DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2017.11.034
烧结矿余热回收竖罐内气固传热过程数值分析
冯军胜,董辉,高建业,梁凯,刘靖宇
(东北大学 国家环境保护生态工业重点实验室,辽宁 沈阳,110819)
摘要:以某钢铁企业年产390万t烧结矿为研究对象,基于多孔介质理论和局部非热力学平衡双能量方程模型,建立烧结矿竖罐内气固稳态传热模型,并借助Fluent软件及其二次开发平台,以回收的空气热量和空气 为判定基准,对不同操作参数对竖罐内气固传热过程的影响进行模拟研究。研究结果表明:回收的空气热量和空气
为判定基准,对不同操作参数对竖罐内气固传热过程的影响进行模拟研究。研究结果表明:回收的空气热量和空气 随烧结矿入口温度的升高而逐渐增加,随烧结矿颗粒直径的增大而逐渐减少;随着气料比的增加,回收空气热量的增加趋势逐渐变缓,空气
随烧结矿入口温度的升高而逐渐增加,随烧结矿颗粒直径的增大而逐渐减少;随着气料比的增加,回收空气热量的增加趋势逐渐变缓,空气 则呈现出先增大后减少的趋势;随着空气入口温度的升高,回收的空气热量逐渐减少,空气
则呈现出先增大后减少的趋势;随着空气入口温度的升高,回收的空气热量逐渐减少,空气 则逐渐增加。在实际操作工况改变时,通过气料比的调节可达到最佳气固换热效果,获得最大的空气
则逐渐增加。在实际操作工况改变时,通过气料比的调节可达到最佳气固换热效果,获得最大的空气 。
。
关键词:烧结矿;竖罐;多孔介质;气固传热;数值分析
中图分类号:TK11+5; TK124 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2017)11-3100-08
Numerical analysis of gas-solid heat transfer process in vertical tank for sinter waste heat recovery
FENG Junsheng, DONG Hui, GAO Jianye, LIANG Kai, LIU Jingyu
(SEP Key Laboratory on Eco-industry, Northeastern University, Shenyang 110819, China)
Abstract: Choosing the annual output of 3 900 000 t sinter in an iron and steel company as the subject, the gas solid steady-state heat transfer model in sinter vertical tank was established on the basis of the porous medium theory and the two-equation energy model of local non-equilibrium thermodynamics. By employing Fluent software and the user defined functions (UDF), the recovered air energy and the air exergy were used as the criteria to study the effects of different operation parameters on gas solid heat transfer in vertical tank. The results show that the recovered air energy and the air exergy gradually increase with the increase of sinter inlet temperature, and gradually decrease with the increase of sinter particle diameter. With the increase of gas sinter ratio, the increasing tendency of air energy becomes slower, and the air exergy firstly increases and then decreases. In addition, with the increase of air inlet temperature, the recovered air energy gradually decreases and the air exergy gradually increases. When operation conditions change, optimal gas solid heat transfer performance as well as the maximal air exergy can be achieved through the adjustment of gas sinter ratio.
