DOI:10.11817/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2020-37161
电磁性能可调控金属陶瓷Y2Ti2O7/Fe的制备与表征
罗思杰1, 2,江 勇1, 2,贺 涔1, 2,解培涛3,范润华3
(1. 中南大学 材料科学与工程学院,长沙 410083;
2. 中南大学 有色金属材料科学与工程教育部重点实验室,长沙 410083;
3. 山东大学 材料科学与工程学院,济南 250061)
摘 要:采用固相反应与真空烧结先后制备Y2Ti2O7粉末与Y2Ti2O7/Fe金属陶瓷。XRD分析表明,所得Y2Ti2O7粉末为纯相,Y2Ti2O7/Fe金属陶瓷化学性质稳定,金属相与陶瓷相之间无界面反应产物。在10 MHz~1 GHz频段进行测试,发现Y2Ti2O7/Fe金属陶瓷的逾渗阈值处于Fe含量20%~30%(体积分数)之间。当Fe含量低于逾渗阈值时,介电常数、交流导电和磁导率均随Fe含量的增加而增加。当Fe含量超过30%时,金属陶瓷电抗与交流电导率发生突变,在整个测试频段都呈现负介电常数。Fe含量为40%的样品的磁导率在整个测试频段内小于1,且随频率增加不断下降,应归因于逾渗导电网络导致的抗磁性。在频率大于1 GHz时可能出现负磁导率,即实现电磁性能的双负性。
关键词:Y2Ti2O7;金属陶瓷;介电常数;磁导率
文章编号:1004-0609(2020)-01-0122-07 中图分类号:TG146.1 文献标志码:A
双负材料(Double negative materials, DNMs)是指在特定电磁波频段可以实现介电常数与磁导率同时为负值的一类材料。这类材料展现出负折射、逆多普勒效应、逆切伦科夫效应等奇特的物理现象,在电磁屏蔽、隐形、电磁波衰减和微带天线等领域有巨大应用潜力。前苏联科学家VESELAGO[1]于1968年首次提出双负材料的理论概念,并预测当电磁波在这类材料中传播时,其磁场矢量、电场矢量和波矢均遵循左手定则,因此也可称之为“左手材料”。直至1996年,PENDRY等[2]从理论上预言了周期性排列的开口谐振环结构可以获得双负性质。2000年,SMITH等[3]首次报道在周期性排列金属线及金属环的超材料中出现负折射的现象。一般认为,超材料的双负特性主要来源于其特殊的介观结构。近十年来的,许多具有不同特殊构型的超材料陆续被研究者成功制备[4-6],对其电磁特性的表征也相应成为研究热点。与之同时,能否和如何通过材料的本征性质低成本地实现双负性能,也一直是研究者们积极探索的新课题。山东大学范润华等[7]通过浸渍还原法制备的多孔氧化铝负载镍,在750 MHz~1 GHz频段成功实现了金属陶瓷双负性能的突破。近几年来,又陆续在不同金属陶瓷复合材料中多次实现了双负性能[8-10]和负介电性能[11-14]。
金属陶瓷是由金属或合金与至少一种陶瓷相组成的非均质复合材料,其整体材料性能介于金属与陶瓷之间。通过改变金属与陶瓷相的成分比例,可以对材料的介观结构,进而对其电磁性能进行设计调控。当金属陶瓷中的金属含量超过它的逾渗阈值时,材料介电常数可能发生突变,获得负介电性能。同时,金属相一旦构成了大量环形微结构,会对外磁场的变化产生抵抗,从而降低材料的磁导率,甚至获得负磁导率。若金属相具有铁磁性,负磁导率也可能由磁共振获得。
Y2Ti2O7是具有烧绿石结构的一种复杂氧化物,属于中介电常数材料(30<εr<80)[15],有很高的热力学稳定性,从室温到1673 K既不会发生分解也不会有相 变[16]。由于其性质稳定,烧绿石结构Y2Ti2O7在热障涂层、催化、固体燃料电池、上转换发光等功能材料领域中有着广泛应用前景[17-22]。而作为一种氧化物,其弹性模量却与Fe相近[21],与Fe之间也不发生化学反应[23-27],显然也是铁基金属陶瓷中的理想陶瓷相。本文采用固相法合成Y2Ti2O7,再利用粉末冶金方法制备Y2Ti2O7/Fe金属陶瓷,并对其物相组成、显微结构、及其电磁性能开展表征,评估其实现双负或单负性的可能性。
