DOI:10.19476/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2019.05.14
极耳对叠片式动力电池温度分布的影响
安富强1, 2,周伟男1, 3,李 平1
(1. 北京科技大学 新材料技术研究院,北京 100083;2. 山西长征动力科技有限公司, 山西 048400;
3. 北京智行鸿远汽车有限公司,北京 102202)
摘 要:从仿真建模的角度出发,对一款40 A·h软包叠片式动力电池建立电化学-热耦合模型,并对该构型电池的极耳结构进行了相关研究及优化工作。仿真结果显示,极耳与电芯间由于产热率的差异而引起的热流交换是电芯域内出现温度梯度分布的主要因素。在对极耳尺寸的优化中发现,电芯的最高温度随极耳宽度和厚度的增大而逐渐减小;电芯的最大温差随极耳宽度和厚度的增大在一定范围内逐渐减小,而当两者超过一定阈值(极耳宽度大于70 mm,极耳厚度大于0.5 mm)后,电芯的最大温差反而呈现出增大的趋势。原因在于极耳产热率的降低以及散热率的增加,使得在放电中后期极耳温度低于电芯温度,起到给电芯持续散热的效果,但这种散热作用随极耳尺寸的增大反而恶化了电芯温度分布的均匀性。
关键词:电化学-热耦合模型;热参数;极耳尺寸;温度梯度
文章编号:1004-0609(2019)-05-1008-11 中图分类号:TM911 文献标志码:A
锂离子动力电池是电动汽车的核心部件,相比于3C产品用小型电池,动力用大型电池由于体积和特定方向尺度的显著增大,易引起内部温度极值的增加,以及电流和温度的不均一性,严重影响其性能、寿命和安全[1-6]。为解决这方面的问题,除选定材料体系以满足电池的能量密度外,还需开展结构设计方面的相关工作,以改善单体电池的热特性。对于广泛使用的软包叠片式动力电池,极耳是影响该型电池温度分布不均匀、局部温度过高的主要因素[7-15]。XU等[11]对一款叠片式电池建立了由正负集流体、正负极涂层和隔膜堆叠而成的电芯单元结构简化模型,并考虑电芯两端正负极耳的作用,研究了极耳位置和放电倍率对电池放电均匀性的影响。仿真结果表明在该型电池放电过程中,靠近极耳端的区域内的电化学反应速率和产热速率均较高,且随着放电倍率的增加,这种不均匀性更加显著。在LI等[12]的仿真研究中同样发现在大 电流充放电下,电池内部存在物理化学特性分布的不均匀,尤其在极耳与电芯的连接处,易形成较大的电势、电流密度及产热率的梯度分布。AHMADOU等[13]研究了4种典型的极耳位置布置方式对电池性能的影响,发现极耳于电芯对侧的中间位置布置时,可获得较为均匀的电势和电流密度分布,以实现更为均匀的活性材料利用率和温度分布。GUO等[14]研究了电池在放电过程中极耳与电芯出现温度差异的原因,并讨论了不同的散热速率对这种温度差异的影响。吴彬等[15]提出了一款大型软包叠片式电池的分析解,并利用分析解全面考察了电芯高度、电芯宽度、极耳位置等多设计参数同时变化下对电池最高温度与温差的影响,以实现多参数的全局优化。计算结果表明,对于同侧极耳布置方案,极耳位置和电芯长宽比均存在最优取值,通过优化可使电芯最高温度下降约1.5 ℃,最大温差下降约2 ℃;而对于对侧极耳布置方案,极耳于中间布置时电池的热特性最佳,可使电芯的最高温度与温差均降低约2 ℃。
以上研究大多集中在对软包叠片式电池充放电行为的研究,并指出极耳对电芯内部的物质分布状态,尤其是产热率与温度的分布有较大影响,后多从极耳位置、电芯尺寸等方面进行改进优化,却缺少对极耳尺寸的研究。极耳尺寸是影响极耳自身欧姆产热,进而影响电芯的温度分布状态的一个重要因素。李腾等[16]提出宜采用厚、宽和短的极耳以使电池电芯域内的电流密度和温度分布更加均匀。但使用较厚和较宽的极耳增加了电池的质量,降低了电池的能量密度,且会加大后期电池模组工艺的难度,故需对其参数进行合理的设置。
