


Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 22(2012) 2087-2091
Microstructure evolution in cooling process of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy and kinetics description
ZHANG Yu-hua1, YANG Shu-cai1, JI Hong-zhi2
1. Engineering Training Center, Harbin University of Science and Technology, Harbin 150080, China;
2. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150001, China
Received 7 November 2011; accepted 13 April 2012
Abstract: The microstructure evolution of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy was studied by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) during different rate cooling processes. Based on the DSC results, the kinetics analysis was carried out. The results indicate that the precipitation of η phase is the predominant transformation for the alloy during the cooling process after the solution treatment. And the η phase nucleates on dispersoids and at grain boundaries. The amount of η phase decreases with increasing cooling rate, and reduces by 75% as the cooling rate increases from 5 to 50 ℃/min. The kinetics of the precipitation of η phase can be described by the Kamamoto transformation model when the cooling rate is a constant.
Key words: Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy; microstructure evolution; precipitation; kinetics model
1 Introduction
Al-Zn-Mg-Cu (7xxx series) aluminum alloys have outstanding features of high specific strength, hardness, toughness and corrosion resistance, and present a wide application in aviation field [1,2]. The alloys can be strengthened through the solution and aging treatment. The major strengthening phase is GP zones and η’ (MgZn) phase in Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloys [3-5]. Because of the high quenching sensitivity of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloys, the cooling rate will directly influence the hardening effects obtained in the following aging treatments [6-8]. With a lower cooling rate, more second phase will precipitate in the cooling process. On one hand, the precipitation will decrease the supersaturation of the solid solution [9,10]; on the other hand, the precipitates will play a role on crystal nucleus, which will cause the inhomogeneous precipitation reducing the strengthening effects. So, it is important to study the effects of the cooling rate on the second phase precipitation and the kinetics characters of the precipitation process.
Kinetics analysis methods for microstructure evolution mainly include hardness, resistance and differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) method. KADI- HANIFI and TIRSATINE [11] obtained the volume fraction of GP zones in aging treatments of two aluminum alloys with different aging time by hardness method. HIROSAWA et al [12] analyzed the kinetics characters of the precipitation in the aging treatment of aluminum alloy by the resistance method, and achieved a series of kinetic parameters. JENA et al [13] studied the transformation mechanism of the precipitation and dissolution reaction in Al-Li-Cu alloy through the DSC method. They established the kinetics equation and calculated the kinetics parameters. DONOSO [14] and PAPAZIAN [15] analyzed the kinetics characters of phase transitions in the different aging technologies of the aluminum alloys by the DSC method. LUO et al [16] proposed a new analysis method to analyze the phase transition process of the Al-Li-Cu-Mg alloy by using the DSC method with single heating rate, from which they obtained a series of kinetics parameters of precipitation and dissolution reaction.
Although studies on the microstructure evolution of the Al-Zn-Mg-Cu aluminum alloys have been widely developed, there are few reports about the kinetics analysis of precipitation during the cooling process. In the present study, the experimental method of TEM was combined with DSC to determine the solid phase transition during the cooling process of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy. A kinetics model was built for the precipitation of η phase.
2 Experimental
The material used was 7A09 aluminum alloy in T6 tempered state. The chemical composition of material is shown in Table 1. All the samples used for the experiments came from the same diameter circle in a 7A09 alloy bar. The DSC thermal analysis was made on a NETZSCH DSC 200F3 instrument. Samples were polished to disks of 3 mm in diameter and 0.5 mm in thickness. They were heated up to 470 ℃ with the heating rate of 10 ℃/min, kept at 470 ℃ for solution treatment and then quenched to room temperature at the cooling rates of 5, 10, 50 ℃/min, respectively. Samples for TEM underwent the same thermal cycle used in DSC experiments. Then they were polished mechanically to 100 μm and electropolished in a solution of 75% methanol and 25% nitric acid at -20 ℃. The TEM samples were observed on a Philips CM12 transmission electron microscope.
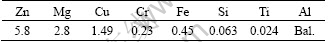
Table 1 Chemical composition of investigated 7A09 alloy (mass fraction, %)
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Microstructure evolution
The DSC result shown in Fig. 1 is obtained in the cooling process of the solid solution alloy with the cooling rate of 5 ℃/min. This curve has an exothermic peak (396 ℃) which arose from the precipitation of second phase.
Figure 2 shows TEM microstructure and diffraction pattern of 7A09 alloy cooled at the cooling rate of 5 ℃/min. Precipitates can be found in the grain interiors and at the grain boundaries, as shown in Fig. 2(a). In the grain interiors, precipitates are all attached to Cr-containing dispersoids. The precipitates may nucleate on the dispersoids [17].
