文章编号:1004-0609(2015)-01-0227-06
低电场强度下非均相含钛冶金熔渣的流变特性
姜 涛1, 2,张 璐1,廖德明1,薛向欣1, 2
(1. 东北大学 材料与冶金学院,沈阳 110819;
2. 东北大学 辽宁省冶金资源循环科学重点实验室,沈阳 110819)
摘 要:研究1500 ℃下低强度电场对含TiC非均相含钛冶金熔渣流变特性的影响,借助SEM-EDS检测手段对渣样进行表征分析,揭示含钛熔渣流变响应机理。结果表明:随电场强度的增加,含钛熔渣在不同剪切速率下表观黏度增大,表现出正电致流变效应;在电场作用下,TiC固相质点由分散状态变为呈链状或簇状分布,钙钛矿由分散状逐渐聚集,且晶粒随电场强度增大逐渐粗化;TiC固相质点的规律性变化以及高温下形成的钙钛矿在电场作用下的结构演变行为共同影响非均相含钛熔渣的流变特性。
关键词:非均相含钛冶金熔渣;电场强度;黏度;电致流变
中图分类号:TF01 文献标志码:A
Rheological properties of heterogeneous phase titanium-bearing metallurgical slag under low electric field intensity
JIANG Tao1, 2, ZHANG Lu1, LIAO De-ming1, XUE Xiang-xin1, 2
(1. School of Materials and Metallurgy, Northeastern University, Shenyang 110819, China;
2. Liaoning Key Laboratory for Circulation Science of Metallurgy Resource,
Northeastern University, Shenyang 110819, China)
Abstract: The effect of low intensity electric field on the rheological properties of heterogeneous phase titanium-bearing metallurgical slag containing TiC was studied at 1500 ℃, and the samples were characterized by SEM-EDS to reveal the rheological response mechanism. The results show that, with the increase of the electric field intensity, all samples show viscosity increment and positive electrorheological effect at different shear rates. The distribution of solid conductive particles TiC changes from dispersed distribution to chain or clustered distribution. The distribution of perovskite changes from dispersed distribution to aggregation, and the grains are coarsened with the changes of electric field intensity. Regular changes of TiC, as well as the structural evolution behaviors of perovskite formed at high temperature, affect the electrorheological behavior of heterogeneous phase titanium-bearing slag together.
Key words: heterogeneous phase titanium-bearing metallurgical slag; electric field intensity; viscosity; electrorheological effect
