DOI:10.19476/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2017.06.014
铝合金/低碳钢点焊界面反应物生长机制
邱然锋1, 2,李久勇1,贺玉刚1,石红信1, 2,SATONAKA S3
(1. 河南科技大学 材料科学与工程学院,洛阳 471023;
2. 有色金属共性技术河南省协同创新中心,洛阳 471023;
3. 日本熊本大学 自然科学研究科,熊本 860-8555)
摘 要:采用电阻点焊对铝合金与低碳钢进行焊接,分析了接合界面区反应层形貌及分布等显微组织特征。结果表明:在接合界面上观察到反应物层的生成,其厚度随位置的变化而变化;界面反应物是由靠近铝合金侧的反应物为FeAl3和靠近钢侧反应物为Fe2Al5构成;FeAl3的生成归结于其生成自由能较低,而Fe2Al5的生长主要因其结构上在c轴方向存有大量Al原子空位而造成的各向异性扩散。
关键词:铝合金;钢;反应物;点焊
文章编号:1004-0609(2017)-06-1176-06 中图分类号:TG441.2 文献标志码:A
日趋严峻的环保与能源问题要求汽车车身轻量化,而汽车轻量化的最主要途径是以铝合金等轻质材料取代传统的钢铁材料用于汽车车身结构。在这种“钢+铝”车身结构里,主要承重件仍使用钢铁材料以确保其安全性,其余覆盖件则采用铝合金以实现车身整体的轻量化。因此,铝/钢异种金属的连接将不可避免。为此,国内外诸多学者对铝合金与钢异种材料间的爆炸焊[1]、搅拌摩擦焊[2]、扩散钎焊[3]、摩擦焊[4]、熔钎焊[5-8]与激光焊[9-10]等进行了深入研究。已有研究表明:生成于铝/钢接合界面的金属间化合物是影响接头性能的主要因素。因此,理解铝/钢异种材料接合界面区的组织特性及界面反应物生长机理将有助于优化工艺,进而为获得优质接头提供理论支撑。
不同铝/钢材料组合采用不同焊接方法焊接,其接合界面生成的反应物种类、形貌及其分布都有所不同。然而,关于铝合金与低碳钢异种材料电阻点焊界面反应物生长机制的研究仍鲜见报道。对此,本文作者采用电阻点焊方法焊接铝合金与低碳钢,在对其接头界面组织分析的基础上,探讨界面反应物的生长机制。
1 实验
试验材料为1.0 mm厚的A5052铝合金和SPCC低碳钢,其化学组成见表1。利用固定式交流点焊机进行焊接。焊接时,为克服熔核偏移,在铝合金板上附加一枚材质为SPCC低碳钢(厚1.0 mm)的热补偿工艺垫片。关于热补偿工艺垫片电阻点焊的详细报道见文献[11]。焊接前,被焊材料和所用热补偿工艺垫片表面用无水乙醇洗净后烘干。所用点焊参数如下:焊接电流10 kA;焊接时间0.2 s;电极压力1715 N。所用电极的端面直径为6 mm。
焊接后,垂直于接合界面沿焊点直径横切焊接接头,研磨、抛光其断面。用扫描电子显微镜(SEM)沿接合面观察界面区微观形貌。在界面区选取试样,经机械研磨、离子减薄(3 keV Ar+)后,用透射电子显微镜(TEM)观察分析界面区的显微组织与结构。
2 结果与分析
