DOI:10.19476/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2018.01.05
合金元素对Cu/γ-Fe界面特性影响的第一性原理研究
徐沛瑶1, 2,王宇飞1, 2,高海燕1, 2, 3,王 俊1, 2, 3,孙宝德1, 2, 3
(1. 上海交通大学 材料科学与工程学院,上海 200240;
2. 上海市先进高温材料及其精密成形重点实验室,上海 200240;
3. 上海交通大学 金属基复合材料国家重点实验室,上海 200240)
摘 要:采用基于密度泛函理论的第一性原理方法,计算合金原子在Cu/γ-Fe界面不同点阵位置的置换能,确定合金元素在Cu/γ-Fe界面模型的占位。通过对晶格错配度、界面结合能、界面能和电子结构的计算分析合金元素对Cu/γ-Fe界面特性的影响。计算结果表明:合金元素B、Si、P、Al、Zr使界面结合能增大,增强Cu/γ-Fe界面稳定性;B、Si、P等11种合金元素则会使界面能降低,有利于γ-Fe的时效析出形核。因此,B、Si、P、Al、Zr可以促进γ-Fe的析出,同时形成稳定的γ-Fe相。通过合金原子相对体积、晶格错配度和差分电荷密度的计算,分析合金元素的作用机制。
关键词:Cu/γ-Fe界面;第一性原理;界面能;界面结合能
文章编号:1004-0609(2018)-01-0039-07 中图分类号:TG146.1+1 文献标志码:A
形变 Cu-Fe原位复合材料是一种极具潜力的高强度高导电铜基材料[1],具备原料来源广、制备成本低、理论上具有高强高导性能等优势。然而由于Fe在Cu中的高温固溶度较大,低温下Fe析出动力学缓慢,导致过饱和Fe原子引起强烈的杂质散射,严重降低电导率。多元合金化是改善Cu-Fe原位复合材料性能的重要途径,Ag、P、Cr等元素已被报导应用于Cu-Fe合金的多元合金化中[2-6]。WANG等[7]通过在 Cu基体中溶质原子-空位结合能的计算,筛选出了可行的14种合金元素:Ag、Al、B、Bi、Cd、Ge、In、Mg、P、S、Sb、Si、Sn、Zr。如何在这诸多合金元素中筛选出有利的合金元素的一直是个尚待解决的问题。加快Fe的时效析出是改善Cu-Fe合金性能的关键。过饱和Cu-Fe合金在时效过程首先析出介稳的FCC结构γ-Fe[8],其时效析出过程包括形核、长大和粗化3个阶段。WANG等[9]研究了多元合金化对长大和粗化过程中扩散速率的影响[9],而针对合金元素对γ-Fe形核过程的研究仍未见报道。
形核过程与界面能等界面性质息息相关,本文作者通过研究Cu-Fe原位复合材料Cu/γ-Fe的界面性质,探究合金元素对γ-Fe时效析出形核过程的影响。由于界面能等数值较难通过实验方法直接得出,而第一性原理提供了从原子尺度研究材料性质的方法,近年被广泛应用于表、界面性质的研究中。该方法在Al基[10]、Cu基[11]、Ni基[12-13]等固-固界面形核机理的研究都有着成功的应用。通过第一性原理方法,通过构建合理的Cu/γ-Fe界面模型,计算了Cu/γ-Fe界面的晶格错配度、界面结合能、界面能以及差分电荷分布,分析合金元素对Cu-Fe合金γ-Fe时效析出形核的影响及其作用机理,为Cu-Fe合金多元合金化的元素选择提供了理论依据。
1 计算方法与结构模型
采用基于密度泛函理论(DFT)的Vienna Ab-initio Simulation Package (VASP)[14]软件包。第一性原理计算模拟的精度和效率取决于计算参数,其中包括:交互关联函数、赝势、平面波截断能、k点网格划分、收敛精度、温度等。计算中采用广义梯度近似(GGA)[15]交互关联函数,赝势为Projector Augmented Wave (PAW)[14]。平面波截断能统一采用400 eV。表面及界面计算中,每层原子分别采用1×1和2×2个晶胞组成超级元胞进行计算,布里渊区则分别采用10×10×1和5×5×1的K点网格进行划分。为了获得一个精确的晶体结构,计算中所有的自由度,即原子位置以及晶胞体积和形状是完全放开的。弛豫的收敛标准均为1.0×10-5 eV。已有文献证实可以用0 K下的第一原理计算结果来解释T>0 K的固相体系中的实验现象[16],因此温度统一设置为0 K。所有结构模型均使用Materials Studio软件构建。
