DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2020.06.024
基于正态信息扩散原理的极值型工程参数概率分布推断方法
宫凤强1, 2,王天成1,黄天朗1
(1. 中南大学 资源与安全工程学院,湖南 长沙,410083;
2. 东南大学 土木工程学院,江苏 南京,211189)
摘要:在工程可靠度分析中存在大量的极值型工程参数,为了获得这类参数的最优概率分布,提出基于正态信息扩散原理的极值型工程参数概率分布推断方法。在考虑偏度的“3 ”统计原理的截尾区间下,以年最大标准风压和内摩擦角样本为例,分别利用正态信息扩散分布和极值型分布拟合2组样本,并运用K-S方法进行假设检验。为了考察样本个数对2种分布在拟合精度方面的影响,利用Monte-Carlo方法生成母函数为极值型分布的8组模拟样本,样本个数分别为15,20,30,50,100,200,500和1 000,并采用K-S检验法对不同样本个数下推断得到的概率分布进行检验。结合正态信息扩散分布的拟合优势,将其应用于核管道工程最大腐蚀深度预测。研究结果表明:不论是实际工程样本还是模拟样本,正态信息扩散分布和极值型分布均通过K-S检验,其中正态信息扩散分布的检验值均低于极值型分布的检验值;随着样本个数增加,正态信息扩散分布表现出更好的收敛优势。正态信息扩散分布的累积概率在10-4误差量级上表现出等于1的效果,而极值型分布的累积概率在同样的误差量级上达不到1。算例结果表明:利用正态信息扩散分布作为核管道腐蚀深度的预测模型,能够更加精确地预测其最大腐蚀深度。
”统计原理的截尾区间下,以年最大标准风压和内摩擦角样本为例,分别利用正态信息扩散分布和极值型分布拟合2组样本,并运用K-S方法进行假设检验。为了考察样本个数对2种分布在拟合精度方面的影响,利用Monte-Carlo方法生成母函数为极值型分布的8组模拟样本,样本个数分别为15,20,30,50,100,200,500和1 000,并采用K-S检验法对不同样本个数下推断得到的概率分布进行检验。结合正态信息扩散分布的拟合优势,将其应用于核管道工程最大腐蚀深度预测。研究结果表明:不论是实际工程样本还是模拟样本,正态信息扩散分布和极值型分布均通过K-S检验,其中正态信息扩散分布的检验值均低于极值型分布的检验值;随着样本个数增加,正态信息扩散分布表现出更好的收敛优势。正态信息扩散分布的累积概率在10-4误差量级上表现出等于1的效果,而极值型分布的累积概率在同样的误差量级上达不到1。算例结果表明:利用正态信息扩散分布作为核管道腐蚀深度的预测模型,能够更加精确地预测其最大腐蚀深度。
关键词:岩土工程;可靠度;极值型参数;最优概率分布;正态信息扩散
中图分类号:TU45 文献标志码:A
文章编号:1672-7207(2020)06-1692-11
An inference method for probability distribution of extreme value engineering parameters based on normal information diffusion principle
GONG Fengqiang1, 2, WANG Tiancheng1, HUANG Tianlang1
(1. School of Resources and Safety Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. School of Civil Engineering, Southeast University, Nanjing 211189, China)
Abstract: There are a lot of extremum-types of engineering parameters in the reliability analysis. In order to obtain the optimal probability distribution of such parameters, an inferential method for the probability distributions of extremum-type of engineering parameters based on the normal information diffusion(NID) principle was proposed. Considering the truncated interval combining “3 ” statistical principle and the effect of skewness, the annual maximum standard wind pressure and friction angle were used as the engineering examples. The NID distribution and extremum-type distribution were used to deduce the corresponding probability distribution,and the K-S method was used to test the goodness of fit of the corresponding distributions. In order to investigate the influence of sample numbers on the fitting accuracy for two distributions,the Monte-Carlo method was used to generate eight groups of simulated samples,and the sample numbers were 15, 20, 30, 50, 100, 200, 500 and 1 000,respectively. And the corresponding K-S test method was also used to test the inferred probability distributions at different sample numbers. Combining the fitting advantages of the NID distribution, it was applied to the prediction of the maximum corrosion depth for nuclear pipelines engineering. The results show that whether for engineering samples or simulated samples, both the NID distribution and extremum-type distribution pass the test. The K-S test values of the NID distribution are always lower than those of extremum-type distribution and show great advantages in convergence with the increase of sample numbers. The cumulative probabilities of the NID distribution are equal to 1 at the fitting error magnitude of 10-4, while these extremum-type distributions are less than 1 at the same of fitting error magnitude. The NID distribution is used as a predictive model for the corrosion depth of nuclear pipelines,which can predict the maximum corrosion depth more accurately.
” statistical principle and the effect of skewness, the annual maximum standard wind pressure and friction angle were used as the engineering examples. The NID distribution and extremum-type distribution were used to deduce the corresponding probability distribution,and the K-S method was used to test the goodness of fit of the corresponding distributions. In order to investigate the influence of sample numbers on the fitting accuracy for two distributions,the Monte-Carlo method was used to generate eight groups of simulated samples,and the sample numbers were 15, 20, 30, 50, 100, 200, 500 and 1 000,respectively. And the corresponding K-S test method was also used to test the inferred probability distributions at different sample numbers. Combining the fitting advantages of the NID distribution, it was applied to the prediction of the maximum corrosion depth for nuclear pipelines engineering. The results show that whether for engineering samples or simulated samples, both the NID distribution and extremum-type distribution pass the test. The K-S test values of the NID distribution are always lower than those of extremum-type distribution and show great advantages in convergence with the increase of sample numbers. The cumulative probabilities of the NID distribution are equal to 1 at the fitting error magnitude of 10-4, while these extremum-type distributions are less than 1 at the same of fitting error magnitude. The NID distribution is used as a predictive model for the corrosion depth of nuclear pipelines,which can predict the maximum corrosion depth more accurately.
