文章编号:1004-0609(2009)03-0445-07
CaC2对电磁?悬浮铸造AZ61合金组织和力学性能的影响
马玉涛1,张兴国1, 2,郝 海1, 2,王云波1,金俊泽1
(1. 大连理工大学 材料科学与工程学院,大连 116024;
2. 大连理工大学 三束材料改性国家重点实验室,大连 116024)
摘 要:利用电磁搅拌技术,结合悬浮铸造方法,在浇铸AZ61镁合金的过程中加入微纳米颗粒CaC2,使CaC2弥散分布于母相金属液中,促进合金形核,改善合金铸造组织形态和分布,提高合金的力学性能。结果表明:利用电磁?悬浮铸造制备的镁合金,其显微组织细化,晶间β相细小并且网状结构减少,当CaC2悬浮剂加入量(质量分数)为0.36%时,镁合金的细化效果最佳,其晶粒最小尺寸为75 μm,抗拉强度为211.4 Pa,伸长率为8.5%,与普通金属型铸造制备的镁合金相比,晶粒尺寸减小64.3%;抗拉强度提高约24.2%;伸长率提高46.6%。
关键词:AZ61镁合金;CaC2;电磁?悬浮;显微组织;力学性能
中图分类号:TG 146.4 文献标识码:A
Effects of CaC2 on microstructure and tensile properties of AZ61 magnesium alloys by electromagnetic-suspension casting
MA Yu-ao1, ZHANG Xing-guo1, 2, HAO Hai1, 2, WANG Yun-bo1, JIN Jun-ze1
(1. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian 116024;
2. State Key Laboratory of Materials Modification by Laser, Ion and Electron Beams,
Dalian University of Technology, Dalian 116024, China)
Abstract: The electromagnetic suspension casting of AZ61 wrought magnesium alloy was studied using electromagnetic stirring technique and the suspension casting during the casting process. The electromagnetic suspension casting not only can diffuse CaC2 powders distribution into the melt evenly, but also can refine the development of dendrite. The results show that electromagnetic suspension casting is found to be effective on refining the microstructure of magnesium materials, thinning the β-Mg17Al12 and improving the distribution uniformity of β-Mg17Al12 phase. The 0.36% CaC2 addition refines the grains most effectively, and the size is 75 μm. The ultimate tensile strength of alloys is 211.4 MPa, and the elongation is 8.5%. The grain size decreases by 64.3%, and the ultimate tensile strength and the elongation of alloys increase by 24.2% and 46.6% respectively compared with those of the die-casting Mg alloys.
