DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2017.02.007
2E12铝合金均匀化过程微观组织演变规律
陈宇强1,潘素平2,易丹青3,刘文辉1, 4,蔡志华1,唐昌平1, 4
(1. 湖南科技大学 难加工材料高效精密加工湖南省重点实验室,湖南 湘潭,411201;
2. 中南大学 高等研究中心,湖南 长沙,410083;
3. 中南大学 材料学科与工程学院,湖南 长沙,410083;
4. 湖南科技大学 高温耐磨材料及制备技术湖南省国防技术重点实验室,湖南 湘潭,411201)
摘要:采用SEM,EPMA,TEM和硬度测试等技术,研究2E12铝合金铸锭在均匀化过程中的非平衡相溶解、元素分布特征以及第二相析出行为。研究结果表明:合金铸锭的晶界处连续分布着粗大的α+θ+S共晶组织。合金中的Cu和Mg元素存在明显的偏析,而Mn元素分布较为均匀。随着均匀化处理的进行,合金中的粗大共晶组织逐渐溶解,Cu,Mg和Si元素逐步溶入合金基体,而Fe和Mn元素则从合金基体中脱溶。在均匀化处理过程中,合金基体中析出大量T相粒子。伴随着T相的析出,合金的硬度逐渐升高,同时电导率也明显增加。当合金于490 ℃均匀化1 000 h后,晶界附近出现明显的PFZ。
关键词: 2E12铝合金;均匀化;T相
中图分类号:TG146.2 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2017)02-0316-09
Microstructure evolutions of 2E12 Al alloy during homogenization
CHEN Yuqiang1, PAN Suping2, YI Danqing3, LIU Wenhui1, 4, CAI Zhihua1, 4, TANG Changping1, 4
(1. Hunan Provincial Key Laboratory of High Efficiency and Precision Machining of Difficult-to-cut Material,
Hunan University of Science and Technology, Xiangtan 411201, China;
2. Advanced Research Center, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
3. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
4. Key Laboratory of High Temperature Wear Resistant Materials Preparation Technology of
Hunan Province, Xiangtan 411201, China)
Abstract: The dissolution of non-equilibrium phase, element distribution characteristics and the second phase precipitation of 2E12 alloy ingot during homogenization were investigated by using scanning electron microscopy(SEM), electron probe micro-analyzing (EPMA), transmission electron microscopy(TEM) and hardness testing. The