图1所示为接头横断面的宏观照片。 从图1可以看出,有一个横断面为鼓型的熔核生成于铝合金内,而在低碳钢内没有观察到熔融的痕迹,这说明接头是液态铝和固态钢之间形成的。利用扫描电子显微镜沿铝合金/低碳钢接合界面进行了观察,图2所示为界面区的SEM像,其中,图2(a)、(b)、(c)与(d)所示分别取自图2中A、B、C和D处。
表1 材料的化学成分
Table 1 Chemical composition of materials (mass fraction, %)
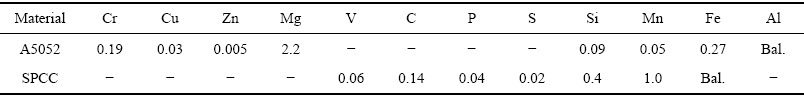
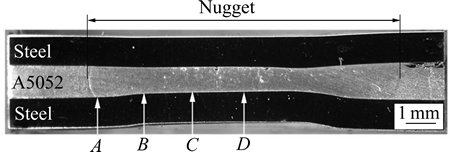
图1 接头横断面宏观照片
Fig. 1 Appearance of joint cross-section
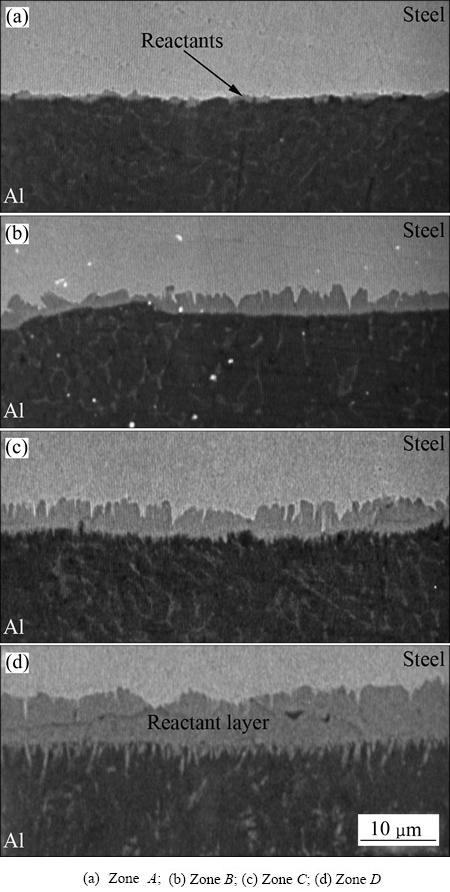

图2 接合界面区的扫描电镜图像
Fig. 2 SEM images of interface in Fig. 1
如图2所示,在铝合金与低碳钢接合界面观察到了有反应物形成。生成的反应物在焊点外缘处(见图2(a))呈非连续层状分布;随至焊点中心距离的减少,反应物逐渐转变为连续层状分布(见图2(b))。
对连续的反应层,靠近焊点外缘处的反应层/铝合金界面形貌相对较为平直(见图2(b));靠近焊点中心的该界面处有指向铝合金侧的微凸起(见图2(c));至焊点中心处,界面微突起变得稍微粗大,如同针一样指向铝合金侧(见图2(d))。
在形貌上,反应层和低碳钢间的界面凹凸起伏很大,表现为参差不齐。低碳钢一侧反应物像舌状,指向低碳钢侧(见图2(b)和(c))。随至焊点中心距离的减少,这些舌状反应物块逐渐增大,并且相邻舌状反应物块间的间隙也逐渐减小。在焊点中心处,相邻的舌状反应物块彼此接近,整个反应层如图2(d)所示变为带状层。
观察结果显示,反应层厚度X也沿界面发生变化。图3所示为反应层厚度在界面上的分布。反应层厚度测量方法如下:沿界面每隔100 μm 取一个30 μm×30 μm 的视野,在每一视野上测量5点取其平均值作为该视野的反应层厚度。反应层厚度在焊点中心处最大,随距焊点中心距离增加而逐渐减小,直至焊点外周缘处呈非连续分布。反应层厚度在界面呈中心厚外缘薄的分布[12]被认为与焊接过程中的温度场有关。
反应层的生长与原子的扩散速率和扩散程度有关。根据Arrehenius公式,原子扩散系数主要由温度决定,温度越高,扩散系数越大。而界面区高温停留时间决定了原子扩散的程度,时间愈长,扩散愈充分。电阻点焊时,由于母材的热传导作用,焊接区外围的温度低于焊接中心区的温度,且焊接区外围高温停留时间也比中心区域的高温反应时间要短[13]。这被认为是反应层厚度沿接合界面变化的原因。接合界面上形成如此反应物层的铝合金/低碳钢接头抗剪力达3.95 kN。
图4(a)所示为处于焊点边缘的不连续界面反应物的TEM明场像。由图4(a)可知,界面反应物是由100~200 nm微细晶粒构成。图4(b)显示了该区域反应物的衍射斑点图像,通过解析得知这些反应物为金属间化合物FeAl3。也就是说,生成于焊点外缘处的不连续反应物层主要由微细的FeAl3构成。
