文章编号:1004-0609(2016)-11-2319-07
Gd离子注入对固溶态Mg-Nd-Sr-Zr合金生物腐蚀行为的影响
陶学伟1, 2,王章忠1, 2,章晓波1, 2,巴志新1, 2,董强胜1, 2
(1. 南京工程学院 材料工程学院,南京 211167;
2. 南京工程学院 江苏省先进结构材料与应用技术重点实验室,南京 211167)
摘 要:对固溶态Mg-Nd-Sr-Zr合金进行了钆(Gd)离子注入改性处理;采用SRIM 2008软件对Gd离子注入过程进行了模拟分析;采用光学显微镜(OM)观察了镁合金的显微组织,并利用X 射线衍射仪(XRD)分析改性层中的物相组成,同时结合X射线光电子能谱(XPS)表征改性层中化学成分与元素价态,采用电化学实验及析氢实验评价了基体镁合金与注入镁合金在模拟体液(SBF)中的生物腐蚀行为。结果表明:Gd离子注入有助于提高固溶态Mg-Nd-Sr-Zr合金在SBF中耐生物腐蚀性能,且当注入剂量为2.5×1016 cm-2时,注入镁合金的耐生物腐蚀性能最佳。
关键词:镁合金;Gd;离子注入;生物腐蚀行为
中图分类号:TG174.44;TG146.4 文献标志码:A
人口老龄化加速以及人类对健康长寿的不断追求,令生物医用材料的需求迅速增加。镁合金作为新一代生物医用材料,与其他生物材料相比,具有以下突出优点[1-4]:1) 镁合金具有优异的生物降解性,能够自行在人体内降解,不需要通过二次手术将其植入件取出,可减轻患者的痛苦与经济负担;2) 镁是人体必需的元素之一,对治疗与预防神经肌肉亢进、骨质疏松及心血管等疾病有重要作用,溶出的镁离子不会诱发组织病变;3) 镁合金的密度和弹性模量与人体骨骼相近,能够有效避免“应力遮挡”效应。然而,镁合金在人体内的腐蚀速率极快,特别在服役初期,植入件周围产生大量的氢气,并造成局部pH值升高,破坏其机械整体性,使其过早失效而导致植入失败[2, 5]。因此,镁合金在临床应用前必须通过有效处理以抑制其过快的腐蚀速率。
表面改性技术是延缓镁合金腐蚀速率的重要手段之一,主要包括化学转化[6-7]、激光表面处理[8-9]、微弧氧化[10-11]、离子注入[5, 12-13]等。其中,离子注入技术具有工艺选择性强、不存在突变界面和膜层脱落问题、且注后植入体尺寸不发生变化等优点,因而被广泛采用于生物材料表面改性中[1, 3]。WU等[13]研究发现,将Al注入到镁合金中能够有效抑制其在模拟体液(SBF溶体)中腐蚀速率,但Al元素对人体有一定的毒性,可能诱发阿兹海默症等疾病发生[3-4]。Zn元素能够促进细胞免疫功能,具有较强的抗菌性,但注入Zn的镁合金由于“电偶腐蚀”效应反而加速了镁合金的腐 蚀[3, 14]。适量的稀土元素(Nd和Pr等)不仅使细胞毒性降至极低,而且注入后能够延缓镁合金的降解速度[15-17],但Gd离子注入改性生物镁合金的研究工作鲜见报道。Gd元素对血管收缩及新内膜形成具有抑制作用[18],又可以改善镁合金的力学性能和耐蚀性能[2],且前期研究结果显示,含有微量Gd元素的镁合金无明显细胞毒性[19]。因此,本课题组在Mg-Nd-Sr-Zr生物镁合金的基础上[20],结合本文作者对离子注入的初步研究成果[15, 21],提出采用Gd离子注入来延缓镁合金降解的工艺方法,研究Gd离子注入对固溶态Mg-Nd-Sr-Zr合金生物腐蚀行为的影响规律,以开发出具有优异耐生物腐蚀性能的镁合金。
