DOI: 10.11817/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2021-35986
我国金属矿山废石资源化综合利用现状与发展
姚华辉1, 2,蔡练兵1, 3,刘 维1, 2,覃文庆1, 2,焦 芬1, 2,杨聪仁1, 2
(1.中南大学 资源加工与生物工程学院,长沙 410083;
2.中南大学 战略含钙矿物资源清洁高效利用湖南省重点实验室,长沙 410083;
3.湖南郴州金贵有色金属(集团)有限公司,郴州 4230383)
摘 要:
随着社会的发展,我国对矿产资源的需求日益增加,矿山废石的大量堆积不仅造成矿产资源的严重浪费,而且占据大量土地,还会带来严重的安全问题和环境污染。针对我国矿山废石堆存量大、增长快、废石种类及成分复杂、废石资源化综合利用率低等特点,本文总结了矿山废石的危害和现行的处理及利用方式,详述矿山废石用于回收有价金属及进一步的废石回填、覆土造田、制造建筑材料等主要处理方式的特点、发展及应用情况,并归纳展望矿山废石未来可能研究发展的重点方向,提出矿山废石资源化利用的可行性建议。指出矿山废石的资源化综合利用的跨区域集聚处理、多领域多产业协同处理和分类分段处理是日后研究的关键。确定矿山废石堆存量以及成分、粒度、有价金属的含量是矿山废石综合利用的重要前提。制定合理方案对矿山废石进行分类分段处理是提高矿山废石综合利用率的重要步骤。
关键词:
文章编号:1004-0609(2021)-06-1649-12 中图分类号:X751 文献标志码:A
引文格式:姚华辉, 蔡练兵, 刘 维, 等. 我国金属矿山废石资源化综合利用现状与发展[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2021, 31(6): 1649-1660. DOI: 10.11817/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2021-35986
YAO Hua-hui, CAI Lian-bing, LIU Wei, et al. Current status and development of comprehensive utilization of waste rock in metal mines in China[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2021, 31(6): 1649-1660. DOI: 10.11817/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2021-35986
矿业是社会发展的支柱行业,是人类生存发展的基石。随着现代化进程的快速推进,人们对矿产资源的需求量与日俱增,矿产资源开发的进程不断加快,矿产资源日渐枯竭,各类矿产资源逐渐向着贫、细、杂的方向发展。基于我国目前的矿产资源的特点和开发技术,矿产资源开发不可避免的会产生大量的废石、尾矿等矿山固体废弃物。矿石和非矿石的划分并不是绝对的,矿体中某种主要有用的元素含量达到了该种矿石的工业品位,就形成了工业矿床。但是矿石的工业品位不是一成不变的,它随着矿产资源的开发利用水平和经济可行性的变化而变化[1-2]。随着矿产资源的逐渐减少和开发利用水平的提高,原来矿产资源开发条件下被定义的废石也有可能变成矿石。对矿山废石的放任不管,或是仅简单堆存处理不仅会污染环境,而且会造成矿产资源和土地资源的严重浪费。因此,对矿山废石进行资源化利用既可以解决环境污染问题、缓解资源紧张问题,又可以提高企业的经济效益、促进可持续性发展。矿山废石的资源化利用是技术进步和社会发展的必然要求,也是打造“无废矿山”、“绿色矿山”的一条必经之路。
1 矿山废石概况
