文章编号:1004-0609(2007)10-1622-05
12 mm厚钛合金平板电子束焊接的数值模拟
胡美娟,刘金合
(西北工业大学 材料科学与工程学院,西安 710072)
摘 要:采用ANSYS有限元分析软件,建立12 mm厚TC4钛合金平板电子束焊接温度场和应力场的三维有限元数值计算模型。模型采用圆锥体热源考虑电子束焊接时的小孔效应;材料的热学、力学性能参数随温度变化;相变和熔池内液体的对流散热通过比热和热导率的变化实现。计算结果表明:钛合金电子束焊接时,熔池呈典型的卵形分布。高值纵向残余拉应力集中分布在焊缝中心线两侧距焊缝中心线4 mm的区域内,平板内部出现接近材料屈服极限的局部三维残余拉应力状态。实验得到的焊缝宏观形貌和小孔释放法检测到的焊接残余应力对计算结果进行验证, 实验结果和计算结果吻合较好,证明了有限元模型的正确性。
关键词:钛合金;电子束焊接;数值模拟;小孔法;残余应力
中图分类号:TG 456.3 文献标识码:A
Numerical simulation for electron beam welding
of 12 mm-thickness titanium alloy plate
HU Mei-juan, LIU Jin-he
(School of Materials Science and Engineering, Northwestern Polytechnical University, Xi’an 710072, China)
Abstract: A three dimensional finite element model used for calculating electron beam welding temperature and stress fields of 12 mm-thickness TC4 titanium alloy plate was developed through employing ANSYS software code. Cone body heat source model was chosen to simulate keyhole effect of electron beam welding. Temperature-dependent thermal and mechanical properties were used. Phase change and liquid convection in molten bath were simulated by the change of specific heat and heat conductivity. The results of the simulation show that the shape of the weld pool is typically oval. The longitudinal stresses with high value mainly lie in the region which extends a distance 4 mm away from the weld centerline. The phenomenon of local three dimensions residual tensile stresses, which are equivalent to the yield stress of the material, appears in the plate center. Macrograph of the fusion zone in the transverse section obtained from experiment and residual stresses determined by hole-drilling method are used to validate the simulated results. The experimental and numerical results are in sufficient overall agreement, which proves the validity of the finite element model.
Key words: titanium alloy; electron beam welding; numerical simulation; hole-drilling method; residual stress