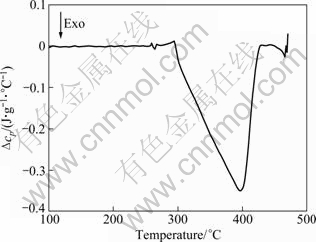
Fig. 1 DSC thermogram of solution annealed 7A09 alloy during cooling process (cooling rate 5 ℃/min)
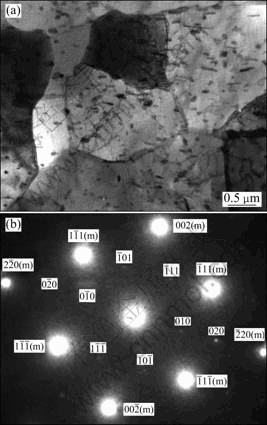
Fig. 2 Microstructure and diffraction pattern of 7A09 alloy cooled at 5 ℃/min: (a) TEM images; (b) Diffraction pattern for [110]Al zone axis (Letter “m” refers to matrix)
The precipitates are easy to nucleate at the gain boundaries because the high dislocation density is suitable for the diffusion of the solute elements at the grain boundaries. The precipitates belong to η phase and the orientation relationship (in the selected area) between precipitates and matrix can be confirmed according to selected area electron diffraction (SAED) pattern (Fig.2 (b)): η2—{00.1}η∥{111}Al, {10.0}η∥{011}Al.
3.2 Kinetics analysis
Figure 3(a) shows the DSC thermograms of 7A09 alloy cooled at different cooling rates. The heat signals have been normalized by the cooling rate so that the different curves can be directly compared. The area under the exothermic peak is proportional to the volume fraction formed and the peak is only related to the precipitation of η phase. Therefore, the volume fraction ratio can be determined by comparing the area of the exothermic peak. The transformation enthalpy equals the area of the exothermic peak. The relationship curve between transformation enthalpy and cooling rates is shown in Fig. 3(b). It indicates that the volume fraction of the η phase decreases with increasing the cooling rate. When the cooling rate changes from 5 ℃/min to 50 ℃/min, the volume fraction decreases by 75%. Moreover, the temperature range in which the precipitation occurs is independent of the cooling rate, the main precipitation process arises between 300 and 430 ℃ and the peak arises between 378 and 396 ℃. The temperature corresponding to this peak is observed to depend very slightly on the cooling rate. There are many Cr-containing dispersoids in 7A09 alloy, which are stable at the solution temperature and suitable for η phase precipitating in the cooling process to nucleate. The immediate saturation on the nucleation site leads to a constant temperature for the start of precipitation. Moreover, a definite stop of precipitation is related to the slowing down of solute diffusion[17]. TEM microstructure of 7A09 alloy cooled at different cooling rates is shown in Fig. 4. It also can be found that the volume fraction of the η phase will decrease if the cooling rate increases.
The precipitation of η phase belongs to the displacive transition because there is certain orientation relationship between precipitates and matrix and the transition process contains several typical stages, such as solute diffusion, nucleation and growth. The displacive transition can be divided into two categories. One is the non-diffusional transformation, like the martensitic transformation; another is the diffusional transformation, like the bainite transformation. As for a constant rate non-isothermal transformation with nucleation and growth stages, the kinetics model is mainly based on Avrami equation. Johnson-Mehl-Avrami model can be applied to characterizing a constant heating rate of non-isothermal transformation. Koistinen-Marburger and Kamamoto model can be utilized to characterize martensitic and bainite transformations respectively in a constant rate cooling process [18]. The expression of Kamamoto model is given in Eq. (1):
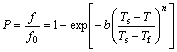 (1)
(1)
where P is the ratio between the volume fraction (f) formed at certain temperature and the volume fraction formed (f0) at final temperature of transformation; T is the transformation temperature; Ts and Tf are start and final temperatures of transformation, respectively; b and n are fit parameters.
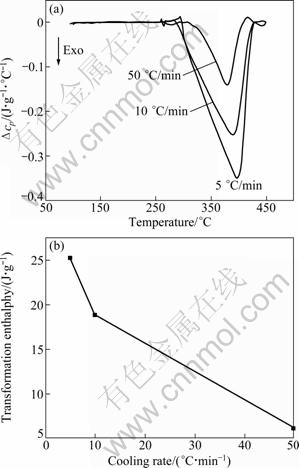
Fig. 3 DSC thermograms of 7A09 alloy cooled at different cooling rates (a) and relationship between transformation enthalpy and cooling rates (b)
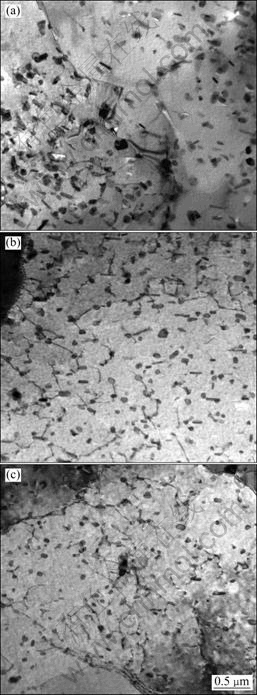
Fig. 4 TEM images showing microstructures of 7A09 alloy cooled at 5 ℃/min (a), 10 ℃/min (b), and 50 ℃/min (c)
Although Kamamoto model was proposed for describing the bainite transformation, it has been utilized to characterize the perlitic transformation [19] and the displacive transition occurring in the cooling process of uranium [20]. As for 7A09 alloy, the precipitation of η phase is also a diffusional transformation. Further, relationship between fraction of precipitation and temperature (Fig. 5) is similar to that of the bainite transformation in kinetics character. Therefore, Kamamoto model can be utilized to fit the temperature- dependent process of the η phase precipitation. It is noteworthy that the model provides a better numerical characterization of certain complex nucleation and growth kinetics but the fit parameters, b and n, are difficult to interpret in terms of a rigorous physical model.
