硅溶胶-煤矸石型壳高温性能及机理分析
郭馨,吕志刚,李晓飞
(清华大学 机械工程系,先进成形制造教育部重点实验室,北京,100084)
摘要:采用高温抗折仪、高温卧式膨胀仪、扫描电镜、X线荧光仪和X线衍射仪等研究高温下型壳强度、热膨胀性能的变化规律和高温断口的形貌特征。研究结果表明:在950~1 150 ℃时,型壳强度基本稳定,线膨胀率缓慢下降;在1 150~1 350 ℃时,型壳强度随温度升高而增加,线膨胀率在1 200 ℃附近基本不变,随后迅速减小;在1 350~1 450 ℃时,型壳高温强度迅速减小,残留强度显著增加,线膨胀率直线下降。不同温度条件下,型壳材料物相成分相同,但相对含量存在差异。在1 350 ℃附近,型壳迅速软化变形,可见硅溶胶-煤矸石型壳不适宜长时间处于1 350 ℃以上高温环境。原材料中的碱性元素在高温下生成低共熔点玻璃相,降低型壳软化温度,应严格控制氧化物杂质的含量。
关键词:熔模铸造;型壳;强度;热膨胀;微观结构
中图分类号:TG249.5 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2013)11-4442-06
High temperature properties of silica sol-gangue shell and its mechanism analysis
GUO Xin, L Zhigang, LI Xiaofei
Zhigang, LI Xiaofei
(Key Laboratory for Advanced Materials Processing Technology, Ministry of Education,
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China)
Abstract: The strength, thermal expansion and the surface morphology of the silica-gangue shell under high temperature condition were studied by hot strength device, horizontal thermal expansion device (TED), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray fluorescence (XRF) and X-ray diffraction (XRD). The results show that from 950 ℃ to 1 150 ℃, the strength of the shell keeps constant, while the linear expansion percentage (LEP) decreases; from 1 150 to 1 350 ℃, the strength increases, LEP stays the same at around 1 200 ℃, then decreases quickly; from 1 350 ℃ to 1 450 ℃, the hot strength decreases rapidly and the residual strength increases significantly, while LEP decreases dramatically. By the phase analysis it is proved that there are no new phases formed during heating, but the content of each phase varies. Calcination temperature over 1 350 ℃, the shell begins to soften, so it does not fit to work over 1 350 ℃ for a long time. To avoid the shell softening at lower temperature, it is necessary to control the percentage of alkaline oxide impurities which may produce low viscosity and low melting point substance in refractory cast material.
