文章编号:1004-0609(2013)10-2846-05
不同结构纳米晶镍钴合金的力学性能
秦丽元1,连建设2,蒋恩臣1,刘中原1
(1. 东北农业大学 工程学院,哈尔滨 150030;
2. 吉林大学 材料科学与工程学院,长春 130022)
摘 要:采用直流电沉积方法制备晶粒尺寸为15 nm的Ni-49.2 %Co(质量分数)和16 nm的Ni-66.7%Co(质量分数)合金。采用XRD、TEM和MTS-810万能材料试验机对其微观结构和力学性能进行分析。结果表明:两种合金分别是单相FCC结构和FCC与HCP共存的双相结构。固溶强化和晶粒细化的作用使两种Ni-Co合金都具有很高的抗拉强度;且Co元素的引入降低材料的层错能,提高其应变硬化能力,使Ni-Co合金的塑性也明显提高;Ni-49.2 %Co合金的抗拉强度(σb)和断裂伸长率(δ)分别为1 650 MPa和9%,Ni-66.7%Co合金的σb和δ分别为2 200 MPa和12%。Ni-66.7%Co合金中FCC和HCP结构相互协调,在变形过程中释放内应力,使材料应变硬化能力得以保持,所以获得更高的强度和塑性。
关键词:镍钴合金;电沉积;纳米晶;双相结构;力学性能
中图分类号:TG 113 文献标志码:A
Mechanical properties of nanocrystalline Ni-Co alloy with different microstructures
QIN Li-yuan1, LIAN Jian-she2, JIANG En-chen1, LIU Zhong-yuan1
(1. College of Engineering, Northeast Agricultural University, Harbin 150030, China;
2. College of Materials Science and Engineering, Jilin University, Changchun 130022, China)
Abstract: Nanocrystalline Ni-49.2%Co (mass fraction) and Ni-66.7%Co (mass fraction) alloys were synthesized by direct current electrodeposition with grain sizes of 15 and 16 nm, respectively. The Ni-49.2%Co alloy shows single FCC phase, and Ni-66.7%Co alloy possesses a mixture structure of FCC and HCP phase. The microstructure and mechanical properties of were studied by XRD, TEM and tensile tests carried out on MTS-810 tester. The high strength of Ni-Co alloys is attributed to the grain refinement and solid-solution hardening effects. The addition of Co element decreases the stacking fault energy of nanocrystalline Ni alloy, which improves the strain hardening ability and thus enhances the ductility. The ultimate tensile strength (σb) and elongation to failure (δ) of Ni-49.2%Co alloy are 1 650 MPa and 9%, respectively. Correspondingly, the σb and δ of Ni-66.7%Co alloy are 2 200 MPa and 12%, respectively. Cooperative deformation of the two phases releases the stress during deformation effectively, which contributes to the sustained high strain hardening and ductility of the Ni-66.7%Co alloy.