1 实验
以TiO2(汕头市西陇化工厂生产、纯度为AR、锐钛矿型)粉末与Y2O3(赣州万臻矿产有限公司生产、纯度为99.99%)粉末作为原料,按比例进行球磨混合(转速300 r/min、时间20 h),经1200 ℃固相反应8 h,一次性获得纯相Y2Ti2O7粉末。Y2Ti2O7粉末经球磨细化后,与不同体积分数的Fe粉末(10%、20%、30%、40%,分别标记为F10、F20、F30、F40)进行球磨混料(转速200 r/min、时间8 h)。通过模压制成圆环与圆片形试样,在真空下压坯烧结(1400 ℃,2 h)成金属陶瓷。
Y2Ti2O7粉末与金属陶瓷的相分析采用BRUER AXS D8 ADVANCE型X射线衍射仪,粉末颗粒与金属陶瓷的微观形貌分析采用Quanta-200环境扫描电子显微镜观察。金属陶瓷的介电常数与磁导率采用Aglient E4991A RF阻抗分析仪,测试频段为10 MHz至1 GHz频段。介电常数的实部由试样的电容换算,换算公式为 ,其中C为样品电容,d是样品厚度,A是电极面积,
,其中C为样品电容,d是样品厚度,A是电极面积,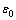 是真空介电常数约为8.85×10-12 F/m。
是真空介电常数约为8.85×10-12 F/m。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 物相与微观组织形貌
图1所示为固相合成法制备的Y2Ti2O7粉末的XRD谱。可以看到,各特征衍射峰都比较尖锐,说明结晶度良好,且没有TiO2或Y2O3残余,可以认定获得了烧绿石结构的Y2Ti2O7单相粉末。图2所示为Y2Ti2O7粉末的SEM像。粉末形状不规则,粒径主要分布在数百纳米到7 μm之间,以1 μm左右的颗粒最多。
图3所示为不同成分配比获得的Y2Ti2O7/Fe金属陶瓷的XRD谱。图3中所有特征衍射峰都属于Fe与Y2Ti2O7,随Fe含量的增加,Fe衍射峰逐渐增强,Y2Ti2O7衍射峰逐渐减弱,且没有出现任何其他杂质相的衍射峰,这说明Y2Ti2O7与Fe化学相容性良好,即使在1673 K下烧结也没有发生化学反应,获得的Y2Ti2O7/Fe金属陶瓷具有很强的高温化学稳定性。
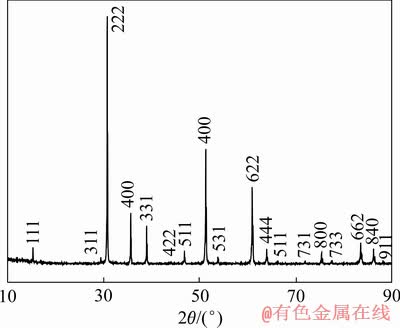
图1 Y2Ti2O7粉末的XRD谱
Fig. 1 XDR pattern of Y2Ti2O7 powder
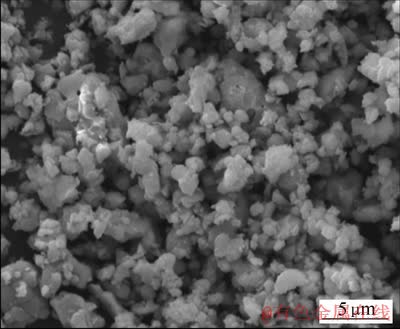
图2 Y2Ti2O7粉末的SEM像
Fig. 2 SEM image of Y2Ti2O7 powder
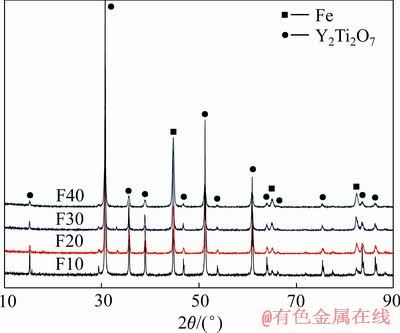
图3 Y2Ti2O7/Fe金属陶瓷XRD谱
Fig. 3 XRD patterns of Y2Ti2O7/Fe cermet
图4所示为Y2Ti2O7/Fe金属陶瓷微观组织的SEM像。图4中亮衬度相为Fe,暗衬度相为Y2Ti2O7基体。Fe含量较低的试样,如F10,Fe颗粒弥散地分布在Y2Ti2O7基体中,相互之间没有连通。随着Fe含量的增加,Fe颗粒变大,相邻的Fe颗粒产生了连通合并,颗粒尺寸的分布散度更大,形貌也变得更加不规则,甚至融合在了一起形成金属环或开口的环状。另外,Y2Ti2O7陶瓷基体存在一定的孔隙率,这是由于烧结温度仍然远远低于它的熔点,烧结后无法形成完全致密。但Fe含量增加有利于减少基体孔隙率,这可能是烧结时出现了Fe的液相,有利于填充部分基体孔隙,从而改善了材料致密度。
