反循环钻进中水龙头弯管磨损数值模拟
黄勇1,殷琨1,朱丽红2
(1. 吉林大学 建设工程学院,吉林 长春,130026;
2. 中国石油大学(华东) 石油工程学院,山东 青岛,266580)
摘要:针对反循环钻进中水龙头弯管磨损失效问题,应用计算流体动力学方法对水龙头弯管内气固两相流场进行数值模拟,研究弯管内岩屑颗粒的运动轨迹及壁面磨损分布,并进一步分析岩屑特性对壁面磨损的影响。研究结果表明:气固两相流经过弯管时,岩屑与壁面在弯管30°,90°和150°转角位置存在碰撞集中区,对应形成3个壁面磨损区,其中30°转角位置磨损最严重,形成刺漏点;此外,岩屑颗粒特性对弯管磨损存在影响,随颗粒速度或质量流量的增大,弯管磨损速率显著增大;随颗粒直径增大,磨损速率先增大后减小;颗粒密度对弯管磨损影响不明显。
关键词:反循环;弯管;气固流;磨损;岩屑;数值模拟
中图分类号:P634.5 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2013)05-2053-07
Numerical simulation of swivel elbow erosion in reverse circulation drilling
HUANG Yong1, YIN Kun1, ZHU Lihong2
(1. College of Construction Engineering, Jilin University, Changchun 130026, China;
2. School of Petroleum Engineering, China University of Petroleum, Qingdao 266580, China)
Abstract: Aiming at the serious problem of erosion of swivel elbow by cuttings in reverse circulation drilling, the gas-solid two-phase flow field in swivel elbow was simulated based on the computational fluid dynamics (CFD). The particle trajectories of cuttings and erosion of elbow were studied and the effects of cuttings characteristics on erosion rate of the elbow were further analyzed. The simulation results show that during the gas-solid two-phase flow process, there are three main impact regions in 30°, 90° and 150° positions of the elbow. Corresponding to the impact regions, there are three erosion areas. And the most serious location of perforation caused by cuttings is at 30° position of the elbow. With the increase of the velocity or the mass flow of cuttings, the erosion rate of elbow significantly increases. The erosion rate increases at first then decreases with the increase of cuttings size. Density of particles has no obvious effect on the erosion rate.