BITTER等[8]研究发现,过饱和Cu-Fe合金在时效过程中析出的γ-Fe与Cu基体之间的位向关系为(100)[010]Cu//(100)[010]γ-Fe。基于此位向关系,采用包含真空层(厚度15 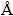 )的超晶胞建模方法,分别建立Cu(100)面和γ-Fe(100)面的表面模型,进行收敛性测试,考察其表面能随原子层厚度的收敛趋势,计算得到其表面能,并取定合适的原子层数。采用具有真空层的超晶胞建模方法,将两表面堆垛形成Cu(100)/γ-Fe(100)界面模型。计算合金元素在Cu-Fe合金界面模型不同置换位置的置换能,确定合金元素在界面区域的占位。在此基础上,对界面结构进行弛豫优化,分别计算界面结合能、界面能、晶格错配度、界面电子结构,分析合金元素对界面稳定性和界面结合强度的影响,预测合金元素对Cu-Fe合金Fe时效析出形核的影响。
)的超晶胞建模方法,分别建立Cu(100)面和γ-Fe(100)面的表面模型,进行收敛性测试,考察其表面能随原子层厚度的收敛趋势,计算得到其表面能,并取定合适的原子层数。采用具有真空层的超晶胞建模方法,将两表面堆垛形成Cu(100)/γ-Fe(100)界面模型。计算合金元素在Cu-Fe合金界面模型不同置换位置的置换能,确定合金元素在界面区域的占位。在此基础上,对界面结构进行弛豫优化,分别计算界面结合能、界面能、晶格错配度、界面电子结构,分析合金元素对界面稳定性和界面结合强度的影响,预测合金元素对Cu-Fe合金Fe时效析出形核的影响。
2 结果及讨论
2.1 计算参数验证
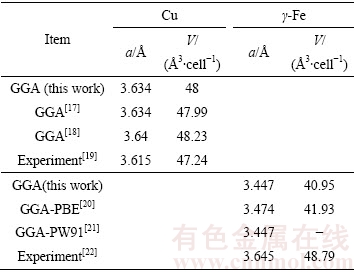
为了确保第一性原理计算中所采用的参数能得到精确的计算结果,首先对Cu及γ-Fe晶胞进行体性质计算,包括晶格常数和晶胞体积。本研究的计算结果与其他文献中采用相同计算方法的计算结果及实验数据列于表1。计算得到的Cu、γ-Fe晶格常数和晶胞体积与其他文献计算结果十分吻合,与实验值也较为接近。说明采用的计算方法和参数能够保证足够的精度。
为了保证Cu/γ-Fe界面两侧原子能够保留体相特征,而又不至于过厚而增加计算量,因此通过考察表面能σ随着原子层数的收敛性来确定界面两侧Cu和γ-Fe原子的最小层数。表面能采用下式计算[23]:
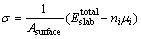 (1)
(1)
式中:Asurface为表面总面积;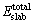 为表面模型的总能量;ni为所含元素的原子个数;μi为所含元素的化学势。其计算结果见表2。可以看出,当原子层数大于等于6层时,Cu(100)和γ-Fe(100)面表面能趋向收敛。因此,后续计算中Cu原子层和Fe原子层均取为6层。此时,Cu(100)面表面能约为1.48 J/m2,γ-Fe(100)面表面能约为3.36 J/m2。
为表面模型的总能量;ni为所含元素的原子个数;μi为所含元素的化学势。其计算结果见表2。可以看出,当原子层数大于等于6层时,Cu(100)和γ-Fe(100)面表面能趋向收敛。因此,后续计算中Cu原子层和Fe原子层均取为6层。此时,Cu(100)面表面能约为1.48 J/m2,γ-Fe(100)面表面能约为3.36 J/m2。