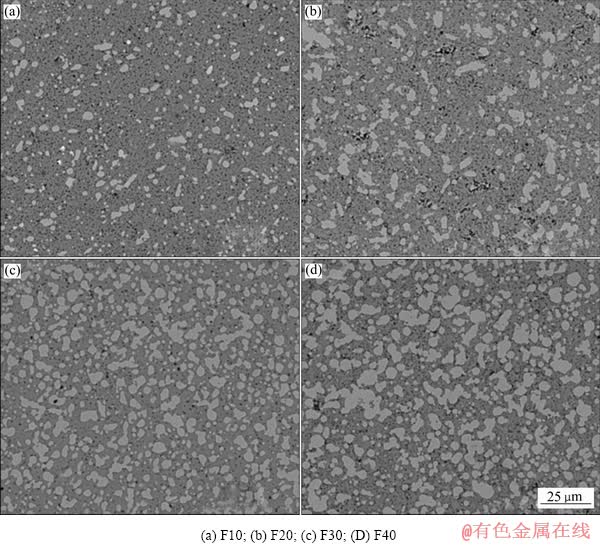

图4 Y2Ti2O7/Fe金属陶瓷的SEM像
Fig. 4 SEM images of Y2Ti2O7/Fe cermet
2.2 介电性能
图5所示为纯相Y2Ti2O7和不同Fe含量的Y2Ti2O7/Fe金属陶瓷的介电谱。纯相Y2Ti2O7试样的介电常数先随着频率增加而显著降低,这可能是介电弛豫引起的,在200 MHz以上介电常数逐渐趋于稳定值,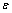 约为30。相比之下,纯相Al2O3的高频介电常数仅为10[28]。F10试样的介电常数则非常稳定,在整个被测试的频段,介电常数值均能够稳定在40左右。随着Fe含量的增多,F20的介电常数比F10有进一步的提高,其频散现象也更为明显。这是由于加入的金属与氧化物形成了大量界面,在外加电场驱使下电荷会在界面富集,产生界面极化作用。从材料微观结构考虑,Fe颗粒的引入,在Y2Ti2O7基体中产生了许多极小的等效电容,从而使F20的介电常数相较于纯相Y2Ti2O7试样有显著提高。当Fe含量达到30%,F30的介电常数在整个测试频段都为负值,表现出与金属材料相似的介电性能,这可以用金属陶瓷的逾渗现象来解释,即当金属含量低于某一临界值时,材料介电性能与绝缘体类似,一旦金属含量超过这个临界值时,材料介电性能会发生突变,此临界值也称为逾渗阈值。由图5可知,Y2Ti2O7/Fe金属陶瓷逾渗阈值应在Fe含量为20%~30%之间。当Fe含量超过这一逾渗阈值时,原本相互孤立的Fe颗粒有机会连接起来,形成有三维连通的金属相网络,金属中的自由电子可以在此网络中自由移动,因此,整个金属陶瓷的介电行为变得与金属类似。
约为30。相比之下,纯相Al2O3的高频介电常数仅为10[28]。F10试样的介电常数则非常稳定,在整个被测试的频段,介电常数值均能够稳定在40左右。随着Fe含量的增多,F20的介电常数比F10有进一步的提高,其频散现象也更为明显。这是由于加入的金属与氧化物形成了大量界面,在外加电场驱使下电荷会在界面富集,产生界面极化作用。从材料微观结构考虑,Fe颗粒的引入,在Y2Ti2O7基体中产生了许多极小的等效电容,从而使F20的介电常数相较于纯相Y2Ti2O7试样有显著提高。当Fe含量达到30%,F30的介电常数在整个测试频段都为负值,表现出与金属材料相似的介电性能,这可以用金属陶瓷的逾渗现象来解释,即当金属含量低于某一临界值时,材料介电性能与绝缘体类似,一旦金属含量超过这个临界值时,材料介电性能会发生突变,此临界值也称为逾渗阈值。由图5可知,Y2Ti2O7/Fe金属陶瓷逾渗阈值应在Fe含量为20%~30%之间。当Fe含量超过这一逾渗阈值时,原本相互孤立的Fe颗粒有机会连接起来,形成有三维连通的金属相网络,金属中的自由电子可以在此网络中自由移动,因此,整个金属陶瓷的介电行为变得与金属类似。
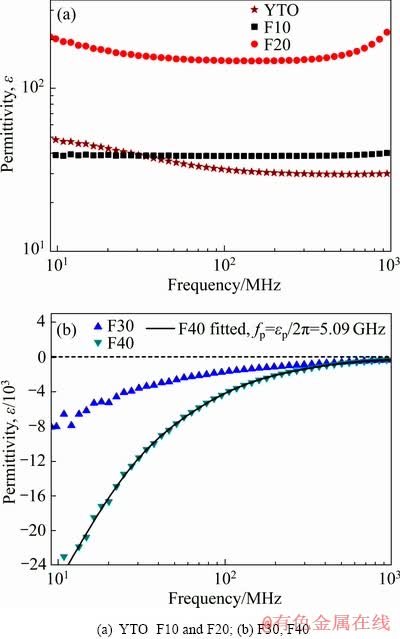
图5 Y2Ti2O7/Fe金属陶瓷的介电谱
Fig. 5 Permittivity spectra of Y2Ti2O7/Fe cermet
F40试样的介电谱与F30类似,但介电常数的绝对值有显著提高。其介电常数与频率的关系可由Drude模型[29-30]进行拟合:
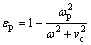 (1)
(1)
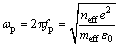 (2)
(2)
式中: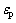 为介电常数;
为介电常数;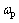 与vc分别为等离子频率及碰撞频率;