Key words: sinter; vertical tank; porous medium; gas-solid heat transfer; numerical analysis
烧结余热资源的高效回收利用是目前降低烧结工序能耗乃至炼铁工序能耗的主要途径之一[1]。烧结余热竖罐式回收是针对传统烧结余热回收系统的不足[2],借鉴干熄焦炉的结构形式而提出的一种烧结矿余热高效回收方式[3-4]。竖罐内气固传热过程是决定烧结余热竖罐式回收可行性的主要因素之一,直接影响烧结矿出口温度的高低和出口热载体的品质,进而影响烧结矿余热回收率和后续的余热发电量:因此,研究竖罐内气固传热过程,对提高烧结矿余热回收利用率以及优化竖罐的结构和操作参数都具有十分重要的意义。由于烧结矿竖罐床层内气固传热过程的复杂性,床层内气固传热尚处于理论研究阶段,从而造成现有烧结矿竖罐的设计以及竖罐结构和操作参数的确定更多是基于经验而缺乏理论上的指导。目前,有关烧结矿床层内气固传热过程的研究主要集中于烧结矿环冷机中。CAPUTO等[5]提出环冷机床层内气固传热模型,同时采用动态模拟方法研究了烧结环冷机内气固传热过程。LEONG等[6]基于多孔介质和局部热力学平衡理论建立了环冷机内气固传热的非稳态模型,研究了床层空隙率对气体流动和烧结矿温度分布的影响,但该模型认为烧结矿温度和冷却空气温度是相同的,忽略了冷却空气和烧结料层之间的对流换热。JANG等[7]采用CFD和实验相结合的方法研究了三维烧结矿床层内的湍流和传热过程,但该模型对实际情况进行了比较理想的简化,将烧结矿床层作为1个4排球形填充床层来处理。刘斌等[8]建立了烧结料层内流动和传热的二维非稳态模型,并考虑颗粒直径、空隙率等参数变化对模拟计算的影响,研究了冷却风量、给料温度和燃料配比等参数对烧结过程的影响。张家元等[9]对环冷机内不同分层布料工况和常规布料工况进行模拟研究,并以余热回收率最大化为目标,得到了环冷机内适宜的分层布料参数。ZHANG等[10]以多孔介质模型为基础,采用局部非热力学平衡理论建立了环冷机内三维气固传热模型,并对环冷机内烧结矿冷却过程进行模拟研究和参数优化分析。LIU等[11]基于局部非热力学平衡理论建立了环冷机内的气固传热模型,对进口风速、床层高度和空隙率等参数对床层内压力场、速度场和温度场的影响进行了模拟分析,同时对不同工况下的余热回收量进行了能量分析和 分析。以上关于环冷机床层内气固传热的研究主要集中于非稳态气固传热模型和参数影响分析。但烧结矿竖罐内气固传热过程是气固移动床式逆流稳态传热过程,求解环冷机的非稳态气固传热模型很难用于求解烧结矿竖罐内的稳态传热过程。董辉等[12-13]虽然采用了数值模拟和解析计算的方法对烧结矿竖罐内气固传热过程进行研究,但并没有考虑颗粒直径对气固传热过程的影响。同时,数学模型中的气流黏性阻力系数和惯性阻力系数以及气固传热系数均采用传统经验关联式,因此,也不适用于求解竖罐内的气体流动和气固传热过程。由于对烧结矿床层内气固传热过程的稳态研究较少,同时考虑到烧结矿竖罐自身结构的复杂性,一些重要的操作参数(如气料比、空气入口温度等)和床层几何特性参数(如烧结矿颗粒直径、床层空隙率等)对床层内气固传热过程的影响仍有待研究。为此,本文作者以多孔介质模型为基础,基于局部非平衡热力学双能量方程,建立竖罐内三维稳态移动床式气固传热模型,从余热回收的“量”和“质”2个方面,模拟分析并研究烧结矿入口温度、气料比、烧结矿颗粒直径和空气入口温度对竖罐内气固传热过程的影响,以便为烧结矿余热竖罐的设计和运行提供理论依据。
分析。以上关于环冷机床层内气固传热的研究主要集中于非稳态气固传热模型和参数影响分析。但烧结矿竖罐内气固传热过程是气固移动床式逆流稳态传热过程,求解环冷机的非稳态气固传热模型很难用于求解烧结矿竖罐内的稳态传热过程。董辉等[12-13]虽然采用了数值模拟和解析计算的方法对烧结矿竖罐内气固传热过程进行研究,但并没有考虑颗粒直径对气固传热过程的影响。同时,数学模型中的气流黏性阻力系数和惯性阻力系数以及气固传热系数均采用传统经验关联式,因此,也不适用于求解竖罐内的气体流动和气固传热过程。由于对烧结矿床层内气固传热过程的稳态研究较少,同时考虑到烧结矿竖罐自身结构的复杂性,一些重要的操作参数(如气料比、空气入口温度等)和床层几何特性参数(如烧结矿颗粒直径、床层空隙率等)对床层内气固传热过程的影响仍有待研究。为此,本文作者以多孔介质模型为基础,基于局部非平衡热力学双能量方程,建立竖罐内三维稳态移动床式气固传热模型,从余热回收的“量”和“质”2个方面,模拟分析并研究烧结矿入口温度、气料比、烧结矿颗粒直径和空气入口温度对竖罐内气固传热过程的影响,以便为烧结矿余热竖罐的设计和运行提供理论依据。
1 模型的建立
1.1 物理模型及其基本假设
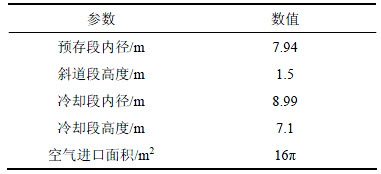
