文章编号:1004-0609(2011)09-2168-07
丝束电极研究镀锌层存在点缺陷的锌/钢电偶腐蚀行为
张大磊1, 王 伟2, 金有海1, 唐 晓1, 李 焰1
(1. 中国石油大学(华东) 机电工程学院,东营 257061;2. 中国海洋大学 化学化工学院,青岛 266100)
摘 要:采用3种不同配置比例的锌/碳钢异材质丝束电极,模拟镀锌层存在不同大小点缺陷时的热浸镀钢,研究锌/钢电偶在不同腐蚀阶段的电位和电流密度分布。结果表明,在钢丝与锌丝面积比为1?120、9?112和25?96的3种情况下,锌丝均能给钢丝提供足够的阴极保护,且锌丝之间存在明显的电位、电流分布不均现象,主要阳极区先随机地在邻近钢丝的锌丝区域内转移,而后逐渐向远端锌丝扩展;钢丝之间也存在电化学参数分布不均一现象,钢丝在受到保护的同时表面会有氢原子析出,且随着阴、阳极面积比的增大,析氢电流密度逐渐减小。
关键词:丝束电极;镀锌层;电偶腐蚀;阴极保护;氢析出
中图分类号:TG172.2; TG172.5 文献标志码:A
Wire beam electrode technique for investigating galvanic corrosion behavior of galvanized steel-spot defect
ZHANG Da-lei1, WANG Wei2, JIN You-hai1, TANG Xiao1, LI Yan1
(1. College of Machinery and Electronic Engineering, China University of Petroleum, Dongying 257061, China;
2. College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Ocean University of China, Qingdao 266100, China)
Abstract: Three kinds of wire beam electrodes(WBE) composed of zinc and mild steel wires were developed, which were used to simulate hot-dip galvanized steel with spot coating defect at different dimensions, to obtain the spatial distributions of potential and current density and their variations with time during the galvanic corrosion. The results show that the zinc wires within WBEs can provide enough cathodic protection to steel wires after immersed in seawater, with surface area ratio of zinc wires to steel wires as 1:120, 9:112, and 25:96, respectively. The potential and current density distributions are found to be inhomogeneous among zinc wires; firstly, the main anodic areas shift randomly among the zinc wires adjacent to steel wires, then transfer to the direction away from steel wires, and