钛合金由于具有比强度高、工作温度范围宽、工艺塑性和高温抗蠕变性能良好等优点,在航空航天领域,特别是航空发动机制造中得到了广泛的应用。由于真空电子束焊接具有能量密度高、焊缝和热影响区窄、焊接变形小、工艺参数容易精确控制及真空焊接环境等其它焊接方法难以比拟的优势,常常成为钛合金焊接方法的首选[1-5]。
电子束焊接时,采用的功率密度足够大时会形成穿透型的蒸汽毛细孔。尽管电子束焊接后构件变形量很小,但是焊接残余应力由于温度梯度大可能达到相当高的数值。焊接残余应力是影响结构脆性断裂强度、疲劳强度以及尺寸稳定性的重要因素[6-7]。构件残余应力的三维检测常受到局限,采用非破坏性检测时通常只能确定工件表面的应力状态,即使采用破坏性方法也不可能有足够的精度确定构件内部完整的三维应力状态[8]。数值模拟技术的发展为研究焊接热过程、焊接应力的动态变化以及焊接残余应力的分布提供了一个有效的方法。
Stone等[9]采用SYSWELD有限元分析软件,对9 mm厚的镍基高强合金平板电子束焊接过程进行了三维模拟计算,热源参数通过实验结果和模拟结果的对比获得,纵向残余应力的模拟结果同实验结果有良好的一致性,横向残余应力的差别较大,模拟结果指出横向残余应力表面为压应力,中心为拉应力。刘敏 等[10]分析6 mm厚TC11钛合金不同工艺参数下的残余应力分布规律,指出电子束焊接后焊缝及近缝区存在达到材料屈服极限的纵向残余拉应力。
目前采用数值模拟技术对传统焊接过程进行分析的例子较多,针对激光、电子束等高能焊接方法进行模拟计算的报道较少,而且主要集中在厚度为10 mm以下的平板对接焊。本文作者采用ANSYS有限元分析软件,对12 mm厚TC4钛合金平板真空电子束焊接时的温度场和应力场进行了数值模拟计算,详细分析了焊接时温度场和残余应力场的分布规律,实验得到的焊缝形貌和小孔释放法检测到的焊接残余应力对计算结果进行了验证。
1 三维有限元计算模型
1.1 有限元网格与焊接工艺
实验用平板材料为TC4钛合金,试件的尺寸为120 mm×120 mm×12 mm。考虑到结构的对称性,仅取焊缝中心线一侧的工件进行建模以提高计算效率。三维有限元数值模拟网格划分示意图如图1所示,采用过渡的映射六面体网格划分方式,焊缝附近采用小的网格尺寸,而在远离焊缝的区域采用较大的网格尺寸,最小单元尺寸为0.5 mm×0.5 mm×3 mm,整个有限元模型共有8 780个单元,12 622个节点。
钛合金平板电子束焊接的工艺参数列于表1,电子枪真空度为2.0×10-4 Pa,焊接室真空度为2.0×10-3 Pa,电子束表面聚焦。电子束焊接时,会聚的电子束垂直于工件平板沿z轴正方向入射,工件沿着x轴负方向直线进给形成熔透的对接接头。
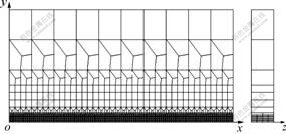
图1 有限元数值模拟网格划分示意图
Fig.1 Finite element mesh used for numerical simulation
表1 电子束焊接工艺参数
Table 1 Parameters of electron beam welding

1.2 焊接温度场有限元计算模型
电子束焊接时,考虑小孔效应和实际焊缝形状,采用圆锥体热源模型计算焊接部位的热输入,焊接热效率取为0.9[11-12]。
电子束焊接在真空室中进行,不存在对流,只考虑热辐射。焊缝中心线所在的对称面为绝热边界条件,其他面通过表面效应单元施加辐射载荷,材料的辐射率随温度增加而增加。通过增加焊接熔池金属的热导率来考虑熔池中液体的对流热扩散作用。相变对温度场的影响通过相变温度区间内比热的均匀变化实现。TC4钛合金0~500 ℃的热传导率、比热容由文献[13]查取。通过对已知参数进行线性拟合,确定材料高温范围的热物性参数值。
1.3 焊接应力场有限元计算模型
变形热对焊接温度场的影响相对较弱,因此采用顺序耦合法,即先进行温度场的分析,然后将不同时刻的节点温度作为体载荷施加到结构上,从而实现焊接应力场的有限元计算。焊接热应力计算时的材料模型选为热-弹塑性,材料遵循Von Mises屈服准则。
由于结构的对称性,不允许垂直于对称平面的位移。TC4钛合金的相变发生在约980 ℃,此时材料的屈服极限很低,并且β→α时,相变体积变化约为0.17%,所以计算时未考虑相变应力的影响。材料不同温度下的屈服极限、弹性模量等力学性能参数取自文献[13]。
