PHC管桩金属端头在土壤模拟液中的腐蚀行为
林碧兰1,路新瀛1, 李龙2
(1. 清华大学 深圳研究生院,广东 深圳,518055;
2. 广东三和管桩有限公司, 广东 中山,518424)
摘要:通过自然浸泡、动电位极化、电化学阻抗谱测量、电偶腐蚀试验研究预应力高强混凝土(PHC)管桩金属端头处端板和主筋在氯盐土、盐碱土、中性草甸土和酸性土模拟液中的腐蚀速率、电化学腐蚀行为以及电偶腐蚀行为。研究结果表明:主筋的耐蚀性能比端板的差,盐渍土中主筋的耐蚀程度差;端板和主筋的阴极过程受氧扩散控制;盐渍土中端板和主筋的锈层不具保护作用;主筋与端板偶接时主筋为阳极,端板为阴极;主筋在酸性土中的电偶腐蚀效应最大,而在草甸土中最小。
关键词:PHC管桩;端板;腐蚀;土壤;电偶腐蚀
中图分类号:TU503;TG172.4 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2011)02-0434-07
Corrosion behaviors of metal end of PHC pipe pile in
simulated soil solutions
LIN Bi-lan1, LU Xin-ying1, LI Long2
(1. Graduate School at Shenzhen, Tsinghua University, Shenzhen 518055, China;
2. Guangdong Sanhe Pipe-pile Co. Ltd., Zhongshan 518424, China)
Abstract: The corrosion rate, electrochemical corrosion and galvanic corrosion behaviors of the end plate and the steel bar at metal end of prestressed high-strength concrete (PHC) pipe pile in simulated solutions of chloride salt soil, salina soil, neutral meadow soil and acid soil were investigated by natural immersion tests, potentiodynamic polarization and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy measurements and galvanic corrosion tests. The results show that the corrosion resistance of the end plate is inferior to that of the steel bar, and in saline soil the corrosion resistance grade of the steel bar is poor. The cathodic processes of the end plate and the steel bar in four simulated soil solutions are controlled by oxygen diffusion. The corrosion products on end plate and steel bar immersed in saline soil are hardly protective. Steel bar is anodic and end plate is cathodic when they were coupled and immersed in four solutions. The galvanic corrosion effect of stell bar in acid soil is maximal, while that in neutral meadow soil is minimal.
