晶粒尺寸对细晶TC4钛合金高温应力松弛行为的影响
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2020年第3期
论文作者:彭赫力 李细锋 陈旭 姜军 罗经锋 熊炜 陈军
文章页码:668 - 677
关键词:应力松弛;晶粒尺寸;细晶结构;TC4钛合金;位错
Key words:stress relaxation; grain size; fine-grained microstructure; TC4 titanium alloy; dislocation
摘 要:为了分析晶粒尺寸对应力松弛机制的影响,对三种晶粒尺寸的TC4钛合金在650~750 °C温度范围内进行应力松弛试验。基于一种修改立方延时函数建立每种晶粒尺寸的应力松弛模型。根据经典的 Arrhenius方程,提出一种简化算法来计算变形激活能。采用微观手段观察晶粒尺寸分布及变化。实验结果表明,在相同温度下晶粒越细的合金初始应力越小,且松弛速率越快,因而更易达到松弛极限。在650 °C,应力松弛极限随晶粒尺寸减小而降低;而在700 °C和750 °C合金达到完全松弛,导致晶粒尺寸对应力松弛极限影响不显著;随着晶粒尺寸的增大,变形激活能升高,在700 °C应力松弛机制从晶粒转动和晶界滑移变换为位错运动和动态回复。
Abstract: In order to analyze the effect of grain size on stress relaxation (SR) mechanism, the SR tests of TC4 alloy with three kinds of grain size were performed in a temperature range of 650-750 °C. A modified cubic delay function was used to establish SR model for each grain size. A simplified algorithm was proposed for calculating the deformation activation energy based on classical Arrhenius equation. The grain size distribution and variation were observed by microstructural methods. The experimental results indicate that smaller grains are earlier to reach the relaxation limit at the same temperature due to lower initial stress and faster relaxation rate. The SR limit at 650 °C reduces with decreasing grain size. While the effect of grain size on SR limit is not evident at 700 and 750 °C since the relaxation is fully completed. With the increase of grain size, the deformation activation energy is improved and SR mechanism at 700 °C changes from grain rotation and grain boundary sliding to dislocation movement and dynamic recovery.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 30(2020) 668-677
He-li PENG1,2, Xi-feng LI3, Xu CHEN1,2, Jun JIANG3, Jing-feng LUO3, Wei XIONG3, Jun CHEN3
1. Shanghai Spaceflight Precision Machinery Institute, Shanghai 201600, China;
2. Shanghai Engineering Technology Research Center of Near-Net Shape Forming for Metallic Materials, Shanghai 201600, China;
3. Institute of Forming Technology & Equipment, School of Materials Science and Engineering, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200030, China
Received 24 May 2019; accepted 30 December 2019
Abstract: In order to analyze the effect of grain size on stress relaxation (SR) mechanism, the SR tests of TC4 alloy with three kinds of grain size were performed in a temperature range of 650-750 °C. A modified cubic delay function was used to establish SR model for each grain size. A simplified algorithm was proposed for calculating the deformation activation energy based on classical Arrhenius equation. The grain size distribution and variation were observed by microstructural methods. The experimental results indicate that smaller grains are earlier to reach the relaxation limit at the same temperature due to lower initial stress and faster relaxation rate. The SR limit at 650 °C reduces with decreasing grain size. While the effect of grain size on SR limit is not evident at 700 and 750 °C since the relaxation is fully completed. With the increase of grain size, the deformation activation energy is improved and SR mechanism at 700 °C changes from grain rotation and grain boundary sliding to dislocation movement and dynamic recovery.
Key words: stress relaxation; grain size; fine-grained microstructure; TC4 titanium alloy; dislocation
1 Introduction
Titanium alloys nowadays play an important role in aerospace industry for lightweight demand, which have high specific strength as well as excellent corrosion and thermal resistance [1-3]. Ti-6Al-4V (TC4) titanium alloy is most widely used in this alloy family [4]. Due to poor plasticity and high yield ratio at room temperature, hot working technique is usually used to produce various kinds of complicated TC4 parts. The creep forming is one of the most important hot working methods. Actually, it involves two aspects including hot forming (thermal softening) and hot sizing (SR). Material characteristics (grain size, heat treatment condition, phase distribution, etc.) and process parameters (temperature, holding time, strain rate, etc.) prominently determine SR behavior of titanium alloy [5,6]. Additionally, the fatigue failure of many aerospace parts at service temperature is mainly attributed to creep deformation. Consequently, SR behavior of titanium alloy attracts wide attention in aerospace field.
