大变形量Al-Zn-Mg-Cu合金的热轧板再结晶行为
林亮华,刘志义,韩向楠,陈旭,李尧
(中南大学 材料科学与工程学院,湖南 长沙,410083)
摘要:采用光学显微镜、维氏硬度计和透射电子显微镜研究Al-Zn-Mg-Cu合金大变形热轧板退火过程中的组织演变和力学性能变化,探讨再结晶形核和长大机制,并通过分析位错和储存能变化规律研究动态回复对再结晶的影响。研究结果表明:Al-Zn-Mg-Cu合金在390 ℃热轧变形时,其主要软化机理为动态回复;当变形至90%时,其组织由直径为0.3~0.6 μm的位错胞和亚晶组成,这种回复时发生的多边形化促进了随后退火过程中静态再结晶的进行。根据硬度曲线和组织分析确定总变形量为90%的Al-Zn-Mg-Cu热轧板再结晶起始温度为400 ℃,完全再结晶温度为420 ℃;超过450 ℃时再结晶晶粒明显长大,再结晶形核机制以亚晶合并形核为主。
关键词:Al-Zn-Mg-Cu合金;动态回复;再结晶;热轧;退火
中图分类号:TG146.2 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2011)10-2990-06
Recrystallization behavior of hot-rolled Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy after great deformation
LIN Liang-hua, LIU Zhi-yi, HAN Xiang-nan, CHEN Xu, LI Yao
(School of Materials Science and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: Optical microscope, Vickers hardness tester and transmitted electron microscope were employed to study microstructure evolution and mechanical properties of hot-rolled Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy during annealing. Mechanism for nucleation and its growth of recrystalized grains were discussed. The influence of dynamic recovery on recrystallization behavior was also investigated by analyzing the change rule of the dislocation and stored energy. The results show that the softening mechanism deformed at 390 ℃ is dynamic recorery. When the deformation reaches 90%, the microstructure is comprised of dislocation cell structures and subgrains with diameter of 0.3-0.6 μm. Polygonization occurs during dynamic recovery accelerates recrystallization during subsequent annealing. Hardness measurements and microstructure evolution suggest that the start recrystallized temperature and full recrystallized temperature are 400 ℃ and 420 ℃, respectively. Recrystallized grain grows apparently when the temperature is higher than 450 ℃. The dominant mechanism for recrystallized nucleation is boundary merging mechanism.