Key words: investment casting; shell; strength; thermal expansion; microstructure
硅溶胶是熔模铸造生产中常用的优质黏结剂,是由无定形二氧化硅的微小颗粒分散在水中而形成的稳定胶体溶液[1]。煤矸石是一种硬质高岭土,与煤炭伴生,主要成分为SiO2和Al2O3,有时还含有少量的方石英[2]。优选的煤矸石经高温煅烧后可作为熔模铸造背层耐火材料,近年来,由于价格低廉、性能优良,在熔模铸造中得到了广泛的应用。优质型壳是确保熔模铸铸件的尺寸精度、表面粗糙度甚至冶金质量和力学性能的关键,但型壳高温性能的检测一般在1 000~ 1 200 ℃进行[3-4],与型壳实际承受温度存在较大差异。在此,本文作者研究了高温下硅溶胶-煤矸石型壳强度及线膨胀性能的变化规律,分析型壳的宏观和微观结构。
1 实验材料及方法
1.1 实验材料
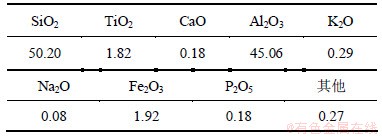
硅溶胶黏结剂GS30,煤矸石粉砂,浆料流杯黏度为(35±1) /s。黏结剂GS30的性能参数见表1;XRF分析测定煤矸石粉料的成分见表2。
表1 20 ℃硅溶胶黏结剂GS30的性能参数
Table 1 Property parameters of silica sol GS30 at 20 ℃
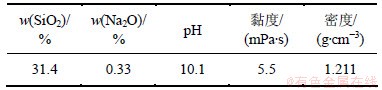
表2 煤矸石粉料的成分
Table 2 Composition and mass percentage of coal gangues 质量分数/%
1.2 实验方法
型壳的常温、高温和残留强度按照GB/T 4741—1999[5]规定的三点抗弯法在GKZ数显式材料高温抗折仪上进行,试样为逐层制壳,长×宽×高为40 mm×20 mm×3 mm,实验的温度为950~1 450 ℃;型壳热膨胀性能按照GB/T 7320—2008[6]在PCY型高温卧式膨胀仪上进行,试样逐层制壳,长×宽×高为51 mm×10 mm×5 mm,测定型壳从室温至1 450 ℃的线膨胀率。
型壳的结构分析包括型壳物相检测和型壳高温断口观察。利用XRD分析对型壳的物相组成与变化进行研究,利用KH-1000视频显微分析仪观察型壳断面的宏观特征,利用JSM-6301F场发射SEM观察和分析不同温度作用后型壳高温断口的形貌特征,进而对硅溶胶型壳高温性能的变化机理进行分析和探讨。
2 实验结果
2.1 型壳的强度
强度性能是表征型壳质量的重要指标。实验测定型壳的常温强度为4.5 MPa。高温与残留强度的关系如图1所示。由图1可知,在实验温度范围内,型壳强度的变化可分为3个阶段。
阶段(1)为950~1 150 ℃,型壳高温强度相对稳定,为11.7~12.3 MPa;残留强度由9.3 MPa增至10.4 MPa。
阶段(2)为1 150~1 350 ℃,型壳高温强度随温度而增加,至1 350 ℃达到最大值16.7 MPa,相比1 150 ℃时增加42%;残留强度由10.4 MPa增至11.4 MPa。
阶段(3)为1 350~1 450 ℃,型壳高温强度减小,1 450 ℃时已降至7.5 MPa,比1 350 ℃时减小55%;型壳残留强度增加,1 450 ℃时为15.0 MPa,比1 350 ℃时增加38%。

图1 型壳的强度
Fig.1 Strength of shell
由图1可以看到:型壳的高温和残留强度具有一定的关系。型壳强度与固相烧结、液相生成和二次莫来石化有关[7]。固相烧结指型壳中的硅凝胶通过固相反应逐步在耐火颗粒表面形成晶态桥连相,将整个型壳固结起来;液相是高温下材料反应的产物,可能是Fe2O3,TiO2,K2O和Na2O等碱性氧化物与SiO2,Al2O3反应生成的低熔点化合物,其数量及性质极大地影响着型壳的强度。液相烧结和固相烧结的推动力都是表面能,烧结过程也都是由颗粒重排、气孔填充和晶粒生长等阶段组成[8],因此,在通常情况下,型壳高温强度高,残留强度也较高,如型壳强度变化的第1和2阶段。但两者的形成机制和影响因素并不完全相同。固相烧结和二次莫来石化将导致型壳高温和残留强度升高,而液相烧结将导致型壳高温强度下降,冷却后液相凝结,将颗粒牢固的连接起来,使残留强度上升[9],这是型壳高温、残留强度的变化趋势在第3阶段产生明显差异的主要原因。