与vc分别为等离子频率及碰撞频率; 为外加电场频率;fp是等离子共振频率。neff和meff分别是有效自由电子浓度和有效电子质量,e和
为外加电场频率;fp是等离子共振频率。neff和meff分别是有效自由电子浓度和有效电子质量,e和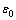 分别是电子电荷(1.6×10-19 C)和真空介电常数(8.85×10-12 F/m)。依照上式对F40的拟合结果与实验数据十分吻合,利用拟合结果可以算出其等离子共振频率为:fp=
分别是电子电荷(1.6×10-19 C)和真空介电常数(8.85×10-12 F/m)。依照上式对F40的拟合结果与实验数据十分吻合,利用拟合结果可以算出其等离子共振频率为:fp=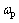 /2π=5.09 GHz。该数值低于纯金属Fe的fp达5个数量级(后者约为9.9×105 GHz)[31],这是由于陶瓷相的存在对纯金属相中的自由电子浓度产生了强烈的稀释作用,由式(2)可知,造成等离子共振频率的显著降低,也即F40处于低频等离子态[32]。Drude模型通常被用于描述电子可自由移动的导体的介电行为,而对于Fe含量处于逾渗阈值之下的F10与F20试样,遵循Lorentz型介电行为[33]。
/2π=5.09 GHz。该数值低于纯金属Fe的fp达5个数量级(后者约为9.9×105 GHz)[31],这是由于陶瓷相的存在对纯金属相中的自由电子浓度产生了强烈的稀释作用,由式(2)可知,造成等离子共振频率的显著降低,也即F40处于低频等离子态[32]。Drude模型通常被用于描述电子可自由移动的导体的介电行为,而对于Fe含量处于逾渗阈值之下的F10与F20试样,遵循Lorentz型介电行为[33]。
2.3 交流导电与电抗性能
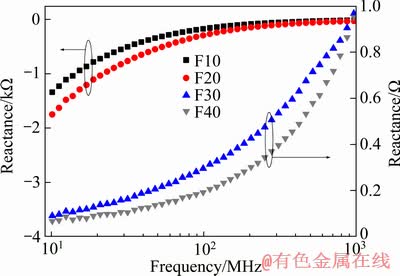
图6 Y2Ti2O7/Fe金属陶瓷的电抗和频率的关系
Fig. 6 Relationship between frequency and reactance of Y2Ti2O7/Fe cermet
图6所示为不同Fe含量的Y2Ti2O7/Fe金属陶瓷的电抗随频率的变化曲线。金属含量较低时,F10与F20的电抗值在整个测试频率范围内都为负,表明样品呈现出容抗性,在交变电场作用下,样品的电压相位滞后于电流的相位。试样的负电抗绝对值随着频率的增加而下降,逐渐趋向于0。当Fe含量较高时,F30和F40的电抗值在整个测试频率范围都为正,表现为感抗性,在交变电场中,样品中电流的相位滞后于电压的相位,并且正电抗值与频率大小呈正相关性。这种感抗性-容抗性的转变,与介电常数的逾渗现象类似,其逾渗阈值在Fe含量为20%~30%之间。
图7所示为不同Fe含量的Y2Ti2O7/Fe金属陶瓷的交流电导率随频率的变化曲线。低Fe含量的F10、F20试样在较低频段电导率很低,并随频率的增加而增加,试样的导电机制为电子跳跃电导[34]。当Fe含量超过逾渗值,F30、F40试样的交流电导率显著提高,在低于100 MHz频率的范围高出F10和F20试样约2个数量级,这是由于材料中形成了金属相网络。并且电导率随着频率的升高而降低,由于高频电场下电流集中在导体表面,即趋肤效应,频率升高使趋肤深度减小,小的导电面积产生高的电阻,进而导致电导率的降低。
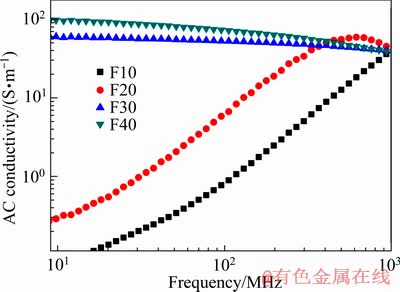
图7 Y2Ti2O7/Fe金属陶瓷的交流电导率随频率的变化
Fig. 7 Relationship between frequency and AC conductivity of Y2Ti2O7/Fe cermet
2.4 磁导率