Key words: reverse circulation; elbow; gas-solid flow; erosion; cuttings; numerical simulation
反循环钻进技术是一种以压缩空气作为循环介质的新型、高效钻进方法,与正循环钻进相比,反循环钻进利用钻具中心通道上返钻进产生的岩石碎屑,有效保护孔壁,消除孔口岩粉污染,在提高钻进效率的同时,增强对环境和施钻人员进行保护[1-2]。双通道气水龙头是反循环排屑的重要通道,含有岩屑颗粒的高速气流流经水龙头时,岩屑颗粒对水龙头弯管造成冲蚀磨损。现场经验表明:平均每钻进30 m,弯管即发生1次刺漏。反循环钻进平均机械钻速一般为5~10 m/h,较高的钻速使得钻进中频繁更换弯管,严重降低钻孔时效,因此,有必要深入了解反循环钻进中弯管磨损分布及岩屑特性对弯管磨损的影响,以便为弯管抗磨结构设计提供指导。弯管磨损问题广泛存在于各种涉及固相颗粒输送的工程领域,由于弯管在实际应用中的普遍性和易损性,对于弯管磨损的预测和分析一直是国内外研究的热门课题[3-4]。Wood等[5]对泥浆管路截面上的磨损情况进行数值和实验分析,发现管路截面底部磨损最为严重。Chen等[6]对气体钻井排屑管路直角弯头和三通型弯头的磨损情况进行研究,结果表明:直角弯管的最大磨损速率位置在弯管转角45°附近。Li等[7]采用计算流体动力学(CFD)方法研究液滴对弯管的冲蚀磨损,发现载粒流体湍动能的衰减对液滴冲蚀磨损影响显著。Deng等[8]进行低碳钢弯管磨损实验并测量磨损弯管的壁面厚度,发现弯管转角20°位置的管壁最薄。柳成文等[9]利用数值模拟方法计算了90°弯管的壁面磨损量,指出磨损与粒子速度、碰撞角度及浓度有关。李永祥[10]总结了气力输送过程中弯管的磨损机理及影响磨损的主要因素。姚建林等[11]对空气钻井中岩屑颗粒对地面排气弯管磨损进行了研究,认为90°排气弯管的最大冲蚀位置处于弯管的40°~60°的范围内。姚军等[12-13]通过改变弯管内壁面结构,有效地降低固相颗粒对弯管壁面的冲蚀磨损。上述研究表明:弯管磨损影响因素复杂,随着弯管结构、固相颗粒与载粒流体性质等因素变化,弯管磨损的速率、位置也随之改变。为深入研究反循环钻进中水龙头弯管磨损问题,本文作者借助计算流体动力学方法,对弯管内气固两相流动过程进行数值模拟,探讨弯管内岩屑颗粒的运移路径及对壁面的冲蚀特性,从而为改进弯管设计和延长弯管使用寿命提供理论依据。
1 水龙头弯管磨损问题
钻进过程中,孔内压缩气体携带岩屑沿钻具中心通道上返,是反循环钻进技术的重要标志。为实现有效携岩,气流的上返流速较高,通常可达到50 m/s左右。高速气流携带岩屑颗粒由中心通道进入水龙头弯管时,在惯性力作用下岩屑与弯管管壁碰撞,造成弯管冲蚀磨损。现场试验用水龙头弯管磨损情况如图1所示.在弯管外壁弓背处有1个长条形切口,而在弯管内壁面刺漏处形成1个近似漏斗的椭圆形凹坑,刺漏点位于弯管进气入口的正上方。由于现场试验的局限性,借助计算流体动力学方法对磨损情况进行进一步研究。
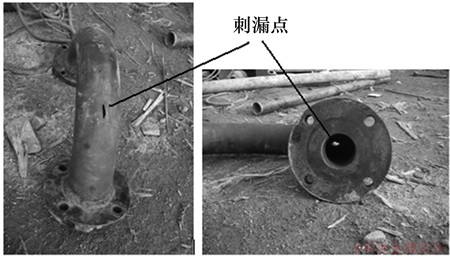
图1 水龙头弯管磨损情况
Fig.1 Erosion in elbow of swivel
2 弯管内气固两相流场数值模拟
水龙头弯管内的气固两相流动是复杂的三维湍流问题。考虑岩屑对气体相的影响,采用相间耦合计算。在数值模拟过程中,对气体在Euler框架下求解N-S方程,对岩屑颗粒在Lagrangian框架下求解颗粒轨道方程,通过交替求解岩屑与气体的控制方程,实现气固相间耦合计算。
2.1 气固两相流场数学模型
2.1.1 气体控制方程
(1) 连续性方程:
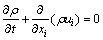 (1)
(1)
(2) 动量方程:
 (2)
(2)
其中: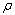 为气体密度;t为时间;ui和uj为气体速度分量;
为气体密度;t为时间;ui和uj为气体速度分量;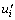 和