Key words: PHC pipe pile; end plate; corrosion; soil; galvanic corrosion
预应力高强混凝土(PHC)管桩作为上部结构和地基之间的传力构件,其耐久性直接影响工程结构的安全。过去PHC管桩多用于温和环境的软土地基工程,对耐久性无明确要求。随着PHC管桩应用范围的日益扩大和对耐久性要求的不断提高,PHC管桩已被应用于如海洋、港口等严酷环境工程,这类环境对PHC管桩耐久性提出了严格要求[1-5]。然而,现行国家标准《先张法预应力混凝土管桩(GB13476—1999)》还未对管桩的耐久性作出任何规定。PHC管桩耐久性涉及桩身和金属端头耐久性2个方面。清华大学深圳研究生院与广东三和管桩有限公司等联合对PHC管桩桩身混凝土耐久性进行了研究,提出了耐久PHC管桩混凝土技术。然而,目前有关PHC管桩金属端头耐久性的研究工作尚未见文献报道。PHC管桩金属端头包括裙板、端板和低合金预应力主筋钢棒墩头。GB 13476—1999中规定端板和裙板均为Q235钢。端板与主筋相互咬合,在土壤环境中,它们可能存在腐蚀电位差而引发电偶腐蚀或者本身不能长期满足苛刻环境下的耐蚀性要求,薄壁裙板一旦受到破坏,土壤中的有害介质将通过端板与混凝土的界面渗透至预应力主筋表面,造成主筋腐蚀,从而可能引发预应力失效等问题的发生。本文作者通过自然浸泡试验、动电位极化、电化学阻抗谱测量、电偶腐蚀试验研究PHC管桩金属端头在滨海氯盐、盐碱、中性草甸和酸性4种土壤模拟液中的腐蚀行为。
1 实验
基于《岩土工程勘察规范》(GB 50021—2008)、PHC管桩的常用环境、土壤腐蚀性评价标准及分级、我国土壤腐蚀试验站的理化性质[6],这里选定滨海氯盐土(大港)、盐碱土、中性草甸土(沈阳)和酸性红土壤(鹰潭) 4种典型土壤。前两者为盐渍土,后两者为非盐渍土[7]。表1所示为土壤模拟液的化学成分和pH。分别用氢氧化钠和醋酸调节pH。化学试剂均为分析纯,用蒸馏水调配溶液。
表2所示为某PHC管桩端板和主筋的化学成分。端板为Q235钢,化学成分符合GB/T 700—88的规定[8];主筋为低合金钢,化学成分符合YB/T 111—1997的规定[9]。
表1 土壤模拟液编号、化学成分及pH
Table 1 ID, chemical composition and pH value of simulated soil solutions

表2 端板和主筋的化学成分
Table 2 Chemical composition of end plate and steel bar

电化学测量通过CS350电化学工作站在室温下进行。端板工作面积为1.0 cm×1.0 cm和0.8 cm×0.8 cm,主筋工作面积为其横截面积即0.64 cm2。
动电位极化和交流阻抗谱测量采用三电极体系,辅助电极为铂电极,参比电极为饱和甘汞电极(SCE)。动电位极化是待腐蚀电位Ecorr稳定后从(Ecorr-200 mV)向(Ecorr+300 mV)进行扫描,扫描速率为1 mV/s。电化学阻抗谱测量在开路电位上进行,频率范围为0.01~105 Hz,测量信号的幅值为10 mV。用Zview软件对交流阻抗数据进行拟合解析。
电偶腐蚀采用零电阻法测量。偶接时,主筋接电极Ⅰ,端板接电极Ⅱ。当电偶电流为正时,主筋为阳极,端板为阴极;反之,端板为阳极。电偶对中端板和主筋的面积比为1.0。对电偶腐蚀效应进行计算。
腐蚀速率采用失重法测量。测量腐蚀前后试样的质量,精度为0.1 mg。1个腐蚀速率取3个平行试样的平均值。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 腐蚀速率
图1所示为端板和主筋在4种土壤模拟液中浸泡12 d的腐蚀速率vcorr。从图1可以看出:1#模拟液、2#模拟液、4#模拟液和3#模拟液对主筋和端板的腐蚀速率依次减小,主筋的腐蚀速率均大于端板的腐蚀 速率。
土壤中金属耐蚀性评价分级标准为:(1) vcorr<1 g/(dm2?a) (优);(2) vcorr为1~3 g/(dm2?a) (良);(3) vcorr为3~7 g/(dm2?a) (中);(4) vcorr>7 g/(dm2?a) (差)。可见:主筋在氯盐土和盐碱土即盐渍土中的耐腐蚀程度较差,主筋在其他情况下及端板的耐蚀程度均为中等。
