Stacking fault energy and electronic structure of molybdenum under solid solution softening/hardening
来源期刊:中南大学学报(英文版)2021年第1期
论文作者:龚浩然 刘攀 刘柳成
文章页码:39 - 47
Key words:stacking fault energy; electronic structure; molybdenum; solid solution softening/hardening; ab initio calculation
Abstract: Ab initio calculations are used to understand the fundamental mechanism of the solid solution softening/hardening of the Mo-binary system. The results reveal that the Mo-Ti, Mo-Ta, Mo-Nb, and Mo-W interactions are primarily attractive with negative heats of formation, while the interactions of Mo-Re, and Mo-Zr would be mainly repulsive with positive heats of formation. It is also shown that the addition of Re and Zr would cause the solid solution softening of Mo by the decrease of the unstable stacking fault energy and the increase of ductility. On the contrary, the elements of W, Ta, Ti, and Nb could bring about the solid-solution hardening of Mo through the impediment of the slip of the dislocation and the decrease of ductility. Electronic structures indicate that the weaker/stronger chemical bonding due to the alloying elements should fundamentally induce the solid solution softening/hardening of Mo. The results are discussed and compared with available evidence in literatures, which could deepen the fundamental understanding of the solid solution softening/hardening of the binary metallic system.
Cite this article as: LIU Pan, LIU Liu-cheng, GONG Hao-ran. Stacking fault energy and electronic structure of molybdenum under solid solution softening/hardening [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2021, 28(1): 39-47. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-021-4584-2.

J. Cent. South Univ. (2021) 28: 39-47
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-021-4584-2
LIU Pan(刘攀), LIU Liu-cheng(刘柳成), GONG Hao-ran(龚浩然)
State Key Laboratory of Powder Metallurgy, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China
 Central South University Press and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2021
Central South University Press and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2021
Abstract: Ab initio calculations are used to understand the fundamental mechanism of the solid solution softening/hardening of the Mo-binary system. The results reveal that the Mo-Ti, Mo-Ta, Mo-Nb, and Mo-W interactions are primarily attractive with negative heats of formation, while the interactions of Mo-Re, and Mo-Zr would be mainly repulsive with positive heats of formation. It is also shown that the addition of Re and Zr would cause the solid solution softening of Mo by the decrease of the unstable stacking fault energy and the increase of ductility. On the contrary, the elements of W, Ta, Ti, and Nb could bring about the solid-solution hardening of Mo through the impediment of the slip of the dislocation and the decrease of ductility. Electronic structures indicate that the weaker/stronger chemical bonding due to the alloying elements should fundamentally induce the solid solution softening/hardening of Mo. The results are discussed and compared with available evidence in literatures, which could deepen the fundamental understanding of the solid solution softening/hardening of the binary metallic system.
Key words: stacking fault energy; electronic structure; molybdenum; solid solution softening/hardening; ab initio calculation
Cite this article as: LIU Pan, LIU Liu-cheng, GONG Hao-ran. Stacking fault energy and electronic structure of molybdenum under solid solution softening/hardening [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2021, 28(1): 39-47. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-021-4584-2.
1 Introduction
Molybdenum (Mo) is a refractory transition metal and has been potentially used as turbine engines to replace nickel superalloys in the field of aerospace [1-7], structural components in nuclear fusion reactors [8, 9], heat sinks and heat elements in heating treating industry [10], etc. These important high-temperature applications are principally attributed to its high melting temperature of 2610 °C, good heat-conducting capability, excellent high-temperature strength, relatively low sputtering yield, high stability, and superior creep resistance [1, 5, 8, 11-20]. Nevertheless, the main disadvantage of Mo is its poor ductility at room temperature, and radiation may even aggravate the brittleness of Mo [2, 8, 21-25].
Generalized stacking fault energy (GSFE) has been well regarded as a suitable physical property to express the intrinsic ductility/brittleness of a given material, since the magnitude of GSFE is closely related to dislocation movement and subsequent plastic deformation [26-29]. In this respect, however, the theoretical GSFE values of Mo in literatures are not consistent with each other [30-33]. For instance, the unstable stacking fault energies of the (110)<111> slip system of Mo derived from the full-potential linear muffin-tin orbital method and ultrasoft pseudopotentials are 1.8 and 1.68 J/m2 [30-32], respectively, while the corresponding value from the bond-order potential is 1.3 J/m2 [33]. It is well known that the addition of alloying elements is an effective way to improve the ductility of Mo [10, 30, 34]. Specifically, the elements of Re, Ir, and Os could reduce the GSFE value of Mo and bring about the so-called solid solution softening [30, 34]. Experimental evidence also reveals that Re can considerably decrease the ductile-brittle transition temperature (DBTT) of Mo [10, 35]. On the other hand, the elements of Hf, Ta, and W increase the GSFE value of Mo and therefore induce the solid-solution hardening of Mo [30, 34]. It should be pointed out that further theoretical studies are needed to investigate the fundamental mechanism of the solid solution softening/hardening in Mo.