1 实验
本实验中采用重力铸造制备Mg-2.2Nd-0.4Sr- 0.3Zr(质量分数)合金,并对铸锭进行固溶处理,在550 ℃下保温12 h。用线切割将合金切成d14 mm×4 mm的圆片,然后经过机械打磨、抛光、酒精超声清洗、冷风吹干,得到基体试样。离子注入在配备Gd靶(纯度≥99.99%)阴极源的离子注入机上进行。靶室真空度为2×10-3 Pa,注入电压60 kV。试样分为3组,注入量分别为2.5×1016、5×1016 和1×1017 cm-2 (以下分别表示A合金、B合金和C合金)。
采用SRIM 2008软件对Gd离子注入镁合金后的注入元素分布进行模拟分析,注入电压60 kV。采用光学显微镜观察Mg-Nd-Sr-Zr合金的显微组织。利用X 射线衍射仪对注入层进行表面物相结构分析,X射线源采用Cu Kα靶,波长0.l54056 nm,加速电压40 kV,电流40 mA,扫描速度10 (°)/min,扫描范围20°~80°。同时,结合X射线光电子能谱对镁合金改性层的化学成分及特定元素价态进行测定,X射线源采用Al Kα,靶电压40 kV。试样用氩离子溅射剥离40 nm后进行XPS测试,溅射速度为6 nm/min。采用电化学实验及析氢实验对镁合金在模拟体液(SBF)中的耐蚀性能进行评定,实验分别参照标准ASTM G5-94和ASTM G31-72。极化曲线测量在电化学工作上进行,电极体系为三电极体系,参比电极为饱和甘汞电极(SCE),辅助电极为铂电极。试样测试温度为(37±0.5) ℃,测试面积为100 mm2,浸泡时间1 h,扫描速度1 mV/s,腐蚀介质为模拟体液,溶液成分如下:NaCl (8.0 g/L),KCl (0.4 g/L),MgCl2.6H2O (0.1 g/L),NaHCO3 (0.35 g/L),MgSO4.7H2O (0.06 g/L),CaCl2 (0.14 g/L),Glucose (1.0 g/L),Na2HPO4.2H2O (0.06 g/L),KH2PO4 (0.06 g/L)。采用析氢实验评价镁合金在SBF中腐蚀行为,测试温度(37±0.5) ℃,单位测试面积(平方厘米)的溶液用量为160 mL,试样浸泡时间120 h,每隔24 h更换一次溶液。采用扫描电子显微镜(SEM)观察浸泡后试样的表面腐蚀形貌。
2 实验结果
2.1 Gd离子注入模拟分析
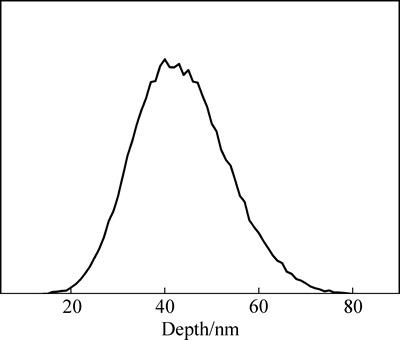
图1 Gd离子注入的Mg-Nd-Sr-Zr合金中Gd元素分布
Fig. 1 Gd element distribution in Mg-Nd-Sr-Zr alloy implanted by Gd ions
采用SRIM 2008软件对Gd离子注入Mg-Nd-Sr-Zr合金后的注入元素分布进行模拟,其结果如图1所示。从图1可以看出,注入元素在镁合金表层中呈高斯分布,其中最大深度约80 nm,在距离表面约40 nm的深度处,Gd元素浓度达到最高。由纵向静态稳定性理论[22]可知,注入剂量不改变注入元素在合金中的射程(即深度)和最大浓度位置,因此,由模拟结果可知,3种剂量下Gd改性层的厚度约为80 nm,且在距表面约40 nm的深度处Gd元素浓度最高。
