文章编号:1004-0609(2014)08-2065-08
TLM合金在含蛋白质模拟体液中的腐蚀行为
黄伟九,刘成龙,余永梅,谢 霖
(重庆理工大学 材料科学与工程学院,重庆 400050)
摘 要:采用开路腐蚀电位、动态极化曲线、电化学交流阻抗谱、扫描电镜等研究TLM合金在含白蛋白或免疫球蛋白G的PBS溶液(pH=7.4)中的腐蚀行为。结果表明:在PBS溶液中,该合金具有良好的耐腐蚀性能,合金的腐蚀以点蚀为主;随浸泡时间的延长合金的腐蚀速率降低。两种蛋白质的单独或共同加入均可抑制TLM合金在PBS溶液中的腐蚀,其中吸附白蛋白主要通过抑制腐蚀性离子的侵入来实现,而吸附免疫球蛋白G主要通过提高合金表面氧化膜的电阻来实现;在两种蛋白质的共同作用下,合金腐蚀的抑制效果增强。EIS测试结果表明TLM合金表面的氧化膜可分为内层致密层和外层疏松层。
关键词:钛合金;免疫球蛋白;白蛋白;腐蚀
中图分类号:TG17 文献标志码:A
Corrosion behavior of TLM alloy in simulated body fluid containing proteins
HUANG Wei-jiu, LIU Cheng-long, YU Yong-mei, XIE Lin
(School of Materials Science and Engineering, Chongqing University of Technology, Chongqing 400050, China)
Abstract: The corrosion behavior of TLM alloy was investigated by open circuit potential, potentiodynamic polarization, electrochemical impedance spectra and scanning electronic microscope in phosphate buffer saline (PBS) solution (pH=7.4) containing albumin or immunoglobulin G (IgG). The results show that the alloy possesses excellent corrosion resistance to the PBS solution, and mainly suffers pitting corrosion attack. The corrosion rate decreases with increasing the immersion period in PBS solution. Single or combined addition of two kinds of protein can both inhibit the corrosion of the alloy, which is attributed to the blocking effect on the penetration of aggressive ions for albumin, but for IgG which is achieved through the improvement of the resistance of TLM alloy surface oxide film. When two kinds of protein are used together, the inhibitive effect is greater than that by single addition of albumin or IgG. The EIS results indicate that the passive film consists of an inner barrier and an out porous layer.
Key words: titanium alloy; immunoglobulin; albumin; corrosion