result shows that coarse ternary α + θ + S eutectics continuously distribute along grain boundaries (GBs) of as-cast alloy. Serious segregations of Cu and Mg elements exist in the cast ingot, Mn element is found to be uniformly distributed. As homogenization proceeds, the ternary eutectics gradually dissolve and Cu, Mg atoms dissolve in Al matrix, while Mn and Fe atoms precipitate. During homogenization, large quantities of T phase precipitate from the matrix, meanwhile micro-hardness and conductivity of alloy increase obviously. After being homogenizated at 490 ℃ for 1 000 h, a wide precipitate-free zone (PFZ) forms near GB.
Key words: 2E12 Al alloy; homogenization; T phase
由于经济性和安全性的原因,大型飞机需采用大尺寸的结构件以减少铆接和焊接带来的重量增加和强度损失[1]。然而,作为最重要的航空结构材料,大型铝材的生产一直是目前制约国内大飞机发展的重要瓶颈。2E12铝合金是在美国2524合金基础上通过成分优化和工艺改进自主研发的一种新型国产航空铝合金[2]。其具有优良的断裂韧性、卓越的抗疲劳损伤性能,是国产大飞机蒙皮的首选材料[3]。2E12合金在均匀化处理过程中的“温度敏感性”问题是影响该合金大型铸锭生产的一个关键因素[4]。研究表明:由于合金化程度较高并且工业浇注速度较快[5],2E12合金铸锭中通常存在明显的枝晶偏析和大量的共晶组织[6]。这些非平衡组织会明显缩小合金的可加工范围,显著降低合金的成型性能[7]。此外,残留的非平衡组织也会对最终型材的耐蚀性能及抗疲劳性能都会带来极其不利的影响[8-10]。因此,2E12合金铸锭在加工前必须进行充分的均匀化处理以消除合金中非平衡组织。然而,由于2E12合金主添加元素(如Cu和Mn元素)在基体中的扩散速率较低,合金通常需要采用很高的均匀化温度(接近于低熔点相的熔点)并经历很长时间来实现元素的充分扩散,这就大大增加了合金发生“过烧”的风险[11]。特别是在大型合金铸锭的均匀化过程中,铸锭温度难以精准控制,铸锭各区间温度分布不均,这都为大型2E12合金铸锭的生产造成了很大困难。尽管国内相关学者对2E12铝合金的均匀化工艺进行了一些探索性的研究[11],但针对该合金在均匀化处理过程中的微观组织演变规律还缺乏报道。为此,本文作者结合微观组织观察、硬度测试以及电导率测试对2E12合金铸锭在不同均匀化处理后的微结构特征以及元素分布情况进行分析,揭示合金在均匀化过程中的微观组织演变规律,对于合金均匀化处理制度的确立以及加工工艺的优化具有指导意义。
1 实验
实验所用的2E12合金铸锭由西南铝业(集团)有限责任公司提供。铸锭采用常规的模铸方法获得,铸造温度为700~720 ℃。铸锭尺寸(长×宽×高)为400 mm×1 620 mm×2 500 mm。合金的化学成分为:Al-4.21Cu-1.41Mg-0.58Mn-0.08Fe-0.06Si(质量分数,%)。
