文章编号:1004-0609(2011)06-1485-06
嗜酸氧化亚铁硫杆菌表面双电层电势分布模拟
王兆慧1,谢学辉1,柳建设1, 2
(1. 东华大学 环境科学与工程学院,上海 201620;
2. 中南大学 资源加工与生物工程学院,长沙 410083)
摘 要:采用离子可透过模型和不可透过模型,通过数值拟合的方法计算嗜酸氧化亚铁硫杆菌的表面电荷密度、空间电荷密度、表面电位和道南电位等。Zeta电位测定结果表明:以硫为能源培养的细菌细胞等电点(IEP)高于报道的以亚铁培养的细菌的。运用表面基团离子化模型模拟实验数据得出:以硫培养的嗜酸氧化亚铁硫杆菌的 IEP>2,这主要是由细菌表面蛋白质的氨基电离引起的。采用离子可透过模型分析表明:pH<5时,细菌表面电位(φ0)和道南电位(φDON)下降较快;细菌表面的pH值等于细胞内的pH(约6~7)后,细菌的φ0和φDon的变化渐缓;计算得到细菌表面的双电层的厚度约为5 nm。细菌表面的双电层将影响浸矿体系中离子迁移和营养物质传输,而细菌彼此表面双电层的相互作用对细菌聚集不利。
关键词:双电层;道南电位;离子可透过模型;软颗粒
中图分类号:TF18 文献标志码:A
Numerical modeling of potential profiles in electrical double layer of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans cell surface
WANG Zhao-hui1, XIE Xue-hui1, LIU Jian-she1, 2
(1. College of Environmental Science and Engineering, Donghua University, Shanghai 201620, China;
2. School of Resources Processing and Bioengineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: The surface charge density, space charge density, surface potential (φ0) and Donnan potential (φDon) on the surface of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans cultivated with elemental sulfur (S-A.ferrooxidans) were calculated by numerical simulation using the ion-impenetrable and ion-penetrable models. Zeta potential measurement show that the isoelectric point (IEP) of S-A.ferrooxidans is higher than that of bacterium cultured with Fe2+. It is concluded from fitting data by ionizable surface group model that S-A.ferrooxidans surface probably consists of much proteins, the ionization of amino group of which causes higher IEP (>2). The ion-penetrable model reveals that φ0 and φDon decrease rapidly at pH<5 but hardly change when pH is 6-7. The thickness of electrical double layer of S-A.ferrooxidans is estimated as 5 nm. The electrical double layer of bacterial cell surface may have significant implications for ions transfer and nutrient transport, but their interaction is unfavorable for bacterial aggration.
Key words: electrical double layer; Donnan potential; ion-impenetrable model; soft particle