图8所示为不同Fe含量的Y2Ti2O7/Fe金属陶瓷的磁谱。纯Y2Ti2O7的磁导率在整个频段保持较好的稳定性,数值稳定在1左右,基本不具备磁性。当Fe含量较少时,F10样品的磁导率也不随外加磁场频率的增加而发生明显变化,数值稳定在1.3左右,表现出一定的顺磁性。F20试样的磁谱具有频散现象,并且可以看出在Fe含量低于30%时,Y2Ti2O7/Fe金属陶瓷的磁导率与金属含量的多少呈正相关性,这显然与其中磁性相含量的增加相对应。当Fe含量继续升高,F30试样频散现象十分明显,磁导率开始敏感地依赖于外磁场频率,随着频率升高出现先降低再升高,在300 MHz左右取得极小值。
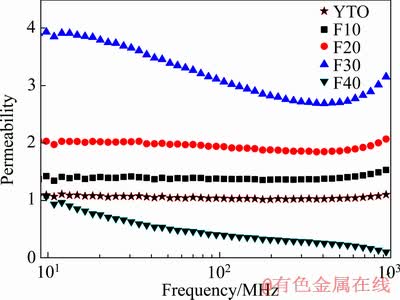
图8 Y2Ti2O7/Fe金属陶瓷的磁谱
Fig. 8 Relationship between frequency and permeability spectra of Y2Ti2O7/Fe cermet
F40的磁谱是典型的弛豫型,在整个测试频段中磁导率始终低于1,表现出抗磁性,并且其磁导率随着频率升高而不断下降,在1GHz时已经十分接近于0,并且降低的趋势没有减弱。可以推测若磁场频率大于1GHz一定值,F40试样磁导率有可能成为负值,从而实现双负性。这是由于F40试样中Fe含量较高,作为具有一定导电能力的磁性材料,在交变磁场的作用下会产生局域涡流以抵抗外磁场的变化,导致材料磁导率降低。
3 结论
1) 通过固相反应制备了纯相的Y2Ti2O7,并通过真空烧结制备了不同Fe含量(体积分数10%~40%)的Y2Ti2O7/Fe金属陶瓷。金属相与陶瓷相之间在烧结温度(1673 K)未发生反应。随Fe含量的增加,金属陶瓷的致密度提高。
2) Y2Ti2O7/Fe金属陶瓷介电常数的逾渗阈值在Fe 含量为20%~30%之间。在10 MHz~1 GHz的整个频段中,F30与F40试样均获得负介电常数,可能与材料内部形成有三维连通的金属相网络有关。
3) Y2Ti2O7/Fe金属陶瓷的交流导电和电抗性同样对组分比例非常敏感。电抗性能突变的逾渗值在Fe含量为20%~30%之间。在10 MHz~1 GHz的整个频段中,F10与F20试样呈容抗性,F30与F40试样呈感抗性。交流电导率随Fe含量增加而增加。
4) 纯Y2Ti2O7的磁导率在10 MHz~1 GHz的整个频段中均稳定在1左右,高频磁场下频散现象不明显。Fe含量低于40%时,随着Fe含量增加,试样的磁导率也增加,频散也逐渐明显。F40试样磁导率随着频率增加而持续降低,在1 GHz时趋于0。进一步提高测试频率,F40试样有可能获得负磁导率,实现双负性。
REFERENCES
[1] VESELAGO V G. The electrodynamics of substances with simultaneously negative values of ε and μ[J]. Soviet Physics Uspekhi, 1968, 10(4): 509-514.
[2] PENDRY J B, HOLDEN A J, STEWART W J, YOUNGS I. Extremely low frequency plasmons in metallic mesostructures[J]. Physical Review Letters, 1996, 76(25): 4773.
[3] SHELBY R A, SMITH D R, SCHULTZ S. Experimental verification of a negative index of refraction[J]. Science, 2001, 292(5514): 77-79.
[4] WILTSHIRE M C K, HAJNAL J V. Microstructured magnetic materials for RF flux guides in magnetic resonance imaging[J]. Science, 2001, 291(5505): 849-851.