Key words: Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy; dynamic recovery; recrystallization; hot roll; annealing
变形超过临界变形度的金属加热时,在变形基体中发生新的无畸变晶粒形成和长大过程称为一次再结晶,在铝合金加工过程中其重要意义在于使材料的塑性变形能力在加工硬化后得到恢复[1-2]。一次再结晶的驱动力来源于变形材料中主要以位错形式保留的储存能,由于冷变形和热变形后的位错组态和组织形貌不同,因而对随后再结晶的影响不同。Vandermeer 等[3]进行了商业纯铝(AA1050)冷、热变形后的再结晶对比研究,发现二者存在较大差异,如在同等条件下热变形后完全再结晶的晶粒尺寸为冷变形的3~4倍,并且前者出现第二相粒子诱发形核(PSN)的概率要明显低于后者。Talamantes-Silva等[4]采用有限元方法建立Al-Mg合金热轧板在退火时的再结晶行为和动力学方程模型,得到较满意的结果,但该模型并不适用于冷变形之后再结晶研究。Liu等[5]通过研究两者对AA5052合金再结晶织构的影响,发现2种情况下立方织构和高斯织构的比例各异。高强Al-Zn-Mg-Cu系合金作为航空航天领域重要的结构材料,再结晶将直接影响到其最终产品的使用性能[6],但目前有关Al-Zn-Mg-Cu合金再结晶的研究主要集中在冷变形方面,而对于热变形后再结晶尤其是对组织演变和再结晶机理的研究较少。为此,本文作者对Al-Zn-Mg-Cu合金大变形热轧板退火过程组织演变、力学性能的变化以及动态回复对它们的影响进行研究,并探讨再结晶形核和长大机制,以便为热轧变形后的中间退火和后续冷轧工艺提供理论参考。
1 实验材料及方法
实验材料为某铝厂提供的Al-Zn-Cu-Mg合金铸锭,其化学成分(质量分数)为:6.11% Zn,2.76% Mg,1.91% Cu,0.04% Ti,0.25% Cr,Al余量。铸锭经465 ℃均匀化24 h,铣面后在390 ℃下保温1 h(本实验轧制温度的选择以热模拟实验为依据),在270T热轧机下进行热轧,变形前后的厚度分别为25 mm和3 mm,道次变行量为10%~20%,总变形量为90%。热轧后在350~450 ℃下退火1 h,使用HV-5型小负荷维氏硬度计迅速测量退火后硬度,在直角坐标系中作硬 度-温度曲线,采用POLYVER-MET型金相显微镜观察退火后的显微组织变化,将硬度和组织分析结合确定再结晶温度,在TecanaiG220型透射电镜下观察其显微组织,并研究不同温度退火试样的再结晶形核和长大机制。
2 结果与分析
2.1 热轧组织分析
图1所示为合金在390 ℃下经90%热轧变形后的透射电子显微照片。从图1(a)可以看出:变形后大量位错首先在晶界和第二相粒子附近塞积并缠结形成位错胞,小部分位错胞通过多边形化转化成界面平直的亚晶,在亚晶内位错密度较低,表现为典型的动态回复组织。图1(b)所示为局部位错胞明场像,位错胞呈等轴状,直径在0.3~0.6 μm之间,胞壁为具有厚度差别的高密度位错缠结,胞壁的厚度反映了回复的程度,回复程度越高,其胞壁越薄。因为高温变形时胞内位错处于激活的可运动状态,在热变形过程中胞内位错易滑移至胞壁,并与胞壁上异号位错对消,使胞壁位错密度下降、胞壁厚度减小而逐渐形成清晰明锐的亚晶界。从图1还可以看出:亚晶界一旦形成,便成为继续变形时新的位错塞积障碍。
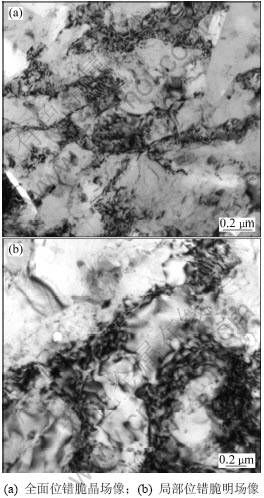
图1 390 ℃热轧变形的显微组织
Fig.1 Microstructures of hot deformation at 390 ℃
2.2 退火过程中性能变化
合金热轧后在300~450 ℃下进行1 h退火,测量硬度变化,如图2所示(图中,其横坐标为0表示未退火的热轧板硬度)。从图2可以看出,于300 ℃退火时,板材的硬度已经大幅度下降;在300~350 ℃退火时,硬度下降缓慢;随退火温度的升高,合金进一步软化且软化速率较高,硬度曲线上形成一个下降台阶,至400 ℃硬度降至最低;当退火温度高于400 ℃时,硬度几乎保持不变。这种硬度上的变化间接反映了组织的演变:于300 ℃以下位错通过滑移和攀移大部分畸变能被释放,在300~350 ℃之间释放较少的储存能组织也只发生回复过程;在380~400 ℃则是合金再结晶阶段。回复后的能量主要在这个阶段释放,高能变形组织全部被无畸变组织代替,相应的合金硬度达到最低。