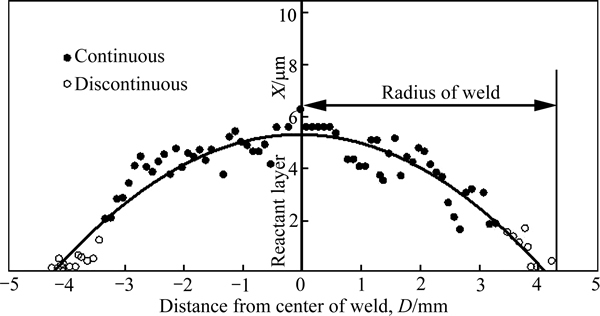
图3 反应层厚度分布
Fig. 3 Distribution chart of reactant layer thickness
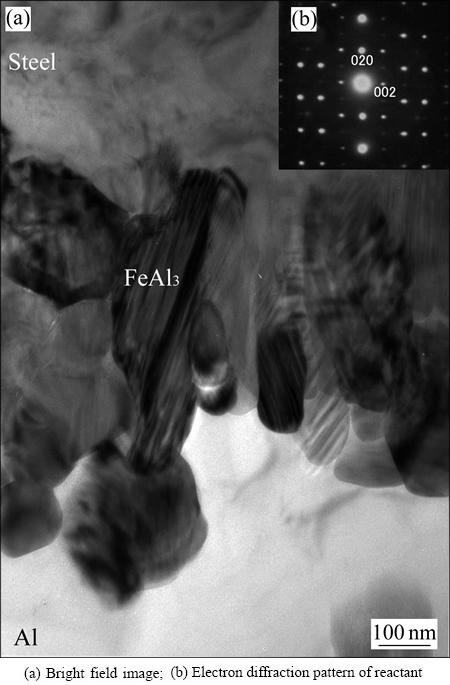
图4 接合界面明场像(焊点边缘处)和反应物衍射斑点
Fig. 4 Bright field image (peripheral region of weld) and electron diffraction pattern of reactant
图5(a)所示为焊点中心附近的界面区TEM明场像。由图5(a)可知,界面反应物层有两层构成。靠近铝合金侧是由大小约为0.2 μm的细小晶粒组成的反应物层,其厚度较薄。而靠近低碳钢侧则是由舌状的粗大晶粒构成的反应物层,其厚度也较厚。界面反应层的形貌也与图2所示的界面区SEM像较吻合。通过对图5(b)和(c)所示为反应物电子衍射斑点进行解析,可判断靠近铝合金侧微细的反应物为金属间化合物FeAl3,靠近低碳钢侧较为粗大的反应物是金属间化合物Fe2Al5。
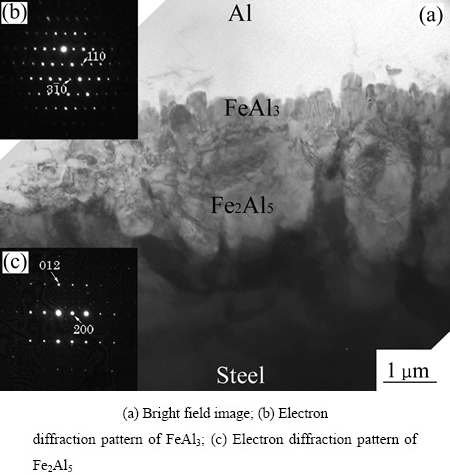
图5 界面明场像(焊点中心附近)和反应物衍射斑点
Fig. 5 Bright field image (near weld center) and electron diffraction pattern of reactant
根据Fe-Al二元相图[14]可知,Fe-Al间金属间化合物有多种。但是,本研究中在界面主要检测出Fe2Al5和FeAl3两种平衡相。这是因为在Fe-Al系化合物中,FeAl3的生成自由能最低而最容易生成[7, 14-16]。而Fe2Al5的生成自由能比FeAl3的较高,却生成的Fe2Al5晶粒较大,其层也较厚。这主要由两种金属间化合物在生长动力学方面的不同所致。如图6所示,在Fe2Al5的[001]方向(沿c轴方向)存在大量Al 原子空位[17],存在浓度差,致使Al 原子沿该方向扩散速度较大、其生长速度较大。
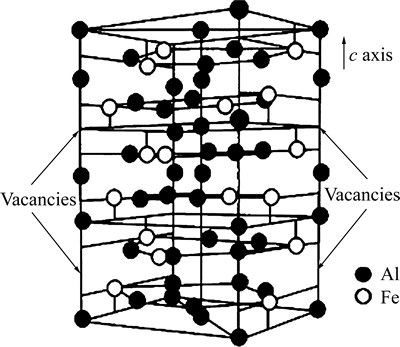
图6 Fe2Al5结构示意图
Fig. 6 Structure diagram of Fe2Al5
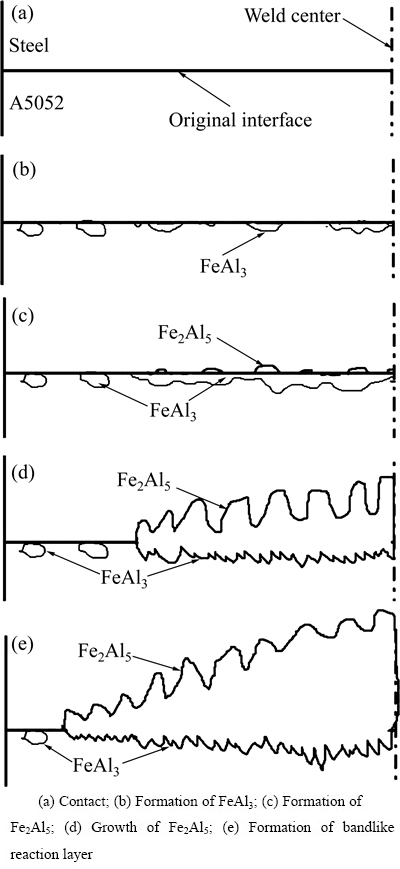
图7 界面反应物生长示意图
Fig. 7 Schematic explanation of reaction in A5052/SPCC interface
图7所示为铝合金/低碳钢点焊界面金属间化合物生长机制模型示意图。在点焊初期阶段,铝合金与钢的接触实际依靠表面微凸起进行接触的。进行通电焊接时,首先电流是从这些微凸起流经的,所以致使这些微凸起部位温度升高,Al、Fe原子相互扩散。由于时间较短,当扩散来的原子不能及时向远处扩散,在界面附近发生聚集,超过其溶解度后,生成了金属间化合物。
