DOI:10.19476/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2019.05.12
电磁场下液相线等温处理对镍基高温合金凝固组织及偏析的影响
高中堂1,胡 锐2,郭 卫1,张传伟1,尚可超1
(1. 西安科技大学 机械工程学院,西安 710054;
2. 西北工业大学 凝固技术国家重点实验室,西安 710072)
摘 要:借助光学显微镜(OM)、X射线衍射仪(XRD)、扫描电镜(SEM)以及电子探针X射线显微分析仪(EPMA)等方法,系统研究镍基高温合金电磁场下液相线等温处理后的凝固组织与传统铸造组织析出相以及微观偏析的差异、有无电磁场下不同温度(1420 ℃、1400 ℃和1390 ℃)等温处理后凝固组织。结果表明:电磁场下近液相线等温处理后得到的组织为细小等轴晶,晶粒圆整度较好。与传统铸造组织相比,细晶铸造组织中碳化物含量少于传统铸造组织的,且碳化物更为细小,分布更弥散。电磁场下近液相线等温处理得到组织偏析系数更接近于1,微观偏析较小。电磁场可通过均匀温度场和溶质场的方式使凝固组织细化。
关键词:镍基高温合金;电磁场;近液相线;微观偏析;等轴晶
文章编号:1004-0609(2019)-05-0990-08 中图分类号:TG146.4 文献标志码:A
高温合金是目前军用和民用航空发动机以及燃气轮机高温零部件不可替代的关键结构材料[1-2]。然而高温合金铸锭或者铸件通常存在晶粒粗大、枝晶组织发达、微观偏析大、显微缺陷多等问题。细晶铸造可消除铸锭或铸件微观缩孔,减小偏析,消除三晶区[3-4],同时可提高高温合金塑性和低周疲劳性能[5],改善高温合金铸锭的塑性加工能力,使其开坯成功率明显提高。因此,控制高温合金铸锭晶粒组织对高温合金的制备以及应用十分重要。
利用温度对熔体结构的影响来改善金属材料的组织和性能业已证明是一种行之有效的方法[6-8]。电磁场作用下的冶金相变以及凝固已成为我国基础研究领域重点研究方向,且电磁场作用在冶金生产中的应用已经过人们几十年的探索,越来越受到科学工作者的重视[9]。电磁场可以促进溶质元素的扩散和对流,改善温度场分布,活化异质,促进溶体的均质形核与异质形核[10]。许多学者对于熔体的热历史显著影响凝固组织进行了大量摸索,由于大部分合金在液相线附近存在一个过渡态,因此对液相线附近熔体处理成为研究重点[11-12],东北大学与墨尔本大学更提出了近液相线铸造法(Near liquidus casting)[13-14],即主要通过控制合金熔体的浇注温度、等温时间及凝固条件等因素获得理想的非枝晶组织。采用循环过热与熔融玻璃净化相结合的方法可使K4169高温合金Laves相的分布更均匀进而提高合金的抗拉强度和伸长率[15]。不同磁场强度对凝固组织形貌和偏析的影响研究表明,磁场下热电磁对流可对偏析产生影响[16]。KHALIFA等[17]研究发现超声场处理可以得到析出相弥散分布细化的组织。电磁场下液相线等温熔体处理技术,由于其设备简单且处理的熔体流动性和充型性好,成为细晶铸造发展的一个重要方向。电磁场下液相线等温处理技术不仅可细化组织,同时也对凝固后组织中偏析以及析出相有较大影响,而组织形貌、偏析以及析出相对铸件的性能又起到至关重要作用。
基于此,本文以Ni-Cr-W基高温合金为研究对象,采用电磁场下液相线等温处理方法对凝固组织进行分析,系统研究有无等温处理后凝固组织、析出相、微观偏析以及晶体学特征变化规律。同时,研究电磁场下液相线等温处理凝固组织、析出相及偏析行为,为进一步开发液相线铸造技术提供一定的理论依据,为关键铸造高温合金构件组织改性有指导意义,同时对高品质金属材料的生产具有重要的理论和工程意义。
