
Microstructure and mechanical properties of AZ61 Mg alloy prepared by multi directional forging
H. MIURA1, G. YU1, X. YANG2, T. SAKAI1
1. Department of Mechanical Engineering and Intelligent Systems,
University of Electro-Communications, Chofu, Tokyo 182-8585, Japan;
2. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China
Received 23 September 2009; accepted 30 January 2010
Abstract: AZ61Mg alloy was multi directionally forged (MDFed) during decreasing temperature condition from 643 K to 483 K at a true strain rate of 3×10-3 s-1 up to cumulative strain of ∑?ε=4.0 at maximum. A pass strain of ?ε=0.8 was employed. While average grain size decreased gradually with increasing cumulative strain, the evolution of fine-grained structure strongly depended on the MDF temperature. Under the condition where the temperature was higher than the most adequate one, grain coarsening partially took place during MDF. In contrast, at lower temperature, inhomogeneous microstructure composed of the initial coarse and newly appeared fine grains was evolved. After straining over ∑?ε=3.2 (i.e., over 4 passes of MDF), equiaxed ultrafine grains (UFGs) having average size of about and lower than 1 μm were uniformly evolved. While the MDFed alloy to ∑?ε=4.0 possessed relatively high hardness of HV 99, and it accepted further about 20% cold rolling almost without cracking. Because of the superior formability of the UFGed AZ61Mg alloy, the hardness was further easily raised to HV 120 by following cold rolling.
Key words: AZ61 magnesium alloy; ultrafine grain; plastic deformation; multi directional forging
1 Introduction
A plenty of researches on severe plastic deformation (SPD) have been carried out to obtain ultrafine grained (UFGed) materials[1-4], because it is assumed that UFGed structure induces notable improvement of mechanical properties of strength and plasticity. Various methods of SPD processes are actually applied also to Mg alloys[2-4]. Because of poor ductility of Mg alloys, SPD is mostly carried out at elevated temperatures. From such researches, it is revealed that UFGed Mg alloys exhibit quite large ductility as well as high strength. XING et al[3] reported that the UFGed AZ31 Mg alloy produced by multi directional forging (MDF), where its grain size is about 300 nm, shows superior balance of strength and ductility, ultimate tensile strength of 530 MPa, ductility of about 20% at room temperature and superplasticity at 423 K. KAI et al[2] processed AZ90 Mg alloy by high pressure torsion and also reported superplasticity of about 800% at 423 K. Such large ductility of the UFGed Mg alloys is assumed to be induced by grain boundary sliding (GBS). Actually, GBS takes place even at room temperature in Mg [5]. Because the temperature where the superplasticity occurred was relatively low, it can be classified as low temperature superplasticity[3].
Even while the improvement of strength and formability of Mg alloys are being performed by means of grain refinement and alloying, further strengthening is highly desirable. MIURA et al[6] suggested from the experiments of MDF that AZ61Mg alloy possesses quite higher potentials of easier evolution of UFGs by MDF, higher strength at room temperature and higher thermal stability than those of AZ31 Mg alloy. However, the researches about UFGed AZ61 Mg alloy are quite few, as far as the authors know. In the present study, MDF temperature effect on the microstructural evolution in AZ61 Mg alloy was investigated. Furthermore, further improvement of the mechanical property of the MDFed AZ61 Mg alloy by cold rolling was also studied.
2 Experimental
AZ61 Mg alloy with a initial grain size of 57 μm obtained by annealing at 773 K for 2 h was spark cut to rectangular sample with dimensions of 31 mm×21 mm×14 mm. They were MDFed on an Instron-type mechanical testing machine at a true strain rate of 3×10-3 s-1 in vacuum. A pass strain of ?ε=0.8 was employed. During MDF, forging temperature was gradually decreased pass by pass from 643 K to 483 K. The procedure of MDF is schematically represented in Fig.1. While the aspect ratio of the sample is theoretically unchanged during MDF, the sample had to be re-shaped by mechanical polishing because of the shape change especially after the 1st and 2nd passes of MDF. The shape change at such early pass of MDF should be due to the strong texture in the initial sample. MDF was carried out to cumulative strain of ∑?ε=4.0 at maximum, i.e., 5 passes. The sample could be uniformly forged without any cracking even at 483 K. Such obvious improvement of plasticity at such relatively low temperature of AZ61 Mg alloy was induced by evolution of UFGs, as will be shown later. After MDF, the evolved microstructure was observed on the plane parallel to the final forging axis using optical microscopy (OM). The MDFed alloy was subsequently cold rolled to investigate formability and potential of further strengthening by the effect of work hardening. The rolling direction and plane were normal and parallel respectively to the final forging axis. Hardness change during MDF and after cold rolling was also examined.