Key words: AZ61 magnesium alloy; CaC2; electromagnetic suspension; microstructure; tensile properties
电磁搅拌技术是利用电磁感应产生的电磁力来推动金属有规律地运动,从而减少枝状晶,增加等轴晶率,达到改善合金质量的目的。电磁搅拌凝固理论的发展促进了电磁搅拌技术的广泛应用。悬浮铸造技 术[1]是20世纪60年代苏联发明的一种铸造方法,该方法能有效地控制铸件凝固过程,减少和消除铸件缺陷,提高铸件的性能和质量,已广泛应用于碳钢、合金钢、铸铁、钛合金和铝合金等有色合金的生产中[1?4],而在镁合金方面还没有相关的报道。本文作者将电磁搅拌技术与悬浮铸造相结合,提出镁合金制备的新方法,即电磁悬浮铸造技术。在浇铸镁合金的过程中,结合氩气压力喷入悬浮剂,使微纳米悬浮剂能均匀地混合到金属液中,在合金凝固的过程中起到吸热、形核、促进凝固, 阻止二次相连续长大的作用,从而细化晶粒,优化合金的微观组织结构[5]。
Mg-Al系镁合金由于使用性能优良,不含稀土等贵重元素,其生产成本低,熔炼工艺简单,因此生产应用前景广泛[6]。钙是一种有效的阻燃和细化镁合金晶粒元素,在镁合金中加入少量的钙,可以细化晶粒,提高合金的室温和高温力学性能[7?9]。含碳化合物具有细化镁合金晶粒的能力,碳质材料变质处理法因熔体处理温度低、细化效果保持时间长等原因,已成为Mg-Al系合金最主要的晶粒细化技术[10?11]。
本文作者结合钙和碳两者对镁合金的综合作用,选用两者的化合物CaC2作为悬浮剂,采用电磁?悬浮铸造的成型方法铸造AZ61镁合金,以细化合金晶粒,提高合金的力学性能。
1 实验
实验所用的熔炼设备为SG?5?10型电阻坩埚炉,并配有KSW?8D?13型温度控制器,采用低碳钢坩埚熔炼合金,熔炼过程中添加RJ?2熔剂覆盖保护。悬浮杯内置在具有保温功能的电磁搅拌器中,镁合金熔化后,把熔液倒入电磁驱动器内预热至720 ℃的坩埚中。浇注过程中,悬浮剂通过氩气压力喷入的方法喷入坩埚中,同时进行电磁搅拌,搅拌时间为2 min,悬浮剂与镁合金母液充分混合,将熔液浇入金属铸型中。
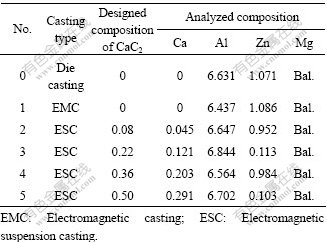
采用CaC2颗粒作为悬浮剂,CaC2 颗粒尺寸为200 μm。悬浮剂的化学配比如表1所列。为了分析电磁?悬浮铸造对合金的影响,本研究中还进行了镁合金的普通金属型铸造和不加悬浮剂只进行电磁搅拌铸造的对比实验。
表1 合金的化学配比
Table 1 Designed compositions of alloys (mass fraction, %)
合金的成分分析采用XRF?1800X射线荧光光谱仪,显微组织分析采用MEFS型多功能金相显微镜和JSM?5600LV型扫描电镜(SEM),合金微区成分分析采用LINK ISIS 6587能量分散谱仪(EDS),合金的相组成分析在XRD?6000型X射线衍射分析仪上进行,利用EPMA?1600型电子探针对合金组织元素分布状况进行分析,室温短时力学拉伸性能测试在WD?1OA电子万能试验机上进行。
2 结果
2.1 显微组织
