文章编号:1004-0609(2008)01-0090-06
电沉积工艺对镀锌层的表面形态及
电化学性能的影响
张 辉,朱立群,韩永祥
(北京航空航天大学 材料科学与工程学院,北京 100083)
摘 要:采用电沉积技术制备几种电沉积式锌电极,考察镀液中KOH浓度和沉积电流密度对所制得镀锌层的微观形貌与性能的影响规律。结果表明:镀锌层的枝晶随着KOH浓度(250~400 g/L)的增加而变得粗大,且其析氢量、腐蚀电位和腐蚀电流密度均呈现先减小而后增加的趋势;随着电流密度(25~100 mA/cm2)的增长,镀锌层由块状结晶向枝晶转变,相应地电极反应活性随之增大,而耐蚀性则随之变差,并发现沉积电流密度为75 mA/cm2时,锌电极的综合性能最好,以200 mA/g充放电循环10周次,其放电容量仍可达504 mA?h/g。解释了主要工艺参数对结晶形态及电极性能影响的原因,并说明适当的KOH浓度和沉积电流密度有利于提高电极的综合性能。
关键词:锌电极;镀锌层;电沉积;微观形貌;循环寿命
中图分类号:TM 912.2; TQ 153.1 文献标识码:A
Effect of electrodeposited process on surface morphology and electrochemical performance of galvanization coating
ZHANG Hui, ZHU Li-qun, HAN Yong-xiang
(School of Material Science and Engineering, Beihang University, Beijing 100083, China)
Abstract: Several electrodeposited zinc electrodes were prepared by electrodeposition technique in order to investigate the influence of the concentration of KOH and current density on the micrograph and performance of galvanization coating. The results show that the dendritic deposits become bulky as the concentration of KOH (250?400 g/L) increases. Moreover the amount of hydrogen gas evolution, corrosion potential and corrosion current initially decrease and then increase. With increasing of current density (25?100 mA/cm2), the massive crystal grains of galvanization coating gradually change into dendritic formation, the reaction active of zinc electrode is accordingly raised and the property of corrosion resistance is depressed. In addition, it is found that the galvanization coating exhibits the best electrochemical and discharge performance when the current density is 75 mA/cm2. Its discharge capacity at the 10th charge-discharge cycle with a current of 200 mA/g achieves 504 mA?h/g. The influence of chief process parameters on the morphology and properties of galvanization coating is also explained and it is confirmed that the appropriate concentration of KOH and current density are beneficial to improve the integrative performance of zinc electrode.