1 实验
实验所用材料的化学成分(质量分数)为:Cr20.1%,W18.5%,Mo1.2%,Al0.5%,C0.1%,Ni余量。该合金是固溶强化与碳化物弥散强化型镍基高温合金,其固/液相线温度分别为1350 ℃和1400 ℃。将该高温合金原料放进感应熔炼炉内把熔体反复过热到1500 ℃,保温30 min后,开始缓慢降温,一组降温到液相线温度1400 ℃保温15 min,然后浇注到预热的模壳中随炉冷却。另一组在1500 ℃保温30 min后直接浇注到预热的模壳中,然后断开真空炉电源使其在模壳中随炉冷却,本实验所用模壳尺寸为d 120 mm×400 mm。采用以上方法分别得到液相线等温处理的铸锭和传统铸造铸锭。
研究电磁场对凝固组织影响的实验:从母合金30 kg铸锭中取35 g的原料为等温试样,放入尺寸为d 16 mm×50 mm的Al2O3坩埚中,通过坩埚外加石墨套的方式来屏蔽电磁场。用GP-35AB型频率为20 kHz,感应线圈尺寸为d 16 mm×35 mm,最大功率为35 kW的感应加热电源将熔体过热至1500 ℃并保温5 min,然后分别把熔体降温到1420 ℃、1400 ℃和1390 ℃,并在此温度保温10 min,带有石墨套的试样在等温处理后直接关掉加热电源让熔体在坩埚中空冷,无石墨套包裹的试样通过逐渐减小电源的方式使其缓慢冷却,以便保证两者冷却速率相同。为了研究电磁场对凝固组织的影响,其他外在条件均保证相同。其中等温处理后冷却速率是影响凝固组织至关重要的因素,在没有外在加热电源情况下外加石墨套的试样其冷却速率明显比不加石墨套的试样冷却速率慢,为了保证两者其冷却速率相同,本文中在等温处理后采用精度较高的红外测温仪对其冷却曲线进行表征(采用ZX-100B型双色红外测温仪,响应时间为100 ms,误差为 ±2 ℃,量程为1073~2273 ℃)。通过冷却曲线的表征结果来调节电源功率大小,最终对不加石墨套的试样通过逐渐调小加热电源方式,使其冷却速率与直接关掉电源的外加石墨套试样冷却速率相同。最终保证其坩埚外加石墨套和不加石墨套的冷却曲线基本相同,即两者的冷却条件相同,最终获得35g圆柱型铸锭的尺寸为d 16 mm×35 mm。
对采用不同工艺得到的组织以及析出相进行分析,从不同工艺方法得到的铸锭切取所需的试样,经机械打磨抛光后使用王水(V(HCl):V(HNO3)=3:1)腐蚀30 s。采用光学显微镜(OM)、JSM-6700型扫描电镜(SEM)、X射线衍射仪(XRD)及EPMA-1720型电子探针分别对试样进行金相、析出相及特定试样不同区域(点或面)的元素分布进行分析。同时对其凝固后的微观偏析进行讨论分析,分析电磁场对合金微观组织特性的影响。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 凝固组织及偏析行为分析
在铸锭冒口下方10 mm处切取尺寸为d 110 mm×10 mm的圆柱型试样进行宏观组织分析,Ni-Cr-W高温合金液相线等温处理和无液相线等温处理后的宏观组织如图1所示。对比图1(a)和(b)可得,经过液相线等温处理后的凝固组织为均匀细小的全等轴晶(见图1(b))。而不经过液相线等温处理,即熔体过热完直接凝固得到组织为传统的凝固组织,有典型三晶区存在,且枝晶组织较发达(见图1(a))。为了进一步分析液相线等温处理后的组织,分别沿图1(b)中细晶铸锭横截面方向进行取样,其取样示意图以及局部微观组织如图2所示。