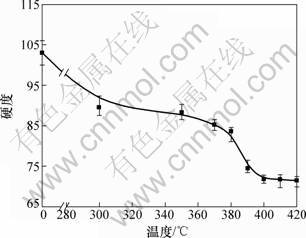
图2 合金硬度随退火温度的变化
Fig.2 Effect of annealing temperature on hardness
材料在回复阶段减少的储存能由位错运动引起,主要的2种机制即位错抵消和位错的重排形成低能位错组态[7]。这2种机制都是通过位错滑移、攀移和交滑移完成,而回复时释放的能量则是与合金的层错能(γ(SEE))有关,不同层错能的合金回复曲线存在较大差别[8],低层错的金属如铜(γ(SEE)=20 mJ·m-2)、银(γ(SEE)=22 mJ·m-2)的硬度在再结晶开始之前几乎无明显变化,而在图2中铝合金在再结晶之前硬度下降十分明显。这是因为铝合金层错能高,回复方式显然与前者不同,在相同温度下位错更易于进行充分的交滑移和位错攀移且伴随有大量变形能的释放,使硬度得到强烈恢复。在通常情况下,位错密度ED和储存能ρ满足ED=cρGb2(其中c为常数,b为柏氏量,G为剪切模量),因此,两者的变化规律必定是一致的。温度的进一步升高将引起热激活的再结晶发生,表现为图中380~400 ℃之间能量又一次下降。
2.3 再结晶组织演变
图3所示为合金在不同温度下退火时的再结晶组织演变图。可见:390 ℃时退火组织(图3(a))由细长晶粒构成,表明该温度下只发生回复过程;于400 ℃时在晶界处开始出现细小新晶粒(图3(b)),但原始长条晶粒仍可见,大晶粒内部保留未再结晶组织;温度升高进一步促进再结晶,图3(c)所示为420 ℃退火后完全再结晶形貌,由无畸变的小尺寸等轴晶晶粒组成,此时,再结晶和冷轧板再结晶组织大致相同[9],与于420 ℃退火时的形貌相比,于450 ℃退火时组织中原细小的晶粒长大,组织变化与图2所示的相吻合。
图4(a)和图4(b)所示分别是于390 ℃和400 ℃退火后的透射组织照片。由图4(a)可见:透射组织由粒径为几百纳米的亚晶构成,说明在390 ℃时组织回复较完善,在此温度下,退火主要发生刃位错的交滑移和螺位错的攀移,这些运动的结果就是异号位错相互抵消和重排导致晶内位错密度明显下降和亚晶组织的逐渐形成,在金相显微镜下表现为未再结晶的变形组织(如图3(a)所示)。图4(a)中箭头所指位置为退火过程中同号刃型位错沿原滑移面水平排列形成的位错 墙[10],这些位错墙以小角晶界分割原始晶粒为亚晶。为了降低界面能在随后的退火中将转变成亚晶界(称为位错阵列(Arrays of dislocation))[11-12],其运动方式为2组相近的位错阵列相互合并形成单一位错列。在位错列的运动中,若遇到第二相粒子易分解成几个位错片断或自由位错,最后被晶界或亚晶界吸收抵消[12],则小角晶界便合并成大角度的晶界。随着退火温度的升高,原子热振动增强、空位浓度提高,使得位错攀移变得更容易实现,在400 ℃时亚晶有所长大,亚晶界清晰平直位错密度很小(见图4(b)),其组织基本被无畸变的等轴晶取代,事实上已经发生静态再结晶。

图3 不同温度退火后的金相组织
Fig.3 Optical microstructures of hot roll sheet following annealing at different temperatures
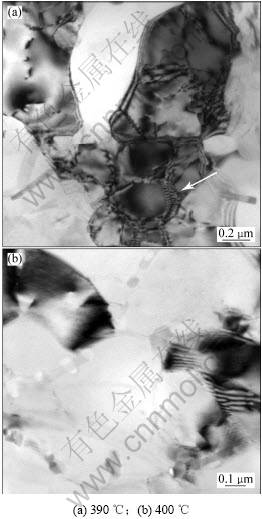
图4 不同温度退火后Al-Zn-Mg-Cu合金的透射组织
Fig.4 TEM micrographs of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy following annealing at different temperatures
2.4 再结晶机制
在一般情况下,满足成为再结晶形核核心的条件是具备与周边晶粒的取向差达到15°以上或晶核尺寸为1~3 μm[7, 13]。这是因为作为可长大的核心,必须具备界面迁移率的条件,再结晶前的亚晶以小角晶界为主[14],其界面迁移速率vb可表示为[7]:
 (1)
(1)
其中:c1为常数;R为晶界弯曲曲率;M为晶界迁移系数;θ为位向差角。从式(1)可知:晶界迁移率随θ的增大而增大,所以,作为形核核心对取向角的要求是必需的。图5所示为于400 ℃退火时Al-Zn-Mg-Cu合金热轧板的透射照片。从图5可看出Al-Zn-Mg-Cu合金热变形后再结晶的形核机制:几个位向差角较小的亚晶合并成1个大角亚晶(图正中深色区域),合成后亚晶尺直径为2~5 μm,满足前述的形核条件,图中数字1和数字2分别代表2组正在消失的取向较小亚晶界。相邻亚晶边界上的位错网络通过解离、拆散转移到其他亚晶界上,导致亚晶界消失或与亚晶合并形成再结晶晶核。从图5还可以看出:再结晶核心是5~8个亚晶共同作用聚合到一块,这种亚晶合并的驱动力显然来自于减小的亚晶界面能。这种形核也需要孕育期,亚晶界的解离和位错列的重排需要破坏亚晶界的界面平衡和位错列的弹性平衡,这又受到交滑移和攀移的影响,这些都是热激活的条件,从而也解释了图2中硬度曲线在再结晶前出现1个平缓阶段的原因。
再结晶核心形成后是晶核的长大阶段,晶粒长大的实质是晶界在晶体中迁移。小角度晶界转变为大角晶界以后,界面的迁移率将不断提高,从而吞并相近的亚晶使晶粒长大,直到长成无畸变的等轴晶为止。晶粒长大驱动力主要来源于晶界界面能,晶界移动方向指向其曲率中心(图中箭头所指方向),使晶界趋向于平直化。
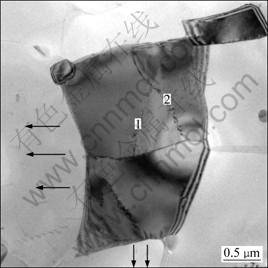
图5 Al-Zn-Mg-Cu合金热轧板在400 ℃退火时TEM照片
Fig.5 TEM micrograph of hot roll sheet following annealing at 400 ℃
3 讨论
由图1可知Al-Zn-Mg-Cu合金在390 ℃热轧变形过程中发生动态回复,按照动态回复理论位错的变化可以简单地表示为[15]:
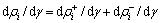 (2)
(2)
其中: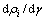 为位错密度变化率。很明显,
为位错密度变化率。很明显,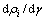 由加工硬化时位错增加部分
由加工硬化时位错增加部分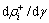 和动态回复时位错消失部分
和动态回复时位错消失部分 组成。利用统计分析得出位错的增量[16]:
组成。利用统计分析得出位错的增量[16]:
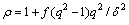 (3)
(3)
则总的变化速率可以表示为:
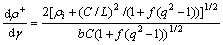 (4)
(4)
其中:f为晶界所占的体积分数;δ为胞直径;q为度量系数(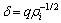 );L为位错运动距离;C为常数。从式(4)可见:在晶界和亚晶界处塞积位错密度明显比晶内和亚晶内的高;位错密度除了与应变速率有关外,还与胞的尺寸和位错滑移距离有关,在未达到稳定变形时,位错密度持续增大;在位错密度增加的同时,回复也正在发生。Nes等[17]建立了位错偶极子模型(NM模型),描述了铝合金动态回复时位错的消失,其机理与静态回复的机理相类似,认为位错网(Network)是由于众多两两异号的位错偶极子分解形成,位错偶极子是一个可动位错移动至固定位错附近时形成,它们处于相邻的滑移面上且满足两者之间距离lg小于固定位错之间的平均距离,通过位错的攀移和位错的扩散,位错偶极子最终分解消失。因此,动态回复的速率由位错偶极子的分解速率决定:
);L为位错运动距离;C为常数。从式(4)可见:在晶界和亚晶界处塞积位错密度明显比晶内和亚晶内的高;位错密度除了与应变速率有关外,还与胞的尺寸和位错滑移距离有关,在未达到稳定变形时,位错密度持续增大;在位错密度增加的同时,回复也正在发生。Nes等[17]建立了位错偶极子模型(NM模型),描述了铝合金动态回复时位错的消失,其机理与静态回复的机理相类似,认为位错网(Network)是由于众多两两异号的位错偶极子分解形成,位错偶极子是一个可动位错移动至固定位错附近时形成,它们处于相邻的滑移面上且满足两者之间距离lg小于固定位错之间的平均距离,通过位错的攀移和位错的扩散,位错偶极子最终分解消失。因此,动态回复的速率由位错偶极子的分解速率决定:
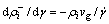 (5)
(5)
式中: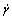 为应变速率;vg为位错偶极子分解频率,它与位错偶的距离和位错运动速率有关,在固定的应变速率和温度下,vg为常数。当位错储能的增加和回复达到动态平衡时形成固定密度的位错可表示为:
为应变速率;vg为位错偶极子分解频率,它与位错偶的距离和位错运动速率有关,在固定的应变速率和温度下,vg为常数。当位错储能的增加和回复达到动态平衡时形成固定密度的位错可表示为:
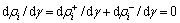 (6)
(6)
分别将式(4)和(5)代入式(6)得到:
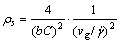 (7)
(7)
式(7)说明以动态回复为软化机制的热轧过程中,回复无法抵消加工硬化产生的位错增殖,整体位错密度仍较高且是应变速率和温度的函数;当合金到达稳定流变时,位错密度为稳定值,不随时间而变化。图1进一步表明:高密度位错区主要分布在晶界和亚晶界处,从微观上看固定密度的位错是加工硬化和回复软化过程中小角度晶界持续形成和分解后转变而成,这些动态回复时未抵消的位错能可作为再结晶驱动力,而部分亚晶具有聚集形核的优势条件。
当热变形合金退火时,在位错胞内发生位错的各种运动使异号位错互相抵相,胞壁中的位错缠结逐渐形成低能量的位错网;而原先已形成的相邻小角度亚晶界只要发生旋转和亚晶界的迁移便可以较容易地转化成大角晶粒,也意味着动态回复时多边形化产生的亚晶促进了随后退火再结晶。早期的一些研究认 为[18]:回复降低变形组织再结晶驱动力不利于再结晶形核。而Gourdet等[19]的研究表明适当的回复提高了小角晶界向大角晶界转变的速率,从而加速以亚晶形核方式的再结晶过程;Kassner等[20-21]也证实了回复对再结晶的促进和竞争的双重作用。实际上,回复时形成的多边形化可以分为2类[22]:稳定多边形化和再结晶前多边形化。稳定多边形化是具有均匀位错结构的变形材料加热时位错重新分布的过程,该过程引起异号位错消失并形成新的具有低曲率和低位向差角的稳定亚晶界,这种多边形化模式是与再结晶相互竞争的,文献[21]中的模式即属于这种情况;而再结晶前多边形化是指具有胞结构的变形材料加热时位错重排的过程,该过程引起形成胞壁的位错塞积中部分位错消失并导致这些位错塞积平直化,成为具有高曲率和迁移率的平直亚晶界,从再结晶驱动力上看是有利于再结晶的。同理,强烈热轧变形时动态回复也有利于再结晶的进行,且由于晶界和亚晶界附近位错密度高或有亚晶存在,因此,细小再结晶晶粒优先在这些位置形核长大,形核方式趋向于亚晶合并形核。
4 结论
(1) Al-Zn-Mg-Cu合金在390 ℃热轧变形时,其主要软化机理为动态回复;在变形量为90%时,其组织由尺寸为0.3~0.6 μm的位错胞和亚晶组成,这种回复形成再结晶前的多边形化促进了随后退火过程中静态再结晶的进行。
(2) 总变形量为90%的Al-Zn-Mg-Cu热轧板再结晶起始温度为400 ℃,完全再结晶温度为420 ℃,超过450 ℃时退火再结晶晶粒明显长大,再结晶形核机制为亚晶合并形核,主要为5~8个亚晶聚集成直径为2~5 μm的再结晶核心。
参考文献:
[1] Vandermeer R A, Jensen D J. Microstructural path and temperature dependence of recrystallization in commercial aluminum[J]. Acta Material, 2001, 49(22): 2083-2094.
[2] Birol Y. Recrystallization of a supersaturated Al-Mn alloy[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2008, 59(6): 611-614.
