Cu/Ti在模拟海水中的电偶腐蚀行为
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2014年第2期
论文作者:杜小青 杨青松 陈 宇 杨 洋 张 昭
文章页码:570 - 581
关键词:Cu/Ti电偶;电偶腐蚀;电化学阻抗谱;电化学噪声
Key words:Cu/Ti galvanic couple; galvanic corrosion; electrochemical impedance spectroscopy; electrochemical noise
摘 要:采用电化学阻抗谱、电化学噪声和扫描电镜等技术研究了纯铜、铜/钛耦合电极在模拟海水中的腐蚀行为。结果表明:纯铜的腐蚀过程分2个阶段,其腐蚀阻抗和点蚀参数SE均遵循先增后降的规律,而其腐蚀参数SG的变化规律则正好相反;铜/钛耦合电极的腐蚀过程则由3个阶段组成,其腐蚀阻抗和点蚀参数SE均遵循先降后升到最后再降的规律,而其腐蚀参数SG则同样反向变化。铜和钛之间的电势差加速了纯铜的点蚀萌生,同时铜/钛耦合电极的腐蚀电位总是正于纯铜的腐蚀电位。
Abstract: The corrosion behaviors of copper and copper/titanium galvanic couple (GC) in seawater were studied by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) and electrochemical noise (EN) techniques in conjunction with scanning electron microscopy (SEM) method. The results show that the corrosion process of copper in seawater can be divided into two stages, in which corrosion resistance and SE show the same evolution trend of initial increase and subsequent decrease, while SG changes oppositely. However, the ensemble corrosion process of copper/ titanium GC in seawater includes three stages, in which corrosion resistance and SE show the evolution features of initial decrease with a subsequently increase, and the final decrease again; while SG changes oppositely. The potential difference between copper and titanium in their galvanic couple can accelerate the initiation of pitting corrosion of copper, and both the minimum and maximum corrosion potentials of copper/ titanium GC are much more positive than those of pure copper.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 24(2014) 570-581
Xiao-qing DU1, Qing-song YANG2, Yu CHEN1, Yang YANG1, Zhao ZHANG1
1. Department of Chemistry, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310027, China;
2. Zhanjiang Corrosion and Protection Center, Zhanjiang 524000, China
Received 22 January 2013; accepted 31 May 2013
Abstract: The corrosion behaviors of copper and copper/titanium galvanic couple (GC) in seawater were studied by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) and electrochemical noise (EN) techniques in conjunction with scanning electron microscopy (SEM) method. The results show that the corrosion process of copper in seawater can be divided into two stages, in which corrosion resistance and SE show the same evolution trend of initial increase and subsequent decrease, while SG changes oppositely. However, the ensemble corrosion process of copper/ titanium GC in seawater includes three stages, in which corrosion resistance and SE show the evolution features of initial decrease with a subsequently increase, and the final decrease again; while SG changes oppositely. The potential difference between copper and titanium in their galvanic couple can accelerate the initiation of pitting corrosion of copper, and both the minimum and maximum corrosion potentials of copper/ titanium GC are much more positive than those of pure copper.
Key words: Cu/Ti galvanic couple; galvanic corrosion; electrochemical impedance spectroscopy; electrochemical noise
1 Introduction
Copper and its alloys are widely used in industry, especially in naval construction, heat exchangers, oil transportation and so on [1], due to their good machinability and durability, intricate functionality and low cost [2]. In the design of industrial products, a pure copper material needs to couple with titanium, magnesium, stainless steel or other materials by wire connection [3], welding [4] or other mechanical processing, so as to meet the mechanical and electrical demands [5]. Because the free corrosion potentials of various components are different [5,6], two main metals or alloys can transfer their own electrons through combination, and therefore the galvanic corrosion is inevitable when they are immersed in the seawater [7-9].
Galvanic corrosion is an enhanced corrosion between two or more electrically connected different metals originally [10], where the more active one acts as anode and corrodes, while the less active one is cathode [5]. This will increase the corrosion rate of the anodic metal and reduces that of the cathodic alloy [10]. Up to now, galvanic corrosion is very common in municipal infrastructure and industrial [11], and has been studied by many researchers.
KIRAN [7] predicted the corrosion rate of galvanic corrosion through establishing a numerical model, and verified its accuracy by scanning vibrating electrode technique (SVET) and immersion tests. Many techniques such as mass-loss [6,10], potentiodynamic polarization [12-15] and zero resistance ammeter (ZRA) [15-17] have been adopted to determine the galvanic corrosion parameters, such as corrosion potential and galvanic current. Then some relations, such as the relation of galvanic current with anodic dissolution current and the equation between the corrosion current and polarization potential, were deduced according to those parameters [10].
Most researchers focused on the influence factors of galvanic corrosion. The results show that the galvanic corrosion current increased with the increase of area ratio Sc/Sa [10,18], where Sc and Sa are the areas of cathode and anode respectively; while the research from MUJIBUR RAHMAN et al [4] on galvanic corrosion of laser weldments of AA6061 Al alloy indicated that the galvanic corrosion current increased with either the accumulation of intermetallic phase or the increase of corrosion surface area. The influence of temperature is complicated. Generally, the galvanic corrosion current increases with the corrosion temperature [16,19]. In addition, the factors such as the flow velocity of the medium [14,18,20], the dissolved oxygen content [21], pH [22] and the distance between electric dipoles [23,24] have also been studied. As to the materials and medium, the researchers paid much more attention to the galvanic corrosion of Mg alloy [25,26], Al alloy [27], steel [28] in the solutions containing Cl-, S2- [15] and Br- [29].
This work aims to research the galvanic corrosion behavior of electric couple made of copper and titanium, being immersed in seawater for a long time at 25 °C, as the early researches were mostly focused on corrosion for a short time, which could not give any information about the exchange of anode and cathode in a galvanic couple. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS), electrochemical noise (EN) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) techniques are adopted to analyze the reaction resistance, corrosion product layer, galvanic potential and corrosion morphologies.
2 Experimental
2.1 Material and specimen preparation
The rod specimens of 0.40 cm in diameter were cut from copper rod. Then the specimens were connected respectively to a copper wire at one end, sealed using nylon with the other end exposed as the working surface. Before experiments, the working surface was polished with abrasive papers through 500-1200 grade and velvet, washed with twice distilled water, and finally degreased with acetone.