矿山废石指在采矿和选矿过程中产生的固体废弃物,其包括预抛废石、选矿尾矿和其他的固体废物等,废石主要产生于矿石开采过程中剥离围岩的过程。我国是世界第三大矿业大国,据近几年的数据统计,我国拥有的大小矿山共约15万座[3]。同时,我国矿山废石和尾矿的堆存量大、排放增长速度快、排放强度高,在矿产资源的开发利用过程中每年会排出大量的废石和尾矿。到目前为止,我国矿山固体废弃物的堆存量接近700亿t,其中废石堆存量520亿t[4]。由于我国矿产资源的资源特点以及开发利用水平的限制,我国矿产开采的采剥比相对较大。相较于非金属矿山,有色金属矿山采剥比更大,一般质量比可达1:(2~8),最高可以达到1:14;其中黄金矿山可以达到1:(10~14)[5]。
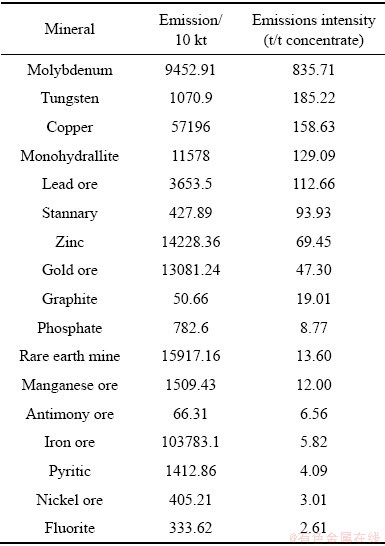
国土资源部发布的《重要矿产资源开发利用水平通报》对我国重要的20种矿产资源开发利用水平进行了数据统计与分析。统计显示:近年来,虽然我国废石、尾矿的排放量逐年增加,但增长速度逐渐下降,废石和尾矿的利用率不断提高。我国矿山废石的平均排放强度为11 t/t精矿,即每生产1 t精矿产生11 t废石。相比于其他矿产,有色金属矿产每吨精矿的废石排放强度最大,其中排放强度较大的有钼、钨、铜矿、铝土矿、铅矿等,不同种矿产具体排放强度如表1[6-7]。被统计的20种矿产每年排放废石19.56亿t,废石的平均年利用量为3.49亿t,废石利用率相比于“十二五”初期11.76%,提高到17.77%,同比提高了6.01% [8]。虽然废石利用率有较大的提高,但是相比于废石巨大的堆存量和排放量仍然相形见绌,废石的资源化综合利用仍然潜力巨大。
由于我国对矿产资源的巨大需求以及独立矿产少,共生伴生矿产资源多的矿产资源分布特点,导致我国矿山废石的堆存和每年的新增数量庞大[9]。矿山废石处理前期投入较大,投入产出不成正比。并且以前我国的资源开发以粗放式为主,过分追求经济的高速增长,忽视了对生态环境造成的危害。种种原因导致矿山废石的处理没有得到重视,企业不愿意投入大量的人力物力处理矿山废石。随着社会发展到新的阶段,社会观念发生改变,在谋求发展的同时,更加关注对生态环境造成的影响[10]。
表1 不同矿种废石排放强度[6-7]
Table 1 Emission intensity of waste rock of different minerals[6-7]
面对矿山废石大量堆存所造成的资源浪费和环境污染,人们开始逐渐重视矿山废石的资源化综合利用。在十二五初期,国家就先后制定发布了《“十二五”资源综合利用指导意见》(发改环资〔2011〕2919号)、《矿产资源节约与综合利用“十二五”规划》(国土资发〔2011〕184号)和《大宗工业固体与废物综合利用“十二五”规划》(工信部规〔2011〕600号)加强对矿产资源和矿山固废综合利用的规划和指导,鼓励引导企业注重矿山固废的综合利用,实施清洁生产,推进矿山固废的综合利用,并对固废的综合利用率提出了相应要求。《矿产资源节约与综合利用专项资金管理办法》(财建〔2013〕81号)设立专项资金用于奖励提高“三率”和矿产资源综合利用的示范工程,通过“以奖代补”的方式,重点支持矿产资源综合利用方面新技术、新工艺、新设备的研发和应用。《工业固体废物资源综合利用评价管理暂行办法》(工信部公告〔2018〕26号)和《国家工业固体废物资源综合利用产品目录》(工信部公告〔2018〕26号)科学规范了固体废弃物综合利用评价制度,有效促进了固废的资源化利用。《“无废城市”建设试点工作方案》(国办发〔2018〕128号)要求大力推进固废的源头处理和资源化利用,以解决我国固废排放强度高,综合利用率低的问题。开展“无废城市”建设试点,探索城市绿色发展,循环发展的新模式。《关于推进大宗固体废弃物综合利用产业集聚发展的通知》(发改办环资〔2019〕44号)建设大宗固废综合利用基地,促进产业集聚与协同发展,深入推进固废资源综合利用,提高综合利用水平。
2 矿山废石的危害
矿山废石任意堆放不仅造成资源的大量浪费,而且容易引发一系列的环境问题。矿产资源开发破环矿山的生态环境,容易诱发一系列的地质灾害和环境污染,对矿山及周边的生态环境造成严重的破环[11]。目前,我国大量的矿山废石只能长期堆存在废石库、尾矿库或矿山周围的排土场,有些技术落后的小矿山甚至直接将矿山废石直接排放到河沟、山沟之中,严重危害跨周边环境[12-13]。堆存在废石库、排土场中的废石,也会对矿区周围环境造成严重的污染,矿山废石大量堆存在一起,形成“二次矿山”,废石中没有被提取的有价成分以及有毒有害物质会通过各种环境介质进入矿区的生态圈,对矿山周边的空气、水体以及土壤环境造成严重的污染,危害动植物的健康[14]。矿山废石的危害主要表现在占用土地,造成资源浪费、引发地质灾害以及污染环境等方面。