Key words: geotechnical engineering; reliability; extremum-type parameters; optimal probability distribution; normal information diffusion(NID)
在工程可靠度分析中,工程随机参数的最优概率密度或分布函数模型直接影响可靠度结果的准确性[1-2],因此,对最优概率模型推断方法的研究始终是一项基础性工作[3-4]。在很多工程可靠度领域,经常遇到大量的极值型参数。所谓极值型参数,主要是考虑一系列最大(小)值参数,如建(构)筑物抗震设计中需要考虑的年最大地震荷载、海洋岩土工程中需要考虑的年最大风荷载等。当采用可靠度方法分析上述参数时,获取它们的最佳概率分布函数是首要步骤。目前,很多学者通常采用极值型分布对该类参数进行拟合检验。例如,张延年等[5]统计了中国159个代表性城市在1951—2008年的历年最大风速,选取Gumbel(极值Ⅰ型)分布进行拟合分析;李凯平等[6]利用极值Ⅲ型分布拟合地震烈度;程思军[7]利用现场试验数据,对局部腐蚀钢筋的最大腐蚀深度进行概率统计,揭示Gumbel分布可作为局部腐蚀钢筋的最大腐蚀深度概率模型。另外,一些研究者认为其他经典分布(正态分布、对数正态分布等)也可以用于拟合极值型参数的概率模型,如莫华美[8]研究最大积雪深度的概率分布时,认为对数正态分布代替极值Ⅰ型分布更具优越性;段忠东等[9]认为极值风速的最优分布为威布尔分布。从上述研究可知,极值型参数的最优概率分布并不一定是极值型分布,但是均从经典分布范围中选取。这种拟合方法存在以下2个不易解决的根本问题:1) 区间不匹配。经典分布的定义区间一般为无限区间或半无限区间,但极值型工程参数的分布区间为有限数值区间,因此,利用经典分布拟合此类参数时在理论上无法满足累积概率等于1的要求。2) 经典分布无法反映工程参数实际分布的随机波动性。经典分布均为单峰值型分布,但极值型工程参数的分布可能存在多个峰值,呈现一定波动性,因此,发展能够满足有限区间上累积概率等于1并能够体现实际分布随机波动性的概率分布推断方法十分必要。在这方面,很多专家提出了很多种推断方法。如苏永华等[10]提出了利用一般多项式推断岩土参数概率分布的方法;LI等[4]提出了正交多项式方法;张道兵等[11]运用最大熵原理估计了隧道衬砌结构参数的密度函数;李松辉[12]引入了车辆荷载效应的截尾分布模型。此外,HUANG等[13]在自然灾害风险分析中引入了信息扩散理论,目前该方法在岩土工程中得到了广泛应用。宫凤强等[14]利用正态信息扩散方法推断了小样本岩土参数的概率分布,取得了较好的拟合效果。周道成等[15]用正态信息扩散方法确定了河冰抗压强度概率分布,证明了正态信息扩散分布更加接近河冰抗压强度的真实分布,并优于经典分布的拟合方法;徐志军等[16]基于正态信息扩散理论,拟合了路基沉降的概率分布,并通过工程实例验证了此方法的正确性和有效性;黄达等[17-18]将正态信息扩散原理广泛用于推断岩体抗剪强度参数、岩体质量参数和粗粒土参数的单变量边缘分布,取得了良好效果;宫凤强等[19]利用正态信息扩散方法研究了Mohr-Coulomb强度准则参数概率模型推断方法,其概率分布更加接近参数的实际分布规律。根据上述研究,本文作者提出基于正态信息扩散原理的极值型工程参数概率分布的推断方法,并考察该方法是否满足上述2个根本条件。在研究过程中,以样本个数分别为25和61的年最大标准风压样本和内摩擦角样本为例,分别采用正态信息扩散分布和Gumbel分布进行拟合,对比分析2种分布拟合所得结果的优良性。在此基础上,利用模拟样本,考察样本个数对拟合精度的影响,并将正态信息扩散分布应用于2组核管道最大腐蚀深度的预测。
1 极值分布理论
极值理论研究的主要问题是极大(小)值的极限分布问题,是统计数学中的重要分支。设X1,X2,…,Xn为独立同分布的随机变量,分布函数为 (称为底分布),对自然数n,令Mn=max{X1, X2,
(称为底分布),对自然数n,令Mn=max{X1, X2,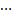 ,Xn},mn=min{X1, X2,
,Xn},mn=min{X1, X2,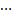 ,Xn},分别表示n个随机变量的最大值与最小值,则[20]
,Xn},分别表示n个随机变量的最大值与最小值,则[20]
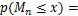
 (1)
(1)
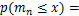
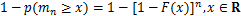 (2)
(2)
若已知分布函数 ,则可以根据式(1)和(2)精确求出最大值和最小值的分布函数。但在实际应用中,随机变量的分布函数