嗜酸氧化亚铁硫杆菌(Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans, 简称为A. ferrooxidans)是硫化矿微生物浸出过程中广泛应用且研究最为深入的浸矿细菌[1-2]。它是一种嗜酸性化能自养细菌,可以通过氧化亚铁 离子与硫单质或含硫化合物获得能量生长[3]。A. ferrooxidans属革兰氏阴性菌,细菌细胞壁由脂聚糖、脂蛋白、细菌表面蛋白质等组成,其中的羧基 (—COOH)、氨基(—NH2)和羟基(—OH)官能团质子化或去质子化使得细菌带电[4]。由于A.ferrooxidans表面带电,在溶液中吸附溶液离子在其表面,形成吸附双电层。然而,以前的研究往往忽视了细菌表面双电层的存在,事实上双电层的形成对于细菌与固体表面的吸附、金属离子的吸附以及细胞的聚集都有重要的影 响[5];同时,应用DLVO或扩展DLVO理论来计算细菌与矿物作用的吸附能时,也必须考虑到双电层的存在对总吸附能ΔG的贡献[6]。由此可见,研究细菌表面双电层电势分布规律对于揭示细菌吸附规律和营养元素(如Fe2+和S2-)的摄入机理有重要的意义。
与胶体类似,细菌表面双电层结构也与溶液电解质、pH和表面形态等环境因素密切相关[7],同时也会随着表面成分的变化而改变。DEVASIA等[8]研究发现,生长在固体基质上的氧化亚铁硫杆菌细胞表面蛋白质含量远高于液体中培养的细菌的,将其用蛋白酶K处理后,硫中生长的细胞电动行为与液体培养的细菌相似,由此证明细菌表面蛋白质含量对细胞电性质的改变。本文作者在此基础上研究了以硫单质培养的嗜酸氧化亚铁硫杆菌表面双电层电势分布的变化。通过数值拟合的方法分别计算了离子可透过模型和不可透过模型中细菌的表面电荷密度、空间电荷密度、表面电位和道南电位等。
1 实验
1.1 实验菌株
实验A.ferrooxidans菌株样品采自湖南株洲某废水厂,采用9K无机盐培养基,以FeSO4·7H2O (80 g/L)为能源对细菌进行富集培养[9]。具体操作如下:将已配好的9K培养基100 mL分别装入5个250 mL锥形瓶中,然后分别向其中加入8 g FeSO4·7H2O。用移液管移取10 mL原废水至各锥形瓶后,用体积比1:1的硫酸调节溶液pH至2.0,置于空气浴振荡器中恒温培养(30 ℃, 160 r/min)。待锥形瓶中培养基由浅绿色转为红棕色后,选择5瓶中颜色最深的继续扩大培养,传代3次后接种5 mL菌种至100 mL 9K无机盐培养基中,加入1.0 g升华硫粉30 ℃恒温培养。
1.2 实验试剂
实验中使用的NaCl为优级纯,硫粉为化学纯,其它试剂均为分析纯。实验所用溶液均由二次蒸馏水配制。
1.3 实验方法
以硫粉为能源的细菌生长达到对数期后,取50 mL离心管分装培养液,在1 000 r/min下低速离心分离1 min,除去溶液中悬浮的硫粉。然后取上清液在 4 000 r/min高速下离心分离25 min后弃去上清液,反复用双蒸水吹洗离心3次,最后获得蒸馏水中的细胞悬浮液。向离子强度为 0.1 mol/L NaCl溶液加入制备好的细胞悬浮液,用HCl和NaOH调整悬浮液的pH值,在磁力搅拌器上搅拌30 min,然后在Delsa 440S II Zeta电位测定仪上测定细菌Zeta电位。为保证实验结果的精度,每个样品的pH值重复测3次以上,直到有3个值互相接近为止。实验数据的数值拟合通过Origin 7.0软件的非线性拟合功能模块实现。
2 结果与分析
2.1 细菌的Zeta电位
溶液的pH影响细菌表面各种官能团的电离,从而影响细菌表面电荷的情况。在研究Zeta电位时,通常采用等电点(IEP)来反映了阴离子和阳离子酸-碱基团之间的平衡。图1所示为溶液离子强度为0.1 mol/L时pH 2.5~10.5范围内细菌Zeta电位的变化曲线。由图1可知,以单质硫为能源培养的A.ferrooxidans的等电点(IEP)为3.8,这与亚铁为能源培养的A.ferrooxidans明显不同。Devasia等[8]曾经研究过以黄铁矿、黄铜矿、硫粉和亚铁为基质培养的A.ferrooxidans的电泳行为,结果发现,所有在以固体能源培养的细菌的IEP都大于液体中培养的细菌的IEP。通过FTIR证实,前者表现出大量的氨基基团,即—NH2的电离可能是细菌在pH小于3.8时带正电的原因。
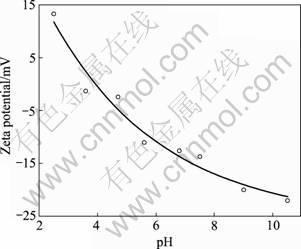
图1 离子强度为0.1 mol/L时单质硫培养的A.ferrooxidans菌的Zeta电位与溶液pH的关系
Fig.1 Relationship between Zeta potential of A.ferrooxidans cultivated with elemental sulfur and pH of solution at ion strength of 0.1 mol/L
2.2 细菌表面的双电层模型
通过测定细菌的电泳行为来推导细菌表面的双电层结构的有关信息是个简单而有效的方法。但是细菌不是由简单、均匀的分子组成,有时能改变外形,细胞内的新陈代谢也会改变其表面组成,如细菌胞外多聚物的分泌。因此,细菌是个形体不规则、动态变化、组成复杂的开放系统[4]。为了数学上处理方便,有必要将细菌的表面进行简化。本文作者采用离子不可透过和离子可透过模型分别对单质硫培养的A.ferrooxidans菌的双电层结构进行模拟分析。