根据实验规律和硅酸盐耐火材料的反应规律,型壳的反应与主要成分为αAl2O3·H2O和Al2O3·2SiO2·2H2O的铝硅材料焙烧的反应相符:低于1 200 ℃时,型壳材料发生分解反应;在1 200 ℃附近,αAl2O3与无定形SiO2反应,生成二次莫来石,该反应在达到1 300 ℃后明显;二次莫来石生成后,型壳发生再结晶,莫来石晶体发育长大[7, 10]。如图1所示,在1 150 ℃的型壳强度低于1 050 ℃及1 250 ℃的强度,成为该温度范围内的极小值。它的出现与低熔点化合物生成和二次莫来石化反应的综合作用有关:在1 050~1 200 ℃时,型壳内生成少量低熔点化合物,造成型壳高温强度降低,而随后发生的二次莫来石化反应会逐步提高型壳高温强度,导致高温强度在1 150 ℃出现极小值。之后,二次莫来石化反应持续提高型壳高温强度。1 350 ℃左右时发生莫来石的再结晶烧结,高温强度下降,残留强度上升。
2.2 型壳的热膨胀
型壳的热膨胀性能影响着型壳的尺寸稳定性和铸件的尺寸精度,是型壳的另一重要性能指标,其测试结果如图2所示。由图2可知:硅溶胶型壳的高温收缩开始于985 ℃,高温段的线膨胀率变化大致可分为4个阶段。
阶段(1)为900~985 ℃,型壳尺寸基本稳定,线膨胀百分率达到最大值,为0.55 %;阶段(2)为985~1 150 ℃,型壳线膨胀率随温度升高迅速下降,至1 150 ℃已降至985 ℃时的一半,为0.28 %;
阶段(3)为1 150~1 300 ℃,型壳线膨胀率相对稳定,为0.20 %~0.28 %;
阶段(4)为1 300 ℃以上,型壳线膨胀率继续下降,至1 400 ℃左右已为负值。
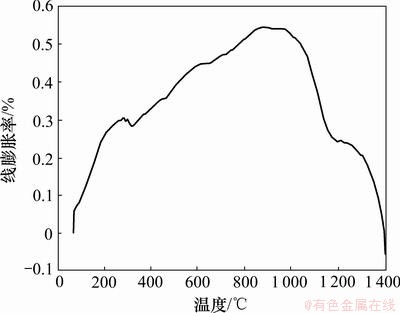
图2 型壳线膨胀曲线
Fig.2 Linear expansion percentage of shell
受热情况下,型壳的线膨胀包括型壳材料的热膨胀和相变膨胀,而线收缩是由于相变、液相生成、孔隙充填和颗粒拉紧、重结晶等过程使型壳致密化引起的[11]。因此,型壳的线量变化既能反映型壳的热膨胀性能,又能作为判断型壳是否发生状态和物相变化的依据[12]。
温度低于900 ℃时,线膨胀率斜率的变化主要是由于型壳内石英的相变,石英在常压下存在8种变体,各种变体的结构不同,其密度不同,在不同温度下转变时伴随有体积效应,如α方石英在180~270 ℃转变为β方石英,体积增加2.8%,线膨胀率显著增大[13]。900 ℃以上,引起型壳收缩的因素较为复杂。由表2可知,型壳原材料中含有一定量的K,Na和Ca等碱性氧化物元素,K的存在能使型壳材料生成熔点985 ℃的莫来石-钾长石-鳞石英共熔物,而Na的存在能形成熔点为1 050 ℃的莫来石-鳞石英-钠长石的共熔物,或是熔点为1 063 ℃的刚玉-钠长石-霞石共熔物,Ca的存在能形成熔点1 345 ℃的钙长石-莫来石-鳞石英共熔物[7],这些玻璃相熔融后形成液相,会产生塑性甚至黏性流动,引起型壳的高温收缩。
在1 200 ℃左右,型壳线膨胀率的下降趋势减弱,这是由于二次莫来石化反应一般伴有10%左右的体积膨胀,使型壳的收缩减缓。之后随着温度的升高,液相含量进一步增加,型壳明显收缩,至1 400 ℃时型壳已软化,在膨胀仪压头作用下变形,从而使线膨胀率下降。
3 结构分析
3.1 型壳的主要物相
由图2可知,在1 150 ℃,1 350 ℃和1 450 ℃,型壳的高温强度存在明显差异,测定不同温度型壳的物相组成,衍射图谱如图3所示。
由图3可知,尽管受热温度不同,型壳的主要结晶相都是莫来石、石英和氧化铝,物相成分没有发生变化。但型壳各物相的含量存在一定变化。受热温度为1 150 ℃时,型壳的衍射图谱在21.6 °附近基底衍射强度较高,而1 450 ℃时型壳α方石英含量较高。这是由于在1 200 ℃无定形SiO2转变为晶型的α方石英,该反应在1 450 ℃附近达到最高值[7]。受热温度为1 350 ℃和1 450 ℃,型壳内莫来石含量基本一致,高于1 150 ℃时,型壳内莫来石的含量,说明1 350 ℃时,型壳莫来石化进程已基本结束,以后是莫来石的长大过程。

图3 型壳 XRD衍射图谱
Fig.3 XRD analysis of shell
3.2 型壳宏观断口
温度为1 350 ℃以上,随着加热温度的升高,型壳颜色逐渐由白变黄,高温断口的形貌也存在明显差异。图4所示为受热温度为1 350 ℃和1 450 ℃型壳的变形和断裂情况。