图1所示为6组实验镁合金的显微组织照片。从图1中可以看出:6组合金的显微组织典型特征是相似的,都是由非平衡凝固产生的α-Mg基体和分布在晶界周围的呈灰白色衬度的条状共晶组织β-Mg17Al12相构成的。这说明电磁-悬浮铸造对合金显微组织特征影响不大,但能显著改变合金的晶粒尺寸。图1(a)所示为AZ61镁合金普通金属型铸造显微组织,α-Mg基体尺寸较大,β-Mg17Al12相呈连续网状分布。如图1(b)所示,当引入电磁搅拌时,基体α-Mg的尺寸减小,晶间β-Mg17Al12相也有所细化,但细化效果不是很明显。采用电磁?悬浮铸造方法得到的合金,如图1(c)~(f)所示,合金的显微组织更加细小,晶粒细化,网状共晶组织析出量也减少,晶间相数量减少且更加弥散细小。从图1可以看出,加入0.36%CaC2悬浮剂的合金4,晶粒最小,组织细化效果最佳。
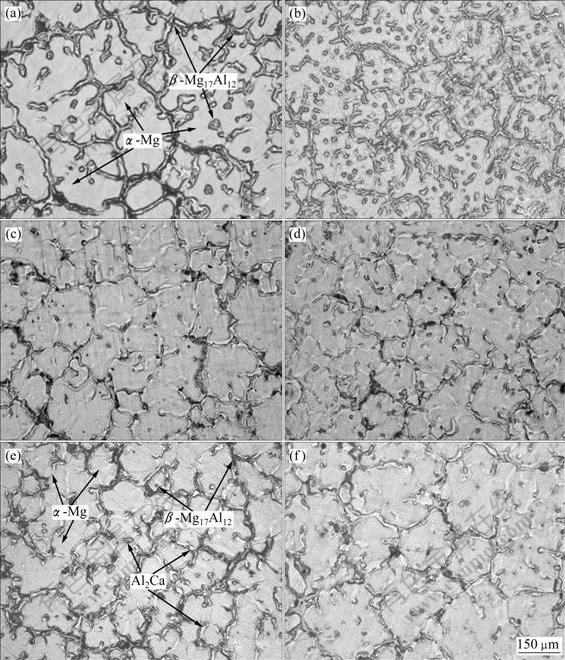
图1 镁合金的显微组织
Fig.1 Microstructures of AZ61 Mg alloys: (a) No.0; (b) No.1; (c) No.2; (d) No.3; (e) No.4; (f) No.5
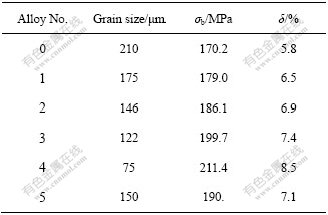
6组镁合金的晶粒尺寸测量结果如表2所列。由表2可以看出,普通金属型铸造的合金晶粒最大,晶粒尺寸为210 μm。在只采用电磁搅拌铸造的情况 下,合金的晶粒尺寸为175 μm,减小了16.7%。采用电磁?悬浮铸造技术并加入0.36%CaC2悬浮剂时,合金的平均晶粒度最小为75 μm,比普通金属型铸造减小了64.3%。同时,合金的晶粒也变得均匀。可见,利用电磁搅拌加入悬浮颗粒的方法,采用CaC2颗粒作为悬浮剂,可以显著细化镁合金的晶粒尺寸。
表2 镁合金的晶粒尺寸和拉伸性能
Table 2 Grain size and tensile properties of AZ61 Mg alloys
合金2和4的XRD谱如图2所示。由图2可看出,合金主要由α-Mg基体及β相Mg17Al12组成,在合金4中还存在少量的Al2Ca,合金中未发现CaC2,CaC2与合金液发生了反应。镁合金中,少量Ca元素以固溶原子形式存在,随着Ca含量的增加,Ca与Al发生反应,生成Al2Ca强化相,分布于晶界上。
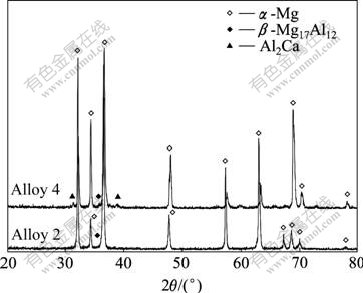
图2 合金2和4的XRD谱
Fig.2 XRD patterns of alloys 2 and 4
合金2和4的晶内和晶界SEM像及EDS分析分别如图3与表3所示。可以看出,合金的晶内主要是由Mg和少量固溶在Mg基体中的Al组成,没有发现Ca。合金晶界处的Al含量增加,并且存在少量的Ca,这说明Ca主要以固溶原子的形式存在于Mg17Al12相中,结合XRD分析表明,少量的Ca在AZ61合金中不形成新相。合金4的SEM及EDS分析表明,随着Ca含量的增加,Ca除了以固溶原子形式存在外,还与Al发生反应,生成Al2Ca强化相,主要分布于晶界上。
表3 合金的晶内和晶界EDS分析
Table 3 EDS analysis results of alloys (mass fraction, %)
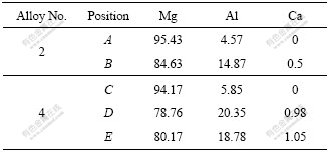
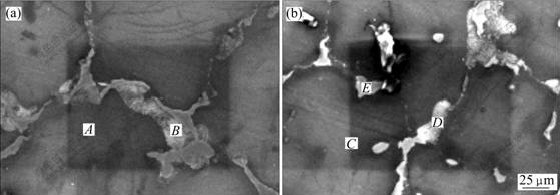
图3 合金的SEM像
Fig.3 SEM images of alloys: (a) Alloy 2; (b) Alloy 4
图4所示为合金4的微观形貌的元素面扫描分析。与前述分析相同,少量的Ca固溶于Mg基体和Mg17Al12相中。在晶界处,Ca富集的地区Al含量很高,这说明Ca与Al在晶界处形成化合物。结合XRD分析可知此化合物为Al2Ca相。

图4 合金4的微观形貌和元素面扫描分析