Special coupled electrodes for experiment were prepared by embedding copper column into the titanium cylinder with inner and outer diameters of 0.40 cm and 0.56 cm respectively, then the couple was encapsulated with nylon, and the exposed area of each metal was equal to 0.13 cm2.
2.2 Measurement methods
EIS tests were recorded with an impedance measurement apparatus (PARSTAT 2273, Advanced Electrochemical System) at the rest potential, the applied sinusoidal voltage amplitude was 5 mV and the sweep always initiated from the frequency of 100 kHz to 0.01 Hz. The tests were performed at different immersion times in a conventional three-electrode compartment cell. The rod copper or the coupled copper/ titanium specimen prepared in section 2.1 was the working electrode, a large platinum foil was used as auxiliary electrode and a saturated calomel electrode (SCE) was employed as the reference.
EN was monitored as a function of time between the working electrode and SCE with a Powerlab/4s apparatus (e-DAQ), which was controlled by Chart4 software using the Windows XP operating system. This equipment allows resolutions of 1 μV for voltage signals and 1 pA for current signals. EN data of 4096 points were collected at 4 point/s each time, under which a frequency window was defined in which most usual corrosion processes can be detected. The analytical results for maximum entropy method (MEM) technique were obtained by specific data technique.
All tests were carried out in artificial seawater (pH 7.5) whose main components are listed in Table 1 at room temperature (25±2) °C. During the above experiments, the corrosion morphologies of the samples were observed at different immersion time using a JEOL USA JSM-5510LV scanning electron microscope (SEM) with a field emission gun operated at 3 kV.
Table 1 Chemical compositions of seawater
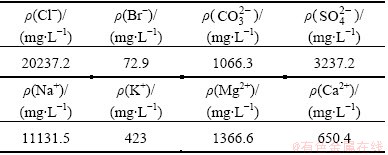
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Corrosion behavior of copper
In order to elucidate the galvanic corrosion behavior of the coupled copper/ titanium in seawater, the corrosion behavior of copper has been first investigated using EIS and EN techniques.
Figure 1 shows the typical EIS evolution features of copper corrosion in seawater. With the help of both the features of the EIS diagrams (such as the number and the width of the phase angle peak of the peak in Bode plots and the number of the capacitance loops in Nyquist plots) and the method developed by WEIJDE et al [30] and CAMPESTRINI et al [31] simultaneously, two time-constants of the EIS plots can be determined. The equivalent electrical circuit (EEC) shown in Fig. 2 has been adopted to fit the EIS plots by Z-view software. In Fig. 2, Rs is the solution resistance, CPE1 is the capacitance of outer passivating film and corrosion product layer, R2 is the membrane resistance of outer passivating film and corrosion products, CPE2 is the double layer capacitance and R3 is charge transfer resistance. And the analysis results are listed in Table 2.
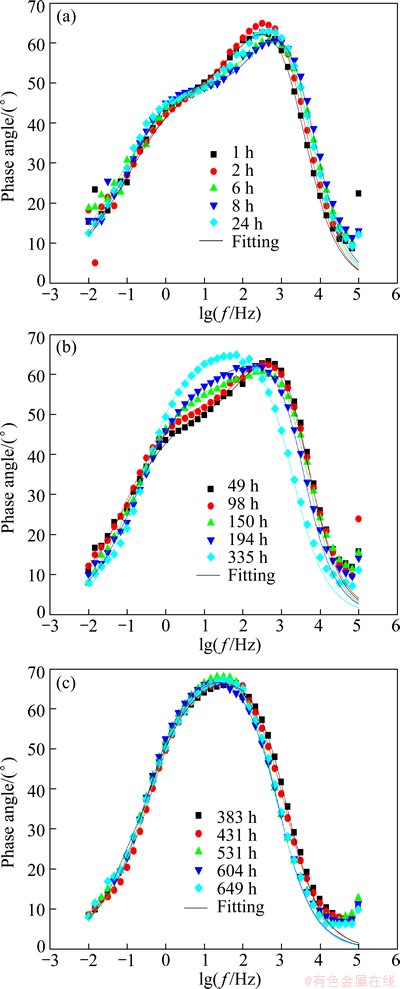
Fig. 1 EIS plots of copper corrosion at different times

Fig. 2 EEC used for simulating impedance spectra of copper corroding in seawater
Table 2 EIS results for copper corrosion in seawater at different immersion times
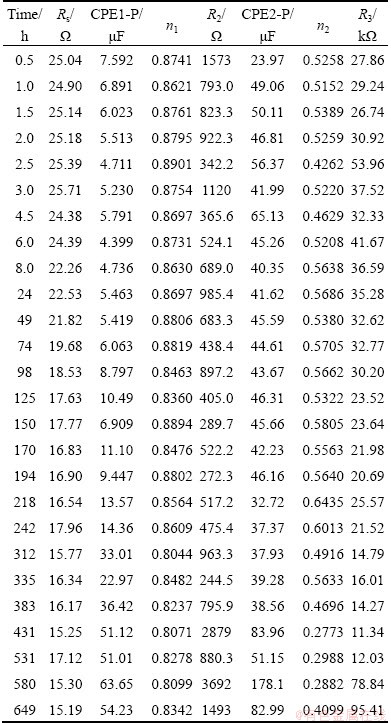
During the corrosion process of copper in seawater, the value of CPE1-P shows the trend of initial slow decrease (see Table 2), due to the surface thermodynamic refining effects (the surface is not holistically smooth) [32], and subsequently fast increase due to the corrosion process (see Fig. 3). Capacitance has a relationship with the corroding area as follows:
 (1)
(1)
where C is the capacitance, S is the film area, ε is dielectric constant and d is the thickness. The ongoing corrosion process will gradually enlarge the interface between the electrode and the aggressive solution, which consequently results in the increase of CPE1-P. The influence of corrosion process on the surface area can be verified by the corroding morphologies of copper (Fig. 4). Figure 4(a) indicates that the matrix surface is smooth with smaller effective corrosion area at the beginning, which results in a small value of CPE1-P. With the extending of immersion time, copper surface becomes rougher as shown in Fig. 4(c), which induces a larger corrosion area and consequently larger CPE1-P values.