2.1 占用土地,资源浪费
矿产资源的开发利用会破坏地表形态,我国矿山开发破环的土地资源中,废石堆积占用土地占比27%左右,尾矿库占比15%左右[15]。我国拥有各类矿产开发企业15.3万个,发现矿种168种,这些矿山企业在矿产开采过程中产生大量废石[16-17]。据统计显示,我国有色金属矿山每年排出废石近12亿t,黑色金属矿山每年约为6.2亿t[18]。这些废石堆积在废石库、排土场以及自然场地中,侵占了大量土地资源,其中不乏优质的耕地和林地资源。矿山每堆存1万t的矿山固体废弃物需要占用0.067 hm2土地,仅2015年一年,矿山土地资源破坏占用达26.2 hm2[19-20]。到目前为止,我国矿山固废堆存将近700亿t,占用土地面积超过29.49 万hm2[4, 21]。以陕西省为例,矿山固态废弃物累计占用土地超过1411.71 hm2,尾矿库累计占用土地519.96 hm2[22]。同时,一些矿山回收率较低,伴生矿产资源利用率不高,相当部分的有价金属和非金属矿物留存在废石和尾矿中,我国每年在其中损失的矿产价值超过1000亿元,造成了严重的资源浪费[23]。
2.2 造成地质灾害
矿山固体废弃物大量排放堆积在废石场、尾矿库或直接堆积在河沟山沟之中,堆存场地加固防护措施不到位,甚至就没有防护措施。随着矿山固废堆积量的增加,堆积高度和坡度的增大,极易发生崩塌、滑坡等灾害。尤其当降水较多时,固废和周围环境中含水量增加,更加容易导致滑坡、泥石流等地质灾害的发生[24-25]。这些固废堆存导致的地质灾害在世界各国均有发生,我国也是发生了多次由于矿山固体废弃物大量堆存引发的地质灾害。统计显示,自20世纪80年代起,我国发生此类滑坡和泥石流等灾害近百起[26-27]。2008年8月,山西太原钢铁集团尖山铁矿排土场发生滑坡造成45人死亡,1人受伤[28]。同年9月,山西襄汾塔矿业公司尾矿库溃坝导致277人死亡[29]。2015年12月,深圳一排土场发生滑坡,导致73人伤亡,4人失踪[30]。每次此类地质灾害的发生都会造成严重的后果。
2.3 污染环境
矿山固体废弃物对矿山周围环境的污染是全方面的,会同时造成大气污染、水污染和土壤污染。矿山废石对大气造成的污染主要表现在:矿山废石在排放时本身含有一些粒度较小的颗粒以及在堆存时经过风化作用会产生微小的颗粒,在气候干旱的时候,这些小颗粒会随着风扩散到大气中,形成扬尘,严重污染大气环境,这些微尘是PM2.5一个重要的来源[31]。有调查研究表明,矿山周边粉尘含量超标十几倍,矿山粉尘也是沙尘暴的一个重要尘源[32-34];同时,部分矿山废石会产生有害气体,严重污染大气环境,硫化矿的废石里含有相当部分的硫化物,当这些硫化物被氧化进入大气环境造成污染[35-36]。
矿山固体废弃物对土壤和水资源造成的污染形式基本相同。矿山废石中残留的有害成分随着雨水的冲刷进入地表径流和地下水体,当有害成分浓度超过一定标准,就会污染水资源。这些受污染的水资源一部分直接进入人体,另一部分通过农作物间接进入人体,危害人类的身体健康。同时,矿山废石中有害物质经过物理、化学或生物转化直接迁移或者通过水体间接迁移进入土壤中,导致土壤中的矿物质超标,污染土壤环境[37-38]。
3 矿山废石的综合利用
在矿山废石资源化利用这一研究领域,国外起步相对较早。随着我国对环保重视程度的不断上升,各大企业、高校和研究机构在矿山废石资源化利用的研究投入不断加大。目前,在矿山废石综合利用上,和国际水平还有一定的差距,但在某些具体领域的应用研究上有我国自身的独到性和开创性。矿山废石处理的发展主要经过了两个阶段,在废石处理的初期阶段,对矿山废石的处理主要侧重于堆存技术和防止二次污染。现阶段,对矿山废石的处理则侧重于回收资源和废弃物转换。目前,废石综合利用的研究主要在于废石中有用矿物或元素的分离与回收以及利用矿山废石制备其他有用材料。对矿山废石的处理思路和对策主要从两方面考虑:一方面对堆存的矿山废石再碎再磨,利用混合选矿方法对废石中的有用矿物进行进一步回收;另一方面,改进选矿设备、技术以及流程,使用更加合理的技术设备和混合选矿流程,减少废石的产生,降低其排放强度[21]。矿山废石的应用领域十分广泛,目前最主要的应用领域有采矿充填、制造微晶玻璃、覆土造田、生产建筑材料等。