表1 Cu和γ-Fe的晶格常数和晶胞体积
Table 1 Lattice constants and cell volumes of Cu and γ-Fe
2.2 合金元素占位
合金元素在界面处的占位直接影响到计算建模及结果,因此开展了在不同点阵位置的置换能计算。界面结构模型如图1所示,图1(b)中1~4和5~8分别为合金元素在Cu原子侧和在Fe原子侧的不同置换位置。置换能可以通过以下公式计算得到:
 (2)
(2)
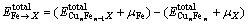 (3)
(3)
式中: 为一个合金原子X置换Cu原子的置换能;
为一个合金原子X置换Cu原子的置换能; 和
和 分别为置换前和置换后界面体系的总能量;μCu、μX分别为Cu、合金原子X的化学势。式(3)与式(2)类似。
分别为置换前和置换后界面体系的总能量;μCu、μX分别为Cu、合金原子X的化学势。式(3)与式(2)类似。
置换能的计算结果见表3。合金原子置换能最低的点阵位置全都处于Cu原子侧,其中Mg和Ag原子处于最远离界面的位置1;Cd原子处于Cu原子侧次近邻界面位置3;其余B、Si、P等原子处于Cu原子侧最近邻界面位置4。后续计算中,所有合金元素位置都确定为置换能最低的点阵位置。Cu基中Fe-合金原子结合能是导致合金元素置换位置不同的重要原因。项目组前期研究结果表明[10]:在Cu基体中,合金原子B、Si、P、Al、Ge、S、In、Zr与Fe之间有较强的结合能,位于Fe原子的最近邻位置;而Mg、Ag、Cd、Sn、Sb、Bi和Fe原子结合较弱,倾向于远离Fe原子,这与本研究的计算结果基本相符。
表2 Cu(100)和γ-Fe(100)表面能
Table 2 Surface energies of Cu(100) and γ-Fe(100)
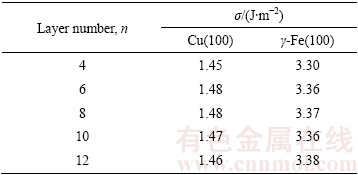
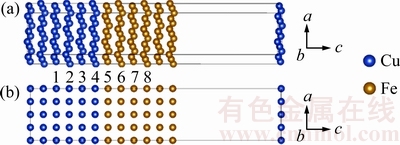
图1 Cu(100)/γ-Fe(100)界面结构模型以及合金元素在界面模型中不同的替换位置
Fig. 1 Interface structure of Cu(100)/γ-Fe(100) (a) and different sites of alloying atoms in interface region (b)
2.3 界面结合能
Cu/γ-Fe界面的稳定性可以用界面结合能定性描述。FINNIS[24]认为,界面结合能Wad在数值上等于把一个界面分离为两个自由表面所需要的可逆功,可由下式计算:
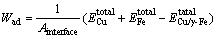 (4)
(4)
式中: 、
、 、
、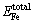 分别为充分驰豫后的界面体系总能量及分离的Cu、Fe自由表面的能量;Ainterface为界面面积。合金原子体积大小不同导致Cu/γ-Fe界面晶格错配度发生变化,是界面结合能发生变化的重要原因。合金原子的相对体积即合金原子溶于Cu基体中造成的体积变化,其计算公式如下所示:
分别为充分驰豫后的界面体系总能量及分离的Cu、Fe自由表面的能量;Ainterface为界面面积。合金原子体积大小不同导致Cu/γ-Fe界面晶格错配度发生变化,是界面结合能发生变化的重要原因。合金原子的相对体积即合金原子溶于Cu基体中造成的体积变化,其计算公式如下所示:
 (5)
(5)
式中: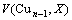 和
和 分别为合金原子置换前后Cu基体的晶胞体积。
分别为合金原子置换前后Cu基体的晶胞体积。