[5] YEN T J, PADILLA W J, FANG N, VIER D C, SMITH D T, PENDRY J B, BASOV D N, ZHANG X. Terahertz magnetic response from artificial materials[J]. Science, 2004, 303(5663): 1494-1496.
[6] LINDEN S, ENKRICH C, WEGENER M, ZHOU J, KOSCHNY T, SOUKOULIS C M. Magnetic response of metamaterials at 100 terahertz[J]. Science, 2004, 306(5700): 1351-1353.
[7] SHI Z C, FAN R H, ZHANG Z D, QIAN L, GAO M, ZHANG M, ZHENG L T, ZHANG X H, YIN L W. Random composites of nickel networks supported by porous alumina toward double negative materials[J]. Advanced Materials, 2012, 24(17): 2349.
[8] SHI Z C, FAN R H, YAN K L, SUN K, ZHANG M, WANG C G, LIU X F, ZHANG X H. Preparation of iron networks hosted in porous alumina with tunable negative permittivity and permeability[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2013, 23(33): 4123-4132.
[9] SUN K, FAN R H, ZHANG Z D, YAN K L, ZHANG X H, XIE P T, YU M X, PAN S B. The tunable negative permittivity and negative permeability of percolative Fe/Al2O3 composites in radio frequency range[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2015, 106(17): 193104.
[10] SHI Z, FAN R, ZHANG Z, YAN K L, ZHANG X H, SUN K, LIU X F, WANG C G. Experimental realization of simultaneous negative permittivity and permeability in Ag/Y3Fe5O12 random composites[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2013, 1(8): 1633-1637.
[11] XIE P, SUN K, WANG Z, LIU Y, FAN R, ZHANG Z, SCHUMACHER G. Negative permittivity adjusted by SiO2-coated metallic particles in percolative composites[J]. Journal of Alloys & Compounds, 2017.