在横截面中沿半径方向依次选取4个试样(见图2(a))。与传统铸造组织相比,细晶铸锭由边缘到心部组织为近等轴晶组织,铸锭组织基本不存在微观缩松,晶界间隙小,晶粒度致密度高。从图2(b)可以得出,细晶铸锭中沿铸锭径方向由边缘到中心部位的组织为近球状晶粒,晶粒度级别R=2.34(平均晶粒尺寸为200 μm),铸锭底部全部为细小等轴晶,晶粒圆整度较好(见图2(b))。这是由于熔体过冷,熔体内存在大量的近程有序排列的准固态原子集团,这些原子集团在一定过冷度下,便迅速长大变成稳定的结晶核心[18],近液相线凝固时温度场分布比较均匀,有利于大量晶核的形成,形核率增大,晶粒来不及长大,所以形成细小的等轴晶组织。

图1 30 kg Ni-Cr-W高温合金铸锭横截面宏观组织
Fig. 1 Macrostructures of transverse section of 30 kg ingot in Ni-Cr-W superalloy

图2 铸锭横截面取样示意图及不同位置微观组织
Fig. 2 Schematic diagram of transverse section of 30 kg ingot(a) and microstructures of samples in different positions(b)
等温处理和无等温处理后分别得到细晶铸造组织与传统铸造组织,两者在晶粒尺寸、组织类型、组织的均匀性方面存在明显差异,这将对合金的力学性起到显著影响。除此之外,该镍基高温合金属于固溶强化以及碳化物强化型高温合金,该合金中碳化物析出类型及分布将对该高温合金后续塑性变形有较大影响,同时对细晶铸造组织和传统铸造组织中碳化物析出差异进行分析至关重要,因此研究析出相对该合金力学性能提高非常有意义。
图3所示为碳化物析出形貌对比分析结果。对比图3(a)和(b)可得,细晶铸造组织晶界处和晶内都存在碳化物的分布,细晶铸造组织碳化物少于传统铸造组织,且碳化物更为细小。细晶铸造组织晶内碳化物分布在一个比较集中的区域,该区域位于临近晶界的一个带状区域内,且碳化物形貌为六棱柱型以及圆棒型两种,晶界碳化物呈弥散分布。传统铸造组织晶内和晶界处均存在碳化物,且晶界处碳化物呈聚集分布,有大块状碳化物存在于晶界处。结果表明,细晶铸造组织碳化物分布更弥散,颗粒更细小,该分布特征对后续该合金的塑性变形以及锯齿流变都会产生影响。

图3 Ni基高温合金中碳化物析出相形貌
Fig. 3 Morphologies of precipitated carbide of Ni-based superalloy
碳化物分布结果表明,在凝固过程中该高温合金常常在枝晶间形成碳化物,这些碳化物在合金变形过程中主要起固溶强化作用,从而有利于提高合金的强度。析出相受凝固方式的显著影响,凝固路径首先是从液相凝固析出富Ni的γ初生相,由于是爆发式形核,所以凝固过程瞬间发生,因而凝固组织趋于均匀、细小、球化,所以γ初生相呈现典型的等轴晶形貌;随着凝固的进行,Cr、W、Mo向液相不断富集,凝固末端在晶界间形成了共晶组织以及碳化物析出相,其组织形貌如图4所示。第二相碳化物为M6C、碳化物与基体相互交织析出,EDS能谱分析表明,此种碳化物中Ni元素含量超过从基体中直接析出M6C的,元素在晶界间的偏析可以造成共晶碳化物析出,可以推断该碳化物为共晶M6C。Ni-Cr-W基高温合金中M6C型碳化物是在凝固过程中形成,属于初生碳化物,因此,需要进一步利用XRD对析出相进行分析,以确定合金中M6C的类型。由图4可以得出,M6C型碳化物为Ni3W3C型结构,骨架状的碳化物分布在晶界 处,碳化物之间相互联通。Ni3W3C为金刚石立方结构,分别由48个W原子、48个Ni原子及16个C原子组成单个晶胞[19]。晶胞的八面体中W原子位于单胞的 顶角及面心,8个八分之一亚点阵中4个体心也由W原子组成。