图2所示为合金原子相对体积和晶格错配度、界面结合能关系图。Cu/γ-Fe界面结合能为3.822 J/m2;Ge、S、Mg、Ag、Cd、Sn、In、Sb、Bi元素的加入使界面结合能降低,即界面的稳定性下降;而B、Si、P、Al、Zr元素的加入则使界面结合能增大,增强了Cu/γ-Fe界面的稳定性。从图2中可见,界面结合能和合金元素相对体积之间呈现明显的线性关系,合金原子相对体积与晶格错配度成正比,与界面结合能大小成反比。即加入相对体积较小的原子后可以使晶格错配度变小,晶格畸变变小,从而使界面结合能变大,有利于形成稳定的Cu/γ-Fe界面。
表3 合金原子在不同点阵位置的置换能
Table 3 Calculated substitutional energies for alloying atoms at different sites


图2 合金原子相对体积与Cu/γ-Fe界面晶格错配度、界面结合能的关系
Fig. 2 Lattice misfit and work of adhesion of Cu/γ-Fe interface as a function of solute volume
2.4 界面能
界面能是阻碍γ-Fe析出形核的因素之一,直接影响形核功和临界形核半径。Cu/γ-Fe界面能可用下式表示[25]:
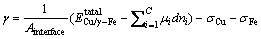 (7)
(7)
式中:σCu、σFe分别为Cu(100)与γ-Fe(100)自由表面的表面能。界面能与合金元素相对体积的关系见图3。
Cu/γ-Fe界面的界面能为0.819 J/m2。加入Mg、Ag、Cd元素后,界面能有所上升,表明Cu/γ-Fe界面形成所需的能量增大,不利于Fe的析出形核过程;加入B、Si、P、Al、Ge、S、Sn、In、Sb、Zr、Bi元素后,界面能均有所降低,有利于Fe的形核。整体而言界面能随着合金原子相对体积的增大而升高,这是由于相对体积越大的合金原子造成晶格错配度越大,晶格畸变能较大,导致界面能升高。
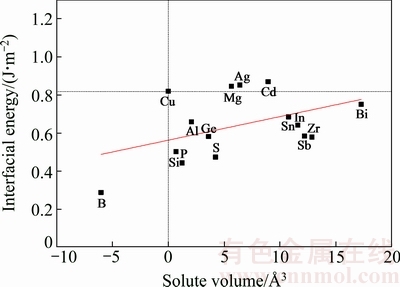
图3 合金原子相对体积与Cu/γ-Fe界面能的关系
Fig. 3 Interfacial energies of Cu/γ-Fe interface as a function of solute volume
除了晶格畸变能外,界面处化学交互作用能是影响界面能大小的另一因素。化学交互作用能受界面处原子键合情况影响,原子间键合越强,形成界面所需的能量越低,界面能越低。原子键合可以通过差分电荷密度△ρ来表征:
 (8)
(8)
式中: 为Cu/γ-Fe界面构型的总电荷密度;ρCu(100)和ργ-Fe(100)分别为由Cu/γ-Fe界面构型分离成的Cu(100)、γ-Fe(100)层构型的电荷密度。图4给出了计算得到的界面区域典型的差分电荷密度,虚线代表界面所在位置,电荷富集和电荷缺失区域分别由红色和蓝色标出,等高线的间隔为0.002 e/
为Cu/γ-Fe界面构型的总电荷密度;ρCu(100)和ργ-Fe(100)分别为由Cu/γ-Fe界面构型分离成的Cu(100)、γ-Fe(100)层构型的电荷密度。图4给出了计算得到的界面区域典型的差分电荷密度,虚线代表界面所在位置,电荷富集和电荷缺失区域分别由红色和蓝色标出,等高线的间隔为0.002 e/ 3,具体结果见图5。在不添加合金元素时,Cu/γ-Fe界面电荷富集程度较低,如图4(a)所示;加入Mg、Ag、Cd 3种合金元素后,界面电荷富集程度也都处于较低水平,界面处原子间化学键合较弱;加入P、Al、Ge、Sn、In、Sb、Bi后,界面电荷富集有所增强,以Al为例,界面处差分电荷密度如图4(b)所示,界面处原子间化学键合强度中等;而在加入B、Si、S、Zr后,界面电荷富集大大增强,以Si为例,界面处差分电荷密度如图4(c)所示,原子间化学键合较强。