20世纪中期,具有良好生相容性、综合生物力学性能的钛及钛合金开始被应用于人工骨、整形外科、心脏外科等医学领域。在临床使用过程中,被广泛使用的纯钛与Ti-6Al-4V存在力学相容性、植入物表面生物活性、耐磨性、耐蚀性等问题[1]。由此先后出现以Ti-5Al-2.5Fe与Ti-6Al-7Nb为代表的第二代α+β型钛合金以及具有更好相容性和更低弹性模量的第三代β型钛合金,如Ti-12Mo-6Zr-2Fe、Ti-14Nb-13Zr、Ti-35Nb-5Ta-7Zr和Ti-25Nb-3Zr-2Sn-3Mo等[2-4]。
用于替代人体组织或器官的金属材料植入人体时,材料表面最先与机体内的血液和组织液接触。植入数秒后,继水和无机盐离子吸附后,蛋白质会通过分子传递、吸附、重排、交换、解吸等步骤竞相吸附在材料表面,形成一层厚度为20~100 nm的蛋白质吸附层。该蛋白质吸附层不但会影响金属表面的凝血、细胞及细菌黏附作用,而且会显著金属材料与植入环境间的界面反应[5-8]。钛及钛合金表面易形成一层厚度为几纳米~几十纳米的氧化膜,其植入物与组织间的界面作用主要与该氧化膜层相关。在生理环境(pH 7.2~7.4)中,钛及钛合金的表层氧化膜带负电荷,而蛋白质分子的等电点一般低于生理环境的pH值,呈现负电性[9]。当植入物与机体的体液或血液接触时,在静电作用下Ca2+离子首先吸附到材料表面使其带正电,从而再吸附表面暴露酸性基团的蛋白质分子。此外,体液中的Mg2+也会起到一定的介导作用[10-11]。目前,对影响钛及钛合金腐蚀行为的蛋白质研究较为关注的是白蛋白(Albumin, Ab)、纤维蛋白原(Fibrinogen, Fb)和球蛋白。已有研究发现,蛋白质对纯钛及钛合金腐蚀行为的影响大致可分为3类:没有影响,促进或降低腐蚀速率。其影响效果主要与其表面的氧化膜状态与生理环境存在直接的关系[12]。
本文作者以新开发的人工关节用近β型TLM合金为研究对象,研究其在含有免疫球蛋白G或牛血清白蛋白的PBS溶液中的腐蚀行为,从而得到上述两种有机成分对其腐蚀行为的影响规律,为其临床应用提供实验与理论依据。
1 实验
1.1 材料及腐蚀试样的制备
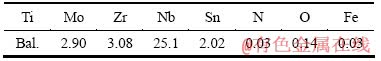
实验中所选用的材料为医用TLM钛合金,由西北有色金属研究院提供。其化学成分如表1所列。
表1 实验用TLM钛合金的化学成分
Table 1 Chemical composition of TLM alloy (mass fraction, %)
首先,将钛合金板材加工成33 mm×23 mm×4.5 mm的长方体,然后依次用280~1200号金相砂纸逐级打磨,随后分别用丙酮、酒精、二次蒸馏水进行超声清洗10 min,冷风吹干后置于干燥器中待用。
1.2 实验过程及方法
实验中选用的模拟体液为PBS溶液(pH 7.4),配方如下:NaCl(8.0 g/L),KCl(0.2 g/L),Na2HPO4(1.15 g/L),KH2PO4(0.2 g/L),采用HCl和NaOH溶液调节缓冲液pH至7.4。实验过程中PBS溶液温度为(37±0.5) ℃。
牛血清白蛋白(Bovine serum albumin, BSA)与免疫球蛋白G(Immunoglobulin G, IgG)购自Sigma公司。考虑人血浆蛋白中白蛋白(38~48 g/L)与纤维蛋白原(2~4 g/L)的浓度,选择一中间浓度值配置含蛋白的测试溶液。将冻干的IgG粉末溶于PBS缓冲溶液中,浓度为2.5 g/L,简称PBS+IgG溶液;将冻干的BSA粉末缓慢溶解于PBS缓冲溶液中,浓度为10 g/L,简称PBS+BSA溶液;将BSA与IgG粉末先后溶解于PBS缓冲溶液中,两者浓度分别为10 和2.5 g/L,简称PBS+BSA+IgG溶液。