RAI et al [20] introduced the parameter of the cooling rate into Kamamoto model in their research, and Eq. (1) was changed into Eq. (2):
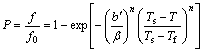 (2)
(2)
where b′ is a fit parameter, and β is the cooling rate. A simple two-parameter Kamamoto model can be obtained
by setting (b'/β)n=b in Eq. (2). According to experimental data, the fitting results of parameters using Eq. (2) are tabulated in Table 2 and the fitting curve is shown in Fig. 5.
The strength of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloys can be improved greatly through the solution and aging treatment. The strength of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloys will increase with increasing strengthening phase obviously. The amount of strengthening phase is directly decided by the supersaturation of solid solution, which is sensitive to the cooling rate. Usually, more strengthening phase can be precipitated from the solid solution with higher supersaturation. Therefore, it is quite beneficial for the strength increase of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloys to get higher rate in the cooling process of solution before the aging treatment.
Table 2 Kinetics parameters obtained by fitting observed η phase precipitation data to Eq. (2)
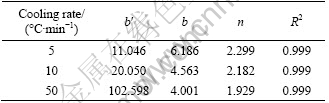
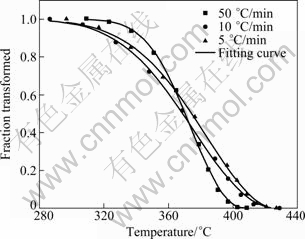
Fig. 5 Relationship between fraction of precipitation and temperature for 7A09 alloy cooled at different cooling rates
4 Conclusions
1) The precipitation of η phase is the predominant reaction during the cooling process of 7A09 alloy. Precipitates nucleate at the grain boundaries and on the Cr-containing dispersoids in the grain interiors. The orientation relationship between precipitates and matrix can be confirmed according to the SEAD pattern: η2—{00.1}η∥{111}Al, {10.0}η∥{011}Al.
2) The volume fraction of the η phase decreases with increasing the cooling rate. When the cooling rate changes from 5 ℃/min to 50 ℃/min, the volume fraction decreases by 75%. Moreover, the main temperature range of the η phase precipitation is from 300 to 430 ℃, which depends on the cooling rate slightly.
3) In the constant rate cooling process, the precipitation of the η phase can be described by Kamamoto model. Kinetics parameters in the model can be obtained by fitting the observed precipitation data.
References
[1] FRIDLYANDER N, DOBROMYSLOV A V, TKACHENKO E A, SENATOROVA O G. Advanced high-strength aluminum-base materials [J]. Metal Science and Heat Treatment, 2005, 47(7-8): 269-275.
[2] FAN Xi-gang. Study on the microstructures and mechanical properties and the fracture behavior of the Al-Zn-Mg-Cu-Zr alloys [D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2007. (in Chinese)
[3] ADLER P N, DEIASI R. Calorimetric studies of 7000 series aluminum alloys: II. Comparison of 7075, 7050 and RX720 alloys [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 1977, 8(7): 1185-1190.
[4] LI Zhi-hui, XIONG Bai-qing, ZHANG Yong-an, ZHU Bao-hong, WANG Feng, LIU Hong-wei. Investigation of microstructural evolution and mechanical properties during two-step ageing treatment at 115 and 160 ℃ in an Al–Zn–Mg–Cu alloy pre-stretched thick plate [J]. Materials Characterization, 2008, 59(3): 278-282.
[5] LI Zhi-hui, XIONG Bai-qing, ZHANG Yong-an, ZHU Bao-hong, WANG Feng, LIU Hong-wei. Microstructural evolution of aluminum alloy 7B04 thick plate by various thermal treatments [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2008, 18(1): 40-45.
[6] DESCHAMPS A, BR?CHET C. Nature and distribution of quench-induced precipitation in an Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy [J]. Scripta Materialia, 1998, 39(11): 1517-1522.