The present paper is therefore dedicated through ab initio calculations [36, 37] to find out the stacking fault energy and related ductility of Mo with the addition of several alloying elements. Particularly, two slip systems of 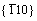 <111> and
<111> and 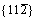 <111> as well as six transition elements of W, Ta, Ti, Nb, Re, and Zr are intentionally selected as typical examples to find out solid solution hardening/softening of Mo [1-25, 29-32, 34, 38-43], and the elements of Ir, Os, and Hf are not included in the present study due to their clear effects in literatures [30, 34]. The heats of formation and electronic structure of these elements in Mo will be also derived and discussed, in order to deeply understand the fundamental mechanism of the solid solution softening/hardening of the Mo-binary system.
<111> as well as six transition elements of W, Ta, Ti, Nb, Re, and Zr are intentionally selected as typical examples to find out solid solution hardening/softening of Mo [1-25, 29-32, 34, 38-43], and the elements of Ir, Os, and Hf are not included in the present study due to their clear effects in literatures [30, 34]. The heats of formation and electronic structure of these elements in Mo will be also derived and discussed, in order to deeply understand the fundamental mechanism of the solid solution softening/hardening of the Mo-binary system.
2 Method of calculation
The present calculation is performed via the well-known software of Vienna ab initio Simulation Package [44] with the projector- augmented wave (PAW) method under the framework of density functional theory [45, 46]. The generalized gradient approximation (GGA) is used to express the exchange and correlation function [47], and the plane-wave basis is chosen with a cutoff energy of 400 eV. Moreover, the temperature-smearing method [48] is selected for the relaxation calculations, and the modified tetrahedron method [49] is conducted for the static calculations.
A supercell of 48 atoms is first constructed for pure BCC Mo bulk, and a Mo atom is replaced by an alloying X atom (X=W, Ta, Ti, Nb, Re and Zr) to form the binary Mo47X1 (X=W, Ta, Ti, Nb, Re, and Zr) bulk. The lattice constants of pure Mo and Mo47X1 bulks are obtained through fully optimization, and the heats of formation of Mo47X1 bulks are also calculated for comparison. It should be pointed out that the Mo47X1 (X=W, Ta, Ti, Nb, Re, and Zr) bulks can maintain the BCC structure during optimization, and the derived lattice parameters of BCC Mo and Mo47X1 bulks will be utilized in the subsequent calculations.
A surface unit cell of 2×2 with 12 surface layers and 12 vacuum layers is then chosen for the slip systems of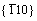 <111> and
<111> and 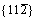 <111> after a series of test calculations. Consequently, Figure 1 displays the
<111> after a series of test calculations. Consequently, Figure 1 displays the and
and surface models of Mo47X1 (X=W, Ta, Ti, Nb, Re, and Zr) with 12 surface layers. One can observe from this figure that the alloying element is located at the seventh layer of the surface model, and that the x, y, and z axes of the
surface models of Mo47X1 (X=W, Ta, Ti, Nb, Re, and Zr) with 12 surface layers. One can observe from this figure that the alloying element is located at the seventh layer of the surface model, and that the x, y, and z axes of the surface model are [111],
surface model are [111], 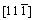 , and
, and 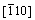 , respectively, whereas the x, y and z axes of the
, respectively, whereas the x, y and z axes of the surface are [111],
surface are [111], 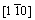 and
and 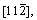 respectively.
respectively.
In order to create the stacking fault, the upper half (from the seventh to twelfth layers) of each surface in Figure 1 is set to move along the [111] direction (x axis) with a certain displacement ranged from 0.0 to 1.0 with a spacing of 0.1, whereas the lower half (from the first to sixth layers) remains unchanged. It should be noted that the above displacement is a normalized value, and 1.0 corresponds to the length of the Burgers vector of a/2<111>. After the displacement, the atoms in the whole surface model are only permitted to relax along the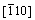 or
or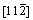 direction (z axis) [50]. The total energy of the surface model after relaxation is calculated before and after each displacement, for the purpose of deriving the stacking fault energy. During each relaxation and static calculation, the k meshes of Monkhorst-Pack [45] are 7×7×1 and 9×9×1, respectively, while the energy criteria are 0.01 and 0.001 meV, respectively.
direction (z axis) [50]. The total energy of the surface model after relaxation is calculated before and after each displacement, for the purpose of deriving the stacking fault energy. During each relaxation and static calculation, the k meshes of Monkhorst-Pack [45] are 7×7×1 and 9×9×1, respectively, while the energy criteria are 0.01 and 0.001 meV, respectively.
3 Results and discussions
To begin with, the lattice parameters of Mo and Mo47X1 (X=W, Ta, Ti, Nb, Re, and Zr) bulks with the BCC structure are optimized and the derived values are summarized in Table 1. One can see that the obtained lattice constant of Mo from the present PAW-GGA method is 3.150 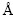 , which is in good agreement with the corresponding value of 3.147
, which is in good agreement with the corresponding value of 3.147 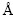 from experimental measurements [51]. Interestingly, the lattice constants of Mo47X1 bulks are similar to that of Mo. This similarity would be probably attributed to the low composition of the alloying atom as well as its close atomic radius to that of Mo.
from experimental measurements [51]. Interestingly, the lattice constants of Mo47X1 bulks are similar to that of Mo. This similarity would be probably attributed to the low composition of the alloying atom as well as its close atomic radius to that of Mo.