电化学腐蚀实验采用三电极体系,饱和甘汞电极(SCE)为参比电极,Pt片为辅助电极,工作电极为测试试样,测试面积为1 cm×1 cm。分别对浸泡期间的开路腐蚀电位、动态极化曲线与电化学交流阻抗谱进行测量。测量动态极化曲线时,将待测试样进入实验介质中,分别稳定不同时间(1,6,24,48和72 h)后,进行极化测试。电位扫描速度为1 mV/s。电化学交流阻抗谱(Electrochemical impedance spectra, EIS)的测量所用正弦激励信号幅值为10 mV,测试电位为工作电极的开路腐蚀电位(OCP),频率范围100 kHz~10 mHz,数据分析软件为ZView2。
采用配有能谱仪的电子扫描显微镜(JSM-6460LV)对腐蚀后的试样表面进行腐蚀形貌观察与微区成分分析。
2 实验结果
2.1 开路腐蚀电位
TLM合金浸入4种测试溶液中不同时间后的开路腐蚀电位(Open circuit potential, OCP)变化规律如图1所示。在PBS溶液中,合金的OCP值首先向正电位方向移动,然后向负电位方向移动,浸泡时间超过24 h后,OCP值逐渐稳定在-0.15 V (vs SCE)左右。在PBS+ BSA溶液中,几乎在任一时间点,合金的OCP值明显比其在PBS溶液中的电位值要负。但电位值变化较小,浸泡时间超过1 h后,该值基本稳定在-0.37 V左右。在PBS+IgG溶液中,合金的OCP值先向正方向移动,后负移。浸泡6 h后,该值基本稳定在-0.23 V左右。与单独加入IgG或BSA相比,在含有IgG (2.5 g/L)与BSA(10 g/L)的PBS溶液中,浸泡1 h后,TLM合金的OCP值就比其在PBS溶液中的电位值要正,浸泡时间达到24 h时,该值约为-0.03 V。开路腐蚀电位的高低表明材料腐蚀的倾向性大小,该电位值越负,材料越容易发生腐蚀[13]。可见,牛血清白蛋白的加入可导致TLM合金在PBS溶液中的腐蚀倾向性增大。而免疫球蛋白G的影响作用与合金在溶液中的浸泡时间相关,浸泡超过6 h,合金在PBS溶液中的腐蚀倾向性变小。而当两种蛋白质共同作用时,合金在PBS溶液中的溶解被显著抑制。
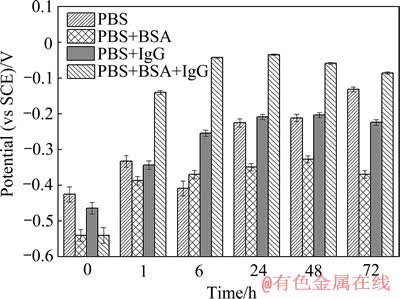
图1 TLM合金在PBS溶液、含IgG及BSA的PBS溶液中分别浸泡不同时间后的开路腐蚀电位变化
Fig. 1 Variations of open circuit potential of TLM alloy in PBS simulated solution with and without IgG or BSA after immersion
2.2 电化学交流阻抗谱
当金属材料植入人体后,首先发生水和无机盐离子在材料表面的吸附,然后是蛋白质的吸附。蛋白质吸附层会显著改变植入金属材料表面钝化膜的形成行为,影响其腐蚀行为[12]。为了进一步获得TLM合金浸泡过程中表面钝化膜的生长与溶解信息,进行了EIS测量,获得的Bode图如图2所示。
从实验获得的TLM合金在4种测试溶液中的EIS可知,其Nyquist图都由两个容抗弧构成:直径较小的中高频区容抗弧与直径较大的低频区容抗弧。随着浸泡时间的延长,低频区容抗弧直径明显改变。VASILESCU等[14]认为钛合金在模拟体液中EIS中低频区容抗弧直径的变化缘于表面钝化膜的变化。从图2的Bode图可知,存在两个时间常数。PAN等[15]认为该类结果可以利用两层氧化膜结构来模拟,内层致密层与外层疏松。在PBS中,使用Rs(QpRp)(QbRb)进行拟合,其中Rs表示测试溶液电阻,Rb表示表面致密氧化膜层电阻,Qb表示致密氧化膜层与溶液之间形成的电双层常相位角元件,Rp表示表面疏松氧化膜层电阻,Qp表示疏松氧化膜层与溶液之间形成的电双层常相位角元件;而在含有BSA与IgG的PBS溶液中,Bode图中的相位角出现明显变化,中频区的相位角明显较图2(a)中的要大,而在高频区的相位角较图2(a)中的要小。图3所示为TLM合金在不同测试溶液中浸泡72 h后的EIS测量结果对比图。在含有蛋白质的溶液中,使用Rs(QpRp)(CbRb)进行拟合。其中,Cb表示致密氧化膜层与溶液之间形成的电双层电容。利用相应的等效电路对获得的EIS结果进行拟合,实验拟合误差控制在10%以内,拟合结果见表2~5。
