文章编号:1004-0609(2013)08-2200-06
放电等离子烧结温度对Ti-3Zr-2Sn-3Mo-15Nb合金微观组织和力学性能的影响
黄平军1, 2,张玉勤1, 2,蒋业华1,周 荣1
(1. 昆明理工大学 材料科学与工程学院,昆明 650093;
2. 云南省钛材应用产品工程技术研究中心,昆明 650093)
摘 要:利用放电等离子烧结技术(SPS)制备Ti-3Zr-2Sn-3Mo-15Nb合金,研究烧结温度对合金致密度、微观组织与力学性能的影响。结果表明:在1 000~1 150 ℃烧结温度范围内,合金具有较高致密度和抗压强度,合金主要由β-Ti相与Ti-Nb-Zr-Mo固溶体形成的混合基体组织及少量α-Ti相和未熔化的Nb金属颗粒组成;随着烧结温度的升高,合金的致密度和抗压强度呈增大趋势,合金中Ti-Nb-Zr-Mo固溶体含量越来越低,其尺寸越来越小,残留的α-Ti相出现了向β-Ti相的转变;合金的压缩弹性模量值在45~54 GPa之间,显示出良好的力学相容性,而烧结温度的升高使得压缩弹性模量值出现缓慢增大现象。
关键词:Ti-Zr-Sn-Mo-Nb合金;放电等离子烧结;烧结温度;微观组织;力学性能
中图分类号:TF124;TG146.2 文献标志码:A
Effect of spark plasma sintering temperatures on microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti-3Zr-2Sn-3Mo-15Nb alloy
HUANG Ping-jun1, 2, ZHANG Yu-qin1, 2, JIANG Ye-hua1, ZHOU Rong1
(1. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Kunming University of Science and Technology, Kunming 650093, China;
2. Engineering Technology Research Center of Titanium Products and Application of Yunnan Province, Kunming 650093, China)
Abstract: Ti-3Zr-2Sn-3Mo-15Nb alloys were prepared by spark plasma sintering (SPS) technology. The effects of the different sintering temperatures on the relative density, microstructure and mechanical properties of the alloys were investigated. The results show that, in the sintering temperature range from 1 000 to 1 150 ℃, the alloys present high densification and compressive strength. The alloys mainly contain the mixed matrix consisting β-Ti phase and the Ti-Nb-Zr-Mo solid solution and some α-Ti phase and unmelted Nb metal particles. With the increase of the sintering temperature, the relative density and the compressive strength of the alloys increase. The size and the amount of the Ti-Nb-Zr-Mo solid solution decrease, and the alloys appear in the transformation process from α-Ti to β-Ti phase. The alloys exhibit low compressive elastic modulus in 45-54 GPa, which reveals the better mechanical compatibility. With the increase of the sintering temperature, the compressive elastic modulus of the alloys increases slowly.