2.2 电化学腐蚀行为
图2所示为PHC管桩金属端板和主筋在4种土壤模拟液中的动电位极化曲线;表3所示为相应的极化参数,其中Jcorr为腐蚀电流密度;ba为阳极极化斜率。

图1 端板和主筋在4种土壤模拟液中浸泡12 d的腐蚀速率
Fig.1 Corrosion rate of end plate and steel bar immersed in four simulated soil solutions for 12 d
由图2可见:4种模拟液中,端板和主筋的阳极过程均受活化极化控制,阴极过程均受氧扩散控制;端板的阳极极化分支均在主筋的左侧,即相同电位下端板的阳极电流密度比主筋的小,说明端板在4种模拟液中的阳极溶解速率均小于主筋的阳极溶解速率。其中,4#模拟液中端板和主筋的阳极溶解速度差别最大,3#模拟液中的溶解速度相差最小。而4种模拟液中,端板与主筋的阴极极化分支几乎重合。
表3 端板和主筋在4种土壤模拟液中的极化参数
Table 3 Polarization parameters for end plate and steel bar in four simulated soil solutions
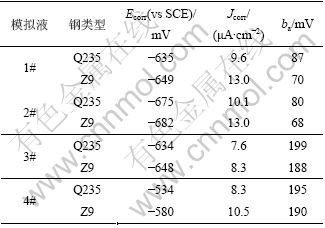

图2 端板和主筋在4种土壤模拟液中的动电位极化曲线
Fig.2 Potentiodynamic polarization curves for end plate and steel bar immersed in four simulated soil solutions
由表3可见:4种模拟液中,端板的腐蚀电流密度Jcorr均比主筋的小,前者的腐蚀电位Ecorr和阳极极化斜率ba均比后者的大,说明端板的耐蚀性能优于主筋的耐蚀性能。1#和2#模拟液中端板和主筋的腐蚀电流密度比3#和4#模拟液的大,而1#和2#模拟液中端板和主筋阳极极化斜率均比3#和4#模拟液的小,说明1#和2#模拟液中端板和主筋的阳极溶解速度均大于3#和4#模拟液的阳极溶解速率。这是由于前2种溶液中氯离子与硫酸根离子含量明显比后两者的大,说明氯离子和硫酸根离子能明显加速铁的溶解。
图3所示为端板和主筋在4种土壤模拟液中浸泡20 min所测得的Nyquist谱(其中:Z′为阻抗Z的实部;Z″为阻抗Z的虚部)。由图3可见:4种模拟液中,端板和主筋的阻抗谱均有2个时间常数,其中,第1个时间常数(高频部分)表征试样表面锈层的信息,与锈层的致密性和厚度有关,第2个时间时间常数(低频部分)表征试样表面电化学反应的信息[10-14]。与3#和4#模拟液相比,端板和主筋在1#和2#模拟液中高频容抗环的特征不明显,说明端板和主筋表面的锈层较薄或者不致密;低频容抗环出现了收缩,可能与氯离子和硫酸根离子在试样表面的吸附有关[10-14]。此外,4种模拟液中,端板的容抗环半径均比主筋的大。
用图4所示等效电路对阻抗谱进行解析拟合。其中:Rs为溶液电阻;Qr为锈层电容;Rr为锈层电阻;Qdl为试样表面的双电层电容;Rct为电荷转移电阻。实际电化学体系中的电极/溶液界面双电层电容的频响特性与“纯电容”存在一定的偏离,Nyquist谱上表现为半圆的畸变,通常用常相位角元件Q来表征双电层电容,其阻抗ZQ=1/[Y0(jω)n]。式中:Z为阻抗,Ω?cm2;Y0表示发生偏离时的电容,Ω-1?cm-2?s-n;ω为角频率,rad/s;n=1-2α/180; 为半圆畸变的抑制角[15]。当n=1时,Q为电容;当n=0时,Q为电阻;当n=0.5时,Q为扩散阻抗;当0<n<1时,Q表示双电层电容的“弥散效应”[15]。因锈层的不致密性和厚度的不均匀性,锈层电容也会产生“弥散效应”,故用常相位角元件来表征锈层电容[15]。
为半圆畸变的抑制角[15]。当n=1时,Q为电容;当n=0时,Q为电阻;当n=0.5时,Q为扩散阻抗;当0<n<1时,Q表示双电层电容的“弥散效应”[15]。因锈层的不致密性和厚度的不均匀性,锈层电容也会产生“弥散效应”,故用常相位角元件来表征锈层电容[15]。