Some research works have been carried out to investigate SR phenomena of titanium alloys. POVAROV [7] found that the atom diffusion plays a predominated role during SR process of Ti-2Al-1.5Mn and Ti-5Al-2.5Sn alloys at 500-850 °C while the dislocation slip becomes the main mechanism below 500 °C. LIU et al [8] performed SR bending tests of TC4 alloy and analyzed the different mechanisms at 400 and 600 °C. The relaxation mainly relies on dislocation slip, twinning and grain boundary movement at 400 °C while the deformation mechanism attributes to dislocation slip and atom diffusion due to subgrains forming on grain boundaries at 600 °C. ZONG et al [9] conducted short-term creep and SR tests of TC4 alloy at 650-850 °C. It was concluded that the vacancy diffusion is the main mechanism of creep and SR at 650 °C. Above 650 °C, these two behaviors are controlled by dislocation climb. XIAO et al [10] built an implicit creep-type constitutive equation of TC4 alloy based on transformation relationship between elastic strain and plastic strain. The relationship between SR and creep was quantitatively described.
Grain refinement is a mainstream method for improving material properties. Classical Hall-Petch formula indicates that the yield strength improves as grain size reduces [11]. Furthermore, smaller grains induce better plasticity and even excellent superplasticity at high temperature [12,13]. Low-temperature (550-650 °C) superplasticity is demonstrated in an ultrafine microstructure consisting of α grains (~0.51 μm) and a small amount of β phase, which was achieved in a friction stir-processed TC4 alloy [14]. Additionally, the superplasticity is remarkably affected by other factors. The initial martensitic and lamellar TC4 alloys processed by high-pressure torsion exhibit maximum elongations of 815% and 690% at 700 °C, respectively. The development of an fcc phase in the former can inhibit grain growth and promote grain boundary sliding [15]. The stir zone with a fine lamellar microstructure in a hydrogenated friction stir welded TC4 joint has a largest elongation of 660% at 825 °C, which results from the globularization of the lamellar microstructure and the high fraction of β phase induced by the hydrogen element [16].
In the previous works, the effect of grain size on SR behavior has been investigated. AKHTAR et al [17] studied SR behavior of polycrystalline Ti-Nb alloy. The significant influence of grain size on SR rate in the range of 67-117 μm was found. Nevertheless, there is no obvious relationship between grain size and SR rate in the range of 612-751 μm due to dislocation pile-ups at grain boundaries, which impedes the mobility of new dislocations from grain interior. LIU et al [18] performed bending SR tests of two kinds of TC4 alloys with different grain sizes at 600 °C. The alloy with smaller grain size reveals a higher relaxation rate.
In the previous studies, the grain size was deemed as an important factor of SR behavior. Furthermore, the grain size is usually above 10 μm. As fine-grained titanium alloy is widely utilized in aerospace industry, SR behavior of fine-grained titanium alloy (less than 10 μm) needs to be further investigated for excellent hot forming process. In this work, TC4 titanium alloy with three kinds of grain sizes was performed for high-temperature SR tests. Based on experimental data, a modified delay function was established for each grain size. Moreover, an implicit creep-type constitutive equation was built to calculate the deformation activation energy during SR process. The SR mechanism for each grain size was also discussed.
2 Experimental
TC4 alloy sheet with a thickness of 0.5 mm in annealed state was applied by Baoti Group Co., Ltd., China. In order to obtain three kinds of grain size, as-received sheets were heated to 900 °C in an electrical resistance furnace and held for 2 and 4 h, respectively. During the heating treatment process, the antioxidant was coated on sheet surface to avoid some severe defects. The grain size was measured by electron backscattered diffraction (EBSD) method. The samples for EBSD analysis were prepared by vibration polishing and electro- polishing method. The specific grain size was calculated by a software named Channel 5.
The tested specimens with a gauge size of 25 mm × 9 mm were prepared along the rolling direction by wire-electrode cutting, and their geometric dimensions are revealed in Fig. 1. The SR tests were performed on a high-temperature mechanical testing machine. The specimens were heated to the setting temperature (650, 700 and 750 °C) and held for 10 min in order to achieve uniform temperature distribution. The temperature error was ±2 °C. They were stretched with an initial strain rate of 1×10-4 s-1. The tensile clamp was stopped when the displacement of 4 mm was reached and no obvious necking appeared. Since the parallel length of tensile specimens was 30 mm, the pre-stretched elongation of 13.3% was obtained. Then, the SR tests began and relevant data were recorded. When the SR tests terminated, the specimens were cooled to 400 °C in the furnace and then cooled in air to room temperature. True stress-relaxation time curves show the dependence of SR result on grain size at different temperatures, which were fitted by the delay function. The established implicit creep-type constitutive equations were used for quantitatively calculating the deformation activation energy.

