新型竹活性炭对水体违禁药物孔雀石绿吸附性能的影响
谭艳芝,王秀芳,钟国英
(广东药学院 药科学院,广东 广州,510006)
摘 要:
摘 要:为去除水体残留的违禁药物孔雀石绿,采用自制竹活性炭以及3种市售竹炭为吸附剂,将孔雀石绿溶液作为吸附体系,研究27,35和40 ℃时孔雀石绿在活性炭上的吸附平衡与动力学,检测违禁药物孔雀石绿的残留量,并对自制和市售吸附剂的吸附性能进行对比。研究结果表明:高比表面积活性炭对废水中残留孔雀石绿去除效果明显;Freundlich吸附等温线模型可较好地用于描述孔雀石绿在活性炭上的吸附平衡,Freundlich常数KF随比表面积和孔容的增大而增大,自制竹活性炭性能更佳;准二级方程可用于描述孔雀石绿在活性炭上吸附的最佳动力学模型,并可得到相应动力学参数;对同一种吸附剂,温度对吸附动力学速率常数有较大的影响,在35 ℃时,速率常数最小。
关键词:
中图分类号:TQ424 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2010)04-1287-05
Effect of novel bamboo-based activated carbons on adsorption properties of prohibited drug malachite green in aquatic system
TAN Yan-zhi, WANG Xiu-fang, ZHONG Guo-ying
(College of Pharmacy, Guangdong Pharmaceutical University, Guangzhou 510006, China)
Abstract: For the removal of residue Malachite green which is highly poisonous and carcinogenic, the adsorption equilibrium and dynamics of malachite green from aqueous solution on three commercial bamboo charcoals and a self-prepared bamboo-based activated carbon were determined at 27, 35 and 40 ℃. The residue of malachite green was detected. At the same time, comparison between the self-prepared and three commercial adsorbents was made. The experimental results show that activated carbons with high specific surface area are effective adsorbents for the removal of residue malachite green in wastewater. Freundlich equation is the best for describing the adsorption equilibrium of residue malachite green on activated carbons. Freundlich constant KF varies with the increase of BET surface area and pore volume. The adsorption property of the self-prepared bamboo-based activated carbon is better than that of the commercial adsorbents. The pseudo-second-order equation is proved to be the best for describing the dynamic adsorption, and the dynamic parameters are calculated and the dynamic parameters are obtained. As for the same kind of adsorbent, temperature has a great influence on the dynamic adsorption rate constant, which is the smallest at 35 ℃.