表4是根据图4等效电路拟合得到端板和主筋各等效元件的拟合参数值。由表4可见;端板和主筋的锈层电阻明显小于电荷转移电阻,尤其是1#和2#模拟液,其电阻小于10 Ω·cm2;1#和2#模拟液中的n(Qr)也比3#和4#模拟液的小,盐渍土中锈层电容的弥散现象比较严重,说明盐渍土中的锈层几乎不具有保护作用。3#和4#模拟液中的溶液电阻比1#和2#模拟液的电阻大得多,这可能与非盐渍土模拟液中的离子浓度比盐渍土中的离子浓度小有关。
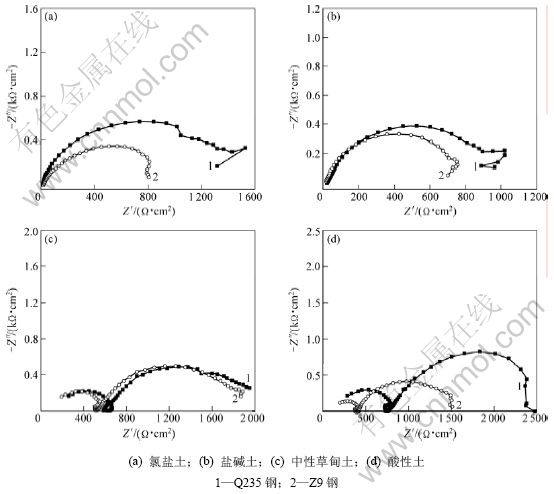
图3 端板和主筋在模拟液中浸泡20 min的Nyquist谱
Fig.3 Nyquist diagrams for end plate and steel bar immersed in four simulated soil solutions for 20 min
表4 端板和主筋在四种土壤模拟液中浸泡20 min所得交流阻抗谱的拟合结果
Table 4 Fitted parameters for end plate and steel bar immersed in four simulated solutions for 20 min


图4 端板和主筋在土壤模拟液中浸泡20 min的交流阻抗等效电路
Fig.4 Equivalent circuit for end plate and steel bar immersed in simulated soil solutions for 20 min
由表4还可以看出:4种模拟液中,端板的电荷转移电阻均比主筋的大,说明端板表面电化学反应的电子转移阻力均比主筋的大。由于锈层也会阻碍材料腐蚀的发生,锈层电阻和电荷转移电阻之和能更准确表征材料发生腐蚀的难度。3#和4#模拟液中端板和主筋的总电阻分别比1#和2#模拟液的大;4种溶液中端板的总电阻均比主筋的大;4#模拟液中端板与主筋的总电阻相差最大,约1 kΩ·cm2,其次是1#模拟液和2#模拟液,3#模拟液电阻相差最小。
2.3 主筋与端板的电偶腐蚀
图5所示为端板与主筋偶接后在4种土壤模拟液中的电偶电流密度随时间变化的曲线。可以看出:偶接0.5 h后,电偶电流密度趋于一稳定正值,说明电偶对中主筋为阳极,端板为阴极;3#模拟液中的电偶电流密度明显比其他3种溶液的小,1#模拟液中的电偶电流密度最大,2#和3#模拟液中的电偶电流密度相近。
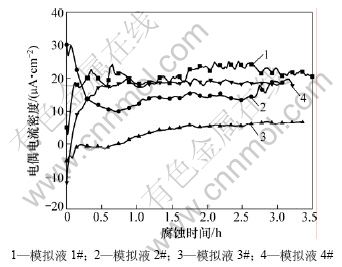
图5 Z9/Q235钢电偶对在4种土壤模拟液中电偶腐蚀电流密度随时间的变化关系
Fig.5 Changes of galvanic current density of Z9/Q235 galvanic couple in four simulated soil solutions
因端板和主筋在4种土壤模拟液中的阴极反应均由氧扩散控制,故面积相同时,电偶对中阳极主筋的平均腐蚀电流密度ia=ig+icorr,电偶腐蚀效应γ=ia/icorr=1+ig/icorr[16](其中:ig为电偶电流密度ig=Ig/Aa,Ig为试验测得电偶电流的平均值,Aa为阳极材料的面积)。
表5所示为Z9/Q235电偶对在4种土壤模拟液中以相同面积偶接时的电偶腐蚀参数。由表5可见:2#模拟液中的电偶电位最小,其次分别为1#模拟液、3#模拟液、4#模拟液。这是由于电偶电位与电偶对中电极的腐蚀电位有关[17-18]。电极阳极过程的电位通常与溶液的离子活度有关,离子浓度越大,阳极过程的腐蚀电位越小;阴极过程通常发生吸氧或析氢反应,其电位随溶液pH的增大而减小[17-18]。所以,电极在1#和2#模拟液中的腐蚀电位小于3#和4#模拟液的腐蚀电位在理论上是可行的。同理也可说明电偶电位的。
表5 Z9/Q235电偶对在4种土壤模拟液中的电偶腐蚀参数
Table 5 Galvanic corrosion parameters for Z9/Q235 galvanic couple in four simulated soil solutions