Figure 1  (a) and
(a) and (b) surfaces of Mo47X (X=W, Ta, Ti, Nb, Re, and Zr) with 12 surface layers, seventh layers of
(b) surfaces of Mo47X (X=W, Ta, Ti, Nb, Re, and Zr) with 12 surface layers, seventh layers of (c) and
(c) and (d) surfaces with one Mo atom replaced by the X atom (The green and yellow spheres refer to Mo and X atoms, respectively)
(d) surfaces with one Mo atom replaced by the X atom (The green and yellow spheres refer to Mo and X atoms, respectively)
Table 1 Lattice constants (a), unstable stacking fault energy (Eus),and ductility (D) of BCC Mo and Mo47X1 (X=W, Ta, Ti,Nb, Re, and Zr) bulks. The heats of formation (△Hf) of Mo47X1 bulks from the present study and the thermodynamic model [52] are also listed for comparison. (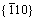 <111> and
<111> and  <111>are two slip systems)
<111>are two slip systems)
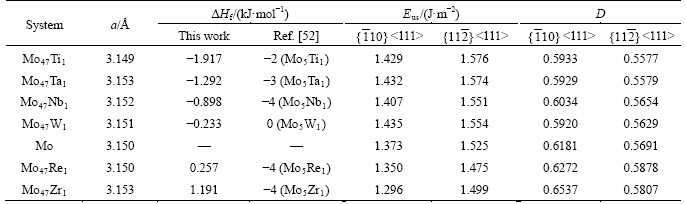
For each BCC Mo47X1 (X=W, Ta, Ti, Nb, Re, and Zr) bulk, the heat of formation (△Hf) could be obtained as follows:
 (1)
(1)
where  EMo and EX are total energies of BCC Mo47X1, BCC Mo, and alloying atom of W, Ta, Ti, Nb, Re, or Zr at the equilibrium state, respectively. Consequently, Table 1 lists the derived ΔHf values of Mo47X1 bulks as well as other available data in Ref. [52]. One can discern from this table that the present heats of formation (-1.917 kJ/mol) of Mo47Ti1 are in nice agreement with the corresponding value (-2 kJ/mol) of Mo5Ti1, while ΔHf of Mo47Ta1, Mo47Nb1 and Mo47W1 bulks from the present calculation are different, to some extent, from the thermodynamic values of Mo5Ta1, Mo5Nb1, and Mo5W1 bulks [52]. On the other hand, Mo47Re1 and Mo47Zr1 possess the positive heats of formation of 0.257 and 1.191 kJ/mol, respectively, which are quite distinct from the negative values (-4 kJ/mol) of Mo5Re1 and Mo5Zr1 by the Miedema model [52]. These divergences would be probably due to the computational errors as well as the compositional differences. The above negative or positive values of ΔHf from the present study also indicate that the Mo-Ti, Mo-Ta, Mo-Nb and Mo-W interactions are primarily attractive, while the interactions of Mo-Re and Mo-Zr would be mainly repulsive.
EMo and EX are total energies of BCC Mo47X1, BCC Mo, and alloying atom of W, Ta, Ti, Nb, Re, or Zr at the equilibrium state, respectively. Consequently, Table 1 lists the derived ΔHf values of Mo47X1 bulks as well as other available data in Ref. [52]. One can discern from this table that the present heats of formation (-1.917 kJ/mol) of Mo47Ti1 are in nice agreement with the corresponding value (-2 kJ/mol) of Mo5Ti1, while ΔHf of Mo47Ta1, Mo47Nb1 and Mo47W1 bulks from the present calculation are different, to some extent, from the thermodynamic values of Mo5Ta1, Mo5Nb1, and Mo5W1 bulks [52]. On the other hand, Mo47Re1 and Mo47Zr1 possess the positive heats of formation of 0.257 and 1.191 kJ/mol, respectively, which are quite distinct from the negative values (-4 kJ/mol) of Mo5Re1 and Mo5Zr1 by the Miedema model [52]. These divergences would be probably due to the computational errors as well as the compositional differences. The above negative or positive values of ΔHf from the present study also indicate that the Mo-Ti, Mo-Ta, Mo-Nb and Mo-W interactions are primarily attractive, while the interactions of Mo-Re and Mo-Zr would be mainly repulsive.
The generalized stacking fault energies (GSFE) [41] of both BCC Mo and Mo47X1 (X=W, Ta, Ti, Nb, Re, and Zr) surfaces are calculated according to the following form:
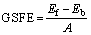 (2)
(2)
where Ef and Eb are total energies of the surface after and before a certain displacement along the Burgers vector (a/2<111>), respectively; and A is the area of the surface model. After a series of calculations, the derived GSFE values of 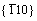 <111> and
<111> and 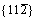 <111> slip systems are shown in Figure 2 for BCC Mo and Mo47X1 (X=W, Ta, Ti, Nb, Re, and Zr) under several displacements along the Burgers vector (a/2<111>). The summit of each curve in Figure 2 has been regarded as the energy barrier of the dislocation emission, and named as the unstable stacking fault energy (Eus) [36]. The calculated Eus values of BCC Mo and Mo47X1 are thus included in Table 1.
<111> slip systems are shown in Figure 2 for BCC Mo and Mo47X1 (X=W, Ta, Ti, Nb, Re, and Zr) under several displacements along the Burgers vector (a/2<111>). The summit of each curve in Figure 2 has been regarded as the energy barrier of the dislocation emission, and named as the unstable stacking fault energy (Eus) [36]. The calculated Eus values of BCC Mo and Mo47X1 are thus included in Table 1.