3,具体结果见图5。在不添加合金元素时,Cu/γ-Fe界面电荷富集程度较低,如图4(a)所示;加入Mg、Ag、Cd 3种合金元素后,界面电荷富集程度也都处于较低水平,界面处原子间化学键合较弱;加入P、Al、Ge、Sn、In、Sb、Bi后,界面电荷富集有所增强,以Al为例,界面处差分电荷密度如图4(b)所示,界面处原子间化学键合强度中等;而在加入B、Si、S、Zr后,界面电荷富集大大增强,以Si为例,界面处差分电荷密度如图4(c)所示,原子间化学键合较强。
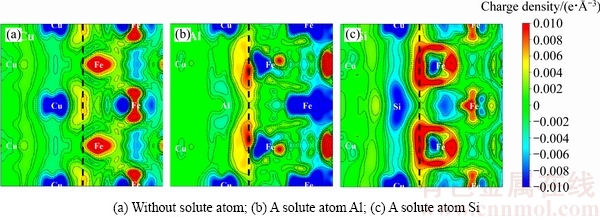
图4 Cu/γ-Fe界面差分电荷密度图
Fig. 4 Difference charge density of Cu/γ-Fe interface

图5 合金元素对Cu/γ-Fe界面差分电荷密度等高线电位最大值的影响
Fig. 5 Maximum value of contour lines of Cu/γ-Fe interface influenced by alloying elements
晶格错配度和原子键合共同导致界面能的变化,以图3中拟合曲线作为对比:添加Mg、Ag、Cd后,界面处电荷富集程度较低,原子间化学键合较弱,形成界面所需的能量较高,导致界面能较高;加入P、Al、Ge、Sn、In、Sb、Bi等7种合金元素后,界面处原子间化学键合强度中等,界面能大小与拟合值相当;而加入B、Si、S、Zr后Cu/γ-Fe界面电荷富集明显,原子间化学键合较强,形成界面所需的能量较低,界面能明显较低。因此,相对体积较小、同时能够增强界面原子间化学键合的合金元素B、Si、S等可以起到降低界面能的作用,有利于γ-Fe的析出形核。
3 结论
1) 所研究的合金元素均倾向富集于Cu/γ-Fe界面Cu原子侧,Mg、Ag位于最远离界面的位置1,Cd位于次近邻界面的位置3,其余合金原子位于最近邻界面的位置4。
2) B、Si、P、Al、Zr使Cu/γ-Fe界面结合能增大,增强界面稳定性。B、Si、P等11种合金元素使Cu/γ-Fe界面能降低,有利于γ-Fe的形核热力学,即B、Si、P、Al、Zr合金元素有助于在形核过程中促进γ-Fe的析出并形成稳定的γ-Fe相。
3) 揭示了合金元素对Cu/γ-Fe界面结合能和界面能的作用机制,即相对体积较小、增强界面处原子键合强度的合金元素可以起到增加界面结合能、降低界面能的作用,为高强高导Cu-Fe合金的设计提供了理论依据。
致谢:衷心感谢上海“魔方”超算计算中心提供模拟计算的硬件平台(曙光5000A)。
REFERENCES
[1] 葛继平, 姚再起. 高强度高导电的形变Cu-Fe原位复合材料[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2004, 14(4): 568-573.
GE Ji-ping, YAO Zai-qi. High strength and high electrical conductivity deformation-processed Cu-Fe in situ composites[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2004, 14(4): 568-573.
[2] GAO H Y, WANG J, SHU D, SUN B D. Effect of Ag on the microstructure and properties of Cu-Fe in situ composites[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2005, 53(10): 1105-1109.