由表5还可以看出:主筋在4种溶液中的电偶腐蚀效应均大于1.00,说明与端板偶接后,主筋的腐蚀速率均增大。其中,4#模拟液中的电偶腐蚀效应最大,3#模拟液的最小。这与动电位极化和电化学阻抗的结果一致。说明在酸性土壤介质中,主筋的腐蚀速率增大的幅度最大;其次是弱碱条件下的氯离子和硫酸根离子的盐渍土,中性非盐渍土中的增大幅度最小。主筋的面积远小于与其接触端板的面积,所以,将形成对主筋极为不利的“小阳极大阴极”的腐蚀体系。
3 结论
(1) 4种土壤模拟液中端板的腐蚀速率均比主筋的小,端板和主筋在盐渍土中的腐蚀速率均大于非盐渍土的腐蚀速率,主筋在盐渍土中的耐蚀程度较差。
(2) 4种模拟液中,端板和主筋的阳极过程受活化极化控制,阴极过程受氧扩散控制。
(3) 4种土壤模拟液中,端板和主筋的电荷转移电阻均大于锈层电阻,盐渍土中的锈层电阻极小,端板和主筋在盐渍土中不形成有保护作用的锈层;非盐渍土中端板和主筋的总电阻比盐渍土的大。
(4) 4种土壤模拟液中,主筋与端板偶接时,主筋为阳极,端板为阴极,可构成对主筋不利的“小阳极大阴极”的腐蚀体系;酸性土中主筋的电偶腐蚀效应最大,盐渍土次之,草甸土最小。
参考文献:
[1] 张春文. 预应力混凝土管桩在腐蚀性地质中应用的探讨[J]. 建筑结构, 2002, 32(6): 47-50.
ZHANG Chun-wen. Discussion on the application of prestressed concrete pipe pile in corrosive geology [J]. Building Structure, 2002, 32(6): 47-50.
[2] 蒋元海, 匡红杰. 国标GB13476—1999 修订应注意的几个问题[J]. 混凝土与水泥制品, 2007, 34(3): 24-27.
JIANG Yuan-hai, KUANG Hong-jie. Several problems paid attention in revision of GB13476—1999[J]. China Concrete and Cement Products, 2007, 34(3): 24-27.
[3] 严志隆, 陆酉教, 仲以林, 等. PHC管桩混凝土耐久性[J]. 混凝土与水泥制品, 2008, 35(6): 26-27.
YAN Zhi-long, LU Qiu-jiao, ZHONG Yi-lin, et al. Concrete durability of PHC pipe pile[J]. China Concrete and Cement Products, 2008, 35(6): 26-27.
[4] 林渝榕. PHC管桩基础设计与施工中若干问题的探讨[J]. 福建建筑, 2006, 24(4): 59-61.
LIN Yu-rong. A discussion on some problems in the design and construction of PHC pipe pile foundation[J]. Fujian Architecture & Construction, 2006, 24(4): 59-61.
[5] 洪乃丰. 基础设施腐蚀防护和耐久性[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2003: 2-11.
HONG Nei-feng. Problem and answer for durability of infrastructure and its prevention[M]. Beijing: Chemistry Industry Press, 2003: 2-11.
[6] 全国土壤腐蚀试验网站. 全国土壤腐蚀试验网站资料选编: 第二集[M]. 上海: 上海交通大学出版社, 1992: 32-35.
The selected information of the national soil corrosion, test networks & stations: No.2[M]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiaotong University Press, 1992: 32-35.