相较于实验的方法,数值仿真模拟可从电池内部反应的机理上研究电池充放电行为的变化,并能够快速评测任意设计下的电池性能,找寻最优设计方案,从而大大缩短研发时间,降低成本[17-18]。本文基于一款40 A·h软包叠片式电池,搭建了其电化学-热耦合模型。利用验证准确的模型首先讨论了该电芯区域出现温度梯度的主要因素,后研究了不同的极耳尺寸对电池热特性的影响机制,以及相应的优化工作。
1 模型搭建
本研究基于一款40 A·h软包叠片式动力电池,如图1所示。首先建立热-电化学耦合模型。其中,电化学模型几何为电芯单元结构,用于计算电极上的电位分布、电流密度分布和产热率分布,而热模型几何为真实的三维结构,用于计算电池的温度分布。

图1 40 A·h软包型锂离子动力电池
Fig. 1 40 A·h laminated lithium-ion cell
1.1 电化学-热耦合模型
图2所示为该电池的热-电化学耦合模型计算域。其中电化学模型(见图2(a))由5层不同厚度的极板(正集流体、正极涂层、隔膜、负极涂层、负集流体)堆叠而成。而热模型为真实的三维几何结构(见图2(b)),其中电芯域假定为宏观均匀介质,具有等效的比热容与导热系数。同时,在该热模型中,考虑了极耳自身产热、极耳与螺栓连接所造成的接触电阻热以及导线散热的影响。
1.2 控制方程及边界条件
1.2.1 电化学模型
本文所采用的电化学模型基于Newman多孔电极理论所构建,描述包括多孔电极中的物质守恒、电荷守恒以及电化学反应动力学等过程。
描述正负电极颗粒表面的电化学反应过程的Buter-Volmer方程为
 (1)
(1)
式中:j0为交换电流密度,A/cm2;η是局部过电位,V;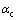 和
和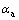 是正负电极电化学反应的转移系数,一般均取0.5;F为法拉第常数,96485 C/mol;R为摩尔气体常数,8.314 J/( mol·K)。
是正负电极电化学反应的转移系数,一般均取0.5;F为法拉第常数,96485 C/mol;R为摩尔气体常数,8.314 J/( mol·K)。
交换电流密度表达式为
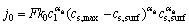 (2)
(2)
式中:k0为反应速率常数;cs, max为材料最大固相锂离子浓度;cs,surf为电极和电解液界面处的锂离子浓度。
局部过电位表达式为
 (3)
(3)
式中: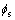 为固相电势;
为固相电势; 为液相电势;
为液相电势;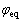 为材料的平衡电位。
为材料的平衡电位。
固相欧姆定律和液相欧姆定律分别为
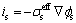 (4)
(4)
 (5)
(5)
式中:is和i1分别代表固相电子电流和液相离子电流; 和
和 代表固相和液相电势;t+为迁移数。
代表固相和液相电势;t+为迁移数。
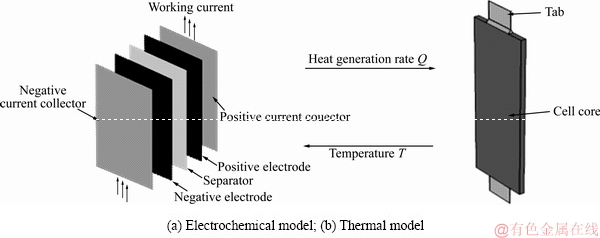
图2 计算域示意图
Fig. 2 Schematic diagram of computational domain
锂离子在固相中的质量守恒方程,用菲克第二定律来描述为
 (6)
(6)
式中:cs代表固相锂离子浓度;Ds为锂离子的固相扩散系数;r为球形颗粒的半径。
锂离子在液相中的质量守恒方程,用浓溶液理论来描述为
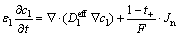 (7)
(7)
 (8)
(8)
式中:ε1为电极和隔膜中的液相体积分数;Jn为液相锂离子流量; 为电解液中的等效扩散系数;采用布拉格曼系数修正。