Fig. 1 Geometric dimension of SR testing specimens (unit: mm)
The gauge section of each specimen after SR tests was cut for subsequent microstructural analysis. The thin slices with a diameter of 3 mm were prepared by mechanical polishing method and twin-jet electropolishing for transmission electron microscope (TEM) observation. The SR mechanisms were discussed by combining deformation activation energy variation with microscopic observations.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Stress relaxation curves
The optical microstructure of as-received alloy is revealed in Fig. 2, where β phases uniformly distribute along the grain boundaries of equiaxed primary α phase. As shown in Fig. 3, the grains grow up with the increase of holding time. The initial average grain size is about 1.25 μm while it rises to 4.58 and 8.38 μm by heating at 900 °C for 2 and 4 h, respectively. In addition, since β transus temperature of TC4 alloy is much higher than 900 °C [15,19], the β transformation during heating and dwelling stages may be ignored.

Fig. 2 Optical microstructure of as-received TC4 alloy
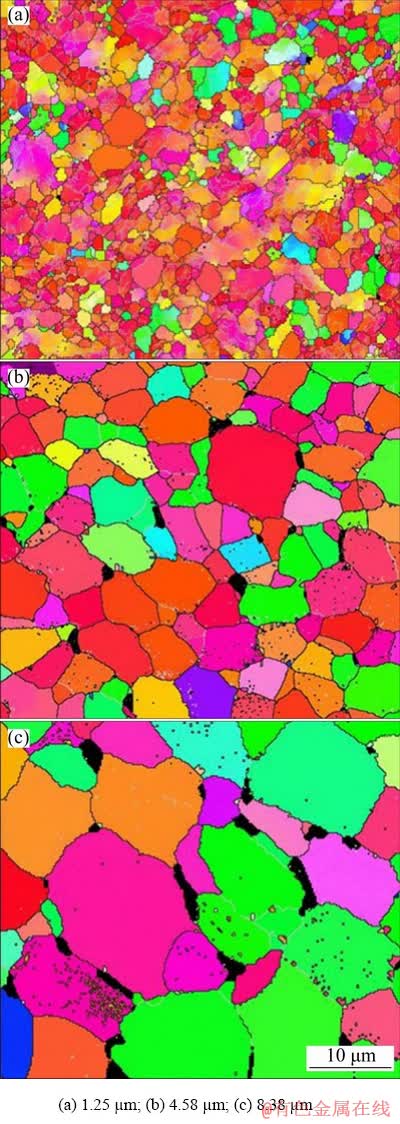
Fig. 3 EBSD images of TC4 alloy with different grain sizes

Fig. 4 True stress-relaxation time curves of TC4 alloy with three kinds of grain size at different temperatures
According to previous studies about metallic SR behaviors [18,20-23], some fundamental parameters of SR consist of initial stress, SR rate,SR end time and SR limit. SR rate indicates the relationship between residual stress and relaxation time. Higher initial stress and relaxation temperature generally result in a faster relaxation. SR limit represents that the residual stress declines to a stable value. Figure 4 shows the true stress-relaxation time curves of TC4 alloy with three kinds of grain size at different temperatures. In a whole, SR rates decrease as the relaxation time extends. At the beginning of SR, the initial stress rapidly declines. With further increasing relaxation time, SR rate becomes small and tends to zero or nearly zero. As the temperature increases and grain size decreases, the initial residual stress of TC4 alloy reduces. The decrement trend of initial stress is not obvious at 650 and 700 °C when the grain size is reduced from 8.38 to 4.58 μm. However, the initial stress seriously reduces at 750 °C. Consequently, both grain size and relaxation temperature are the main factors influencing the initial stress. The similar result is found in previous study [18]. Additionally, TC4 alloy with smaller grain size relaxes faster at higher temperature. The influence of grain size gradually weakens with increasing relaxation temperature. The detailed results are given in Table 1. TC4 alloy with average grain size of 8.38 μm cannot completely relax and the residual stress still has an obvious descendant tendency at 650 °C after 1 h. However, a distinct stress platform can be achieved for the other two grain sizes. SR limits with grain size of 1.25 and 4.58 μm are about 0.5 and 4.2 MPa at 650 °C, respectively. The SR end time is an estimated value according to the variation tendency of relaxation curves, which is also related to holding time during SR forming process. Higher temperature and smaller grains are beneficial to shortening SR period. The alloy with two small grain sizes relaxes completely and SR limit is nearly zero at 700 °C while SR limit with large grain size is about 1.43 MPa. Furthermore, the complete relaxation occurs at 750 °C for three kinds of grain size. It can be concluded that smaller grain size and higher temperature lead to lower SR limit.