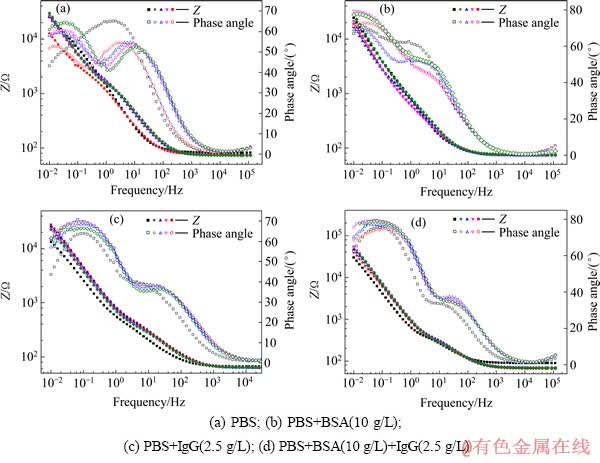
图2 TLM合金在4种测试溶液中浸泡不同时间后的Bode图
Fig. 2 Effect of immersion period on Bode spectra of TLM alloy in four types of test solution
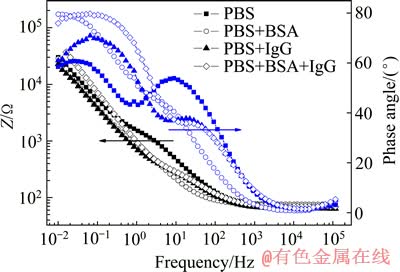
图3 TLM合金在4种测试溶液中浸泡72 h后的Bode图
Fig. 3 Bode spectra of TLM alloy in four types of test solution after 72 h immersion
从拟合结果可知,牛血清白蛋白的加入对PBS溶液电阻的影响不大,而免疫球蛋白G则明显导致溶液电阻的降低。此外,与TLM合金在PBS溶液中的实验结果相比,牛血清白蛋白的加入明显导致合金内层氧化膜电阻降低,而免疫球蛋白G的影响则与之相反。可见,牛血清白蛋白与免疫球蛋白G在PBS溶液中的存在的确会导致合金表面氧化膜的变化。
表2 在PBS溶液中浸泡不同时间后TLM合金的电化学交流阻抗谱拟合数据
Table 2 Fitting parameters of TLM alloy after immersion in PBS solution for different times by equivalent circuit (EC) from EIS data
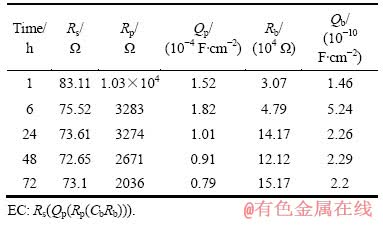
表3 在PBS+BSA溶液中浸泡不同时间后TLM合金的电化学交流阻抗谱拟合数据
Table 3 Fitting parameters of TLM alloy after immersion in PBS+BSA solution for different times by equivalent circuit (EC) from EIS data
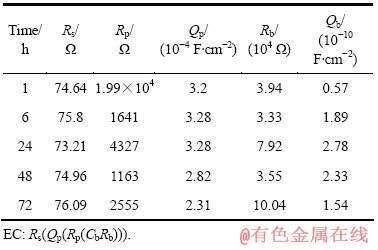
表4 在PBS+IgG溶液中浸泡不同时间后TLM合金的电化学交流阻抗谱拟合数据
Table 4 Fitting parameters of TLM alloy after immersion in PBS+IgG solution for different times by equivalent circuit (EC) from EIS data
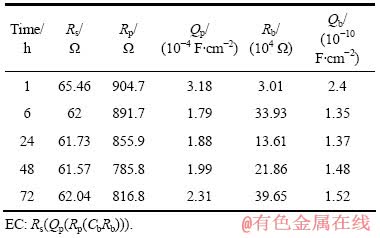
表5 在PBS+BSA+IgG溶液中浸泡不同时间后TLM合金的电化学交流阻抗谱拟合数据
Table 5 Fitting parameters of TLM alloy after immersion in PBS+BSA+IgG solution for different times by equivalent circuit (EC) from EIS data
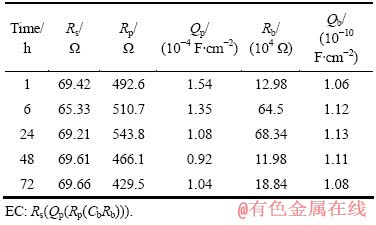
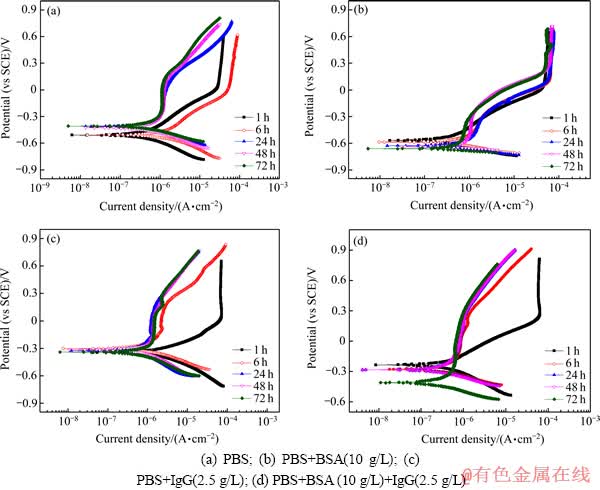
图4 TLM合金在4种测试溶液中的动态极化曲线
Fig. 4 Potentiodynamic polarization curves for TLM alloy in four types of test solution