图4 Ni-Cr-W高温合金凝固组织及XRD谱
Fig. 4 Microstructure(a) and XRD pattern(b) of Ni-Cr-W superalloy
能谱分析基本确定基体相由γ基体以及分布在晶界间白亮的固溶体组成,平衡凝固条件在高温合金的实际生产中是不可能遇到的,因为溶质扩散系数只有温度扩散系数的10-3~10-5倍,当溶质还没有来得及扩散时,温度早已降低很多。Ni-Cr-W 系合金中固溶了大量的W、Mo、Cr 等原子,溶质在固相中的扩散系数小,所以合金在凝固过程中必然存在着元素偏析,元素的偏析行为与凝固行为密切相关。基于此,借助电子探针设备,采用5点法对其晶粒内的主要化学元素进行元素分布测试分析(见图5),以研究近液相线凝固得到等轴晶和传统凝固柱状晶区成分的偏析差异。
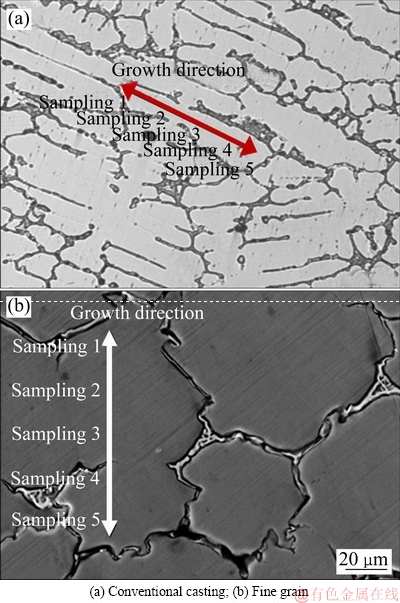
图5 Ni-Cr-W高温合金凝固组织元素分布测试
Fig. 5 Element distribution of Ni-Cr-W superalloy micro- structure
图6(a)~(d)所示分别为Ni、Cr、W、Mo沿着晶粒生长方向变化曲线图。由图6可以得出,无论在等轴晶还是柱状晶中4种元素偏析规律一致,Ni为负偏析元素,即晶内元素含量高于晶界元素含量,Cr、W、Mo为正偏析元素,晶内元素含量低于晶界元素含量。Ni、Cr、W、Mo 4种元素含量在柱状晶体内沿生长方向逐渐增加,而在等轴晶内元素基本无偏析存在,其元素含量在名义成分值上下小波动。偏析系数为枝晶间最高元素含量与枝晶干最低元素含量比值,而采用近液相线得到等轴晶不存在枝晶以及枝晶间之说,所以偏析系数简化为晶界与晶内元素比值。并以此计算了元素偏析系数,可知传统凝固组织的偏析系数KCr=2.03、KW=1.96、KMo=1.81,电磁场下近液相线凝固得到组织的偏析系数分别为KCr=1.8、KW=1.6、KMo=1.5。相对传统凝固组织,电磁场近液相线得到凝固组织的偏析系数更接近于1,合金元素的偏析比越偏离1,则表明凝固偏析越严重,得到等轴晶微观偏析较小。可见在电磁场作用下保持在液相线附近凝固后的组织均匀性好、偏析小。
2.2 电磁场的施加对凝固组织演化的影响
电磁场下液相线等温处理得到微观偏析小的等轴晶组织,为了更进一步单独分析电磁场对凝固组织的影响规律。采用Al2O3坩埚外包套石墨套方法屏蔽电磁场形成有无电磁场的环境的方法。由于石墨具有良好的导热性、导电性和不导磁性,因此它可以起到两方面作用,其一屏蔽电磁场作用,其二石墨套在感应电源作用下温度升高,进而通过辐射加热方式使Al2O3坩埚内的试样熔化。以此研究有无电磁场作用下等温处理对凝固组织演化的差异。无石墨套包裹坩埚下的实验为有电磁场的情况,外加石墨套坩埚下的实验为无电磁场的情况。

图6 Ni、Cr、W、Mo元素含量沿着晶粒生长方向变化曲线图
Fig. 6 Variation diagrams of content of Ni(a), Cr(b), W(c) and Mo(d) in direction of grain growth