由图4可见:1 350 ℃时型壳为白色,略带有褐色斑点,宏观断口为脆性断裂,断裂型壳未发生明显变形;1 450 ℃时型壳为暗黄色,带有褐色斑点,断裂型壳发生明显塑性变形,断口参差不齐,呈现出韧性断裂的特征,且实验中,部分加热温度高于1 400 ℃的型壳仅发生一定程度的变形和开裂,在仪器测量的变形范围(3 mm)内未断裂,表明此时型壳已软化。

图4 型壳变形和断裂情况
Fig.4 Fractures and deformations of shell
3.3 型壳微观断口
型壳材料的性能不仅与材料的组成有关,还与材料的显微结构有密切关系[14]。不同温度下,型壳材料的烧结程度和高温断口形貌存在差异,如图5所示。

图5 型壳高温断口SEM图像
Fig.5 SEM images of fracture surfaces
常温下,型壳的大部分颗粒(耐火材料)由基质结合相(黏结剂)包裹,颗粒与基质间没有发生的反应,两者之间没有通过新的反应生成相结合,使得颗粒基质间的结合强度较低;在950 ℃时型壳颗粒边缘与基质已紧密结合;在1 150 ℃时已经难以区分基质和颗粒边界,型壳材料的烧结程度进一步提高;1 350 ℃时型壳材料发生了二次莫来石化反应,具有一定的方向性,材料体积膨胀,造成颗粒间产生少量空隙;1 450 ℃时型壳材料已发生再结晶反应,晶粒尺寸明显增加。
研究表明[13],材料的断裂强度(σ)与晶粒尺寸(G)有函数关系:σ=f(G-1/2),即材料晶粒越小,其断裂强度越高。这与型壳高温断口的形貌与型壳高温强度的测试结果相一致。常温下,型壳内材料结合并不紧密,因此型壳常温强度较低;在950 ℃时,材料间已紧密结合,型壳高温强度较高;随着受热温度的提高,材料的烧结程度进一步增加,高温强度也逐渐增加,至1 350 ℃左右其高温强度达到最高值;随后,型壳发生再结晶烧结,该反应是在液相存在的条件下进行的,以液相烧结为主[7],再结晶后颗粒粒径由几微米增加至几十微米,型壳高温强度显著下降。
4 讨论
型壳的高温性能受加热温度、型壳材料的成分含量、显微结构等因素的影响。根据硅溶胶型壳的高温性能测试结果和结构分析,可将型壳在950~1 450 ℃范围内的反应分为3个阶段。
阶段(1)为950~1 150 ℃。在此阶段,型壳强度相对稳定,线膨胀率在985 ℃开始下降。这一温度范围内,型壳材料主要发生固相烧结,但开始产生少量液相,固、液相烧结的综合作用使型壳高温强度相对稳定在12 MPa,残留强度升高,但相对稳定在10 MPa;固相拉紧和少量液相的产生造成型壳线膨胀率下降。少量的液相足以使型壳在金属浇注过程中软化变形[15],因此,严格控制K和Na等碱性氧化物的含量,降低型壳内低黏度低共熔点玻璃相的生成,对提高型壳该温度段的高温性能具有重要的意义。
阶段(2)为1 150~1 350 ℃。在此阶段,型壳高温、残留强度均随温度升高而增加,线膨胀率在1 200 ℃附近相对稳定,随后减小。该温度段内型壳烧结程度增加,1 200 ℃附近发生二次莫来石化反应,导致型壳的高温、残留强度均提高;型壳强度受二次莫来石化和生成液相的共同影响,液相的存在有助于二次莫来石化反应进行,但过多的液相会降低型壳高温强度。二次莫来石化引起材料体积膨胀,型壳尺寸收缩趋势减缓,之后随着温度升高,液相含量进一步增加,型壳尺寸继续收缩。在该温度范围内,控制型壳内碱性氧化物的含量对提高型壳的强度,保证型壳的尺寸稳定性依然具有积极的意义。
阶段(3)为1 350~1 450 ℃。在此阶段,型壳高温强度减小,残留强度增加,线膨胀率下降。该温度范围内,型壳颜色由白变黄,物相成分没有发生变化,但形态发生变化,说明型壳材料已发生再结晶反应。此时型壳已软化,在外力作用下变形,其高温断口具有韧性断裂的特征,高温强度和线膨胀率下降,但由于液相烧结作用,型壳残留强度增加。
5 结论
(1) 受热温度不同,型壳的高温性能存在差别。温度高于1 350 ℃以上时,硅溶胶-煤矸石型壳发生再结晶烧结反应,在外力作用下软化变形,高温强度和线膨胀百分率均下降,已难以满足熔模铸造对型壳的要求。因此,对于这种硅溶胶型壳,不适宜长时间处于1 350 ℃以上的高温环境。
(2) 型壳的高温性能受烧结程度和碱性氧化物含量的影响。K和Na等元素的存在会使型壳内生成低熔点化合物,导致型壳在较低温度下发生软化,因此,为提高型壳的高温性能,需尽可能降低型壳原材料中碱性氧化物的含量。
参考文献:
[1] 叶久新, 文晓涵. 熔模精铸工艺指南[M]. 长沙: 湖南科学技术出版社, 2006: 104-105.