图4所示为TLM合金在不同测试溶液中测得的动态极化曲线。图5所示为TLM合金在不同测试溶液中浸泡72 h后的动态极化曲线对比图。利用Tafel外推法,获得其腐蚀电流密度,如表6所列。由图4可知,虽然合金在4种测试溶液中都出现明显的活化-钝化行为,但存在明显的区别。在PBS溶液中浸泡24 h后,合金从阳极活化进入钝化的时间明显缩短,在腐蚀电位约为-0.3 V (vs SCE)时由活化转变为钝化状态,而浸泡1 h和6 h后,在腐蚀电位超过0.02 V时才由活化转变为钝化。在PBS+BSA溶液中浸泡6 h后,腐蚀电位达到-0.6 V时,合金的腐蚀电流密度随着腐蚀电位的升高而维持不变,出现第一次钝化。第一次钝化的电流密度随着浸泡时间的延长而降低;当腐蚀电位达到-0.3 V左右时,电流密度随着电位的增大而增加;当电位达到0.3 V左右时,合金进入第二次钝化,钝化电流密度约为6.0×10-7 A/cm2。在PBS+IgG、PBS+BSA+IgG溶液中,浸泡6 h后的第一次钝化区间则比其在PBS+BSA溶液中的要宽,在PBS+IgG溶液中,第一次钝化区间约为-0.2~0.2 V,钝化电流密度约为1.0×10-6 A/cm2,而在PBS+BSA+ IgG溶液中,第一次钝化区间约为-0.2~0.3 V,钝化电流密度约为8.0×10-7 A/cm2。
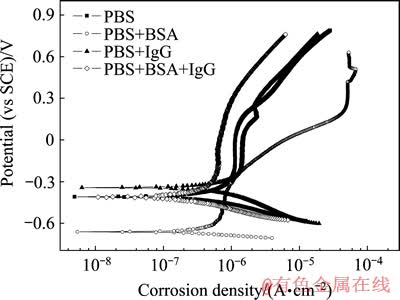
图5 TLM合金在4种测试溶液中浸泡72 h后的动态极化曲线
Fig. 5 Potentiodynamic polarization curves for TLM alloy in four types of test solution after 72 h immersion
表6 TLM合金在4种测试溶液中浸泡不同时间后的腐蚀电流密度变化
Table 6 Variations of corrosion current density of TLM alloy in four types of test solution after different immersion periods
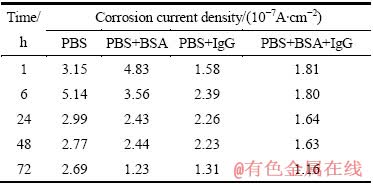
图6所示为TLM合金在PBS+BSA溶液中动态极化后的腐蚀表面形貌,腐蚀后的TLM表面发生孔蚀现象,腐蚀迹象多出现在加工后留下的表面缺陷位置,在其他溶液中获得的腐蚀形貌与其类似。通过能谱仪分析发现,发生孔蚀的位置无Nb元素存在或微量。
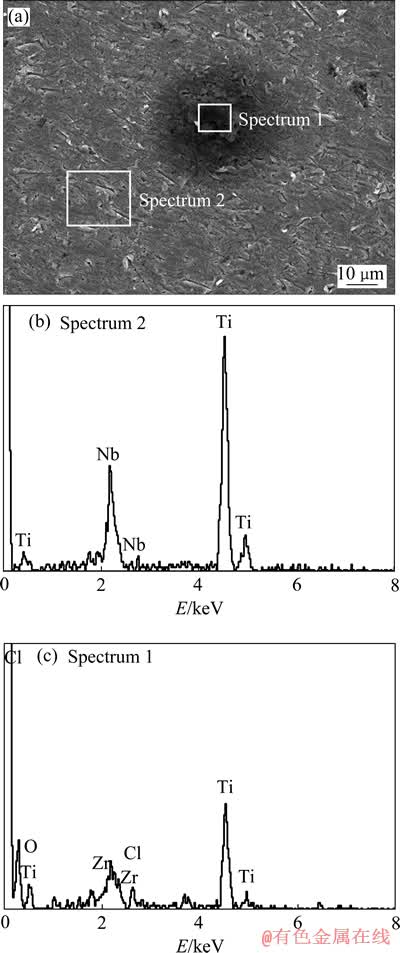
图6 动态极化测试后TLM合金的表面腐蚀形貌及相应区域EDS谱
Fig. 6 Corroded morphology of TLM alloy after potentiodynamic polarization test and EDS patterns of corresponding patterns of zones shown in (a)
3 讨论
开路腐蚀电位、EIS及动态极化曲线的测试结果都表明,白蛋白与免疫球蛋白G的确会影响TLM合金在PBS溶液中的腐蚀行为。
3.1 白蛋白对TLM合金腐蚀行为的影响
PETERS[16],HODGSON等[17],CONTU等[18]曾研究了白蛋白在纯钛表面的吸附,发现白蛋白分子吸附到纯钛表面后会变为扁平状,覆盖完整的白蛋白吸附层会抑制腐蚀性离子从溶液到金属表面的迁移或氧的扩散。
从开路腐蚀电位的测量结果(见图1)可知,在任一浸泡时间点,TLM合金在含有牛血清白蛋白的PBS溶液中的OCP值明显比其在PBS溶液中的要负。在PBS+BSA溶液中浸泡1 h后,该值基本稳定在-0.37 V左右,而在PBS溶液中浸泡时间超过24 h后,OCP值逐渐稳定在-0.15 V左右,两者相差约0.22 V。从TLM合金在上述两种溶液中的EIS测量结果(见表2)可知,Rb表示表面致密氧化膜层电阻,Rp表示表面疏松氧化膜层电阻,两者之和表征钝化膜的电阻。在PBS+BSA溶液中,(Rb+Rp)值明显小于TLM合金在PBS溶液中的测得值。此外,动态极化曲线测量结果表明浸泡时间超过24 h后,合金阳极活化向钝化的转化速度加快。合金在PBS溶液中浸泡24 h后,第一次钝化电流密度大约在1.3×10-6 A/cm2,而在PBS+BSA溶液中浸泡24~72 h后,第一次钝化电流密度约从1.4×10-6 A/cm2逐渐降低到7.3×10-7 A/cm2,其腐蚀电流密度也略有降低。