2.2 显微组织分析
图2所示为Mg-Nd-Sr-Zr合金固溶处理后的光学显微组织。由图2可以看出,合金组织主要由α-Mg、少量第二相以及大量黑色细颗粒组成。由于Sr在Mg中固溶度有限,因此,Sr不能充分溶入Mg晶格内,以第二相形式存在于晶界处,通过XRD分析表明第二相为Mg41Nd5和Mg17Sr2[23]。此外,前期工作已分析在α-Mg晶粒内观察到的颗粒状和针状黑色细颗粒为富Zr化合物[19]。
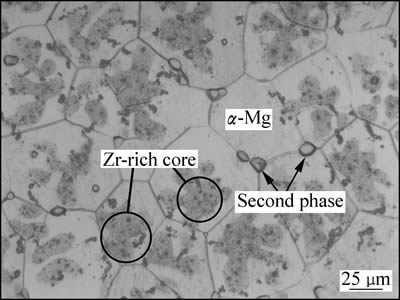
图2 固溶态Mg-Nd-Sr-Zr合金显微组织
Fig. 2 Microstructure of solution treated Mg-Nd-Sr-Zr alloy
2.3 XRD与XPS分析
图3所示为镁合金注入Gd前后的XRD谱。由图3可以看出,基体镁合金的XRD谱主要以典型的α-Mg衍射峰为主,还有少量的Mg41Nd5和Mg17Sr2第二相衍射峰。经Gd离子注入后,镁合金的衍射谱中除了α-Mg和第二相衍射峰外,还出现Gd2O3、Nd2O3、Gd等衍射峰,且随着注入剂量的增加,衍射峰的相对强度呈增强趋势。此外,将图中局部衍射谱放大可以发现,离子注入后,α-Mg衍射峰发生偏移,这说明局部晶格发生变化,其原因可能是离子轰击镁合金表面时,发生原子碰撞或塑性变形,导致其晶格内产生内应力[24-25]。
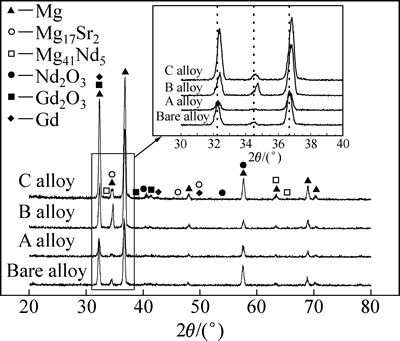
图3 镁合金注入Gd前后的XRD谱
Fig. 3 XRD patterns of magnesium alloy before and after Gd implantation
由于注入层的厚度较薄(约80 nm),此时XRD采集的注入层物相信号有限,因此,本实验中采用XPS对注入层(B合金)进行了进一步分析。为提高信号收集量,首先采用氩离子将注入镁合金溅射至Gd浓度最高处(即距表面约40 nm的深度处),由此得到XPS谱如图4所示。从图4可以看出,注入层中有Mg、Nd、Gd、Sr、Zr、O及C等元素出现。O元素源于真空室中残余的空气或氧化,C元素可能来源于清洗的乙醇溶液或外来杂质,Sr和Zr元素是镁合金的组成元素,但注入层中的含量较少。图5所示为Mg 1s、Gd 4d及Nd 3d的XPS谱。从图5(a)中可以看出,Mg 1s存在能量为977.50 eV的峰位,对应MgO。图5(b)所示的Gd 4d出现了双峰结构,能量分别为142.7和148.1 eV,对应Gd 4d5/2和Gd 4d3/2,分别与Gd及Gd2O3峰位值相吻合[26]。Nd 3d同样存在977.50和983.10 eV两个峰位(见图5(c)),与Nd2O3峰位值对应[27]。由上述XPS测试结果可知,Gd离子注入Mg-Nd-Sr-Zr合金后,其表面形成由Gd2O3、Nd2O3、少量MgO及金属态Gd组成的混合层,该测试结果与XRD测试结果基本吻合。
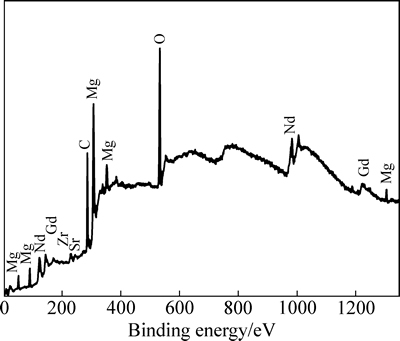
图4 注入层的XPS全谱图
Fig. 4 XPS survey spectra of implanted layer