Table 1 SR data of TC4 alloy with three kinds of grain size at different temperatures

3.2 Stress relaxation models
SR model can quantitatively describe the relaxation behavior and provide a relatively accurate prediction of instantaneous stress. The exponential, logarithmic and Maxwell formulas were used to fit true stress-relaxation time curves [24]. In this study, a modified delay function is used to establish SR model. The basic equation is expressed as follows [10]:
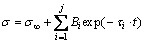 (1)
(1)
where σ, σ∞ and t denote instantaneous stress, SR limit and SR time, respectively. Bi and τi refer to material properties and experimental conditions. j is the number of exponential terms and determines the prediction precision of SR model.
When t equals 0, the formula is obtained:
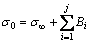 (2)
(2)
where σ0 is the initial stress. By combining Eq. (1) with Eq. (2), a new equation can be derived:
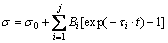 (3)
(3)
SR limit σ∞ is usually unknown beforehand. Since σ0 can be artificially controlled during SR test, it may be regarded as a constant. The condition that TC4 alloy with grain size of 1.25 μm relaxed at 700 °C is chosen to determine j value. The preliminary fitting results are evaluated by Matlab software. The root mean square error (RMSE) between experimental and fitting data decreases with increasing j value when j value is below 3.
RMSE almost maintains invariant with further increasing j value, as given in Table 2. This indicates that the fitting accuracy cannot be prominently improved with higher j value. Hence, j is selected as 3 and a modified SR model can be expressed as follows:
 (4)
(4)
Table 2 RMSE values corresponding to different j values

Nine groups of experimental data are fitted by Eq. (4). The fitting results are listed in Table 3. The largest RMSE value is only 1.6779, which indicates that the established SR model has a high prediction accuracy. Figure 5 shows the experimental and fitting curves of SR tested at 650 °C. There is a slight difference between them. This also verifies the availability of SR model built.
Previous studies indicated that the intrinsic mechanism of SR is same as creep [25,26]. During SR process, elastic strain is gradually converted into creep strain and total strain keeps invariant [27]. SR rate can be expressed as
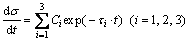 (5)
(5)
where Ci=-Bi·τi. The creep strain rate-stress curves are revealed in Fig. 6. At same stress level, the creep strain rate increases as the grain size decreases [28]. This may be explained by SR end time reduction with decreasing grain size.
Table 3 Fitting results of Bi and τi

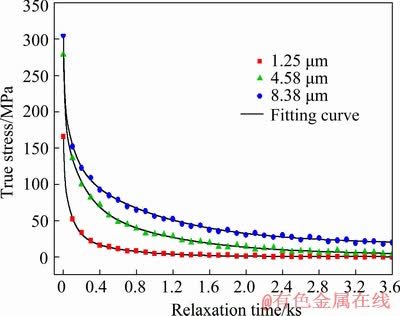
Fig. 5 Experimental and fitting results of SR tests at 650 °C
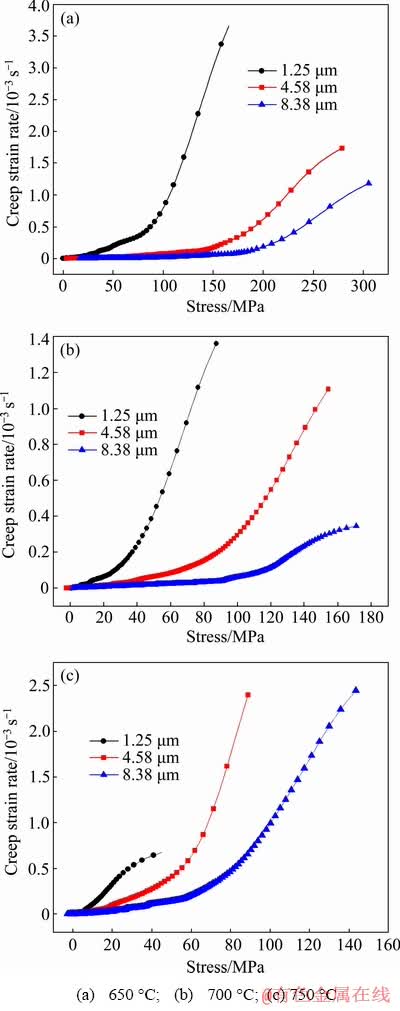
Fig. 6 Relationship between creep strain rate and stress at different temperatures

Fig. 7 Fitting curves of  against
against 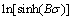 of TC4 alloy with different grain sizes
of TC4 alloy with different grain sizes
Based on Arrhenius equation, a modified creep constitutive model is established and expressed as follows [29-33]:
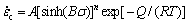 (6)
(6)
where 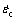 is the steady strain rate; A, B, n, R, T and Q denote material structure factor, stress level factor, stress exponent, gas constant, temperature and deformation activation energy, respectively.