Key words: activated carbon; malachite green; adsorption equilibrium; dynamics
孔雀石绿(Malachite green)是一种有毒的三苯甲烷类化学物,既是染料,也是杀菌剂,可用于治理鱼类或鱼卵的寄生虫、真菌或细菌感染,其功效显 著,但它具有高毒性、高残留、致畸、致癌、致突变等副作用[1-2],很多国家已经禁用,可有部分渔民为了防治鱼类感染真菌仍在使用,也有运输商用于消毒以延长鱼类长途贩运的存活时间。国内市场调查结果表明:我国很多地方尤其是在水产养殖业和水产品贩运中,孔雀石绿仍在普遍使用[3]。2002年我国农业部将孔雀石绿列入《食品动物禁用的兽药及其化合物清单》,禁止用作所有食品动物原料。国家质检总局、国家标准委发布实施了国家标准,要求孔雀石绿在水产品中的检出率不得超过1 g/kt,因此,迫切需要一种高效吸附剂对孔雀石绿进行吸附处理,以便最大限度地减小孔雀石绿对环境乃至人类的危害。活性炭是一种优良的吸附材料,具有丰富的孔隙结构和较高的比表面积,广泛应用于化工制药、环境保护、食品加工、电极材料和催化剂载体等领域[4-12]。由于活性炭的生物相容性极佳,无毒副作用,近年来受到医药行业的极大关注。目前,活性炭作为一种高效吸附剂在药物吸附领域的应用已成为研究热点[13-16]。国内相继开展了活性炭对扑热息痛的吸附行为和体外释放性能及对万古霉素等7种抗生素吸附的实验研究[13],但有关用活性炭作为高效吸附剂,有效去除残留孔雀石绿的研究很少。为此,本文作者选用自制高性能竹活性炭以及3种市售竹炭为吸附剂,以孔雀石绿溶液作为吸附体系,测定常温下4种吸附剂对孔雀石绿的吸附等温线,并测试自制活性炭吸附剂在27,35和40 ℃时的吸附动力学,研究不同温度下竹活性炭对孔雀石绿的吸附处理和检测违禁药物残留量,并研究活性炭对孔雀石绿高效吸附的可行性。
1 实验
1.1 实验原料及仪器
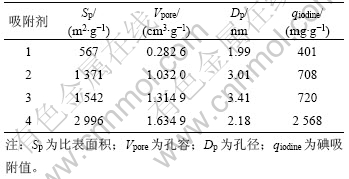
实验原料为:孔雀石绿(分析纯);吸附剂,分别是3种市售竹炭和 1 种自制活性炭,编号分别为样品1~4,相关孔结构参数见表1。其中:样品1,2和3是由竹材干馏炭化生成,粒径均为180~380 μm;4号样品用竹屑为原料,采用KOH活化法在活化温度为 800 ℃、浸渍比为1.0和活化时间为2 h 的条件下制得,粒径为150~180 μm。为防止活性炭表面和孔隙内部存在的无机盐以及其他杂质的干扰,在使用前需进行预处理,即首先将样品在去离子水中煮沸1 h,滤去水及粉尘,在110 ℃干燥24 h,密封,备用。
表1 吸附剂的孔结构参数
Table 1 Pore diameters of various adsorbents
仪器为ASAP 2010型物理吸附仪(Micrometrics)和TU-1810型紫外分光光度计。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 吸附平衡实验
采用瓶点试验法,即分别将不同质量的活性炭样品放入一组6个100 mL的具塞三角烧瓶中,再加入体积V =100 mL、初始质量浓度ρ0=10 mg/L的孔雀石绿溶液,在常温下充分振荡后,静置24 h至吸附平衡。根据平衡前、后孔雀石绿浓度的变化求出吸附容量,用qe表示。
1.2.2 力学吸附实验
采用间隔取样法,即将一定量的活性炭样品(1 g)在搅拌下加入初始质量浓度为10 mg /L的孔雀石绿溶液中,同时开始计时,间隔取样,测定水溶液中孔雀石绿残余质量浓度(ρt) 随时间(t)的变化规律,求出t时刻单位质量的活性炭所吸附的溶质量qt。所有浓度均在波长617.0 nm处测定。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 吸附剂的孔结构特征