为电解液中的等效扩散系数;采用布拉格曼系数修正。
1.2.2 热模型
锂离子电池的热模型方程由式(9)~(12)来描述。能量守恒方程为
 (9)
(9)
式中:电池电芯区域的产热量主要包括三部分,分别为可逆热(qrea)、极化热(qact)与欧姆热(qohm),其计算公式分别如式(10)~(12)所示:
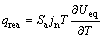 (10)
(10)
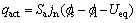 (11)
(11)
 (12)
(12)
此外,极耳区域还存在由极耳的电阻和极耳与导线连接的接触电阻所引起欧姆热,见式(13):
 (13)
(13)
式中:Itab为通过极耳处的电流;Atab为极耳的横截面积;σtab为极耳自身材料的电导率;σc为极耳与导线连接引起的接触电阻的折算电导率。
1.2.3 宏观边界条件
电化学模型中正集流体上端部极耳区域为电池的工作电流边界,用式(14)和(15)来表示:
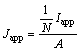 (14)
(14)
A=t·W (15)
式中:Japp为该边界的工作电流密度;Iapp为该边界的工作电流;N为该软包叠片式电池电芯中电极对的个数;A为仿真模型中极耳与电芯间的有效接触面积;t为正集流体的厚度;W为极耳的宽度。
在热模型中的电池外表面,存在空气的对流散热边界为
 (16)
(16)
2 模型参数与模型精度验证
2.1 电化学模型参数及相关传输参数的修正
表1所列为该电化学模型参数的具体值,主要来自厂商提供、实验测量和文献参考[18-20]。
电化学模型中的相关反应与传输参数受温度的影响,通过Arrhenius方程和其他相关经验方程所修正[21-22],具体修正公式见表2。
2.2 热模型参数
准确获取电池的相关热参数是构建高精度热模型的关键。对于软包叠片式电池,重要的热参数包括电芯域内的导热系数K、比热容cp和接触热阻λ;以及极耳域内的接触电阻和表面对流换热系数ht。其中需要注意的是,电芯域的导热系数存在电极平面内的展向导热系数K∥和垂直电极平面内的法向导热系数K⊥之分,且后者显著小于前者,其对电芯内部的传热过程影响较大[23]。
采用“瞬态平面热源数值解优化法[24-25]”对该构型电池的多个热参数进行测量计算。图3(a)所示为具体的实验装置图,图3(b)所示为采用该方法得到的实验与仿真的温度数据对比,从中可辨识出电芯域的4个热参数值。具体的为K∥=18.5 W/(m·K),K⊥=1.2 W/(m·K),cp=972.63 W/(m·K),λ=1 300 W/(m2·K)。
对接触电阻(以折算电导率σct来衡量)和极耳表面对流换热系数ht的确定同样需要设计特殊的实验进行测量。本实验中采用吴彬[25]的测量方法,通过给极耳通电得到的温度响应,结合其表面的温度解析解辨识出这两个参数值(见图4),对于正极耳,σct=7×107 S/m,ht=9.7 W/(m·K);对于负极耳,σct=1.3×108 S/m,ht= 10.3 W/(m·K)。
2.3 模型精度验证
图5所示为对该款40 A·h电池模型精度的实验验证,包括对不同放电倍率下的电压验证和温度验证。
仿真模型计算的结果与实验测试得到的数据吻合较好,说明本文对电化学模型中的相关电池结构设计参数、电极特性参数和电解液特性参数以及热模型中的产热源项及热参数的设置均较为准确。
表1 该模型所用到的相关参数
Table 1 Model parameter values used in simulations

表2 电化学模型中相关反应与传输参数的温度相关性修正
Table 2 Correction of temperature dependence for relevant reaction and transmission parameters in electrochemical model