冷却空气(即热载体)分别从风帽口和罐体底部鼓入烧结矿竖罐内,与罐体内炽热烧结矿进行逆流式气固热交换,然后从斜道段出风口排出。烧结机尾部的烧结矿自罐体顶部进入竖罐预存段内,自上往下缓慢下移,在冷却段与上行的冷却空气进行热交换而得以冷却,最后由罐体底部排出。由于竖罐内气固换热的区域基本集中在冷却段和斜道段,故本文针对竖罐冷却段和斜道段建立物理模型,如图1所示。烧结矿竖罐结构参数如表1所示[14]。由于竖罐中心风帽与竖罐冷却段之间的内径和高度差距较大,考虑到网格边界的光滑性和正交性对模拟计算精度和收敛性的影响,采用分块网格生成技术对竖罐本体区域进行网格划分,在换热强烈区域使用加密网格,对于其他计算区域使用稀疏网格,同时对所划分网格进行无关性验证。
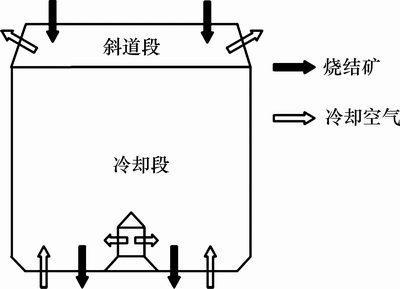
图1 烧结矿竖罐物理模型
Fig. 1 Physical model of sinter vertical tank
表1 烧结矿竖罐结构参数
Table 1 Structural parameters of sinter vertical tank
烧结矿颗粒的不均匀性和不规则性导致竖罐内气体流动和气固传热过程极其复杂,难以对其整个传热过程进行精确的数学描述和数值计算。由于竖罐内烧结矿颗粒直径远小于竖罐内径,因此,可对其进行平均化和统计处理,将烧结矿堆积区域假设为多孔介质区域来进行数值计算[15]。为此,对烧结矿竖罐的物理模型进行如下假设:
1) 烧结矿竖罐在稳定工况下运行,各操作参数为定值,没有波动变化。
2) 竖罐内的气体流动被视为单相稳态非Darcy 流动。
3) 烧结矿为各相同性的多孔介质,不考虑烧结矿自身的多孔性及在高温下的形变。
4) 竖罐内的气体为不可压缩流体,但气体密度变化符合理想气体状态方程。
5) 忽略烧结矿颗粒之间的辐射换热及竖罐壁面热损失。
1.2 数学模型
根据不可压缩黏性流体非定常流动的 Navier- Stokes方程,选用标准 k-ε湍流模型来描述竖罐内气体流动传热规律。根据质量守恒、动量守恒和能量守恒原理,竖罐内气固流动与传热过程三维稳态数学模型控制方程如下。
1) 连续性方程:
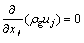 (1)
(1)
2) 动量传输方程:
 (2)
(2)
式中: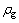 为空气密度,kg/m3;ui为流体在i方向上的速度,m/s;Pij为表面压力矢量,包括静压力和流体黏性压力;gi为流体在i方向上的体积作用力,N/m3;fi为作用在单位体积流体上的反方向阻力,N/m3。
为空气密度,kg/m3;ui为流体在i方向上的速度,m/s;Pij为表面压力矢量,包括静压力和流体黏性压力;gi为流体在i方向上的体积作用力,N/m3;fi为作用在单位体积流体上的反方向阻力,N/m3。
考虑到多孔介质对流体黏性和惯性的影响,可以通过增加源项Si对多孔介质模型中动量传输方程进行修正,如式(3)所示。源项由2部分组成:第1部分为黏性损失项,即式(3)右边第1项;第2部分为惯性损失项,即式(3)右边第2项。
 (3)
(3)
式中: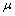 为空气动力黏度,kg/(m·s);
为空气动力黏度,kg/(m·s);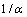 为空气阻力系数;C2为空气惯性阻力系数。
为空气阻力系数;C2为空气惯性阻力系数。
本文采用修正Ergun型方程计算竖罐床层内的黏性阻力系数和惯性阻力系数[16]。
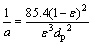 (4)
(4)
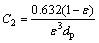 (5)
(5)
式中: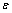 为床层空隙率;dp为烧结矿颗粒当量直径(即烧结矿实际筛分颗粒直径与颗粒形状因子的乘积,下文中均简称为烧结矿颗粒直径),m。
为床层空隙率;dp为烧结矿颗粒当量直径(即烧结矿实际筛分颗粒直径与颗粒形状因子的乘积,下文中均简称为烧结矿颗粒直径),m。
3) 局部非热力学平衡双能量方程。当颗粒床层内气固两相热容和热导率相差较大时,各相局部温度变化率明显不同[17]。本文将固相温度 Ts和气相温度 Tg作为2个单独的变量,分别表征同一微元体内固相和气相的热状态,把多孔介质内的传热视为气固之间的传热,得到以下通用方程组[18]:
对于固相,
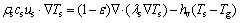 (6)
(6)
对于气相,
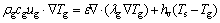 (7)
(7)
式中:ρs为烧结矿的密度,kg/m3;cs和cg分别为烧结矿和空气的比热容,J/(kg·K);us和ug别为颗粒表观下移速度和气体表观流速,m/s;Ts和Tg分别为烧结矿和空气温度,K;λs和λg分别为烧结矿和空气的导热系数,W/(m·K);hv为气固对流体积换热系数,J/(m3·s·K)。
hv可利用Achenbach准则关系式[19]计算:
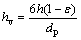 (8)
(8)
其中,气固传热系数h可由下式确定[20]:
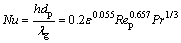 (9)
(9)
其中:
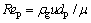 (10)
(10)
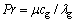 (11)
(11)
式中:h 为气固对流面积换热系数,J/(m2·s·K);Nu为对流传热努塞尔数;Pr为普朗特数;Re为颗粒雷诺数;μ为空气动力黏度,kg/(m·s)。
在模拟分析中,余热回收的“量”和“质”分别用竖罐回收的空气热量Q和空气 Ex来确定[21]。二者计算公式如下。
Ex来确定[21]。二者计算公式如下。
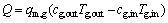 (12)
(12)
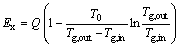 (13)
(13)
式中:Q为回收的空气热量,GJ/h;Ex为回收的空气 ,GJ/h;qm,g为空气质量流量,kg/h;T0为环境温度,K;
,GJ/h;qm,g为空气质量流量,kg/h;T0为环境温度,K;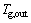 和
和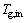 分别为竖罐出口空气温度和竖罐进口空气温度,K。
分别为竖罐出口空气温度和竖罐进口空气温度,K。
1.3 边界条件
竖罐底部和中心风帽的气体进口采用速度进口边界条件,速度及温度由实际给定的参数通过理论计算得出。对于竖罐冷却段和斜道段壁面,设置为绝热壁面。对于斜道段空气出口,设置为压力出口边界条件,设置相对压力为0。
1.4 数值计算方法
本文采用流体力学计算软件Fluent对竖罐内的气固传热过程进行数值求解,采用隐式格式对求解方程进行离散,采用SIMPLE算法对压力与速度的耦合进行求解。由于烧结矿和空气的物性参数随温度发生变化,同时考虑到动量方程源项和气固传热公式需要编译到求解方程中,因此,本文借助Fluent软件的二次开发平台,通过用户自定义函数(user defined function, UDF)得出动量方程源项、能量方程中的气固传热源项以及气固两相物性参数随温度的变化等。
1.5 模型验证
目前烧结矿竖罐正处于理论研究阶段,无法获得全面的竖罐运行数据。烧结矿竖罐和干熄焦炉同属大颗粒移动床,颗粒床层内均为气固逆流式换热,二者的区别主要在于颗粒特性参数、设备结构参数和气固换热温区不同。本文以宝钢三期75 t/h干熄焦炉2种运行工况为例,干熄焦炉焦炭参数和主要设计参数见文献[13, 22]。将多孔介质模型和局部非热力学平衡模型所得模拟计算结果与实测结果进行对比分析,以验证模型的可靠性。干熄焦炉不同工况下实测值与计算值对比结果如表2所示。
从表2可以看出:采用本模型所得焦炭出口温度和热载体出口温度的实际测量值与模拟计算值基本一致,平均相对误差为5.57%,最大相对误差也在8%以下,说明二者较吻合,同时也证明本文所建模型是正确和可靠的。
2 结果分析与讨论
由于烧结机烧结终点位置和竖罐底部入口空气预热效果的不同,进入竖罐的烧结矿温度和冷却空气温度并不是恒定的,而气料比是烧结矿冷却过程重要的调节参数,同时,烧结矿的颗粒直径又是影响竖罐内气固传热过程的主要参数。因此,利用已建立的数值模型,计算并讨论烧结矿入口温度、气料比、烧结矿颗粒直径和空气入口温度对竖罐内气固传热过程的影响。不同影响因素的变化情况如表3所示。
2.1 烧结矿入口温度的影响
在气料比为800 m3/t,烧结矿颗粒直径为0.025 m,空气入口温度为313 K条件下,沿竖罐高度方向上的空气温度随烧结矿入口温度变化的规律如图2所示。
由图2可知:沿竖罐高度方向上的空气温度随烧结矿入口温度的升高而逐渐升高,烧结矿入口温度越高,空气温度沿竖罐高度方向上的变化趋势就越大。这是因为,烧结矿入口温度的升高将导致竖罐内气固换热温差的增大,烧结矿与冷却空气间的传热将会增强,传热量也会随之增加。当烧结矿入口温度由873.0 K增加到973.0 K时,冷却空气出口温度由 736.2 K升高到831.5 K,增加12.94%。烧结矿入口温度每升高10 K,空气出口温度平均升高9.53 K。
图3所示为竖罐回收的空气热量和空气 随烧结矿入口温度的变化规律。由图3可知:回收的空气热量和空气
随烧结矿入口温度的变化规律。由图3可知:回收的空气热量和空气 均随烧结矿入口温度的升高而逐渐增大。
均随烧结矿入口温度的升高而逐渐增大。
表2 不同工况下实测值与计算值比较
Table 2 Comparison of measured and calculation results under different conditions
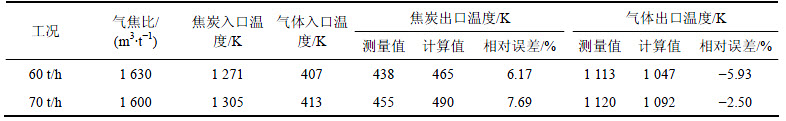
表3 数值模拟计算工况
