


Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 22(2012) 661-664
First–principles study of stacking fault energies in Ni3Al intermetallic alloys
WEN Yu-feng, SUN Jian, HUANG Jian
School of Materials Science and Engineering, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200240, China
Received 9 September 2011; accepted 12 January 2012
Abstract: The first-principles method based on the projector augmented wave method within the generalized gradient approximation was employed to calculate the superlattice intrinsic stacking fault (SISF) and complex stacking fault (CSF) energies of the binary Ni3Al alloys with different Al contents and the ternary Ni3Al intermetallic alloys with addition of alloying elements, such as Pd, Pt, Ti, Mo, Ta, W and Re. The results show that the energies of SISF and CSF increase significantly with increase of Al contents in Ni3Al. Addition of Pd and Pt occupying the Ni sublattices does not change the SISF and CSF energies of Ni3Al markedly in comparison with the Ni–23.75Al alloy. While addition of alloying elements, such as Ti, Mo, Ta, W and Re, occupying the Al sublattices dramatically increases the SISF and CSF energies of Ni3Al. The results suggest that the energies of SISF and CSF are dependent both on the Al contents and on the site occupancy of the ternary alloying element in Ni3Al intermetallic alloys.
Key words: Ni3Al; superlattice intrinsic stacking fault; complex stacking fault; alloying element; first–principles
1 Introduction
L12 Ni3Al intermetallic alloys have attracted considerable attention for their excellent physical and mechanical properties, such as high melting point, low density and good resistance to oxidation at high temperatures [1,2]. It is well known that there are three different types of dislocation dissociations in the L12 Ni3Al intermetallic compounds. A stable dissociation of dislocation is that the á110? superdislocation dissociates into two 1/2á110? superpartials bounding with an antiphase boundary (APB) on the (111) and (010) planes, respectively. Another stable dissociation of dislocation is that the á110? superdislocation dissociates into two 1/3á112? Shockley superpartial dislocations bounding with a superlattice intrinsic stacking fault (SISF). A metastable dissociation of dislocation is that the á110? superdislocation dissociates into one 1/2á110? superpartial and two 1/6á112? Shockley partials bounding with a complex stacking fault (CSF). The dissociated core geometry of these planar defects, in particular, the width of APB and CSF plays an important role in the dislocation mobility, which drastically affects the mechanical properties of the L12 Ni3Al intermetallic alloys at high temperatures. The width of APB and CSF is governed by the energies of APB and CSF defects. Addition of alloying elements usually affects the energies of APB and CSF, and is often used to improve mechanical properties of the L12 Ni3Al intermetallic alloys [3-7]. Therefore, it is critical to reveal the effect of alloying elements on the energies of APB and CSF for designing advanced Ni3Al intermetallic alloys.
The crystal structure of the L12 Ni3Al intermetallic compounds consists of two sublattices, i.e., the Ni sublattice at the face centers and Al sublattice at the cubic corner in the unit cell. The added ternary alloying elements may occupy the Ni sublattices or the Al sublattices exclusively or the both sites in Ni3Al. Several studies on site preference of alloying elements in Ni3Al were performed and the results showed that Pd and Pt elements have a predominant preference for the Ni sublattices, while Ti, Mo, Ta, W and Re have a predominant preference for the Al sublattices in Ni3Al [8–10]. The effects of some ternary alloying elements on the planar fault energies of Ni3Al intermetallic alloys were also studied theoretically and experimentally. For example, KRUML et al [6] investigated the effect of Al content on the planar fault energies experimentally. SUN et al [5] measured the planar fault energies of the Ni3Al and (Ni,Pd)3Al intermetallic alloys by transmission electron microscopy. KARNTHALER et al [7] also measured the planar fault energies of the Ni3Al and Ni3(Al,Ta) intermetallic alloys. However, since the component and content of those Ni3Al intermetallic alloys scattered in the literature, the effect of the ternary alloying elements additions on the energies of the planar defects of Ni3Al alloys has not been understood comprehensively. In this work, the energies of SISF and CSF of the binary Ni3Al alloys with different Al contents and the ternary Ni3Al alloys with addition of alloying elements, such as Pd, Pt, Ti, Mo, Ta, W and Re, were calculated by the first-principles, based on the projector augmented wave (PAW) method within the generalized gradient approximation (GGA). The main focus will be placed on the effect of alloying elements on the SISF and CSF energies in the Ni3Al intermetallic alloys. Based on the above results, the effects of ternary alloying elements on the mechanical properties of Ni3Al alloys were also discussed.