is the steady strain rate; A, B, n, R, T and Q denote material structure factor, stress level factor, stress exponent, gas constant, temperature and deformation activation energy, respectively.
An equation can be obtained by taking the natural logarithm of Eq. (6):
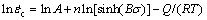 (7)
(7)
The linear relationship between 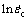 and ln[sinh(Bσ)] is derived from Eq. (7). Since n is related to grain size, n values of TC4 alloy with three kinds of grain size at different temperatures can be calculated by fitting the
and ln[sinh(Bσ)] is derived from Eq. (7). Since n is related to grain size, n values of TC4 alloy with three kinds of grain size at different temperatures can be calculated by fitting the 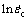 - ln[sinh(Bσ)] curves, as shown in Fig. 7. They are 1.326, 1.339 and 1.538 corresponding to 1.25, 4.58 and 8.38 μm, respectively.
- ln[sinh(Bσ)] curves, as shown in Fig. 7. They are 1.326, 1.339 and 1.538 corresponding to 1.25, 4.58 and 8.38 μm, respectively.
From Eq. (7), the linear relationship exists between ln[sinh(Bσ)] and 1/T at same creep strain rate and grain size. The slope of this line equals Q/(R·n). Then, the deformation activation energy Q is calculated as follows:
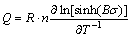 (8)
(8)
During SR tests, large quantities of creep strain rates are recorded. Q value is usually obtained by averaging the slopes of straight lines which depict the relationship between ln[sinh(Bσ)] and 1/T. Since the calculation process is very complicated, a simple algorithm is introduced below. Based on the fitting results in Fig. 7 and Eq. (7), the equation is deduced as follows:
ln[sinh(Bσ)]=Ki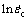 +Ci (i=1, 2, 3) (9)
+Ci (i=1, 2, 3) (9)
where i=1, 2, 3 denotes the temperature condition. The constants of Ki and Ci are obtained according to the fitting results in Fig. 7. Under the premise of same grain size, three points of (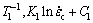 ), (
), (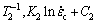 ) and (
) and ( ) are in a straight line according to Eqs. (8) and (9). The least square method is used to fit these three points. Then, the slope can be expressed as follows:
) are in a straight line according to Eqs. (8) and (9). The least square method is used to fit these three points. Then, the slope can be expressed as follows:
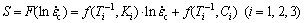 (10)
(10)
where  T1, T2 and T3 represent 650, 700 and 750 °C, respectively.
T1, T2 and T3 represent 650, 700 and 750 °C, respectively.
In order to obtain more precise results, the average value  of the slope S can be calculated within
of the slope S can be calculated within 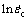 variation range:
variation range:
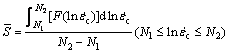 (11)
(11)
where N1 and N2 refer to lower and upper bounds of  , respectively.
, respectively.
Based on Eqs. (8)-(11), Q values of TC4 alloy with grain sizes of 1.25, 4.58 and 8.38 μm are 116.7, 128.5 and 211.8 kJ/mol, respectively, as given in Table 4. With increasing grain size, Q value obviously rises. Therefore, the increase of grain size can impede SR behavior.
Table 4 Values of modified creep constitutive model coefficients

3.3 SR microstructural mechanism
Figure 8 shows grain size variations of the specimens with three kinds of grain size before and after SR testing at 700 °C. For as-received specimen with average grain size of 1.25 μm, the grain size distribution indicates a little change after SR. The grains slightly grow up and the average grain size increases to 1.77 μm. Figure 8(b) reveals that the amount of submicron grains significantly increases when the initial grain size is 4.58 μm. Moreover, the quantity of grain size above 4 μm obviously decreases. These grains are inclined to become smaller. Actually, the average grain size decreases to about 2.71 μm. Similar grain size variation trend appears in the specimens with initial grain size of 8.38 μm. But its reduction tendency is not obvious as that of the specimens with initial grain size of 4.58 μm.