Table 3 Conditions of numerical simulation
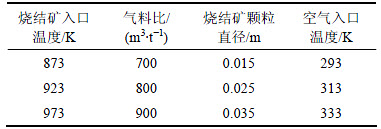
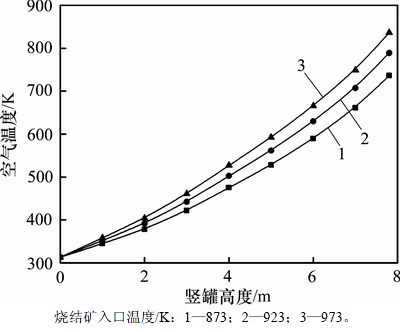
图2 烧结矿入口温度对沿竖罐高度方向上空气温度的影响
Fig. 2 Effect of sinter inlet temperature on air temperature along height of vertical tank
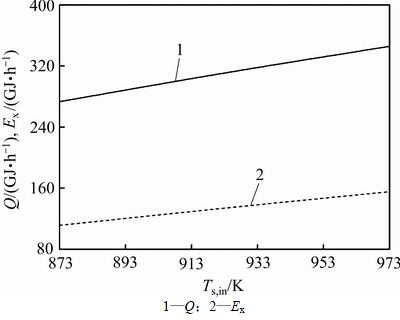
图3 烧结矿入口温度对回收的空气热量Q和空气 Ex的影响
Ex的影响
Fig. 3 Effect of sinter inlet temperature on air energy recovered and air exergy
这是因为烧结矿入口温度升高将导致竖罐出口空气温度升高。在空气进口流量和入口温度不变的条件下,回收的空气热量和空气 必然会随之增加。当烧结矿入口温度由873 K升高到973 K时,回收的空气热量由273.24 GJ/h增加到345.62 GJ/h,提高26.49%;空气
必然会随之增加。当烧结矿入口温度由873 K升高到973 K时,回收的空气热量由273.24 GJ/h增加到345.62 GJ/h,提高26.49%;空气 由111.44 GJ/h增加到155.46 GJ/h,提高39.5%。烧结矿入口温度每升高10 K,回收的空气热量平均增加7.24 GJ/h,空气
由111.44 GJ/h增加到155.46 GJ/h,提高39.5%。烧结矿入口温度每升高10 K,回收的空气热量平均增加7.24 GJ/h,空气 平均增加4.40 GJ/h。
平均增加4.40 GJ/h。
2.2 气料比的影响
在烧结矿入口温度为923 K,烧结矿颗粒直径为0.025 m和空气入口温度为313 K条件下,沿竖罐高度方向上的空气温度随气料比的变化规律如图4所示。
由图4可知:沿竖罐高度方向上的空气温度随气料比的增大而逐渐降低。气料比越大,空气温度沿竖罐高度方向上的降低趋势就越明显。这是因为在烧结矿处理量不变的条件下,气料比的增大将导致冷却空气进口流量的增加,烧结矿与冷却空气间的传热将会增强,但由于烧结矿入口热容量不变,冷却空气流量的增大必然会导致出口空气温度的降低。当气料比由700 m3/t增加到900 m3/t时,冷却空气出口温度由815.0 K下降到744.1 K,降低8.7%;气料比每增大20 m3/t,空气出口温度平均降低7.09 K。
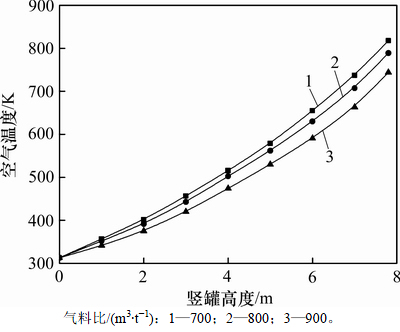
图4 气料比对沿竖罐高度方向上空气温度的影响
Fig. 4 Effect of gas sinter ratio on air temperature along the height of vertical tank
图5所示为竖罐回收的空气热量和空气 随气料比的变化规律。由图5可知:随着气料比的增大,回收的空气热量逐渐增加,并在气料比到达某一特定值后,回收的空气热量随气料比增大而增加的趋势逐渐变缓,最后基本保持不变。这是因为气料比的增大导致竖罐内气固换热效果增强,烧结矿出口温度降低,出口空气温度也随之降低,由于气固传热过程的发生需要固体和气体存在一定的温差,这使得烧结矿出口温度的下降趋势越来越小,导致回收的空气热量的增加趋势也越来越小,最终保持不变。当气料比由700 m3/t增加到800 m3/t时,回收的空气热量由289.02 GJ/h增加到311.41 GJ/h,提高7.75%。而当气料比由800 m3/t增加到900 m3/t时,回收的空气热量由311.41 GJ/h增加到314.27 GJ/h,仅提高0.92%。
随气料比的变化规律。由图5可知:随着气料比的增大,回收的空气热量逐渐增加,并在气料比到达某一特定值后,回收的空气热量随气料比增大而增加的趋势逐渐变缓,最后基本保持不变。这是因为气料比的增大导致竖罐内气固换热效果增强,烧结矿出口温度降低,出口空气温度也随之降低,由于气固传热过程的发生需要固体和气体存在一定的温差,这使得烧结矿出口温度的下降趋势越来越小,导致回收的空气热量的增加趋势也越来越小,最终保持不变。当气料比由700 m3/t增加到800 m3/t时,回收的空气热量由289.02 GJ/h增加到311.41 GJ/h,提高7.75%。而当气料比由800 m3/t增加到900 m3/t时,回收的空气热量由311.41 GJ/h增加到314.27 GJ/h,仅提高0.92%。
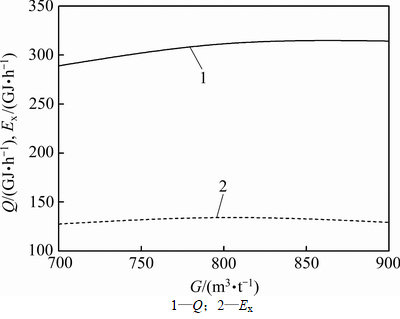
图5 气料比对回收的空气热量Q和空气 Ex的影响
Ex的影响
Fig. 5 Effect of gas sinter ratio on air energy recovered and air exergy
由图5可知空气 随气料比的增大而先增加后减小。这是因为随着空气出口温度降低,单位空气