Key words: Ni-Co alloy; electrodeposition; nanocrystalline; dual-phase microstructure; mechanical property
纳米晶材料,特别是晶粒尺寸小于100 nm的纳米晶材料,在最近一些报道中作为潜在的新一代高强材料引起了研究者们的兴趣。然而,与同成分的粗晶材料相比,纳米晶材料表现出很低的室温塑性,一般只有3%~5%的断裂伸长率[1-4]。所以在不降低纳米晶材料高强度的情况下,很多方法被用来提高其塑性。这些方法包括在纳米结构材料中引入大角晶界[5]、纳米孪晶[6]、双峰或多峰晶粒尺寸分布[7]等。上述方法虽然可以有效地提高材料塑性,但它们一般常用于晶粒尺寸大于50 nm的材料中,对于晶粒尺寸20 nm以下的纳米晶单质及合金材料的高塑性和变形机理仍需充分的研究。因此,制备不同结构的具有临界晶粒尺寸的试样对研究纳米晶材料力学性能是十分必要的。在目前常用的纳米晶材料制备方法当中,电沉积法在制备高纯度的纳米晶块体材料方面是一种既科学又经济的方法,近年来该方法常用来制备纳米晶金属单质及合金材料,以便研究纳米晶材料的力学行为与变形机制[1-2, 4-9]。
在此,本文作者采用直流电沉积法制备了晶粒尺寸相近、且小于20 nm的单相和双相纳米晶镍钴合金,并通过室温下拉伸实验对两种合金的力学行为进行研究。
1 实验
通过直流电沉积方法制备了大约350 mm 厚的高纯度块体Ni-Co合金。镀液中主要包含硫酸镍(约200 g/L),氯化镍(约30 g/L),硼酸(约30 g/L)和硫酸钴。通过调整镀液中镍离子与钴离子的含量比来改变镍钴合金中的成分,镀液中的钴离子含量用紫外分光光度计(SP–752PC,上海光谱仪器厂生产)监控。工作温度保持在50 ℃,电流密度是2.5 A/dm2,pH值控制在5.0。阳极采用纯镍板,阴极用低碳钢板(C1008, AISI)。
采用电感耦合等离子体发射光谱仪(ICP-AES,Plasma/1000)对电沉积纳米Ni-Co合金的成分进行了分析。其晶体结构和显微组织及晶粒尺寸分布分别采用X射线衍射仪(XRD,D/max 2500PC)和透射电子显微镜(TEM,JEM-2000EX)观察。
拉伸实验所用的板状拉伸试样通过线切割方法从块体Ni-Co合金上获得。试样表面经过打磨并抛光,其总长度为33 mm,其工作部分标距为长8 mm,宽2 mm,厚度大约在0.3 mm。室温下采用MTS 810万能材料试验机进行单向静拉伸实验。采用JSM-5600 型扫描电镜(SEM)对变形后试样的断口表面进行观察。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 合金成分
不同于以前研究中较低的Co含量,采用ICP分析所制备的两种合金的Co元素的质量分数分别是49.2%和66.7%。主要杂质是为1.8×10-4S,3×10-4C和1×10-4B。
2.2 合金的微观结构
图1(a)和(b)所示分别为两种所制备合金的XRD谱,从图1(a)看出,Ni-49.2 %Co合金是单一面心立方(FCC)相结构。各晶面衍射峰的位置相对标准峰稍向左偏移,这是由于Co原子固溶到Ni晶格中引起晶格扩张所引起的。图中(111)和(200)两晶面衍射峰的强度比约为2.05,该合金结构是随机生长,晶体没有明显的择优取向。图1(a)中的插图是其TEM选区电子衍射图 (SAD),其结果和XRD结果对应,证明此Ni-Co合金是单相FCC结构。
由图1(b)可以清楚地观察到Ni-66.7%Co合金具有FCC结构中的(111)和(200)晶面衍射峰,且位置比标准峰的稍向左移动。同时,XRD谱中出现了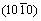 和