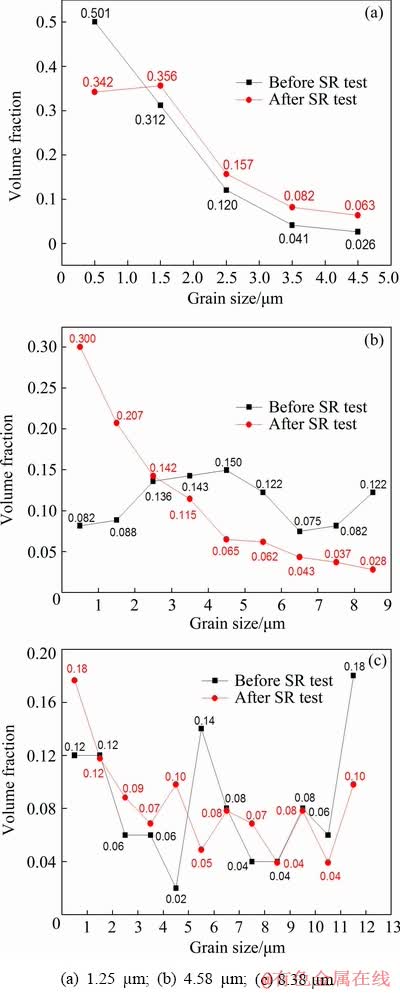
Fig. 8 Grain size distribution before and after SR testing at 700 °C with different initial grain sizes

Fig. 9 TEM images after SR testing at 700 °C with different initial grain sizes
Figure 9 shows TEM images after SR testing at 700 °C with different grain sizes. For small grain size, the grains remain equiaxed structure. There is almost no trace of dislocation movement. Grain rotation and grain boundary sliding are probably the main mechanisms rather than dislocation movement. Actually, the equiaxed grains with an average size of 1.25 μm, initial strain rate of 1×10-4 s-1 and SR temperature of 700 °C almost satisfy the conditions of superplastic deformation [13,34]. Smaller grains lead to more grain boundaries in unit area. Furthermore, the atoms at grain boundaries are very active. Therefore, the grain rotation and grain boundary sliding may be easier to happen. In addition, the self-diffusion activation energy of α phase is 204 kJ/mol [34], which is much greater than the deformation activation energy of 116.7 kJ/mol. This further proves that main SR mechanism for small grain is grain rotation and grain boundary sliding. For medium grain size, there exist dislocation pile-ups and walls or cells at grain boundaries, which are typical characteristics of dynamic recovery. The subgrains easily nucleate from dislocation cells. This results in grain size reduction after SR tests, which accords with the measured result of grain size shown in Fig. 8(b). Therefore, the grain rotation and grain boundary sliding mainly happen in small grains while the dislocation movement and dynamic recovery noticeably exist in medium grains during SR process. Large quantities of dislocations and dislocation cross-slips appear in large grains. The deformation activation energy of TC4 alloy with grain size of 8.38 μm is 211.8 kJ/mol, which is very adjacent to the self-diffusion activation energy of α phase. This indicates that main SR mechanism is still dislocation movement and dynamic recovery. Actually, the fraction of submicron grains with large initial grain is less than that with medium grains after SR tests. Without extensive grain rotation and grain boundary sliding for large grain size, the dislocation movement and dynamic recovery are difficult to release entire residual stress at 700 °C in a limited period. In a word, the grain rotation and grain boundary sliding play a key role in SR behavior for small grain size, which corresponds to lower deformation activation energy. With the increase of grain size, SR mechanism shifts to dislocation movement and dynamic recovery.
4 Conclusions
(1) The initial residual stress of TC4 alloy increases with increasing grain size. Furthermore, smaller grains and higher temperature lead to faster SR rate. The relaxation limit with different grain sizes is nearly zero above 700 °C, which is less affected by the grain size.
(2) Based on a modified cubic delay function, the SR models with different grain sizes are established. Their maximum root mean square error is 1.6779. The smaller grains can result in faster creep strain rate. An implicit creep-type constitutive equation with a simplified algorithm is proposed for calculating the deformation activation energy, which increases with the increase of grain size.
(3) The main SR mechanism of TC4 alloy with small grains at 700 °C is grain rotation and grain boundary sliding while it converts to dislocation movement and dynamic recovery with medium and large grains.