可见,白蛋白能够在一定程度上抑制TLM合金在PBS溶液中的腐蚀。如果仅从合金表面氧化膜的电阻变化来看,动态极化曲线与OCP、EIS的测量结果是相矛盾的。但是,CONTU等[18]和TAKEMOTO等[19]认为白蛋白在钛及钛合金表面的吸附是动态的,随着浸泡时间的延长,白蛋白分子在材料表面的吸附覆盖率会逐渐提高,从而有效抑制腐蚀性离子的侵入,阻碍材料的腐蚀。从表2中Qp的变化可知,在PBS+BSA溶液中,该值逐渐降低,这表明氧化膜表面吸附的白蛋白分子吸附层逐渐变得致密[19-20],从而降低氧原子的扩散或腐蚀产物扩散至溶液中的速率,导致TLM合金在该溶液中腐蚀速率的下降。此外,开路腐蚀电位反映了材料的热力学特性和电极的表面状态,该值的变化可归因于氧还原反应或材料的阳极溶解,当其随时间的变化趋于“正”,常常表示保护膜增强了,可能缘于溶液中氧的作用或腐蚀产物组成了新的保护膜[13]。开路腐蚀电位变负与TLM合金表面内层氧化膜电阻的降低可能源于白蛋白分子与TLM合金表面氧化膜之间形成的螯合作用与阻挡效应的联合作用。螯合作用会导致在开路状态下合金氧化膜的溶液,而阻挡效应会降低氧原子或离子的迁移与电荷的传输,从而抑制内层氧化膜的生长[18, 21]。
3.2 免疫球蛋白G对TLM合金腐蚀行为的影响
JANSSON等[20]研究发现免疫球蛋白非常容易吸附在亲水性的多孔纯钛表面,其吸附量随着浸泡时间的延长与蛋白浓度的提高而增大。蛋白分子主要通过钛及钛合金表面的Ti—OH键来实现吸附[22]。
TLM合金在PBS+IgG溶液中浸泡1 h时,其OCP值比其在PBS溶液中的值负,但是随着浸泡时间的延长,其OCP值逐渐变正,这表明浸泡时间的延长有助于增强合金表面氧化膜层抑制腐蚀的作用。从EIS测量结果(见表4)可知,当浸泡时间6 h后,合金在PBS+IgG溶液中的(Rb+Rp)值明显高于其在PBS溶液中浸泡相同时间的值。其中,Rp随着浸泡时间的增加而逐渐降低,但变化的幅度不大;与之相比,Rb值的增加较为显著,在浸泡1 h时仅为3.01×104 Ω,而浸泡72 h后,Rb值达到3.96×105 Ω,提高了一个数量级,这表明免疫球蛋白G吸附层有利于结合自由氧离子,促进TLM合金表面氧化膜的生长[23]。氧化膜的生长有利于降低材料的腐蚀速率,这一点从动态极化曲线的测试结果得到进一步证明。表6中的数据表明TLM合金在PBS+IgG溶液中的腐蚀电流密度随着浸泡时间的增加而逐渐降低。与白蛋白相比,免疫球蛋白G主要通过促进氧化膜的生长来提高TLM合金在PBS溶液中的腐蚀抵抗力。
3.3 白蛋白与免疫球蛋白G联合作用对TLM合金腐蚀行为的影响
根据合金在含有白蛋白与免疫球蛋白G的PBS溶液中的开路腐蚀电位变化可知,两种蛋白质的联合作用可更加有效地降低TLM合金的腐蚀倾向性,尤其在浸泡24 h时,开路腐蚀电位为-0.03 V左右。EIS测试结果也证实了在两种吸附蛋白质的共同作用下,TLM表面内层氧化膜的电阻显著增大,在浸泡24 h时,该值可达到6.83×105 Ω,比TLM合金在PBS中浸泡24 h时的内层氧化膜电阻约提高一个数量级。腐蚀电流密度的变化也进一步证明两种蛋白质的共同吸附更有利于降低TLM在PBS溶液中的腐蚀速率。
综合白蛋白或免疫球蛋白G单独对TLM合金腐蚀行为的影响,白蛋白的吸附不利于TLM合金内层氧化膜的生长,但对外层疏松氧化膜的电阻影响不大;与之相比,免疫球蛋白G的吸附有利于TLM合金内层氧化膜的生长,但会明显导致外层疏松氧化膜电阻的下降。对抑制合金腐蚀的作用而言,在相同的浸泡时间内,TLM合金在两种测试溶液中的腐蚀电流密度相差不大,在PBS+IgG溶液中的腐蚀电流密度略低一些。这可能缘于两种蛋白质的不同结构,白蛋白分子的横径尺寸约为56 nm2,在吸附到材料表面后可形成致密的球形结构[23],而免疫球蛋白G的横径尺寸约为140 nm2,免疫球蛋白分子的结构域具有典型的三维结构[24]。因此,较为致密的白蛋白吸附层更有利于抑制合金与溶液间的氧原子或离子迁移,从而抑制合金表面氧化膜的生长,但由于白蛋白分子与钛离子间的螯合作用导致其腐蚀电流密度较高;相反,较为疏松的免疫球蛋白G吸附层有利于合金与溶液间的氧原子或离子迁移,促进合金表面氧化膜的生长,从而降低合金的腐蚀电流密度。两者相比,免疫球蛋白G对TLM合金的腐蚀行为影响作用更大。综合比较,TLM合金在上述4种测试溶液中都具有较优的耐腐蚀性能。