2 Computational methods
The first-principles calculation based on the density functional theory (DFT) with pseudo-potentials generated by the projector augmented plane wave (PAW) method implemented in the Vienna ab initio simulation package (VASP) [11-13] was employed in this study. The GGA of Perdew, Burke and Ernzerhof was used for the exchange correlation energy function [14]. The convergence accuracy of total energy calculation was chosen as 10-4 eV and plane–wave cutoff energy was set as 390 eV. The spin polarizations were activated for all calculations. A 8×8×2 k-mesh was used for k-point sampling according to the Monkhorst-Pack scheme [15]. The SISF and CSF energies of the L12 Ni3Al intermetallic alloys were calculated using 80-atom supercell with three basic vectors [1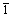 0], [11
0], [11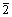 ] and [111]. In this supercell, ten layers of (111) plane of Ni3Al (with 6 Ni atoms and 2 Al atoms per plane) are stacked and a vacuum layer of about 12 ? is added along the [111] direction in order to avoid an interaction between periodic structures. The supercell is divided into two half-crystals with the same atomic layers. The CSF and SISF were formed by the displacement of Shockley partials along the á112? direction. A CSF is produced when the upper half-crystal is shifted by 1/6[11
] and [111]. In this supercell, ten layers of (111) plane of Ni3Al (with 6 Ni atoms and 2 Al atoms per plane) are stacked and a vacuum layer of about 12 ? is added along the [111] direction in order to avoid an interaction between periodic structures. The supercell is divided into two half-crystals with the same atomic layers. The CSF and SISF were formed by the displacement of Shockley partials along the á112? direction. A CSF is produced when the upper half-crystal is shifted by 1/6[11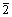 ] relatively to the lower half-crystal, whereas a SISF formed by shifting the upper half-crystal with the lower half-crystal by 1/3[11
] relatively to the lower half-crystal, whereas a SISF formed by shifting the upper half-crystal with the lower half-crystal by 1/3[11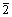 ]. The supercells with CSF and SISF in the L12 Ni3Al intermetallic alloys are shown in Fig. 1. The Ni-rich Ni3Al (or Al-rich Ni3Al) alloy is created by substituting Al (or Ni) atom with Ni (or Al) atom on the glide plane. Alloying elements occupying the Ni sublattice replace the Ni atoms on the glide plane in Ni-rich Ni3Al, meanwhile alloying elements occupying the Al sublattice replace directly the Al atoms on the glide plane in the stoichiometric Ni3Al. Thus, the concentration of alloying elements in the ternary Ni3Al alloys is 1.25% (mole fraction). Ionic relaxations were allowed for all calculations and the optimized atomic positions were generated through minimization of the Hellman-Feynman forces using a quasi-Newton algorithm. The Hellman-Feynman forces were relaxed to less than 0.05 eV/?.
]. The supercells with CSF and SISF in the L12 Ni3Al intermetallic alloys are shown in Fig. 1. The Ni-rich Ni3Al (or Al-rich Ni3Al) alloy is created by substituting Al (or Ni) atom with Ni (or Al) atom on the glide plane. Alloying elements occupying the Ni sublattice replace the Ni atoms on the glide plane in Ni-rich Ni3Al, meanwhile alloying elements occupying the Al sublattice replace directly the Al atoms on the glide plane in the stoichiometric Ni3Al. Thus, the concentration of alloying elements in the ternary Ni3Al alloys is 1.25% (mole fraction). Ionic relaxations were allowed for all calculations and the optimized atomic positions were generated through minimization of the Hellman-Feynman forces using a quasi-Newton algorithm. The Hellman-Feynman forces were relaxed to less than 0.05 eV/?.
The energy variation of the supercell after introducing stacking fault is
ΔESF=ESF-E0 (1)
where E0 is the total energy of the perfect crystal, and ESF is the total energy of the crystal with stacking fault structure. The stacking fault energy is defined as
γSF=ΔESF/ΔS (2)
where ΔS is the area of stacking fault in the supercell.