Based on the derived Eus value, the ductility (D) of BCC Mo and Mo47X1 (X=W, Ta, Ti, Nb, Re, and Zr) can be estimated by [28, 50]:
 (3)
(3)
where Es is the surface energy of the  or
or  surfaces of BCC Mo and Mo47X1. In the present calculation, the surface energies of the
surfaces of BCC Mo and Mo47X1. In the present calculation, the surface energies of the  or
or surfaces of BCC Mo are 2.829 and 2.893 J/m2, respectively, which agree well with the corresponding value (2.807 J/m2) of the
surfaces of BCC Mo are 2.829 and 2.893 J/m2, respectively, which agree well with the corresponding value (2.807 J/m2) of the  surface of BCC Mo from experimental measurements [53]. It should be noted that the Es value of BCC Mo47X1 is very close to that of pure Mo (results not shown). The derived D values of the slip systems of
surface of BCC Mo from experimental measurements [53]. It should be noted that the Es value of BCC Mo47X1 is very close to that of pure Mo (results not shown). The derived D values of the slip systems of  <111> and
<111> and  <111> of both Mo and Mo47X1 (X=W, Ta, Ti, Nb, Re, and Zr) are therefore summarized in Table 1.
<111> of both Mo and Mo47X1 (X=W, Ta, Ti, Nb, Re, and Zr) are therefore summarized in Table 1.
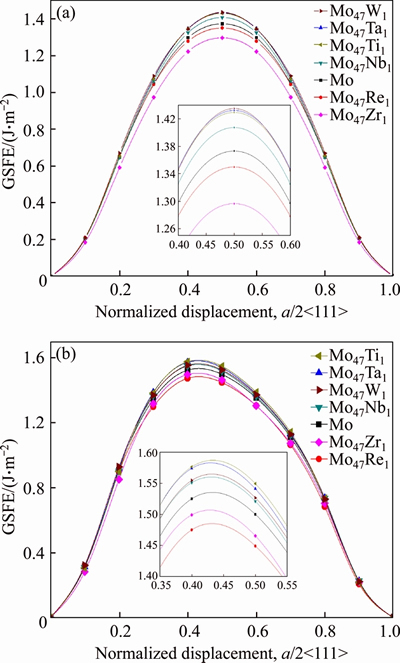
Figure 2 Generalized stacking fault energies (GSFE) of  <111> (a) and
<111> (a) and 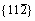 <111> (b) slip systems of BCC Mo and Mo47X1 (X=W, Ta, Ti, Nb, Re, and Zr) under several displacements along the Burgers vector (a/2<111>)
<111> (b) slip systems of BCC Mo and Mo47X1 (X=W, Ta, Ti, Nb, Re, and Zr) under several displacements along the Burgers vector (a/2<111>)
Several characteristics can be discerned from Figure 2 and Table 1. Firstly, the calculated Eus value (1.373 J/m2) of the 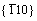 <111> slip system of BCC Mo from the present PAW-GGA method is in good agreement with the corresponding value of 1.3 J/m2 from the bond-order potential [33], while much smaller than the values of 1.8 and 1.68 J/m2 from the full-potential linear muffin-tin orbital method and ultrasoft pseudopotentials,respectively [30-32]. Such a difference of Eus values of BCC Mo should be due to the different theoretical methods, and further studies are welcome to clarify this issue.
<111> slip system of BCC Mo from the present PAW-GGA method is in good agreement with the corresponding value of 1.3 J/m2 from the bond-order potential [33], while much smaller than the values of 1.8 and 1.68 J/m2 from the full-potential linear muffin-tin orbital method and ultrasoft pseudopotentials,respectively [30-32]. Such a difference of Eus values of BCC Mo should be due to the different theoretical methods, and further studies are welcome to clarify this issue.
Secondly, the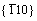 and
and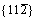 surfaces of both Mo47Re1 and Mo47Zr1 possess smaller unstable stacking fault energy (Eus) than those of pure Mo, whereas their D values are bigger. That is to say, the addition of Re and Zr in Mo is beneficial to the movement of the dislocations and therefore increases the ductility of Mo. This kind of solid solution softening of Re or Zr in Mo from the present calculation matches well with similar experimental observations of Re in Mo from experiments [10, 35] and theoretical calculations of Re [30, 34].
surfaces of both Mo47Re1 and Mo47Zr1 possess smaller unstable stacking fault energy (Eus) than those of pure Mo, whereas their D values are bigger. That is to say, the addition of Re and Zr in Mo is beneficial to the movement of the dislocations and therefore increases the ductility of Mo. This kind of solid solution softening of Re or Zr in Mo from the present calculation matches well with similar experimental observations of Re in Mo from experiments [10, 35] and theoretical calculations of Re [30, 34].
Moreover, for both 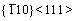 and
and 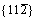 <111> slip systems, the Eus and D values of Mo47X1 (X=W, Ta, Ti, and Nb) are higher and lower than those of BCC Mo, respectively. This comparison implies that the addition of W, Ta, Ti, and Nb could impede the slip of the dislocation and thus decrease the ductility of Mo. Such a solid-solution hardening of Mo due to the alloying elements of W, Ta, Ti, and Nb is consistent with similar predictions of Ta and W [30, 34]. Note that the theoretical methods in Refs. [30] and [34] are full-potential linear muffin-tin orbital and ultra-soft pseudopotentials, respectively, which are quite different from the present PAW-GGA method, the above agreements regarding Re, Ta, and W in Mo [30, 34] provide further support of the relevance of the present results.