Fig. 3 CPE1-P evolution features of copper corroding in seawater at different times
After 240 h in Figs. 4(c-e), a lot of hydroxyl copper CuO—H [33-35] with greater volume generates. In its formation process, stress occurs between each other because of the limited space. When the stress is serious enough, corrosion product film will crack (Fig. 4(d)) or even strip and eventually fall off, especially in the area adjacent to nylon (Fig. 4(f)). Under the effect of Cl- , the corrosion product layer with porous and permeable structure, which is mainly composed of Cu2(OH)3Cl [36], can facilitate and accelerate the corrosion process of base metal (Cu) according to the self-catalysis theory of pitting corrosion, and consequently increase rapidly both the whole corroding area under these films and CPE1-P. Meanwhile, the corrosion product films will dissolve, while the hydroxyl copper will continue to generate and form new corrosion product membrane to cover matrix (Fig. 4(e)). The synthetic influence of the accumulation/dissolution of the corrosion products and the stress-induced film crack result in the oscillation of CPE1-P (Table 2).
The charge transfer resistance (R3) is widely used to characterize the corrosion rate [37]. The larger the charge transfer resistance, the lower the corrosion rate. Figure 5 shows the evolution of the charge transfer resistance (R3).
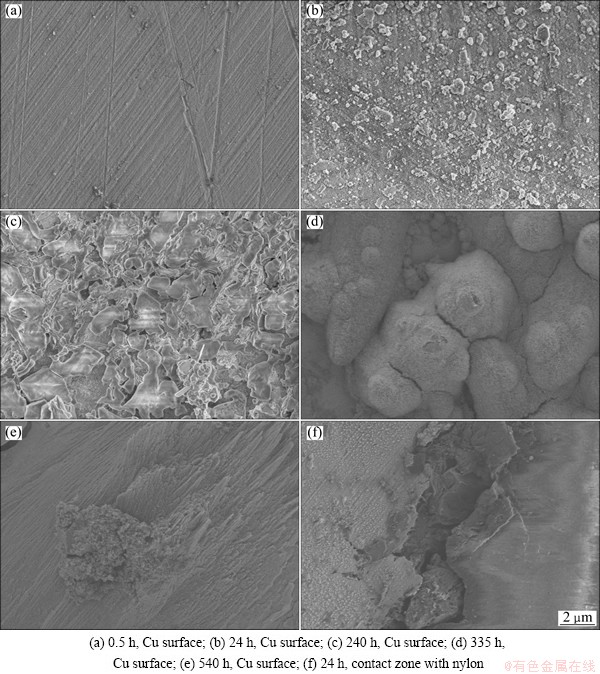

Fig. 4 SEM images of corroding copper at different times
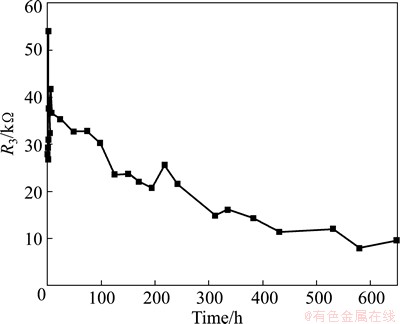
Fig. 5 Charge transfer resistance of copper corrosion in seawater at different times
In the air, a thin layer of discrete copper oxide or hydroxyl copper film with poor electrical conductivity formed, which makes the initial charge transfer resistance much larger (Fig. 5). In the subsequently short time and in solutions, the coverage ratio of hydroxyl copper on copper surface fast increases, which results in the fast increase of R3 (Fig. 5). Meanwhile, the already formed CuO tends to combine with —OH to form hydroxyl copper CuO—H, whose conductivity is better than CuO, and a large amount of Cl- will absorb on the matrix and form Cu2(OH)3Cl [36]. The above influences lead to the initial small oscillation of R3.
With further extension of immersion time, because the volume of hydroxyl copper CuO—H is larger than CuO or Cu, the extrusion each other results in stress. Corrosion product film will crack (Fig. 4(d)), some corrosion products will leave off the matrix and expose nude copper matrix for further corrosion, especially the corrosion products at the interface between nylon and metal (Fig. 4(f)). Both the cracking of corrosion product film and the exposure of nude matrix copper will certainly increase the corrosion area (S) and decrease R3.
During the corrosion process of copper, the possible apparent reactions happening are equations (2)-(4) [38].
2Cu+H2O→Cu2O+2H++2e (2)
Cu+H2O→CuO+2H++2e (3)
Cu+→Cu2++Cu (4)
The generation of H+ in reactions (2)-(3) will certainly acidize the corroding tips, accelerate the dissolution of the copper oxide or hydroxyl copper near these tips, and result in the autoacceleration of the pitting corrosion process [39]. Meanwhile, the aggressive Cl- concentration in the occluded corroding pores, especially near the corroding tips, is much larger compared with bulk solutions [32], which also accelerates the corrosion rate. The above synergetic effects will also certainly decrease the charge transfer resistance R3.
Figure 6 shows the potential noise (without elimination of dc drift) of copper corroding in seawater for 720 h. The ensemble potential noise plot can be divided into two stages, i.e., the initial short corrosion stage with the potential drift positively, the second stage with the first quickly and then gradually negatively potential drift. In the initial short corrosion stage, the potential increases due to the increasing coverage ratio of hydroxyl copper on copper surface, which also results in the fast increase of R3 as elucidated above (Fig. 5). With further extension of immersion time, the synergetic effects, such as the peeling of the corrosion products and the resulted exposure of nude matrix copper, the autoacceleration of the pitting corrosion [39] and the enrichment of aggressive Cl- on the corrosion active points [32], cause the potential drift negatively (Fig. 6).
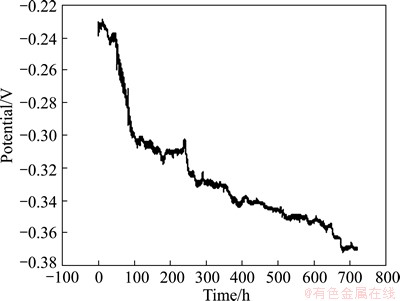
Fig. 6 Electrochemical potential noise of copper corroding in seawater for 720 h
The potential noise shown in Fig. 6 has been analyzed by MEM technique [40] according to its different corrosion stages, and the obtained spectral power density (PSD) plots are shown in Fig. 7. Three parameters of the PSD curve, i.e., white noise level (W), the cut-off frequency (fc) and the high-frequency linear slope (k), can be got by mathematical methods [41-43]. According to the above values, the changing trend of SE and SG with time [44] can be calculated.