[12] YAN K L, FAN R H, SHI Z C, CHEN M, QIAN L, WEI Y L, SUN K, LI J. Negative permittivity behavior and magnetic performance of perovskite La1-xSrxMnO3 at high- frequency[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2014, 2(6): 1028-1033.
[13] SUN K, FAN R, YIN Y, GUO J, LI X, AN L, CHENG C. Tunable negative permittivity with fano-like resonance and magnetic property in percolative silver/yittrium iron garnet nanocomposites[J]. Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2017, 121(13).
[14] CHENG C, FAN R, REN Y, DING T, QIAN L, GUO J, LI X, AN L, LEI Y, YIN Y, GUO Z. Radio frequency negative permittivity in random carbon nanotubes/alumina nanocomposites[J]. Nanoscale, 2017, 9(18): 5779-5787.
[15] DING Jia-yu, XIAO Yuan, HAN Peng-de, ZHANGQi-tu. Effects of rare earth oxides on dielectric properties of Y2Ti2O7 series ceramics[J]. Journal of Rare Earths, 2010, 28(5): 765-768.
[16] NGUYEN S T, NAKAYAMA T, SUEMATSU H, SUZUKI H, SUZUKI T, NANKO M, CHO H B, HUYNH M T T, JIANG W, NIIHARA K. Synthesis of molten-metal corrosion resistant yttria-based refractory by hot-pressing and densification[J]. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2015, 35(9): 2651-2662.
[17] PAN W, PHILLPOT S R, WAN C, CHERNATYNSKIY A, Q Z. Low thermal conductivity oxides[J]. MRS Bulletin, 2012, 37(10): 917-922.
[18] MERKA O, BAHNEMANN P W, WARK P. Improved photocatalytic hydrogen production by structure optimized nonstoichiometric Y2Ti2O7[J]. Chemcatchem, 2012, 4(11): 1819-1827.
[19] GILL J K, PANDEY O P, SINGH K. Ionic conductivity, structural and thermal properties of Ca2+ doped Y2Ti2O7 pyrochlores for SOFC[J].international Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2012, 37(4): 3857-3864.
[20] CHEN Z, GONG W, CHEN T, LI S, WANG D, WANG Q. Preparation and upconversion luminescence of Er3+/Yb3+, codoped Y2Ti2O7, nanocrystals[J]. Materials Letters, 2012, 68(41): 137-139.
[21] 杨锦瑜, 罗 林, 刘雪颖, 苏玉长. Eu3+掺杂RE2Sn2O7 (RE=La,Gd,Y)纳米荧光材料的水热合成与发光性能[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2014, 24(4): 1036-1040.
YANG Jin-yu, LUO Lin, LIU Xue-yin, SU Yu-chang. Hydrothermal synthesis and optical properties of Eu3+ doped RE2Sn2O7 (RE=La,Gd, Y) nanophosphors[J]. Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2014, 24(4): 1036-1040.
[22] YANG Jin-yu, SU Yu-chang, LIU Xue-yin. Hydrothermal synthesis, characterization and optical properties of La2Sn2O7:Eu3+ micro-octahedra[J]. Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2011, 21(3): 535-543.
[23] JIANG Y, SMITH J R, ODETTE G R. Prediction of structural, electronic and elastic properties of YTiO and YTiO[J]. Acta Materialia, 2010, 58(5): 1536-1543.
[24] BARNARD L, ODETTE G R, SZLUFARSKA I, MORGAND. An AB initio study of Ti-Y-O nanocluster energetic in nanostructured ferritic alloys[J]. Acta Materialia, 2012, 60: 935-947.
[25] BARNARD L, CUNNINGHAM N, ODETTE G R, SZLUFARSKA I, MORGAN D. Thermodynamic and kinetic modeling of oxide precipitation in nanostructured ferritic alloys[J]. Acta Materialia, 2015, 91: 340-354.
[26] YANG L, JIANG Y, ODETTE G R, ZHOU W C, LIU Z, LIU Y. Nonstoichiometry and relative stabilities of Y2Ti2O7 polar surfaces[J]. Acta Materialia, 2013, 61: 7260-7270.
[27] 江 勇, 杨力通, 金亚楠, 周张健, 吕 铮. 纳米结构铁素体合金中氦捕获的第一性原理研究[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2015, 25(12): 3370-3380.