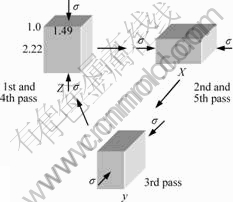
Fig.1 Schematic representation of multi directional forging with aspect ratio of 1.0?1.49?2.22 and pass strain of ?ε=0.8 (Forging axis is changed by 90? at each pass)
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Flow curves
Fig.2 shows the results of true stress vs. cumulative strain curves during MDF at various temperatures within the range of ±20 K. At lower pass number of forging, sharp peaks followed by large work softening appear evidently. Because the peak strains look almost constant independent of MDF temperature, it is not due to the occurrence of classical dynamic recrystallization (DRX).
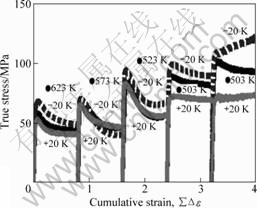
Fig.2 True stress vs cumulative strain curves by multi directionally forged (MDFed) at various temperatures within range of ±20 K at each pass (Temperatures exhibited are those finally employed for MDF)
If the deformation is controlled by classical DRX, i.e., diffusion process, the peak strain becomes smaller gradually with increasing temperature[7]. This is, however, due to the fact that the stronger texture effect of the initial sample is still prevailing even after forging. The softening would be mainly due to the occurrence of kinks and mechanical twinning, which are the most important mechanisms of grain fragmentation in Mg and Mg alloys[6, 8]. The peaks gradually disappear with increasing cumulative strain and decreasing grain size (see Fig.3). This phenomenon is strongly related with disappearance of texture and changes of the deformation mechanisms.
3.2 Evolved microstructure
Fig.3 exhibits that the typical microstructure evolved is dependent on MDF temperature. Because of MDF at high strain region (∑?ε=3.2), pretty fine grains were evolved at all temperatures. It is clear, however, the homogeneity of microstructure is quite different depending on temperature. At 483 K, coarse grains are still prevailed. On the other hand, at 523 K, it can be seen that a part of UFGed area develops before hand grows to coarse grain. This is because UFGed material possesses nature of quite low thermal stability[9]. It is evident that the finest and most uniform evolution of UFGed structure is achieved at 503 K. Although not all temperatures and processes are examined, the temperatures indicated in Fig.2 are actually chosen for MDF of the following study.
The microstructure evolved during MDF, whose temperature condition is exhibited in Fig.2, was observed using OM. It is clear in Fig.4 that grain refinement proceeds quite uniformly pass by pass of MDF at adequate temperature condition. The grain size decreases gradually with increasing cumulative strain from 57 μm

Fig.3 Evolved microstructures at temperature of 483 K (a), 503 K (b), 523 K (c) at 4th pass of MDF (i.e., cumulative strain of ∑?ε=3.2) (Arrow mark indicates final forging axis)
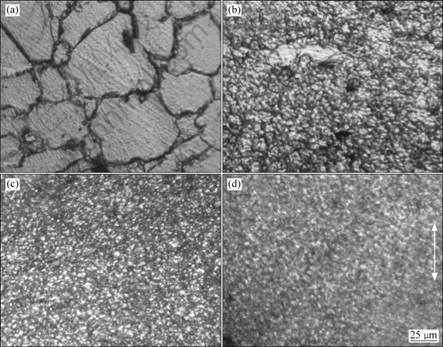
Fig.4 Microstructures of AZ61 Mg alloy evolved during multi directional forging at indicated temperatures in Fig. 2 to strains of as-annealed (e=0) state (a), ∑?ε=0.8 (b), ∑?ε=1.6 (c) and ∑?ε=4.0 (d) (Arrow mark indicates final forging axis)
to about 1.2 μm at ∑?ε= 3.2. The grain size at ∑?ε=4.0 was evaluated by means of transmission electron microscopy to be 0.8 μm, while the photograph is not shown here. Such uniform evolution of equiaxed UFGs at ∑?ε=4.0 is achieved only by the adequate combination of pass strain of ∑?ε=0.8 and MDF temperature. It is remarkable to see that the grain fragmentation at the 1st and 2nd passes of MDF appears quite rapid. When being compared with the average grain size, it was 0.6 μm in the AZ31 Mg alloy MDFed at ∑?ε=4.0[3]. The apparent finer grain size of the AZ31Mg alloy, however, should be caused by the lower MDF temperature (from 623 K to 453 K) and the finer initial grain size (22 μm). The higher MDF temperature is directly connected with grain coarsening as shown in Fig.3. The grain coarsening is affected not only by temperature but also by low thermal stability of SPDed materials. It is reported that recrystallization and extensive grain coarsening took place in the MDFed Cu-Zn alloy only at 0.37Tm, where Tm is the melting point[9].