[7] GB50021—2008. 岩土工程勘察规范[S].
GB50021—2008. Code for investigation of geotechnical engineering [S].
[8] GB/T700—1988. 碳素结构钢[S].
GB/T700—1988. Carbon structural steel[S].
[9] YB/T111—1997. 预应力混凝土用钢棒[S].
YB/T111—1997. Steel bars prestressed concrete[S].
[10] 李晓刚, 杜翠薇, 董超芳, 等. X70钢的腐蚀行为与试验研究[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2005: 112-114.
LI Xiao-gang, DU Cui-wei, DONG Chao-fang, et al. Corrosion behavior and experiment study on X70 steel[J]. Beijing: Science Press, 2005: 112-114.
[11] 陈旭, 杜翠薇, 李晓刚, 等. 含水率对X70钢在鹰潭酸性土壤中腐蚀行为的影响[J]. 石油化工高等学校学报, 2007, 20(4): 55-58.
CHEN Xu, DU Cui-wei, LI Xiao-gang, et al. Influences of soil water content on corrosion behavior of X70 steel in Yingtan acidic soil[J]. Journal of Petrochemical Universities, 2007, 20(4): 55-58.
[12] 费小丹, 李明齐, 许红梅, 等. 湿度对X70钢在卵石黄泥土中腐蚀行为影响的电化学研究[J]. 腐蚀科学与防护技术, 2007, 19(1): 35-37.
FEI Xiao-dan, LI Ming-qi, XU Hong-mei, et al. Influence of soil humidity on corrosion behavior of X70 steel in Yellow pebble soil [J]. Corrosion Science and Protection Technology, 2007, 19(1): 35-37.
[13] 杨余芳, 龚竹青, 李强国. 三价铬的电化学沉积[J]. 中南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2008, 39(1): 112-117.
YANG Yu-fang, GONG Zhu-qing, LI Qiang-guo. Electrochemical deposition of trivalent chromium[J]. Journal of Central South University: Science and Technology, 2008, 39(1): 112-117.
[14] 罗胜联, 周舟, 何德良, 等. 水质稳定剂对模拟工业电解锌回水中电化学行为的影响[J]. 中南大学学报:自然科学版, 2007, 38(1): 84-88.
LUO Sheng-lian, ZHOU Zhou, HE De-liang, et al. Effect of stabilizing agents for water quality on electrochemical behavior in simulated industrial electrolytic zinc reused water[J]. Journal of Central South University: Science and Technology, 2007, 38(1): 84-88.
[15] 曹楚南, 张鉴清. 电化学阻抗谱导论[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2002: 26-32.
CAO Chu-nan, ZHANG Jian-qing. An introduction to electrochemical impedance spectroscopy[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2002: 26-32.
[16] 刘成虎, 柳伟, 赵耀斌, 等. X70异种钢焊接接头的电偶腐蚀行为[J]. 北京科技大学学报, 2008, 30(1): 25-29.
LIU Cheng-hu, LIU Wei, ZHAO Yao-bin, et al. Galvanic corrosion of X70 dissimilar weld joints[J]. Journal of University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2008, 30(1): 25-29.
[17] 曹楚南. 腐蚀电化学原理[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2008: 93-98.
CAO Chu-nan. Principles of electrochemistry of corrosion[M]. Beijing: Chemistry Industry Press, 2008: 93-98.
[18] 王凤平, 康万利, 敬和民, 等. 腐蚀电化学原理、方法及应 用[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2008: 37-43.
WANG Feng-ping, KANG Wan-li, JING He-min, et al. Principles, methods and applications of corrosion electrochemistry[M]. Beijing: Chemistry Industry Press, 2008: 37-43.
(编辑 杨幼平)
收稿日期:2010-01-06;修回日期:2010-04-16
基金项目:中国博士后科学基金面上资助项目(20080440043); 中国博士后科学基金特别资助项目(200902107)
通信作者:林碧兰(1980-),女,福建莆田人,博士,从事金属腐蚀与防护的研究;电话:18259287263;E-mail:linbilan@xmut.edu.cn