JIANG Yong, YANG Li-tong, JIN ya-nan, ZHOU Zhang-jian, LU Zheng. First principles study of helium trapping in nano-structured ferritic alloys[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2015, 25(12): 3370-3380.
[28] GAO M, SHI Z C, FAN R H, QIAN L, ZHANG Z D, GUO J Y. High-frequency negative permittivity from Fe/Al2O3 composites with high metal contents[J]. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2012, 95(1): 67-70.
[29] ZIOLKOWSKI R W, HEYMAN E. Wave propagation in media having negative permittivity and permeability[J]. Physical Review E Statistical Nonlinear & Soft Matter Physics, 2001, 64(5 Pt 2): 056625.
[30] ZIOLKOWSKI R W, KIPPLE A D. Causality and double-negative metamaterials[J]. Physical Review E Statistical Nonlinear & Soft Matter Physics, 2003, 68(2): 026615.
[31] ORDAL M A, BELL R J, ALEXANDER R W, LONG L L, QUERRY M R. Optical properties of fourteen metals in the infrared and far infrared: Al, Co, Cu, Au, Fe, Pb, Mo, Ni, Pd, Pt, Ag, Ti, V, and W[J]. Applied Optics, 1985, 24(24): 4493.
[32] CHENG C, FAN R, REN Y, DING T, QIAN L, GUO J, LI X, AN L, LEI Y, YIN Y, GUO Z. Radio frequency negative permittivity in random carbon nanotubes/alumina nanocomposites[J]. Nanoscale, 2017, 9(18): 5779-5787.
[33] XIE P, WANG Z, SUN K, CHENG C, LIU Y, FAN R. Regulation mechanism of negative permittivity in percolating composites via building blocks[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2017, 111(11): 112903.
[34] DYRE J C, SCHRODER T B. Universality of ac conduction in disordered solids[J]. Review of Modern Physics, 2000, 72(3): 873-892.
Fabrication and characterization of Y2Ti2O7/Fe cermets with tunable electromagnetic properties
LUO Si-jie1, 2, JIANG Yong1, 2, HE Cen1, 2, XIE Pei-tao3, FAN Run-hua3
(1. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. Key Laboratory of Nonferrous Metal Materials, Ministry of Education, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China
3. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Shan Dong University, Jinan 250061, China)
Abstract: Y2Ti2O7 powders and Y2Ti2O7/Fe cermets were fabricated by solid-state synthesis and vacuum sintering, respectively. XRD analysis suggests that the Y2Ti2O7 powders are single-phase, and the Y2Ti2O7/Fe cermets are chemically stable, with no interfacial reaction products between the ceramic phase and the metal phase. During the electromagnetic testing under the frequencies of 10 MHz-1 GHz, the percolation threshold of the Y2Ti2O7/Fe cermets is found within the iron content range of 20%-30% (volume fraction). Under the percolation threshold, the permittivity, AC conductivity, and permeability all increase with the iron content. When the iron content is beyond 30%, the reactance and the AC conductivity change greatly, leading to a negative permittivity within the entire frequency range. For the iron content at 40%, the cermet exhibits a low permeability of less than 1, which decreases consistently with the increasing frequency. This should be attributed to the percolation induced diamagnetism as the result of the formation of conducting networks inside the cermet. Negative permeability can be further expected at the frequencies beyond 1 GHz.
Key words: Y2Ti2O7; cermet; permittivity; permeability
Foundation item: Project(2018YFE0306100) support by the National MCF Energy R&D Program of China; Project (51471189) support by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Received date: 2017-08-24; Accepted date: 2017-11-14
Corresponding author: JIANG Yong; Tel: +86-731-88836320; E-mail: yjiang@csu.edu.cn;
FAN Run-hua; Tel: +86-531-88393396; E-mail: fan@sdu.edu.cn
(编辑 王 超)
基金项目:国家磁约束核聚变能发展研究专项(2018YFE0306100);国家自然科学基金面上项目(51471189)
收稿日期:2017-08-24;修订日期:2017-11-14
通信作者:江 勇,教授,博士;电话:0731-88836320;E-mail:yjiang@csu.edu.cn;
范润华,教授,博士;电话:0531-88393396;E-mail:fan@sdu.edu.cn