Key words: zinc electrode; galvanization coating; electrodeposition; micromorphology; cyclic life
二次碱性锌基电池[1?4]具有能量密度高及无环境污染等优良性能,因而被广泛的应用在航空、军事、能源等各个领域,但作为锌基电池的负极,锌电极存在着自放电[5?6]、循环寿命较短[7?9]等主要问题而限制其实际应用。众所周知,锌电极的制备方法极大地影响着电池的性能和使用范围,其主要制造方法有烧结式、压成式、涂膏式和电沉积式[10]。其中,压成式制备工艺简单,但电极成型比较困难,强度差,寿命短,一般只用于一次电池;烧结式是以电解锌粉为原料加压成型,所形成的电极强度好,但仅用于高速率放电的一次电池;涂膏式所制备的电极是通过粘结剂将氧化锌粉和金属锌粉调成膏状,涂在集流体上模压成型的,一般可用于一次或二次电池,但电极的活性和强度均达不到烧结式锌电极的程度,且其比能量和比功率受到限制;电沉积式锌电极[11?12]是一种活性很高、比表面积很大、应用领域较广的锌电极,它是采用电沉积技术直接在集流体上沉积锌层,所制备出的电极薄而坚固。电沉积式锌电极上的镀锌层的物理化学性能与电沉积工艺条件有着密切的关系[13],即随着电沉积工艺参数的变化而相应的适用于一次或二次电池。
然而,电沉积式锌电极上的镀锌层活性较高,将使得电极自放电现象较为严重,而镀锌层活性较差又会影响电池的使用寿命和放电性能,因此需要对电沉积工艺参数调整,使得电极既可以保持较高的活性,具有较好的放电性能和循环寿命,又使得镀锌层的自放电现象得到缓解,从而提高锌电极的综合电化学性能。随着电池装置高密度化的要求,电极由整体型向薄膜型转化,这也充分体现了电沉积式锌电极研究的必要性,尤其是电沉积工艺条件对镀锌层影响规律研究的重要性。本文作者通过电沉积技术在泡沫镍表面镀上锌层,考察电解液浓度和电流密度对镀锌层的微观形貌和电化学性能的影响,获得适用于二次锌基电池的电沉积式锌电极,为进一步提高锌电极性能的研究提供基础。
1 实验
1.1 电沉积式锌电极的制备
将40 mm×70 mm的片状泡沫镍作阴极,银丝作挂具,两块50 mm×80 mm的锌板作阳极,沉积电镀液为含有饱和ZnO的KOH溶液,沉积电流密度为100 mA/cm2,沉积1 h。然后将镀有金属锌的泡沫镍极板在自来水下冲洗,并多次用蒸馏水浸洗,以去除极板中的OH?,将洗干净的极板放入真空干燥箱内,在 100 ℃下烘干后,自然冷却到室温,取出极板放入模具中,并在压片机上以50 MPa加压成型,制成电沉积式锌电极。实验中,将电镀液中的KOH浓度分别设为250、300、350和400 g/L,制得不同的电沉积式锌电极。另外,在KOH浓度为250 g/L及其它条件相同时,沉积电流密度分别设为25、50、75和100 mA/cm2,以考察沉积电流密度对电极性能的影响。
1.2 分析与测试
通过JSM?5800型扫描电镜观察了不同KOH浓度和不同沉积电流密度下制成的电沉积式锌电极的表面形态。利用锌在碱液中的自放电与氢气的析出是一对共轭反应的原理,自制了析氢装置,其结构示意图如图1所示。测试电沉积式锌电极在45 ℃恒温水浴箱中的析气量,以考察其自放电性能。采用三电极体系对电沉积式锌电极进行Tafel极化曲线的测试,工作电极为电沉积式锌电极,表观面积为1 cm2,辅助电极为大片镍电极,参比电极为Hg/HgO电极,电解液为含有饱和ZnO的6 mol/L KOH溶液,曲线的扫描范围为?1.7~?1.0 V,扫描速度为0.5 mV/s。
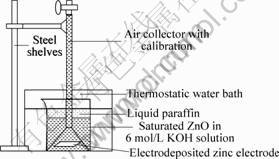
图 1 析氢装置示意图
Fig.1 Schematic diagram of apparatus for measuring hydrogen gas evolution
1.3 电池实验
用一片30 mm×60 mm的电沉积式锌电极为负极,正极为两片镍电极(商业品),正极容量较负极过量,隔膜为耐碱棉纸,电解液采用含有少量LiOH的6 mol/L KOH溶液,组装成模拟锌镍电池,研究不同沉积电流密度所制得的电沉积式锌电极的放电性能。恒电流充放电实验中,循环充放电制式为200 mA/g的电流充电10 h,搁置20 min,然后以相同的电流放电至0.9 V。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 KOH浓度的影响