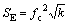 (5)
(5)
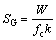 (6)
(6)
Figure 8 shows the evolution features of SE and SG with time. A complete corrosion process should simultaneously contain fast and slow reaction steps. As the SE is only determined by k and fc that are the characteristic parameters of fast reaction steps, SE is used to describe the fast reaction steps, such as the pitting corrosion. So, SG mainly reflects the characteristics of slow reaction steps such as the diffusion and migration of particle, growth of crystal nucleus [44].
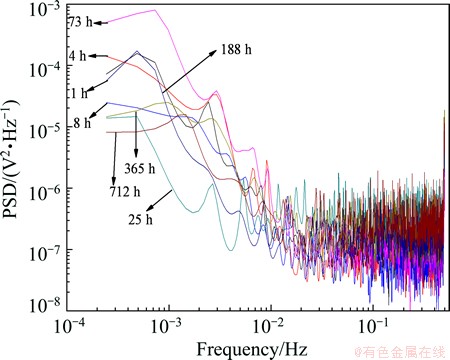
Fig. 7 PSD plots of Cu corrosion in seawater at different times
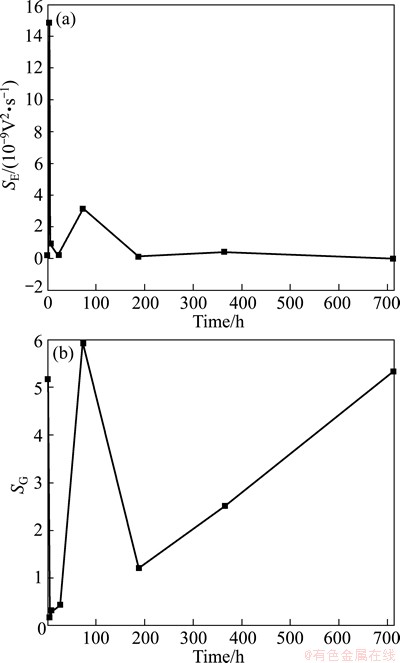
Fig. 8 SE and SG of copper corrosion in seawater at different times
Combining the information in Fig. 6 and Fig. 8, there are two stages in the whole corrosion process of copper. In the first stage (the first point and second point in Fig. 8), the discrete air-formed copper oxide or hydroxyl copper film and the surface thermodynamic refining effects (the surface is not holistically smooth) [32] make pitting corrosion initially difficult, so aggressive particles (eg. O2 and Cl-) must transfer a certain distance on copper surface to a matrix defect to initiate corrosion, which certainly results in the small initial value of SE and large SG (the first point in Fig. 8). Both the hydroxylation of CuO and the enrichment of aggressive Cl- at the surface defects (active points) make pitting corrosion much easier, therefore pitting explodes, which results in the increase of SE while the decrease of SG. In the second stage, the formation, accumulation and their barrier effects of corrosion products such as Cu2(OH)3Cl [36] on the limited metal surface, make diffusion steps of aggressive particles become more and more difficult and finally to be the dominant process, which results in the increase of SG and decrease of SE. Meanwhile, at this second stage, the synthetic influence of the accumulation/dissolution of the corrosion products and the stress-induced film crack (Figs. 4(d)-(f)) result in the oscillation of SE and SG with time. In this case, general corrosion arrives.
3.2 Corrosion behavior of Cu/Ti galvanic couple (GC)
In order to elucidate the influence of titanium on the corrosion of copper, the Cu/Ti GC corrosion behavior is also investigated by the same EIS and EN techniques.
Figure 9 shows the typical EIS plots of Cu/Ti GC in seawater. Two time-constants are also determined by the same methods elucidated above. Therefore, the EIS plots in Fig. 9 are also fitted by the same EEC shown in Fig. 2, and the analyzed results are listed in Table 3.
The material with a lower free corrosion potential in the galvanic couple acts as anode and corrodes preferentially [7], but the rate of the galvanic corrosion is determined not only by the potential differences but also much more by polarization resistance [6]. Ti is a kind of inert metal [45], so a very stable thin oxide film will form on Ti surface even at the room temperature, which consists of TiO2 with a thickness of a few nanometers and possesses remarkable corrosion resistance [29,46, 47]. Therefore, in Cu/Ti galvanic couple, Cu acts as anode while Ti acts as cathode. For the galvanic couple, since the cathode side (Ti) has a higher corrosion- resistance compared with Cu, the characteristics of galvanic couple corrosion mainly reflects the anode side [48], Cu in this study.
For the aim of comparison, the CPE1-P and the R3 evolution features of Cu/Ti GC are also plotted in Fig. 10 and Fig. 11, respectively.