,则可以根据式(1)和(2)精确求出最大值和最小值的分布函数。但在实际应用中,随机变量的分布函数 往往是未知的,因此,很难直接用于统计分析。为求得原始样本的分布函数,必须考虑
往往是未知的,因此,很难直接用于统计分析。为求得原始样本的分布函数,必须考虑 时分布函数的情况即极值渐进分布,简称极值型分布。
时分布函数的情况即极值渐进分布,简称极值型分布。
极值统计理论已经证明对于3种类型的连续型随机变量原始分布,根据其分布尾部的不同形式,当 时,其极限分布只有3种类型,包括极值Ⅰ型(Gumbel)分布、极值Ⅱ型(Frechet)分布、极值Ⅲ型(Weibull)分布。其中,Gumbel分布的概率密度函数和概率分布函数表达式见式(3)和(4),其他2种分布的概率函数表达式见文献[20]。
时,其极限分布只有3种类型,包括极值Ⅰ型(Gumbel)分布、极值Ⅱ型(Frechet)分布、极值Ⅲ型(Weibull)分布。其中,Gumbel分布的概率密度函数和概率分布函数表达式见式(3)和(4),其他2种分布的概率函数表达式见文献[20]。
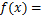
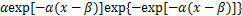 (3)
(3)
 (4)
(4)
式中: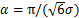 ,为比例参数;
,为比例参数; ,为位置参数(
,为位置参数(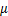 和
和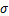 分别为样本均值和标准差)。当已知样本均值和标准差时,Gumbel分布的比例参数和位置参数可精确求解。
分别为样本均值和标准差)。当已知样本均值和标准差时,Gumbel分布的比例参数和位置参数可精确求解。
2 正态信息扩散原理
设随机变量O的概率密度函数为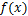 ,定义
,定义 在
在 上的1个波雷尔可测函数,
上的1个波雷尔可测函数, 为常数且大于0,则称[13]
为常数且大于0,则称[13]
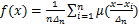 (5)
(5)
为总体密度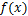 的1个扩散估计;
的1个扩散估计; 为扩散函数;
为扩散函数; 为总体密度
为总体密度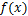 的窗宽;n为随机变量的样本数;xi为样本观测值。根据信息扩散过程,
的窗宽;n为随机变量的样本数;xi为样本观测值。根据信息扩散过程, 由下式确定:
由下式确定:
 (6)
(6)
式(6)满足式(5)对扩散函数的要求,且与概率论中正态分布的密度函数形式一致,称为正态信息扩散函数。将式(5)和式(6)联合求解,则随机变量O的概率密度函数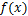 的正态信息扩散估计为
的正态信息扩散估计为
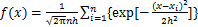 (7)
(7)
式中: ,为标准正态扩散函数;标准正态扩散估计的窗宽为
,为标准正态扩散函数;标准正态扩散估计的窗宽为 。根据正态信息扩散原理中的择近原则,可利用
。根据正态信息扩散原理中的择近原则,可利用 求解。
求解。 的具体数值见文献[21]。样本工程物理力学参数观测最大值为xmax,最小值为xmin。对于具体的岩土工程参数,根据其所得到的试验样本,直接计算正态信息扩散函数中的各项参数,然后,将所有样本数据代入,即可得到所需要的正态信息扩散分布函数表达式。
的具体数值见文献[21]。样本工程物理力学参数观测最大值为xmax,最小值为xmin。对于具体的岩土工程参数,根据其所得到的试验样本,直接计算正态信息扩散函数中的各项参数,然后,将所有样本数据代入,即可得到所需要的正态信息扩散分布函数表达式。
3 截尾区间确定方法和实例样本
Gumbel分布函数的定义区间一般为 ,而样本工程物理力学参数的取值通常大于0且其范围为有限区间。当用Gumbel分布函数拟合这些数据时,必然存在区间不匹配问题。为了解决这个问题,基于“3
,而样本工程物理力学参数的取值通常大于0且其范围为有限区间。当用Gumbel分布函数拟合这些数据时,必然存在区间不匹配问题。为了解决这个问题,基于“3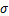 ”统计原则并考虑Gumbel分布的不对称性,确定采用考虑偏度c的“3
”统计原则并考虑Gumbel分布的不对称性,确定采用考虑偏度c的“3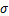 ”分布区间截尾方法,具体的区间截尾公式见表1。