采用物理吸附仪(ASAP 2010,Micrometrics),用静态吸附法测定了4种吸附剂于77 K时的N2吸附等温线,结果如图1所示。图2所示为4号竹活性炭的孔径分布。BET比表面积(Sp)由Brunauer-Emmett- Teller(BET)方程计算而得,氮分子的横截面积取0.162 nm2;孔容(Vpore)和孔径分布采用Barrett-Joyner- Halenda(BJH)模型测定。碘吸附值(qiodine)根据美国国家标准ASTM D4607—94进行测定,结果见表1。由图1和表1可知:随着相对压力p/p0从0增大至1.0,4种吸附剂的氮气吸附量均随相对压力的增大而增大,达到一定值后趋于平衡;在一定相对压力p/p0下,随着吸附剂比表面积从567 m2/g增大到3 135 m2/g,相应的氮气吸附量、碘吸附值和总孔容也依次增大。这充分说明所选用的活性炭具有发达的孔隙结构;1号活性炭比表面积最小,4号竹活性炭的比表面积最大,氮气吸附量和碘吸附值也最大。
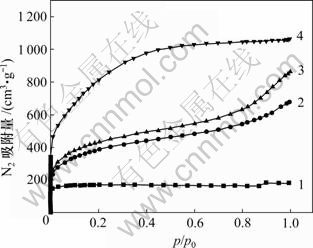
1—吸附剂1;2—吸附剂2;3—吸附剂3;4—吸附剂4
图1 温度为77 K时4种吸附剂的N2吸附等温线
Fig.1 N2 adsorption isotherms of various adsorbents at 77 K
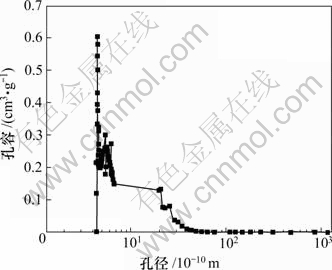
图2 4号吸附剂的孔径分布
Fig.2 Pore distribution of adsorbent type 4
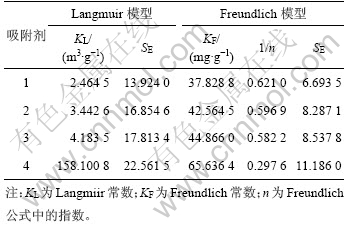
为研究活性炭对水体违禁药物孔雀石绿残留的应用可行性,测定了常温下4种吸附剂对孔雀石绿的吸附等温线,并测试了吸附性能最强的4号吸附剂在27,35和40 ℃时的吸附平衡与动力学。根据Langmuir和Freundlich吸附等温线模型,利用最小二乘法分别对实验吸附平衡数据进行拟合,拟合结果见表2。
2.2 孔雀石绿在吸附剂上的吸附平衡
Langmuir吸附等温线模型是基于吸附剂的表面只能发生单分子层吸附的假设提出的;Freundlich吸附等温线模型则提供了一种单组分吸附平衡的经验描 述,应用范围较广。为便于吸附等温线方程的实际应用,分别计算了平均方差之和SE,结果如表2所示。由表2可见:
(1) Freundlich吸附等温线方程计算的平均方差之和SE均明显比由Langmuir方程所得的小,表明孔雀石绿在活性炭上的吸附等温线能较好地用Freundlich吸附等温线模型来表示。这是因为Langmuir模型是1个理想的吸附公式,它表示在均匀表面上吸附分子彼此没有相互作用,且吸附是单分子层情况下吸附达到平衡时的规律性,对于具体体系还需修正。
(2) 随着吸附剂比表面积和孔容的增大,拟合所得到的常数KF逐渐增大,其中4号自制吸附剂的KF最大;此外,吸附剂的吸附性能与比表面积有直接关系,但要达到较好的有效吸附效果,还要考虑孔径、孔容等结构参数与吸附质的相互作用。
表2 由Langmuir和Freundlich吸附等温线模型拟合得到的参数
Table 2 Parameters obtained by fitting of Langmuir and Freundlich equations
2.3 动力学吸附
准二级方程是在吸附平衡基础上建立的,表达式为:
![]() (1)
(1)
式中:qe为平衡时吸附剂对吸附质的吸附量;qt为时间t时吸附剂对吸附质的吸附量;k2为二级吸附反应速度常数;t为反应时间。k2和qe可以通过t/qt与t关系曲线求得,不必要预先知道其他参数。
粒子内扩散模型也被用来证明吸附质-吸附剂之间的作用机理。在1个快速搅拌的间歇反应器中,当活性炭加到孔雀石绿溶液时,吸附质会因粒子内扩散/转移过程从本体溶液转移到固相中。数学表达式为:
![]() (2)
(2)
其中:kp为粒子内扩散速率常数;C为曲线截距。
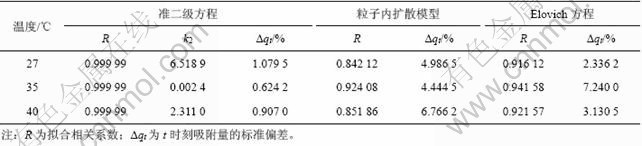
表3 采用准二级方程、粒子内扩散模型、Elovich方程分别拟合得到的参数
Table 3 Parameters obtained by fitting of pseudo-second-order equation, intra-particle diffusion model and Elovich equation
Elovich方程[13]是用来描述此类“活化”化学吸附的最有用的模型之一,其表达式为:
![]() (3)
(3)
其中:a和b为常数。