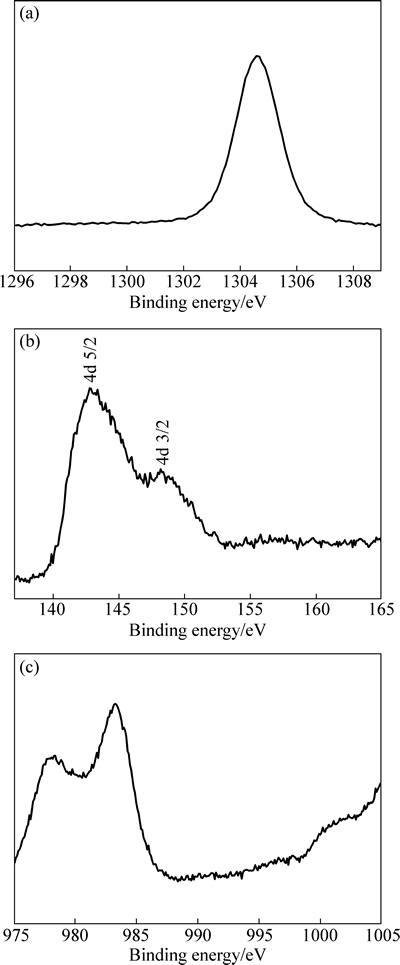
图5 注入层中Mg 1s峰、Gd 4d峰及Nd 3d峰的高分辨谱图
Fig. 5 High-resolution XPS spectra of Mg 1s (a), Gd 4d (b) and Nd 3d (c) peakes of implanted layer
2.4 生物腐蚀行为分析
图6所示为基体镁合金和注入镁合金在SBF溶液中浸泡1 h的极化曲线。由图6可知,Gd离子注入后,镁合金的极化曲线向正电位方向移动,说明Gd离子注入增强了镁合金在SBF中的耐蚀性能。由极化曲线拟合得到的腐蚀电位与腐蚀电流密度如表1所示。由拟合数据可知,随注入剂量的增加,镁合金的腐蚀电位不断升高,腐蚀电流密度先降低后上升。腐蚀电流密度与腐蚀速率密切相关,且腐蚀电流密度越小,腐蚀速率越慢。当注入剂量为5×1016 cm-2时,注入镁合金(即B合金)的腐蚀电流密度最小,为6.7μA/cm2,低于基体两个数量级,说明B合金在SBF中的腐蚀速率最慢。但注入剂量继续增加,注入镁合金的腐蚀速率又开始加快,说明过高剂量的Gd离子注入会削弱镁合金耐蚀性能增强程度。
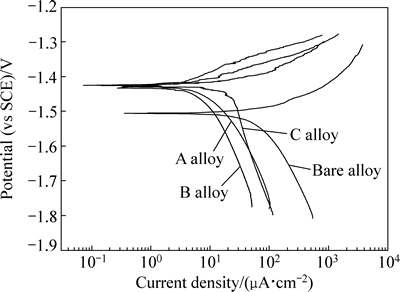
图6 基体镁合金和注入镁合金在SBF溶液中的极化曲线
Fig. 6 Polarization curves of bare and implanted magnesium alloys in SBF
表1 合金的极化曲线拟合结果
Table 1 Fitted results of polarization curves of alloys

图7所示为基体镁合金与注入镁合金在SBF中氢气析出量随浸泡时间的变化曲线。由图7可见,3种注入镁合金表现出相同的析氢趋势,随着浸泡时间延长,氢气析出量先升高后逐渐趋于稳定,其中A合金的析氢量最少,B合金的次之,C合金的最多。而基体镁合金的氢气析出量随着浸泡时间延长不断升高,且其析氢量明显多于上述3种注入合金的析氢量。与基体相比,A、B、C 3种合金的腐蚀速率分别降低81%、79%和70%,这说明Gd离子注入能有效抑制镁合金在SBF中的腐蚀速率,且A合金在SBF中的腐蚀速率最小,但注入剂量过高,镁合金耐蚀性增强程度降低。浸泡初期,合金的析氢量最少,可能源于其表面形成了保护膜,在一定程度上抑制了合金的腐蚀。
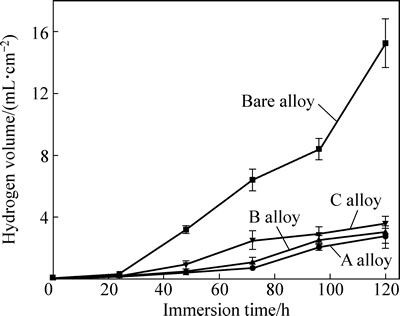
图7 基体镁合金与注入镁合金在SBF中的析氢曲线
Fig. 7 Hydrogen evolution curves of bare and implanted alloys in SBF
通过电化学实验及析氢实验分析可知,经Gd离子注入后,镁合金在SBF中的腐蚀速率明显减慢,且过高剂量的离子注入会减弱对镁合金腐蚀的抑制作用。但电化学实验与析氢实验反映出的结果略有不同,电化学实验显示B合金在SBF中的腐蚀速率最小,而析氢实验表明A合金在SBF中腐蚀最慢。这与两种测试方法的固有属性有关,电化学实验测试的是瞬时结果,数据稳定性弱;析氢实验能够真实反映出腐蚀速率随时间变化的本质[28]。因此,对评价镁合金的降解行为而言,析氢实验的测试结果比电化学实验测试结果更可靠。