Fig.4 Morphology(a) and analysis of area distribution of elements Mg(b), Al(c), Ca(d) and Zn(e) of alloy 4
根据Mg-Al和Al-Ca二元相图[10?11]和ZHOU等[12]的价电子浓度计算可知,Al2Ca和Mg17Al12的熔点分别为1 079 ℃和437 ℃。因此,在合金凝固过程中,Al2Ca在凝固早期优先于其他合金相形成,首先形成的Al2Ca相主要在晶界聚集,并在固/液界面前沿的扩散层内形成成分过冷,阻止凝固和冷却后期晶粒的长大,使合金组织细化。
2.2 力学性能
对不同工艺下所得试样的力学性能测试,结果如表2所列。电磁?悬浮铸造中,加入0.36%CaC2悬浮剂的合金4的抗拉强度最大,为211.4 MPa,比金属型铸造的合金的抗拉强度提高约20%。当进一步加大CaC2悬浮剂加入量时,镁合金的抗拉强度下降。这表明在电磁?悬浮铸造中加入适量的悬浮剂,可以提高合金的力学拉伸性能,结合显微分析,电磁?悬浮铸造可以显著地细化晶粒,提高合金的力学性能。
图5所示为合金2~5的断口表面形貌。从图5中可以看出,不同悬浮剂加入量的合金断口都是以脆性断裂为主的解理断裂,断口表面可以看到大量的解理片层,存在少许韧窝和撕裂棱。由于晶界中存在形状不规则的脆性金属间化合物相β-Mg17A1l2,裂纹从这些脆性相处沿晶萌发和扩展,在断口表面可以观察到沿晶裂纹,还可看到脆性β-Mg17A1l2金属间化合物相本身在拉伸过程中产生了裂纹,α-Mg固溶体呈现出微塑性变形特性,主要以撕裂棱的形式出现。如图5(a)、(d)所示,合金2和5的晶粒较大,合金在拉伸断裂的过程中裂纹迅速萌生和扩展,撕裂棱粗大、平滑。如图5(b)、(c)所示,在合金3和4中添加适量悬浮剂时,合金的晶粒变小,拉伸断口的撕裂棱的解理小刻面增多,减少了合金在拉伸断裂过程中的应力集中和裂纹的萌生,导致强度和塑性明显提高。
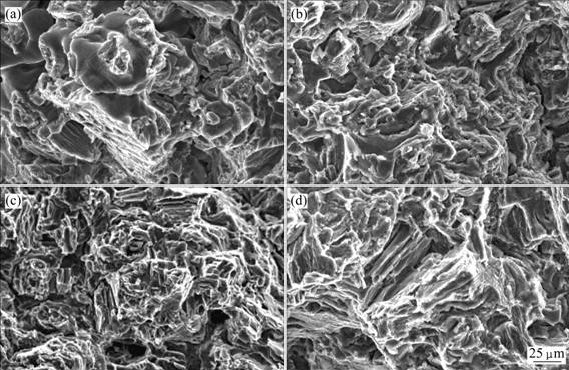
图5 合金的断口形貌
Fig.5 SEM images of tensile fracture surface of alloys: (a) No.2; (b) No.3; (c) No.4; (d) No.5
3 分析与讨论
在镁合金电磁?悬浮铸造中,悬浮剂的加入使合金液中产生了较大的能量起伏和成分起伏,有助于形成细晶组织[13]。随着CaC2悬浮剂加入量的增加,合金的晶粒尺寸逐渐变小,这主要是由于悬浮剂在随液流冲入金属液时,由于受到电磁搅拌的作用,悬浮剂很快分散于金属液中并在金属液中形成弥散分布的固相质点。这些固相质点在金属液中有三方面的作 用[14]:1) 它可作为外来晶核衬底,或是与金属液中的某些元素反应,生成新相,阻碍合金晶粒的长大。结合合金4的XRD谱和元素EPMA分析结果可知,合金中形成的新相Al2Ca相主要在晶界聚集,这样在 固/液界面前沿的的扩散层内形成成分过冷,使处于该过冷区的其他部分可能的形核质点被激活,进而导致更多晶核产生而细化晶粒;另外,Ca原子的扩散速度较慢,在界面阻碍了晶粒生长,从而使得晶粒细化。2) 加入悬浮剂相当于加入内冷铁,吸收周围合金液的热量,使金属液形成一个过冷度。在此过冷度下,合金液中原子集合体的稳定性得到提高。在整个合金液中,由此类原子集合体开始形成结晶核心并进一步长大。因此,加入的CaC2悬浮剂吸收金属液的热量产生一个过冷度,在金属液中形成成分起伏区,初晶α相集合体团簇形成结晶核心并进一步长大。同时,由于电磁搅拌的作用,使枝晶内部成分均匀,不易发生成分偏析,网状共晶组织析出量减少,β相更加弥散分布,合金组织得到改善。3) 悬浮剂在金属液中形成大量的弥散质点,造成更大的成分起伏和能量起伏,有助于形成细晶组织,如图1(c)~(f)所示,合金液中加入CaC2悬浮剂粉体,合金的组织得到了细化。