图3 电芯域热参数辨识
Fig. 3 Comparison of temperature curves between test data and simulation results

图4 实验和仿真得到的极耳温升曲线对比
Fig. 4 Comparison of tab temperature curves between test data and simulation results
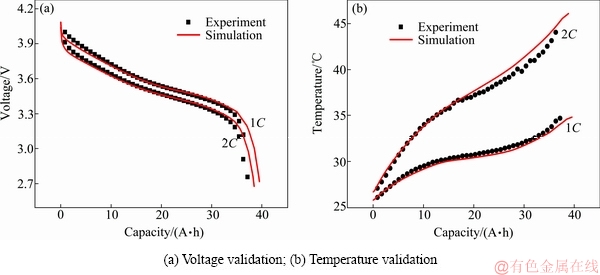
图5 模型精度验证
Fig. 5 Model accuracy validation
3 结果与讨论
3.1 电芯域内产生温度梯度分布的原因
图6所示为该软包叠片式电芯域内的温度分布显示了在2C(80 A)恒流放电下随放电时间的演变结果(测试环境为25 ℃下的自然对流条件)。在放电开始仅100 s时,电芯域内即出现较大的温度分布梯度,具体表现为靠近正负极耳的两个端部温度较高,而远离极耳的中间区域温度较低。随着放电过程的进行,温度梯度出现的范围逐渐扩大。电池的最高温度在放电末端达到,位置靠近正极耳端,温升超过了20 ℃;但电池的最大温差一般出现在放电过程中间时段,超过2 ℃。单体电池温度分布的不均匀性对电池的热安全性和寿命均有重要影响,故需要对出现这种现象的原因进行探讨,以找寻改进的措施。

图6 电芯温度分布随放电时间的演变
Fig. 6 Temperature distribution in core during discharge
图7所示为在2C放电过程中电芯域内的最大产热率和最小产热率的变化趋势:在大部分放电阶段都相差甚小,但是电池的温度在整个放电过程中都存在明显分布,因此电芯域内产热率的差异不是电芯温度产生分布的主要原因。
图8所示为电芯不同部件的产热率随时间的演变。从图8可看出,极耳与电芯的产热率存在数量级上的差异(正极耳为1.65×106 W/m3,负极耳为1.23×106 W/m3,电芯为5×104 W/m3)。电芯域内靠近极耳端的温度较高,而远离极耳端的区域温度较低,说明电芯与极耳之间可能发生了较大的热量交换。
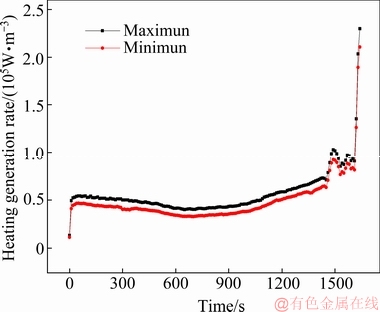
图7 电芯域内最大和最小产热率随放电时间的演变
Fig. 7 Maximum and minimum heating generation rate in core during discharge

图8 电池不同部件的产热率随放电时间的演变
Fig. 8 Heat generation rate of different parts in cell during discharge

图9 极耳与电芯的热流交换随时间的变化
Fig. 9 Change of heat flow exchange between tabs and core during discharge with time
正、负极耳传向电芯的热流密度随时间的演变如图9所示。当放电开始时(100 s),因极耳的欧姆产热较高,且远高于电芯产热率,故极耳温度迅速升高,与邻近的电芯区域形成了较大的温度梯度(见图6),此时极耳传向电芯的热流量迅速增加,起着给电芯加热的作用;而随着极耳在环境中散热率的增加,极耳传向电芯的热流量逐渐减小。由图9可知,在整个放电过程中,始终存在极耳向电芯传导热流。因此,可以认为极耳与电芯之间的热流交换是引起该电芯域内出现温度梯度分布的主要因素。而极耳的欧姆产热与其自身的内阻有关,由其结构尺寸所决定。故可以通过优化极耳的尺寸来控制其与电芯之间的热流交换行为,以改善电芯域内的温度分布。
3.2 极耳尺寸研究