”分布区间截尾方法,具体的区间截尾公式见表1。
表1 截尾区间确定方法
Table 1 Truncated interval determination method

选择高大钊[22]列举的年最大标准风压和张蕾等[23]列举的内摩擦角这2种工程参数为例进行研究,具体数据见表2。
表2 实际工程样本数据
Table 2 Sample data of actual engineering

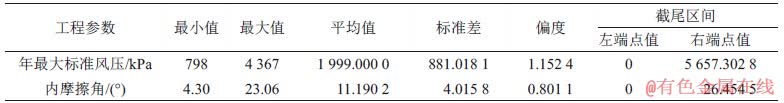
为了后续拟合检验计算的需要,对实际工程样本参数(如最值、平均值、标准差及偏度)进行统计,并计算相应的截尾区间左、右端点值,具体结果见表3。
表3 样本数据统计信息
Table 3 Statistical information of sample data
4 2种方法所得概率分布的对比分析
为了对比正态信息扩散分布与Gumbel分布的拟合效果,从概率分布曲线、K-S检验值和累积概率3个方面进行具体分析。
4.1 概率分布曲线对比
图1(a)和图1(b)所示分别为2组实际工程样本的累积概率分布曲线。从图1(a)可见:NID累积概率分布曲线与Gumbel累积概率分布曲线在前半段几乎重合;在后半段,NID累积概率分布曲线完全沿着经验分布折线的变化趋势延伸,而Gumbel累积概率分布曲线与经验分布折线的偏差较大。图2(a)和图2(b)所示分别为2组实际工程样本的概率密度函数曲线。从图2(a)可见,年最大标准风压样本的直方图反映了实际分布具有很大的波动性,而Gumbel分布曲线呈单峰值型分布,显然无法很好地刻画实际分布的波动特性;NID概率密度分布曲线具有多峰值特点,更加贴近直方图的分布趋势。同理,对图2 (b)的分析结果类似。综上分析可知NID概率密度分布比Gumbel分布更优。
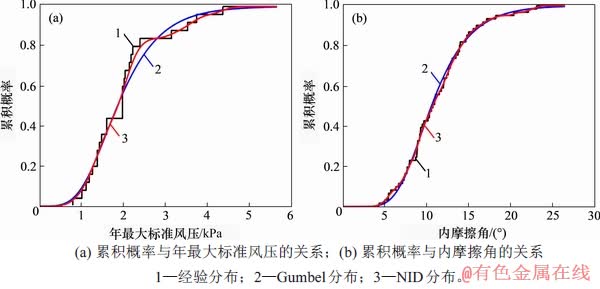
图1 实际工程样本的概率分布函数曲线比较
Fig. 1 Comparison of probability distribution function curves for actual engineering samples
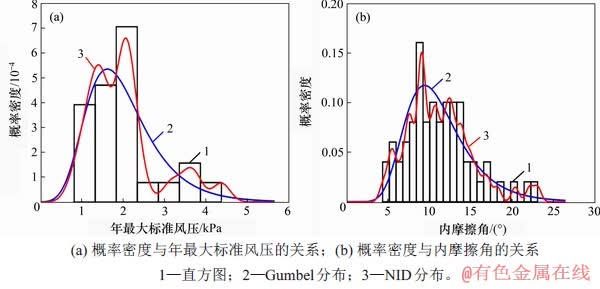
图2 实际工程样本的概率密度函数曲线比较
Fig. 2 Comparison of probability density function curves for actual engineering samples
4.2 K-S检验值和累积概率对比
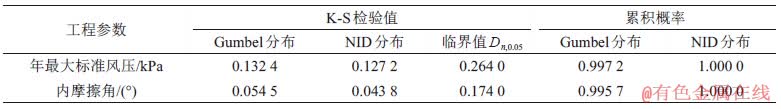
表4所示为2组实际工程样本的K-S检验值计算结果。根据K-S检验方法的特点,对2种工程参数的分布检验均在显著性水平为0.05(置信水平为95%)时进行。从表4可见:在同一置信水平下,2组样本的K-S检验法临界值分别为0.264 0和0.174 0;NID分布检验值的计算结果分别为0.127 2和0.043 8,而Gumbel分布检验值的计算结果分别为0.132 4和0.054 5。显然,这2组样本中NID分布和Gumbel分布的检验结果均通过临界值检验,但Gumbel分布的检验值均比NID分布的检验值高,这表明NID分布具有更优的拟合效果。
从表4还可见:根据确定后的截尾区间计算整个区间上的累积概率,对于Gumbel分布,2个实例样本所得到的累积概率分别为0.997 2和0.995 7,而NID分布的累积概率均为1.000 0。上述结果表明在截尾区间下,Gumbel分布无法满足累积概率等于1的先决条件。
5 样本个数对2组分布拟合精度的影响
在实际工程中,所获得的样本很多都是小样本,很难考察不同样本个数对上述2种拟合方法在拟合精度上的影响。为了研究样本个数对2种分布拟合精度的影响,基于Monte-Carlo方法抽取不同个数的样本,分别利用上述2种分布进行拟合,并根据K-S检验值与累积概率2种指标,评判2种分布的拟合效果。
表4 实际工程样本K-S检验值和累积概率计算结果
Table 4 Calculation results of K-S test values and cumulative probability for actual engineering samples
5.1 模拟样本的生成
以年最大标准风压样本为例,并以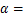 0.001 5和
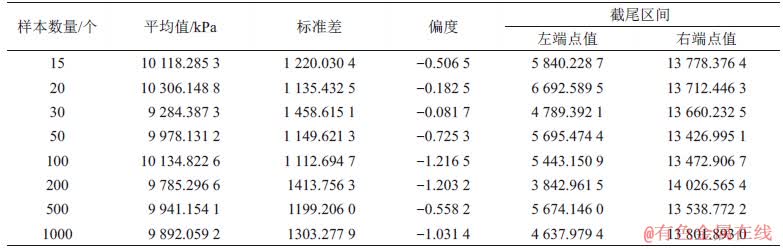