In the MDFed AZ31 Mg alloy, grain fragmentation at the early stage of MDF is caused by mechanisms of mechanical twinning and kinking in addition to continuous dynamic recrystallization[3, 8]. The grain refinement of AZ61 Mg alloy during MDF should be induced by the similar mechanisms in AZ31 Mg alloy. Actually, it is reported that kinking as well as twinning frequently takes place also in AZ61 Mg alloy[6]. The disorientation at kink becomes almost 8? only at strain of 0.3. The observed extraordinary rapid grain refinement at the early stages of MDF in AZ61 Mg alloy would be promoted to the easy and highly dense occurrence of twins and kinks. This should be investigated more in detail in the future. It can be estimated, however, that the mechanisms of continuous DRX and kinking should become more important for grain fragmentation as grain size decreases, because twinning becomes more difficult with decreasing grain size[10]. The evolved UFGs, therefore, would be dominantly subdivided by mechanical twins and kinks at low and medium strain regions, and then, by kinking and continuous dynamic recrystallization at further higher strain regions.
3.3 Hardness and formability of MDFed AZ61 Mg alloy
Hardness change during MDF was investigated and the results are summarized in Fig.5. It can be seen in Fig.5 that the hardness increases almost proportionally with increasing cumulative strain, and HV 99 is achieved only after 5 passes of MDF at warm temperature range. While MDF is ceased at ∑?ε=4.0 in the present study. Fig.5 implies the potential of further strengthening of the MDFed AZ61 Mg alloy. MIURA et al[6] reported that hardness of about HV 120 was achieved by MDF of an AZ61 Mg alloy with initial grain size of about 22.2 μm. Because UFG evolution is accelerated with decreasing initial grain size[11], the relatively low hardness in the present study should be affected by the coarser initial grain size (57 μm) and delay of UFG evolution as mentioned above. The hardness of the present MDFed AZ61 Mg alloy is, however, higher or almost same compared with that of AZ31 Mg MDFed to cumulative strains of 4.0 and 6.4 where the hardnesses are about HV 80 and HV 105, respectively[3]. The higher hardness of the MDFed AZ61 Mg alloy than that of AZ31 would be strongly affected by higher density of precipitates.
It is well known that SPDed alloy possesses poor ductility and formability at ambient temperature. Nevertheless, it is reported that ductility of the UFGed Mg alloy recovers when the gain size becomes lower than about 1 μm[3, 6]. This recovery of ductility is assumed to be caused by GBS. Formability of the MDFed
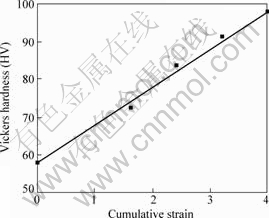
Fig.5 Change of Vickers hardness at room temperature of multi directionally forged AZ61Mg alloy with different cumulative strains
AZ61 Mg alloy was examined by cold rolling. Cold rolling up to 20% reduction is almost successfully carried out irrespective of MDF cumulative strain, although large crack takes place suddenly by 25 % cold rolling of the MDFed sample at ∑?ε=4.0. Quite few large cracks appear by 20 % reduction in the MDFed one at ∑?ε=4.0. This suggests that the formability of the AZ61 Mg alloy MDFed at ∑?ε=4.0 is not so much different compared with that of the as-annealed sample, while the upper limit of cold reduction seems to be around 20%. The results of hardness change after cold rolling are summarized in Fig.6. It is obvious in Fig.6 that hardness gradually increases with increasing reduction irrespective of cumulative strain of MDF. That is to say, work hardening can contribute to further strengthening even in the SPDed or MDFed Mg alloy. The slope of the hardness change appears slightly smaller with increasing MDF cumulative strain. This would be closely related with saturation of dislocation density and probability of mechanical twinning (see Fig.7). To be exact, the coarser grains, which are MDFed at higher temperature and therefore recovered, contain lower dislocation density and accept more frequent mechanical twinning.