References
[1] LIU L H, YANG C, WANG F, QU S G, LI X Q, ZHANG W W, LI Y Y, ZHANG L C. Ultrafine grained Ti-based composites with ultrahigh strength and ductility achieved by equiaxing microstructure [J]. Materials and Design, 2015, 79: 1-5.
[2] LIU L H, YANG C, KANG L M, QU S G, LI X Q, ZHANG W W, CHEN W P, LI Y Y, LI P J, ZHANG L C. A new insight into high-strength Ti62Nb12.2Fe13.6Co6.4Al5.8 alloys with bimodal microstructure fabricated by semi-solid sintering [J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 23467.
[3] FAN X G, ZENG X, YANG H, GAO P F, MENG M, ZUO R, LEI P H. Deformation banding in β working of two-phase TA15 titanium alloy [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2017, 27: 2390-2399.
[4] SESHACHARYULU T, MEDEIROS S C. Hot working of commercial Ti-6Al-4V with an equiaxed α-β microstructure: Materials modeling considerations [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2000, 284: 184-194.
[5] LIU Y, YIN Z D, ZHU J C, LI M W. Stress relaxation behavior of Ti-6Al-4V alloy [J]. Transactions of NonferrousMetalsSocietyofChina, 2003, 13: 881-884.
[6] LUO J, WANG B Z, WANG L F, LI L, LI M Q. Sensitivity analysis on globularized fraction of α lamellae in titanium alloys [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2019, 29: 305-312.
[7] POVAROV I A. Stress relaxation in structural titanium alloys [J]. Metal Science and Heat Treatment, 1980, 22: 433-438.
[8] LIU Y, ZHU J, YIN Z. Stress relaxation behavior and microstructure observation in TC4 alloy [J]. Chinese Journal of Rare Metals, 2002, 26: 509-512.
[9] ZONG Y Y, LIU P, GUO B. Investigation on high temperature short-term creep and stress relaxation of titanium alloy [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2015, 620: 172-180.
[10] XIAO J J, LI D S, LI X Q. Modeling and simulation for the stress relaxation behavior of Ti-6Al-4V at medium temperature [J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2015, 44: 1046-1051.
[11] WANG J N, XIE K. Grain size refinement of TiAl alloy by rapid heat treatment [J]. Scripta Materialia, 2000, 43: 441-446.
[12] BUSSIBA A, ARTZY A B. Grain refinement of AZ31 and ZK60 Mg alloys-Towards superplasticity studies [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2001, 302: 56-62.
[13] LI X F, LV X C, WU H P, JI B Y, CHEN J, LI J F. Effect of grain size on the superplastic deformation behavior of Ti-55 alloy [J]. Procedia Engineering, 2017, 207: 1880-1885.
[14] ZHANG W J, DING H, CAI M H, YANG W J, LI J Z. Ultra-grain refinement and enhanced low-temperature superplasticity in a friction stir-processed Ti-6Al-4V alloy [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2018, 727: 90-96.
[15] SHAHMIR H, NAGHDI F, PEREIRA P H R, HUANG Y, LANGDON T G. Factors influencing superplasticity in the Ti-6Al-4V alloy processed by high-pressure torsion [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2018, 718: 198-206.
[16] WU L H, JIA C L, HAN S C, LI N, NI D R, XIAO B L, MA Z Y, FU M J, WANG Y Q, ZENG Y S. Superplastic deformation behavior of lamellar microstructure in a hydrogenated friction stir welded Ti-6Al-4V joint [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2019, 787: 1320-1326.
[17] AKHTAR M K, KHWAJA F A, BUTT M Z. Effect of grain size on the stress-relaxation rate in Ti-6.5at%Nb alloy crystals [J]. Physica Status Solidi A, 1994, 143: 59-63.
[18] LIU Yong, YIN Zhong-da, ZHU Jing-chuan. Effects of temperature, stress and grain size on stress relaxation of the alloy TC4 [J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2003, 32: 644-646. (in Chinese)
[19] ZONG Y Y, HUANG S H, GUO B, SHAN D B. In situ study of phase transformations in Ti-6Al-4V-xH alloys [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2015, 25: 2901-2911.
[20] LIN Zhao-rong, XIONG Zhi-qing. Investigation on high temperature short-term stress relaxation of TA2, TC1 and TC4 titanium alloys [J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 1983, 6: 4-10. (in Chinese)
[21] LI X F, LI J J, DING W, ZHAO S J, CHEN J. Stress relaxation in tensile deformation of 304 stainless steel [J]. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 2017, 26: 630-635.