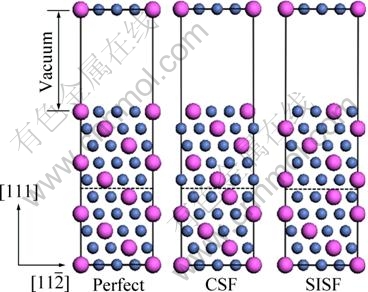
Fig. 1 Supercells of perfect crystal and crystals with CSF and SISF (Small balls stand for Ni atoms and big balls stand for Al atoms.)
3 Results and discussion
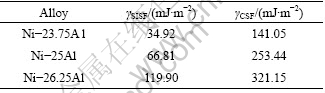
The SISF and CSF energies of the binary Ni3Al with different Al contents were firstly calculated, which are listed in Table 1. It can be seen from Table 1 that the SISF energy of the stoichiometric Ni3Al is 66.81 mJ/m2, which falls into a range from 40 mJ/m2 theoretically achieved by FU et al [16] to 80 mJ/m2 by MRYASOV et al [17]. These theoretical results are higher than those obtained from experimental measurements [18,19]. The CSF energy of the stoichiometric Ni3Al is 253.44 mJ/m2, which agrees well with the result of (236±29) mJ/m2 measured experimentally by KRUML et al [6], using weak-beam dark field transmission electron microscopy technique. MRYASOV et al [17] reported a theoretical CSF energy of 290 mJ/m2. One can also see from Table 1 that both the SISF and the CSF energies significantly increase with the increase of Al contents in Ni3Al alloys, which is consistent with the experimental result reported by KRUML et al [6].
Table 1 Calculated CSF and SISF energies of binary Ni3Al alloys with different Al contents
The effects of the ternary alloying elements on the SISF and CSF energies of the Ni3Al intermetallic alloys were further studied. The SISF and CSF energies of the Ni3Al intermetallic alloys with the ternary alloying elements of Pd and Pt occupying the Ni sublattices are listed in Table 2. It can be seen from Table 2 that the calculated SISF and CSF energies of the Ni75Pd1.25Al23.75 and Ni75Pt1.25Al23.75 intermetallic alloys are lower than those of the stoichiometric Ni3Al. They are comparable with those of the Ni-rich Ni-23.75Al alloy. This means that the role of the ternary alloying elements of Pd and Pt occupying the Ni sublattice is somewhat similar to that of Ni anti-site defects (Ni atoms occupy the Al sublattices) in Ni-rich Ni3Al alloys.
Table 2 Calculated CSF and SISF energies of Ni3Al alloys with ternary alloying elements occupying Ni sublattices

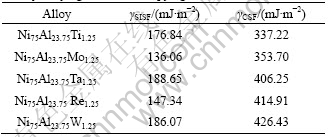
Table 3 shows the calculated SISF and CSF energies of Ni3Al intermetallic alloys with the ternary alloying element of Ti, Mo, Ta, W and Re, which occupy the Al sublattice in Ni3Al. The SISF energy of Ni75Al23.75Ti1.25 is comparable with 133 mJ/m2 of Ni3(Al,Ti) reported experimentally by KAWABATA et al [20]. BALUC et al [21,22] performed an experimental study of the CSF energy of the Ni74.3Al24.7Ta1.0 alloy by weak-beam dark field transmission electron microscopy technique. The theoretical result from the first principles is also comparable with the experimental one of (352±50) mJ/m2 of the Ni74.3Al24.7Ta1.0 alloy. In comparison with the CSF and SISF energies of stoichiometric Ni3Al in Table 1, it can be found that the ternary alloying elements of Ti, Mo, Ta, W and Re occupying the Al sublattices significantly increase the CSF and SISF energies of Ni3Al. These results suggest that the energies of SISF and CSF are dependent both on the Al contents and on the site occupancy of the ternary alloying element in Ni3Al intermetallic alloys.