钒钛磁铁矿作为我国的特色冶金资源,综合利用难度较大[1-4]。在强还原和高温条件下,一些含钛矿物被还原成高熔点的TiCxOy和TiCxNy,形成气-固-液三相复杂的非均相熔渣体系,由此在高炉冶炼过程中引起炉渣变稠、炉缸堆积以及渣铁不分等一系列特殊的问题[5-10]。一般认为,熔渣在较高温度下是牛顿流体,但在熔渣中存在气相、固相质点或产生硅酸盐的网状结构时会表现出非牛顿流体的特性。目前,关于非均相含钛冶金熔渣的生成以及演变规律开展了较多的理论研究[11-12],但由于该熔渣的组成、结构和质点间相互作用形式复杂,导致其理论研究进展缓慢,特别是对含钛冶金熔渣的流变特性及其实验表征的研究明显欠缺,相关研究落后于工业化生产实践。非牛顿流体具有一系列区别于牛顿流体的奇特物理现象[13-15],如韦森伯格效应、无管虹吸、挤出胀大、剪切稀化和电致流变等。这些特有流变现象的出现对揭示并验证含钛冶金熔渣非牛顿流体的本质及其类型具有重要作用。但截至目前为止,关于含钛熔渣本征流变现象的实验表征尚未开展。
外加电场导致分散体系的结构和流变性质的变化称为电致流变效应(Electrorheological effect,简称ER效应)。电致流变效应的主要评价参数是电致流变液体的粘性或屈服应力[16-18]。对于含有异相质点的熔渣体系施加一定强度的电场,同时改变电场强度,通过高温黏度测量系统,测量熔渣在电场作用下表观黏度的变化。如果随着电场强度的增加,熔渣体系的黏度变大,而撤去电场后黏度又恢复至原始状态,则证明该体系产生了正电致流变效应;若相反,则可产生了负电致流变效应。
为进一步揭示非均相含钛熔渣的流变特性,本文作者重点研究了低强度电场下含固相质点TiC非均相冶金熔渣的流变特性。通过对比不同电场强度下含TiC熔渣体系的黏度变化,表征和分析含钛冶金熔渣的流变规律,为揭示非均相含钛熔渣生成、演变的物理化学规律奠定理论和实验基础。
1 实验
本研究中以攀钢现场含钛高炉渣化学组成为基础,采用化学纯试剂配制CaO-SiO2-Al2O3-MgO-TiO2五元渣系,并添加不同含量的TiC,渣系组成如表1所列。配制前将纯试剂在900 ℃高温下焙烧2 h,TiC粉末在烘箱中150 ℃下干燥2 h。
将配置好的混合料放入聚氨酯球磨罐混合12 h,然后将混合均匀的原料放入内衬钼片的石墨坩埚(内径d 55 mm×110 mm)中,置于二硅化钼电阻炉内,在Ar气氛下升温至1500 ℃并保温20 min,使渣样充分熔化,确保熔渣成分均匀稳定。将冷却后的渣样经制样机粉碎后备用。
实验在东北大学研制的RTW熔体物性测定仪上进行,采用旋转法定温测黏度,盛渣用坩埚为刚玉坩埚(内径d 40 mm×120 mm)。通过引入外加电场并改变电场强度,测定1500 ℃时不同电场强度(0,2.5,5.0,7.5,10和12.5 V/cm)和不同剪切速率(8,9,10,11和12 s-1)下各渣样的黏度,绘制黏度随电场强度变化曲线。采用SEM-EDS表征技术对实验渣样进行微观表征分析,揭示低强度电场对非均相含钛冶金熔渣流变特性的影响。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 实验结果
图1~4所示分别为不同含量TiC的非均相含钛熔渣黏度随电场强度变化曲线。图中还包括了不同剪切速率下渣样的电场-黏度曲线。
由图1~4可见,随着电场强度的增加,在不同剪切速率下,4种含钛熔渣黏度均明显增大,表现出非牛顿流体具有的正电致流变效应。并且在相同电场强度和剪切速率下,随渣中TiC含量的增加,熔渣黏度明显增大。
2.2 分析与讨论
电场作用下,非均相含钛熔渣的流变响应机理与其微观结构的演化密不可分。电场作用下,高温熔渣的结构演化分为聚集阶段(成链状结构)和粗化阶段(成柱状结构)。动态剪切时,颗粒在电场下形成的链状结构随剪切发生破坏和重组。图5所示为渣样3(添加6%TiC)的SEM像和特征晶粒的EDS谱。
表1 添加TiC的渣样成分
Table 1 Chemical composition of slag examples adding TiC
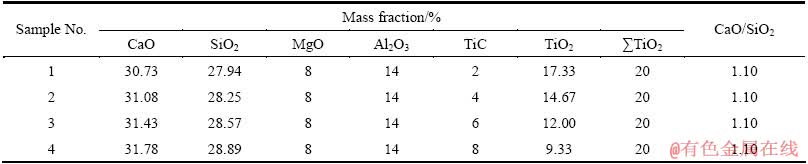
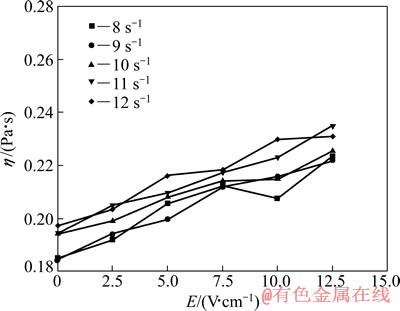
图1 不同剪切速率下渣样1的黏度-电场强度曲线