电磁搅拌的引入加速了悬浮剂和合金母液的均匀混合,有效地限制了由于机械搅拌而给合金液带来的杂质和氧化夹杂,避免了悬浮剂在合金液中的聚集“搭桥”现象和悬浮剂在铸件中的夹生。电磁搅拌力形成的强迫对流使悬浮剂质点在合金母液中分散更加弥散,更有利于微观不均匀系统的形成,从而加速了结晶速度,提高了形核率,非匀质晶核数量提高必然带来晶体尺寸的细化。此外,电磁搅拌力对新生晶核的振荡作用使新生晶核松动和破碎,晶核的破碎促使更多的形核质点形成[5]。
镁为IIA族碱土金属,密排六方结构,晶轴c与a的比值为1.623 6,与密排原子堆集的理想值1.633差别不大,这种晶体结构是镁比面心立方的铝合金力学性能更差的因素之一。但是镁的Hall-Petch系数ky=280 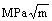 ,为纯铝的4倍。可见,与铝合金相比,镁合金的晶粒细化对改善合金抗拉强度和伸长率具有更大的潜力。描述镁合金的强度和晶粒尺寸关系的Hall-Petch公式为
,为纯铝的4倍。可见,与铝合金相比,镁合金的晶粒细化对改善合金抗拉强度和伸长率具有更大的潜力。描述镁合金的强度和晶粒尺寸关系的Hall-Petch公式为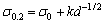 ,其中d为晶粒粒径。由此可见,晶粒越细小,同样体积材料内晶界面积越大,室温强度越高。所以通过晶粒细化工艺减小合金的晶粒尺寸,可以显著提高镁合金的抗拉强度和伸长率[15]。
,其中d为晶粒粒径。由此可见,晶粒越细小,同样体积材料内晶界面积越大,室温强度越高。所以通过晶粒细化工艺减小合金的晶粒尺寸,可以显著提高镁合金的抗拉强度和伸长率[15]。
4 结论
1) 利用电磁搅拌?悬浮铸造技术结合氩气压力喷入方法制备的镁合金显微组织特征相似,主要由固溶体α-Mg基体和分布在晶界周围的呈灰白色衬度的条状共晶和少量的层片状组织β相Mg17Al12构成。
2) 采用电磁?悬浮铸造方法制备的镁合金显微组织细小,晶间β相数量减少。当CaC2加入量为0.36%时,AZ61镁合金的细化效果最佳,晶粒尺寸为75 μm,比金属型铸造制备的镁合金减少约64.3%。
3) 采用电磁?悬浮铸造制备的镁合金抗拉强度大,当CaC2加入量为0.36%时,抗拉强度最大为211.4 MPa,比金属型铸造制备的镁合金的提高约24.2%;当进一步增加CaC2悬浮剂加入量时,合金的抗拉强度下降。
REFERENCES
[1] EFIMOV V A. Suspension casting technological fundametals [C]//48th International Foundry Congress, Varna, Bulgaria, 1981: 23.
[2] BARNHURST R J. Gravity casting of zinc-aluminum(ZA) alloys: Dependence of mechanical properties on soundness, microstructure and inclusion content[M]. 1985.
[3] 刘根生, 王文才, 张志明, 刘金海, 李丘林. 悬浮铸造工艺对EPC铸造低铬白口铸铁性能的影响[J]. 铸造, 2001, 50(11): 666?669.
LIU Gen-sheng, WANG Wen-cai, ZHANG Zhi-ming, LIU Jin-hai, LI Qiu-lin. Effect of suspension casting on the property of low-chromium white cast iron produced by the EPC process[J]. Foundry, 2001, 50(11): 666?669.