2 计算结果和实验验证
2.1 温度场计算结果与分析
图2所示为焊接开始工件运动10 s时上表面的温度场分布云图。从图2可以看出,表面温度高于800 ℃的区域集中在焊缝中心线两侧距焊缝中心线3.5 mm内(即y=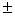 3.5 mm范围内)。在纵向(沿x轴),电子束直接作用区域的温度最高,达2 640 ℃,超过TC4钛合金的汽化温度。热源前方温度梯度大,等温线密集,热源后方温度梯度小,等温线呈拉长的椭圆形状。在横向(沿y轴),随着与焊缝中心线距离的增加,温度逐渐降低。熔池在上表面呈典型的卵形分布,在热源移动方向上,熔池长约7.5 mm,在垂直热源移动方向上,熔池的最大宽度约2.1 mm。
3.5 mm范围内)。在纵向(沿x轴),电子束直接作用区域的温度最高,达2 640 ℃,超过TC4钛合金的汽化温度。热源前方温度梯度大,等温线密集,热源后方温度梯度小,等温线呈拉长的椭圆形状。在横向(沿y轴),随着与焊缝中心线距离的增加,温度逐渐降低。熔池在上表面呈典型的卵形分布,在热源移动方向上,熔池长约7.5 mm,在垂直热源移动方向上,熔池的最大宽度约2.1 mm。

图2 上表面温度场分布云图
Fig.2 Temperature contour of upper surface
图3所示为x=60 mm处与焊缝中心线垂直的横截面在工件上表面焊缝中心和距焊缝中心线不同距离点的热循环。从图3可以看出,在热源还没有作用以前,各点的温度都等于周围介质的温度,在电子束束斑直接作用区域温度急剧上升达到最高温度,随着工件向前移动,一方面焊缝中心的温度迅速下降,另一方面焊缝旁边各点通过热传导作用温度逐渐升高,离焊缝中心线越远,达到局部最高温度所需时间越长,最高温度也越低。距焊缝中心线2、4、8 mm处的最高温度分别为1 630、728、352 ℃,这充分反映了电子束焊接时能量集中和局部高温的特点[14-15]。
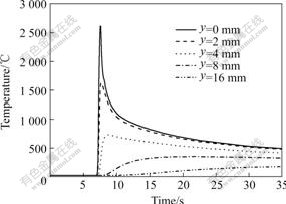
图3 电子束焊接时不同位置的热循环
Fig.3 Thermal cycles at different locations in electron beam welding condition
2.2 应力场计算结果与分析
图4所示为x=60 mm处与焊缝中心线垂直的横截面在上表面和1/2厚度处残余应力的分布。可以看出,纵向残余应力在焊缝和近缝区为拉应力,工件表面最大纵向残余拉应力值为670 MPa,约为TC4钛合金室温屈服极限的70%,工件1/2厚度处最大纵向残余拉应力值为905 MPa,接近材料的屈服极限。在近缝区边缘距焊缝中心线4 mm处纵向残余应力值迅速陡降,并由拉应力转变为压应力,在达到最大压应力值-125 MPa后缓慢变化,至横向板边趋近于零。横向残余应力在工件表面焊缝和近缝区为压应力,最大值约为-150 MPa;工件1/2厚度处为拉应力,最大值约为150 MPa。平板在传统电弧焊焊接后,横向残余应力在焊缝和近缝区通常为拉应力,电子束焊接时加速速度快,冷却速度大,TC4钛合金熔点高,但是导热系数仅为钢的1/2,在热源后方凝固过程中工件中心的温度相对高于上下表面的温度,中心冷却较慢的金属变形受到周围金属的制约导致表面焊缝和近缝区的横向残余应力为压应力。工件中除纵向残余应力和横向残余应力外,还存在不可忽视的厚度方向上的垂直残余应力。由图4可知,垂直残余应力在工件表面焊缝区的拉应力值较小,并随着距焊缝中心线的距离增大逐渐减小。在工件表面近缝区和母材交界处,垂直残余应力值由200 MPa变为-240 MPa。在工件1/2厚度处垂直残余应力在焊缝区为拉应力,最大值约为234 MPa。
图4 残余应力沿焊缝中心线垂直方向的分布
Fig.4 Plots of residual stresses with distance away from weld centerline
图5所示为残余应力在工件上表面和1/2厚度处焊缝中心线上的分布曲线。从图5可以看出,纵向残余拉应力值在焊缝中部基本保持稳定。在焊缝两端部位,纵向残余应力由恒定值逐渐降至零。工件1/2厚度处焊缝中心线稳定区域的纵向残余拉应力值接近材料的屈服极限。横向残余应力在工件表面焊缝中心线上整体表现为压应力,焊缝两端的压应力值接近材料的屈服极限,焊尾处应力最大值达-921 MPa。横向残余应力在工件1/2厚度处焊缝中心线的两端为压应力,中部为拉应力,稳定值约为150 MPa。由图5还可知,垂直残余应力在焊缝中心线的两端为压应力,中间为拉应力。工件1/2厚度处焊缝中心线上垂直残余应力的稳定值高达233 MPa。