Key words: Ti-Zr-Sn-Mo-Nb alloy; spark plasma sintering; sintering temperature; microstructure; mechanical property
钛及钛合金具有低密度、高比强度、耐腐蚀、低模量及良好的生物相容性等特性,因而在生物医疗器件特别是人造植入材料方面得到了日益广泛的应用[1-2]。近年来,为了实现用于骨头、关节、牙齿等人造植入体的钛合金低模量(接近于天然骨头模量,20~30GPa)、无生物毒性(合金元素均无毒且在人体中不会引起不良反应)以及较高的抗疲劳强度和良好的耐磨耐腐蚀性能的目的,研究人员通过添加Nb、Zr、Ta、Sn、Mo、Fe等β相稳定及合金强化元素,开发了一系列低弹性模量、高比强度、良好生物相容性的近β型医用钛合金,在其性能均优于传统的Ti-6Al-4V、316L不锈钢以及CoCrMo等合金[3-4]。在目前研究的各种β型钛合金中,于振涛等[5-9]研制开发了Ti-Zr-Sn-Mo-Nb(TLM)系列钛合金,如Ti-3Zr-2Sn- 3Mo-15Nb、Ti-3Zr-2Sn-3Mo-25Nb、Ti-4Zr-1Sn-3Mo- 25Nb等,其研究发现Sn、Nb元素的添加可有效降低TLM钛合金的弹性模量,并且其组织状态为亚稳a″、ω和亚稳β相共存。TLM合金经过固溶时效处理后可获得较低弹性模量、较高强度、优良塑韧性和高疲劳极限的综合匹配,是用于制造外科植入体、矫形器械、血管内支架等医疗器件的理想材料。
Ti-Zr-Sn-Mo-Nb合金目前主要采用真空熔炼法来制备,但由于合金中加入Nb、Zr、Mo等难熔金属元素,为了避免在制备合金过程中可能产生的成分偏析、组织不均匀及疏松、缩孔等缺陷,往往需要对材料进行2~3次重熔,这样会造成材料成本的增加和制备工艺过程的复杂化。放电等离子烧结(Spark plasma sintering,SPS)是一种新型特种粉末烧结成形技术,与传统的粉末烧结技术相比,SPS烧结技术具有烧结温度低、升降温速率快(100 ℃/min 以上)、烧结时间短、致密度高(可达99%以上)等优点[10]。利用SPS烧结技术制备Ti-Zr-Sn-Mo-Nb合金可以有效地解决合金成分偏析和组织不均匀问题。同时,采用该方法可以获得较高的致密度和实现材料的组织细化,从而提高材料的综合性能。目前,有关利用SPS方法制备Ti-Zr- Sn-Mo-Nb合金的报道涉及极少。因此,本文作者利用放电等离子烧结技术制备Ti-3Zr-2Sn-3Mo- 15Nb合金,研究烧结温度对合金致密度、微观结构、显微组织及力学性能(压缩强度、压缩弹性模量)的影响。
1 实验
实验原料为Ti、Nb、Zr、Mo、Sn粉末(纯度为99.9%,粒度<45 μm,北京蒙泰有研技术开发中心提供),按Nb 15%、Zr 3%、Mo 3%、Sn 2%(质量分数),余量Ti进行称量,然后进行球磨混粉10 h。将混合均匀的粉末烘干后装入石墨模具中,在SPS-515S型放电等离子烧结设备(SPS Syntex Inc., Japan)上进行烧结成形。放电等离子烧结工艺为:按100 ℃/min的速度升温至所需烧结温度,然后在该温度下保温5 min后随炉冷却,烧结过程中持续外加40 MPa的轴向压力,系统真空度2~10 Pa。烧结温度分别为1 000、1 050、1 100和1 150 ℃。
烧结成形后的试样密度利用阿基米德(Archimedes)方法测量;微观结构分析在Bruker D8 Advance 型X射线衍射仪上进行;显微组织利用Ziess大型金相显微镜分析;组织分布状态与成分检测利用Philips XL30型扫描电镜(SEM)结合EDS能谱进行。用电火花线切割机将制备的合金坯块切成压缩试样,根据GB/T 7314—2005,实验所用压缩强度试样尺寸为d 4 mm×10 mm、压缩弹性模量试样尺寸为d 2 mm×10 mm,室温压缩性能测试在岛津AG-X万能材料试验机上进行,加载速率为2 mm/min。
2 结果与分析
2.1 烧结温度对Ti-3Zr-2Sn-3Mo-15Nb合金致密度的影响