随气料比的增大而先增加后减小。这是因为随着空气出口温度降低,单位空气 的下降幅度越来越大。当气料比由700 m3/t增加到800 m3/t时,由于回收的空气热量的增加幅度大于单位空气
的下降幅度越来越大。当气料比由700 m3/t增加到800 m3/t时,由于回收的空气热量的增加幅度大于单位空气 的下降幅度,导致空气
的下降幅度,导致空气 随气料比的增加而逐渐增加,由127.59 GJ/h增加到134.18 GJ/h,提高5.65%。而当气料比由800 m3/t增加到900 m3/t时,由于回收的空气热量的增加幅度减小,单位空气
随气料比的增加而逐渐增加,由127.59 GJ/h增加到134.18 GJ/h,提高5.65%。而当气料比由800 m3/t增加到900 m3/t时,由于回收的空气热量的增加幅度减小,单位空气 下降幅度变大,导致空气
下降幅度变大,导致空气 随气料比增加而逐渐降低,由134.18 GJ/h下降到129.30 GJ/h,降低3.64%。
随气料比增加而逐渐降低,由134.18 GJ/h下降到129.30 GJ/h,降低3.64%。
2.3 烧结矿颗粒直径的影响
在烧结矿入口温度为923.0 K,气料比为800 m3/t和空气入口温度为313.0 K的条件下,沿竖罐高度方向上的空气温度随烧结矿颗粒直径的变化规律如图6所示。
由图6可知:沿竖罐高度方向上的空气温度随烧结矿颗粒直径的减小而逐渐升高。这是因为在竖罐结构参数和烧结矿处理量不变的条件下,烧结矿颗粒直径的减小将导致床层空隙率的减小,竖罐内颗粒的填充体积减小,颗粒的下移速度也随之降低,气固换热时间增加。另外,烧结矿颗粒直径减小将导致颗粒导热热阻减小,烧结矿与冷却空气之间综合传热系数增加。同时,床层空隙率的减小使得床层内气固换热面积增加,烧结矿与冷却空气之间的传热量随之增加, 空气出口温度也随之升高。当烧结矿颗粒直径由 0.015 m增加到0.035 m时,冷却空气出口温度由 810.4 K下降到765.4 K,降低5.55%。烧结矿颗粒直径每增加0.005 m,空气出口温度平均降低11.25 K。
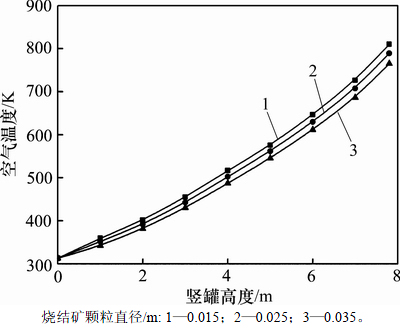
图6 烧结矿颗粒直径对沿竖罐高度方向上空气温度的影响
Fig. 6 Effect of sinter particle diameter on air temperature along height of vertical tank
图7所示为竖罐回收的空气热量和空气 随烧结矿颗粒直径的变化规律。由图7可知回收的空气热量和空气
随烧结矿颗粒直径的变化规律。由图7可知回收的空气热量和空气 均随烧结矿颗粒直径的增大而逐渐减少。这是因为,烧结矿颗粒直径增大将导致竖罐出口空气温度的降低,回收的空气热量和空气
均随烧结矿颗粒直径的增大而逐渐减少。这是因为,烧结矿颗粒直径增大将导致竖罐出口空气温度的降低,回收的空气热量和空气 也随之减少。当烧结矿颗粒直径由0.015 m增加到0.035 m时,回收的空气热量由326.28 GJ/h下降到293.93 GJ/h,降低9.91%,空气
也随之减少。当烧结矿颗粒直径由0.015 m增加到0.035 m时,回收的空气热量由326.28 GJ/h下降到293.93 GJ/h,降低9.91%,空气 由143.38 GJ/h下降到123.65 GJ/h,降低13.76%。烧结矿颗粒直径每增加0.005 m,回收的空气热量平均减少8.09 GJ/h,空气
由143.38 GJ/h下降到123.65 GJ/h,降低13.76%。烧结矿颗粒直径每增加0.005 m,回收的空气热量平均减少8.09 GJ/h,空气 平均减少4.93 GJ/h。
平均减少4.93 GJ/h。
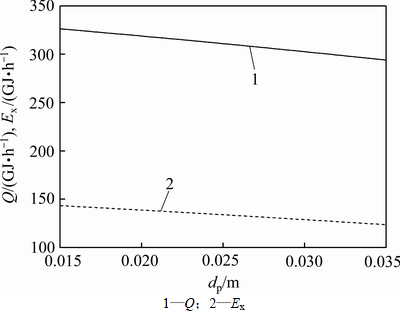
图7 烧结矿颗粒直径对回收的空气热量Q和空气 Ex的影响
Ex的影响
Fig. 7 Effect of sinter particle diameter on air energy recovered and air exergy
2.4 空气入口温度的影响
在烧结矿入口温度为923 K,气料比为800 Nm3/t和烧结矿颗粒直径为0.025 m的条件下,沿竖罐高度方向上的空气温度随空气入口温度的变化规律如图8所示。
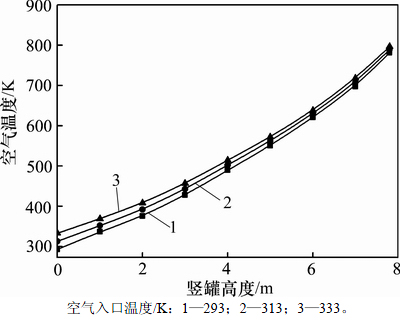
图8 空气入口温度对沿竖罐高度方向上空气温度的影响
Fig. 8 Effect of air inlet temperature on air temperature along height of vertical tank
由图8可知:沿竖罐高度方向上的空气温度随空气入口温度升高而逐渐增加。这是因为在气料比一定时,空气入口温度的升高将导致冷却空气实际入口流量的增加,床层内气固对流换热系数随之增加,从而引起烧结矿与空气间对流换热量的增加,导致空气出口温度的升高。当空气入口温度由293 K升高到333 K时,空气出口温度由780.9 K升高到796.2 K,提高1.96%。空气入口温度每升高10 K,空气出口温度平均升高3.83 K。