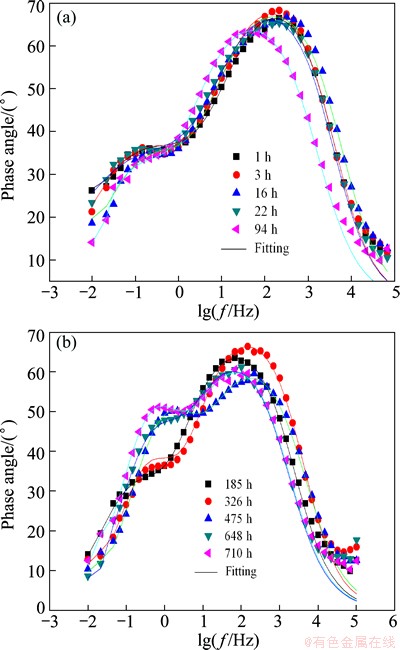
Fig. 9 EIS plots of Cu/Ti GC in seawater at different times
Table 3 EIS results for Cu/Ti GC corrosion in seawater at different times
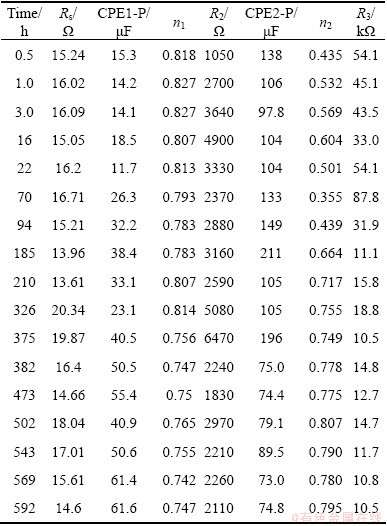

Fig. 10 CPE1-P evolution features of Cu/Ti GC corrosion in seawater at different times
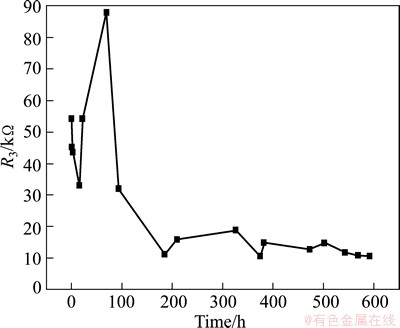
Fig. 11 Charge transfer resistance of Cu/ Ti GC corrosion in seawater at different times
Both the CPE1-P values of Cu and Cu/Ti GC present the same ascending trend (Fig. 3 and Fig. 10), except that the latter is much larger than the former at the initial corrosion stage. In order to elucidate the difference, the surface morphologies of Cu in Cu/Ti GC are also studied by SEM technique; the results are shown in Figs. 12 and 13. Initially, the GC surface is even and relatively smooth (Fig. 12), the real corrosion area is much smaller. However, when comparing the surface morphologies of Cu (Fig. 4) and the Cu in Cu/Ti GC (Fig. 13) at the same corrosion time, it can be concluded that the potential difference between the Cu/Ti GC metals accelerates the corrosion process of Cu, especially the corrosion rate of the area adjacent to Ti (Fig. 13(c)), which consequently causes the fast increase of the Cu area exposed to the solutions and the larger value of CPE1-P.
There exists a difference for the evolution features of R3 between Cu and Cu/Ti GC. In the case of the former, R3 increases firstly due to the surface thermodynamic refining effects (the surface is not holistically smooth) [32], and then decreases due to the corrosion process (Fig. 5). However, in the case of the latter, R3 decreases firstly (Fig. 11). The above difference should be mainly attributed to the different potentials between Cu and Ti in their galvanic couple.

Fig. 12 SEM images of Cu/ Ti GC corrosion surface in seawater for 0.5 h
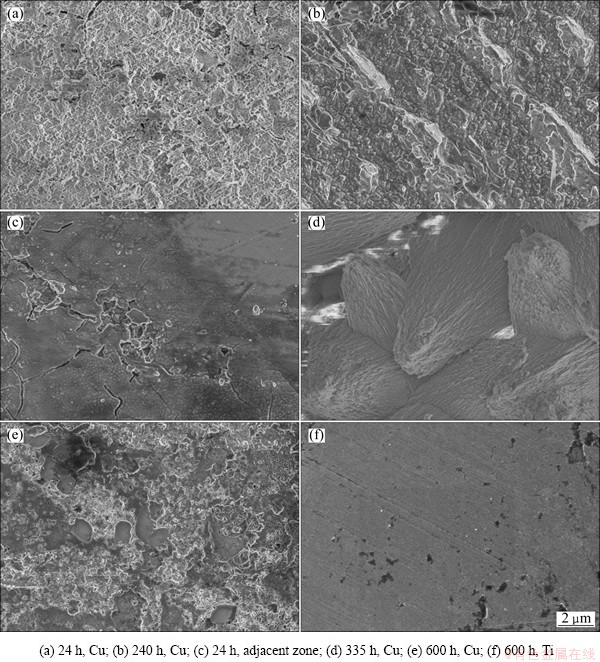
Fig. 13 SEM images of Cu/Ti GC
In the case of Cu/Ti GC, the potential difference between their components can initially partly hinder the surface thermodynamic refining actions, accelerate the diffusion of aggressive Cl- to the corrosion active points on Cu and initiate pitting corrosion, which consequently results in the decrease of R3. Then, the initially formed corrosion products block the pitting holes, decrease the potential difference between GC components and accelerate the surface thermodynamic refining action, which certainly increases the R3. With the prolongation of corrosion time, the synergism of the increasing coverage ratio of hydroxyl copper, the cracks induced by the stress of mutual extrusion of large volume hydroxyl copper (Figs. 13(a), (c), (d)), the peeling/dissolution of the corrosion products and the resulted exposure of nude matrix copper (Figs. 13(a), (b), (e)), the autoacceleration of pitting corrosion [39] and the enrichment of aggressive Cl- on the corrosion active points [32], will decrease R3 finally. The corrosion product film of copper can be divided into an inner compact layer and an outer loose porous layer. After 30 d of corrosion, the outer layer can be easily washed off by slow-moving water (Fig. 13(e)).
In comparison of Fig. 12(b) and Fig. 13(f), it can be seen that the corrosion of Ti is extremely slight, and its main corrosion type is pitting.
Figure 14 shows the potential noise (without elimination of DC drift) of Cu/Ti GC corrosion in seawater for 580 h. For any galvanic couple, which corrosion characteristics mainly reflect on the anode side [48]. In the case of Cu/Ti GC corrosion, Cu acts mainly as anode and corrodes preferentially (Fig. 13). Consequently, the variation trend of the Cu/Ti GC corrosion potential (Fig. 14) is much similar to that of copper (Fig. 6) except the last investigated corrosion time. Briefly, the corroding potential variation can be divided into three stages, i.e., the initial short time of positive drift with a subsequently negative drift, finally followed by a quickly positive drift. The reason of the finally quick positive drift is still under investigation, and it should be related to the pitting corrosion of Ti (Fig. 13(f)).
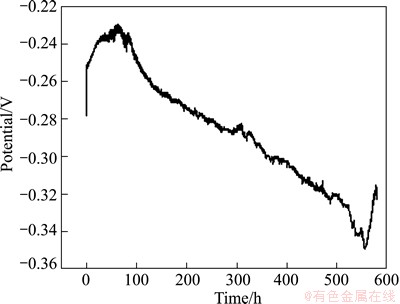
Fig. 14 Electrochemical potential noise of Cu/Ti GC in seawater for 580 h
Another difference between Fig. 14 and Fig. 6 is that, both the minimum and maximum potentials of Cu/Ti GC are more positive than those of copper. For Cu/Ti GC, the measured potential is the mixed potential of Cu and Ti, and the free corrosion potential of Ti is much higher than that of copper. Consequently, the measured potential of GC should be higher.