实验在铸锭中间部位选取边长为40 mm×40 mm×40 mm的立方体试样。随后,将试样置于马弗炉中不同时间和温度的保温处理,利用水淬保留合金的原始组织状态。最后,对试样进行微观形貌观察以及电导率和硬度测试。
合金的硬度测试在KB-3000布氏硬度试验机上进行,实验采用的加载荷为20 N,加载时间为15 s。合金电导率采用SMP10涡流电导仪进行测量。实验采用POLYVER-MET型金相显微镜对合金的晶粒尺寸和形貌进行分析。合金的元素分布特征采用JXA-8230电子探针显微分析仪(EPMA)进行分析。采用FEI Sirion 200场发射扫描电镜(SEM)和TecnaiG2 F20透射电镜(TEM)对合金第二相的形貌和分布进行观察。透射电镜样品在-25 ℃以下利用MT-PI型双喷电解减薄仪进行减薄,双喷液采用25%硝酸+75%甲醇混合溶液(体积分数)。
2 结果与分析
2.1 铸态合金的微观组织
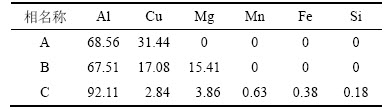
图1所示为铸态2E12合金的微观结构。由图1(a)可见:合金的晶粒近似成等轴状,粒度为80 μm左右,存在明显的枝晶形貌特征。由图1(b)可以看出:合金沿晶界连续分布着众多粗大的共晶组织。通过观察可以发现(图1(c)):这些共晶组织包括3种不同衬度和形貌的第二相。结合EDS分析(表1)以及参考文献可知[12],这3种第二相分别为:白色的θ(Al2Cu)相,灰色的S(Al2CuMg)相以及黑色的α(Al)相。因此,可以判断,合金晶界附近连续分布着α(Al)+θ(Al2Cu) +S(Al2CuMg)相的三元共晶组织。
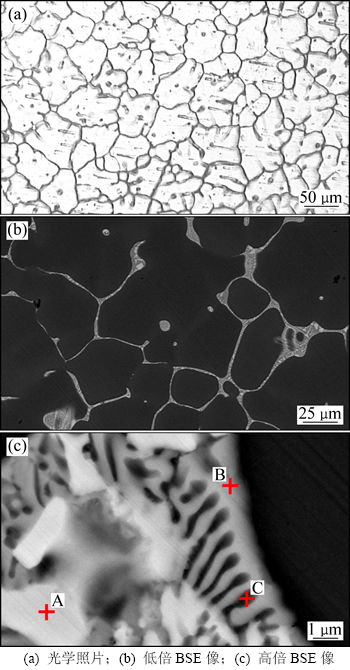
图1 铸态2E12合金的微观结构
Fig. 1 Microstructures of as-cast 2E12 alloy
表1 图1(c)中第二相的EDS分析结果(质量分数)
Table 1 EDS analysis result of second phases in Fig.1(c) %
2.2 铸锭合金的DSC分析
为了确定铸锭的过烧温度(低熔点化合物的熔点),首先对合金进行DSC分析,结果如图2所示。由图2可见:合金铸锭的DSC曲线中出现了2个明显的吸热峰。第1个吸热峰出现在496.5~509.6 ℃温度区间,峰值温度为501.2 ℃。第2个吸热峰出现在610.8~670.1 ℃温度区间,峰值温度为642.8 ℃。参照三元相图并根据文献[11]可知:第1个吸热峰对应的是合金三元共晶组织(α(Al)+θ(Al2Cu)+ S(Al2CuMg))的熔点,而第2个吸热峰对应的是合金α(Al)基体的熔点。
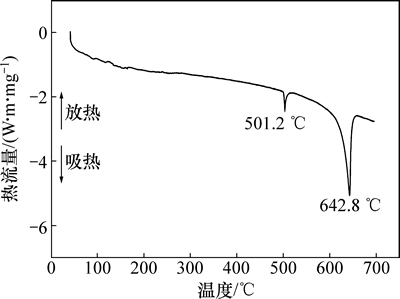
图2 铸态2E12合金的DSC分析结果
Fig. 2 DSC analysis result of 2E12 Al alloy
2.3 合金在均匀化处理过程中的电导率和硬度的变化
参考DSC测试的分析结果,选取460,470,480,490和500 ℃ 5个实验温度,对试样依次进行不同保温时间的均匀化处理。
图3 (a)所示为不同均匀化温度下合金电导率随保温时间的变化曲线。由图3(a)可见:随着均匀化温度的提高,合金的电导率明显升高。特别地,当均匀化温度为470~500 ℃时,合金电导率的升高尤为明显,而当均匀化温度为460 ℃时,合金电导率的上升幅度要小很多。图3(b)所示为不同均匀化温度下合金硬度随保温时间的变化曲线。同样地,随着均匀化温度的提高,合金的硬度也明显升高。此外,在保温8 h之前,合金硬度的曲线斜率较大,而保温8 h后,曲线的斜率明显减小,近似呈平台状。