图8所示为基体镁合金与注入镁合金(A合金)在SBF中浸泡120 h后的腐蚀形貌图。由图8可以看出,基体镁合金表面附着一层厚厚的腐蚀产物,合金表面完全腐蚀,而注入镁合金表面均匀分布着较少的腐蚀产物,且仍存在未腐蚀区域。这进一步说明离子注入后,镁合金的腐蚀速率降低。
镁合金在SBF中发生腐蚀主要源于溶液中Cl-的侵蚀。在水溶液中,镁合金中的镁元素与水反应,在表面生成疏松的Mg(OH)2,在一定程度上阻碍了腐蚀溶液中有害离子的侵蚀,因此,在腐蚀初期,镁合金腐蚀速率缓慢。然而,随着腐蚀时间的延长,溶液中的Cl-渗入Mg(OH)2中,将其转变为可溶性MgCl2,造成合金表面Mg溶解,形成腐蚀[29-30]。
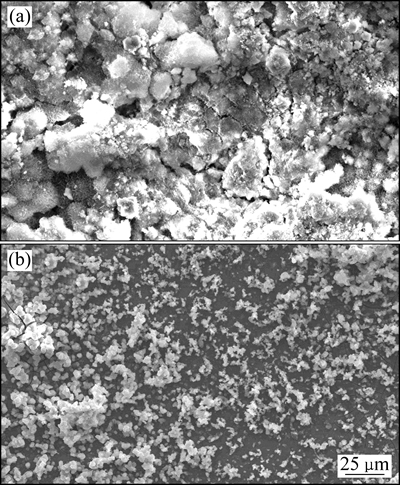
图8 基体镁合金与注入镁合金在SBF中浸泡120 h后的腐蚀形貌
Fig. 8 Corrosion morphologies of bare (a) and implanted (b) alloys immersed in SBF for 120 h
由于基体镁合金中没有连续分布的耐蚀性第二相(见图2),对Cl-等缺乏足够的抵制能力[31],同时,少量的第二相和富Zr化合物与基体镁之间形成微电偶,从而加速Cl-对镁合金表面侵蚀[31-32],因此,基体中Mg溶解加快。而镁合金经Gd离子注入后,镁合金的耐蚀性增强,这与其表面形成的改性层有关。由于改性层中Gd2O3[33]和Nd2O3[34]等在溶液中稳定,能够有效阻碍Cl-向内部镁合金基体传递,从而降低了Cl-与基体表面接触率,减缓了基体中Mg溶解速度。此外,实验中还发现,当注入剂量过大(1×1017 cm-2)时,离子注入的改性效果下降,WANG等[35-36]也发现类似的情况,这归因于注入离子对镁合金晶格产生损伤作用,弱化改性层的保护能力,且注入剂量越大,对改性层损伤越严重,其保护效果下降[35-36]。由本实验可知,离子注入后镁合金表面晶格发生了变化。这可能是由于离子轰击造成晶格内产生内应力,从而导致离子注入改性效果减弱,其原因还需要进行进一步的研究。
3 结论
1) 由SRIM 2008软件模拟可知,Gd元素在镁合金表层中呈高斯分布,最大深度约80 nm,且在距离表面约40 nm深度处,Gd元素浓度达到最高。
2) 固溶态Mg-Nd-Sr-Zr合金经Gd离子注入后,在其表面形成了由Gd2O3、Nd2O3、少量MgO及金属态Gd组成的改性层。
3) 经Gd离子注入后,镁合金在SBF中的腐蚀速率明显减慢,但离子注入剂量过高,会削弱镁合金耐蚀性增强程度。析氢实验结果更可靠反映出镁合金在SBF中的生物腐蚀行为,当注入剂量为2.5×1016 cm-2时,注入镁合金的腐蚀速率最低,与基体相比,其腐蚀速率降低81%。
REFERENCES
[1] WU G S, IBRAHIM J M, CHU P K. Surface design of biodegradable magnesium alloys-a review[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2013, 233: 2-12.