finally occur on the zinc wires farther. The similar heterogeneous phenomenon also appears on steel wires surface on which hydrogen evolution may take part in the cathodic process occurred. Meanwhile, the current density of water molecule reduction reaction decreases with the ratio of the surface area of steel wires to zinc wires increasing.
Key words: wire beam electrode; zinc coating; galvanic corrosion; cathodic protection; hydrogen evolution
丝束电极(WBE)技术又称为阵列电极技术,是使用一系列排列规则的电极丝组成复合电极来进行电化学参数分布信息测量的新技术。与大面积的单一电极相比,丝束电极能给出前者无法提供的局部信息;而相对于其他微区电化学测试技术(例如扫描振动电极等),丝束电极技术对电极表面的要求较低,尤其在电极表面被腐蚀产物或微生物膜覆盖后,仍可对电极表面电位及电流密度分布进行精确的测量。TAN[1]采用这种特制的电极研究了碳钢腐蚀过程的不均匀性,ZHONG和ZHANG[2]使用丝束电极研究了防锈膜的保护性能,两者取得的成功极大促进了丝束电极技术在微区电化学领域的推广。WANG等[3-4]进一步研制了高速、高精度的NI PXI丝束电极测试系统,并利用此技术研究了微生物膜下不锈钢的腐蚀。然而,以往有关丝束电极的研究多数集中在单种金属或者合金的不均匀腐蚀过程[5-9],实际上,丝束电极技术也能够被用来研究异种金属材料的电偶腐蚀过程。锌/钢电偶对是腐蚀体系最常见的电偶对之一,以锌/钢丝束电极进行电偶腐蚀过程研究,不仅可以获得此电偶对腐蚀发生-发展过程的微区电化学信息,还可以为研究其他异种金属之间的电偶腐蚀问题提供基础。考虑到锌常作为涂层材料对钢材基体进行保护,因此,本文作者采用按不同的锌丝、钢丝配比制备的3种锌/碳钢混合丝束电极,模拟和研究当镀锌层出现不同尺度的点缺陷时,锌/碳钢电偶对表面的电位和电流密度分布,并比较具有不同阴、阳极面积比的混合丝束电极之间的电化学性能差异。
1 实验
1.1 电极制备
实验所用丝束电极的电极丝由直径为0.15 cm的锌丝(纯度为99.95%)及Q235钢丝组成。每个电极所用电极丝均为121根,固定成11行、11列的规则电极阵列,保持电极丝之间的横向和纵向间隔均为0.10 cm。分别按钢丝和锌丝的数量比例为1?120、9?112和25?96进行匹配,并且将钢丝置于电极的正中央,分别构成1×1、3×3和5×5阵列,以模拟镀层出现不同尺度点缺陷时暴露的钢材基体;锌丝则对称地分布在钢丝的四周,以模拟无破损的镀锌层。电极丝之间彼此绝缘,并分别用导线焊接后连接至开关。电极阵列经环氧树脂封装后构成锌/钢-混合丝束电极,以下分别将钢丝阵列为1×1、3×3和5×5的3种丝束电极,分别称为WBE-1×1S、WBE-3×3S和WBE-5×5S。丝束电极的工作面积约2.14 cm2,用水砂纸将工作面逐级打磨至1 000#水砂纸后,用丙酮清洗,干燥后备用。
1.2 电化学测试