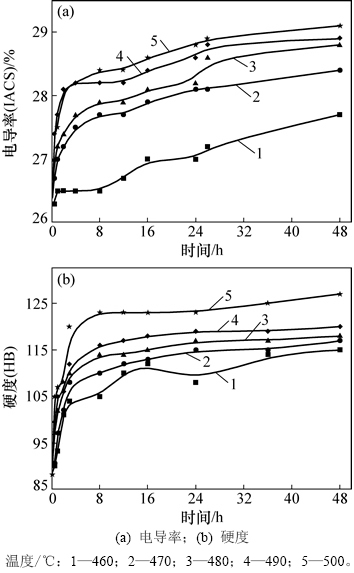
图3 不同均匀化温度下铸态2E12合金电导率和硬度随保温时间的变化曲线
Fig. 3 Electric conductivities and hardnesses of as-cast 2E12 alloy during different homogenization treatments
2.4 合金在均匀化过程中的微观形貌分析
图4所示为试样在经过5个实验温度保温48 h后的BSE形貌照片。由图4可见:均匀化温度越高,合金晶界处第二相的溶解越充分。其中,合金在460 ℃和470 ℃均匀化48 h后,粗大第二相的溶解效果不明显,晶界处仍然连续分布着大量共晶组织。在480 ℃和490 ℃均匀化48 h后,合金晶界处的粗大第二相大部分回溶入基体,只有少部分第二相间断地分布在晶界上。合金在500 ℃保温48 h后,第二相溶解较为充分,但是晶界附近出现许多形成了黑色的过烧坑。
图5所示为试样在不同均匀化温度下经48 h退火后的金相组织。由图5可见:合金在460~490 ℃均匀化时,不存在明显的过烧迹象;在500 ℃均匀化48 h后,晶界上的过烧现象十分明显,局部区域过烧坑的直径超过50 μm。
众所周知,固溶元素在合金中的扩展速率是一个与温度相关的函数。温度越高,固溶元素的扩散速率越快。根据图4和图5的分析可知:虽然在500 ℃下合金晶界粗大第二相的溶解速率较快,但是容易发生过烧现象。因此,实验主要关注合金在490 ℃均匀化过程中的微观结构演变特征。
为了研究合金中各主要元素分布特征随均匀化时间的变化情况,对铸态2E12合金在490 ℃经不同时间保温后的试样进行EPMA面扫描分析,结果如图6所示。由图6(a)可知:铸态合金中的Cu,Mg,Fe和Si元素存在明显的偏聚现象,其中Cu和Mg元素的偏聚最为严重,而Mn元素在铸态合金中整体分布较为均匀。随着均匀化处理的进行,合金中粗大共晶组织逐渐溶解,Cu,Mg和Si元素回溶入Al基体中,而Mn和Fe元素则在合金第二相中逐渐聚集,如图6(b)所示。经过490 ℃,1 000 h的均匀化处理后可以看出(图6(c)):合金晶界处的第二相主要富集Cu,Mn和Fe元素,而Mg和Si元素基本全部溶入合金基体。
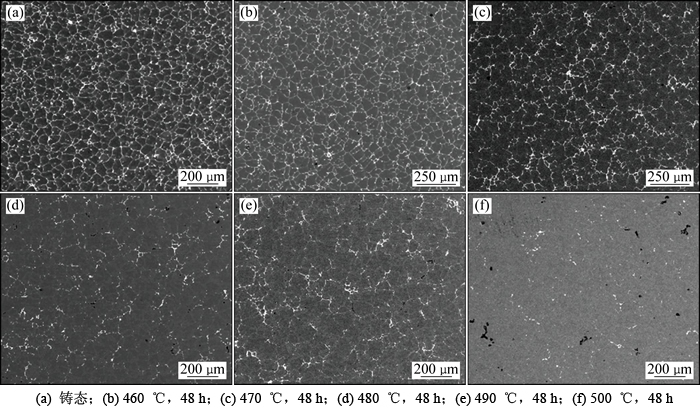
图4 铸态2E12合金在不同均匀化温度下保温48 h后的BSE形貌
Fig. 4 BSE images of as-cast 2E12 alloy holding at different temperatures for 48 h
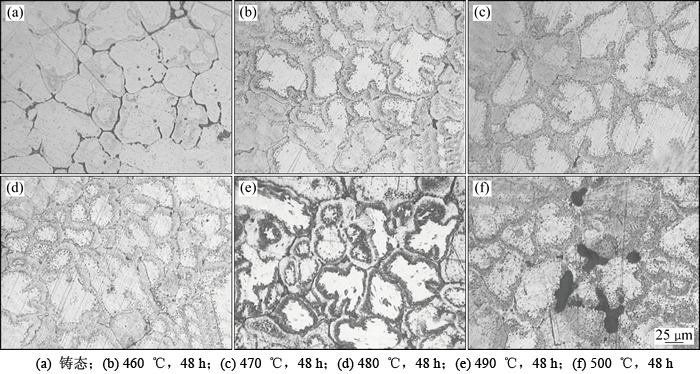
图5 铸态2E12合金在不同均匀化温度下保温48 h后的金相组织形貌
Fig. 5 Optical micrographs of as-cast 2E12 alloy holding at different temperatures for 48 h
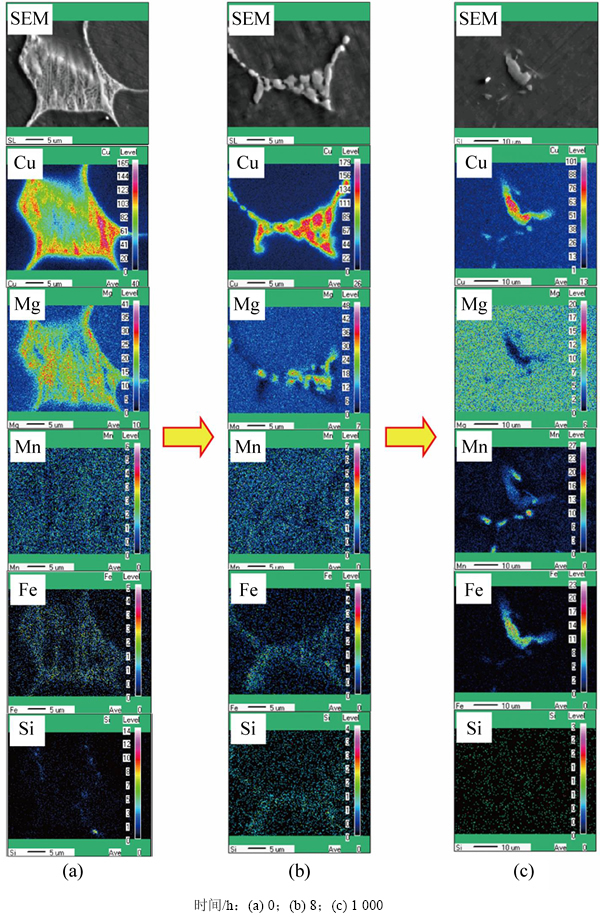
图6 铸态2E12合金在490 ℃经不同时间保温后的EPMA元素面扫描分析结果
Fig. 6 Element mapping of as-cast alloy holding at 490 ℃ for different time
众所周知,在铝合金中,杂质元素Fe和Si原子容易与Al原子结合形成针状的脆性AlFeSi相,从而对合金的力学性能产生不利影响。但是,在该合金中并没有出现十分粗大的针状AlFeSi相。由图6可知:这主要是由于合金添加的Mn元素容易与Fe元素结合并形成椭球状的AlFeMn相,从而抑制了针状AlFeSi相的生成。