和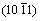 晶面衍射峰,证明形成了HCP结构,这两个晶面衍射峰通常出现在Co和Co基合金的HCP结构中[10-11]。这是在电沉积制备Ni-Co合金过程中Ni和Co元素在沉积过程中偏聚所致,在Ni元素主导的区域形成与其FCC结构相同的Ni-Co固溶体相,在Co元素主导的区域形成HCP结构的Ni-Co固溶体相。Ni-66.7 %Co合金中各相所占比例通过XRD的参照强度比率法(RIR)测定,其HCP和FCC相的质量分数分别是22%和78%。图1(b)中的SAD谱呈均匀的环形花样,表明此合金晶粒细小。另外,最靠近中心位置的衍射环非常宽,这是因为在FCC结构的(111)和(200)晶面衍射峰之间加入了HCP的
晶面衍射峰,证明形成了HCP结构,这两个晶面衍射峰通常出现在Co和Co基合金的HCP结构中[10-11]。这是在电沉积制备Ni-Co合金过程中Ni和Co元素在沉积过程中偏聚所致,在Ni元素主导的区域形成与其FCC结构相同的Ni-Co固溶体相,在Co元素主导的区域形成HCP结构的Ni-Co固溶体相。Ni-66.7 %Co合金中各相所占比例通过XRD的参照强度比率法(RIR)测定,其HCP和FCC相的质量分数分别是22%和78%。图1(b)中的SAD谱呈均匀的环形花样,表明此合金晶粒细小。另外,最靠近中心位置的衍射环非常宽,这是因为在FCC结构的(111)和(200)晶面衍射峰之间加入了HCP的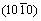 和
和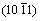 晶面的衍射峰。但较宽的衍射环与非晶不同,是由几个晶面的衍射环叠加而成的,因为最外面(311)和(222)晶面的衍射环依然清晰可见。XRD和SAD谱都表明在此合金中FCC和HCP结构共存,所以称此合金为双相合金。
晶面的衍射峰。但较宽的衍射环与非晶不同,是由几个晶面的衍射环叠加而成的,因为最外面(311)和(222)晶面的衍射环依然清晰可见。XRD和SAD谱都表明在此合金中FCC和HCP结构共存,所以称此合金为双相合金。
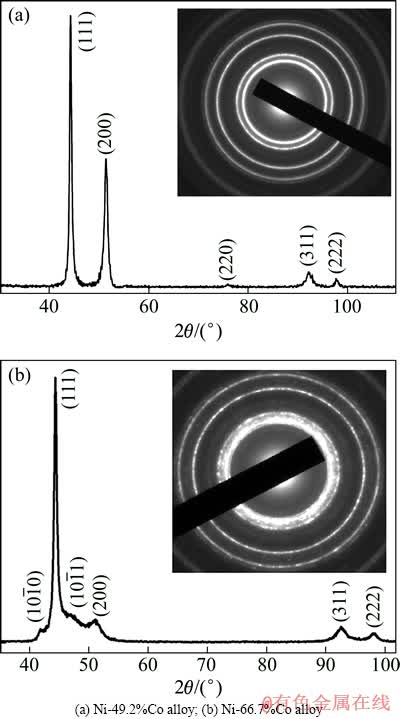
图1 两种纳米晶Ni-Co合金的XRD谱及其选区衍射图
Fig. 1 XRD patterns and selected area diffraction (inset) patterns
两种纳米晶Ni-Co合金的TEM像如图 2所示。图 2(a)所示为单相纳米Ni-49.2%Co合金的TEM像,从图中可以看出,合金的晶粒都是等轴晶,并且尺寸分布窄,晶界处没有发现薄层或第二相粒子。并且根据约对500个晶粒的统计结果分析,其晶粒尺寸为15 nm。
图2(b)所示为双相Ni-66.7%Co合金的TEM像,从中可以观察到大角晶界和一些尺寸在纳米级的小孪晶。图2(b)中插图是其低倍TEM像,此合金晶粒多为等轴晶,并且尺寸均匀,没有柱状晶粒出现。根据对500个晶粒的统计,此双相合金的晶粒尺寸是16 nm。
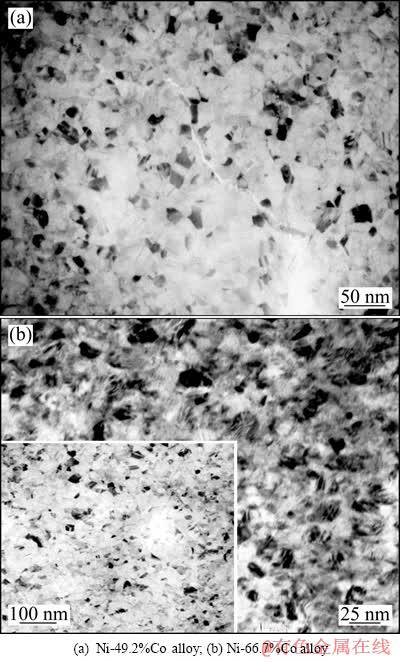
图2 两种纳米晶Ni-Co合金的TEM像
Fig. 2 TEM images of NC Ni-Co alloys
2.3 合金的拉伸性能