图7所示为Ni-Cr-W高温合金有无电磁场下不同温度等温处理后的凝固组织。对比图7可得,无论是液相线以上和液相线以下等温处理,电磁场下熔体处理后其凝固组织明显细化,这说明电磁场处理对熔体的作用一直影响到合金的凝固过程。液相线以上等温处理凝固组织由一定取向的枝晶和柱状晶组成(见图7(a)和(d)),电磁场处理后枝晶组织或柱状晶组织(见图7(d))比无电磁场下等温处理凝固组织(见图7(a))细小。这是由于电磁场的强制对流作用,液相线以上熔体宏观温度场和微观溶质场更均匀,进而使枝晶组织细化。液相线等温处理后凝固组织为等轴晶或球形组织,有电磁场等温处理后凝固组织主要为球形组织(见图7(e)),无电磁场等温处理后凝固组织主要为等轴晶组织(见图7(b)),在液相线处等温处理后其凝固组织颗粒大小及形貌分布较均匀。这是由于在该温度下熔体中存在类固态中程原子团簇,这些原子团簇可以作为后续凝固过程中潜在形核质点,增加了结晶核心数量,电磁场的存在改善了溶质场与温度场的均匀性,所以电磁场作用下液相线等温处理后合金的凝固组织为分布均匀的细小球晶组织。液相线以下等温处理后凝固组织为蔷薇状组织和枝晶欠发达的等轴晶组织(见图7(c)和(f)),与无电磁场等温处理的情况相比,电磁场作用下等温处理后,组织枝晶臂熟化,没有发达枝晶臂存在。众所周知,液相线以下熔体在电磁场强制对流作用下,其熔体树枝晶球化[9-10];电磁场影响熔体温度场和流场,降低固/液界面前沿的浓度梯度,提高固/液界面的稳定性,使晶粒周围的溶质分布更均匀,即增大较小过冷度下球晶稳定化半径。所以液相线以下熔体在电磁场作用下凝固组织为无取向的非枝晶组织。

图7 Ni-Cr-W高温合金有无电磁场下不同温度等温处理后凝固组织
Fig. 7 Microstructures of Ni-Cr-W superalloy non-sheared in electromagnetic field((a), (b), (c)) and sheared in electromagnetic field((d), (e), (f)) by isothermal treatment at different temperatures
3 结论
1) 电磁场下近液相线等温处理可得到全等轴晶组织,与传统铸造组织相比,细晶铸造组织中碳化物含量少于传统铸造组织,且碳化物更为细小,分布更弥散,碳化物形貌多为圆棒状或六棱柱状碳化物。传统铸造组织晶内和晶界处存在较大尺寸的碳化物,且晶界处碳化物呈聚集分布,有大块状碳化物存在于晶界处,晶内存在大块状以及聚集式网状碳化物分布。
2) 电磁场下近液相线凝固得到组织的偏析系数分别为KCr=1.8、KW=1.6、KMo=1.5,传统凝固组织的偏析系数为KCr=2.03、KW=1.96、KMo=1.81。相对传统凝固组织,电磁场近液相线得到凝固组织的偏析系数更接近于1,凝固组织细小、微观偏析较小。
3) 电磁场可以使熔体溶质场和温度场分布更均匀,均匀的温度场和溶质场可以使熔体中中程原子团簇尺寸、形状及分布发生改变。电磁场可通过提高形核率以及减小晶粒生长速率共同作用而细化凝固组织。
REFERENCES
[1] LEE H J, KIM H, KIM D. Microstructure evolution of a Ni-Cr-W superalloy during long-term aging at high temperatures[J]. Materials Characterization, 2015, 106: 283-291.