<111> slip systems, the Eus and D values of Mo47X1 (X=W, Ta, Ti, and Nb) are higher and lower than those of BCC Mo, respectively. This comparison implies that the addition of W, Ta, Ti, and Nb could impede the slip of the dislocation and thus decrease the ductility of Mo. Such a solid-solution hardening of Mo due to the alloying elements of W, Ta, Ti, and Nb is consistent with similar predictions of Ta and W [30, 34]. Note that the theoretical methods in Refs. [30] and [34] are full-potential linear muffin-tin orbital and ultra-soft pseudopotentials, respectively, which are quite different from the present PAW-GGA method, the above agreements regarding Re, Ta, and W in Mo [30, 34] provide further support of the relevance of the present results.
It is of importance to find out the fundamental mechanism of the above solid solution softening/ hardening. The electronic structures of both Mo and Mo47X1 (X=W, Ta, Ti, Nb, Re and Zr) are thus calculated and compared with each other. As a typical example, Figure 3 shows the density of states (DOS) of the Mo atom in the seventh layer of the surface of BCC Mo and Mo47Zr1. One can see clearly from Figure 3 that compared with BCC Mo, the DOS peaks of Mo in Mo47Zr1 experience right shifts and have slightly smaller binding energies. These features suggest that the chemical bonding of Mo in the seventh layer of Mo47Zr1 should become weaker due to the addition of Zr atom. Such a weaker chemical bonding would therefore bring about the decrease of the Eus and solid solution softening of Mo47Zr1 or Mo47Re1, and is also consistent with the positive heats of formation of Mo47Zr1 or Mo47Re1 as related before.
surface of BCC Mo and Mo47Zr1. One can see clearly from Figure 3 that compared with BCC Mo, the DOS peaks of Mo in Mo47Zr1 experience right shifts and have slightly smaller binding energies. These features suggest that the chemical bonding of Mo in the seventh layer of Mo47Zr1 should become weaker due to the addition of Zr atom. Such a weaker chemical bonding would therefore bring about the decrease of the Eus and solid solution softening of Mo47Zr1 or Mo47Re1, and is also consistent with the positive heats of formation of Mo47Zr1 or Mo47Re1 as related before.
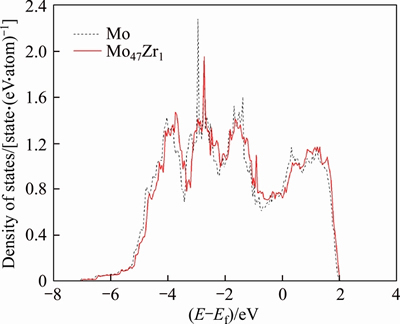
Figure 3 Density of states of Mo atom in seventh layer of surface of BCC Mo and Mo47Zr1
surface of BCC Mo and Mo47Zr1
In addition, Figure 4 displays another example, the charge density plots of Mo and Mo47W1 under a displacement of a/4<111> through the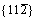 <111> slip system. It can be discerned clearly from this figure that the W-Mo bonding between the seventh and sixth layers of Mo47W1 seems much stronger than the original Mo-Mo bonding in pure Mo. This stronger chemical bonding of W-Mo would be originated from the attractive interaction between W and Mo with negative heat of formation as shown in Table 1. In other words, it is the stronger bonding due to the attractive Mo-X (X=W, Ti, Ta,and Nb) interaction which intrinsically impedes the slip of the dislocation, increases the stacking fault energy, decreases the ductility, and fundamentally causes the solid solution hardening of Mo47X1 (X=W, Ta, Ti, and Nb).
<111> slip system. It can be discerned clearly from this figure that the W-Mo bonding between the seventh and sixth layers of Mo47W1 seems much stronger than the original Mo-Mo bonding in pure Mo. This stronger chemical bonding of W-Mo would be originated from the attractive interaction between W and Mo with negative heat of formation as shown in Table 1. In other words, it is the stronger bonding due to the attractive Mo-X (X=W, Ti, Ta,and Nb) interaction which intrinsically impedes the slip of the dislocation, increases the stacking fault energy, decreases the ductility, and fundamentally causes the solid solution hardening of Mo47X1 (X=W, Ta, Ti, and Nb).
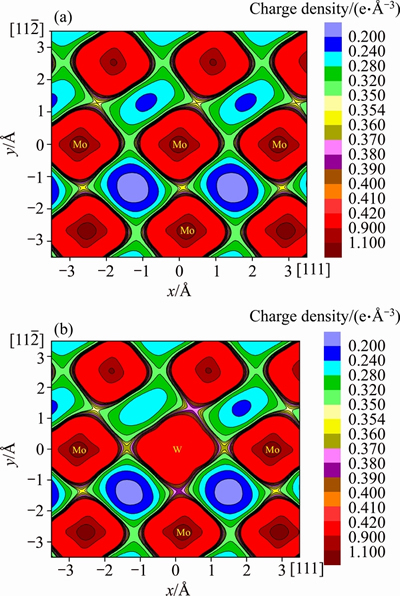
Figure 4 Charge density plots of Mo (a) and Mo47W1 (b) under a displacement of a/4<111> through  <111> slip system
<111> slip system
4 Conclusions
The present Ab initio calculation has been performed to find out the stacking fault energy and related ductility of Mo with the addition of several alloying elements such as W, Ta, Ti, Nb, Re, and Zr. It is found that the addition of Re and Zr in Mo is beneficial to the movement of the dislocations and therefore increases the ductility of Mo. On the other hand, the addition of W, Ta, Ti, and Nb could impede the slip of the dislocation and thus decrease the ductility of Mo. The heats of formation and electronic structure of these elements in Mo have been discussed and compared with each other, which could therefore bring about a deep understanding of the fundamental mechanism of the solid solution softening/hardening of the Mo-binary system.