电化学测试在室温下进行,电解质为取自青岛海域的清洁海水。丝束电极的电位、电流数据均使用NI PXI电化学自动测试系统进行测量[10-11],参比电极为饱和甘汞电极。测试初期将丝束电极于NI PXI测试系统相连,先保持电极彼此断开,于海水中静置0.5 h,利用阵列开关测得每根电极丝稳定的开路电位后,将其全部短接以进行电偶腐蚀测试。测量电位时,将待测电极丝与其他电极丝断开,测量其相对于参比电极的电极电位,测量过程由NI PXI测试系统中的高速开关自动控制,整个测试过程为6 s;测量电流时,将待测的某根电极丝断开,测量其与其余短接电极丝之间的电偶电流。测量数据由计算机自动记录,其中,负值代表阴极电流,正值代表阳极电流。经后处理得到偶合不同时间的电位、电流的分布图。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 丝束电极的开路电位分布特征
锌/钢混合丝束电极的开路电位分布如图1所示。3种丝束电极在未偶合时表现出一致的电位分布特征:位于电极中央的钢丝的电位较正,分布在-547~-551 mV之间,而位于钢丝四周的锌丝的电位则较负,在-1071~-1078 mV之间。在每种丝束电极中,钢丝与钢丝之间、锌丝与锌丝之间的电位差异均较小,而钢丝和锌丝之间的电位差较大,达530 mV左右。这一结果与ZHANG等[10]在研究镀层划痕型缺陷时所得的开路电位分布特征是一致的,如果在丝束电极的电极丝偶合后,锌丝和钢丝之间的电位差小于此数值,则说明钢丝将处于被锌丝保护的状态[12]。
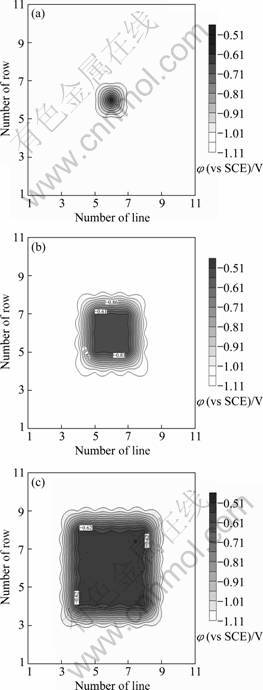
图1 3种锌/钢-混合丝束电极的开路电位分布
Fig.1 Spatial open circuit potential distributions of zinc/steel- WBEs after immersed in seawater for 0.5 h: (a) WBE-1×1S; (b) WBE-3×3S; (c) WBE-5×5S
2.2 WBE-1×1S的电化学参数分布特征
图2所示为WBE-1×1S在电极丝偶合不同时间后的电位及电流密度分布。偶合0.5 h后,钢丝电位由开路电位负移至-892 mV(见图2(a)),由于碳钢在海水中合适的阴极保护电位为-830~-850 mV(vs SCE)[13],所以,在此电位下,碳钢表面很可能也会有氢析出;由图2(b)可知,此时碳钢表面的阴极电流密度为279 μA/cm2,而氧还原反应(四电子还原机理)的极限扩散电流密度通常为50~100 μA/cm2[14-15],因此,除溶解氧还原外,必然还有水分子还原反应参与钢丝表面的阴极过程,即其表面会析出氢原子。随着时间的推移,碳钢的电位在偶合4 h后负移至-945 mV(见图2(d)和(f))。其原因主要在于极化使得电偶腐蚀的驱动力减小,以及电极表面生成的腐蚀产物阻碍了电极反应的进行[16-17],所以钢丝表面的析氢仍不容忽略。

图2 WBE-1×1S表面的电化学参数分布
Fig.2 Spatial electrochemical parameter distributions of WBE-1×1S after being coupled for different times: (a) Potential, 0.5 h; (b) Current density, 0.5 h; (c) Potential, 4 h; (d) Current density, 4 h; (e) Potential, 24 h; (f) Current density, 24 h
锌丝之间存在明显的电化学参数分布不均一现象。偶合0.5 h后,其电位在-1044~-1 101 mV之间,电位差别比偶合前的明显增大,部分锌丝由于表面氧化膜的溶解发生负移[12],另一部分的电位因极化而发生正移;钢丝右上方第7行第7列处锌丝电位最负,电流密度最大,是主要阳极区;大部分锌丝的表面流过阳极电流,也有少数锌丝表面流过阴极电流。偶合24 h后,大部分锌丝流过较小的阴极电流,而电位最负和阳极电流最大的阳极区则集中在距钢丝较远的左下方锌丝上。
2.3 WBE-3×3S的电化学参数分布特征