3.1 废石中有价成分的提取
依照目前的矿产资源开采选水平,尚无法做到有用矿物百分百的回收利用,矿山排放的废石当中仍然含有相当部分的有用矿物。我国矿产共生、伴生资源丰富,但综合利用率相比国际水平却相对较低。据研究数据表明:发达国家金属矿产平均综合利用率约为70%,而我国平均却不到50%。我国仅有2%的有色金属矿山矿产的综合利用率能够达到70%,综合利用率超过50%的有色金属矿山不到15%[39-42]。从矿山废石中回收有价金属的潜力巨大,同时也是矿山废石资源化利用的重要一步。先从矿山废石中回收有价成分,再对剩余的废石,尾砂进行资源化处理,已经有很多企业联合高校和科研院所进行了研究并投入工业化应用,取得了良好综合效益。
凉山矿业[43]对四川拉拉山铜品位低于0.25%的铜矿废石通过磨矿-浮选选矿流程进行再处理。从正式投入工业生产开始仅一年半时间,处理废石300多万t,回收铜精矿2.7 万t、钴精矿1.55 万t、黄金白银数百千克、铁精矿约18.4万t以及钼精矿420.7 t,创造利润近3000万元。
紫金山金矿[44-46]剥离废石中,其中金品位为0.3~0.7 g/t的废石有9300多万t,紫金矿业对剥离的废石分类,按粒度采用堆浸或碳浸工艺,每年回收低品位矿石数十万吨,直接获利数百万元。
江西德兴铜矿[47-48]最初将开采铜矿石的边界品位定位0.3%,品位低于0.3%的矿石均当作废石排放到废石场,后面出于资源回收等多方面的考虑,决定对铜的品位为0.25%~0.3%的废石进行资源综合回收处理,这部分矿石占总储量20%。德兴铜矿采用湿法冶金技术回收废石中的铜。处理废石5500多万t,回收铜14.7万t,黄金11.6 t,取得了良好综合效益。
3.2 废石充填
矿产资源的开采会形成采空区,据不完全统计,我国由于矿产资源开发破坏的土地中约有57%为采空区[15]。将采矿废石回填采空区可以提高回采率,降低贫化,同时可以防止地面开裂,崩塌等各种地质灾害。废石充填技术历经多个发展阶段,最早采用干式充填技术,但应为其效率低,劳动强度大逐渐被淘汰。第二阶段采用水砂充填,随着对成本的控制以及环保的要求不断提高,在前面两种充填技术的基础上,结合混凝土的理论,形成了目前大量应用的胶结充填技术[49]。废石胶结充填技术将废石和胶结料浆混合作为充填骨料,将其充填进采空区,再在缝隙中灌入砂浆使其凝结成一个整体。其充填难度低,充填体强度大,因而在金属矿山得到广泛应用[50-53]。凡口铅锌矿利用废石回填矿坑,每年处理废石超过4万m3[54-55]。张马屯铁矿使用全尾矿回填采空区,实现了无尾矿排放,取得了良好的经济效益[56]。废石回填既防止了地质灾害,又减少了废石堆存,具有良好的环境效益。
3.3 覆土造田
矿山废石尾矿中成分基本上为无机物,不含有机质,如果将植物直接栽种于矿山废石或者尾矿之上,植物不具备生长条件。为了植物能够生长,一般采用掺土或者覆土的方式对废石场和尾矿库进行处理以达到复垦、绿化的目的[57]。对稳固的尾矿库,废石厂覆土造地,再在上面覆盖植被可以控制粉尘、减少水资源和土壤污染、减少水土流失以及地质灾害。覆土造田最早开始于美国,处理了大量的废石场和排土场,当时美国的复垦率达到40%左右[18]。近年来,覆土造田在我国部分矿山得到应用,例如金川公司对尾矿库和废石库进行覆土造田处理,取得了良好的综合效益[58]。
3.4 生产建筑材料