Contributors
GONG Hao-ran provided the concept and edited the draft of manuscript. LIU Pan conducted the literature review and wrote the first draft of the manuscript. LIU Liu-cheng edited the draft of manuscript.
Conflict of interest
LIU Pan, LIU Liu-cheng and GONG Hao-ran declare that they have no conflict of interest.
References
[1] LIU G, ZHANG G J, JIANG F, DING X D, SUN Y J, SUN J, MA E. Nanostructured high-strength molybdenum alloys with unprecedented tensile ductility [J]. Nature Materials, 2013, 12(4): 344-350. DOI: 10.1038/NMAT3544.
[2] SCHNEIBEL J H, TORTORELLI P F, RITCHIE R O, KRUZIC J J. Optimization of Mo-Si-B intermetallic alloys [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2005, 36: 525-531. DOI: 10.1007/s11661-005-0166-4.
[3] YU J L, LI Z K, ZHENG X, ZHANG J J, LIU H, BAI R, WANG H. Tensile properties of multiphase Mo-Si-B refractory alloys at elevated temperatures [J]. Materials Science & Engineering A, 2012, 532(15): 392-395. DOI: 10.1016/j.msea.2011.11.001.
[4] ZHANG C, GAO M C, YANG Y, ZHANG F. Thermodynamic modeling and first-principles calculations of the Mo-O system [J]. Calphad, 2014, 45: 178-187. DOI: 10.1016/j.calphad.2013.12.006.
[5] DIMIDUK D M, PEREPEZKO J H. Mo-Si-B Alloys: Developing a revolutionary turbine-engine material [J]. MRS Bulletin, 2003, 28(9): 639-645. DOI: 10.1557/mrs2003. 191.
[6] TOTEMEIER T C, WRIGHT R N, SWANK W D. FeAl and Mo-Si-B intermetallic coatings prepared by thermal spraying [J]. Intermetallics, 2004, 12(12): 1335-1344. DOI: 10.1016/j.intermet.2004.04.034.
[7] SUPATARAWANICH V, JOHNSON D R, LIU C T. Effects of microstructure on the oxidation behavior of multiphase Mo-Si-B alloys [J]. Materials Science & Engineering A, 2003, 344(1, 2): 328-339. DOI: 10.1016/S0921-5093(02) 00446-X.
[8] BYUN T S, LI M, COCKERAM B V, SNEAD L L. Deformation and fracture properties in neutron irradiated pure Mo and Mo alloys [J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2008, 376(2): 240-246. DOI: 10.1016/j.jnucmat.2008.03.004.
[9] EL-GENK M S, TOURNIER J M. A review of refractory metal alloys and mechanically alloyed-oxide dispersion strengthened steels for space nuclear power systems [J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2005, 340(1): 93-112. DOI: 10.1016/j.jnucmat.2004.10.118.
[10] LEONHARDT T, CARLEN J C, BUCK M, BRINKMAN C R, REN W, STEVENS C O. Investigation of mechanical properties and microstructure of various molybdenum- rhenium alloys [C]// AIP Conference Proceedings. 1999: 685-690. DOI: 10.1063/1.57638.
[11] ALOUANI M, ALBERS R C, METHFESSEL M. Calculated elastic constants and structural properties of Mo and MoSi2 [J]. Physical Review B, 1991, 43(8): 6500-6509. DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevB.43.6500.
[12] PEREPEZKO J H. The hotter the engine, the better [J]. Science, 2009, 326: 1068-1069. DOI: 10.1126/science. 1179327.
[13] ZHAO J, LIU L C, GONG H R, GONG X. Cohesion strength and fracture toughness of Mo-TiC interfaces [J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2019, 382: 125158. DOI: 10.1016/ j.surfcoat.2019.125158.
[14] PARASCHIV A, MATACHE G, PUSCASU C, GRIGORESCU M. A correlation between fracture toughness and cohesion strength of molybdenum thermal sprayed coatings [J]. MATEC Web of Conferences, 2018, 145: 02007. DOI: 10.1051/matecconf/ 201814502007.
[15] CAI Zhen-yang, LIU S, XIAO L, FANG Z, LI W, ZHANG B. Oxidation behavior and microstructural evolution of a slurry sintered Si-Mo coating on Mo alloy at 1650°C [J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2017, 324(15): 182-189. DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2017.05.054.
[16] OUYANG G Y, RAY P K, THIMMAIAH S, KRAMER M J, AKINC M, RITT P, PEREPEZKO J H. Oxidation resistance of a Mo-W-Si-B alloy at 1000-1300 °C: The effect of a multicomponent Mo-Si-B coating [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2019, 470(15): 289-295. DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc. 2018.11.167.