为了研究不同结构Ni-Co合金的变形机理,将Ni-49.2%Co和Ni-66.7%Co合金与其他材料的拉伸曲线进行了对比。图3(a)所示为Ni-49.2%Co合金、Ni-66.7%Co合金、晶粒尺寸16 nm Ni和晶粒尺寸为2 μm的粗晶Ni在应变速率1.04×10-3 s-1下的真应力—应变曲线。图3(b)所示为与图3(a)中曲线相对应的应变硬化率(Θ)和真应变关系图。Θ被定义为
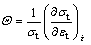 (1)
(1)
式中: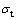 是真应力,
是真应力,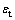 是真应变,
是真应变,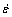 为应变速率。
为应变速率。
从图3(a)可以看出,晶粒尺寸与两种Ni-Co合金近似的16 nm Ni的断裂伸长率(δ)仅约为3%,并且没有颈缩变形过程。而Ni-49.2%Co合金(单相)与Ni-66.7%Co合金(双相)的δ都有明显提高。Ni-49.2%Co合金的抗拉强度(σb)为1.65 GPa,δ约为9%;Ni-66.7%Co合金的δ已达到12%,稍小于粗晶Ni的(16%),但是其σb大约是2.20 GPa,是粗晶Ni强度的4倍。与同样用电沉积方法制备的HCP结构纳米晶Co[6](晶粒尺寸为12 nm)相比,强度相当,塑性更好。而且晶粒尺寸相近的双相和单相Ni-Co合金拉伸曲线的过颈缩区伸长量基本相同,形状也基本相同,所以双相Ni-66.7%Co合金塑性的提高主要来源于变形过程中均匀变形量的增加。
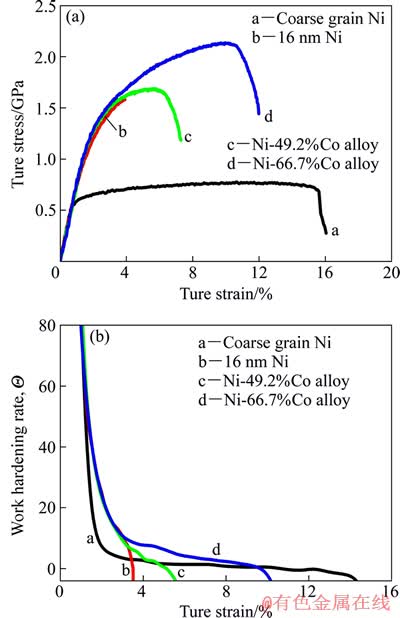
图3 室温下不同材料的真应力—应变曲线和相应标准应变硬化速率与真应变关系曲线
Fig. 3 True stress—strain curves of four types of materials (a) and corresponding normalized work hardening rate (Θ) plot versus true strain (b)
Ni-66.7%Co合金的另一个重要力学特征是它在变形过程中较强的应变硬化能力。从图3(b)中能清楚地看到,纳米晶材料在变形最初阶段的应变硬化率都大于粗晶Ni的。但随着变形过程的继续,16 nm Ni和单相Ni-49.2%Co 合金的应变硬化率分别在ε=3.4%和ε=5.2%时迅速减小为零。但一直到ε=9%,双相Ni-66.7%Co合金的应变硬化率仍然能保持在较高值。
双相合金具有较高应变硬化率,首先是由于形成合金时在Ni晶格中固溶了Co元素,引起了固溶强化和合金整体层错能的降低。以前的研究[12-13]中报道了随材料层错能的降低在晶界处形成分位错所需要的应力降低。而且,层错能的降低将促进电沉积过程中孪晶结构的形成[14],如图2(b)中所示。材料微观结构中出现纳米尺寸孪晶结构能有效地提高材料的应变硬化率[6]。因此,添加Co元素所引起的层错能降低是NC Ni-Co合金具有较高应变硬化能力的主要原因。另外,NC金属材料变形最初较高的应变硬化率还可能源自于不同变形晶粒之间的应力不相容所产生的内应力[8]。