电沉积电流密度为100 mA/cm2时,不同KOH浓度镀锌层的表面形貌如图2所示。由图可知,在不同KOH浓度下制得的电沉积式锌电极均呈现树枝状的结晶形态。当KOH浓度为250和300 g/L时锌枝晶较为细小,这使得锌电极上沉积的锌粉的比表面积较大,活性较高,有利于锌电极充放电反应的进行。KOH浓度继续增大时,电沉积出锌粉的颗粒较粗大,而不利于锌电极的充放电。
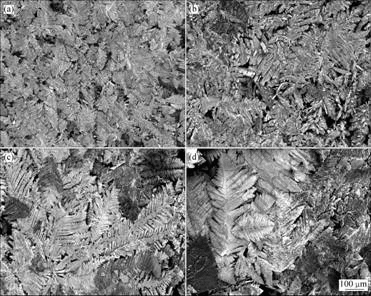
图 2 不同KOH浓度下电沉积式锌电极的SEM照片
Fig.2 SEM images of electrodeposited zinc electrodes with different concentrations of KOH: (a) 250 g/L; (b) 300 g/L; (c) 350 g/L; (d) 400 g/L
图3所示为沉积电流密度为100 mA/cm2时,不同KOH浓度所制得的几种电沉积镀锌层在48 h后的析氢量。利用塔菲尔极化曲线考察不同KOH浓度得到的电沉积式锌电极的极化性能,结果如图4所示,并由Tafel曲线外推法得出表1所列的数据。
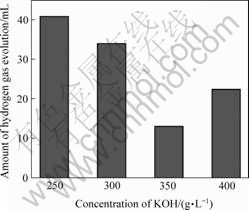
图 3 KOH浓度对镀锌层析氢量的影响
Fig.3 Effects of concentration of KOH on amounts of hydrogen gas evolution for galvanization coating
由图3可知,在不同的KOH浓度下制得的电沉积式锌电极的析氢量由大到小的顺序为:250 g/L>300 g/L>400 g/L>350 g/L。说明镀锌层抑制阴极析氢反应来减缓锌粉自放电能力是先增强而后又有所降低的。从图4和表1可以看出,随KOH浓度的增大,这几种锌电极的腐蚀电位φcorr和腐蚀电流密度Jcorr的变化与析氢量的结果一致。即φcorr和Jcorr均先随KOH浓度的增加而减小,当KOH浓度增大到350 g/L时达到最小,说明此时锌电极的耐蚀性最好,电极活性最差。而后继续增大KOH浓度,φcorr和Jcorr均有所回升。说明OH?浓度过大和过小均有利于提高锌电极的反应活性,但却不利于抑制镀锌层的自放电,即适当的OH?浓度有利于提高锌电极的综合性能。
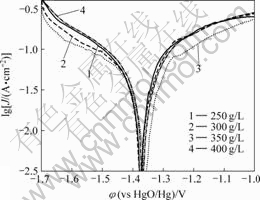
图 4 不同KOH浓度得到的电沉积式锌电极的极化曲线
Fig.4 Polarization curves of electrodeposited zinc electrodes with different concentrations of KOH
表 1 不同KOH浓度得到的电沉积式锌电极的Tafel曲线参数
Table 1 Parameters of Tafel curves for electrodeposited zinc electrodes with different concentrations of KOH

这是由于随着OH?浓度的增大,浓差极化加剧,晶核的形成速度降低,锌枝晶趋向于长大,使得镀锌层的比表面积变小,从而电极活性变差,耐蚀性变好。但当OH?浓度过大时,镀液的分散能力和覆盖能力变化较小,浓差极化的影响较小,在相同沉积时间下沉积出锌粉的量较多,从而提高电极的活性,使腐蚀电流密度升高。
2.2 沉积电流密度的影响
KOH浓度为250 g/L时,不同沉积电流密度制得的电沉积式锌电极的微观形貌如图5所示。由图5可知,电流密度为25 mA/cm2时,镀在泡沫镍上的锌以块状结晶,且由于电流密度过小,不能在泡沫镍的孔隙处均匀填充。当电流密度增大到50和75 mA/cm2时,锌电极的表面形态为树枝晶和苔状晶的混合,这有利于锌电极的充放电。而当电流密度继续增大到100 mA/cm2时,锌电极的表面则完全由树枝晶组成。说明随着电流密度的增长,沉积的锌是由块状逐渐向枝晶状转变。

图 5 电流密度对镀锌层表面形貌的影响
Fig.5 Effects of current density on surface morphology of galvanization coating: (a) 25 mA/cm2; (b) 50 mA/cm2; (c) 75 mA/cm2; (d) 100 mA/cm2
根据电沉积理论,电沉积过电位ηk与电流密度J具有如下关系:

式中 A和B是常数。由此可知,电流密度越大,过电位就越高,电化学极化作用就越大。一般情况下,电流密度过低时,电化学极化作用较小,晶核的形成速度慢,而成长速度快[14],这使得镀层结晶以垂直方向生长。因而,在25 mA/cm2的沉积电流密度下所制得的镀锌层呈块状结晶,并且由于形成晶核的数目少而不能完整均匀的覆盖泡沫镍集流体表面。增大电流密度时,电化学极化增大,锌结晶的成核速度开始远大于生长速度[15],这使得沉积的锌以二维形式生长,从而锌结晶为树枝晶和苔状晶的混合,有效提高了电极的活性。当增大沉积电流密度到一定值时(极限电流密度),阴极附近严重缺乏放电金属离子,放电离子能达到的部分晶面也就是棱角和突出部分还能继续长大,从而导致镀锌层呈现二维或三维的枝晶状。
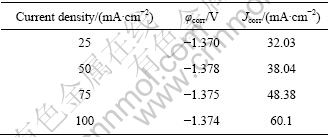
图6和7所示分别为不同沉积电流密度下,电沉积式锌电极48 h的析氢量和Tafel极化曲线。表2所列为由极化图得到的电化学参数。由图6可知,电流密度为25 mA/cm2时,镀锌层的析氢量较大,这与电极表面的孔隙过大有关。当电流密度从50 mA/cm2时,电极析氢量最小为18.3 mL,有效抑制了锌电极的自放电。此后随着电流密度的增大,电极的析氢量增大。从图7和表2可知,通过不同沉积电流密度制得的几种电沉积式锌电极的φcorr几乎没有差别,而Jcorr变化较大,其顺序由大至小依次为:25 mA/cm2<50 mA/cm2<75 mA/cm2<100 mA/cm2,说明锌电极的反应活性随着电流密度的增大而增大,但正由于锌电极的电化学活性高而使得锌电极的耐蚀性随之变差,这与电沉积式锌电极的微观形貌是相对应的。而且对比图4得知,电流密度对镀锌层的自放电与活性的影响比KOH浓度的大。
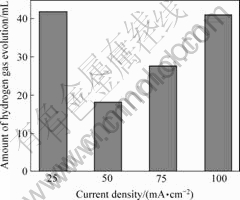
图 6 不同电流密度时刻得的电沉积式锌电极的析氢量
Fig.6 Amounts of hydrogen gas evolution for electrodeposited zinc electrode under different current densities

图 7 电流密度对电沉积式锌电极极化性能的影响
Fig.7 Effects of current density on polarization performance of electrodeposited zinc electrodes
表 2 不同电流密度得到的电沉积式锌电极的Tafel极化曲线参数
Table 2 Parameters of Tafel curves for electrodeposited zinc electrodes with different current density
2.3 锌电极的放电性能
图8所示为沉积电流密度分别为25、50、75和100 mA/cm2时所制得的电沉积式锌电极的放电容量随循环周期的变化曲线。由图可知,当沉积电流密度为100 mA/cm2时,电沉积式锌电极最初的放电容量很大,但容量衰减较快,循环寿命很短,这是由于生成的锌枝晶使锌电极具有较高的活性,但同时枝晶的生长也易于迅速的降低电极的循环寿命。虽然沉积电流密度下75 mA/cm2时所制得的电沉积式锌电极的起始放电容量小于100 mA/cm2时制备的,但是随着循环的进行,锌电极的电性能较为稳定,第10次放电时放电容量仍可达504 mA?h/g,而且循环寿命很高,说明该镀锌层具有高效长久的放电性能,这也充分的说明了树枝晶和苔状晶混合的镀锌层具有最好的电极综合性能,从而可以满足一般用电设备的使用要求。
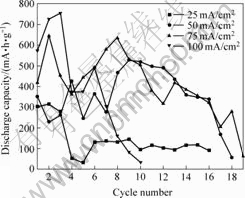
图 8 不同电流密度所得的电沉积式锌电极的放电容量变化曲线
Fig.8 Curves of discharge capacity change for electro- deposited zinc electrodes with different current density
REFERENCES
[1] Hariprakash B, Martha S K, Shukla A K. Galvanostatic non-destructive characterization of alkaline silver-zinc cells[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2003, 117: 242?248.