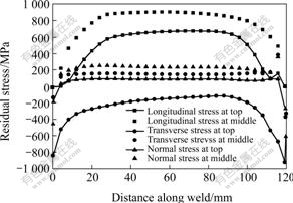
图5 残余应力在焊缝中心线上的分布
Fig.5 Plots of residual stresses along weld centerline
由以上的分析可知,12 mm厚TC4钛合金平板电子束焊接后残余应力以纵向残余应力为主,高值纵向残余拉应力集中分布在焊缝中心线两侧距焊缝中心线4 mm的焊缝和近缝区内。工件1/2厚度处焊缝中心线上的纵向残余拉应力值和工件表面焊缝两端的横向残余压应力值接近材料的屈服极限。在工件中心焊缝和近缝区出现了危险的局部三维残余拉应力状态。
2.3 实验验证
为了验证12 mm厚钛合金平板电子束焊接温度场和应力场三维有限元数值模拟计算结果的正确性,进行相关的实验并采用小孔释放法对残余应力进行检测,试件尺寸及焊接条件与数值模拟中所用条件相同。
图6所示为电子束焊缝剖面的宏观形貌。由图6可知焊缝是典型的上宽下窄的钉形焊缝,上表面宽度为4.1 mm,下表面宽度为2.2 mm。这同数值模拟计算中上表面4.2 mm,下表面2.1 mm处温度达到TC4钛合金固态熔融温度1 540 ℃的结果基本一致。

图6 电子束焊缝剖面宏观形貌
Fig.6 Macrograph of fusion zone in transverse section
本文小孔释放法实验利用CCZ-1磁力测钻台在被测部位钻孔,孔深为4.5 mm,孔径为2 mm。小孔加工后,该处的金属连同其中的残余应力即被释放,原有的残余应力也失去平衡。这时孔周围将产生一定量的释放应变,其大小与被释放的应力是相应的。用BE120-2CA-1K电阻应变花及CM-1A-10静态电阻应变仪对释放的应变进行检测,实验测得的数据用Visual Fortran语言编制程序处理,计算焊接残余应力。
图7所示为12 mm厚钛合金平板表面纵向残余应力和横向残余应力的实验结果和计算结果的对比。从图7可以看出,有限元计算结果和小孔法检测到的残余应力总体分布规律基本一致,证明了有限元数值计算模型的正确性。检测前对焊缝余高的打磨可能导致焊缝中心纵向残余应力释放,纵向残余拉应力测试结果小于计算值。横向残余应力不仅受到焊缝冷却时的横向收缩的影响,而且同焊缝的纵向收缩、表面和内部不同的冷却过程以及相变过程有关,数值计算过程中模型的简化导致实验和计算结果存在一定差异。

图7 纵向和横向残余应力的实验结果和计算结果的对比
Fig.7 Plots of numerical and experimental results: (a) Longitudinal residual stress; (b) Transversal residual stress
3 结论
1) 建立了12 mm厚TC4钛合金平板真空电子束焊接温度场和应力场的三维有限元数值计算模型,计算结果同实验结果具有良好的一致性,证明了有限元数值计算模型的正确性。
2) 12 mm厚钛合金平板真空电子束焊接时高温区集中在焊缝中心线两侧距焊缝中心线3.5 mm的区域内,焊接熔池呈典型的卵形分布,模拟的焊缝形貌与实验结果吻合良好。
3) 12 mm厚钛合金平板真空电子束焊接后的残余应力以纵向残余应力为主,高值纵向残余拉应力集中分布在焊缝中心线两侧距焊缝中心线4 mm的焊缝和近缝区内。工件1/2厚度处焊缝中心线上的纵向残余拉应力值和工件表面焊缝中心线两端的横向残余压应力值接近材料的屈服极限。
4) 工件中除纵向残余应力和横向残余应力外,还存在不可忽视的厚度方向上的垂直残余应力,垂直残余应力最大值高达233 MPa,在工件中心焊缝和近缝区出现了接近屈服极限的局部三维残余拉应力状态。
REFERENCES
[1] Caiazzo F, Curcio F, Daurelio G, et al. Ti6Al4V sheets lap and butt joints carried out by CO2 laser: Mechanical and morphological characterization[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2004, 149(1/3): 546-552.