图1所示为烧结温度对Ti-3Zr-2Sn-3Mo-15Nb合金密度的影响。由图1可看出,在1 000、1 050、1 100和1 150 ℃的烧结温度下,Ti-3Zr-2Sn-3Mo-15Nb合金试样的密度分别为5.01、5.034、5.039和5.084 g/cm3,而该合金的理论密度约为5.1 g/cm3。通过计算可知,烧结试样的相对致密度均在98%以上,具有较高的致密度。从图1中还可以看出,随着烧结温度的升高,合金的密度呈增大的趋势,在1 150 ℃时达到99.7%,已经接近于合金的理论密度。将粉末烧结制备Ti-3Zr-2Sn-3Mo-15Nb合金与BOTTINO等[11-12]的研究结果进行对比,其采用传统真空粉末烧结方法制备Ti-13Nb-13Zr合金,烧结温度分别为1 000、1 300和1 500 ℃,保温时间分别为5、3和2 h,获得试样的相对致密度分别为68%、88%和93%。通过对比可知,采用SPS方法制备的Ti-3Zr-2Sn-3Mo-15Nb合金致密度远高于采用传统真空粉末冶金制备方法的相对致密度,使材料在较低的烧结温度下和较短的保温时间内获得了较高的致密度,体现出了SPS烧结技术的优 点,而较高的相对致密度将有利于合金获得较好的综合性能。

图1 烧结温度对Ti-3Zr-2Sn-3Mo-15Nb合金密度的影响
Fig. 1 Effect of sintering temperature on density of Ti-3Zr-2Sn-3Mo-15Nb alloy
2.2 烧结温度对Ti-3Zr-2Sn-3Mo-15Nb合金显微组织的影响
利用XRD分析了烧结试样的微观结构,图2所示为Ti-3Zr-2Sn-3Mo-15Nb合金在不同烧结温度时的XRD谱。从图2中可以看出,在1 000、1 050、1 100和1 150 ℃ 4种烧结温度下,合金均主要由β-Ti相和少量的α-Ti相组成,未发现形成其他金属间化合物。合金中添加的Nb、Zr元素的衍射峰与β-Ti相的衍射峰重合,通过XRD无法区分出来。Mo、Sn的含量极低,未能检测到其衍射峰。XRD检测结果表明,利用SPS烧结方法制备的Ti-3Zr-2Sn- 3Mo-15Nb合金属于近β型钛合金,与熔炼法获得的合金微观结构一致。
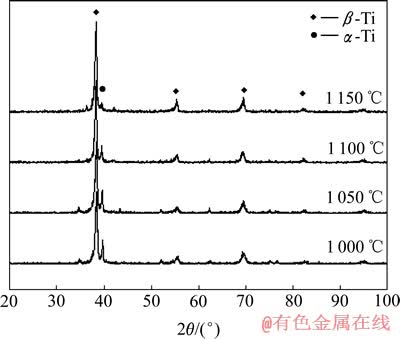
图2 Ti-3Zr-2Sn-3Mo-15Nb合金在不同烧结温度时的 XRD谱
Fig. 2 XRD patterns of Ti-3Zr-2Sn-3Mo-15Nb alloy at different sintering temperatures
同时,从图中还可以看出,随着烧结温度的升高,合金中的少量α-Ti相出现了向β-Ti相逐渐转变的现象,且含量越来越低。
进一步利用金相显微镜、背散射SEM与EDS能谱分析合金试样的组织形貌及分布状态。图3所示为Ti-3Zr-2Sn-3Mo-15Nb合金在不同烧结温度下的光学显微组织照片;图4所示为1 150 ℃烧结时合金背散射SEM形貌及EDS能谱分析结果。结合合金金相组织形貌及化学成分分析结果可知,合金主要由β-Ti相与Ti-Nb-Zr-Mo固溶体形成的混合基体组织及少量α-Ti相和未熔化的Nb金属颗粒组成。从图3可以看出,当烧结温度为1 000 ℃时(见图3(a)),合金中除了β-Ti相及少量α-Ti相与未熔化的Nb金属颗粒外,还存在较多的Ti-Nb-Zr-Mo固溶体;随着烧结温度的升高(见图3(b)~(d)),合金中Ti-Nb-Zr-Mo固溶体的含量逐渐减少,部分尺寸较小的Ti-Nb-Zr-Mo固溶体完全融入到β-Ti相基体中,剩余的尺寸较大的Ti-Nb-Zr-Mo固溶体与β-Ti相基体从边缘融合而且尺寸减小。同时,合金中α-Ti相含量也越来越低,未熔化的Nb金属颗粒的尺寸也由于熔化越来越小。这表明组织分析结果与XRD的检测结果是互相吻合的,出现上述组织演变现象与SPS烧结机理存在密切的关系。在放电等离子烧结过程中,电极通入直流脉冲电流时瞬间产生放电等离子体,并使颗粒表面活化,在颗粒之间产生局部极高温度,使得颗粒表面保持非常高的温度而引起蒸发和熔化[13]。合金中Ti、Zr和Sn金属颗粒由于熔点较低,在温度和外加轴向压力作用下,互相融合形成包括β-Ti相及少量α-Ti相在内连续的基体组织。熔点较高的Nb、Mo局部熔化扩散进入基体组织,残余的Nb、Mo与Ti、Zr形成Ti-Nb-Zr-Mo固溶体镶嵌在基体组织中。随着烧结温度的升高,脉冲电流不断增大,组织内部温度也不断升高,因而,Ti-Nb-Zr-Mo固溶体不断熔化扩散进入基体中,固溶体含量越来越低且尺寸减小;温度的升高也有利于α-Ti相向β-Ti相转变,残留的未熔化Nb金属颗粒尺寸也由于熔化越来越小。