[3] Vandermeer R A, Jensen D J. Recrystallization in hot vs cold deformed commercial aluminum: A microstructure path comparison[J]. Acta Materialia, 2003, 51(10): 3005-3018.
[4] Talamantes-Silva J, Abbod M F, Cabrera E S . Microstructure modelling of hot deformation of Al-1%Mg alloy[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2009, 525(1/2): 147-158.
[5] Liu W C, Man C S, Raabe D, Effect of hot and cold deformation on the recrystallization texture of continuous cast AA5052 aluminum alloy[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2005, 53(11): 1273-1277.
[6] Kugler G, Turk R. Study of the influence of initial microstructure topology on the kinetics of static recrystallization using a cellular automata model[J]. Computational Materials Science, 2006, 37(3): 284-291.
[7] Humphreys F J, Hatherly M. Recrystallization and related annealing phenomena[M]. London: Oxford Press, 2004: 121-135.
[8] Rohatgi A, Kenneth S. The influence of Stacking fault energy on the mechanical behavior of Cu and Cu-Al alloys:Deformation Twinning, work hardening and dynamic recovery[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions, 2001, 32(1): 135-145.
[9] Sarkar S, Wells M A, Poole W J. Softening behaviour of cold rolled continuous cast and ingot cast aluminum alloy AA5754[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2006, 421(1/2): 276-285.
[10] Mughrabi H. Dislocation wall and cell structures and long –range internal stresses in deformed metal crystals[J]. Acta Metallurgia, 1983, 31(9): 1367-1379.
[11] Dougherty L M, Robertson I M, Vetrano J S. Direct observation of the behavior of grain boundaries during continuous dynamic recrystallization in an Al-4Mg-0.3Sc alloy[J]. Acta Materialia, 2003, 51(15): 4367-4378.
[12] Myshlyaev M M, McQueen H J, et al. Twinning, dynamic recovery and recrystallization in hot worked Mg-Al-Zn alloy[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2002, 337(1/2): 121-133.
[13] Paul H, Driver J H, Maurice C. Recrystallization mechanisms of low stacking fault energy metals as characterized on model silver single crystals[J]. Acta Materialia, 2007, 55(3): 883-847.
[14] Prettersen T, Nes E. Microstructure development during hot deformation of aluminum to large strains[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions, 2003, 34(12): 2737-2744.
[15] Nes E, Marthinsen K, Brechet Y. On the mechanisms of dynamic recovery[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2002, 47(9): 607-611.
[16] Nes E, Mathinsen K. Modelling the evolution in microstructure and properties during processing of aluminium alloys[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2001, 117(3): 333-340.
[17] Nes E, Marthinsen K. Modeling the evolution in microstructure and properties during plastic deformation of f.c.c. metals and alloys: An approach towards a unified model[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2002, 322(1/2): 176-193.
[18] Avramovic-Cingara G, McQueen H J, Salama A, et al. Hot working and resultant 300 ℃ductility of Al-Fe and Al-Fe-Co alloys[J]. Scripta Metallurgica, 1989, 23(2): 273-278.
[19] Gourdet S, Montheillet F. An experimental study of the recrystallization mechanism during hot deformation of aluminium[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2000, 283(1/2): 274-288.
[20] Kassner M E, Pollard J, Evangelista E, et al. Restoration mechanisms in large-strain deformation of high purity aluminum at ambient temperature and the determination of the existence of steady-state[J]. Acta Metallurgica Materialia, 1994, 42(9): 3223-3230.
[21] Stuwe H P, Padilha A F. Competition between recovery and recrystallization[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2002, 333(1/2): 361-367.
[22] S.S.葛列里克. 金属和合金的再结晶[M]. 仝健民译. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 1985: 70-82.
Gorelid S S. Recrystalization of metals and alloys[M]. TONG Jian-min, transl. Beijing: China Machine Press, 1985: 70-82.
(编辑 陈灿华)
收稿日期:2010-11-15;修回日期:2011-03-08
基金项目:国家重点基础研究发展计划(“973”计划)项目(2005CB623705-04)
通信作者:刘志义(1962-),男,湖南邵阳人,教授,博士生导师,从事高性能铝合金研究;电话:0731-88836011;E-mail:liuzhiyi@csu.edu.cn