为了从更微观的层次观察合金的组织演变规律及相变机理,实验采用TEM和HRTEM等研究手段对合金在均匀化过程中的第二相的析出过程进行系统研究。
图7(a)所示为铸态2E12合金在<010>Al入射方向下的典型TEM形貌。在此入射方向下,在合金晶粒内部并没有观察到明显的第二相粒子。此外,在合金晶内的选取衍射(SADP)中也没有观察到第二相的衍射斑。在合金的晶界处,合金中的粗大第二相呈链状连续分布。EDS分析结果(图7(b))表明:这些第二相主要富集Cu和Mg元素,并有少量Si元素的聚集,这与表1的分析结果基本吻合。
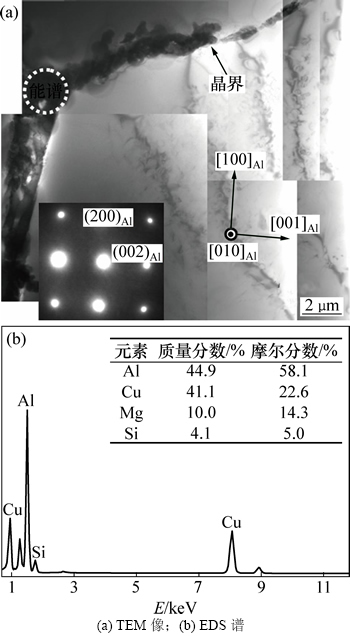
图7 铸态2E12合金在<010>Al带轴的TEM形貌和晶界粗大第二相的EDS分析结果
Fig. 7 Typical TEM micrographs of an as-cast 2E12 alloy and EDS analysis result of the second phase at GB
图8(a)所示为铸态合金经485 ℃保温48 h后在<010>Al入射方向下TEM形貌照片。由图8(a)可见:经过485 ℃,48 h的均匀化处理后,合金中原本呈链状连续分布的第二相颗粒变为间断分布的椭球状第二相粒子。此外,晶内弥散分布着大量细小的棒状第二相颗粒。这些棒状第二相粒子粒度为0.5~2.0 μm,其轴向平行于Al基体的3个<010>方向。结合HRTEM分析(图8(b)和图8(c))以及元素面扫描分析(图8(d))可知:该第二相粒子为T(Al20Cu2Mn3)相(T相是Al-Cu-Mg合金的一种主要弥散强化相,通常被认为在合金的均匀化处理过程中析出)。可以看出:T相沿自身的{101}面发生多次孪生(图8(c)),横截面呈现多种复杂形状(图8(b)),这也与文献[13]报道结果一致。通过观察可以发现:在经过485 ℃,48 h的均匀化处理后,合金晶界附近区域并没有出现明显的无沉淀析出带(PFZ)。
随着均匀化时间的延长,合金中的T相粒子粒度逐渐增加。在490 ℃保温1 000 h以后,合金中晶内分布的T相粒子已经显著长大。此外,在合金晶界处析出了十分粗大的第二相粒子。此外,在晶界附近出现了宽度约为1.8 μm的PFZ。
PFZ在铝合金的时效过程中十分常见,但针对铝合金均匀化过程中的PFZ研究较少[4]。一般认为,在时效过程中,合金PFZ的形成主要由2种机制导致,即贫空位机制和贫溶质机制。贫空位机制认为:在时效前的淬火过程中,合金晶界附近区域的过饱和空位容易扩散至晶界等晶体缺陷处泯灭,致使晶界附近区域的空位浓度显著降低,从而抑制了该区域第二相粒子的析出。贫溶质机制则认为:PFZ的形成是由于第二相在晶界处的优先析出抢夺了晶界附近基体的溶质原子,致使这部分区域的“溶质原子浓度贫化”从而无法析出第二相粒子[4]。
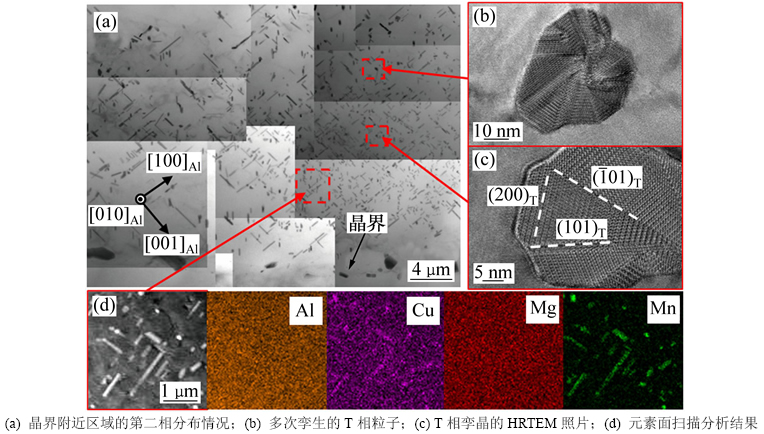
图8 铸态合金在490 ℃保温48 h后的微观形貌
Fig. 8 Microstructures of as-cast alloy homogenized at 490 ℃ for 48 h
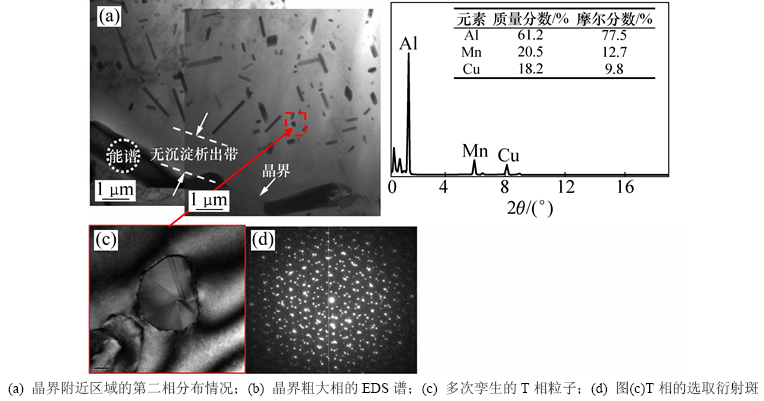
图9 铸态合金在490 ℃保温1 000 h后的微观形貌
Fig. 9 Microstructures of as-cast alloy homogenized at 490 ℃ for 1 000 h