2.2.1 离子不可透过模型
简化方法认为,细菌是个表面存在生物大分子的胶体颗粒,表面所带的电荷完全集中分布在其外层表面。此时,用古依-切普曼-斯特恩(GCS)双电层模型可以来描述细菌的表面双层结构。表面电荷密度(σ0)的计算公式如下[10]:
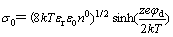 (1)
(1)
式中: 为相对介电常数;
为相对介电常数;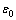 为真空介电常数;n0为离子数量;z为离子价;k为玻尔兹曼常数;T为绝对温度;e为电子电量;φd为分散层电位。将Zeta电位近似等于表面的分散层电位φd,根据所得的Zeta电位pH关系绘出σ0—pH的曲线。在离子不可透过模型中认为细菌表面电荷集中在表面极薄的一层,或者认为表面电荷固定在表面生物大分子的延伸长度内。根据文献[4]可知,革兰氏阴性菌具有较薄的肽聚糖层,厚度为1~2nm。本模拟中这层膜的平均厚度取为l=1.5 nm,于是可以近似得到固定空间电荷密度(
为真空介电常数;n0为离子数量;z为离子价;k为玻尔兹曼常数;T为绝对温度;e为电子电量;φd为分散层电位。将Zeta电位近似等于表面的分散层电位φd,根据所得的Zeta电位pH关系绘出σ0—pH的曲线。在离子不可透过模型中认为细菌表面电荷集中在表面极薄的一层,或者认为表面电荷固定在表面生物大分子的延伸长度内。根据文献[4]可知,革兰氏阴性菌具有较薄的肽聚糖层,厚度为1~2nm。本模拟中这层膜的平均厚度取为l=1.5 nm,于是可以近似得到固定空间电荷密度( ):
):
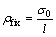 (2)
(2)
根据所得的固定空间电荷密度表面基团离子化模型[11-12](Ionizable surface group model)可以反推细菌表面的荷电基团情况。这个模型认为,固定空间电荷密度由酸/碱基团解离/结合平衡关系所决定。设细菌表面含N1个不带电酸基团和N2个不带电碱基团,其单位体积的解离常数分别为Ka1和Ka2,则固定空间电荷密度(ρfix)可表示成:

 (3)
(3)
式中:N1、N2、Ka1和Ka2分别为常数,运用Levenberg- Marquardt法和通用全局优化算法(Universal global optimization)通过非线性拟合得到上述参数的拟合值,其结果如图2和表1所示。
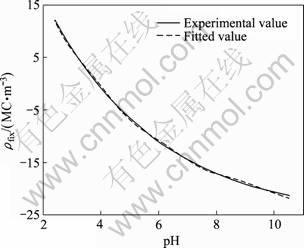
图2 细菌表面基团离子化模型模拟曲线
Fig.2 Modeling curves of ionizable surface group model of A.ferrooxidans
根据文献[4]报道的电离常数值,可以预测以硫培养的A.ferrooxidans 细菌表面可能含有多糖、蛋白质和磷脂等。实验拟合的结果支持DEVASIA等[8]的推断,即以固体能源培养的A.ferrooxidans表面因为蛋白质氨基的电离使得细菌等电点大于2。
2.2.2 离子可透过模型
离子可透过模型与离子不可透过模型的差别在于:前者认为离子可穿过表面,因此,离子可透过模型不存在紧密层。在离子可透过模型中,电泳池中的电解质可以穿过细胞可透过层,这种细菌被定义为“软电泳”细菌。OHSHIMA[13-15]于1995年提出软颗粒电泳理论,将细菌简化为一个硬核周围包裹一层有限厚度的可透过层。SONOHARA等[16]首次应用此理论来解释一些革兰氏阴性菌和阳性菌的电泳数据,证实了细菌存在软颗粒行为。虽然这个理论还未被广泛证实,但是国内外已经有很多学者根据它来解释细菌的电泳行为和吸附现象。只是关于浸矿微生物的软颗粒行为的还鲜见报道。
表1 细菌表面基团离子化模型拟合结果
Table 1 Fitting results of ionizable surface group model

在软颗粒电泳理论中定义的电泳软度(1/λ)如下:
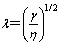 (4)
(4)
式中:γ为液体流经离子可透过层的摩擦因数;η为溶液黏度。
根据文献中关于相关理论的公式推导,得到Zeta电位(ξ),道南电位(φDon)和表面电位(φ0)的关系式分别如下:
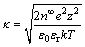 (5)
(5)
 (6)
(6)
 (7)
(7)
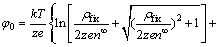
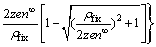 (8)
(8)