本研究测定了27,35和40 ℃时孔雀石绿在4号吸附剂上的动力学吸附曲线,结果如图3所示。为验证以上模型的真实性,分别采用粒子内扩散模型作qt与t1/2的关系图,采用准二级方程作t/qt与t的关系图,采用Elovich作qt与lnt关系图,对孔雀石绿在活性炭上的动力学吸附行为进行拟合分析,分析结果见表3。同时,还分别根据式(4)计算了每一个模型t时刻吸附量的归一化标准偏差?qt:
![]() (4)
(4)
其中:N为数据点个数;qt,exp为t时刻吸附量实验值;qt,cal为t时刻吸附量理论值。
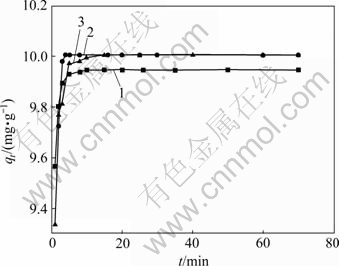
温度/℃:1—27;2—35;3—40
图3 孔雀石绿在4号吸附剂上的qt随时间t的变化
Fig.3 Relationship between qt and t for adsorbent type 4
从图3和表3可看出:随着温度的升高,吸附容量逐渐增大,采用粒子内扩散模型和Elovich方程并不适合,由该方法拟合得到的相关系数R与1有较大偏离,线性关系不太明显,标准偏差均较大。这是由于Elovich方程式是基于t≥t0的假设建立起来的,孔雀石绿在本研究中吸附剂表面上的吸附可能还受吸附剂表面官能团的影响,从而使得吸附速率有较大偏 差。由准二级方程拟合得到的曲线有很好的线性关系,R几乎趋于1;标准偏差均明显低于由粒子内扩散模型和Elovich 方程拟合得到的标准偏差,由此可以判断准二级方程是用来描述不同温度下孔雀石绿在活性炭上吸附的较好动力学模型;对同一种吸附剂,吸附体系的温度对吸附速率常数有较大的影响,35 ℃时速率常数最小。
3 结论
(1) 活性炭对水体残留孔雀石绿去除效果显著,与商用竹炭相比,自制高比表面积竹活性炭吸附效果更好。本研究为废水中孔雀石绿在活性炭上的吸附提供了科学依据。
(2) Freundlich吸附等温线模型可较好地用来描述孔雀石绿在竹活性炭上的吸附平衡。
(3) 准二级方程是用来描述孔雀石绿在竹活性炭上吸附的最佳动力学模型,在35 ℃时其吸附速率常数最小。
参考文献:
[1] Rao K V K. Inhibition of DNA synthesis in primary rat hepatocyte cultures by malachite green: A new liver tumor promoter[J]. Toxicol Lett, 1995, 81(2/3): 107-113.
[2] Gouranchat C. Malachite green in fish culture (state of the art and perspectives)[R]. France: Ecole Natl, 2000: 142.
[3] 翟毓秀, 郭莹莹, 耿霞, 等. 孔雀石绿的代谢机理及生物毒性研究进展[J]. 中国海洋大学学报: 自然科学版, 2007, 31(1): 27-30.
ZHAI Yu-xiu, GUO Ying-ying, GENG Xia, et al. Advances in studies on metabolic mechanism and bio-toxicity of malachite green[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2007, 31(1): 27-30.
[4] Murakami T, Ajima K, Miyawaki J, et al. Drug-loaded carbon nanohorns:![]() Adsorption and release of dexamethasone in vitro[J]. Molecular Pharmaceutics, 2004, 1(6): 399-405.
Adsorption and release of dexamethasone in vitro[J]. Molecular Pharmaceutics, 2004, 1(6): 399-405.
[5] Wei Y Z, Fang B, Iwasa S, et al. A novel electrode material for electric double-layer capacitors[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2005, 141(2): 386-391.
[6] 王秀芳, 田勇, 张会平. 高比表面积煤质活性炭的制备与活化机理[J]. 化工学报, 2009, 60(3): 733-737.