和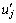 为气体脉动速度分量;p为气体压力;μ为气体动力黏度;Si为广义源项。
为气体脉动速度分量;p为气体压力;μ为气体动力黏度;Si为广义源项。
2.1.2 标准k-ε两方程模型
 (3)
(3)
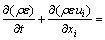
 (4)
(4)
其中:k为湍动能;μt为湍流黏度;Gk为平均速度梯度引起的湍动能k的产生项;ε为湍流耗散率;σk和σε分别为k和ε所对应的Prandtl数;C1ε和C2ε为经验常数。
2.1.3 岩屑运动方程
 (5)
(5)
其中: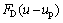 为岩屑的单位质量曳力;
为岩屑的单位质量曳力;
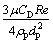 ;CD为曳力系数;Re为雷诺数;up为岩屑速度;
;CD为曳力系数;Re为雷诺数;up为岩屑速度;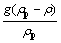 为岩屑重力;up为岩屑速度;ρp为岩石的密度;Fx为岩屑的其他作用力。
为岩屑重力;up为岩屑速度;ρp为岩石的密度;Fx为岩屑的其他作用力。
2.2 弯管壁面磨损模型
用于预测壁面冲蚀磨损的数学模型较多,但大多为基于实验结果的经验公式[14-15]。Edwards等[16]给出一种应用于CFD的磨损预测模型,该模型考虑颗粒的碰撞速度、侵入角、形状、直径和质量流量等因素,其表达式为
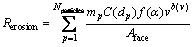 (6)
(6)
其中:Rerosion为壁面磨损速率;Nparticles为碰撞颗粒数目;mp为颗粒质量流量;C(dp)为颗粒直径的函数;α为颗粒对壁面的侵入角; 为侵入角的函数;v为颗粒相对于壁面的速度;b(v)是此相对速度的函数,Aface为壁面计算单元的面积。
为侵入角的函数;v为颗粒相对于壁面的速度;b(v)是此相对速度的函数,Aface为壁面计算单元的面积。
2.3 网格划分及边界条件
试验用水龙头弯管结构如图2所示。弯管内腔为转角150°的圆形通道,内腔直径D为50 mm,弯管轴线半径R为200 mm,连接用法兰盘厚度H为15 mm。提取弯管内部流场,建立气固两相流场几何模型,并进行网格划分。将弯管流场入口设为源面,该面采用四边形网格并按外圆内方形布置,通过扫描源面网格,得到整个流场的六面体网格,划分结果见图3。流场入口为速度入口边界,出口为自由流出口边界,壁面无滑移。颗粒相在壁面边界类型为弹性反弹,在出口边界类型为逃逸。

图2 弯管结构示意图
Fig.2 Schematic view of elbow geometry
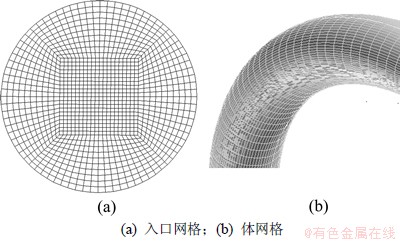
图3 计算流场网格划分
Fig.3 Grid distribution of computational domain
3 模拟结果分析
3.1 模拟结果验证
为验证数值模型的可靠性,按照现场试验条件设定初始条件,先模拟现场试验条件下弯管的磨损量,再将数值模拟结果与试验测试弯管磨损量进行对比。根据试验情况,模拟初始条件如下:气体进口速度为50 m/s,岩屑进口速度为50 m/s,岩屑质量流量为0.05 kg/s,岩屑粒径1 mm,岩屑密度为2.7 t/m3。试验过程中每15 min测量1次弯管质量,经过2 h后弯管总磨损量为51.6 g。图4所示为CFD模拟得到的磨损量与试验测得磨损量对比图,2组磨损量数据基本吻合,说明模拟结果可用来预测弯管磨损。图4中试验初期磨损量低于计算流体动力学(CFD)模拟结果,是因为试验用弯管经过渗碳处理,壁面具有一定抗磨性,随着渗碳层逐渐磨蚀,磨损加快。
3.2 岩屑颗粒运动规律