图9所示为竖罐回收的空气热量和空气 随空气入口温度的变化规律。由图9可知:竖罐回收的空气热量随空气入口温度的升高而逐渐减少,而空气
随空气入口温度的变化规律。由图9可知:竖罐回收的空气热量随空气入口温度的升高而逐渐减少,而空气 随空气入口温度的升高而逐渐增加。这是由于空气入口温度的升高将导致烧结矿出口温度的升高,竖罐回收的空气热量随之减少。同时,由于空气入口温度的升高,竖罐内气固换热加剧,空气出口温度也会随之升高,竖罐出口空气的热品质增加,空气
随空气入口温度的升高而逐渐增加。这是由于空气入口温度的升高将导致烧结矿出口温度的升高,竖罐回收的空气热量随之减少。同时,由于空气入口温度的升高,竖罐内气固换热加剧,空气出口温度也会随之升高,竖罐出口空气的热品质增加,空气 会随之增加。当空气入口温度由293 K升高到333 K时,回收的空气热量由317.32 GJ/h下降到304.95 GJ/h,降低3.9%,空气
会随之增加。当空气入口温度由293 K升高到333 K时,回收的空气热量由317.32 GJ/h下降到304.95 GJ/h,降低3.9%,空气 由130.52 GJ/h增加到136.8 GJ/h,增加4.81%。空气入口温度每升高10 K,回收的空气热量平均减少3.09 GJ/h,空气
由130.52 GJ/h增加到136.8 GJ/h,增加4.81%。空气入口温度每升高10 K,回收的空气热量平均减少3.09 GJ/h,空气 平均增加1.57 GJ/h。
平均增加1.57 GJ/h。
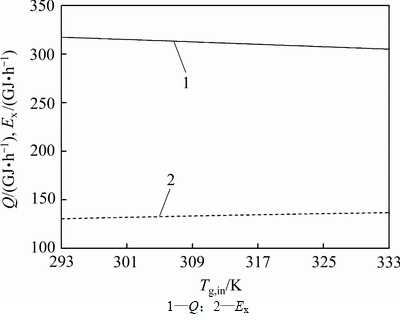
图9 空气入口温度对回收的空气热量Q和空气 Ex的影响
Ex的影响
Fig. 9 Effect of air inlet temperature on the air energy recovered and air exergy
3 结论
1) 建立移动床层内气固稳态传热模型,利用该模型模拟计算得到的干熄焦炉在不同运行条件下焦炭出口温度和热载体出口温度与实测温度之间的平均误差为5.57%,较好地描述了干熄焦炉内的气固传热过程,验证了气固稳态传热模型的可靠性。
2) 对于给定结构参数的烧结矿余热回收竖罐,当烧结矿处理量一定时,烧结矿入口温度越高,气料比越小,烧结矿颗粒直径越小,空气入口温度越高,竖罐出口空气温度也就越高。当其他影响因素不变时,竖罐回收的空气热量和空气 随烧结矿入口温度的升高而逐渐增加,随烧结矿颗粒直径的增加而逐渐减少。随着气料比的增加,回收的空气热量逐渐增加,并且增加趋势逐渐变缓,空气
随烧结矿入口温度的升高而逐渐增加,随烧结矿颗粒直径的增加而逐渐减少。随着气料比的增加,回收的空气热量逐渐增加,并且增加趋势逐渐变缓,空气 则出现先增大后减少的趋势。随着空气入口温度的升高,回收的空气热量逐渐减少,而空气
则出现先增大后减少的趋势。随着空气入口温度的升高,回收的空气热量逐渐减少,而空气 则逐渐增加。
则逐渐增加。
3) 烧结矿入口温度和气料比是影响竖罐内气固传热过程、回收的空气热量和空气 最主要的因素。在实际试验工况中,可通过气料比的调节达到最佳气固换热效果,获得最大的空气
最主要的因素。在实际试验工况中,可通过气料比的调节达到最佳气固换热效果,获得最大的空气 。本研究可为竖罐设计运行中在改变试验工况的条件下通过气料比的调节以获得最大空气
。本研究可为竖罐设计运行中在改变试验工况的条件下通过气料比的调节以获得最大空气 提供理论参考。
提供理论参考。
参考文献:
[1] 蔡九菊, 王建军, 陈春霞, 等. 钢铁工业余热资源的回收与利用[J]. 钢铁, 2007, 42(6): 1-7.
CAI Jiuju, WANG Jianjun, CHEN Chunxia, et al. Waste heat recovery and utilization in iron and steel industry[J]. Iron and Steel, 2007, 42(6): 1-7.
[2] 董辉, 赵勇, 蔡九菊, 等. 烧结-冷却系统漏风问题研究[J]. 钢铁, 2012, 47(1): 95-99.
DONG Hui, ZHAO Yong, CAI Jiuju, et al. On the air leakage problem in sintering cooling system[J]. Iron and Steel, 2012, 47(1): 95-99.
[3] 蔡九菊, 董辉. 烧结过程余热资源的竖罐式回收与利用方法及其装置: 200910187381.8[P]. 2009-09-15.
CAI Jiuju, DONG Hui. The method and device of sintering waste heat recovery and utilization with vertical tank: 200910187381.8[P]. 2009-09-15.
[4] 董辉, 李磊, 刘文军, 等. 烧结矿余热竖罐式回收利用工艺流程[J]. 中国冶金, 2012, 22(1): 6-11.