图9所示为铸态合金在490 ℃保温1 000 h后的微观形貌。合金的均匀化处理温度较高(接近固溶处理温度),在该温度下,合金很难出现“贫空位”的现象。因此,合金均匀化过程中形成的PFZ是贫溶质机制所引起的。此外,根据EDS检测显示(图9(b)),晶界处的粗大第二相富含Cu和Mn元素,可以判断为T相。所以,该PFZ的形成主要是因为晶界处析出了十分粗大的T相粒子,抢夺了附近区域的Mn和Cu溶质原子进而抑制了周边区域T相粒子的形成。
经过长时间均匀化处理后,合金中的T相粒子仍大多保持着多次孪生的形貌特征(图9(c))。由于T相孪生面之间的夹角约为36°[13],T相每沿{101}面孪生1次,就相当于沿b轴旋转36°。经过多次孪生后,T相最终会形成5种不同的取向。因此,其衍射斑存在明显的5次对称型花样特征(图9(d))。
3 讨论
3.1 合金铸锭中的元素分布
合金的铸造属于一个非平衡凝固的过程,先凝固区域溶质原子含量低,后凝固区域溶质原子含量高。在2E12合金中,Cu和Mg是其主要合金元素。在铸造过程中,由于首先发生凝固区域的溶质原子含量低于合金的平均溶质原子含量。因此,随着铸造过程的进行,液相中的溶质原子含量持续增加。在铸造末期,液相中的Cu和Mg元素含量过高,导致这部分被固相包围的液相最终以共晶反应的形式发生凝固,并在晶界处形成粗大的α+θ+S三元共晶组织,因此,晶界处富集大量Cu和Mg等元素。
合金中的Fe和Si属于杂质元素,其原子含量很低。受到元素偏析的影响,Fe和Si也在合金晶界处存在一定程度的富集,但偏析程度远比Cu和Mg元素的偏析程度低。相比于Fe和Si,Mn元素在合金中的成分要高很多,但是在铸锭中并没有观察到明显的元素偏聚现象。其原因主要是由于Mn元素在Al基体中的扩散系数较小,在铸造过程中,Mn元素来不及发生偏聚,因此在合金中的分布较为均匀。
3.2 合金在均匀化过程中的元素扩散
由于铸锭冷却速度较快,固相中的元素扩散和平衡相析出均来不及进行,铸锭处于一个非平衡状态。此外,铸锭中晶粒心部溶质原子浓度低,而晶界附近区域溶质原子含量高。因此,在均匀化保温过程中,合金中的溶质原子逐渐从晶界到晶内发生扩散。
在2E12合金中,由于Cu,Mg和Si元素在Al基体中的溶解度较高,经过长时间均匀化处理后,晶界处富集的这些溶质原子通过扩散溶入合金基体。由于合金中Cu元素含量较高,略高于490 ℃时Cu元素在Al基体中的固溶度,因此即便合金在490 ℃保温1 000 h后第二相中仍然残留有一定的Cu元素。而在490 ℃时Mg元素在Al基体中的固溶度约为12%(质量分数)左右,远大于合金中Mg元素的含量,所以Mg基本全部回溶入基体而在第二相中几乎不存在Mg元素(图6(c))。
不同于Cu,Mg和Si元素,Mn和Fe元素的偏聚程度随着均匀化的进行逐步增加。尽管Fe元素在合金中的含量很低,但由于490 ℃时Fe元素在Al中几乎不固溶。因此,Fe元素从合金基体中脱溶出来并富集在合金的粗大第二相中。此外,作为重要的添加元素,Mn元素的含量明显高于Fe元素的含量。由于Mn元素在合金中的固溶度很低,因此,在均匀化保温过程中,Mn元素以第二相的形式从合金基体中大量脱溶出来。
3.3 合金在均匀化过程中的相变
在2E12合金铸锭中主要存在2种组织:一种是晶粒内部的初生α(Al)相,另一种是聚集在晶界处的α+θ+S三元共晶组织。其中,α+θ+S三元共晶组织属于非平衡组织,在均匀化过程中逐步溶解消除。此外,合金中过剩的Cu原子与基体中的Mn原子结合,形成棒状的T相粒子。因此,合金在均匀化过程中主要存在2个相变,即
 (1)
(1)
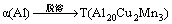 (2)
(2)