[7] ZHANG Xin-ming, LIU Sheng-dan, YOU Jiang-hai, ZHANG Chong, ZHANG Xiao-yan. Influence of aging on quench sensitivity effect of 7055 aluminum alloy [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2007, 17(2): 260-264. (in Chinese)
[8] ARCHAMBAULT P, GODARD D. High temperature precipitation kinetics and TTT curve of a 7xxx alloy by in-situ electrical resistivity measurements and differential calorimetry [J]. Scripta Materialia, 2000, 42(7): 675-680.
[9] EVANCHO J W, STALEY J T. Kinetics of precipitation in aluminum alloys during continuous cooling [J]. Metallurgical Transactions A, 1974, 5: 43-47.
[10] DUMONT D, DESCHAMPS A, BR?CHET C, SIGLI C, EHRSTR?M J C. Characterization of precipitation microstructures in aluminium alloys 7040 and 7050 and their relationship to mechanical behavior [J]. Materials Science and Technology, 2004, 20(5): 567-576.
[11] KADI-HANIFI M, TIRSATINE K. Influence of Cd and Sn on the kinetics of the GP zones formation in Al-Zn-Mg [J]. Materials Science Forum, 2000, 331-337: 1067-1070.
[12] HIROSAWA S, SATO T, KAMIO A. Effects of Mg addition on the kinetics of low-temperature precipitation in Al-Li-Cu-Ag-Zr alloys [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 1998, 242(1-2): 195-201.
[13] JENA A K, GUPTA A K, CHATURVEDI M C. A differential scanning calorimetric investigation of precipitation kinetics in the Al-1.53 wt% Cu-0.79 wt% Mg alloy [J]. Acta Metallurgica, 1989, 37(3): 885-895.
[14] DONOSO E. Calorimetric study of the dissolution of Guinier-Preston zones and η’ phase in Al-4.5at.% Zn-1.75at.%Mg [J]. Materials Science and Engineering, 1985, 74(1): 39-46.
[15] PAPAZIAN J M. Differential scanning calorimetry evaluation of retrogressed and re-aged microstructures in aluminum alloy 7075 [J]. Materials Science and Engineering, 1986, 79(1): 97-104.
[16] LUO A, LLOYD D J, GUPTA A, YOUDELIS W V. Precipitation and dissolution kinetics in Al-Li-Cu-Mg alloy 8090 [J]. Acta Metallurgica et Materialia, 1993, 41(3): 769-776.
[17] DECHAMPS A, TEXIER G, RINGEVAL S, DELFAUT-DURUT L. Influence of cooling rate on the precipitation microstructure in a medium strength Al-Zn-Mg alloy [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2009, 501: 133-139.
[18] KAMAMOTO S, NISHIMORI T, KINOSHITA S. Analysis of residual stress and distortion resulting from quenching in large low-alloy steel shafts [J]. Materials Science and Technology, 1985, 1(10): 798-804.
[19] BOYADJIEV I, THOMSON P F, LAM Y C. Computation of the diffusional transformation of continuously cooled austenite for predicting the coefficient of thermal expansion in the numerical analysis of thermal stress [J]. ISIJ international, 1996, 36(11): 1413–1419.
[20] RAI K, RAJU S, JEYAGANESH B, MOHANDAS E, SUDHA R, GANESAN V. Effect of heating and cooling rate on the kinetics of allotropic phase changes in uranium: A differential scanning calorimetry study [J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2009, 383: 215-225.
Al-Zn-Mg-Cu合金冷却过程中组织演变及其动力学分析
张玉华1,杨树财1,纪宏志2
1. 哈尔滨理工大学 工程训练中心,哈尔滨 150080;
2. 哈尔滨工业大学 材料科学与工程学院,哈尔滨 150001
摘 要:采用透射电镜(TEM)和差示扫描量热法(DSC)相结合的分析方法,研究不同冷却速率条件下固溶态Al-Zn-Mg-Cu合金冷却过程中的组织演变,并根据DSC结果对该过程进行动力学分析。结果表明:在冷却过程中,合金的主要相转变是η 相(MgZn2)的析出,且η 相在晶内弥散体处以及晶界上形核析出。η 相的析出量随着冷却速率的增大而明显减少, 当冷却速率从5 ℃/min增大到50 ℃/min时,η 相的析出量减少了约75%。在冷却速率恒定的情况下,可以根据DSC曲线,使用Kamamoto相变模型来描述η 相的析出过程。
关键词:Al-Zn-Mg-Cu合金;组织演变;析出;动力学模型
(Edited by YANG Hua)
Foundation item: Project (50975053) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Corresponding author: ZHANG Yu-hua; Tel: +86-451-86393962; E-mail: zhangyuhua1981@sina.com
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(11)61432-5