由Fe-Al二元相图[14]可知,Al在Fe中的溶解度远大于Fe在Al中的溶解度。而Al在Fe中的扩散系数为DAl=6.79×10-13 m2/s;Fe在Al中的扩散系数为DFe=3.57×10-17 m2/s;Al在Fe中的扩散系数明显较 大[18]。也就是说,Al在Fe中的溶解度既大又向远处扩散的快,所以在靠近界面的钢侧不易发生Al原子聚集。相反,在靠近界面的铝合金侧容易发生Fe原子的聚集,而生成金属间化合物。所以,界面金属间化合物在靠近界面铝合金侧生成(见图7(b))。由于FeAl3的生成自由能较低,优先生成。
对于点焊的边缘处,由于散热速度较快,高温停留时间较短。刚刚在微凸起处生成FeAl3,其温度就迅速下降。所以只生成不连续的FeAl3反应层,如图7(c)所示。
在加热、加压的条件下,微凸起接触点会在极短的时间内发生塑性变形、进而消失,铝合金与钢的接触面积也随之增大。在热的作用下,新的反应物继续生成,已有的反应物则进行长大,在界面连成层状,如图7(c)所示。
在靠近界面的铝合金侧,FeAl3反应层的生成阻碍了Fe原子向Al中的扩散,使FeAl3反应层与钢的界面处发生Fe原子聚集,形成富Fe区。在热的作用下,自由能较高的富Fe金属间化合物Fe2Al5生成于界面。如前所述,由于Fe2Al5在[001]方向存在大量Al原子空位、沿该方向的生长速度较大。在新生成Fe2Al5中,[001]方向与接合界面垂直的晶粒生长速率较快,如图7(d)所示形成舌状组织。原子Al和Fe在Fe2Al5中的扩散能分别为107和171 kJ/mol[14]。与Fe原子相比,Al在Fe2Al5中更易扩散。所以,Fe2Al5向钢侧生长。
在焊点中心部位,温度较高、高温停留时间也长,生成的Fe2Al5反应层较厚。这也减缓了原子垂直于接合界面方向的扩散,导致反应物Fe2Al5沿该方向生长的速度减慢。同时,Fe2Al5晶粒沿平行于接合界面方向的横向长大,导致相邻的Fe2Al5晶粒间的间隙减小,直至二者接触。这样形成如图7(e)所示的带状反应物层。
3 结论
1) 在接合界面上观察到反应物的生成。在焊点外缘处生成的不连续状反应物为FeAl3;而在非焊点外缘处,反应物层由两层构成,靠近铝合金侧的反应物为FeAl3;靠近钢侧反应物为Fe2Al5。
2) 反应层厚度随其在界面上的位置的变化而变化,其厚度呈中心厚外缘薄状分布。
3) FeAl3的生成归结于其生成自由能较低,而Fe2Al5的生长主要因其结构上在C轴方向存有大量Al原子空位而造成的各向异性扩散。
REFERENCES
[1] GUO Xun-zhong, WANG Hui, LIU Zhong-li, WANG Liu-an, MA Fu-ye, TAO Jie. Interface and performance of CLAM steel/aluminum clad tube prepared by explosive bonding method[J]. Int J Adv Manuf Technol, 2016, 82: 543-548.