图3所示为WBE-3×3S模拟镀层出现稍大的点缺陷时,锌/钢电偶对偶合不同时间后微区电化学参数分布。钢丝之间也开始出现电化学不均一现象。偶合0.5 h后,与锌丝紧邻的钢丝电位相对较负,而位于阵列正中央的钢丝电位较正(见图3(a)),说明距锌丝较近的钢丝极化程度较大。随偶合时间延长,钢丝的电位继续负移,24 h时最负电位出现在电极中央的钢丝上(见图3(e))。另外,从电流密度数据看,随偶合时间的延长,钢丝表面的阴极电流密度逐渐减小至62~77 μA/cm2,但仍存在明显的析氢电流。
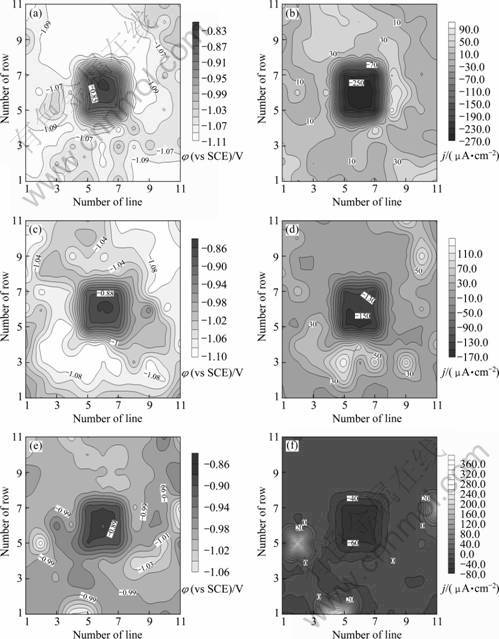
图3 WBE-3×3S表面的电化学参数分布
Fig.3 Spatial electrochemical parameter distributions of WBE-3×3S after being coupled for different times: (a) Potential, 0.5 h; (b) Current density, 0.5 h; (c) Potential, 4 h; (d) Current density, 4 h; (e) Potential, 24 h; (f) Current density, 24 h
锌丝之间虽然存在电化学参数分布不均一现象,但主要阳极区随时间的分布呈现一定的规律性。随着电偶腐蚀过程的进行,主要的阳极区首先在靠近钢丝的周边锌丝上随机地交替转移,而后逐渐向外扩展,最终出现在较远处的部分锌丝上。锌丝的电位先小幅负移,而后正移,在偶合24 h后正移至-912~-1037 mV。这与作者使用丝束电极模拟和研究划痕型镀层缺陷时的锌/钢电偶腐蚀行为是一致的[10]。
2.4 WBE-5×5S的电化学参数分布特征
图4所示为用WBE-5×5S偶合不同时间电化学参数的分布特征。钢丝之间的电化学不均一现象更加明显。偶合0.5 h后,与锌丝紧邻的钢丝电位为最负 (见图3(a));此时碳钢表面的阴极电流分布在182~227 μA/cm2之间,仍然远大于溶解氧还原的极限扩散电流,说明析氢反应依然不可避免(见图3(b))。偶合4 h后,流过其表面的阴极电流开始减小,最大电流出现在电极左侧与锌丝相邻的几根钢丝上(见图3(d))。偶合24 h后,钢丝电位继续负移,流过其表面的阴极电流则进一步减小至32~64 μA/cm2,极化所引起的电偶腐蚀驱动力的减小,是造成阴极电流减小的主要原因(见图3(e)和(f))。
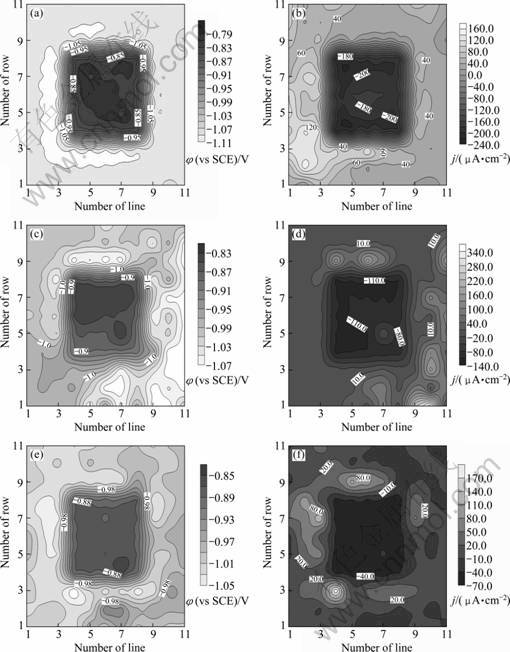
图4 WBE-5×5S表面的电化学参数分布
Fig.4 Spatial electrochemical parameter distributions of WBE-5×5S after being coupled for different times: (a) Potential, 0.5 h; (b) Current density, 0.5 h; (c) Potential, 4 h; (d) Current density, 4 h; (e) Potential, 24 h; (f) Current density, 24 h
如图4所示,锌丝在整个测试过程中,所有锌丝均流过阳极电流。其主要阳极区的转移规律与WBE-3×3S相似。
2.5 锌/钢混合丝束电极的电化学参数分布规律
具有不同阴、阳极面积比的3种锌/钢混合丝束电极表面的电化学参数分布数据表明,在发生电偶腐蚀的过程中,钢丝之间和锌丝之间均存在明显的电化学不均一现象。钢丝的电位发生明显的负移,在测试过程中始终处于被保护的状态;其中,靠近锌丝的钢丝率先极化,电位负移最大,成为主要的阴极区。随着电偶腐蚀的进行,主要阴极区发生转移并不断扩展。图5所示为3种丝束电极中钢丝表面在不同腐蚀阶段的平均电流密度。由图5可见,随着电极中钢丝比例的提高,钢丝表面的电流密度逐渐降低。这表明,随着镀层破损和暴露的钢材基体面积的增加,碳钢表面的析氢反应对阴极电流的贡献逐渐减小。这是由于随着阴、阳极面积比的不断提高,电偶电位正移,碳钢表面的析氢反应减弱造成的[18]。