0.001 5和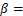 17 602.505 8(即9 602.505 8+8 000)的Gumbel分布函数作为母函数,利用Monte-Carlo方法生成8组样本,个数分别为15,20,30,50,100,200,500和1 000。表5所示为模拟样本数据的统计结果(由于生成的模拟数据较多,文中没有给出具体的模拟样本数据)。
17 602.505 8(即9 602.505 8+8 000)的Gumbel分布函数作为母函数,利用Monte-Carlo方法生成8组样本,个数分别为15,20,30,50,100,200,500和1 000。表5所示为模拟样本数据的统计结果(由于生成的模拟数据较多,文中没有给出具体的模拟样本数据)。
表5 年最大标准风压的模拟数据统计信息
Table 5 Statistical information for simulated data of annual maximum standard wind pressure
5.2 概率分布的拟合优良性检验
以样本个数分别为15,50,200和1 000的4组模拟样本为例进行说明,绘制概率分布函数曲线,见图3。从图3可以看出:不论样本个数较少还是较多,相对于Gumbel分布曲线,NID分布曲线和经验分布曲线都更加接近。图3所示概率概率分布曲线还表明:不论样本数据的实际分布完全符合经典分布还是有一定的波动性,正态信息扩散方法均可以很好地刻画样本的实际分布。
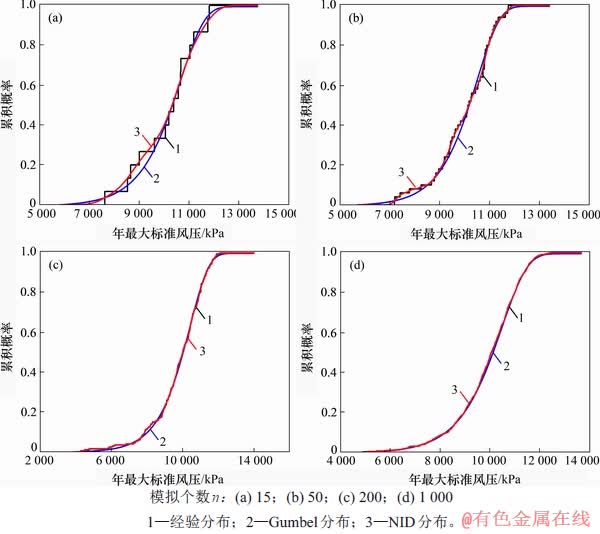
图3 模拟样本的概率分布函数曲线随样本个数增加的比较
Fig. 3 Comparison of probability distribution function curves for simulated samples with the increase of sample numbers
参考4.2节的检验对比过程,得出模拟数据的K-S检验值和累积概率的计算结果,见表6。从表6可见:对于每一组模拟样本而言,NID分布和Gumbel分布均通过了置信水平为95%的临界值检验,但Gumbel分布的检验结果均大于NID分布的检验结果,这说明在不同的样本个数下,NID分布的拟合优良性更佳。此外,在截尾区间下,Gumbel分布的累积概率始终小于1.000 0,但NID分布的累积概率恒等于1.000 0,并不受样本个数变化的影响。
表6 年最大标准风压的模拟数据K-S检验值和累积概率计算结果
Table 6 Calculation results of K-S test values and cumulative probability for simulated data of annual maximum standard wind pressure
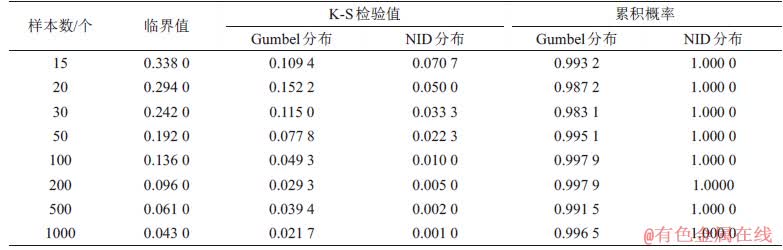
根据表6绘制模拟样本个数递增下Gumbel分布与NID分布的K-S检验值变化曲线,如图4所示。从图4可见:在样本个数递增时,临界值和NID分布的检验值均逐渐递减并趋于收敛,而Gumbel分布的检验值在n=20和n=500的点附近存在先增后减的情况,即存在一定波动性。

图4 模拟样本的K-S检验值随样本个数增加的比较
Fig. 4 Comparison of K-S test values for simulated samples with the increase of sample numbers
同样,根据表6中的数据绘制模拟样本个数递增下Gumbel分布与NID分布的累积概率变化曲线,如图5所示。由图5可知:在样本个数递增时,Gumbel分布的累积概率波动范围较大且毫无规律性,而NID分布的累积概率始终为1.000 0,与样本个数的变化无关。
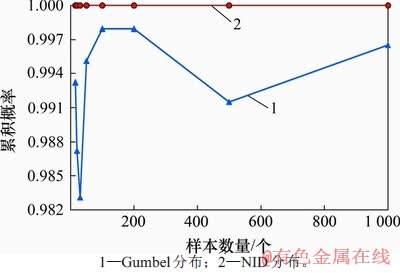
图5 模拟样本的累积概率随样本个数增加的比较
Fig. 5 Comparison of cumulative probability values for simulated samples with increase of sample numbers
6 工程应用:核管道最大腐蚀深度的预测
为了进一步说明正态信息扩散分布推断方法的可行性与有效性,以2个核管道腐蚀深度的预测问题作为工程实例进行对比分析[24-25]。
1) 某被腐蚀核管道在一定时间内的平面观测深度实测值分别为2.82,2.96,3.08,3.09,3.18,3.19,3.22,3.32,3.33,3.52,3.58,3.61,3.62,3.95和4.12 mm。周国强等[26]认为其分布符合极值Ⅱ型分布并预测该核管道最大腐蚀深度为4.840 3 mm。用正态信息扩散分布拟合该组数据并计算相应的K-S检验值,结果显示:极值Ⅱ型分布的检验结果(即以核管道最大腐蚀深度为变量的检测结果,量纲一参数)为0.115 0,NID分布的检验结果为0.106 4。这2种分布的检验值均小于临界值0.338 0,显然,上述分布均通过了临界值检验。根据张博庭[27]提出的有限比较法可知,极值Ⅱ型分布的有限比较结果大于NID分布的有限比较结果,这说明NID分布更适合作为此核管道腐蚀深度的概率分布。以NID分布作为最大腐蚀深度的预测模型,计算得到该核管道最大腐蚀深度为4.284 9 mm。由此可知:选择拟合效果更好的NID分布作为预测模型,其最大腐蚀深度的预测结果会更加精确。