式中:κ为德拜-休克尔常数;n∞为最大离子数量(mol)。将实验中得到的不同pH下的Zeta电位值代入上述公式,就可以根据式(5)计算得到ρfix,从而解决细菌固定空间电荷密度难以从实验获得的困难。计算结果表明,相比离子不可透过模型,离子可透过模型中的细菌固定空间电荷密度要小两个数量级,原因就在于前者假设细菌表面电荷集中在极薄的一层,因此,相对固定空间的电荷密度也较大。
根据式(6)~(8)以及ρfix可以计算不同pH下的φDon和φ0, 如图3所示。两条曲线的交点应该是细菌的等电点,即此时细菌表面剩余电荷密度为零(φDon=φ0=0)。pH<5时,细菌表面和道南电位下降较快,原因可能是细菌在可承受的pH范围内,表面可以通过有机官能团的质子化和去质子化来调节表面电位和道南电位以适合环境的变化。当细菌表面pH等于细胞内的pH(约6~7) 后,细菌的φDon和φ0的变化渐缓,对pH的变化不再敏感。具体的细菌表面电荷的调节机制有待进一步研究,这对于研究离子的跨膜运动和营养物质的迁移有重要价值。
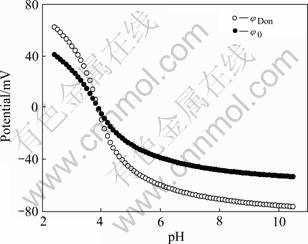
图3 细菌表面电位(φ0)和道南电位(φDon)随pH的变化
Fig.3 Change of bacterial surface potential (φ0) and Donnan potential (φDon) with pH
根据古依-切普曼双电层模型还可以计算不同pH下电位-距离的衰减规律。通过式(9)和(10)可以计算出pH为2.5、4.5、6.5、8.5和10.5时φ(x)的关系式。其中,κm为等效德拜-休克尔常数。图4中虚线表示细菌表面位置,±x分别表示朝外、朝内离开细菌表面的距离。
 (9)
(9)
 (10)
(10)
由图4可见,无论pH高低,φ(x)在±2.5 nm内变化明显,即细菌表面的双电层的厚度约为5.0 nm。这也就意味着当pH=2.5时在细胞表面内外2.5 nm的空间内将产生一个6×106 V/m的巨大场强,这将对细菌浸矿中的电子和离子迁移产生深远的影响。例如,在以硫为能源培养细菌的过程中,细菌将分步氧化低价态的酸根离子,细菌表面的双电层可能会加速阴离子在近细胞区的传质速率。同样,文献报道的以亚铁培养的细菌等电点小于2,即在细菌的生长环境中其带负电荷,那么同样表面的双电层会对亚铁离子的传输起到促进作用,其具体机制有待进一步研究。
2.3 细菌表面双电层的相互作用
假设细菌近似于球形,半径r=0.5 μm[17],那么当两个相同形状的A.ferrooxidans 细菌相互接近时,两者表面的双电层的相互作用而产生静电能GEL。按照
文献报道的球形颗粒表面的静电能式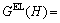
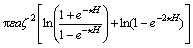 ,可以计算出GEL(H)
,可以计算出GEL(H)
随两细菌之间距离(H)的变化规律,其结果如图5所示。
由于两细菌荷电性质相同,二者相互排斥,表现为静电能为正值,说明细菌表面双电层的相互作用不利于细菌之间的聚集[6]。当pH=4时,细菌表面基本无剩余电荷,因此二者静电作用能几乎为零。当两细菌表面距离大于5 nm以后,静电能也趋近于零。
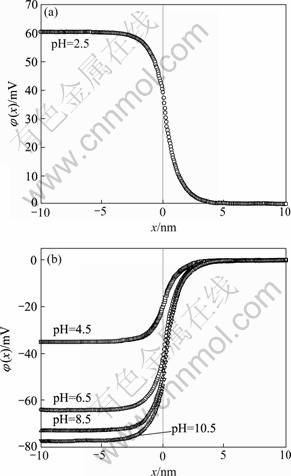
图4 不同pH时细菌表面双电层电位随离开细菌表面距离的变化
Fig.4 Changes of potenital profiles of electrical double layer at bacterial surface with different pH values
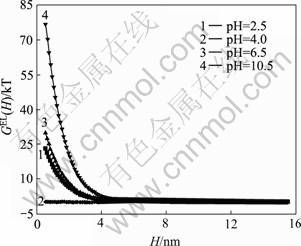
图5 菌/菌作用体系静电能GEL(H)随两细菌之间距离的变化曲线
Fig.5 Plots of electrostatic interaction energy GEL(H) of two bacterial cell with separation distance (H)
3 结论
1) 细菌细胞的Zeta电位的测定表明以硫为能源培养的细菌等电点(IEP)高于报道的以亚铁培养的细菌的IEP,原因是它分泌的胞外多聚物中含有较多的蛋白质,氨基的电离使得IEP>2。
2) 依据离子不可透过模型,通过数据非线性拟合得到细菌表面主要官能团的电离常数,支持以硫培养的细菌分泌有较多蛋白的论断。
3) 运用离子可透过模型,根据软颗粒电泳公式,分别得到了φDon和φ0与pH的关系图以及φ(x)的双电层电位分布图。结果表明,细菌表面双电层中不存在紧密层,双电层厚度约为5 nm。细菌表面双电层的相互作用不利于浸矿细菌的聚集。
REFERENCES
[1] BRIERLEY J A. A perspective on developments in biohydrometallurgy[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2008, 94(1/4): 2-7.