[17] KUMAR N K, MITRA R, DAS J. Effect of moist environment on the oxidation behavior of Mo76-Si14B10Fe (x=0, 0.5, 1 at.%) ultrafine composites in the range of 700-800°C [J]. Corrosion Science, 2019, 155: 86-96. DOI: 10.1016/j.corsci.2019.04.032.
[18] CAI Z, WU Y, LIU H, TIAN G Y, PU R, PIAO S M, TANG X Y, LIU S N, ZHAO X J, XIAO L R. Formation and oxidation resistance of a new YSZ modified silicide coating on Mo-based alloy [J]. Materials & Design, 2018, 155: 463-474. DOI: 10.1016/j.matdes.2018.06.011.
[19] XI H H, HE P F, WANG H D, LIU M, CHEN S Y, XING S G, MA J Z, LV Z L. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Mo coating deposited by supersonic plasma spraying [J]. International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials, 2019, 86(7): 193-201. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrmhm. 2019.105095.
[20] DENG X K, ZHANG G J, WANG T, REN S, LI Z B, SONG P, SHI Y. Characterization and oxidation resistance of B-modified Mo3Si coating on Mo substrate [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2019, 807: 151693. DOI: 10.1016/ j.jallcom.2019.151693.
[21] SCHADE P, BARTHA L. Deformation and properties of PM molybdenum and tungsten [J]. International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials, 2002, 20(4): 259-260. DOI: 10.1016/S0263-4368(02)00071-9.
[22] WADSWORTH J, NIEH T G, STEPHENS J J. Recent advances in aerospace refractory metal alloys [J]. Int Mater Rev, 1988, 33: 131-150. DOI: 10.1179/09506608879032 4076.
[23] COCKERAM B V. The fracture toughness and toughening mechanism of commercially available unalloyed molybdenum and oxide dispersion strengthened molybdenum with an equiaxed, large grain structure [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2009, 40(12): 2843. DOI: 10.1007/s11661-009-9919-9.
[24] COCKERAM B V, SMITH R W, HASHIMOTO N, SNEAD L L. The swelling, microstructure, and hardening of wrought LCAC, TZM, and ODS molybdenum following neutron irradiation [J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2011, 418(1-3): 121-136. DOI: 10.1016/j.jnucmat.2011.05.055.
[25] MORITO F, SHIRAISHI K. Mechanical properties and neutron-irradiation effects in the welds of molybdenum and its alloys [J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 1991, 179: 592-595. DOI: 10.1016/0022-3115(91)901 57-3.
[26] SHANG S L, WANG W Y, ZHOU B C, WANG Y, DARLING K A, KECSKES L J, MATHAUDHU S N, LIU Z K. Generalized stacking fault energy, ideal strength and twinnability of dilute Mg-based alloys: A first-principles study of shear deformation [J]. Acta Materialia, 2014, 67: 168-180. DOI: 10.1016/j.actamat.2013.12.019.
[27] OGATA S, LI J, YIP S. Ideal pure shear strength of aluminum and coper. [J]. Science, 2002, 298: 807-811. DOI: 10.1126/ science.1076652.
[28] RICE J R. Dislocation nucleation from a crack tip: An analysis based on the Peierls concept [J]. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids, 1992, 40(2): 239-271. DOI: 10.1016/S0022-5096(05)80012-2.
[29] RIETH M, BOUTARD J L, DUDAREV S L. Review on the EFDA programme on tungsten materials technology and science [J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2011, 417(1-3): 463-467. DOI: 10.1016/j.jnucmat.2011.01.075.
[30] MEDVEDEVA N I, GORNOSTYREV Y N, FREEMAN A J. Solid solution softening in bcc Mo alloys: Effect of transition-metal additions on dislocation structure and mobility [J]. Physical Review B, 2015, 72: 134107. DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevB.72.134107.
[31] MEDVEDEVA N I, GORNOSTYREV Y N, FREEMAN A J. Electronic origin of solid solution softening in bcc molybdenum alloys [J].Physical Review Letters, 2005, 94(13): 136402. DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.94.136402.
[32] FREDERIKSEN S L, JACOBSEN K W. Density functional theory studies of screw dislocation core structures in bcc metals [J].Philosophical Magazine, 2010, 83: 365-375. DOI: 10.1080/0141861021000034568.
[33] MROVEC M, NGUYEN-MANH D, PETTIFOR D G, VITEK V. Bond-order potential for molybdenum: Application to dislocation behavior [J]. Physical Review B, 2004, 69(9): 094115. DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevB.69.094115.
[34] TRINKLE D R, WOODWARD C. The chemistry of deformation: How solutes soften pure metals [J]. Science, 2006, 310(5754): 1665-1667. DOI: 10.1126/science.1118 616.
[35] MUELLER A J, BIANCO R, BUCKMAN R W. Evaluation of oxide dispersion strengthened (ODS) molybdenum and molybdenum–rhenium alloys [J]. International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials, 2000, 18: 205-211. DOI: 10.1016/S0263-4368(00)00028-7.
[36] SUN L, GONG H R, GONG X. Magnetic ground state of face-centered-cubicstructureofiron [J]. Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter, 2020,32:165806. DOI: 10.1088/1361- 648x/ab6869.
[37] WU C Y, SUN L, LIANG C P, GONG H R, CHANG M L, CHEN D C. Electronic structures and thermoelectric properties of polytype phases of bismuth [J]. Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 2019, 134(5): 117-128. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpcs.2019.05.042.