图10所示为该40 A·h软包叠片式电池的极耳结构示意图。因为极耳与电芯直接连接的区域是极耳的宽度和厚度这两个方向构成的横截面,故这两个参数的尺寸变化对电芯热分布的影响较大。而极耳长度方向上的尺度变化仅仅单方面影响电芯端部的最高温度,对电芯整体范围内的热分布影响不大,且对于电池生产来说,考虑到电芯的体积能量密度,极耳的长度一般被限定在一定的范围之内,不会有太大的设计空间。故本文通过对极耳宽度和厚度这两个参数的调整,寻找其最优解,以改善该电池的热特性(降低最高温度与最大温差)。
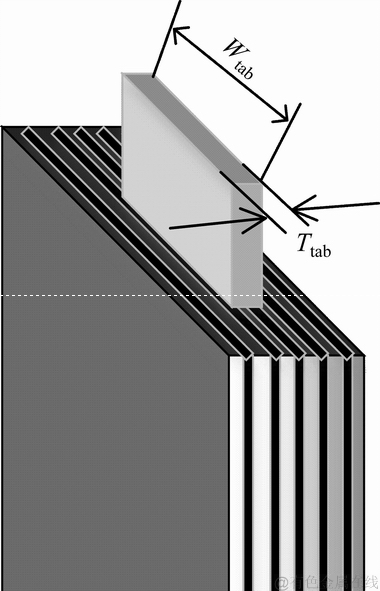
图10 极耳结构示意图
Fig. 10 Schematic diagram of tab structure
3.2.1 极耳宽度对电池热特性的影响
图11(a)和(b)所示为保持极耳位置、极耳厚度0.3 mm不变的情况下电芯的最高温度和最大温差随极耳宽度W变化的关系曲线,该参数的变化区间为30~90 mm,变化步长为10 mm。测试工况为2C(80 A)恒流放电,自然对流。可见,随极耳宽度的增加,电池的最高温度逐渐降低;一方面是由于其自身内阻减小,导致欧姆产热降低,另一方面是其与空气接触的外表面积增大,散热能力增强,故传入电芯的热流量减少,表现出对电芯的“加热能力”减弱。然而,电芯域内的最大温差却随极耳宽度的增加,呈现先降低,后增大的变化趋势,具体为在极耳宽度从30 mm增大至70 mm时,电芯的最大温差逐渐减小,而大于70 mm后,最大温差逐渐增大。即存在最佳的极耳宽度值(约为70 mm),使得该热特性评价指标存在最小值。
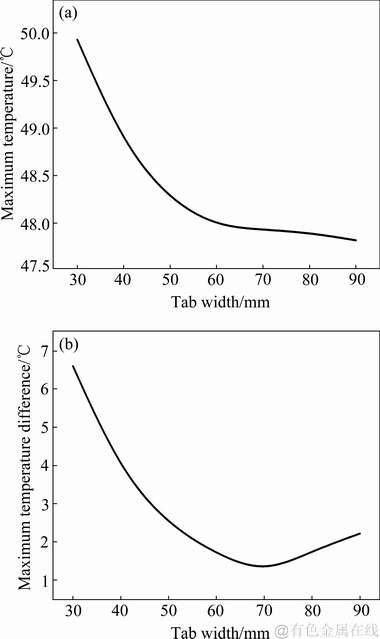
图11 电芯的最高温度以及最大温差随极耳宽度的变化曲线
Fig. 11 Change of maximum temperature (a) and maximum temperature difference curves (b) of cell core varies with tab width
3.2.2 极耳厚度对电池热特性的影响
图12所示为在保持极耳位置、极耳宽度W不变的情况下电芯的最高温度和最大温差随极耳厚度T变化的关系曲线。该参数的变化区间为0.1~ 0.7 mm,变化步长为0.1 mm。
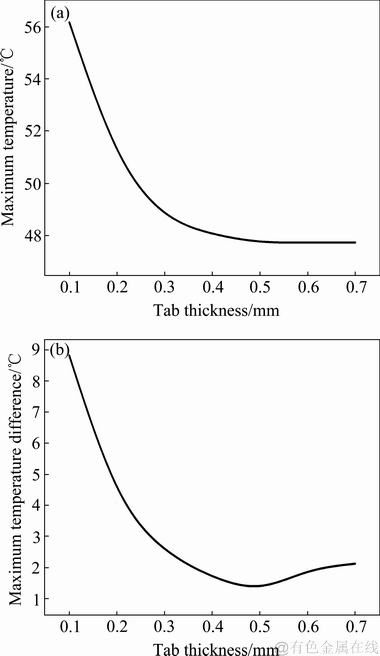
图12 电芯的最高温度和最大温差随着极耳厚度的变化
Fig. 12 Change curves of maximum temperature (a) and maximum temperature difference (b) of cell core varies with tab thickness
与极耳宽度的影响类似,随极耳厚度的增加,其内阻降低,欧姆产热减少,同时散热面积增大,使得传入电芯的热流量减少,引起电池最高温度的降低;而电芯的最大温差同样出现随极耳厚度的增加呈现先降低,后增大的变化趋势。当极耳厚度从0.1 mm增大到约0.5 mm,电芯的最大温差逐渐降低,而当极耳厚度超过0.5 mm后,电芯的最大温差却有所增大。即存在最佳的极耳厚度值(约为0.5 mm),使得该热特性评价指标存在最小值。
3.2.3 电芯温差增大的原因

图13 极耳电芯温度分布随时间的演变
Fig. 13 Cell core temperature of tab varies with time
由于极耳的宽度与厚度的变化对电芯域内热分布的影响效果大致相同(见图11和12),故在探究上述温差增大的原因时,本文仅研究当极耳宽度取不同值(30、60和90 mm)时,电池内部的产热、传热,及温度分布的演变情况。图13所示为3种不同极耳宽度设计下电芯域内温度分布随时间的演变图;图14所示为不同极耳宽度设计下正极耳与电芯的产热率的比较;图15所示为不同极耳宽度设计下正极耳传向电芯的热流对比图。