在材料变形过程中,位错的运动和增殖被像孪晶界等特殊的晶界所阻碍,通常导致其应变硬化能力增强[15]。应变硬化能抑制塑性变过程形中的失稳,从而提高材料的整体塑性,但同时也会引起应力集中,这会促使微裂纹的形成和扩展。普通单相纳米晶材料变形过程中,由于应力释放机制受到制约,微裂纹在变形过程中将引起断裂[16]。但当双相Ni-66.7%Co合金微观结构中同时存在硬相(HCP)和软相(FCC)结构,而且FCC结构中也包括孪晶和等轴晶两种结构时,变形过程中FCC等轴晶粒首先参与变形并会在晶界和相界处引起应力集中。但随后HCP和FCC孪晶结构中的位错被激活并参与变形能有效释放应力,从而保持应变硬化能力。另外,HCP相的主要元素Co本身既有很高的强度又有良好的塑性[11],同时其在双相合金中又起到第二相粒子强化的作用。所以对比单相Ni-Co合金,通过双相协调变形有效的释放应力,使双相合金在变形过程中具有持续的应变硬化能力,从而提高了整体塑性。
2.4 合金的断口形貌
对应于图3(a)中拉伸曲线,两种纳米晶Ni-Co合金拉伸变形断裂后的试样宏观表面和断口形貌如图4所示。单相Ni-49.2%Co合金(见图4(a))断口形貌呈细小的韧窝状。这是由于变形过程中某些晶粒共同运动,形成包含许多晶粒的剪切带,最后扩展断裂所致[17]。双相Ni-66.7%Co合金的断裂形貌如图4(b)所示,从试样宏观照片中可以看到适当颈缩的存在,拉伸方向与断裂方向约为65°角。断口形貌与传统塑性材料的断口形貌非常接近,是尺寸500 nm~4 μm、大而深的韧窝状形貌。另外,图4(b)中白框标记出的区域存在与图4(a)中类似的小韧窝。所以,纳米晶材料的断口形貌主要与材料塑性有关,晶粒尺寸对其影响不大,只要纳米晶材料的塑性足够好,也可以具有类似粗晶塑性材料的断口形貌。

图4 应变速率1.04×10-3 s-1下拉伸试样宏观和断口表面形貌
Fig. 4 Macroscopic and fracture surface morphologies at strain rate of 1.04×10-3 s-1
3 结论
1) 采用直流电沉积方法分别制备了NC Ni-49.2%Co合金和Ni-66.7%Co合金。Ni-49.2%Co平均晶粒尺寸为15 nm,晶粒尺寸分布范围较窄,具有单一的FCC结构。NC Ni-66.7%Co合金具有FCC和HCP双相共存结构,平均晶粒尺寸为16 nm。
2) 通过固溶强化和晶粒细化,两种合金都具有较高的强度。NC Ni-Co合金塑性提高的一个共同原因是固溶Co元素降低了合金的层错能,材料在变形过程中保持较高的应变硬化能力,从而提高材料的塑性。因为FCC和HCP结构协调作用,有效地释放了变形过程中的内应力,使材料具有持续应变硬化能力,所以,双相合金具有较高的强度和更好的塑性。
3) 材料断口形貌主要取决于其塑性,晶粒尺寸对其影响不大。所以,双相Ni-66.7%Co合金具有与粗晶Ni类似的断口形貌。
REFERENCES
[1] HIBBARD G D, AUST K T, ERB U. Thermal stability of electrodeposited nanocrystalline Ni-Co alloys[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2006, 433(1/2): 195-202.
[2] 许伟长, 戴品强. 电沉积微纳米镍的组织结构与力学性能[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2009, 19(10): 1815-1821.
XU Wei-chang, DAI Pin-qiang. Microstructures and mechanical properties of electrodeposited microcrystalline and nanocrystalline Ni[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2009, 19(10): 1815-1821.