[2] GAO Zhong-tang, GUO Wei, ZHANG Chuan-wei, TAN Jin-qiang. Development of fine-grained structure in Ni-Cr-W based superalloy and its effect on the mechanical properties [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2017, 682: 156-163.
[3] Chaudhuria A, Raghupathya Y, Srinivasanb D, Suwasa S. Microstructural evolution of cold-sprayed Inconel 625 superalloy coatings on low alloy steel substrate[J]. Acta Materialia, 2017, 129: 11-25.
[4] Zhang Xiao-rong, Guo Jing, Liu Hai-peng, Song Yue-peng, Xu Ling-feng, Liu Jing-tao. Influence of melt superheat treatment on corrosion resistance of Gd-based BMG in 3.5% NaCl solution[J]. Materials Design, 2016, 100: 217-222.
[5] Matuszewski K, Rettig R, Matysiak H, Peng Z, Povstugar I. Effect of ruthenium on the precipitation of topologically close packed phases in Ni-based superalloys of 3rd and 4th generation[J]. Acta Materialia, 2015, 95: 274-283.
[6] Campo K, Lopes E, Parrish C, Caram R. Rapid quenching of semisolid Ti-Cu alloys: Insights into globular microstructure formation and coarsening[J]. Acta Materialia, 2017, 139: 199-210.
[7] 戴贤创, 李振锋, 陈继光, 丁晗晖, 吴红宇, 刘 锋, 江 亮. 镍基高温合金端淬梯度冷却过程中γ′相演化规律[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2017, 27(2): 258-264.
DAI Xian-chuang, LI Zhen-feng, CHEN Ji-guang, DING Han-hui, WU Hong-yu, LIU Feng, JIANG Liang. Gamma prime phase evolution rule during end quench cooling in nickel-based superalloy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2017, 27(2): 258-264.
[8] 张志强, 乐启炽, 崔建忠. 电磁场施加方式对半连续铸造镁合金锭坯组织与性能的影响[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2009, 38(8): 1467-1471.
ZHANG Zhi-qiang, LE Qi-chi, CUI Jian-zhong. Effect of different electromagnetic field application ways on microstructures and mechanical properties of semi-continuous cast magnesium alloy billets[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2009, 38(8): 1467-1471.
[9] Fatoumata S, Yves D, Antoine A. Electromagnetic stirring and retention to improve segregation in silicon for photovoltaics[J]. Journal of Crystal Growth, 2012, 340: 41-46.
[10] 冀焕明, 罗天骄, 杨院生. AZ80镁合金低压脉冲磁场半连续铸造过程的数值模拟和实验研究[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2017, 27(3): 468-475.
JI Huan-ming, LUO Tian-jiao, YANG Yuan-sheng. Numerical simulation and experimental research of low voltage pulsed magnetic field DC casting of AZ80 magnesium alloy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2017, 27(3): 468-475.
[11] FATCHURROHMAN N, SULAIMAN S. Solidification analysis in permanent mould casting of aluminium alloy lm6 reinforced titanium carbide particulates metal matrix composites[J]. Materials Science Forum, 2017, 889: 148-151.
[12] Wang Jiang, Yue Shen, FAUTRELLE Y, PETER D, Ren Zhong-min. Refinement and growth enhancement of Al2Cu phase during magnetic field assisting directional solidification of hypereutectic Al-Cu alloy[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 5: 53-57.
[13] HAGHAYEGHI R, NASTAC L. On microstructural refinement of an AA7449 aluminium alloy through shearing above liquidus temperature[J]. Materials Letter, 2011, 65: 3230-3234.
[14] WANG Kai, LIU Chang-ming, ZHAI Yan-bo, ZOU Mao-hua. Microstructural characteristics of near-liquidus cast AZ91D alloy during semi-solid die casting[J]. Transaction of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2010, 20(1): 170-171.