2.3 烧结温度对Ti-3Zr-2Sn-3Mo-15Nb合金的力学性能的影响
图5所示为不同烧结温度下Ti-3Zr-2Sn-3Mo- 15Nb合金的抗压强度和压缩弹性模量。从图5中可以看出,在1 000、1 050、1 100和1 150 ℃ 4种烧结温度下,合金的抗压强度均较高(1 500 MPa以上),具有良好的室温压缩性能;随着烧结温度的升高,合金的抗压强度呈增大趋势,与合金致密度的变化趋势互相吻合。合金抗压强度随烧结温度的变化与显微组织的变化存在密切的联系,根据前面的分析,合金在1 000 ℃烧结时,组织中存在较多的Ti-Nb-Zr-Mo固溶体和α-Ti相,导致抗压强度最低;随着烧结温度的不断升高,Ti-Nb-Zr-Mo固溶体和α-Ti相的含量越来越低,β-Ti相含量越来越高,合金的抗压强度提高。

图3 Ti-3Zr-2Sn-3Mo-15Nb合金在不同烧结温度时的光学显微组织照片
Fig. 3 Optical micrographs of Ti-3Zr-2Sn-3Mo-15Nb alloy at different sintering temperatures
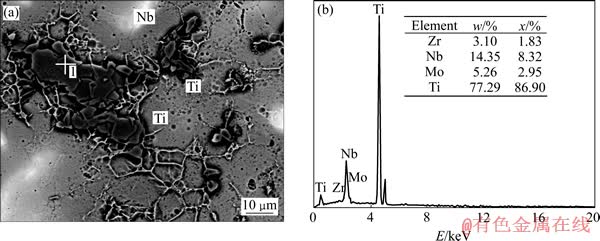
图4 Ti-3Zr-2Sn-3Mo-15Nb合金在1 150 ℃烧结时的背散射SEM像及位置1的EDS谱
Fig. 4 SEM image of Ti-3Zr-2Sn-3Mo-15Nb alloy sintered at 1 150 ℃(a) and EDS spectrum of position 1(b)
对于合金的压缩弹性模量,在1 000、1 050、1 100和1 150 ℃ 4种烧结温度下,压缩弹性模量在45~54 GPa范围内;随着烧结温度的升高,合金的压缩弹性模量呈缓慢增大趋势。分析其原因,主要与合金致密度的变化有关。根据前面的检测结果,合金在1 000 ℃烧结时致密度最小,此时合金的压缩弹性模量最低;随着烧结温度的升高,合金致密度呈增大趋势,合金的压缩弹性模量也随之增大。由于到了一定的烧结温度后,合金致密度增大趋势越来越小,因而,压缩弹性模量值增大趋势变得缓慢。对于显微组织的演变,烧结温度的升高只是使得合金中残留的少量α-Ti相向β-Ti相转变,但β-Ti相仍然是合金的主要组成相,因而对合金压缩弹性模量的影响非常有限[14]。合金弹性模量与文献[3]报道的熔炼法Ti-6Al-4V的弹性模量(110 GPa)和Ti-13Nb-13Zr的弹性模量(80 GPa)相比有大幅下降;同时与文献[15-16]报道的真空熔炼法制备的TLM合金弹性模量相比(44~88 GPa),SPS法制备的合金弹性模量也在其下限,显示良好的力学相容性。

图5 Ti-3Zr-2Sn-3Mo-15Nb合金在不同烧结温度下的抗压强度和压缩弹性模量
Fig. 5 Compressive strength and compressive elastic modulus of Ti-3Zr-2Sn-3Mo-15Nb alloy at different sintering temperatures
3 结论
1) 采用放电等离子烧结制备的Ti-3Zr-2Sn-3Mo- 15Nb合金主要由β-Ti相与Ti-Nb-Zr-Mo固溶体形成的混合基体组织及少量α-Ti相和未熔化的Nb金属颗粒组成;随着烧结温度的升高,合金中Ti-Nb-Zr-Mo固溶体含量越来越低,其尺寸越来越小,残留的α-Ti相转变为β-Ti相。
2) 采用放电等离子烧结制备的Ti-3Zr-2Sn-3Mo- 15Nb合金具有较高的致密度和抗压强度,随着烧结温度的升高,合金致密度和抗压强度呈增大趋势;合金的压缩弹性模量在45~54 GPa之间,显示出良好的力学相容性,而烧结温度的升高使得压缩弹性模量值出现缓慢增大现象。