矿山固体废弃物用于生产建筑材料主要有三个方面:生产建筑用砖、生产如微晶玻璃等新型高端建筑用材,以及生产建筑用砂石骨料[59-60]。生产建筑用砖主要使用废石尾矿等代替砖块烧烧制中所需要的黏土。考率到黏土替代材料的粒度以及性能等方面的要求,生产砖块一般使用尾矿,使用废石的研究及生产情况较少。微晶玻璃又称陶瓷玻璃,是一种国外研究开发的新型高端建筑材料,相对于不同玻璃,它机械强度高、耐磨性高、韧性强、光泽度高,具有较好的市场应用前景。我国生产建筑用微晶玻璃一般采用烧结法,利用矿山废弃物,一般为高硅低铁的尾矿或者冶炼渣[61-62]。
利用矿山废石生产建筑用砂石骨料是矿山废石利用一种最常见的方式,也是废石利用量相对较大的一种方式。砂石骨料按其粒度分为粗骨料和细骨料,粒度大于5 mm为粗骨料,小于5 mm为细骨料。随着我国社会和基础建设的快速发展,建设用砂与日俱增,经过多年的开采,天然砂石越来越匮乏,建设用砂的供需矛盾不断加。并且,随着近些年发展观念的转变,对环境保护愈加重视,我国基本上禁止天然河砂的开采,砂石行业将更多的目光投向了机制砂。在机制砂刚开始的阶段,一般建设采石场,将开采的石头制成机制砂,但是由于采石场造成的环境污染过大,出于环保考虑,人工采石逐渐被禁止,大量采石场被关闭,种种原因,加剧了建设用砂的供需矛盾,建设用砂石骨料价格飞涨[63]。据中国砂石协会统计,目前,全国机制砂均价98元/t,天然沙131元/t,碎石92元/t。因此,人们逐渐将目光聚集矿山废石上。不同的废石来源,具有不同的岩性,不同破碎工艺生产的机制砂性能也各不一样。能够作为机制砂原料的岩石种类很多,如砂岩、石英砂岩、石灰石、玄武岩、花岗岩等,其中玄武岩花岗岩性能最好,是优良的机制砂原料[64-65]。
机制砂的制备方式主要分为干式制砂和湿式制砂,由于湿式制砂需要大量水资源且会对水资源造成污染,因而目前基本都采用干式制砂。机制砂质量高低主要取决于机制砂对混凝土性能的影响,其主要的影响因素有机制砂的破碎工艺及破碎后机制砂中的石粉含量、颗粒形状、细度模数等。对于上述影响因素国内外均有较多的研究[66-70]。通过大量的研究探索,目前对制备的机制砂已经有了较为完整的规范和标准,如《GB/T 25176—2010混凝土和砂浆用再生细骨料》、《GB/T 14684—2011建设用砂》和《GB/T 14685—2011建设用碎石卵石》等。利用矿山废石制备建设砂石在矿山已有较为广泛的应用。如研山铁矿采用三段一闭路破碎干选筛分的制砂工艺流程,年处理废石达500万t,年利润约为8300万元[71]。金源矿业公司对小秦岭金矿废石进行综合利用处理,每100 t废石可以生产60.42 t建设砂石、24.19 t石英砂,回收金精矿1.02 t。每年处理废石33万t,年利润约1411万元[72]。
4 存在的问题和建议
我国矿产资源丰富,矿产种类较为齐全。我国各类大小矿山繁多,因而产生废石的种类多,数量大,废石的岩性也各不相同。目前,我国矿山废石资源化利用取得了不错的成就,但面临的问题也还有很多,主要有:我国各种规模的矿山与矿产开发企业数量庞大,其中中小型矿山及企业占比较大,因而导致矿产开发不成规模,自动化、集约化程度低。同时,矿产开发过程中产生的废弃物,存在乱排乱放、不处理或处理不达标等各种问题;不同种类的矿产,不同矿山的废石成分及其含有的伴生矿物、有价成分各不相同,难以处理或者处理流程复杂;废石堆存量不明;矿山废石中含有的伴生矿物、有价成分勘察不明;部分企业环保意识较差,过分追求经济效益,不考虑矿产开发带来的环境影响,矿产资源回收率和综合利用率低,废石大量堆存:矿山废石管理体制、资源综合利用激励机制不完善,废石资源化综合利用投入不足;废石利用途径较少,矿山废石产品单一,综合利用程度低,各类废石处理企业、厂家仅进行最简单的废石处理利用,利用废石生产的产品大部分附加价值不高。
针对上述存在的问题,提出如下建议。首先,应该转变发展观念,提高环保意识、节约资源,将矿山废石的资源化利用作为保护环境和解决资源紧张的重要途径之一,重视矿山废石的资源化利用,倡导无废矿山、清洁循环理论[73],从源头上解决矿山废石大量堆存的问题。其次,学习国外先进的技术和管理体制,建立押金返还制度[74],健全矿山废石管理体制、标准体系和废石资源化利用的激励机制,加大矿山废石资源化利用的科研和资金投入,扩展矿山废石的利用途径,在降低生产成本的同时,研发生产附加价值更高的利用矿山废石生产的产品。再后,构建数字矿山、智能矿山[75],建立完备的矿山废石数据库和信息共享服务系统,如各个矿山的废石储量,不同矿山废石的有价金属成分和含量,以及各种类废石的工艺矿物学数据等,为矿山废石的研究与资源化利用提供相应的数据服务。最后,对矿山与矿产开发企业进行区域性调研,将各类矿山按距离,与运输条件进行区域划分,以区域为单位,在区域中寻找合适中心点,建立矿山废石产品多领域多产业协同的区域生产处理中心,提高矿山废石的综合利用率和综合利用的规模化、集约化以及自动化水平,从而提高废石综合利用的经济效益与环保效益。