[15] 张可人, 谢发勤, 胡 锐, 吴向清. 深过冷K4169高温合金凝固组织演变和力学性能的关系[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2016, 26(7): 1885-1991.
ZHANG Ke-ren, XIE Fa-qin, HU Rui, WU Xiang-qing. Relationship between microstructure and mechanical properties of undercooled K4169 superalloy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2016, 26(7): 1885-1991.
[16] 余建波, 侯 渊, 张超, 杨志彬, 王 江, 任忠鸣. 静磁场对新型Co-Al-W基高温合金定向凝固组织的影响[J]. 金属学报, 2017, 53(12): 1620-1626.
YU Jian-bo, HOU Yuan, ZHANG Chao, YANG Zhi-bin WANG Jiang, REN Zhong-ming. Effect of high magnetic field on the microstructure in directionally solidified Co-Al-W alloy[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2017, 53(12): 1620-1626.
[17] KHALIFA W, TSUNEKAWA Y. Production of grain-refined AC7A Al-Mg alloy via solidification in ultrasonic field[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2016, 26(4): 930-937.
[18] SRIRANGAM P, KRAMER M, SHANKAR S. Effect of strontium on liquid structure of Al-Si hypoeutectic alloys using high-energy X-ray diffraction[J]. Acta Materialia, 2011, 59: 503-513.
[19] BAI Guang-hai, LI Jin-shan, HU Rui, Tang Zeng-wu, Xue Xiang-yi, FU Heng-zhi. Effect of temperature on tensile behavior of Ni-Cr-W based superalloy[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2011, 528: 1974-1978.
Effect of electromagnetic field and isothermal treatment near liquidus on solidification microstructure and segregation of Ni-based superalloy
Gao Zhong-tang1, Hu Rui2, GUO Wei1, Zhang Chuan-wei1, SHANG Ke-chao1
(1. School of Mechanical Engineering, Xi’an University of Science and Technology, Xi’an 710054, China;
2. State Key Laboratory of Solidification Processing, Northwestern Polytechnical University, Xi’an 710072, China)
Abstract: The differences of macrostructure, microstructure, precipitate and microsegregation of solidification structure by isothermal treatment near the liquids in electromagnetic field and traditional casting of Ni-based superalloy were investigated by optical microscope (OM), X-ray diffractometer (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and electron probe X-ray microanalyzer (EPMA). The results show that the microstructure is small and uniform equiaxed grain by isothermal treatment near the liquidus and electromagnetic field. Compared with traditional microstructure, the content of carbide in fine grained casting is less than that of traditional casting, and the carbide is smaller and more dispersed than that of traditional casting. The segregation coefficient of the microstructure by isothermal treatment near the liquidus and electromagnetic field is closer to 1. The electromagnetic field can refine microstructure by making the temperature field and the solute field become more uniform.
Key words: Ni-based superalloy; electromagnetic field; near liquidus; microsegregation; equiaxed grain
Foundation item: Project(51804251) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project (2017M613165) supported by China Postdocteral Foundation; Project(SKLSP201727) supported by the State Key Laboratory of Solidification Processing, China; Project(2018YQ3-05) supported by the Excellent Youth Scholars Foundation of Xi’an University of Science and Technology, China
Received date: 2018-04-17; Accepted date: 2018-10-12
Corresponding author: Gao Zhong-tang; Tel: +86-29-85583159; E-mail: zhongtanggao@xust.edu.cn
(编辑 李艳红)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(51804251);中国博士后基金资助项目(2017M613165);凝固技术国家重点实验室开发课题(SKLSP201727);西安科技大学优秀青年科技基金资助项目(2018YQ3-05)
收稿日期:2018-04-17;修订日期:2018-10-12
通信作者:高中堂,副教授,博士;电话:029-85583159;E-mail:zhongtanggao@xust.edu.cn