冲蚀磨损是由固相颗粒对管壁的摩擦与碰撞造成的,因此弯管磨损与岩屑颗粒在管内的运动路径有着密切关系。经数值模拟得到弯管内岩屑颗粒的运移轨迹图和轴截面颗粒质量浓度等值线图,分别如图5和图6所示。由图5可知:固相颗粒进入弯管后,岩屑颗粒在惯性力作用下,与气流分离并向弯管外侧壁面汇聚。汇聚过程中,岩屑颗粒形成3种流向,沿弯管轴截面(图2中A—A′)180°位置进入弯管的岩屑颗粒沿弯管外壁轴线滑移;位于弯管轴截面两侧的岩屑颗粒进入弯管后因受弯管壁面限制,逐渐向外壁轴线颗粒流靠拢,并在弯管30°转角附近汇聚,形成第1汇聚点(图6(b))。经过第1汇聚点后,三向颗粒流分离,岩屑颗粒向截面两侧分流(图6(d))后在弯管90°转角附近再次汇聚,但颗粒速度与浓度均低于第1汇聚点(图6(f))。经过第2汇聚点后,颗粒的气流跟随性增强,与壁面的碰撞减少,虽在150°截面处形成第3汇聚点,但外侧壁面颗粒浓度已明显降低,颗粒运动速度也进一步减小(图6(g))。

图4 CFD结果与试验结果对比
Fig.4 Comparison between experimental results and CFD results

图5 岩屑颗粒在弯管内的运移轨迹
Fig.5 Cuttings particle trajectories in elbow
从整个岩屑颗粒运动轨迹来看,固相颗粒与弯管内侧壁面的碰撞很少,进入弯管的颗粒在30°位置与壁面发生第1次直线碰撞后,以约60°转角在弯管外壁面交错汇聚前进,运动过程中外侧壁面颗粒速度与浓度逐渐降低,颗粒逐渐向弯管中心汇聚。
3.3 弯管磨损分布
弯管壁面磨损分布情况如图7所示。沿气固两相流动方向,在弯管外侧壁面存在3个磨损集中区,即图7中A,B和C。A处位于弯管30°转角位置,冲蚀强度与范围均最大,在A区中心存在1个最大冲蚀点,即弯管刺漏点,以最大冲蚀点为中心,冲蚀强度逐渐降低;B处位于弯管90°转角位置,该处磨损区域沿壁面轴向呈带状分布,冲蚀强度较A处有明显降低;C处位于弯管150°转角位置,冲蚀强度与范围均最小。图8所示为弯管z=0截面上的壁面磨损速率曲线,沿x轴正向依次出现3个峰值区,分别对应图7中的A,B和C 3个磨损集中区。

图6 弯管轴截面岩屑质量浓度分布等值线图
Fig.6 contour map of cuttings concentration in different sections of elbow
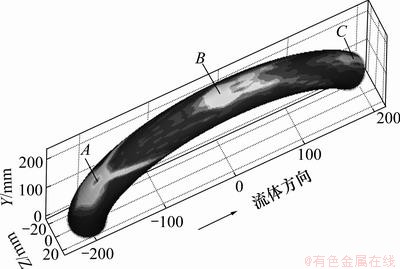
图7 弯管磨损分布图
Fig.7 Spatial distribution of erosion in elbow
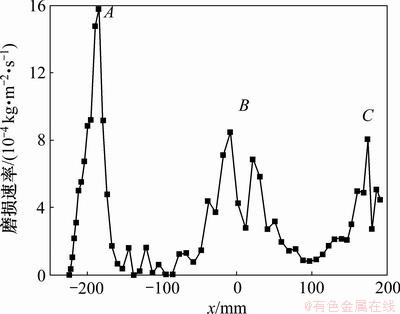
图8 弯管z=0截面上的磨损速率
Fig.8 Erosion rate in z=0 section of elbow
3.4 岩屑对弯管磨损的影响规律
为进一步分析岩屑特性对弯管壁面磨损的影响,保持其它初始条件不变,分别改变岩屑速度、直径、质量流量和密度参数,进行数值模拟,分析岩屑颗粒特性对弯管磨损的影响规律。
3.4.1 岩屑速度
岩屑进入弯管的入口速度直接影响岩屑对壁面的冲蚀速度。图9所示为岩屑入口速度在20~60 m/s下弯管壁面的磨损速率。由图9可见:随着岩屑速度的增大,弯管壁面磨损速率的峰值逐渐变大,弯管刺漏点(图7中A区)的磨损加快,发生刺漏的时间缩短。另外,磨损速率的平均值也随岩屑速度增大而增大,说明弯管壁面的整体磨损也随之加剧。
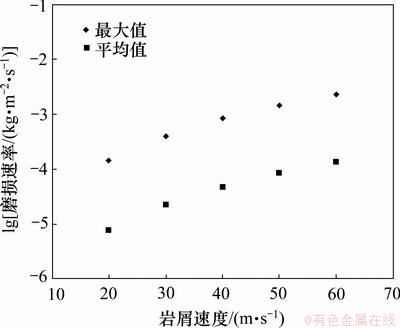
图9 岩屑速度对磨损速率的影响
Fig.9 Effect of cuttings velocity on erosion rate
3.4.2 岩屑直径
反循环钻进过程中,钻头将孔底岩石破碎成粒径不一的岩石碎屑,碎屑的粒度主要分布在0.05~10 mm范围内。不同岩屑颗粒直径对弯管磨损的影响规律如图10所示。从图10可见:整体来看,最大值与平均值均呈先增大后减小趋势,粒径在0.05~1 mm区间上磨损速率缓慢增加,粒径超过1 mm后磨损速率开始下降,当粒径大于5 mm时磨损速率急剧减小。2组数据不同之处在于:磨损速率最大值曲线在0.2 mm达到峰值,而平均值曲线在1 mm处最大。经分析认为:小粒径颗粒的气流跟随性较好,对壁面的磨损以摩擦磨损形式为主,而大粒径颗粒自身惯性较大,对壁面以冲击磨损为主,因此,粒径为0.2 mm的岩屑颗粒对刺漏点磨损影响最大,而1 mm岩屑颗粒对弯管整体磨损影响最大。