Fig. 1 η-E curves of slag sample 1 at different shear rates
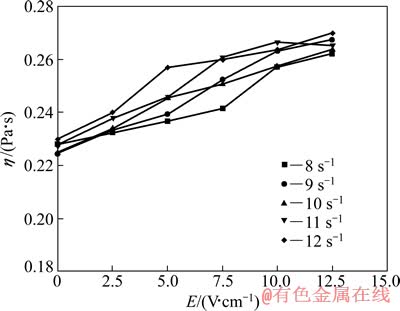
图2 不同剪切速率下渣样2的黏度-电场强度曲线
Fig. 2 η-E curves of slag sample 2 at different shear rates
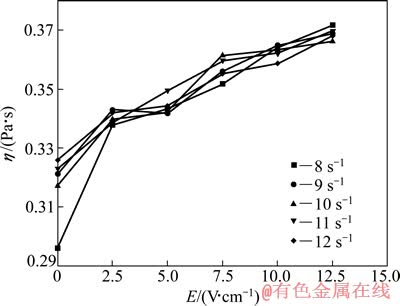
图3 不同剪切速率下渣样3的黏度-电场强度曲线
Fig. 3 η-E curves of slag sample 3 at different shear rates
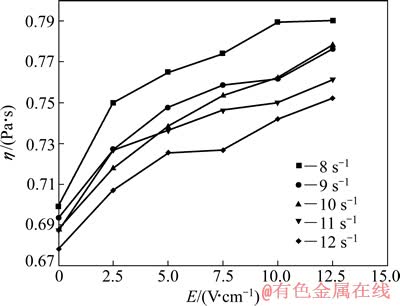
图4 不同剪切速率下渣样4的黏度-电场强度曲线
Fig. 4 η-E curves of slag sample 4 at different shear rates
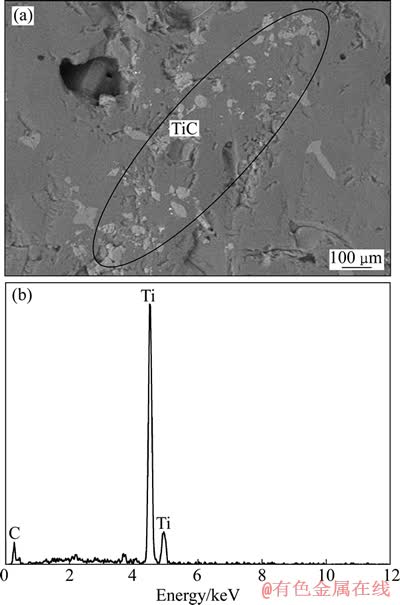
图5 渣样3的SEM像和特征晶粒的EDS谱
Fig. 5 SEM image (a) of slag sample 3 and EDS spectrum (b) of characteristic grain TiC
由图5可见,渣中加入的固相导电粒子TiC多以链带状形式存在,分布相对集中,颗粒尺寸较小且不均匀。研究表明,熔渣中钙钛矿相(CaTiO3)形核不困难,因熔渣中含有一定数量的TiC弥散固体质点,其熔点(3160 ℃)较高,容易成为钙钛矿的结晶核心,只要有适当的过冷度,钙钛矿就能迅速形核。CaO-SiO2-TiO2-Al2O3-MgO五元系熔渣由简单离子(Ca2+,Mg2+,O2-,Ti2+,Ti3+)和复合阴离子(SiO44-,AlO2-,TiO32-)构成[19]。钙钛矿相由Ca2+和TiO32-缔合而成:
 (1)
(1)
 (2)
(2)
 (3)
(3)
钙钛矿相熔点(1915 ℃)较高,随着其较早析出,枝晶周围的Ca2+和TiO32-含量降低,而其他较低熔点矿物的离子或离子集团含量相对增高,枝晶长大受阻[20]。随着熔体继续冷却,枝晶一旦穿过Ca2+和TiO32-贫化层,就能继续正常生长,结果在枝晶生长受阻处形成缩颈。由于颈缩部位的曲率半径较小,表面张力使其熔点下降,易于重熔而变得更细。与之相邻曲率半径较大的枝晶比较稳定,缩颈熔化产生的离子向其扩散,使之长大、变粗,形成树枝节。
图6所示为渣样2(4%TiC含量)不同电场强度处理后的SEM像。图7所示为CaTiO3晶粒的EDS谱。
由图6和7可见,随着电场强度的增加,钙钛矿的分布由分散逐渐聚集,钙钛矿晶粒随电场强度增大逐渐粗化。钙钛矿的分布以及晶粒尺寸随电场强度的规律性变化表明,在电场作用下,除了TiC等固相导电质点发生规律性的变化(由分散分布变为呈链状或成簇分布),高温过程中形成的钙钛矿在电场作用下的结构演变(包括分布和晶粒生长)对电致流变效应的产生也起到一定的作用。
非均相含钛冶金熔渣之所以在电场下流变特性发生改变主要是因为其内在结构的变化。在加外电场之前,熔渣中固相导电粒子TiC和较早析出的固相质点CaTiO呈随机分布状态,此时的电致流变液流动性良好。施加电场后,导电粒子由分散分布变成链状结构,在剪切力作用下,链状结构阻止电致流变液的流动,表现出表观黏度的增加。当电场增加到足够大时,链状结构变得更加紧密,最终形成柱状结构,致使电致流变液表观黏度进一步增大,流动性变差。
由于本实验中研究的是较低电场强度下含钛熔渣的流变现象,按照电致流变产生的结果来看,高电场强度下电致流变现象会更明显,如出现电致流变液从液体状态转变为类固体状态,这有待进一步研究。
3 结论
1) 随电场强度的增加,在不同剪切速率下,不同TiC含量渣样的表观黏度均显著增大,表现出非牛顿流体具有的正电致流变效应。相同电场强度和剪切速率下,随渣中TiC含量的增加,熔渣黏度明显增大。
2) 动态剪切时,渣中TiC颗粒在电场作用下形成的链状结构随剪切发生破坏和重组。
3) 施加电场后,渣中TiC固相质点由分散状态转变为链状或簇状分布,钙钛矿晶粒由分散分布逐渐聚集,且随电场强度增大晶粒逐渐粗化。TiC固相质点的规律性变化,以及高温过程中形成的钙钛矿在电场作用下的结构演变行为共同影响非均相含钛熔渣的流变特性。
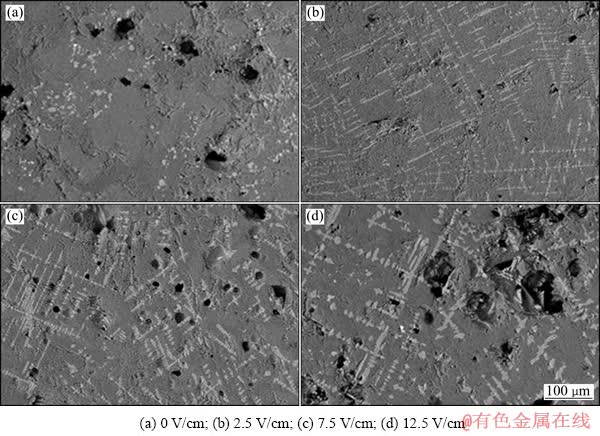