为了更加清晰地看出NID分布的拟合效果,绘制NID分布和极值Ⅱ型分布的拟合曲线,如图6所示。由图6可知:极值Ⅱ型分布的累积概率未达到1,而NID分布的累积概率为1,这说明NID分布函数能够较好地拟合核管道腐蚀深度的数据点分布。图7所示为NID分布与极值Ⅱ型分布的累积概率偏差的变化情况。从图7可明显看出:NID分布的最大偏差小于极值Ⅱ型分布的最大偏差,避免了局部偏差过大的情况,这表明NID分布能够更好地拟合真实分布;另外,核管道腐蚀深度模型的优化能够更好地提高最大腐蚀深度的预测精度。

图6 实例1的NID分布和极值Ⅱ型分布拟合曲线
Fig. 6 Fitting curves of NID and extremum Ⅱ-type distributions for example 1
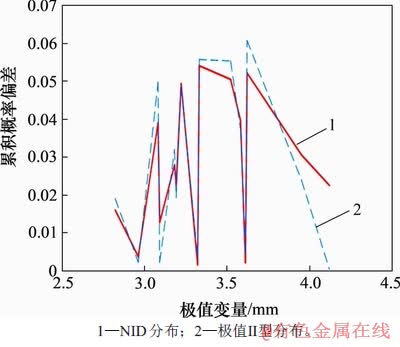
图7 实例1的拟合误差折线
Fig. 7 Fitting error poly-lines for example 1
2) 某核电站设冷水系统除淤管道不锈钢部分运行1 a后的超声测量厚度,在同一条件下,其实测值分别为2.9,3.7,3.9,3.9,4.6,4.7,4.8,5.0,5.4,5.5,5.7,5.9,6.0,6.3,6.3,7.0和8.1 mm。周国强等[26]认为其分布符合极值Ⅲ型分布并预测该核管道最大腐蚀深度为9.3 mm。按照实例1的计算过程,进行K-S检验值计算,结果显示:极值Ⅲ型分布的管道不锈钢部分腐蚀深度检验结果为0.120 1,NID分布的检验结果为0.085 9。这2种分布的检验值均小于临界值0.318 0。同理,这2种分布均通过了K-S检验,但极值Ⅲ型分布的有限比较结果大于NID分布的比较结果。显然,NID分布比极值Ⅲ型分布更适合作为此核管道腐蚀深度的概率分布。利用NID分布预测该核管道最大腐蚀深度为8.7 mm,表明由极值Ⅲ型分布预测的最大腐蚀深度比NID分布的大。与实例1进行比较可得出同样的结论,即选择拟合效果更好的NID分布作为预测模型,其最大腐蚀深度的预测结果会更加精确。
同理,绘制该样本的NID分布和极值Ⅲ型分布的拟合曲线图,如图8所示(其中,极值变量指核管道最大腐蚀深度)。由图8可知:核管道腐蚀深度样本数据点大致分布在NID分布曲线的两侧,表明NID分布有较好的拟合效果。图9所示为该样本的拟合误差折线图。从图9可知:极值Ⅲ型分布的最大偏差大于NID分布的最大偏差,说明NID分布更加接近真实分布。
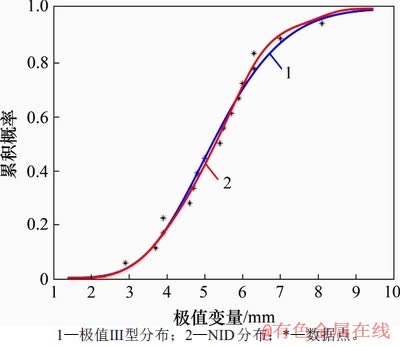
图8 实例2的NID分布和极值Ⅲ型分布拟合曲线
Fig. 8 Fitting curves of NID and extremum Ⅲ-type distributions for example 2
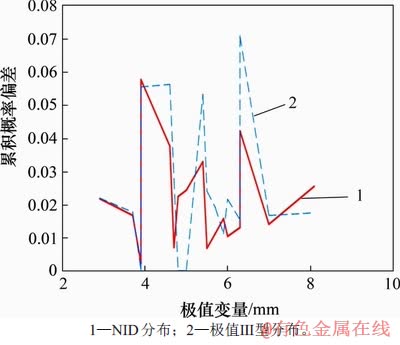
图9 实例2的拟合误差折线
Fig. 9 Fitting error poly-lines for example 2
7 结论
1) 利用正态信息扩散分布和极值型分布分别对年最大标准风压和内摩擦角2组工程样本进行拟合,正态信息扩散分布的K-S检验值比极值Ⅰ型(Gumbel)分布的K-S检验值小;正态信息扩散分布的累积概率等于1,而Gumbel分布的累积概率小于1。正态信息扩散分布的曲线能够更好地反映真实样本的直方图或经验分布折线的波动变化。
2) 在不同样本个数下,正态信息扩散分布与Gumbel分布均通过了K-S检验,但正态信息扩散分布的检验值均低于Gumbel分布的检验值。随着样本个数增加,正态信息扩散分布的K-S检验结果具有更快的收敛速度和更好的收敛稳定性;正态信息扩散分布的累积概率始终等于1,并不受样本个数的影响,而Gumbel分布的累积概率有较大的波动范围并恒小于1。
3) 正态信息扩散分布预测模型比极值Ⅱ型分布或极值Ⅲ型分布的模型精度更高;由正态信息扩散分布预测的最大腐蚀深度比极值Ⅱ型分布或极值Ⅲ型分布的预测结果更加精确。
4) 正态信息扩散方法在推断极值型工程参数的概率密度函数方面具有分布参数唯一、计算过程简便、累积概率恒定、拟合检验值低、对样本个数适应性强的特点。
参考文献:
[1] 许湘华, 曲广琇, 方理刚. 基于节理几何参数不确定性的边坡可靠度分析[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2010, 41(3): 1139-1145.