[2] 章晓波, 薛亚军, 王章忠, 贺显聪, 王 强. Mg-(4-x)Nd-xGd-Sr-Zn-Zr 生物镁合金的组织、力学和腐蚀性能[J]. 金属学报, 2014, 50(8): 979-988.
ZHANG Xiao-bo, XUE Ya-jun, WANG Zhang-zhong, HE Xian-cong, WANG Qiang. Microstructure, mechanical and corrosion properties of Mg-(4-x)Nd-xGd-Sr-Zn-Zr biomagnesium alloys[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2014, 50(8): 979-988.
[3] WAN Y Z, XIONG G Y, LUO H L. Influence of zinc ion implantation on surface nanomechanical performance and corrosion resistance of biomedical magnesium-calcium alloys[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2008, 254(17): 5514-5516.
[4] 章晓波, 袁广银, 王章忠. 铸造镁合金Mg-Nd-Zn-Zr的生物腐蚀性能[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2013, 23(4): 905-911.
ZHANG Xiao-bo, YUAN Guang-yin, WANG Zhang-zhong. Biocorrosion properties of as-cast Mg-Nd-Zn-Zr magnesium alloy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2013, 23(4): 905-911.
[5] WU G S, ZHANG X M, ZHAO Y, IBRAHIM J M, YUAN G Y, CHU P K. Plasma modified Mg-Nd-Zn-Zr alloy with enhanced surface corrosion resistance[J]. Corrosion Science, 2014, 78: 121-129.
[6] YAN Ting-ting, TAN Li-li, XIONG Dang-sheng, LIU Xin-jie, ZHANG Bing-chun, YANG Ke. Fluoride treatment and in vitro corrosion behavior of an AZ31B Mg alloy[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2010, 30(5): 740-748.
[7] 方信贤, 章晓波, 王 强, 巴志新, 王章忠. 镁合金表面氟化镁钠膜形成机制及其生物腐蚀性能[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2014, 24(5): 1285-1292.
FANG Xin-xian, ZHANG Xiao-bo, WANG Qiang, BA Zhi-xin, WANG Zhang-zhong. Formation mechanism and bio-corrosion properties of NaMgF3 film on surface of magnesium alloy[J].The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2014, 24(5): 1285-1292.
[8] SANTHANAKRISHNAN S, HO Y H, DAHOTRE N B. Laser coating of hydroxyapatite on Mg for enhanced physiological corrosion resistance and biodegradability[J]. Materials Technology, 2012, 27: 273-277.
[9] TALTAVULL C, TORRES B, LOPEZ A J, RODRIGO P, OTERO E, ATRENS A, RAMS J. Corrosion behaviour of laser surface melted magnesium alloy AZ91D[J]. Materials Design, 2014, 57: 40-50.
[10] LIN X, YANG X M, TAN L L, LI M, WANG X, ZHANG Y, YANG K, HU Z Q, QIU J H. In vitro degradation and biocompatibility of a strontium-containing micro-arc oxidation coating on the biodegradable ZK60 magnesium alloy[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2014, 288: 718-726.