T相属于高熔点相,在均匀化过程中较稳定不发生分解[14]。一般认为,T相的析出有利于抑制合金晶粒的长大,并会在一定程度上起到弥散强化的效果[15-17]。合金硬度随着均匀化时间的延长而逐步增加(图1(b)),一方面是由于Cu和Mg等元素溶入合金基体所起到的固溶强化作用,另一方面是由于T相析出所产生的弥散强化作用。
此外,在2E12合金的均匀化过程中,Cu和Mg等元素溶入合金基体会显著增加合金基体的晶格畸变,从而导致合金电导率明显降低。然而,实验结果(图1(a))表明:合金的电导率随着均匀化时间的延长而持续增加。这主要是因为,相比于Cu和Mg等元素,Mn元素对铝合金电导率的影响更大[18]。通常Mn元素的添加通常会显著降低合金的电导率[18]。因此,在均匀化过程中,Mn元素以T相的形式从铝基体中脱溶,极大地提高了合金的电导率。合金的电导率从整体上表现为随着均匀化时间的延长而逐渐增加。
4 结论
1) 2E12合金铸锭主要包括初生α(Al)相和α(Al)+ θ(Al2Cu)+S(Al2CuMg)三元共晶2种组织。合金在500 ℃保温48 h后会出现明显的过烧现象。
2) 在460~500 ℃的均匀化处理过程中,合金的电导率和硬度均随着均匀化时间的延长而明显升高。
3) 合金铸锭中的Cu,Mg,Si和Fe元素存在不同程度的元素偏聚,其中Cu和Mg元素偏聚最为显著,而合金铸锭中的Mn元素分布较为均匀。在均匀化过程中,Cu,Mg和Si元素逐步溶入合金基体,而Mn和Fe元素则从合金基体中脱溶。
4) 合金在均匀化过程中主要存在2个相变: ,
,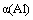
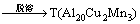
5) 合金在均匀化后期,晶界附近出现明显的PFZ。
参考文献:
[1] CHEN Y Q, PAN S P, ZHOU M Z, et al. Effects of inclusions, grain boundaries and grain orientations on the fatigue crack initiation and propagation behavior of 2524-T3 Al alloy[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2013, 580: 150-158.
[2] 王琪, 傅上, 王斌, 等. 应力-电场耦合时效对2524铝合金微观组织的影响[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 45(5): 1428-1436.
WANG Qi, FU Shang, WANG Bin, et al. Effect of stress coupled with electric field on microstructure of 2524 aluminum alloy[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2014, 45(5): 1428-1436.
[3] 刘兵, 彭超群, 王日初, 等. 大飞机用铝合金的研究现状及展望[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2010, 20(9): 1706-1715.
LIU Bing, PENG Chaoqun, WANG Richu, et al. Recent development and prospects for giant plane aluminum alloys[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2010, 20(9): 1706-1715.