[3] 冯广海, 杜忠泽, 闫 敦, 王经涛. 纳米/微米Cu的力学性能数值模拟[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2012, 22(1): 201-207.
FENG Guang-hai, DU Zhong-ze, YAN Dun, WANG Jing-tao. Numerical simulation of mechanical properties in nano-/microcrystalline Cu[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2012, 22(1): 201-207.
[4] 秦丽元. 电沉积纳米晶镍及镍钴合金的微观组织和性能研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学材料学院, 2010: 1-122.
QIN Li-yuan. Microstructures and properties characteristic of electrodeposited nanocrystalline Ni and Ni-Co alloys[D]. Changchun: College of Materials Science and Engineering, Jilin University, 2010: 1-122.
[5] VALIEV R. Nanostructuring of metals by severe plastic deformation for advanced properties[J]. Nature Materials, 2004, 3(8): 511-516.
[6] LU L, CHEN X, HUANG X, LU K. Revealing the maximum strength in nanotwinned copper[J]. Science, 2009, 323(5914): 607-610.
[7] SHEN X, LIAN J, JIANG Z, JIANG Q. The optimal grain sized nanocrystalline Ni with high strength and good ductility fabricated by a direct current electrodeposition[J]. Advanced Engineering Materials, 2008, 10(6): 539-546.
[8] LI H. EBRAHIMI F. Transition of deformation and fracture behaviors in nanostructured face-centered-cubic metals[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2004, 84(12): 4307-4309.
[9] 许伟长, 戴品强, 郑耀东. 钴含量对电沉积纳米晶镍钴合金组织与力学性能的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2010, 20(1): 92-99.
XU Wei-chang, DAI Pin-qiang, ZHENG Yao-dong. Effect of Co content on structures and mechanical properties of electrodeposited nanocrystalline Ni-Co alloys[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2010, 20(1): 92-99.
[10] LIU Y, YANG H, LIU Y, JIANG B, DING J, WOODWARD R. Thermally induced fcc hcp martensitic transformation in Co-Ni[J]. Acta Materialia, 2005, 53(13): 3625-3634.
hcp martensitic transformation in Co-Ni[J]. Acta Materialia, 2005, 53(13): 3625-3634.
[11] KARIMPOOR A A, ERB U, AUST K T, PALUMBO G. High strength nanocrystalline cobalt with high tensile ductility[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2003, 49(7): 651-656.
[12] LU K, LU L, SURESH S. Strengthening materials by engineering coherent internal boundaries at the nanoscale[J]. Science, 2009, 324(5925): 349-352.
[13] EBRAHIMI F, AHMED Z, LI H. Effect of stacking fault energy on plastic deformation of nanocrystalline face-centered cubic metals[J]. Appl Phys Lett, 2004, 85(17): 3749-3751.
[14] YAMAKOV V, WOLF D, PHILLPOT S R, MUKHERJEE A K, GLEITER H. Deformation-mechanism map for nanocrystalline metals by molecular-dynamics simulation[J]. Nature Materials, 2004, 3(1): 43-47.
[15] YOUSSEF K M, SCATTERGOOD R O, MURTY K L, HORTON J A, KOCH C C. Ultrahigh strength and high ductility of bulk nanocrystalline copper[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2005, 87(9): 091904-091903.
[16] OVID'KO I A. SHEINERMAN A G. Special strain hardening mechanism and nanocrack generation in nanocrystalline materials[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2007, 90(17): 171927-171923.
[17] HASNAOUI A, van SWYGENHOVEN H, DERLET P M. Dimples on nanocrystalline fracture surfaces as evidence for shear plane formation[J]. Science, 2003, 300(5625): 1550-1552.
(编辑 龙怀中)
基金项目:国家博士后基金资助项目(2012M520698);黑龙江省教育厅科技项目(12531002);东北农业大学博士启动基金资助项目(2012RCB97)
收稿日期:2013-01-23;修订日期:2013-05-20
通信作者:秦丽元,讲师,博士;电话:0451-55191476;E-mail:qinliyuan2006@163.com