[22] HARIHARAN K, MAJIDI O, KIM C, LEE M G, BARLAT F. Stress relaxation and its effect on tensile deformation of steels [J]. Materials and Design, 2013, 52: 284-288.
[23] VARMA A, GOKHALE A, JAIN J, HARIHARAN K,CIZEK P, BARNETT M. Investigation of stress relaxation mechanisms for ductility improvement in SS316L [J]. Philosophical Magazine, 2018, 98: 165-181.
[24] WANG Ming-wei, WANG Chun-yan, YANG Ji-xin, ZHANG Li-wen, ZHAO Jie. Study on high temperature stress relaxation behavior of BT20 alloy [J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2012, 41: 502-505. (in Chinese)
[25] SINHA N K, SINHA S. Stress relaxation at high temperatures and the role of delayed elasticity [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2005, 393: 179-190.
[26] SINHA N K, SINHA S. High-temperature yield strength and its dependence on primary creep and recovery [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2011, 528: 5366-5378.
[27] HO K C, LIN J, DEAN T A. Modelling of springback in creep forming thick aluminum sheets [J]. International Journal of Plasticity, 2004, 20: 733-751.
[28] LUO J F, XIONG W, LI X F, CHEN J. Investigation on high-temperature stress relaxation behavior of Ti-6Al-4V sheet [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2019, 743: 755-763.
[29] VISWANATHAN G B, KARTHIKEYAN S, HAYES R W, MILLS M J. Creep behavior of Ti-6Al-2Sn-4Zr-2Mo: II. mechanisms of deformation [J]. Acta Materialia, 2002, 50: 4965-4980.
[30] VISWANATHAN G B, SAROSI P M, HENRY M F, WHITIS D D, MILLIGAN W W, MILLS M J. Investigation of creep deformation mechanisms at intermediate temperatures in René 88 DT [J]. Acta Materialia, 2005, 53: 3041-3057.
[31] SCHUH C, DUNAND D C. An overview of power-law creep in polycrystalline β-titanium [J]. Scripta Materialia, 2001, 45: 1415-1421.
[32] BARBOZA M J R, NETO C M, SILVA C R M. Creep mechanisms and physical modeling for Ti-6Al-4V [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2004, 369: 201-209.
[33] WARREN J, HSIUNG L M, WADLEY H N G. High temperature deformation behavior of physical vapor deposited Ti-6Al-4V [J]. Acta Metallurgica et Materialia, 1995, 43: 2773-2787.
[34] LI X F, JIANG J, WANG S, CHEN J, WANG Y Q. Effect of hydrogen on the microstructure and superplasticity of Ti-55 alloy [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy,2017, 42: 6338-6349.
彭赫力1,2,李细锋3,陈 旭1,2,姜 军3,罗经锋3,熊 炜3,陈 军3
1. 上海航天精密机械研究所,上海 201600;
2. 上海市金属材料近净成形工程技术中心,上海 201600;
3. 上海交通大学 材料学院 塑性成形技术与装备研究院,上海 200030
摘 要:为了分析晶粒尺寸对应力松弛机制的影响,对三种晶粒尺寸的TC4钛合金在650~750 °C温度范围内进行应力松弛试验。基于一种修改立方延时函数建立每种晶粒尺寸的应力松弛模型。根据经典的 Arrhenius方程,提出一种简化算法来计算变形激活能。采用微观手段观察晶粒尺寸分布及变化。实验结果表明,在相同温度下晶粒越细的合金初始应力越小,且松弛速率越快,因而更易达到松弛极限。在650 °C,应力松弛极限随晶粒尺寸减小而降低;而在700 °C和750 °C合金达到完全松弛,导致晶粒尺寸对应力松弛极限影响不显著;随着晶粒尺寸的增大,变形激活能升高,在700 °C应力松弛机制从晶粒转动和晶界滑移变换为位错运动和动态回复。
关键词:应力松弛;晶粒尺寸;细晶结构;TC4钛合金;位错
(Edited by Bing YANG)
Foundation item: Projects (2016ZE57008, 20163657004) supported by Aeronautical Science Foundation of China; Project (USCAST2016-20) supported by the SAST-SJTU Joint Research Centre of Advanced Aerospace Technology, China; Project (51875350) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Corresponding author: Xi-feng LI; Tel: +86-21-62830509; Fax: +86-21-62826575; E-mail: lixifeng@sjtu.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(20)65244-X