5 结语
矿山废石只是放错了时间和地点的资源,随着科技的进步,曾经认定的废弃物也会变成珍贵的资源。我国废石种类繁多,废石堆存量庞大,且废石中含有较为丰富的有价金属。由于处理技术和经济效益的限制,导致废石大量堆存,不仅浪费资源,而且污染环境。相对于发达国家,我国废石综合利用率低,废石资源化利用潜力巨大。未来废石的资源化综合利用应该重视以下几点。
1) 国家提供全面的政策支持和激励引导,企业转变发展关念,加大废石处理的研究投入,研发废石处理的先进设备与技术,建立与市场接轨的运行机制,使废石的资源化综合利用不再是因为环境保护的要求,而应该成为企业一个重要的经济增长点。
2) 矿山废石应当趋向于区域聚集、多产业协同、分段循环的的处理方式。彻底解决目前废石产品单一,附加值低的问题,实现矿山废石产品的多样化、高价值化以及废弃物的零排放。
3) 在废石的处理阶段,因地制宜,根据不同矿山废石的特点以及周边环境和资源的特征,分类分段对相邻地区不同矿山的废石进行综合利用。首先,可以利用拣选设备将含有金属矿物和不含金属矿物的废石分离,确定合适的工艺流程回收其中的有价金属和和非金属矿物,将再选过的废石按照其粒度大小分段利用,可以用作建筑碎石,混凝土粗细骨料以及用于制取新材料等不同用途,基本实现矿山废石的完全利用,避免造成资源的浪费和对环境的污染。
REFERENCES
[1] 余国合. 地下铁矿工业品位优化决策研究[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学, 2013: 1-5.
YU He-guo. Study on optimization decision of industrial grade of iron mine in underground[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences, 2013: 1-5.
[2] 于崇波. 某铜矿床工业品位探讨[J]. 有色矿冶, 2020, 36(1): 54-57, 15.
YU Chong-bo. Discussion on industrial grade of a copper deposit[J]. Nonferrous Mining and metallurgy, 2020, 36(1): 54-57, 15.
[3] 何 瑜. 采矿废弃资源综合利用对策与措施[J]. 建材与装饰, 2018(24): 215.
HE Yu. Countermeasures and measures for comprehensive utilization of mining waste resources[J]. Building Materials and Decoration, 2018(24): 215.
[4] 赵满云, 马 斌, 欧 浩. 矿山固废物主要处理方式及发展前景[J]. 中外企业家, 2019(24): 129.
ZHAO Man-yun, MA Bing, OU Hao. Main treatment methods and development prospects of mine solid waste[J]. Chinese and foreign entrepreneurs, 2019(24): 129.
[5] 杨小聪, 郭利杰. 尾矿和废石综合利用技术[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社,2018: 187-191.