如图13(a)所示,当极耳宽度较小,约为30 mm时,其产热率高(见图14,正极耳产热率约为3.5×106 W/m3,电芯产热率为5×104 W/m3),而尺寸较小带来的散热率同样较小。故在整个放电过程中,均存在极耳向电芯传导热流量(见图15),使得电芯域内的最高温度(约为53 ℃)和最大温差(约为6.6 ℃)均较大,具体表现为电芯上靠近正负极耳端的区域温度较高,而远离极耳的中间区域温度较低。
当极耳宽度增大到60 mm时,在图14中,极耳的产热率由1.65×106 W/m3下降至8.46×105 W/m3,且随尺寸的增大,极耳的散热率有所增大,此时于图15中可见,极耳传向电芯的热流量较极耳宽度为30 mm的电池而言显著下降,表现在图13(b)中电芯最大温差的显著降低(由6.6 ℃下降至约1.5 ℃)。甚至在放电末端出现热流从电芯流向极耳(总热流数值由正变为负),此时电芯域内的最高温度位置逐渐远离正极耳端,向电芯中间位置移动。所以极耳宽度的增大改善了电芯域内温度分布的不均匀性。
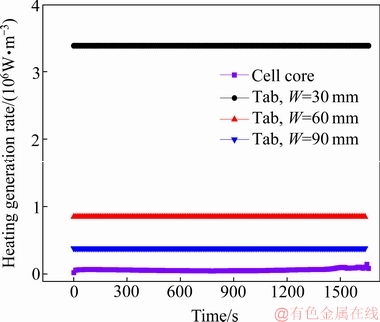
图14 不同极耳宽度下正极耳与电芯的产热率对比图
Fig. 14 Comparison of heat generation rate between cell core and positive tab with different tab widths

图15 不同极耳宽度下正极耳传向电芯的热流对比图
Fig. 15 Comparison of heat flow transferred from positive tab to cell core with different tab widths
当极耳宽度增大至90 mm时,极耳的产热率进一步由8.46×105 W/m3降低至约3.7×105 W/m3,同时其散热率进一步增强(见图15)。在放电约600 s时,电芯与极耳间的热流交换方向即发生反转,此后极耳起到持续给电芯散热的作用,最终表现为在放电末端,电芯上远离极耳的区域温度较高,而靠近极耳的区域温度较低,并形成了较大的温度梯度。从图13(c)中可见,在放电900 s时,电芯域内的温差仅为0.6 ℃,而在放电末端约1700 s时,电芯域内的温差却增大至2.1 ℃,说明此时极耳的散热作用恶化了电芯温度分布的均匀性。
综上所述,当极耳宽度设计大于60 mm后,由于其产热率的减小以及散热率的增大,使得极耳温度低于电芯,起到给电芯散热的效果,而这种散热作用却会随放电过程的进行,降低电芯温度分布的均匀性。
4 结论
1) 针对一款40 A·h软包叠片式电池建立了由电芯单元结构与真实三维结构所构成的电化学-热耦合模型,讨论了其在大倍率放电过程中的热特性,并从极耳结构设计端给出了优化方案。
2) 从模型的数值计算结果中发现,该型电芯域内的展向平面存在较大的温度梯度分布,通过对该电池不同部件之间的产热率、热流交换等方面分析,发现温度分布起因于极耳与电芯间较大的产热率差异,引起两者间发生剧烈的热流交换。
3) 在对极耳尺寸的优化中发现,极耳宽度和厚度越大,电芯的最高温度和最大温差均越低;但当极耳宽度和厚度超过一定阈值(宽度为70 mm,厚度为0.5 mm)后,由于极耳产热率的降低以及散热率的增加,其对电芯温度分布的均匀性反而起到了一定的恶化作用(最大温差增大)。故在进行电池的热优化设计时,应权衡最高温度和最大温差两个指标各自的重要性,以及考虑到实际生产过程中对极耳尺寸的限制,从而做出合理的选择。
4) 在此还需要指出的是,由于本研究下的该款电池其电芯厚度较薄,故温度分布的不均匀性以及极耳尺寸增大后对该热特性的恶化作用主要体现在电芯的展向方向上;而若电芯的厚度较大时,由于电芯内部散热的条件变差,电芯温度分布的不均匀性可能会出现在电芯的厚度方向上,故此时需要重新衡量极耳对电芯温度分布的影响。
REFERENCES
[1] 张剑波, 吴 彬, 李 哲. 车用动力锂离子电池热模拟与热设计的研发状况与展望[J]. 集成技术, 2014, 3(1): 18-26.