XU Xianghua, QU Guangxiu, FANG Ligang. Reliability analysis of rock slope based on uncertainty of joint geometric parameters[J]. Journal of Central South University(Science and Technology), 2010, 41(3): 1139-1145.
[2] 江权, 崔洁, 冯夏庭, 等. 玄武岩力学参数的随机性统计与概率分布估计[J]. 岩土力学, 2017, 38(3): 784-792.
JIANG Quan, CUI Jie, FENG Xiating, et al.Stochastic statistics and probability distribution estimation of mechanical parameters of basalt[J].Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2017, 38(3): 784-792.
[3] 彭康, 李夕兵, 彭述权, 等. 基于响应面法的海下框架式采场结构优化选择[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2011, 42(8): 2417-2422.
PENG Kang, LI Xibing, PENG Shuquan, et al.Optimization of frame stope structure parameters based on response surface method in under-sea mining[J]. Journal of Central South University(Science and Technology), 2011, 42(8): 2417-2422.
[4] LI Xibing, GONG Fengqiang. A method for fitting probability distributions to engineering properties of rock masses using Legendre orthogonal polynomials[J]. Structural Safety, 2009, 31(4): 335-343.
[5] 张延年, 王元清, 张勇, 等. Gumbel分布的基本风压计算与分析[J]. 土木建筑与环境工程, 2012, 34(2): 27-31.
ZHANG Yannian, WANG Yuanqing, ZHANG Yong,et al. Calculation and analysis of basic wind pressure value based on Gumbel distribution[J]. Journal of Civil, Architectural & Environmental Engineering, 2012, 34(2): 27-31.
[6] 李凯平, 石崇, 王如宾, 等. 地震诱发滑坡风险概率模型及其应用[J]. 三峡大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 38(3): 23-27, 40.
LI Kaiping, SHI Chong, WANG Rubin, et al. Risk probability models of earthquake-induced landslides and its application[J]. Journal of China Three Gorges University(Natural Sciences), 2016, 38(3): 23-27, 40.
[7] 程思军. 利用极值分布研究钢筋的最大腐蚀深度[J]. 交通建设与管理, 2014(9): 97-98.
CHENG Sijun. Study the maximum corrosion depth of steel bars by using extreme value distribution[J]. Transport Construction & Management, 2014(9): 97-98.
[8] 莫华美. 我国基本雪压的统计建模与取值研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学土木工程学院, 2016: 23-48.
MO Huamei. Statistical modeling and estimation of basic ground snow pressure for china[D]. Harbin:Harbin Institute of Technology. School of Civil Engineering, 2016: 23-48.
[9] 段忠东, 欧进萍, 周道成. 极值风速的最优概率模型[J]. 土木工程学报, 2002, 35(5): 11-16.
DUAN Zhongdong, OU Jinping, ZHOU Daocheng. The optimal probabilistic distribution for extreme wind speed[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2002, 35(5): 11-16.
[10] 苏永华, 何满潮, 孙晓明. 大子样岩土随机参数统计方法[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2001, 23(1): 117-119.
SU Yonghua, HE Manchao, SUN Xiaoming. Approach on asymptotic approximations of polynomials for probability density function of geotechnics random parameters[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2001, 23(1): 1 17-119.
[11] 张道兵, 杨小礼, 朱川曲, 等. 基于最大熵原理与最优化方法的隧道衬砌结构可靠度分析[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 43(2): 663-668.
ZHANG Daobing, YANG Xiaoli, ZHU Chuanqu, et al.Structural reliability analysis of tunnel lining based on maximal entropy principle and optimization method[J]. Journal of Central South University(Science and Technology), 2012, 43(2): 663-668.
[12] 李松辉. 基于车辆荷载效应截尾分布的桥梁限载分析方法[J]. 工程力学, 2014, 31(2): 117-124.
LI Songhui. Analytical approach for determining truck weight limits with truncated distributions of live load effects on highway bridges[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2014, 31(2): 117-124.
[13] HUANG Chongfu, SHI Yong. Normal diffusion[M]//Towards Efficient Fuzzy Information Processing. Heidelberg: Physica-Verlag HD, 2002: 191-212.
[14] 宫凤强, 李夕兵, 邓建. 小样本岩土参数概率分布的正态信息扩散法推断[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2006, 25(12): 2559-2564.