YANG Xiao-cong, GUO Jie-li. Tailings and waste rock comprehensive utilization technology[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2018: 187-191.
[6] 冯安生, 吕振福, 武秋杰, 等. 矿业固体废弃物大数据研究[J]. 矿产保护与利用, 2018(2): 40-43, 51.
FENG An-sheng, Lü Zhen-fu, WU Qiu-jie, et al. Big data research on mining solid wastes[J]. Conservation and Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2018(2): 40-43, 51.
[7] 冯安生, 许大纯, 吕振福. 重要矿产开发利用技术与指标[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2018: 412-473.
FENG An-sheng, XU Da-chu, Lü Zhen-fu. Key mineral development and utilization technologies and indicators[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2018: 412-473.
[8] 王琼杰. 《重要矿产资源开发利用水平通报》解析[N]. 中国建材报, 2018-02-22(003).
WANG Qiong-jie. Analysis of “Notice of Development and Utilization Level of Important Mineral Resources”[N]. China Building Materials News, 2018-02-22(003).
[9] 范继涛. 矿产资源综合利用效益对福利影响研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2015: 1-5.
FAN Ji-tao. Study on the effect of comprehensive utilization of mineral resources on welfare[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 2015: 1-5.
[10] 王海军, 薛亚洲. 我国矿产资源节约与综合利用现状分析[J]. 矿产保护与利用, 2017(2): 1-5, 12.
WANG Hai-jun, XUE Ya-zhou. Situation analysis on conservation and comprehensive utilization of mineral resources in China[J]. Conservation and Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2017(2): 1-5, 12.
[11] 柴寿军. 废弃矿山生态环境保护与恢复治理问题研究[J]. 世界有色金属, 2020(3): 225-226.
CHAI Shou-jun. Study on the ecological environment protection and restoration of abandoned mines[J]. World Nonferrous Metals, 2020(3): 225-226.
[12] 余 斌, 徐 慧. 矿山固体废弃物综合利用技术现状与发展趋势[J]. 矿冶, 2002, 11(Z1): 236-240.
YU Bing, XU Hui. Present situation and development trend of comprehensive utilization technology of mine solid waste[C]. Mining & Metallurgy, 2002, 11(Z1): 236-240.
[13] 简 荣, 赵常伟. 山东省装饰石材矿山现状及可持续发展几个亟待解决问题探讨[J]. 石材, 2018(4): 39-43.
JIAN Rong, ZHAO Chang-wei. Discussion on the current situation and sustainable development of decorative stone mines in Shandong Province[J]. Stone, 2018(4): 39-43.
[14] 刘淑鹏, 张小伟, 魏 芳. 金属矿山固体废弃物危害及资源再利用[J]. 现代矿业, 2017, 33(2): 122-125.
LIU Shu-peng, ZHANG Xiao-wei, WEI Fang. Metal mine solid waste hazards and resource reuse[J]. Modern Mining, 2017, 33(2): 122-125.
[15] 薛亚洲, 王海军, 汤家轩, 等. 中国矿产资源节约与综合利用报告2015[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2014: 137-169.
XUE Ya-zhou, WANG Hai-jun, TANG Jia-xuan, et al. Report on saving and comprehensive utilization of mineral resources in China 2015[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2014: 137-169.
[16] 李福来, 胡 克, 冯 军, 等. 我国矿山固体废弃物现状与对策分析[J]. 国土资源科技管理, 2005(3): 66-70.
LI Fu-lai, HU Ke, FENG Jun, et al. Mining solid waste in China: Present conditions and countermeasures[J]. Scientific and Technological Management of Land and Resources, 2005(3): 66-70.
[17] 齐文涛, 陈智伟. 海南岛矿山废石资源特征及综合利用研究[J]. 中国矿业, 2019, 28(2): 40-44.
QI Wen-tao, CHEN Zhi-wei. Study on the characteristics and comprehensive utilization of waste rock resources in Hainan Island[J]. China Mining Magazine, 2019, 28(2): 40-44.
[18] 程学斌. 露天矿山废石综合利用探讨[J]. 硅谷, 2011(9): 146, 112.
CHENG Xue-bing. Discussion on comprehensive utilization of open-pit mine waste rock[J]. Silicon Valley, 2011(9): 146, 112.
[19] 朱能武. 固体废物处理与利用[M]. 北京: 北京大学出版社, 2006: 6-20.
ZHU Neng-wu. Solid waste treatment and utilization[M]. Beijing: Peking University Press, 2006: 6-20.