[2] DEHGHANI M, AMADEH A, MOUSAVI S A A A. Investigations on the effects of friction stir welding parameters on intermetallic and defect formation in joining aluminum alloy to mild steel[J]. Materials and Design, 2013, 49: 433-441.
[3] 吴铭方, 司乃潮, 陈 健. 铝/镀银层/钢的扩散钎焊及界面化合物的生长行为[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2010, 20(6): 1209-1213.
WU Ming- fang, SI Nai- chao, CHEN Jian. Diffusion brazing of Al/Ag plating layer/steel and growth behavior of interface compound[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2010, 20(6): 1209-1214.
[4] TABAN E, GOULD J E, LIPPOLD J C. Dissimilar friction welding of 6061-T6 aluminum and AISI 1018 steel: Properties and microstructural characterization[J]. Materials and Design, 2010, 31: 2305-2311.
[5] 顾玉芬, 李 杰, 石 玗, 黄健康, 樊 丁. 铝/钢异种金属电弧熔钎焊焊接接头的腐蚀性能[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2016, 26(4): 758-765.
GU Yu-fen, LI Jie, SHI Yu, HUANG Jian-kang, FAN Ding. Corrosion property of arc welding brazed joint between aluminum and steel[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2016, 26(4): 758-765.
[6] BASAK S, DAS H, PAL T K, SHOME M. Characterization of intermetallics in aluminum to zinc coated interstitial free steel joining by pulsed MIG brazing for automotive application[J]. Materials Characterization, 2016, 112: 229-237.
[7] 陈树海, 马 柯, 黄继华, 夏 军, 张 华, 赵兴科. 钢/铝异种金属双熔池TIG熔钎焊接头的显微组织与力学性能[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2011, 21(12): 3076-3081.
CHEN Shu- hai, MA Ke, HUANG Ji -hua, XIA Jun, ZHANG Hua, ZHAO Xing- Ke. Microstructure and mechanical property of joint by TIG welding brazing with dual weld pools for steel/aluminum dissimilar metals[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2011, 21(12): 3076-3081.
[8] 宋建岭, 林三宝, 杨春利, 马广超. 铝合金/不锈钢预涂层钨极氩弧熔钎焊接头的特性[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2009, 19(7): 1209-1215.
SONG Jian -ling, LIN San- bao, YANG Chun -li, MA Guang -chao. Characteristics of precoating TIG welding brazing joint of aluminum alloy to stainless steel[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2009, 19(7): 1209-1215.
[9] 周惦武, 李宁宁, 刘元利, 徐少华, 刘金水. 胶层辅助激光焊双相钢/铝合金接头显微组织与力学性能[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2015, 25(9): 2381-2388.
ZHOU Dian-wu, LI Ning-ning, LIU Yuan-li, XU Shao-hua, LIU Jin-shui. Microstructure and mechanical properties of dual phase steel/aluminum alloy laser welding with adhesive layer addition[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2015, 25(9): 2381-2388.
[10] 张丽娟, 周惦武, 刘金水, 徐少华, 乔小杰, 李 升. 钢/铝异种金属添加粉末的激光焊接[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2013, 23(12): 3401-3409.
ZHANG Li-juan, ZHOU Dian-wu, LIU Jin-shui, XU Shao-hua, QIAO Xiao-jie, LI Sheng. Laser welding of steel/aluminum dissimilar metal with power addition[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2013, 23(12): 3401-3409.