图5 钢丝表面在偶合不同时间后的平均电流密度
Fig.5 Average cathodic current density of carbon steel wires within zinc/steel-WBEs at different coupling times
对于锌丝而言,其表面电位基本符合先负移、后正移的规律,腐蚀初期的主要阳极溶解区出现在钢丝周边距离较近的局部锌丝区域内,随着腐蚀的进行,主要阳极区在钢丝周边的锌丝上随机转移并逐渐向远端扩展。表1所列为与钢丝阵列相邻的最近一圈锌丝在不同腐蚀阶段的平均电流密度。由表1可见,当缺陷尺度很小时,钢丝周边最近一圈锌丝的平均电流始终维持在较低水平,因为此时所需的保护电流较小。当缺陷尺度增大(WBE-3×3S)时,在腐蚀初期,钢丝周边最近一圈锌丝为主要阳极区;随着腐蚀的进行,主要阳极区逐渐外移,交界处锌丝平均电流迅速减小;当偶合24 h后,钢丝周边最近一圈锌丝变为局部阴极区。当缺陷尺度进一步增大(WBE-5×5S),由于所需保护钢丝数量的增加和能提供保护电流的锌丝数量的减少,钢丝阵列周边最近一圈锌丝的阳极电流密度始终维持在相对较高水平。
表1 钢丝周边最近一圈锌丝在不同腐蚀阶段的平均电流密度
Table 1 Average current density of the nearest zinc wire cycle around steel wires at different coupling time

由本研究可知,丝束电极技术是研究异种金属之间电偶腐蚀的一种有效手段,具有一定的推广应用价值。它同样也可以用来研究其他异种金属之间的电偶腐蚀问题。由于该技术在电极表面被腐蚀产物或各种膜覆盖后仍可对电位及电流密度分布进行精确的测量,在工业领域也会有较为广泛的应用。
3 结论
1) 具有不同阴、阳极面积比的锌/钢-混合丝束电极表面的电化学参数分布表明,在电偶腐蚀的过程中,钢丝之间和锌丝之间都存在着电位和电流密度分布不均匀的现象。
2) 当镀锌层存在点缺陷时,镀层能够给暴露在海水中的钢材基体提供有效的阴极保护,其主要的阳极溶解区由靠近碳钢的区域逐渐向远端扩展;水分子将与溶解氧共同参与钢材表面的阴极过程并导致氢的析出,且阴极电流密度随暴露钢材基体面积的比例增大而逐渐减小。
REFERENCES
[1] TAN Y J. An experimental comparison of three wire beam electrode based methods for determining corrosion rates and patterns [J]. Corrosion Science, 2005, 47(7): 1653-1665.
[2] ZHONG Q D, ZHANG Z. Study of anti-contamination performance of temporarily protective oil coatings using wire beam electrode[J]. Corrosion Science, 2002, 44(12): 2777-2787.
[3] WANG W, LU Y H, ZHANG X, WANG J. The heterogeneous electrochemical characteristics of mild steel in the presence of local glucose—A study by the wire beam electrode method[J]. Corrosion Science, 2010, 52(3): 810-816.