[4] CHEN Y Q, YI D Q, JIANG Y, et al. Concurrent formation of two different type precipitation-free zones during the initial stage of homogenization[J]. Philosophical Magazine, 2013, 93(18): 2269-2278.
[5] CAI M, ROBSON J D, LORIMER G W. Simulation and control of dispersoids and dispersoid-free zones during homogenizing an AlMgSi alloy[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2007, 57: 603-606.
[6] VERLINDEN B, WOUTERS P, MCQUEEN H J, et al. Effect of different homogenization treatments on the hot workability of aluminium alloy AA2024[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 1990, 123: 229-237.
[7] 李玉乾, 叶凌英, 张新明, 等. Cr和Yb复合添加对2519A铝合金组织和力学性能的影响[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 45(7): 2182-2186.
LI Yuqian, YE Lingying, ZHANG Xinming, et al. Effects of Cr and Yb additions on microstructures and mechanical properties of 2519A aluminum alloy[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2014, 45(7): 2182-2186.
[8] 郑玉林, 暨波, 叶凌英, 等. 稀土镱对2519A铝合金抗晶间腐蚀性能的影响[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 44(12): 4806-4810.
ZHENG Yulin, JI Bo, YE Lingying, et al. Influence of Yb addition on intergranular corrosion resistance of aluminum alloy 2519A[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2013, 44(12): 4806-4810.
[9] 周明哲, 易丹青, 王斌, 等. 固溶处理对2E12铝合金组织及疲劳断裂行为的影响[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2010, 43(1): 66-73.
ZHOU Mingzhe, YI Danqing, WANG Bin, et al. Effect of solution treatment on fatigue behavior of 2E12 aluminum alloy[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology),2010, 43(1): 66-73.
[10] GANDIN C A, JACOT A. Modeling of precipitate-free zone formed upon homogenization in a multi-component alloy[J]. Acta Materialia, 2007, 55(7): 2539-2553.
[11] 杜凤山, 邓少奎, 闫亮, 等. 2E12铝合金过烧温度及高温塑性研究[J]. 材料工程, 2008, 7: 18-21.
DU Fengshan, DENG Shaokui, YAN Liang, et al. Study on overheat temperature of ingot and high temperature plasticity of 2E12 aluminum alloy[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering,2008, 7: 18-21.
[12] 周亮, 邓运来, 晋坤, 等. 预处理对 2124 铝合金板材蠕变时效微结构与力学性能的影响[J]. 材料工程, 2012, 2: 81-84.
ZHOU Liang, DENG Yunlai, JIN Kun, et al. Effect of pre-treatment on microstructures and mechanical properties of 2124 Al alloy creep aging sheet[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering, 2010, 2: 81-84.
[13] CHEN Y Q, YI D Q, JIANG Y, et al. Twinning and orientation relationships of T-phase precipitates in an Al matrix[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2013, 48(8): 3225-3231.
[14] FENG Z Q, YANG Y Q, HUANG B, et al. Crystal substructures of the rotation-twinned T (Al20Cu2Mn3) phase in 2024 aluminum alloy[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2014, 583: 445-451.
[15] 陈宇强, 易丹青, 潘素平, 等. 温度对2024铝合金蠕变行为的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2010, 20(4): 632-639.
CHEN Yuqiang, YI Danqing, PAN Suping, et al. Effect of temperature on creep behavior of 2024 aluminum alloy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2010, 20(4): 632-639.
[16] 陈宇强, 易丹青, 潘素平, 等. 蠕变温度对Al-Cu-Mg合金晶内S′相析出过程的影响[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2011, 40(1): 63-68.
CHEN Yuqiang, YI Danqing, PAN Suping, et al. Effects of creep temperatures on the precipitation of S’ phases in Al-Cu-Mg alloys[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2011, 40(1): 63-68.
[17] SHEN Z J, LIU C H, DING Q Q, et al. The structure determination of Al20Cu2Mn3 by near atomic resolution chemical mapping[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2014, 601: 25-30.
[18] LI Y J, ARNBERG L. Evolution of eutectic intermetallic particles in DC-cast AA3003alloyduring heating and homogenization[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2003,347(1/2): 130-135.
(编辑 陈爱华)
收稿日期:2016-03-22;修回日期:2016-06-14
基金项目(Foundation item):国家自然科学基金资助项目(51405153,51475162);国家重点基础研究发展计划项目(2012CB619506)(Projects(51405153, 51475162) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China;Project(2012CB619506) supported by the Major State Basic Research Projections of China)
通信作者:陈宇强,博士,讲师,从事高性能铝合金材料研究;E-mail:yqchen1984@163.com