图10 岩屑直径d对磨损速率的影响
Fig.10 Effect of cuttings diameter on erosion rate
3.4.3 岩屑质量流量
岩屑质量流量不同,弯管内的固相颗粒浓度也不同,如图11所示。从图11可见:随着岩屑质量流量的增大,磨损速率的最大值与平均值均单调增加。原因在于:随着岩屑质量流量的增加,单位时间内进入弯管的岩屑颗粒数量增多,质量浓度增大,弯管壁面单位面积上的磨损次数增多,磨损加剧。
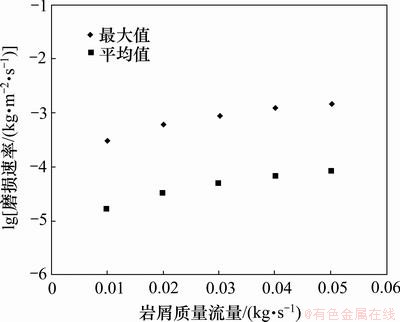
图11 岩屑质量流量对磨损速率的影响
Fig.11 Effect of cuttings mass rate on erosion rate
3.4.4 岩屑密度
岩屑密度与地层岩性有关,随着钻进中地层的变化岩屑密度也随之改变。密度为2 000~3 600 kg/m3范围内岩屑颗粒对弯管的磨损规律如图12所示。从图12可见:磨损速率随岩屑密度变化幅度很小,说明岩屑颗粒密度的变化对弯管磨损的影响不明显。从数据结果来看,弯管磨损速率最大值随岩屑密度增大而略微减小,弯管磨损速率平均值随岩屑密度增大而略微增大。
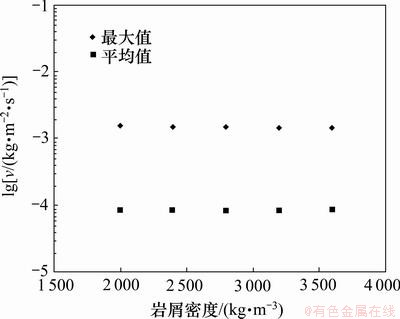
图12 岩屑密度对磨损速率v的影响
Fig.12 Effect of cuttings density on erosion rate
4 结论
(1) 岩屑颗粒进入弯管后,在弯管30°转角位置与壁面发生第1次直线碰撞后,以约60°转角在弯管外壁面交错汇聚前进,运动过程中外侧壁面颗粒速度与浓度逐渐降低,颗粒逐渐向弯管中心汇聚。对应颗粒运动轨迹,在弯管壁面上形成3个主要颗粒磨损区,其中以弯管转角30°位置的磨损强度与范围最大,是刺漏点的形成位置。
(2) 岩屑特性对弯管磨损存在影响。随岩屑速度和质量流量的增加,弯管磨损速率增大;随岩屑粒径增大,弯管磨损速率先增大后减小;岩屑颗粒密度的变化对弯管磨损影响不明显。弯管磨损速率的最大值远高于平均值,说明弯管局部刺漏要远早于弯管的整体磨损失效。
(3) 岩屑颗粒速度和质量流量是影响弯管磨损的主要因素,决定壁面处岩屑颗粒的碰撞速度和质量浓度。后续工作将通过改进弯管内壁面结构来降低近刺漏点处固粒速度和浓度,从而降低弯管局部磨损,提高弯管的使用寿命。
参考文献:
[1] William C L, Boyun G, Frank A S. Air and gas drilling manual[M]. New York: McGraw-Hill Professional, 2001: 1-25.
[2] 范黎明, 殷琨, 张永光, 等. 基于引射原理的侧吸式反循环钻头结构参数数值研究[J]. 中南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2011, 42(1): 220-226.
FAN Liming, YIN Kun, ZHANG Yongguang, et al. Numerical investigation of geometry parameters on side-ejector DTH hammer RC bit[J]. Journal of Central South University: Science and Technology, 2011, 42(1): 220-226.
[3] Chen X H, McLaury B S, Shirazi S A. Numerical and experimental investigation of the relative erosion severity between plugged tees and elbows in dilute gas/solid two-phase flow[J]. Wear, 2006, 261: 715-729.