[2] Iwakura C, Murakami H, Nohara S, Furukawa N, Inoue H. Charge-discharge characteristics of nickel/zinc battery with polymer hydrogel electrolyte[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2005, 152: 291?294.
[3] Lee C W, Sathiyanarayanan K, Eom S W, Yun M S. Novel alloys improve the electrochemical behavior of zinc anodes for zinc/air battery[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2006, 160: 1436?1441.
[4] Espinosa D C R, Bernardes A M, Tenório J A S. An overview on the current processes for the recycling of batteries[J]. Journal Power Sources, 2004, 135: 311?319.
[5] Shunji W, Tsugio S, Hideo S. Alkaline battery without mercury and electronic apparatus powered thereby. US 6723469[P]. 2004.
[6] Martin G Perez, Edward A Kenik, Matthew J O’Keefe, F Scott Miller, Benedict Johnson. Identification of phases in zinc alloy powders using electron backscatter diffraction[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2006, 424: 239?250.
[7] YANG Han-xi, CAO Yu-liang, AI Xin-ping, XIAO Li-fen. Improved discharge capacity and suppressed surface passivation of zinc anode in dilute alkaline solution using surfactant additives[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2004, 128: 97?101.
[8] 张 春, 王建明, 张 昭, 张鉴清, 曹楚南. 钙添加剂对可充锌电极性能的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2001, 11(5): 780?784.
ZHANG Chun, WANG Jian-ming, ZHANG Zhao, ZHANG Jian-qing, CAO Chu-nan. Effects of calcium additive on performance of pasted zinc electrode[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2001, 11(5): 780?784.
[9] Zheng Y, Wang J M, Chen H, Zhang J Q, Cao C N. Effects of barium on the performance of secondary alkaline zinc electrode[J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2004, 84: 99?106.
[10] 陈 军, 陶占良, 苟兴龙. 化学电源——原理、技术与应用[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2006: 104?112.
CHEN Jun, TAO Zhan-liang, GOU Xing-long. Chemistry power—Principle, technology and application[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2006: 104?112.
[11] 冯绍彬, 包 祥, 刘 清, 魏辉强, 潘 军. 电沉积锌合金电极的制备及其性能[J]. 电源技术, 2006, 130(10): 822?825.
FENG Shao-bin, BAO Xiang, LIU Qing, WEI Hui-qiang, PAN Jun. Study on performance and preparation of electrodeposited zinc alloy electrode[J]. Chinese Journal of Power Source, 2006, 130(10): 822?825.
[12] 陈雪梅, 刘 春, 裴 东, 景义军. 电沉积锌电极的性能[J]. 电源技术, 2005, 29(12): 816?818.
CHEN Xue-mei, LIU Chun, PEI Dong, JING Yi-jun. Study on performance of electrodeposited zinc electrode[J]. Chinese Journal of Power Source, 2005, 29 (12): 816?818.
[13] 朱立群, 潘 波. 电沉积结晶形态研究进展[J]. 材料保护, 2007, 37(9): 30?32.
ZHU Li-qun, PAN Bo. Review on the development for crystal morphology of electrodeposition[J]. Materials Protection, 2007, 37(9): 30?32.
[14] 朱立群. 功能膜层的电沉积理论与技术[M]. 北京: 北京航空航天大学出版社, 2005: 21?42.
ZHU Li-qun. Theory and technology of electrodeposition for functional layer[M]. Beijing: Beihang University Press, 2005: 21?42.
[15] 朱晓东, 李 宁, 黎德育, 刘伟华, 李 伟. 高速电镀工艺对镀层粗糙及微观形貌的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2005, 15(1): 145?151.
ZHU Xiao-dong, LI Ning, LI De-yu, LIU Wei-hua, LI Wei. Influence of technology of high-speed galvanization on roughness and micromorphology of coating[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2005, 15(1): 145?151.
收稿日期:2007-06-20;修订日期:2007-10-12
通讯作者:朱立群,教授,博士;电话:010-82317133;E-mail: zhulq@buaa.edu.cn
(编辑 龙怀中)