[4] 田德重, 李显林, 吴茂铭. 悬浮铸造锡青铜收缩管[J]. 特种铸造及有色合金, 1990(6): 25?26.
TIAN De-zhong, LI Xian-lin, WU Mao-ming. Suspend casting tin bronze shrinkable tube[J]. Special Casting and Nonferrous Alloys, 1990(6): 25?26.
[5] 任 政, 张兴国, 房灿峰, 郝 海. 电磁?悬浮铸造对变形镁合金晶粒细化的影响[J]. 材料研究学报, 2007, 21(5): 491?495.
REN Zheng, ZHANG Xing-guo, FANG Can-feng, HAO Hai. Effect of electromagnetic suspension casting on grain refinement for wrought magnesium alloy[J]. Chinese Journal of Materials Research, 2007, 21(5): 491?495.
[6] 黄恢元. 铸造手册: 铸造非铁合金[M]. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 1993.
HUANG Hui-yuan. Foundry handbook: Casting nonferrous alloys[M]. Beijing: China Machine Press, 1993.
[7] 樊建锋, 杨根仓, 程素玲, 谢 辉, 郝维新, 王 梅, 周尧和. 含Ca阻燃镁合金的高温氧化行为[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2004, 14(10): 1666?1670.
FAN Jian-feng, YANG Gen-cang, CHENG Su-ling, XIE Hui, HAO Wei-xin, WANG Mei, ZHOU Yao-he. Oxidation behavior of ignition-proof magnesium-calcium alloys[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2004, 14(10): 1666?1670.
[8] 樊 昱, 吴国华, 高洪涛, 翟春泉, 朱燕萍. Ca对镁合金组织, 力学性能和腐蚀性能的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2005, 15(2): 211?216.
FAN Yu, WU Guo-hua, GAO Hong-tao, ZHAI Chun-qun, ZHU Yan-ping. Effect of calcium on microstructure, mechanical properties and corrosion resistance of magnesium alloy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2005, 15(2): 211?216.
[9] WU Guo-hua, FAN Yu, GOA Hong-tao, ZHAI Chun-qun, ZHU Yan-ping. The effect of Ca and rare earth element on the microstructure mechanical properties and corrosion behavior of AZ91D[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2005, 408: 255?263.
[10] MURRAY J L. The Al-Mg system[J]. Bulletin of Alloy Phase Diagrams, 1982, 3(1): 60?64.
[11] ITKIN V P, ALCOCK C B, Van EKEREN P J, OONK H A J. The Al-Ca system[J]. Bulletin of Alloy Phase Diagrams, 1988, 9(6): 652?657.
[12] ZHOU D W, LIN J S, PENG P. A first-principles study on the structural stability of Al2Ca, Al4Ca and Mg2Ca phases[J]. Mater Lett, 2008, 62(2): 206?210.
[13] 周春明, 冯建华, 龙文元, 樊铁船. 悬浮浇铸对铝铜合金组织遗传性的影响[J]. 南昌航空工业学院学报, 1998(4): 11?15.
ZHOU Chun-ming, FENG Jian-hua, LONG Wen-yuan, FAN Tie-chuan. The effect of floating casting on the structure heredity of Al-Cu alloys[J]. Journal of Nanchang Institute of Aeronautical Technology, 1998(4): 11?15.
[14] 王红霞, 常艳红, 徐 林. 悬浮铸造对ZA27合金组织性能的影响[J]. 铸造设备研究, 2002(2): 5?6.
WANG Hong-xia, CHANG Yan-hong, XU Lin. The effect of suspension casting on the microstructure and properties of ZA27 alloy[J]. Research Studies on Foundry Equipment, 2002(2): 5?6.
[15] MATUCHA K H. Material science and technology: A comprehensive treatment[M]. CAHN R W, HAASEN P, KRAMER E J, ed. New York: Weinheim, Wiley-VCH, 1996.
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(50475157);教育部重点资助项目(105052)
收稿日期:2008-06-25;修订日期:2008-09-10
通讯作者:张兴国,教授,博士;电话/传真:0411-84706183;E-mail: zxgwj@dlut.edu.cn
(编辑 李向群)