[3] 戴姣燕, 尹志民, 宋练鹏, 袁 远. 不同处理状态下Cu-2.5Fe-0.03P合金的组织与性能演变[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2009, 19(11): 1969-1975.
DAI Jiao-yan, YIN Zhi-min, SONG Lian-peng, YUAN Yuan. Structure and properties evolution of Cu-2.5Fe-0.03P alloy under different treatment conditions[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2009, 19(11): 1969-1975.
[4] YAO Z Q, MA M, LIU Q, ZHAO F. Influence of additional element Zr on strength and conductivity of fiber-reinforced Cu-Fe wire[J]. Procedia Engineering, 2011, 16: 594-600.
[5] 刘克明, 陆德平, 周海涛, 魏仕勇, 刘秋香, 余玖明. 强磁场时效对Cu-Fe-Ag合金组织和性能的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2013, 23(11): 3165-3170.
LIU Ke-ming, LU De-ping, ZHOU Hai-tao, WEI Shi-yong, LIU Qiu-xiang, YU Jiu-ming. Influence of high magnetic field aging on microstructure and properties of Cu-Fe-Ag alloy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2013, 23(11): 3165-3170.
[6] 李文有, 李亚明, 李文生, 孔祥波, 王 华. 形变Cu-15Cr-Ce原位复合材料的组织和性能[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2014, 24(6): 1518-1523.
LI Wen-you, LI Ya-ming, LI Wen-sheng, KONG Xiang-bo, WANG Hua. Microstructure and properties of deformed Cu-15Cr-Ce in-situ composites[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2014, 24(6): 1518-1523.
[7] WANG Y F, GAO H Y, HAN Y F, DAI Y B, BIAN F G, WANG J, SUN B D. First-principles study of solute-vacancy binding in Cu[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2014, 608: 334-337.
[8] BITTER F, KAUFMANN A R. Magnetic studies of solid solutions. I. Methods of observations and preliminary results on the precipitation of iron from copper[J]. Physical Review, 1939, 56(10): 1044.
[9] WANG Y F, GAO H Y, HAN Y F, DAI Y B, WANG J, SUN B D. Role of the third element in accelerating Fe diffusivities in Cu from first principles[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2015, 639: 642-647.
[10] HAN Y F, DAI Y B, SHU D, SUN B D. First-principles calculations on the stability of Al/TiB2 interface[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2006, 89: 144107.
[11] 江 勇, 蓝国强, 王怡人, 周松松. 内氧化Cu/Al2O3界面热力学与杂质效应[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2013, 23(11): 3154-3164.
JIANG Yong, LAN Guo-qiang, WANG Yi-ren, ZHOU Song-song. Interfacial thermodynamics and impurity effects on internally oxidized Cu/Al2O3 interface[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2013, 23(11): 3154-3164.
[12] ZHAO Y H, WEN Z Q, HOU H, GUO W, HAN P D. Density functional theory study of the interfacial properties of Ni/Ni3Si eutectic alloy[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2014, 303: 205-209.
[13] WEN Z Q, ZHAO Y H, HOU H, WANG N, FU L, HAN P D. A first-principles study on interfacial properties of Ni(001)/Ni3Nb(001)[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2014, 24(5): 1500-1505.
[14]  P E. Projector augmented-wave method[J]. Physical Review B, 1994, 50(24): 17953.
P E. Projector augmented-wave method[J]. Physical Review B, 1994, 50(24): 17953.
[15] KRESSE G,  J. Efficient iterative schemes for ab initio total-energy calculations using a plane-wave basis set[J]. Physical review B, 1996, 54(16): 11169.
J. Efficient iterative schemes for ab initio total-energy calculations using a plane-wave basis set[J]. Physical review B, 1996, 54(16): 11169.
[16] ZHANG W, SMITH J R, EVANS A G. The connection between ab initio calculations and interface adhesion measurements on metal/oxide systems: Ni/Al2O3 and Cu/Al2O3[J]. Acta Materialia, 2002, 50(15): 3803-3816.