[4] Zhang H, Tan Y Q, Yang D M, et al. Numerical investigation of the location of maximum erosive wear damage in elbow: Effect of slurry velocity, bend orientation and angle of elbow[J]. Powder Technology, 2012, 217: 467-476.
[5] Wood R J K, Jones T F, Ganeshalingam J, et al. Comparison of predicted and experimental erosion estimates in slurry ducts[J]. Wear, 2004, 256: 937-947.
[6] Chen X H, McLaury B S, Shirazi S A. Application and experimental validation of a computational fluid dynamics (CFD)-based erosion prediction model in elbows and plugged tees[J]. Computers & Fluids, 2004, 33: 1251-1272.
[7] Li R, Pellegrini M, Ninokata H, Mori M. A numerical study on turbulence attenuation model liquid droplet impingement erosion[J]. Annals of Nuclear Energy, 2011, 38: 1279-1287.
[8] Deng T, Chaudhry A R, Patel M, et al. Effect of particle concentration on erosion rate of mild steel bends in a pneumatic conveyor[J]. Wear, 2005, 258: 480-487.
[9] 柳成文, 毛靖儒, 俞茂铮. 90°弯管内稀疏气固两相流及固粒对壁面磨损量的数值研究[J]. 西安交通大学学报, 1999, 33(9): 53-57.
LIU Chengwen, MAO Jingru, YU Maozheng. Analysis of gas-solid two-phase flow and erosion in a 90° curved duct[J]. Journal of Xi’an Jiaotong University, 1999, 33(9): 53-57.
[10] 李永祥. 气力输送弯管的磨损及磨损机理研究[J]. 河南工业大学学报: 自然科学版, 2005, 26(1): 68-70.
LI Yongxiang. The wearying away of return bend and its mechanism in energy transmission[J]. Journal of Henan University of Technology: Natural Science Edition, 2005, 26(1): 68-70.
[11] 姚建林, 狄勤丰, 王文昌, 等. 空气钻井中颗粒对排气管的冲蚀分析[J]. 钻采工艺, 2009, 32(5): 13-15.
YAO Jianlin, DI Qinfeng, WANG Wenchang, et al. Abrasion of exhaust pipe by the high-speed gas with the cutting in air drilling[J]. Drilling & Production Technology, 2009, 32(5): 13-15.
[12] 姚军, 陈丽华, 樊建人, 等. 一种气固两相流中弯管抗磨方法的数值试验研究[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2002, 22(5): 134-138.
YAO Jun, CHEN Lihua, FAN Jianren, et al. Numerical simulation of a new method for protecting bends from erosion in gas-particle flows[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2002, 22(5): 134-138.
[13] 林建忠, 吴法理, 余钊圣, 等. 一种减轻固粒对壁面冲蚀磨损的新方法[J]. 摩擦学学报, 2003, 23(3): 231-235.
LIN Jianzhong, WU Fali, YU Zhaosheng. A new way to reduce wall erosion caused by solid particles[J]. Tribology, 2003, 23(3): 231-235.
[14] Shah S N, Jain S. Coiled tubing erosion during hydraulic fracturing slurry flow[J]. Wear, 2008, 264: 279-290.
[15] 赵新学. 气固两相流对旋风分离器壁面磨损机理的研究[D]. 青岛: 中国石油大学(华东)机电工程学院, 2010: 2-13.
ZHAO Xinxue. Research on the erosion mechanism of cyclone separator’s wall caused by gas-solid two-phase flow[D]. Qingdao: China University of Petroleum (East China). College of Mechanical & Electronic Engineering, 2010: 2-13.
[16] Edwards J K, Mclaury B S, Shirazi S A. Evaluation of alternative pipe bend fittings in erosive service[C]//Proceedings of ASME FEDSM ’00: ASME 2000 Fluids Engineering Division Summer Meeting. Boston: ASME, 2000: 959-966.
(编辑 邓履翔)
收稿日期:2012-05-07;修回日期:2012-06-25
基金项目:高等学校博士学科点专项科研基金资助项目(20110133120013);中央高校基本科研业务费专项资金资助项目(27R1202001A);山东省自然科学基金资助项目(ZR2011EEQ012)
通信作者:黄勇(1981-),男,吉林永吉人,博士研究生,从事多工艺冲击回转钻进技术的研究;电话:13756927679;E-mail: huangyongjlu@163.com