[11] YANG X M, LI M, LIN X, TAN L L, LAN G B, LI L H, YIN Q S, XIA H, ZHANG Y, YANG K. Enhanced in vitro biocompatibility/bioactivity of biodegradable Mg-Zn-Zr alloy by micro-arc oxidation coating contained Mg2SiO4[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2013, 233: 65-73.
[12] ZHAO Y, JAMESH M I, LI W K, WU G S, WANG C X, ZHANG Y F, YEUNG K W K, CHU P K. Enhanced antimicrobial properties, cytocompatibility, and corrosion resistance of plasma-modified biodegradable magnesium alloys[J]. Acta Biomaterialia, 2014, 10: 544-556.
[13] WU G S, XU R Z, FENG K. Retardation of surface corrosion of biodegradable magnesium- based materials by aluminum ion implantation[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2012, 258(15): 7651-7657.
[14] WU G S, GONG L, FENG K. Rapid degradation of biomedical magnesium induced zinc ion implantation[J]. Materials Letters, 2011, 65(4): 661-663.
[15] WANG Z Z, TAO X W, ZHANG X B, BA Z X, WANG Q. Corrosion behaviour of Nd ion implanted Mg-Gd-Zn-Zr alloy in simulated body fluid[J]. Materials Technology, 2015, 30(6): 321-325.
[16] JIN W H, WU G S, FENG H Q, WANG W H, ZHANG W M, CHU P K. Improvement of corrosion resistance and biocompatibility of rare-earth WE43 magnesium alloy by neodymium self-ion implantation[J]. Corrosion Science, 2015, 94: 142-155.
[17] WANG W J, ZHANG X L, WU G S, WANG C X, CHU P K. Praseodymium-surface- modified magnesium alloy: Retardation of corrosion in artificial hands weat[J]. Materials Letters, 2016, 163: 85-89.
[18] GEROLD B. Implant with a base body of a biocorrodible magnesium alloy[P]. US 8268235 B2, 2012-09-18.
[19] ZHANG X B, WU Y J, XUE Y J, WANG Z Z, YANG L. Biocorrosion behavior and cytotoxicity of a Mg-Gd-Zn-Zr alloy with long period stacking ordered structure[J]. Materials Letters, 2012, 86: 42-45.
[20] ZHANG Xiao-bo, BA Zhi-xin, WANG Zhang-zhong, XUE Ya-jun, WANG Qiang. Microstructure and biocorrosion behaviors of solution treated and as-extruded Mg-2.2Nd-xSr-0.3Zr alloys[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2014, 24: 3797-3803.
[21] TAO X W, WANG Z Z, ZHANG X B, BA Z X, WANG Y M. Nanomechanical and corrosion properties of ZK60 magnesium alloy improved by Gd ion implantation[J]. Surface Review and Letters, 2014, 21(6): 1450085- (1-6).
[22] 张通河, 吴瑜光. 离子注入表面优化技术[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 1993.
ZHANG Tong-he, WU Yu-guang. Optimizing pressing of ion implantation[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 1993.
[23] ZHANG X B, HE X C, XUE Y J, WANG Z Z, WANG Q. Effects of Sr on microstructure and corrosion resistance in simulated body fluid of as cast Mg-Nd-Zr magnesium alloys[J]. Corrosion Engineering, Science and Technology, 2014, 49(5): 345-351.
[24] LIU B J, DENG B, TAO Y. Influence of niobiumion implantation on the microstructure, mechanical and tribological properties of TiAlN/CrN nano-multilayer coatings[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2014, 240: 405-412.
[25] LIU H X, XU Q, JIANG Y H, WANG C Q, ZHANG X W. Corrosion resistance and mechanical property of AZ31 magnesium alloy by N/Ti duplex ion implantation[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2013, 228: 538-543.
[26] RAISER D, DEVILLE J P. Study of XPS photoemission of some gadolinium compounds[J]. Journal of Electron Spectroscopy and Related Phenomena, 1991, 57(1): 91-97.
[27] UWAMINO Y, ISHIZUKA T, YAMATERA H. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy of rare-earth compounds[J]. Journal of Electron Spectroscopy and Related Phenomena, 2012, 34(1): 67-78.