YE Jiuxin, WEN Xiaohan. Guide to investment casting process[M]. Changsha: Hunan Science and Technology Press, 2006: 104-105.
[2] 中国铸造协会. 熔模铸造手册[M]. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 2000: 209.
China Foundry Association. Investment casting handbook[M]. Beijing: Machine Press, 2000: 209.
[3] 刘振军, 岳春华, 张国宝, 等. 熔模铸造加固层型壳强度性能的研究[J]. 铸造技术, 2007(7): 950-954.
LIU Zhenjun, YUE Chunhua, ZHANG Guobao, et al. Research on strength of reinforced investment casting shell[J]. Foundry Technology, 2007(7): 950-954.
[4] Hendricks M J, Wang P M J, Tistle F A. An evaluation of methods used to determine shell strength and how a material will perform in the Dewax process[EB/OL]. [2012-06-18]. http://www.investmentcasting.org/paper_detail.asp? Paper ID= 217.
[5] GB/T 4741—1999, 陶瓷材料抗弯强度试验方法[S].
GB/T 4741—1999, Standard test method for bending strength of ceramic material[S].
[6] GB/T 7320—2008, 耐火材料: 热膨胀试验方法[S].
GB/T 7320—2008, Refractories: Determination of thermal expansion[S].
[7] 佟天夫, 陈冰, 姜不居. 熔模铸造工艺[M]. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 1991: 158.
TONG Tianfu, CHEN Bing, JIANG Buju. Investment casting process[M]. Beijing: Machine Press, 1991: 158.
[8] 张其土. 无机材料科学基础[M]. 上海: 华东理工大学出版社, 2007: 306.
ZHANG Qitu. Basis for inorganic materical science[M]. Shanghai: East China University of Science and Technology Press, 2007: 306.
[9] 张立同, 曹腊梅, 刘国利, 等. 近净形熔模精密铸造理论与实践[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2007: 66.
ZHANG Litong, CAO Lamei, LIU Guoli, et al. Theory and practice of near net-shape investment casting[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2007: 66.
[10] 杨中正, 钟香崇. 矾土、煤矸石烧结合成莫来石过程的相组成和显微结构研究[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2006(6): 31-34.
YANG Zhongzheng, ZHONG Xiangchong. Study on the phase composition and microstructure in the process of sintering- syntheszing mullite with bauxite and coal gangue[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2006(6): 31-34.
[11] 赵恒义, 佟天夫. 熔模铸造型壳的线量变化研究[J]. 特种铸造及有色合金, 1990(1): 17-20.
ZHAO Hengyi, TONG Tianfu. A study on dimensional change of ceramic shell in investment casting[J]. Special Casting & Nonferrous Alloys, 1990(1): 17-20.
[12] Branscomb T. Thermal expansion of investment casting shells[EB/OL]. [2012-06-18]. http://www.investmentcasting. org/paper_detail.asp? Paper ID= 869.
[13] 袁好杰. 耐火材料基础知识[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2009: 33.
YUAN Haojie. Basic knowledge on refractory material[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2009: 33.
[14] 孙庚辰, 钟香崇. Al2O3-SiO2系耐火材料高温力学性能[J]. 材料科学进展, 1988(4): 61-68.
SUN Gengchen, ZHONG Xiangchong. High temperature mechanical properties of Al2O3-SiO2 system refractories[J]. Material Science Progress, 1988(4): 61-68.
[15] Bauwin H. Commercial experience with low sodium binders[EB/OL]. [2012-06-18]. http://www.investmentcasting. org/paper_detail.asp? Paper ID= 217.
(编辑 赵俊)
收稿日期:2012-08-18;修回日期:2012-11-22
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(50875144)
通信作者:吕志刚(1972-),男,山东巨野人,副教授,从事材料加工工艺研究;电话:010-62784569;E-mail: lvzg@tsinghua.edu.cn