The potential noise shown in Fig. 14 is also analyzed by MEM technique according to its different corrosion stages, and the obtained PSD plots are shown in Fig. 15.
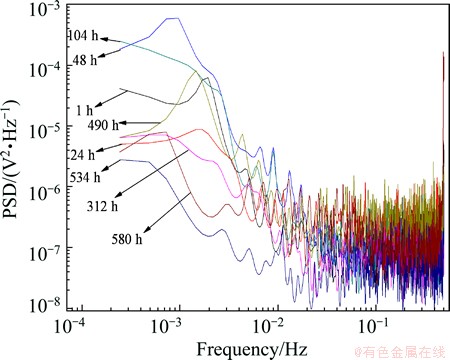
Fig. 15 PSD plots of Cu/Ti GC in seawater at different corrosion times
According to the three parameters of the PSD curve, the values of SE and SG are also calculated [44] and shown in Fig. 16. In comparison of Fig. 16 and Fig. 8, the corrosion difference between Cu and Cu/Ti GC can be obtained. Briefly, the ensemble corrosion process of Cu/Ti GC can be divided into three stages, while two stages for copper. For Cu/Ti GC corrosion in the first stage, SE is large and SG is small due to the potential difference between GC components; then the initially formed corrosion products block the pitting holes, decrease the surface potential difference between GC components and accelerate the surface thermodynamic refining actions, which certainly causes the decrease of SE and the increase of SG. In the second stage, the synergism of the increasing coverage ratio of hydroxyl copper, the cracks induced by the stress of mutual extrusion of large volume hydroxyl copper (Figs. 13(a), (c), (d)), the peeling/dissolution of the corrosion products and the resulted exposure of nude matrix copper (Figs. 13(a), (b), (e)), the autoacceleration of pitting corrosion [39] and the enrichment of aggressive Cl- on the corrosion active points [32], will certainly increase SE and decrease SG. In the last stage, because of the accumulation and thickening of the corrosion products layer, the diffusion steps gradually dominate the whole corrosion process, also because the potential noise caused by the pitting corrosion under the thicker corrosion products layer is difficult to be detected, therefore SE decreases. Also in the last stage, the synthetic influence of the accumulation/dissolution of the corrosion products and the stress-induced film crack result in the oscillation of SE and SG with time. In this case, uniform corrosion of copper also arrives.
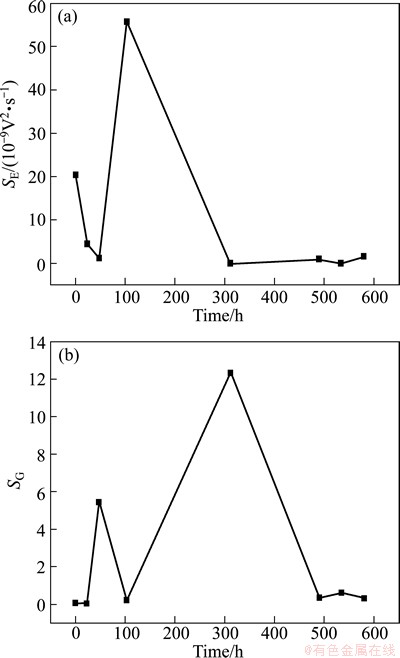
Fig. 16 SE (a) and SG (b) of Cu/Ti GC corrosion in seawater at different times
Lastly, it should be mentioned that, comparing Fig. 11 and Fig. 16, it seems difficult to understand why high corrosion resistance (R3) corresponds to large SE, especially at the first corrosion point. In fact, although both R3 and SE show the same evolution features but different time horizon; meanwhile, our previous studies have demonstrated that the corrosion resistance (R3) obtained from EIS technique mainly corresponds to the ensemble corrosion rate, while SE obtained from EN technique mainly corresponds to pitting corrosion [49,50].
4 Conclusions
1) The ensemble corrosion process of copper in seawater can be divided into two stages. Both the corrosion resistance and SE show the same evolution trend of initial increase and subsequent decrease, while SG changes oppositely.
2) The ensemble corrosion process of Cu/Ti GC in seawater consists of three stages. Both the corrosion resistance and SE show the evolution features of initial decrease with a subsequent increase, and the final decrease again while SG changes oppositely.
3) The potential difference between Cu and Ti in their galvanic couple can initially partly hinder the surface thermodynamic refining actions, accelerate the diffusion of aggressive Cl- to the corrosion active points or defects on copper and consequently accelerate the initiation of pitting corrosion. Meanwhile, both the film capacitance (CPE1-P) values of Cu and Cu/Ti GC present the same ascending trend during the ensemble corrosion process, except that the latter is much larger than the former in the initial corrosion stage, and both the minimum and maximum corrosion potentials of copper/ titanium GC are much more positive than those of copper.
References
[1] GARNER F H, HALE A R. Corrosion in the petroleum industry part 2 [J]. Anti-corrosion Methods and Materials, 1955, 2(6): 177-181.
[2] SARVER E, EDWARDS M. Effects of flow, brass location, tube materials and temperature on corrosion of copper plumbing devices [J]. Corrosion Science, 2011, 53(5): 1813-1824.
[3] AI J Z, GUO X P, CHEN Z Y. The adsorption behavior and corrosion inhibition mechanism of anionic inhibitor on galvanic electrode in 1% NaCl solution [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2006, 253(2): 683-688.
[4] RAHMAN A B M, KUMAR S, GERSON A R. Galvanic corrosion of laser weldments of AA6061 aluminum alloy [J]. Corrosion Science, 2007, 49(12): 4339-4351.
[5] VARELA F E, KURATA Y, SANADA N. The influence of temperature on the galvanic corrosion of a cast iron-stainless steel couple [J]. Corrosion Science, 1997, 39(4): 775-788.
[6] EL-DAHSHAN M E, SHAMS EL DIN A M, HAGGAG H H. Galvanic corrosion in the systems titanium/316L stainless steel/Al copper in Arabian water [J]. Desalination, 2002, 142(2): 161-169.
[7] DESHPANDE K B. Validated numerical modelling of galvanic corrosion for couples: Magnesium alloy (AE44)–mild steel and AE44–aluminium alloy (AA6063) in brine solution [J]. Corrosion Science, 2010, 52(10): 3514-3522.
