperature ceramics coating[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2014: 5-6.
[3] YAN J H, XU H M, ZHANG H A. MoSi2 oxidation resistance coatings for Mo5Si3/MoSi2 composites[J]. Rare Metals, 2009, 28(4): 418-422.
[4] CHEN J X., LI C H , FU Z , TU X Y , SUNDBERG M , POMPE R. Low temperature oxidation behavior of a MoSi2-based material[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 1999, 261(1/2): 234-244.
[5] KUCHINO J, KUROKAWA K, SHIBAYAMA T, TAKAHASHI H. Effect of microstructure on oxidation resistance of MoSi2 fabricated by spark plasma sintering[J]. Vacuum, 2004, 73(3/4): 623-628.
[6] DAI Lei, YU Yao, ZHOU Hui-zhu, YAN Xiao-yong, ZHU Jing, LI Yue-hua, WANG Ling. In-situ synthesis of MoSi2 coating on molybdenum substrate by electro-deoxidation of a SiO2 layer in molten salt[J]. Ceramics International, 2015, 41(10): 13663-13670.
[7] MIKHEEV M V, BAZHIN P M, STOLIN A M, ALYMOV M I. Effect of titanium on the rheological properties of MoSi2-based materials prepared by SHS[J]. Inorganic Materials, 2016, 52(2): 141-146.
[8] SHAHROUZ Z, HAMID R B, ALI S. Synthesis and characterization of MoSi2-Mo5Si3 nanocomposite by mechanical alloying and heat treatment[J]. International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials, 2012, 31: 236-241.
[9] PANNEERSELVAM M, AGRAWAL A, RAO K J. Microwave sintering of MoSi2-SiC composites[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2003, 356(1/2): 267-273.
[10] WU Wen-wen, WANG Zhuo, ZHANG Guo-jun. ZrB2-MoSi2 composites toughened by elongated ZrB2 grains via reactive hot pressing[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2009, 61(3): 316-319.
[11] 王 平, 熊 翔, 闵小兵. 热喷涂制备MoSi2高温结构材料的工艺研究[J]. 矿冶工程, 2013(2): 108-111.
WANG Ping, XIONG Xiang, MIN Xiao-bing. Hot spraying technique for mosi2-based high-temperature structural materials[J]. Mining and Metallurgical Engineering, 2013(2): 108-111.
[12] MUNIR Z A. The effect of external electric fields on the nature and properties of materials synthesized by self-propagating combustion[J]. Materials Science and Engineering, 2000, 287(2): 125-137.
[13] 倪东惠, 谭文昌, 郑军君. Si含量对放电等离子烧结制备(1-x)Ti3SiC2+xSiC复合材料的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2011, 21(6): 1279-1284.
NGAI Tung-wai, TAN Wen-chang, ZHENG Jun-jun. Influence of Si content on (1-x)Ti3SiC2+xSiC composites prepared by spark plasma sintering[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2011, 21(6): 1279-1284.
[14] 黄平军, 张玉勤, 蒋业华. 放电等离子烧结温度对Ti-3Zr-2Sn-3Mo-15Nb合金微观组织和力学性能的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2013, 23(8): 2200-2205.
HUANG Ping-jun, ZHANG Yu-qin, JIANG Ye-hua. Effect of spark plasma sintering temperatures on microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti-3Zr-2Sn-3Mo-15Nb alloy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2013, 23(8): 2200-2205.
[15] 白 玲, 葛昌纯, 沈卫平. 放电等离子技术[J]. 粉末冶金技术, 2007, 25(3): 217-223.
BAI Ling, GE Chang-chun, SHEN Wei-ping. Spark plasma sintering technology[J]. Powder Metallurgy Technology, 2007, 25(3): 217-223.
[16] 钟群鹏, 赵子华, 张 峥. 断口学的发展及微观断裂机理研究[J]. 机械强度, 2005, 27(3): 358-370.
ZHONG Qun-peng, ZHAO Zi-hua, ZHANG Zheng. Development of “fractography” and research of fracture micromechanism[J]. Journal of Mechanical Strength, 2005, 27(3): 358-370.
Microstructure and mechanical properties of MoSi2 prepared by spark plasma sintering
LI Heng1, HAO An-lin2, WANG Ya-lei1, XIONG Xiang1, CHEN Zhao-ke1, SUN Wei1, HAN Xin-xin1
(1. State Key Laboratory of Powder Metallurgy, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. Anyang Institute of Technology, Anyang 455000, China)
Abstract: Using MoSi2 micropowder as raw material, MoSi2 ceramics with relative density of 99% was prepared by spark plasma sintering. The effects of sintering temperature on the densification, microstructure and mechanical properties of MoSi2 ceramics were studied. The results show that the MoSi2 ceramics prepared by SPS are made of MoSi2 and a small amount of Mo5Si3 and SiO2. With the increase of sintering temperature, the relative density of product is improved apparently. When the sintering temperature is 1600 ℃, the comprehensive property of the products is optimal, and the relative density and bending strength are up to 98.9% and 417 MPa, respectively. When the sintering temperature rises to 1800 ℃, the relative density remains the same, while the bending strength reduces due to the grain size growth.
Key words: MoSi2; spark plasma sintering; microstructure; mechanical property
Foundation item: Project(2014M562129) supported by the Postdoctoral Fund Project of China; Project(51405522) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Received date: 2015-12-28; Accepted date: 2016-05-21
Corresponding author: XIONG Xiang; Tel: +86-13308414388; E-mail: xiongx@csu.edu.cn
(编辑 龙怀中)
基金项目:中国博士后科学基金资助项目(2014M562129);国家自然科学基金资助项目(51405522)
收稿日期:2015-12-28;修订日期:2016-05-21
通信作者:熊翔,教授,博士;电话:13308414388;E-mail:xiongx@csu.edu.cn