ZHANG Jian-bo, WU Bing, LI Zhe. Thermal modeling and thermal design of lithium-ion batteries for automotive application: Status and prospects[J]. J Integration Technology, 2014, 3(1): 18-26.
[2] SCROSATI B, GARCHE J. Lithium batteries: Status, prospects and future[J]. Journal of Power Source, 2010, 195(9): 2419-2430.
[3] WANG J, SUN X. Understanding and development of carbon coating on LiFePO4 cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2012, 5(1): 5163-5185.
[4] HU X, LI S E, JIA Z, EGARDT B. Enhanced sample entropy-based health management of Li-ion battery for electrified vehicles[J]. Energy, 2014, 64(1): 953-960.
[5] ARMAND, TARASCONJ J M. Building better batteries[J]. Nature, 2008, 451(7179): 652-662.
[6] LU L, HAN X, LI J, OUYANG M. A review on the key issues for lithium-ion battery management in electric vehicles[J]. Journal of Power Source, 2013, 226(3): 272- 288.
[7] KIM U S, HAN X, LIJ. Modeling for the scale-up of a lithium-ion polymer battery[J]. Journal of Power Source, 2009, 189(1): 841-846.
[8] UI S K, JAESHIN Y, CHEE B S. Modeling the thermal behavior of a lithium-ion battery during charge[J]. Journal of Power Source, 2011, 196(4): 5115-5121.
[9] GUO M, KIM G H, WHITE R E. A three-dimensional multi-physics model for a Li-ion battery[J]. Journal of Power Source, 2013, 240(12): 80-94.
[10] 汤依伟,贾 明,程 昀. 基于电化学与热能的耦合关系演算聚合物锂离子动力电池的温度状态及分布[J]. 物理学报, 2013, 62(15): 490-499.
TANG Yi-wei, JIA Ming, CHENG Yun. Estimation of temperature distribution of the polymer lithium ion power battery based on the coupling relationship between electrochemistry and heat[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2013, 62(15): 490-499.
[11] XU M, ZHANG Z Q, WANG X, XIA W, LI J. A pseudo three- dimensional electrochemical-thermal model of a prismatic LiFePO4 battery during discharge process[J]. Energy, 2015, 80(2): 303-317.
[12] LI J, CHENG Y, AI L H, et al. 3D simulation on the internal distributed properties of lithium-ion battery with planar tabbed configuration[J]. Journal of Power Source, 2015, 293(3): 993-1005.
[13] AHMADOU S, NOSHIN O, HAMID G, CAPRON O, BOSSCHE P V D, MIERLO J V. Impact of tab location on large format lithium-ion pouch cell based on fully coupled three-dimensional electrochemical-thermal modeling[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2014, 147(5): 319-329.
[14] GUO M, WHITE R E. A distributed thermal model for a Li-ion electrode plate pair[J]. Journal of Power Source, 2013, 221(1): 334-344.
[15] 吴 彬, 李 哲, 张剑波. 层叠式锂离子电池展向温度分布的分析解及基于分析解的热设计优化[J]. 中国科学: 科学技术, 2014, 44(11): 1154-1172.
WU Bing, LI Zhe, ZHANG Jian-bo. Thermal design optimization of laminated lithium ion battery based on the analytical solution of planar temperature distribution[J]. Scientia: Sinica Technologica, 2014, 44(11): 1154-1172.
[16] 李 腾, 林成涛, 陈全世. 锂离子电池三维多层多物理场模型[J]. 清华大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 52(7): 995-1000.