图6 不同电场强度处理后渣样2的SEM像
Fig. 6 SEM images of slag sample 2 treated at different voltages
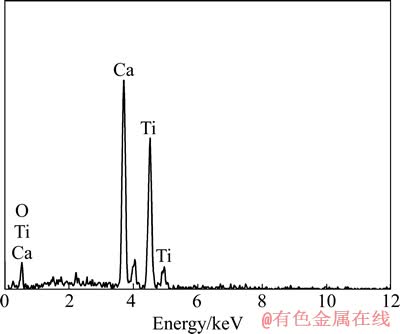
图7 CaTiO3的EDS谱
Fig. 7 EDS spectrum of CaTiO3
REFERENCES
[1] 杜鹤桂. 高炉冶炼钒钛磁铁矿原理[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1996.
DU He-gui. Blast furnace smelting vanadium-titanium magnetite principle[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1996.
[2] 马家源. 高炉冶炼钒钛磁铁矿理论与实践[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2000.
MA Jia-yuan. Blast furnace smelting vanadium-titanium magnetite theory and practice[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2000.
[3] 徐采栋, 林 蓉. 攀枝花钒钛磁铁矿高温还原中的重要物理化学问题[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 1980, 1(1): 2-3.
XUE Cai-dong, LIN Rong. Some important physical chemistry problems of Panzhihua vanadium-titanium magnetite during high temperature reduction[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 1980, 1(1): 2-3.
[4] 马家源, 孙希文, 盛世雄. 钒钛磁铁矿高炉冶炼的强化[J]. 钢铁, 2000, 35(1): 4-5.
MA Jia-yuan, SUN Xi-wen, SHENG Shi-xiong. Intensified smelting of vanadium-titanium magnetite in blast furnace[J]. Iron and Steel, 2000, 35(1): 4-5.
[5] 贾 碧, 齐宝铭. 高炉冶炼全钒钛磁铁矿时渣中带铁量的研究[J]. 钢铁, 1996, 31(10): 14-18.
JIA Bi, QI Bao-ming. Study on metal amount carried by slag during smelting with full V-Ti iron ore[J]. Iron and Steel, 1996, 31(10): 14-18.
[6] 贾 碧, 齐宝铭. 全钒钛矿冶炼时含钛高炉渣起泡现象[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 1996, 17(4): 10-13.
JIA Bi, QI Bao-ming. Experimental study of foaming phenomenon of titaniferous slag during V-Ti-bearing magnetite smelting[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 1996, 17(4): 10-13.
[7] 李永全, FRUEHANR R J. 高炉炉缸内碳氮化钛的生成机理研究[J]. 钢铁, 2003, 38(2): 58-61.
LI Yong-quan, FRUEHANR R J. Study on formation of titanium carbonitride in blast furnace hearth[J]. Iron and Steel, 2003, 38(2): 58-61.