WANG Xiu-fang, TIAN Yong, ZHANG Hui-ping. Preparation and activation mechanism of high specific surface area coal-based activated carbon[J]. CIESC Journal, 2009, 60(3): 733-737.
[7] 王晓静, 胡中华, 陈玉娟, 等. 以偏钛酸为原料制备高效负载型纳米TiO2/活性炭光催化剂[J]. 化学学报, 2008, 66(22): 2445-2450.
WANG Xiao-jing, HU Zhong-hua, CHEN Yu-juan, et al. High performance supported photocatalyst of nano-TiO2/activated carbon from metatitanic acid[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2008, 66(22): 2445-2450.
[8] WANG Xiu-fang, TIAN Yong, SONG Guo-sheng, et al. Synthesis and characterization of bimodal rodlike mesoporous carbons from raffinose by SBA-15 templates[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2010, 45(11): 2958-2966.
[9] Li X T, Chen X H, Song H H. Synthesis of beta-SiC nanostructures via the carbothermal reduction of resorcinol- formaldehyde/SiO2 hybrid aerogels[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2009, 44(17): 4661-4667.
[10] Inomata K, Otake Y. Nanoscopic observation of mesoporous carbons prepared by catalytic carbonization of Fe- and Ni-containing phenol formaldehyde resins[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2009, 44(15): 4200-4204.
[11] 鲁建江, 李维军, 陈景文, 等. 活性炭吸附-微波催化氧化处理番茄酱加工有机废水[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2009, 32(3): 139-142.
LU Jian-jiang, LI Wei-jun, CHEN Jing-wen, et al. Treatment of organic wastewater from tomato paste processing by microwave catalytic oxidation process with activated carbon[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2009, 32(3): 139-142.
[12] 余琼粉, 易红宏, 唐晓龙, 等. 磷化氢在活性炭上的吸附及吸附等温线的预测[J]. 武汉理工大学学报, 2010, 32(1): 34-37.
YU Qiong-fen, YI Hong-hong, TANG Xiao-long, et al. Adsorption and prediction of adsorption isotherm onto activated carbon[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology, 2010, 32(1): 34-37.
[13] 赵旺胜, 唐新, 童明庆. 活性炭体外对万古霉素等7种抗生素吸附的实验研究[J]. 中华医院感染学杂志, 2002, 12(1): 18-20.
ZHAO Wang-sheng, TANG Xin, TONG Ming-qing. Adsorbent ability of active carbon for seven antibiotics as vancomycin and so on in vitro[J]. Chinese Journal of Nosoconmiology, 2002, 12(1): 18-20.
[14] 梁晓, 王凤娇, 唐婧. 活性炭对水中苯酚的吸附[J]. 内蒙古环境科学, 2009, 21(6): 141-143.
LIANG Xiao, WANG Feng-jiao, TANG Jing. The adsorption of phenol in water with activate carbon[J]. Inner Mongolia Environmental Protection, 2009, 21(6): 141-143.
[15] 梁寒, 唐贺文, 郝希山. 活性炭吸附丝裂霉素C腹腔化疗的药代动力学研究[J]. 中华肿瘤杂志, 2005, 27(7): 412-415.
LIANG Han, TANG He-wen, HAO Xi-shan. Pharmacokinetic study of intraperitoneal chemotherapy with mitomycin C bound to activated carbon particals[J]. Chinese Journal Oncology, 2005, 27(7): 412-415..
[16] 侯宝军, 乐清华, 周全, 等. 吸附-热再生法回收废水中醋酸的研究[J]. 高校化学工程学报, 2008, 22(4): 580-584.
HOU Bao-jun, LE Qing-hua, ZHOU Quan, et al. Recovery of acetic acid from wastewater by adsorption and heating regeneration[J]. Journal of Chemical Engineering of Chinese Universities, 2008, 22(4): 580-584.
收稿日期:2010-01-10;修回日期:2010-03-27
基金项目:广东省科技计划项目(2009B030802048)
通信作者:谭艳芝(1975-),女,湖南涟源人,博士研究生,讲师,从事多孔材料研究;电话:020-39352119;E-mail: swallowtyz@163.com
(编辑 陈灿华)