[4] WANG W, ZHANG X, WANG J. The influence of local glucose oxidase activity on the potential / current distribution on stainless steel: A study by the wire beam electrode method [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2009, 54(23): 5598-5604.
[5] FUSHIMI K, NAGANUMA A, AZUMI K, KAWAHARA Y. Current distribution during galvanic corrosion of carbon steel welded with type-309 stainless steel in NaCl solution [J]. Corrosion science, 2008, 50(3): 903-911.
[6] TAN Y J, FWU Y, BHARDWAJ K. Electrochemical evaluation of under-deposit corrosion and its inhibition using the wire beam electrode method [J]. Corrosion Science, 2011, 53(4): 1254-1261.
[7] LEGAT A. Monitoring of steel corrosion in concrete by electrode arrays and electrical resistance probes [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2007, 52(27): 7590-7598.
[8] 张 伟, 王 佳, 李玉楠, 王 伟. WBE联合EIS技术研究缺陷涂层下金属腐蚀[J]. 物理化学学报, 2010, 26(11): 2941-2950.
ZHANG Wei, WANG Jia, LI Yu-nan, WANG Wei. Evaluation of metal corrosion under defective coatings by WBE and EIS technique [J]. Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica, 2010, 26(11): 2941-2950.
[9] 王巧玲, 黄桂芳. 用丝束电极研究NaNO2对钢铁防护性能的影响[J]. 中南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2008, 39(2): 317-321.
WANG Qiao-ling, HUANG Gui-fang. Effect of sodium nitrite on corrosion of mild steel by using wire beam electrode [J]. Journal of Central South University: Science and Technology, 2008, 39(2): 317-321.
[10] ZHANG D L, WANG W, LI Y. An electrode array study of electrochemical inhomogeneity of zinc in zinc/steel couple during galvanic corrosion [J]. Corrosion Science, 2010, 52(4): 1277-1284.
[11] ZHANG X, WANG W, WANG J. A novel device for the wire beam electrode method and its application in the ennoblement study [J]. Corrosion Science, 2009, 51(6): 1475-1479.
[12] YADAV A P, KATAYAMA H, NODA K, MASUDA H, NISHIKATA A, TSURU T. Surface potential distribution over a zinc/steel galvanic couple corroding under thin layer of electrolyte[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2007, 52(9): 3121-3129.
[13] TANG X, ZHANG Y Z, LIU M, LI Y. BEM analysis for galvanic corrosion of galvanized steel in seawater[J]. Journal of Material Science and Technology, 2009, 25(2): 194-198.
[14] ADZIC R. Electrocatalysis[M]. LIPKOWSKI J, ROSS P N, eds. New York: Wiley-VCH, 1998: 197.
[15] VUKMIROVIC M B, VASILJEVIC N, DIMITROV N, SIERADZKI K. Diffusion-limited current density of oxygen reduction on copper [J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2003, 150(1): B10-B15.
[16] SALVAGO G, BOLLINI G. Localized corrosion probability in stainless steels after cathodic protection in seawater [J]. Corrosion, 1999, 55(4): 397-404.
[17] TAHARA A, KODAMA T. Corrosion inhibition at galvanized steel cut edges by phosphate pigments [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2009, 54(15): 3857-3865.
[18] 张大磊, 李 焰. 湿度对热镀锌钢材在海洋大气环境中氢脆敏感性的影响[]J. 中国有色金属学报, 2010, 20(3): 476-482.
ZHANG Da-lei, LI Yan. Effect of humidity on hydrogen embrittlement susceptivity of hot-dip galvanized steel exposed to simulated marine atmosphere[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2010, 20(3): 476-482.
(编辑 何学锋)
基金项目:山东省自然科学基金资助项目(Y2008E09);中国博士后基金资助项目(20100471577)
收稿日期:2010-09-28;修订日期:2011-03-26
通信作者:李焰,教授,博士;电话:0532-86981224;E-mail:yanlee@upc.edu.cn