GONG Fengqiang, LI Xibing, DENG Jian.Probability distribution of small samples of geotechnical parameters using normal information spread method[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2006, 25(12): 2559-2564.
[15] 周道成, 段忠东, 姚迪, 等. 正态信息扩散法在确定河冰抗压强度概率分布中的应用[J]. 防灾减灾工程学报, 2010, 30(4): 424-430.
ZHOU Daocheng, DUAN Zhongdong, YAO Di, et al.Probability distribution of river ice compressive strength using normal information spread method [J]. Journal of Disaster Prevention and Mitigation Engineering, 2010, 30(4): 424-430.
[16] 徐志军, 郑俊杰, 边晓亚. 基于正态信息扩散原理的路基沉降模糊可靠度分析[J]. 土木工程与管理学报, 2012, 29(3): 28-31.
XU Zhijun, ZHENG Junjie, BIAN Xiaoya. Fuzzy reliability analysis of settlement of subgrade based on normal information spread principle[J]. Journal of Civil Engineering and Management, 2012, 29(3): 28-31.
[17] 黄达, 曾彬, 顾东明. 基于Copula理论的粗粒土渗透破坏临界水力比降估值[J]. 岩土力学, 2015, 36(5): 1253-1260.
HUANG Da, ZENG Bin, GU Dongming. Estimation of critical hydraulic gradient of coarse-grained soils based on Copula theory[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2015, 36(5): 1253-1260.
[18] 黄达, 曾彬, 王庆乐. 粗粒土孔隙比及级配参数与渗透系数概率的相关性研究[J]. 水利学报, 2015, 46(8): 900-907.
HUANG Da, ZENG Bin, WANG Qingle. Study on probabilistic relation between permeability coefficient and void ratio and grain composition of coarse grained soils using Copula theory[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2015, 46(8): 900-907.
[19] 宫凤强, 侯尚骞, 岩小明. 基于正态信息扩散原理的Mohr-Coulomb强度准则参数概率模型推断方法[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2013, 32(11): 2225-2234.
GONG Fengqiang, HOU Shangqian, YAN Xiaoming. Probability model deduction method of Mohr-coulomb criteria parameters based on normal information diffusion principle[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2013, 32(11): 2225-2234.
[20] 史道济. 实用极值统计方法[M]. 天津: 天津科学技术出版社, 2006: 8-9
SHI Daoji. Practical extreme statistical method[M]. Tianjin: Tianjin Science and Technology Press, 2006: 8-9
[21] 王新洲. 基于信息扩散原理的估计理论、方法及其抗差性[J]. 武汉测绘科技大学学报, 1999, 24(3): 240-244.
WANG Xinzhou. The theory, method and robustness of the parameter estimation based on the principle of information spread[J]. Journal of Wuhan Technical University of Surveying and Mapping, 1999, 24(3): 240-244.
[22] 高大钊. 土力学可靠性原理[M]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 1989: 129-130.
GAO Dazhao. Principle of soil mechanics reliability[M]. Beijing:China Construction Industry Press, 1989: 129-130.
[23] 张蕾, 唐小松, 李典庆 基于Copula函数的土体抗剪强度参数二维分布模型[J]. 土木工程与管理学报, 2013, 30(2): 11-17, 36.
ZHANG Lei, TANG Xiaosong, LI Dianqing. Bivariate distribution model of soil shear strength parameter using Copula[J]. Journal of Civil Engineering and Management, 2013, 30(2): 11-17, 36.
[24] 陈永红, 张大发, 王悦民, 等. 基于分形理论的核动力管道腐蚀坑深度预测模型研究[J]. 原子能科学技术, 2009, 43(8): 673-677.
CHEN Yonghong, ZHANG Dafa, WANG Yuemin, et al. Corrosion pit depth prediction model of nuclear power pipeline using fractal theory[J]. Atomic Energy Science and Technology, 2009, 43(8): 673-677.
[25] 王水勇, 任爱. 利用Gumbel极值分布预测管道最大腐蚀深度[J]. 腐蚀科学与防护技术, 2008, 20(5): 358-360.
WANG Shuiyong, REN Ai. Evaluation of maximum corrosion depth of pipe by Gumbel extreme value probability distribution[J]. Corrosion Science and Protection Technology, 2008, 20(5): 358-360.
[26] 周国强, 王雪青, 刘锐. 基于改进广义极值分布的核管道最大腐蚀深度预测[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 44(5): 1926-1931.
ZHOU Guoqiang, WANG Xueqing, LIU Rui.A modified generalized extreme value distribution methodology to predict the maximum corrosion depth of nuclear pipes[J]. Journal of Central South University(Science and Technology), 2013, 44(5): 1926-1931.
[27] 张博庭. 用有限比较法进行拟合优度检验[J]. 岩土工程学报, 1991, 13(6): 84-91.
ZHANG Boting. Goodness-of-fit test with finite comparison method[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 1991, 13(6): 84-91.
(编辑 陈灿华)
收稿日期: 2019 -07 -10; 修回日期: 2019 -09 -22
基金项目(Foundation item):国家自然科学基金资助项目(41102170);中南大学中央高校基本科研业务费专项资金资助项目(2017zzts536) (Project(41102170) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(2017zzts536) supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities of Central South University)
通信作者:宫凤强,博士(后),教授,从事岩土工程可靠度和岩石动力学等研究;E-mail:fengqiangg@126.com