REFERENCES
[1] NOURI A, HODGSON P D, WEN C E. Effect of process control agent on the porous structure and mechanical properties of a biomedical Ti-Sn-Nb alloy produced by powder metallurgy[J]. Acta Biomaterialia, 2010, 6(4): 1630-1639.
[2] OSHIDA Y. Bioscience and bioengineering of titanium materials[M]. London: Elsevier Science Press, 2006: 13-19.
[3] GEETHA M, SINGH A K, ASOKAMANI R, GOGIA A K. Ti based biomaterials, the ultimate choice for orthopaedic implants—A review[J]. Progress in Materials Science, 2009, 54(3): 397-425.
[4] 马秀梅, 孙 威, 杨永建. 生物医用Ti-Nb-(Ta)-Zr合金的微观结构与性能[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2010, 20(6): 1195-1202.
MA Xiu-mei, SUN Wei, YANG Yong-jian. Microstructures and properties of biomedical Ti-Nb-(Ta)-Zr alloys[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2010, 20(6): 1195-1202.
[5] 于振涛, 周 廉, 罗丽娟, 牛金龙, 王立新, 袁思波, 皇甫强, 张亚锋. 新型近β型医用钛合金TLM的加工、组织与性能[J]. 稀有金属, 2006, 30(2): 226-230.
YU Zhen-tao, ZHOU Lian, LUO Li-juan, NIU Jin-long, WANG Li-xin, YUAN Si-bo, HUANG Fu-qiang, ZHANG Ya-feng. Process, microstructure, properties of newly developed β-type biomedical titanium alloy TLM[J]. Chinese Journal of Rare Metals, 2006, 30(2): 226-230.
[6] YU Zhen-tao, ZHENG Yu-feng, NIU Jin-long, HUANG Fu-qiang, ZHANG Ya-feng, YU Sen. Microstructure and wear resistance of Ti-3Zr-2Sn-3Mo-15Nb (TLM) alloy[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2010, 17(S): s495-s499.
[7] 麻西群, 于振涛, 牛金龙, 余 森. Ti3Zr2Sn3Mo25Nb医用钛合金相变与力学性能[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2010, 20(S1): s410-s413.
MA Xi-qun, YU Zhen-tao, NIU Jin-long, YU Sen. Phase transformation and mechanical properties of Ti3Zr2Sn3Mo25Nb alloy for biomedical application[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2010, 20(S1): s410-s413.