[2] Casalino G, Curcio F, Capece M F M. Investigation on Ti6Al4V Laser welding using statistical and Taguchi approaches[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2005, 167(2/3): 422-428.
[3] Barreda J L, Santamaria F, Azpiroz X, et al. Electronbeam welded high thickness Ti6Al4V plates using filler metal of similar and different composition to the base plate[J]. Vacuum, 2001, 62(2/3): 143-150.
[4] Huang C C, Pan Y C, Chuang T H. Effects of post-weld heat treatments on the residual stress and mechanical properties of electron beam welded SAE 4130 steel plates[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 1997, 6(1): 61-68.
[5] Ferro P, Zambon A, Bonollo F. Investigation of electron-beam welding in wrought Inconel 706-experimentaland numerical analysis[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2005, 392(1/2): 94-105.
[6] Jha A K, Arumugham S. Metallographic analysis of embedded crack in electron beam welded austenitic stainless steel chemical storage tank[J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2001, 8(2): 157-166.
[7] Brauss M E, Pineault J A, Eckersley J S. Residual stress characterization of welds and post weld processes using X-ray diffraction techniques[C]//Proceedings of SPIE, 1998, 3399: 196-204.
[8] Carmignani C, Mares R, Toselli G. Transient finite element analysis of deep penetration laser welding process in a singlepass butt-welded thick steel plate[J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 1999, 179(3/4): 197-214.
[9] Stone H J, Roberts S M, Reed R C. A process model for the distortion induced by the electron beam welding of a Nickel-based superalloy[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2000, 31(9): 2261-2273.
[10] 刘 敏, 陈士煊, 康继东, 等. 钛合金平板电子束焊接残余应力数值分析[J]. 航空动力学报, 2001, 16(1): 63-66.
LIU Min, CHEN Shi-xuan, KANG Ji-dong, et al. Numerical model for the temperature and stress fields of moving EBW in titanium alloy plates[J]. Journal of Aerospace Power, 2001, 16(1): 63-66.
[11] Koleva E. Electron beam weld parameters and thermal efficiency improvement[J]. Vacuum, 2005, 77(4): 413-421.
[12] 胡美娟, 刘金合, 王亚军, 等. 圆锥体热源模型的电子束焊接温度场数值模拟[J]. 电焊机, 2005, 35(7): 39-42.
HU Mei-juan, LIU Jin-he, WANG Ya-jun, et al. Finite element analysis of temperature field in electron beam welding of titanium[J]. Electric Welding Machine, 2005, 35(7): 39-42.
[13] 中国航空材料手册编辑委员会编. 航空材料手册[M]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2002: 104-132.
Aeronautical materials handbook editorial community. Aeronautical materials handbook[M]. Beijing: Chinese Standards Press, 2002: 104-132.
[14] Stone H J, Withers P J, Holden T M, et al. Comparison of three different techniques for measuring the residual stresses in an electron beam-welded plate of Waspaloy[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 1999, 30A(7): 1797-1808.
[15] Ho C Y. Fusion zone during focused electron-beam welding[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2005, 167(2/3): 265-272.
收稿日期:2007-01-22;修订日期:2007-05-22
通讯作者:胡美娟,电话:029-88492624;E-mail:guyue@mail.nwpu.edu.cn; guyue1103@sina.com
(编辑 陈爱华)