Microstructural change after 20% reduction by cold rolling was observed and the typical photographs are exhibited in Fig.7. After rolling of the as-annealed sample, it is apparent that numerous mechanical twins are uniformly formed. Moreover, some small clacks are seen to nucleate. In contrast, almost no changes could be observed in the previous MDFed sample. This difference indicates that the UFGed structure of Mg alloy appears stable to subsequent deformation at room temperature, even while the dislocation density must be quite high. This may be also because of GBS. It can be summarized, therefore, that UFGed AZ61Mg alloy possesses superior balance of strength and formability even at ambient temperature. Although the microstructure seems quite stable and nucleation of microcracks hardly takes place, the occurrence of failure looks quite abrupt.
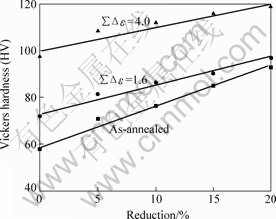
Fig.6 Change in Vickers hardness of multi directionally forged AZ61Mg alloy depending on reduction
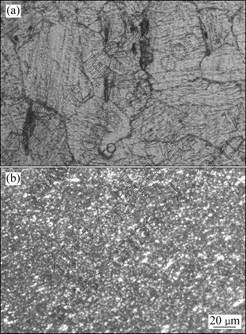
Fig.7 Microstructures after 20% reduction by cold rolling of samples: (a) As-annealed, ε=0; (b) MDFed, ∑?ε=4.0
4 Conclusions
1) AZ61Mg alloy was multi directionally forged (MDFed) under decreasing temperature condition. The grain size gradually decreases with increasing pass number of MDF. Only by the adequate process, homogeneous microstructure could evolve.
2) Over 4 passes of MDF, i.e., cumulative strain of ∑?ε=3.2, uniform evolution of ultrafine grained (UFGed) structure with average grain size around 1 μm is achieved. The MDFed alloy of ∑?ε=4.0 possesses high hardness, and it accepts further cold rolling up to 20 % reduction.
3) By cold rolling, the hardness is further raised because of work hardening to HV 120. Although the microstructure appears unchanged by cold rolling, occurrence of failure due to large cracking is quite abrupt.
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the financial support given by the Light Metals Educational Foundation, Japan, and Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports and Technology, Japan, with Grant No. 20560647.
References
[1] HORITA Z. Nanomaterials by severe plastic deformation [M]. Switzerland: Trans Tech Publications, 2005.
[2] KAI M, HORITA Z, LANGDON T G. Developing grain refinement and superplasticity in a magnesium alloy processed by high-pressure torsion [J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2008, 488: 117-124.
[3] XING J, YANG X, MIURA H, SAKAI T. Ultra-fine grain development in an AZ31 magnesium alloy during multidirectional forging under decreasing temperature conditions [J]. Mater Trans, 2005, 46: 1646-1650.
[4] BUSSIBA A, BEN ARTZY A, SHTECHMANN A, IFERGAN S, KUPIEC M. Grain refinement of AZ31 and ZK60 Mg alloys—Towards superplasticity studies [J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2001, 302: 56-62.
[5] KOIKE J, OHYAMA R, KOBAYASHI T, SUZUKI M, MARUYAMA K. Grain-boundary sliding in AZ31 magnesium alloys at room temperature to 523 K [J]. Mater Trans, 2003, 44: 1-7.
[6] MIURA H, YANG X, SAKAI T. Evolution of ultra-fine grains in AZ31 and AZ61 Mg alloys during multi directional forging and their properties [J]. Mater Trans, 2008, 49: 1015-1020.
[7] SAKAI T, JONAS J J. Dynamic recrystallization: Mechanical and microstructural considerations [J]. Acta Metal, 1984, 32: 189-209.
[8] YANG X, SANADA M, MIURA H, SAKAI T. Effect of initial grain size on deformation behavior and dynamic recrystallization of magnesium alloy AZ31 [J]. Mater Sci Forum, 2005, 488/489: 223-226.
[9] NAKAO T, MIURA H, SAKAI T. Ultra fine grain of Cu-Zn alloy evolved by multi directional forging and its thermal and mechanical properties [J]. J Japan Inst Metals, 2008, 72: 397-406. (in Japanese)
[10] BARNETT M R, KESHAVARZ Z, BEER A G, ATWELL D. Influence of grain size on the compressive deformation of wrought Mg-3Al-1Zn [J]. Acta Mater, 2004, 52: 5093-5103.
[11] BELYAKOV A, SAKAI T, MIURA H, KAIBYSHEV R, TSUZAKI K. Effect of initial microstructures on grain refinement in a stainless steel by large strain deformation [J]. Acta Mater, 2003, 51: 847-861.
(Edited by LI Xiang-qun)
Corresponding author: H. MIURA; E-mail: miura@mce.uec.ac.jp
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(09)60293-4