Table 3 Calculated CSF and SISF energies of Ni3Al alloys with ternary alloying elements occupying Al sublattices
Addition of alloying elements usually affects the energies of APB and CSF and thus dominates the mechanical properties of the L12 Ni3Al intermetallic alloys. KRUML et al [6] investigated the mechanical properties of three binary Ni3Al alloys with different Al contents and the fault energies in the dislocation core experimentally. The results show that increasing the CSF energy increases the strength in the anomalous temperature domain, thus lowering the peak stress temperature in Ni3Al alloys. KARNTHALER et al [7] also studied the critical resolved shear stress (CRSS) against the deformation temperature in the Ni76.3Al23.6 and Ni74.3Al24.7Ta1.0 alloys experimentally. It is found that the anomalous region starts at a lower temperature in the ternary alloy than in the Ni–rich binary Ni3Al alloy. And the CRSS of Ni74.3Al24.7Ta1.0 is higher than that of the in Ni76.3Al23.6 alloys in the anomalous temperature domain, but lower than that of Ni76.3Al23.6 alloys at peak temperature. It is suggested that the higher critical resolved shear stress (CRSS) and the shift of the CRSS to the lower temperature are strongly related to the higher CSF energy of Ni74.3Al24.7Ta1.0 as compared with Ni76.3Al23.6 alloys, because the CSF energy dominates the dissociation width and therefore the constriction energy of the Shockley partials of the screw dislocations in Ni3Al alloys. The present results calculated from first-principles show that the energies of SISF and CSF significantly increase with the increase of Al content in Ni3Al. Addition of Pd and Pt occupying the Ni sublattices does not change the SISF and CSF energies of Ni3Al markedly in comparison with the Ni-23.75Al alloy, while addition of Ti, Mo, Ta, W and Re occupying the Al sublattices increases dramatically the SISF and CSF energies of Ni3Al. Thus, it can be deduced that addition of Pd and Pt occupying the Ni sublattices decreases the strength in the anomalous temperature domain, thus raising the peak stress temperature. Meanwhile, addition of Ti, Mo, Ta, W and Re occupying the Al sublattices increases the strength in the anomalous temperature domain, thus lowering the peak stress temperature in Ni3Al alloys. Because the energies of SISF and CSF are dependent both on the Al contents and on the site occupancy of the ternary alloying element, the mechanical properties are also dominated by these two issues in the L12 Ni3Al intermetallic alloys.
4 Conclusions
1) The energies of SISF and CSF significantly increase with the increase of Al content in Ni3Al.
2) Addition of Pd and Pt occupying the Ni sublattices does not change the SISF and CSF energies of Ni3Al markedly in comparison with the Ni-23.75Al alloy, while addition of Ti, Mo, Ta, W and Re occupying the Al sublattices increases dramatically the SISF and CSF energies of Ni3Al.
3) The energies of SISF and CSF are dependent both on the Al contents and on the site occupancy of the ternary alloying element in Ni3Al intermetallic alloys.
References
[1] LIU C T, POPE D P. Ni3Al and its alloys [M]//WESTBROOK J H, FLEISCHER R L. Intermetallic Compounds-Practice. Chichester: John Wiley & Sons, 1995: 17-51.
[2] MIRACLE D B, DAROLIA R. NiAl and its alloys [M]//WESTBROOK J H, FLEISCHER R L. Intermetallic Compounds-Practice. Chichester: John Wiley & Sons, 1995: 53-72.
[3] POLLOCK T M, FIELD R D. Dislocations in solids [M]. Amdterdam: Elsevier, 2002.
[4] ZHANG Yun, LIN Dong-liang. Mechanical properties of directional-solidified Ni3Al containing boron and carbon [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 1997, 7(2): 86-90.
[5] SUN J, LEE C S, LAI J K L, WU J S. Dislocation dissociations and fault energies in Ni3Al alloys doped with palladium [J]. Intermetallics, 1999, 7(12): 1329-1335.
[6] KRUML T, CONFORTO E, PICCOLO B L, CAILLARD D, MARTIN J L. From dislocation cores to strength and work-hardening: A study of binary Ni3Al [J]. Acta Materialia, 2002, 50(20): 5091-5101.
[7] KARNTHALER H P, MUHLBACHER E T, RENTENBERGER C. The influence of the fault energies on the anomalous mechanical behavior of Ni3Al alloys [J]. Acta Materialia, 1996, 44(2): 547-560.
[8] CHIBA A, HANADA S. Ductilization of Ni3Al by alloying with substitutional elements [J]. Journal of Materials Sciences and Technology, 1993, 9: 391-399.