[8] GLASS G K, ASHWORTH V. The corrosion behaviour of the zinc–mild steel galvanic cell in hot sodium bicarbonate solution [J]. Corrosion Science, 1985, 25(11): 971-983.
[9] PROSEK T, NAZAROV A, BEXELL U, THIERRY D, SERAK J. Corrosion mechanism of model zinc–magnesium alloys in atmospheric conditions [J]. Corrosion Science, 2008, 50(8): 2216-2231.
[10] YIN Z F, YAN M L, BAI Z Q, ZHAO W Z, ZHOU W J. Galvanic corrosion associated with SM 80SS steel and Ni-based alloy G3 couples in NaCl solution [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2008, 53(22): 6285-6292.
[11] ZHANG Da-lei, WANG Wei, LI Yan. An electrode array study of electrochemical inhomogeneity of zinc in zinc/steel couple during galvanic corrosion [J]. Corrosion Science, 2010, 52(4): 1277-1284.
[12] ARRABAL R, PARDO A, MERINO M C, MOHEDANO M,  P, MERINO S. Al/SiC thermal spray coatings for corrosion protection of Mg–Al alloys in humid and saline environments [J]. Surface and Coating Technology, 2010, 204(16-17): 2767-2774.
P, MERINO S. Al/SiC thermal spray coatings for corrosion protection of Mg–Al alloys in humid and saline environments [J]. Surface and Coating Technology, 2010, 204(16-17): 2767-2774.
[13] GROSGOGEAT B, RECLARU L, LISSAC M, DALARD F. Measurement and evaluation of galvanic corrosion between titanium/Ti6Al4V implants and dental alloy by electrochemical techniques and auger spectrometry [J]. Biomaterials, 1999, 20(10): 933-941.
[14]  The effect of temperature on the galvanic corrosion of the copper/AISI 304 pair in LiBr solutions under hydrodynamic conditions [J]. Corrosion Science, 2010, 52(3): 722-733.
The effect of temperature on the galvanic corrosion of the copper/AISI 304 pair in LiBr solutions under hydrodynamic conditions [J]. Corrosion Science, 2010, 52(3): 722-733.
[15] DONG C F, XIAO K, LI X G, CHENG Y F. Galvanic corrosion of a carbon steel-stainless steel couple in sulfide solutions [J]. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 2011, 20(9): 1631-1637.
[16] BLASCO-TAMARIT E, IGUAL-MUNOZ A, GARCIA ANTON J. Effect of temperature on the galvanic corrosion of a high alloyed austenitic stainless steel in its welded and non-welded condition in LiBr solutions [J]. Corrosion Science, 2007, 49(12): 4472-4490.
[17] BAKHTARI A, BRADLEY T G, LOBB W K, BERZINS D W. Galvanic corrosion between various combinations of orthodontic brackets and archwires [J]. American Journal of Orthodontics and Dentofacial Orthopedics, 2011, 140(1): 25-31.
[18] AL-HOSSAIN H I, SABER T M H, MOHAMMED R A, SHAMS EL DIN A M. Galvanic corrosion of copper-base alloy in contact with molybdenum-containing stainless steels in Arabian gulf water [J]. Desalination, 1997, 109(1): 25-37.
[19] BLASCO-TAMARIT E, IGUAL-MUNOZ A,  D. Comparison between open circuit and imposed potential measurements to evaluate the effect of temperature on galvanic corrosion of the pair alloy 31–welded alloy 31 in LiBr solutions [J]. Corrosion Science, 2010, 50(12): 3590-3598.
D. Comparison between open circuit and imposed potential measurements to evaluate the effect of temperature on galvanic corrosion of the pair alloy 31–welded alloy 31 in LiBr solutions [J]. Corrosion Science, 2010, 50(12): 3590-3598.
[20] DONG C F, XIAO K, LI X G, CHENG Y Z. Erosion accelerated corrosion of a carbon steel–stainless steel galvanic couple in a chloride solution [J]. Wear, 2010, 270(1-2): 39-45.
[21] SOUTO R M,  A M. Investigating corrosion processes in the micrometric range: A SVET study of the galvanic corrosion of zinc coupled with iron [J]. Corrosion Science, 2007, 49(12): 4568-4580.
A M. Investigating corrosion processes in the micrometric range: A SVET study of the galvanic corrosion of zinc coupled with iron [J]. Corrosion Science, 2007, 49(12): 4568-4580.
[22] GUINON-PINA V, IGUAL-MUNOZ A,  J. Influence of pH on the electrochemical behaviour of a duplex stainless steel in highly concentrated LiBr solutions [J]. Corrosion Science, 2011, 53: 575-581.
J. Influence of pH on the electrochemical behaviour of a duplex stainless steel in highly concentrated LiBr solutions [J]. Corrosion Science, 2011, 53: 575-581.
[23] SONG G, JOHANNESSON B, HAPUGODA S, STJHON D. Galvanic corrosion of magnesium alloy AZ91D in contact with an aluminium alloy, steel and zinc [J]. Corrosion Science, 2004, 46(2): 955-977.
[24] ARYA C, VASSIE P R W. Influence of cathode-to-anode area ratio and separation distance on galvanic corrosion currents of steel in concrete containing chlorides [J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 1995, 25(5): 989-998.
[25] ZHANG P, NIE X, NORTHWOOD D O. Influence of coating thickness on the galvanic corrosion properties of Mg oxide in an engine coolant [J]. Surface and Coating Technology, 2009, 203(20-21): 3271-3277.
[26] LIU C, CHEN D L, BHOLE S, CAO X, JAHAZI M. Polishing-assisted galvanic corrosion in the dissimilar friction stir welded joint of AZ31 magnesium alloy to 2024 aluminum alloy [J]. Materials Characterization, 2009, 60(5): 370-376.
[27] DING H, HIHARA L H. Electrochemical examinations on the corrosion behavior of boron carbide reinforced aluminum-matrix composites [J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2011, 158(5): 118-124.
[28] ABREU C M,  PENA G,
PENA G,  M C. Galvanic coupling between carbon steel and austenitic stainless steel in alkaline media [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2002, 47(13-14): 2271-2279.
M C. Galvanic coupling between carbon steel and austenitic stainless steel in alkaline media [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2002, 47(13-14): 2271-2279.
[29] BLASCO-TAMARIT E, IGUAL-MUNOZ A, 
 D M. Galvanic corrosion of titanium coupled to welded titanium in LiBr solutions at different temperatures [J]. Corrosion Science, 2009, 59(5): 1095-1102.