DONG Hui, LI Lei, LIU Wenjun, et al. Process of waste heat recovery and utilization for sinter in vertical tank[J]. China Metallurgy, 2012, 22(1): 6-11.
[5] CAPUTO A C, PELAGAGGE P M. Heat recovery from moving cooling beds: transient modeling by dynamic simulation[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 1999, 19(1): 21-35.
[6] LEONG J C, JIN K W, SHIAU J S, et al. Effect of sinter layer porosity distribution on flow and temperature fields in a sinter cooler[J]. International Journal of Minerals Metallurgy and Materials, 2009, 16(3): 265-272.
[7] JANG J Y, CHIU Y W. 3-D transient conjugated heat transfer and fluid flow analysis for the cooling process of sintered bed[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2009, 29(14): 2895-2903.
[8] 刘斌, 冯妍卉, 姜泽毅, 等. 烧结床层的热质分析[J]. 化工学报, 2012, 63(5): 1344-1353.
LIU Bin, FENG Yanhui, JIANG Zeyi, et al. Heat and mass transfer in sintering process[J]. CIESC Journal, 2012, 63(5): 1344-1353.
[9] 张家元, 田万一, 戴传德, 等. 环冷机分层布料仿真与优化[J]. 化工学报, 2012, 63(5): 1385-1390.
ZHANG Jiayuan, TIAN Wanyi, DAI Chuande, et al. Simulation and optimization of sinter circular cooling layer-loading[J]. CIESC Journal, 2012, 63(5): 1385-1390.
[10] ZHANG X H, CHEN Z, ZHANG J Y, et al. Simulation and optimization of waste heat recovery in sinter cooling process[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2013, 54 (1): 7-15.
[11] LIU Y, YANG J, WANG J, et al. Energy and exergy analysis for waste heat cascade utilization in sinter cooling bed[J]. Energy, 2014, 67(4): 370-380.
[12] 董辉, 李磊, 力杰, 等. 烧结余热回收竖罐内料层传热过程数值计算[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 33(9): 1299-1302.
DONG Hui, LI Lei, LI Jie, et al. Numerical simulation of heat exchange in vertical tank of waste heat recovery[J]. Journal of Northeastern University (Natural Science), 2012, 33(9): 1299-1302.
[13] 黄连锋, 田付有, 厉青, 等. 烧结矿立式冷却装置气固传热性能分析[J]. 浙江大学学报(工学版), 2015, 49(5): 916-923.
HUANG Lianfeng, TIAN Fuyou, LI Qing, et al. Analysis of gas-solid heat transfer performance in vertically-arranged sinter coolers[J]. Journal of Zhenjiang University (Engineering Science), 2015, 49(5): 916-923.
[14] 冯军胜, 董辉, 赵勇. 烧结矿余热回收竖罐内气体流动的数值计算[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 36(5): 660-664.
FENG Junsheng, DONG Hui, ZHAO Yong. Numerical investigation of gas flow in vertical tank for recovering sinter waste heat[J]. Journal of Northeastern University (Natural Science), 2015, 36(5): 660-664.
[15] PELAGAGGE P M, CAPUTO A C, CARDARELLI G. Optimization criteria of heat recovery from solid beds[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 1997, 17(1): 57-64.
[16] FENG Junsheng, DONG Hui, DONG Hongda. Modification of Ergun's correlation in vertical tank for sinter waste heat recovery [J]. Powder Technology, 2015, 280: 89-93.
[17] WAKAO N, FUNAZKRI T. Effect of fluid dispersion coefficients on particle-to-fluid mass transfer coefficients in packed beds [J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 1978, 33(10): 1375-1384.
[18] 冯军胜. 烧结矿余热回收竖罐内气固传热模型研究[D]. 沈阳: 东北大学材料与冶金学院, 2014: 45-48.
FENG Junsheng. Study on gas-solid heat transfer model in vertical tank for recycling sinter waste heat[D]. Shenyang: Northeastern University. School of Materials and Metallurgy, 2014: 45-48.
[19] HWANG K S, JUN J H, LEE W K. Fixed-bed adsorption for bulk component system: non-equilibrium non-isothermal and non-adiabatic model[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 1995, 50(5): 813-825.
[20] 冯军胜, 董辉, 刘靖宇, 等. 烧结矿余热回收竖罐内气固传热特性[J]. 化工学报, 2015, 66(11): 4418-4423.
FENG Junsheng, DONG Hui, LIU Jingyu, et al. Gas-solid heat transfer characteristics in vertical tank for sinter waste heat recovery[J]. CIESC Journal, 2015, 66(11): 4418-4423.
[21] BISIO G. First- and second-law analyses of energy recoveries in blast-furnace regenerators[J]. Energy, 1996, 21(2): 147-155.
[22] LIU Huafei, ZHANG Xinxin, WU Maolin, et al. Computational and experimental study of cooling process in coke dry quenching experimental shaft[J]. International Journal of Thermal Sciences, 2002, 11(2): 121-127.
(编辑 伍锦花)
收稿日期:2016-12-29;修回日期:2017-02-22
基金项目(Foundation item):国家自然科学基金资助项目(51274065);辽宁省科技计划项目(2015020074-201) (Project(51274065) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(2015020074-201) supported by the Science and Technology Planning Foundation of Liaoning Province)
通信作者:董辉,教授,博士生导师,从事冶金过程余热余能高效回收利用研究;E-mail: Dongh@smm.neu.edu.cn