[9] JIANG C, GLEESON B. Site preference of transition metal elements in Ni3Al [J]. Scripta Materialia, 2006, 55(5): 433-436.
[10] GENG C Y, WANG C Y, YU T. Site preference and alloying effect of platinum group metals in γ′-Ni3Al [J]. Acta Materialia, 2004, 52(18): 5247-5233.
[11] KRESSSE G, FURTHM?LLER J. Efficient iterative schemes for ab initio total-energy calculations using a plane–wave basis set [J]. Physical Review B, 1996, 54(16): 11169-11186.
[12] KRESSSE G, FURTHM?LLER J. Efficiency of ab-initio total energy calculations for metals and semiconductors using a plane-wave basis set [J]. Computational Materials Sciences, 1996, 6: 15-50.
[13] KRESSE G, JOUBERT D. From ultrasoft pseudopotentials to the projector augmented-wave method [J]. Physical Review B, 1999, 59: 1758-1775.
[14] PERDEW J P, BURKE K, ERNZERHOF M. Generalized gradient approximation made simple [J]. Physical Review Letter, 1996, 77(18): 3865-3868.
[15] MONKHORST H J, PACK J D. Special points for Brillouin-zone integrations [J]. Physical Review B, 1976, 13: 5188-5192.
[16] FU C L, YOO M H. All-electron total-energy theory of crystal elasticity: L12-ordered alloys [J]. Philosophical Magazine Letter, 1988, 58(4): 199-204.
[17] MRYASOV O N, GOMOSTYREV Y N, VAN SCHILFGAARDE M, FREEMAN A J. Superdislocation core structure in L12 Ni3Al, Ni3Ge and Fe3Ge: Peierls-Nabarro analysis starting from ab-initio GSF energetic calculations [J]. Acta Materialia, 2002, 50: 4545-4554.
[18] VEYSSIERE P, DOUIN J, BEAUCHAMP P. On the presence of super lattice intrinsic stacking faults in plastically deformed Ni3Al [J]. Philosophical Magzine A, 1985, 51(3): 469-483.
[19] DOUIN J, VEYSSIERE P, BEAUCHAMP P. Dislocation line stability in Ni3Al [J]. Philosophical Magazine A, 1986, 54(3): 375-393.
[20] KAWABATA T, SHINDO D, HIRAGA K. High-resolution TEM observations of superdislocation in Ni3(Al, Ti) [J]. Materials Transactions, JIM, 1992, 33: 565-570.
[21] BALUC N, KAMTHALER H P, MILLS M J. TEM observation of the fourfold dissociation of superlattice dislocations and the determination of the fault energies in Ni3(Al, Ta) [J]. Philosophical Magazine A, 1991, 64: 137-150.
[22] BALUC N, SCHAUBLIN R. Weak beam transmission electron imaging of superdislocation in ordered Ni3Al [J]. Philosophical Magazine A, 1996, 74: 113-136.
Ni3Al合金层错能的第一性原理研究
温玉锋,孙 坚, 黄 健
上海交通大学 材料科学与工程学院,上海 200240
摘 要:采用第一性原理方法计算了不同Al含量二元Ni3Al合金以及添加Ti、Mo、Pd、Ta、W、Re 和Pt等主要合金元素的三元Ni3Al合金的超内禀层错能和复杂层错能。结果表明:随着Al 含量的增加,Ni3Al合金的超内禀层错能和复杂层错能显著升高;与Ni–23.75Al合金相比,占据Ni3Al中Ni 亚点阵位置的合金元素Pd和Pt不改变合金的超内禀层错能和复杂层错能,而占据Ni3Al中Al 亚点阵位置的合金元素Ti、Mo、Ta、W和Re则显著增大合金的超内禀层错能和复杂层错能。这表明Ni3Al金属间化合物的超内禀层错能和复杂层错能与合金中的Al 含量以及添加合金元素的占位相关联。
关键词:Ni3Al;超内禀层错能;复杂层错能;合金元素;第一性原理
(Edited by LI Xiang-qun)
Foundation item: Project (50871065) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Projects (08DJ1400402, 09JC1407200, 10DZ2290904) supported by the Science and Technology Committee of Shanghai Municipality, China
Corresponding author: SUN Jian; Tel: +86-21-54745593; E-mail: jsun@sjtu.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(11)61229-6