D M. Galvanic corrosion of titanium coupled to welded titanium in LiBr solutions at different temperatures [J]. Corrosion Science, 2009, 59(5): 1095-1102.
[30] van der WEIJDE D H, van WESTING E P M, de WIT J H W. Electrochemical techniques for delamination studies [J]. Corrosion Science, 1994, 36(4): 643-652.
[31] CAMPESTRINI P, van WESTING E P M, de WIT J H W. Influence of surface preparation on performance of chromate conversion coatings on Alclad 2024 aluminium alloy Part I: Nucleation and growth [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2001, 46(16): 2553-2571.
[32] WU C S, ZHANG Z, CAO F H, ZHANG L J, ZHANG J Q, CAO C N. Study on the anodizing of AZ31 magnesium alloys in alkaline borate solutions [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2007, 253(8): 3893-3898.
[33] MARTIN B, IVA B, CHRISTINA LI. A mechanism of interaction of copper with a deoxygenated neutral aqueous solution [J]. Corrosion Science, 2010, 52(9): 2917-2927.
[34] PROTOPOPOFF E, MARCUS P. Potential–pH diagrams for sulfur an hydroxyl adsorbed on copper surfaces in water containing sulfides, sulfites or thiosulfates [J]. Corrosion Science, 2003, 45(6): 1191-1201.
[35] WERME L O, KORZHAVYI P A. Comment on Hultquist et al. Water corrodes copper [J]. Catalysis Letters, 2010, 135(3-4): 165-166.
[36] NUNEZ L, REGUERA E, CORVO F, GONZALEZ E, VAZQUEZ C. Corrosion of copper in seawater and its aerosols in a tropical island [J]. Corrosion Science, 2005, 47(2): 461-484.
[37] FANG Da-jing, MAO Xu-hui, ZHANG Ye-ming, CHEN Zhi-liang, LIU Min, GAN Fu-xing. Preparation of non-chromium polymer films on zinc for corrosion protection due to a compound effect between silane and cerium salt [J]. Anti-Corrosion Methods and Materials, 2009, 56(4): 226-231.
[38] LAFRONTA A M, SAFIZADEHA F, GHALI E, HOULACHI G. Study of the copper anode passivation by electrochemical noise analysis using spectral and wavelet transforms [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2010, 55(7): 2505-2512.
[39] CAO Chu-nan. The principles of corrosion electrochemistry [M]. Beijing: Chemistry Industry Press, 1987: 328-333. (in Chinese)
[40] SEARSON P C, DAWSON J L. Analysis of electrochemical noise generated by corroding electrodes under open-circuit conditions [J]. Journal of Electeochemical Society, 1988, 135(8): 1908-1915.
[41] FLIS J, DAWSON J L, GILL J, WOOD G C. Impedance and electrochemical noise measurements on iron and iron-carbon alloys in hot caustic soda [J]. Corrosion Science, 1991, 32(8): 877-892.
[42] HLADKY K, DAWSON J L. The measurement of corrosion using electrochemical 1/f noise [J]. Corrosion Science, 1982, 22(3): 231-237.
[43] MANSFELD F, XIAO H. Electrochemical noise analysis of iron exposed to NaCl solutions of different corrosivity [J]. Journal of Electrochemistry Society, 1993, 140(8): 2205-2209.
[44] SHI Yan-yan, ZHANG Zhao, SU Jing-xin, CAO Fa-he, ZHANG Jian-qing. Electrochemical noise study on 2024-T3 aluminum alloy corrosion in simulated acid rain under cyclic wet–dry condition [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2006, 51(23): 4977-4986.
[45] KUPHASUK C, OSHIDA Y, ANDRES C J, HOVIJITRA S T, BARCO M T, BROWN D T. Electrochemical corrosion of titanium and titanium-based alloys [J]. Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry, 2001, 85(2): 195-202.
[46] LU Q, ALBERCH J, HASHIMOTO T, GARCIA-VERGARA S J, HABAZAKI H, SKELDON P, THOMPSON G E. Porous anodic oxides on titanium and on a Ti-W alloy [J]. Corrosion Science, 2008, 50(2): 548-553.
[47] MAUNO H, KIINIINEN O, LAVONIUS EEVA T, KIVILAHTI JORMA K. SEM observations on stress corrosion cracking of commercially pure titanium in a topical fluoride solution [J]. Dental Materials, 1995, 11(4): 269-272.
[48] AI J Z, GUO X P, CHEN Z Y. The adsorption behavior and corrosion inhibition mechanism of anionic inhibitor on galvanic electrode in 1% NaCl solution [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2006, 253(2): 683-688.
[49] SHI Yan-yan. The electrochemical studies of atmospheric corrosion of typical metals [D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2008: 66-79. (in Chinese)
[50] CHENG Ying-liang. The electrochemical studies of aluminum alloy in bulk solution or in thin electrolyte layers [D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2003: 43-52. (in Chinese).
杜小青1,杨青松2,陈 宇1,杨 洋1,张 昭1
1. 浙江大学 化学系,杭州 310027;
2. 湛江腐蚀与防护研究中心,湛江 524000
摘 要:采用电化学阻抗谱、电化学噪声和扫描电镜等技术研究了纯铜、铜/钛耦合电极在模拟海水中的腐蚀行为。结果表明:纯铜的腐蚀过程分2个阶段,其腐蚀阻抗和点蚀参数SE均遵循先增后降的规律,而其腐蚀参数SG的变化规律则正好相反;铜/钛耦合电极的腐蚀过程则由3个阶段组成,其腐蚀阻抗和点蚀参数SE均遵循先降后升到最后再降的规律,而其腐蚀参数SG则同样反向变化。铜和钛之间的电势差加速了纯铜的点蚀萌生,同时铜/钛耦合电极的腐蚀电位总是正于纯铜的腐蚀电位。
关键词:Cu/Ti电偶;电偶腐蚀;电化学阻抗谱;电化学噪声
(Edited by Hua YANG)
Foundation item: Projects (21073162, 51131005) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project (Y4100206) supported by the Science and Technology Bureau of Jiaxing Municipality and Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China
Corresponding author: Zhao ZHANG; Tel: +86-571-85615190; E-mail: eaglezzy@zjuem.zju.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(14)63097-1