[11] QIU Ran-feng, SATONAKA S, IWAMOTO C. Mechanical properties and microstructures of magnesium alloy AZ31B joint fabricated by resistance spot welding with cover plates[J]. Science and Technology of Welding and Joining, 2009, 14(8): 691-697.
[12] 石红信, 邱然锋, 张晓娇, 尹丹青, 于 华, 张柯柯, 里中忍. 铝合金与不锈钢热补偿电阻点焊接头性能研究[J]. 中国机械工程, 2013, 24(20): 2815-2819.
SHI Hong-xin, QIU Ran-feng, ZHANG Xiao-jiao, YIN Dan-qing, YU Hua, ZHANG Ke-ke, SATONAKA S. Study on performance of aluminum alloy/stainless steel joint welded by thermal compensation resistance spot welding[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2013, 24(20): 2815-2819.
[13] SHEN Jie, ZHANG Yan-song, WANG P C. Nugget shifting in resistance spot welding of multi-stackup sheets[J]. Quarterly Journal of the Japan Welding Society, 2011, 29(3): 133s-137s.
[14] SHAHVERDI H R, GHOMASHCHI M R, SHABESTARI S, HEJAZI J. Microstructural analysis of interfacial reaction between molten aluminum and solid iron[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2002, 124: 345-352.
[15] 刘邦津. 钢材的热浸镀铝[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 1995: 10-12.
LIU Bang-jin. The hotdip aluminizing of steel[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 1995: 10-12.
[16] 夏 原, 姚 枚, 李铁藩. Q235 钢热浸铝初期镀层组织结构的变化[J]. 金属热处理学报, 1998, 12(2): 34-38.
XIA Yuan, YAO Mei, LI Tie-fan. Initial structure of hot dip aluminizing (HDA) on Q235 steel and its variation behavior[J]. Transaction of Metal Heat Treatment, 1998, 12(2): 34-38.
[17] WANG Nan, YAMAGUCHI T, NISHIO K. Interfacial microstructure and strength of aluminum alloys/steel spot welded joints[J]. The Japan Institute of Metals and Materials, 2013, 77(7): 259-267.
[18] The Japan Institute of Metals and Materials. Metals data book[M]. Tokyo: Maruzen Co. Ltd., 1984.
Growth mechanism of reactants at spot welding interface between aluminum alloy and low carbon steel
QIU Ran-feng1, 2, LI Jiu-yong1, HE Yu-gang1, SHI Hong-xin1, 2, SATONAKA S3
(1. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Henan University of Science and Technology, Luoyang 471023, China;
2. Collaborative Innovation Center of Nonferrous Metals, Luoyang 471023, China;
3. Graduate School of Science and Technology, Kumamoto University, Kumamoto 860-8555, Japan)
Abstract: Aluminum alloy and low carbon steel sheets were welded by resistance spot welding. The interfacial characterization was observed and analyzed. The results show that a reactant layer forms at the welding interface; its thickness varies with the position at the welding interface. A reactant layer consisting of Fe2Al5 adjacent to steel and FeAl3 adjacent to aluminum alloy forms in the welding interface. Low free energy of FeAl3 is considered to be the reason for its formation at the welding interface, whereas anisotropic diffusion, which resulted from large number of aluminum vacancies along the c-axis of the orthorhombic structure of Fe2Al5, is a reason for the growth of Fe2Al5.
Key words: aluminum alloy; steel; reactants; spot welding
Foundation item: Project(U1204520) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project (16HASTIT050) supported by Science & Technology Innovation Talents in Universities of Henan Province, China; Project(162102410023) supported by International Technology Cooperation plan of Henan Province, China; Project(2013GGJS-064) supported by Youth Backbone Teacher Plan of Colleges and Universities in Henan Province, China
Received date: 2016-05-03; Accepted date: 2016-10-12
Corresponding author: QIU Ran-feng; Tel: +86-379-64231269; E-mail: qiurf1221@163.com
(编辑 龙怀中)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(U1204520);河南省高校创新人才支持计划资助项目(16HASTIT050);河南省国际科技合作计划资助项目(162102410023);河南省高等学校青年骨干教师资助计划项目(2013GGJS-064)
收稿日期:2016-05-03;修订日期:2016-10-12
通信作者:邱然锋,副教授;电话:0379-64231269;E-mail: qiurf1221@163.com