[38] COCKERAM B V. The role of stress state on the fracture toughness and toughening mechanisms of wrought molybdenum and molybdenum alloys [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2010, 528(1): 288-308. DOI: 10.1016/j.msea. 2010.09.009.
[39] STURM D, HEILMAIER M, SCHNEIBEL J H. The influence of silicon on the strength and fracture toughness of molybdenum [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2007, 463: 107-114. DOI: 10.1016/j.msea.2006.07.153.
[40] NAGAE M, TAKEMOTO Y, YOSHIO T. Preparation of structurally controlled dilute molybdenum–titanium alloys through a novel multi-step internal nitriding technique and their mechanical properties [J]. Materials Science & Engineering A, 2005, 406(1, 2): 50-56. DOI: 10.1016/j.msea. 2005.06.039.
[41] JEHANNO P, KESTLER H. Assessment of a powder metallurgical processing route for refractory metal silicide alloys [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2005, 36: 515-523.
[42] SOUSA J. Lattice thermal conductivity of Ta-Nb and Nb-Mo solid solution alloys in normal and superconducting states [J]. Journal of Physics C: Solid State Physics, 1969, 2: 629-639.
[43] KRSTAJIC N V, JOVIC V D, GAJIC-KRSTAJIC L, JOVIC B M, ANTOZZI A L, MARTELLI G N. Electrodeposition of Ni-Mo alloy coatings and their characterization as cathodes for hydrogen evolution in sodium hydroxide solution [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2008, 33(14): 3676-3687. DOI: 10.1016/ j.ijhydene.2008.04.039.
[44] KRESSE G, HAFNER J. Ab initio molecular dynamics for liquid metals [J]. Phys Rev B Condens Matter, 1993, 48(1): 13115-13118. DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevB.47.558.
[45] KRESSE G, JOUBERT D. From ultrasoft pseudopotentials to the projector augmented-wave method [J]. Physical Review B, 1999, 59(3): 1758-1775. DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevB.59. 1758.
[46] JOHN P, PERDEW J A, CHEVARY S H. Vosko, Atoms, molecules, solids, and surfaces: Applications of the generalized gradient approximation for exchange and correlation [J]. Physical Review B, 1992, 48(1): 4978-4992. DOI: 10.1103/ PhysRevB.46.6671.
[47] WANG K, SHANG S L, WANG Y, LIU Z K, LIU F. Martensitic transition in Fe via Bain path at finite temperatures: A comprehensive first-principles study [J]. Acta Materialia, 2018, 147: 261-276. DOI: 10.1016/ j.actamat.2018.01.013.
[48] METHFESSEL M, PAXTON A T. High-precision sampling for Brillouin-zone integration in metals [J]. Phys Rev B Condens Matter, 1989, 40(6): 3616-3621. DOI: 10.1103/ PhysRevB.40.3616.
[49] BLOCHL P E. Projector augmented-wave method [J]. Phys Rev B-Condens Matter, 1994, 50: 17953-17979. DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevB.50.17953.
[50] SHI S, ZHU L, ZHANG H, SUN Z. Strength and ductility of niobium alloys with nonmetallic elements: A first-principles study [J]. Materials Letters, 2016, 189: 310-312. DOI: 10.1016/j.matlet.2016.11.011.
[51] GONG H R, KONG L T, LIU B X. Metastability of an immiscible Cu-Mo system calculated from first-principles and a derived n-body potential [J]. Physical Review B- Condensed Matter, 2004, 69(2): 1129-1133. DOI: 10.1103/ PhysRevB.69.024202.
[52] BOER F R D, BOOM R, MATTENS W C, MIEDEMA A R, NIESSEN A K. Cohesion in metals: Transition metal alloys [M]. Amsterdam: North Holland, 1988.
[53] VITOS L, RUBAN A V, SKRIVER H L, KOLLAR J. The surface energy of metals [J]. Surface Science, 1998, 411(1, 2): 186-202. DOI: 10.1016/S0039-6028(98)00363-X.
(Edited by FANG Jing-hua)
中文导读
固溶软化/硬化下钼的层错能与电子结构
摘要:用第一性原理计算方法研究了钼二元系固溶体软化/硬化的基本机理。结果表明,Mo-Ti、Mo-Ta、Mo-Nb和Mo-W之间的作用主要是相互吸引,具有负的生成热,而Mo-Re和Mo-Zr之间的作用主要是相互排斥,具有正的生成热。Re和Zr的加入会降低钼的堆垛层错能,提高合金的塑性,从而导致钼的固溶软化;而W、Ta、Ti、Nb等元素通过阻碍位错滑移和塑性下降,使Mo固溶硬化。电子结构表明,合金元素导致的弱/强化学键合从根本上诱导了钼的固溶体软化/硬化。本文对计算结果进行讨论,并与文献中已有的证据进行了分析比较,加深了对二元金属体系固溶体软化/硬化的基本认识。
关键词:层错能;电子结构;钼;固溶体软化/硬化;第一性原理计算方法
Foundation item: Project(51801129) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project supported by the State Key Laboratory of Powder Metallurgy, China
Received date: 2020-05-17; Accepted date: 2020-07-31
Corresponding author: GONG Hao-ran, PhD, Professor; Fax: +86-731-88710855; E-mail: gonghr@csu.edu.cn; ORCID: https://orcid. org/0000-0001-9767-6776