[8] 麻西群, 于振涛, 牛金龙, 余 森, 韩建业, 张亚峰. Ti-3Zr-Mo-15Nb医用钛合金的显微组织及力学性能[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2010, 39(11): 1956-1959.
MA Xi-qun, YU Zhen-tao, NIU Jin-long, YU Sen, HAN Jian-ye, ZHANG Ya-feng. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti-3Zr-Mo-15Nb medical titanium alloys[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2010, 39(11): 1956-1959.
[9] YU Zhen-tao, ZHOU Lian. Influence of martensitic transformation on mechanical compatibility of biomedical β type titanium alloy TLM[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2006, 438/440: 391-394.
[10] 路 新, 何新波, 李世琼, 曲选辉. 放电等离子烧结TiAl基合金的显微组织及力学性能[J]. 北京科技大学学报, 2008, 30(3): 254-257.
LU Xin, HE Xin-bo, LI Shi-qiong, QU Xuan-hui. Microstructures and mechanical properties of TiAl-based alloys by spark plasma sintering[J]. Journal of University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2008, 30(3): 254-257.
[11] BOTTINO M C, COELHO P G, YOSHIMOTO M,  Jr B. HENRIQUES V A R, BRESSIANI A H A, BRESSIANI J C. Histomorphologic evaluation of Ti-13Nb-13Zr alloys processed via powder metallurgy. A study in rabbits[J]. Materials Science and Engineering C, 2008, 28(2): 223-227.
Jr B. HENRIQUES V A R, BRESSIANI A H A, BRESSIANI J C. Histomorphologic evaluation of Ti-13Nb-13Zr alloys processed via powder metallurgy. A study in rabbits[J]. Materials Science and Engineering C, 2008, 28(2): 223-227.
[12] BOTTINO M C, COELHO P G, HENRIQUES V A R, HIGA O Z, BRESSIANI A H A, BRESSIANI J C. Processing, characterization, and in vitro/in vivo evaluations of powder metallurgy processed Ti-13Nb-13Zr alloys[J]. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research: Part A, 2009, 88(3): 689-696.
[13] 张久兴, 刘科高, 周美玲. 放电等离子烧结技术的发展和应用[J]. 粉末冶金技术, 2002, 20(3): 129-134.
ZHANG Jiu-xing, LIU Ke-gao, ZHOU Mei-ling. Development and application of spark plasma sintering[J]. Powder Metallurgy Technology, 2002, 20(3): 129-134.
[14] 焦泽辉, 宋西平. 放电等离子烧结制备Ti-4.3Fe-7.1Cr-3Al合金[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2012, 41(2): 330-334.
JIAO Ze-hui, SONG Xi-ping. Ti-4.3Fe-7.1Cr-3Al alloy prepared by spark plasma sintering[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2012, 41(2): 330-334.
[15] 于振涛, 张亚峰, 刘 辉, 麻西群, 余 森, 张明华. 合金元素、加工与热处理对新型近β型钛合金TiZrMoNb力学性能的影响及微观分析[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2010, 39(10): 1795-1801.
YU Zhen-tao, ZHANG Ya-feng, LIU Hui, MA Xi-qun, YU Sen, ZHANG Ming-hua. Effects of alloy elements, processing and heat treatment on mechanical properties of a near β type biomedical titanium alloy TiZrMoNb and microstructure analysis[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2010, 39(10): 1795-1801.
[16] MA Xi-qun, YU Zhen-tao, HAN Yong, SONG Xi-ping, SUN Qiao-yan. In situ scanning electron microscopy observation of deformation and fracture behavior of Ti-3Zr-2Sn-3Mo-25Nb alloy[J]. Rare Metals, 2012, 31(4): 318-322.
(编辑 李艳红)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(31160197);云南省中青年学术和技术带头人后备人才培养资助项目(2010CI011)
收稿日期:2012-11-05;修订日期:2013-02-20
通信作者:张玉勤,教授,博士;电话:13708861766;E-mail: zyqkust@163.com