4 结论
1) TLM合金在PBS模拟体液中具有良好的耐腐蚀性能,腐蚀以点蚀为主。合金的钝化膜电阻随浸泡时间的延长而增大,浸泡24 h后,开路腐蚀电位稳定在-0.15 V左右,腐蚀电流密度稳定在2.8×10-7 A/cm2左右。
2) 白蛋白与免疫球蛋白G的单独加入都可抑制TLM合金在PBS溶液中的腐蚀,其中白蛋白主要通过抑制腐蚀性离子的侵入来实现,而免疫球蛋白G主要通过提高TLM合金表面氧化膜的电阻来实现。两者共同作用抑制TLM合金腐蚀的效果更强。
3) EIS测试结果表明TLM合金表面的氧化层可分为两层:内层致密层和外层疏松层。白蛋白在TLM合金表面的吸附可抑制其内层致密氧化层的生长,而免疫球蛋白G在TLM合金表面的吸附可促进其内层致密氧化层的生长。
REFERENCES
[1] 李世普. 生物医用材料导论[M]. 武汉: 武汉工业大学出版社, 2000: 52-55.
LI Shi-pu. Introduction of biomedical materials[M]. Wuhan: Wuhan University of Technology Press, 2000: 52-55.
[2] 李 军, 李佐臣, 陈杜娟. 新型外科植入用钛合金的生物相容性[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2010, 20(4): 756-764.
LI Jun, LI Zuo-chen, CHEN Du-juan. Biocompatibility of new titanium ally TZNT for surgical implant application[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2010, 20(4): 756-764.
[3] 王本力, 李 莉, 郑玉峰. 生物医用Ti-Nb基合金的显微组织与耐磨性[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2010, 20(S1): s953-s957.
WANG Ben-li, LI Li, ZHENG Yu-feng. Microstructure and wear behavior of biomedical Ti-Nb based alloys[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2010, 20(S1): s953-s957.
[4] 马秀梅, 孙 威, 杨永建. 生物医用Ti-Nb-(Ta)-Zr合金的微观结构与性能[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2010, 20(6): 1195-1202.
MA Xiu-mei, SUN Wei, YANG Yong-jian. Microstructure and properties of biomedical Ti-Nb-(Ta)-Zr alloys[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2010, 20(6): 1195-1202.
[5] MUDALI U K, SRIDHAR T M, RAJ B. Corrosion of bio implants[J]. Sadhana, 2003, 28(3/4): 601-637.
[6] 严洪海, 赵士芳, 陈关福. 金属生物材料表面的蛋白吸附的研究方法[J]. 中国口腔种植学杂志, 1998, 3(2): 89-92.