LI Teng, LIN Cheng-tao, CHEN Quan-shi. Lithium-ion battery 3-dimensional multi-layer multi-field model[J]. J Tsinghua University (Science and Technology), 2012, 52(7): 995-1000.
[17] 程 昀, 李 劼, 贾 明. 锂离子电池多尺度数值模型的应用现状及发展前景[J]. 物理学报, 2015, 64(21): 137-152.
CHENG Yun, LI Jie, JIA Ming. Application status and future of multi-scale numerical models for lithium ion battery[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2015, 64(21): 137-152.
[18] ALI J, BARZIN R, MARTIN D, LACROIX M. Review of simplified pseudo-two-dimensional models of lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Power Source, 2016, 327(10): 44-55.
[19] LEE K J, KANDLER S, AHMAD P, KIM G H. Three dimensional three-, electrical-, and electrochemical-coupled model for cylindrical wound large format lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Power Source, 2013, 241(6): 20-32.
[20] YE Y, SHI Y, CAI N, LEE J, HE X. Electro-thermal modeling and experimental validation for lithium ion battery[J]. Journal of Power Source, 2012, 199(1): 227-238.
[21] XU M, ZHANG Z Q, WANG X, LI J, YANG L. Two- dimensional electrochemical-thermal coupled modeling of cylindrical LiFePO4 batteries[J]. Journal of Power Source, 2014, 256(12): 233-243.
[22] LI X, XIAO M, CHOE S Y. Reduced order model(ROM) of a pouch type lithium polymer battery based on electrochemical thermal principles for real time applications[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2013, 97(5): 66-78.
[23] 云凤玲. 高比能量动力锂离子电池热性能及电化学-热耦合性为研究[D]. 北京: 北京有色金属研究总院, 2016.
YUN Feng-ling. Study on thermal performance and electrochemical-thermal couple behavior of high specific energy lithium ion power battery[D]. Beijing: General Research Institute for Nonferrous Metals Beijing, 2016.
[24] ZHANG J B, WU B, LI Z, HUANG J. Simultaneous estimation of thermal parameters for large-format laminated lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Power Source, 2014, 259(7): 106-116.
[25] 吴 彬. 动力电池热设计方法研究[D]. 北京: 清华大学, 2015.
WU Bing. Thermal design methodology for traction lithium- ion batteries[D]. Beijing: Tsinghua University, 2015.
Effect of tabs on temperature distribution in laminated power cell
AN Fu-qiang1, 2, ZHOU Wei-nan1, 3, LI Ping1
(1. School of Institute for Advanced Materials and Technology, University of Science and Technology Beijing, Beijing 100083, China;
2. Shanxi Changzheng Power Technology Co., Ltd., Shanxi 048400, China;
3. Beijing Idrive Automotive Co., Ltd., Beijing 102202, China)
Abstract: A forward design method based on the electrochemical-thermal model was adopted for a 40 A·h laminated lithium-ion cell. Then, the tab structure of this cell was studied and optimized based on the validated model. It is found from the numerical results that the heat flux between the tab and the cell core caused by heat generation rate difference is the main factor that resulting in the temperature gradient distribution of the cell core. Optimization results of tab size show that the maximum temperature of the cell core gradually decreases with the increase in tab width and thickness. Besides, the maximum temperature difference in the cell core decreases with the increase of tab width and thickness in a certain range. But when the two parameters both exceed the threshold values (the tab width is more than 70 mm, and the tab thickness is greater than 0.5 mm), the index tends to increase. The main reason is that the decrease of the heat generation rate and the increase of the heat radiation rate of the tabs makes its temperature lower than that of the cell core, further playing a cooling effect on the cell core. However, the heat dissipation plays a bad effect on the uniformity of the cell temperature distribution to the increase in the tab size.
Key words: electrochemical-thermal model; thermal parameter; tab size; temperature gradient
Foundation item: Project(2018M631335) supported by the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation.
Received date: 2018-05-18; Accepted date: 2018-09-04
Corresponding author: LI Ping; Tel: +86-13661012037; E-mail: liping@ustb.edu.cn
(编辑 龙怀中)
基金项目:中国博士后科学基金资助项目(2018M631335)
收稿日期:2018-05-18;修订日期:2018-09-04
通信作者:李 平,教授,博士;电话:13661012037;E-mail:liping@ustb.edu.cn