[8] 付卫国, 刁日升, 黎健明, 宋国才, 李劲明. 攀钢1号高炉炉底沉积物特点分析[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2003, 24(3): 37-41.
FU Wei-guo, DIAO Ri-sheng, LI Jian-ming, SONG Guo-cai, LI Jin-ming. Characteristics analysis of furnace hearth sediment in no.1 blast furnace at PZH steel[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2003, 24(3): 37-41.
[9] 杜鹤桂, 杜 刚. Ti(C,N)对高炉冶炼的影响[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 1991, 12(3): 1-6.
DU He-gui, DU Gang. The effect of Ti(C,N) on blast furnace smelting[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 1991, 12(3): 1-6.
[10] 朱元凯. 含钛高炉渣泡沫稳定性研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 1983, 4(1): 14-19.
ZHU Yuan-kai. Study on foam stability of titaniferous slag[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 1983, 4(1): 14-19.
[11] 白晨光. 含钛高炉渣的若干物理化学问题研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2003.
BAI Chen-guang. Study on some physical chemistry problems of blast furnace slag-bearing titania[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2003.
[12] 吴 铿. 泡沫冶金熔体的基础理论[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2000.
WU Keng. Basic theory of metallurgical melt foam[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2000.
[13] 毛红霞, 白晨光, 邱贵宝, 陈登福, 温良英, 董凌燕. 非牛顿冶金熔渣流变特性的研究进展[J]. 重庆大学学报, 2005, 28(6): 52-55.
MAO Hong-xia, BAI Chen-guang, QIU Gui-bao, CHEN Deng-fu, WEN Liang-ying, DONG Ling-yan. Development in research rheological characteristics of non-Newtonian metallurgical molten slags[J]. Journal of Chongqing University, 2005, 28(6): 52-55.
[14] 刘海燕, 庞明君, 魏进家. 非牛顿流体研究进展及发展趋势[J]. 应用化工, 2010, 39(5): 740-745.
LIU Hai-yan, PANG Ming-jun, WEI Jin-jia. A progress and trend of the non-Newtonian fluids[J]. Applied Chemical Industry, 2010, 39(5): 740-745.
[15] 吴 铿, 储少军, 潜 伟. 非牛顿流体冶金熔渣的流变特性[J]. 钢铁, 1998, 33(11): 14-18.
WU Keng, CHU Shao-jun, QIAN Wei. Rheologic characteristics of metallurgical molten slags as non-Newtonian fluid[J]. Iron and Steel, 1998, 33(11): 14-18.
[16] TRIBE T S, KINGSTON P W, CALEY W F. Rheology and constitution of the CaO-SiO2-MgO-CaF2 system[J]. Canadian Metallurgical Quarterly, 1998, 36(2): 95-101.
[17] 郑华文, 吴张永, 唐向阳, 杨 用. 电流变液的流变特性分析和研究[J]. 机床与液压, 2000, 28(增刊): 30-31.
ZHENG Hua-wen, WU Zhang-yong, TANG Xiang-yang, YANG Yong. Analysis and study on rheological properties of a kind of electrorheological fluid[J]. Machine Tool and Hydraulics, 2000, 28(suppl): 30-31.
[18] PARTHASARATHY M, KLINGENBERG D J. Electrorheology: Mechanisms and models[J]. Materials Science & Engineering: R-Reports, 1996, 17(2): 57-103.
[19] 傅念新, 卢 玲, 隋智通. 高钛高炉渣中钙钛矿相的析出行为[J]. 钢铁研究学报, 1998, 10(3): 70-72.
FU Nian-xin, LU Ling, SUI Zhi-tong. Precipitating behavior of perovskite phase in the blast furnace slags bearing higher titania[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 1998, 10(3): 70-72.
[20] 娄太平, 李玉海, 马俊伟, 夏玉虎, 隋智通. 等温过程含钛炉渣中钙钛矿相弥散颗粒长大研究[J]. 金属学报, 1999, 35(8): 834-836.
LOU Tai-ping, LI Yu-hai, MA Jun-wei, XIA Yu-hu, SUI Zhi-tong. The isothermal growth of perovskite phase in the blast furnace slag bearing titania[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 1999, 35(8): 834-836.
(编辑 龙怀中)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(51090383,51174051)
收稿日期:2014-01-17;修订日期:2014-10-20
通信作者:姜 涛,教授,博士;电话:024-83670467;E-mail:jiangt@smm.neu.edu.cn