YAN Hong-hai, ZHAO Shi-fang, CHEN Guan-fu. Research methods for protein absorption on the surface of biomedical metal materials[J]. Chinese Journal of Oral Implantology, 1998, 3(2): 89-92.
[7] ROACH P, EGLIN D, ROHDE K, PERRY C C. Modern biomaterials: A review—bulk properties and implications of surface modifications[J]. Journal of Material Science: Materials in Medicine, 2007, 18: 1263-1277.
[8] 李 艺, 程镕时. 蛋白质在固体表面吸附的研究进展[J]. 高分子通报, 2007, 24(2): 41-49.
LI Yi, CHENG Rong-shi. Development of studying for protein adsorption on the solid surface[J]. Chinese Polymer Bulletin, 2007, 24(2): 41-49.
[9] NORDE W, LYKLEMA J. Why proteins prefer interfaces[J]. Journal of Biomaterials Science: Polymer Edition, 1991, 2(3): 183-202.
[10] WILLAMS R L, WILLAMS D F. Albumin adsorption on metal surface[J]. Biomaterials, 1988, 9: 206-212.
[11] KLINGER A, STEINBERG D, KOHAVI D, SELA M N. Mechanism of adsorption of human albumin to titanium in vitro[J]. Journal of Biomedical Material Research, 1997, 36: 387-392.
[12] 刘成龙, 王 猛, 张春艳. 蛋白质作用下医用金属材料的腐蚀行为研究进展[J]. 中国腐蚀与防护学报, 2011, 31(1): 10-17.
LIU Cheng-long, WANG Meng, ZHANG Chun-yan. Progress in corrosion behavior investigation of biomedical metallic materials influenced by proteins[J]. Journal of Chinese Society of Corrosion and Protection, 2011, 31(1): 10-17.
[13] 宋诗哲. 腐蚀电化学研究方法[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 1988: 90-95.
SONG Shi-zhe. Electrochemical corrosion test methods[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 1988: 90-95.
[14] VASILESCU C, DROB S I, NEACSU E I. Surface analysis and corrosion resistance of a new titanium base alloy in simulated body fluids[J]. Corrosion Science, 2012, 65: 431-440.
[15] PAN J, THIERRY D, LEYGRAF C. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy study of the passive oxide film on titanium for implant application[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 1996, 41: 1143.
[16] PETERS T. All about albumin: Biochemistry, genetics and medical applications[M]. New York: Academic Press, 1996: 26-38, 258-260.
[17] HODGSON A W E, MUELLER Y, FORSTER D, VIRTANEN S. Electrochemical characterization of passive films on Ti alloys under simulated biological conditions[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2002, 47: 1913-1923.
[18] CONTU F, ELSENER B, BOHNI H. Characterization of implant materials in fetal bovine serum and sodium sulfate by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Ⅰ. Mechanically polished samples[J]. Journal of Biomedical Material Research, 2002, 62: 412-421.
[19] TAKEMOTO S, HATTORI M, YOSHINARI M, KAWADA E, ODA Y. Corrosion behavior and surface characterization of titanium in solution containing fluoride and albumin[J]. Biomaterials, 2005, 26: 829-837.
[20] JANSSON E, TENGVALL P. Adsorption of albumin and IgG to porous and smooth titanium[J]. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 2004, 35: 45-51.
[21] CHENG X L, ROSCOE S G. Corrosion behavior of titanium in the presence of calcium phosphate and serum proteins[J]. Biomaterials, 2005, 26: 7350-7356.
[22] FABIANA Y O, OSVALDO R C, LUCIA B A. Adsorption of human serum albumin on electrochemical titanium dioxide electrodes: Protein-oxide surface interaction effects studied by electrochemical techniques[J]. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 2009, 633: 19-34.
[23] BROWNE M, GREGSON P J, WEST R H. Characterization of titanium alloy implant surfaces with improved dissolution resistance[J]. Journal of Material Science: Materials in Medicine, 1996, 7: 323-329.
[24] SILVERTON E W, NAVIA M A, DAVIES D R. Three- dimensional structure of an intact human immunoglobulin[C]// Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 1977, 74(11): 5140-5144.
(编辑 龙怀中)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(50405005, 31000430);留学回国人员科研启动基金资助项目(2012-940);重庆市科技攻关计划资助项目(cstc201299-yyjs10040)
收稿日期:2013-07-20;修订日期:2013-09-10
通信作者:黄伟九,教授,博士;电话:023-62563089;E-mail: huangweijiu@cqut.edu.cn