[2] EHRLICH H L. Past, present and future of biohydrometallurgy[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2001, 59(2/3): 127-134.
[3] RAWLINGS D E. Characteristics and adaptability of iron-and sulfur-oxidizing microorganisms used for the recovery of metals from minerals and their concentrates[J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2005, 4: 1-13.
[4] POORTINGA A T, BOS R, NORDE W, BUSSCHE H J. Electric double layer interactions in bacterial adhesion to surfaces[J]. Surf Sci Rep, 2002, 47(1): 1-32.
[5] BLAKE R C, SHUTE E A, HOWARD G T. Solubilization of minerals by bacteria: Electrophoretic mobility of Thiobacillus ferroxidans in the presence of iron, pyrite and sulfur[J]. Appl Environ Microbiol, 1994, 60(9): 3349-3357.
[6] SHARMA P K, RAO K H. Adhesion of Paenibacillus polymyxa on chalcopyrite and pyrite: Surface thermodynamics and extended DLVO theory[J]. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 2003, 29(1): 21-38.
[7] LIU J, WANG Z, CHEN H, ZHANG Y H. Interfacial electrokinetic characteristics before and after bioleaching microorganism adhesion to pyrite[J]. Transaction of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2006, 16(3): 676-680.
[8] DEVASIA P, NATARAJAN K A, SATHYANARAYANA D N, RAMANANDA R G. Surface chemistry of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans relevant to adhesion on mineral surfaces[J]. Appl Environ Microbiol, 1993, 59(12): 4051-4055.
[9] 王兆慧. 嗜酸氧化亚铁硫杆菌与硫化矿物相互作用研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2006: 36-37.
WANG Zhao-hui. Study on the interactions between Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans and sulfide minerals[D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2006: 36-37.
[10] 杨松青, 龚竹青. 理论电化学[M]. 长沙: 中南工业大学出版社, 1996: 109-110.
YANG Song-qing, GONG Zhu-qing. Theoretical electrochemistry[M]. Changsha: Central South University Press, 1996: 109-110.
[11] HEALY T, WHITE L. Ionizable surface group models of aqueous interfaces[J]. Adv Colloid Interf Sci, 1978, 9(4): 303-315.
[12] HEALY T W, CHAN D, WHITE L R. Colloidal behaviour of materials with ionizable group surfaces[J]. Pure Appl Chem, 1980, 52(5): 1207-1222.
[13] OHSHIMA H. Electrophoresis of soft particles[J]. Adv Colloid Interf Sci, 1995, 62(2/3): 189-235.
[14] OHSHIMA H. On the general expression for the electrophoretic mobility of a soft particle[J]. J Colloid Interf Sci, 2000, 228(1): 190-193.
[15] OHSHIMA H. Electrophoresis of soft particles: Analytic approximations[J]. Electrophoresis, 2006, 27(3): 526-533.
[16] SONOHARA R, MURAMATSU N, OHSHIMA H. Difference in surface properties between Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus as revealed by electrophoretic mobility measurements[J]. Biophys Chem, 1995, 55(3): 273-277.
[17] 傅建华. 硫化铜矿浸矿细菌超微结构与吸附机理及SFORase的纯化[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2003: 64-67.
FU Jian-hua. Bioleaching of copper sulfide minerals, the bacterial ultrastructure and the mechanisms of attachment, purifing SFORase of thiobacillus ferrooxidans[D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2003: 64-67.
(编辑 龙怀中)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(50874032, 21007009, 41073060);全国优秀博士学位论文作者专项资金资助项目(200549)
收稿日期:2010-06-13;修订日期:2011-03-10
通信作者:柳建设,教授,博士;电话:021-67792522;传真:021-67792533;E-mail: ljscsu@263.net