[17] LIU L, WANG R, WU X, GAN L Y, WEI Q Y. Temperature effects on the generalized planar fault energies and twinnabilities of Al, Ni and Cu: First principles calculations[J]. Computational Materials Science, 2014, 88: 124-130.
[18] BENALI A, LACAZE-DUFAURE C, MORILLO J. Density functional study of copper segregation in aluminum[J]. Surface Science, 2011, 605(3): 341-350.
[19] BRANDES E A, BROOK G B, PAUFLER P. Smithells metals reference book[M]. London: Butter-worths, 1983.
[20] YU J, LIN X, WANG J J, CHEN J, HUANG W D. First-principles study of the relaxation and energy of BCC-Fe, FCC-Fe and AISI-304 stainless steel surfaces[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2009, 255(22): 9032-9039.
[21] 温玉锋, 孙 坚, 黄 健. 基于特殊准随机结构模型的FCC Fe-Cu无序固溶体合金的弹性稳定性[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2012, 22(9): 2522-2528.
WEN Yu-feng, SUN Jian, HUANG Jian. Elastic stability of face-centered cubic Fe-Cu random solid solution alloys based on special quasirandom structure model[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2012, 22(9): 2522-2528.
[22] ACET M,  H, WASSERMANN E F, PEPPERHOFF W. High-temperature moment-volume instability and anti-Invar of γ-Fe[J]. Physical Review B, 1994, 49(9): 6012.
H, WASSERMANN E F, PEPPERHOFF W. High-temperature moment-volume instability and anti-Invar of γ-Fe[J]. Physical Review B, 1994, 49(9): 6012.
[23] JIANG Y, ADAMS J B, van SCHILFGAARDE M. Density-functional calculation of CeO2 surfaces and prediction of effects of oxygen partial pressure and temperature on stabilities[J]. The Journal of chemical physics, 2005, 123(6): 064701.
[24] FINNIS M W. The theory of metal-ceramic interfaces[J]. Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter, 1996, 8(32): 5811.
[25] SUTTON A P, BALLUFFI R W. Interface in crystalline materials[M]. Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1995: 349.
First-principles study of effects of alloying elements on Cu/γ-Fe interfacial properties
XU Pei-yao1, 2, WANG Yu-fei1, 2, GAO Hai-yan1, 2, 3, WANG Jun1, 2, 3, SUN Bao-de1, 2, 3
(1. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200240, China;
2. Shanghai Key Lab of Advanced High-temperature Materials and Precision Forming, Shanghai 200240, China;
3. The State Key Laboratory of Metal Matrix Composites, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200240, China)
Abstract: The substitutional energies of alloying atoms at different interface sites were calculated by first-principles method based on density functional theory, which gives the most favorable sites of alloying atoms. The lattice misfits, work of adhesion, interfacial energy and electronic structure were calculated to analyze the effects of alloying elements on Cu/γ-Fe interfacial properties. The results show that alloying elements B, Si, P, Al, Zr can improve the stability of Cu/γ-Fe interface by increasing the work of adhesion, while eleven kinds of alloying elements such as B, Si, P etc. reduce the interfacial energy, which is beneficial to the nucleation of γ-Fe. Therefore, B, Si, P, Al, Zr may accelerate the precipitation and form stable γ-Fe phase. The solute volumes of alloying atoms, lattice misfits and charge density difference explain well on the working mechanisms of the alloying elements.
Key words: Cu/γ-Fe interface; first-principles; interfacial energy; work of adhesion
Foundation item: Project(51671131) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Received date: 2016-12-08; Accepted date: 2017-05-12
Corresponding author: GAO Hai-yan; Tel: +86-21-54742661; E-mail: gaohaiyan@sjtu.edu.cn
(编辑 王 超)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(51671131)
收稿日期:2016-12-08;修订日期:2017-05-12
通信作者:高海燕,副研究员,博士;电话:021-54742661;E-mail:gaohaiyan@sjtu.edu.cn