[28] KIRKLAN N T, BIRBILIS N, STAIGER M P. Assessing the corrosion of biodegradable magnesium implant: a critical review of current methodologies and their limitations[J]. Acta Biomaterialia, 2012, 8: 925-936.
[29] ARDELEAN H, SEYEUX A, ZANNA S, PRIMA F, FRATEUR I. MARCUS P. Corrosion processes of Mg-Y-Nd-Zr alloys in Na2SO4 electrolyte[J]. Corrosion Science, 2013, 73: 196-207.
[30] ZHAO Y Z, WU G S, LIU Q, WU J, XU R,YEUNG K W K, CHU P K. Improved surface corrosion resistance of WE43 magnesium alloy by dual titanium and oxygen ion implantation[J]. Thin Solid Films, 2013, 529: 407-411.
[31] 刘 俊, 陈明安, 马聪聪, 黄宇迪, 张新明, 邓运来. 第二相粒子在Mg-Gd-Y-Nd-Zr合金局部腐蚀中的作用机制[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2013, 23(1): 15-21.
LIU Jun, CHEN Ming-an, MA Cong-cong, HUANG Yu-di, ZHANG Xin-ming, DENG Yun-lai. Effect of second phase particles on localized corrosion of Mg-Gd-Y-Nd-Zr alloy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2013, 23(1): 15-21.
[32] SUN M, WU G H, WANG W, DING W J. Effect of Zr on the microstructure, mechanical properties and corrosion resistance of Mg-10Gd-3Y magnesium alloy[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2009, 523: 145-151.
[33] UNE K, KASHIBE S, NOGITA K. Corrosion behavior of unirradiated oxide fuel pellets in high temperature water[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 1995, 227(1/2): 32-39.
[34] CHEVALIERA S, BONNETB G, LARPINA J P. Metal-organic chemical vapor deposition of Cr2O3 and Nd2O3 coatings. Oxide growth kinetics and characterization[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2000, 167: 125-133.
[35] WANG X M, ZENG X Q, YAO S S, WU G S, LAI Y J. The corrosion behavior of Ce-implanted magnesium alloys[J]. Materials Characterization, 2008, 59(5): 618-623.
[36] WANG X M, ZENG X Q, WU G S, YAO S S. Yttrium ion implantation on the surface properties of magnesium[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2006, 253: 2437-2442.
Effect of Gd ion implantation on biocorrosion behavior of solution treated Mg-Nd-Sr-Zr alloy
TAO Xue-wei1, 2, WANG Zhang-zhong1, 2, ZHANG Xiao-bo1, 2, BA Zhi-xin1, 2, DONG Qiang-sheng1, 2
(1. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Nanjing Institute of Technology, Nanjing 211167, China;
2 Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Advanced Structural Materials and Application Technology,
Nanjing Institute of Technology, Nanjing 211167, China)
Abstract: Gadolinium (Gd) ion implantation was carried out to modify the solution-treated Mg-Nd-Sr-Zr alloy. The SRIM 2008 software was used to simulate the Gd ion implantation. The microstructure of alloy was observed by optical microscopy (OM). The phases were analyzed by X-ray diffractometry (XRD), and the chemical composition and element states of modified layer were characterized by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). The biocorrosion behavior of the bare and Gd-implanted alloys in simulated body fluids (SBF) was evaluated by electrochemical tests and hydrogen evolution tests. The results show that the biocorrosion resistance of solution treated Mg-Nd-Sr-Zr alloy is enhanced after Gd ion implantation. When the implantation dose is 2.5×1016 cm-2, the implanted alloy has the optimal anti-biocorrosion performance.
Key words: magnesium alloy; Gd; ion implantation; biocorrosion behavior
Foundation item: Project(51301089) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project supported by Qing Lan Project of Jiangsu Province, China
Received date: 2015-06-29; Accepted date: 2015-12-02
Corresponding author: WANG Zhang-zhong; Tel: +86-025-86118275; E-mail: zzww@njit.edu.cn
(编辑 龙怀中)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(51301089);江苏省“青蓝工程”资助项目
收稿日期:2015-06-29;修订日期:2015-12-02
通信作者:王章忠,教授;电话:025-86118275;E-mail:zzww@njit.edu.cn