[20] 李 畅, 陈云嫩, 何彩庆, 等. 特色产业固体废物环境影响与资源化技术研究进展[J]. 中国资源综合利用, 2019, 37(6): 96-100.
LI Chang, CHEN Yun-nen, HE Cai-qing, et al. Research progress on environmental impact and resource utilization technology of solid waste in characteristic industries[J]. China Resources Comprehensive Utilization, 2019, 37(6): 96-100.
[21] 龙 涛, 余 斌. 露采剥离废石资源化节约综合利用研究综述[J]. 有色金属(矿山部分), 2007(2): 14-16, 34.
LONG Tao, YU Bing. Commentary of study on mullock of open-pit mine stripping resources rational and saving utilization[J]. Nonferrous Metals(Mining Section), 2007(2): 14-16, 34.
[22] 陈建平, 宁建民, 范立民, 等. 陕西省矿山固体废弃物综合利用与治理技术探讨[C]// 2014年陕西省地质灾害防治学术研讨会论文集. 西安: 陕西省地质学会等, 2014: 56-60.
CHEN Jian-ping, NING Jian-ming, FAN Li-ming, et al. Discussion on comprehensive utilization and treatment technology of mine solid waste in Shaanxi Province[C]// Proceedings of the 2014 Shaanxi Provincial Geological Hazards Prevention Symposium. Xian: Shaanxi Geological Society etc, 2014: 56-60.
[23] 陈明莲. 矿山固体废物综合利用的几种途径[J]. 南方金属, 2011(4): 1-4.
CHEN Ming-lian. Ways of comprehensive utilization of solid wastes from mines[J]. Southern Metals, 2011(4): 1-4.
[24] 牛莎莎, 徐明德. 矿山固体废弃物的综合利用及其环保治理分析[J]. 资源节约与环保, 2016(1): 192.
NIU Sha-sha, XU Ming-de. Analysis on comprehensive utilization of mine solid waste and its environmental protection[J]. Resources Economization & Environment Protection, 2016(1): 192.
[25] 荆曼黎, 敖海龙. 矿山固体废弃物的危害及其环保治理技术[J]. 资源节约与环保, 2018(7): 146.
JING Man-li, AO Hai-long. The harm of mine solid waste and its environmental protection treatment technology[J]. Resources Economization & Environment Protection, 2018(7): 146.
[26] 李明立, 原振雷, 朱嘉伟. 矿山固体废物对环境的影响及综合利用探讨[J]. 矿产保护与利用, 2005(4): 38-41.
LI Ming-li, YUAN Zhen-lei, ZHU Jia-wei. Environment effect of solid waste in mines and its multipurpose utilization[J]. Conservation and Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2005(4): 38-41.
[27] 武俊杰, 孙 阳, 刘 强. 我国尾矿库溃坝原因及防治措施[C]//高强度采矿区地质灾害与防控学术研讨会论文集. 西安: 陕西省地质调查院, 2016: 114-119.
WU Jun-jie, SUN Yang, LIU Qiang. Causes and prevention measures of dam break in tailing ponds in China[C]// Proceedings of the Symposium on Geological Hazards and Prevention and Control in High-intensity Mining Areas. Xi’an: Shaanxi Provincial Geological Survey Institute, 2016: 114-119.
[28] 薛 亮. 数百亿吨“废石”, 成灾还是成金?[J]. 国土资源, 2016(2): 21-24.
XUE Liang. Tens of billions of tons of “waste rock”, disaster or gold?[J]. Land & Resources, 2016(2): 21-24.
[29] 刘永强. 我国县级政府应急管理能力的影响因素及提升对策[D]. 西安: 西北大学, 2016: 9-10.
LIU Yong-qiang, The influencing factors and improving countermeasures of China’s county government emergency management ability[D]. Xian: Northwest University, 2016: 9-10.
[30] 邱加州. 突发事件中地方政府网络舆情应对与舆论引导研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉大学, 2017: 10-11.
QIU Jia-zhou. Research of local government response to network public opinion in sudden incident and guidance of public opinion[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University, 2017: 10-11.
[31] 陈 森, 周晓明, 李 靖, 等. 固体废物填埋场对环境的影响及治理对策[J]. 环境与发展, 2018, 30(8): 30, 32.
CHEN Sen, ZHOU Xiao-ming, LI Jing, FU Bin, ZHOU Yan-wen, ZHANG Quan. Environmental impact of solid waste landfill and countermeasures[J]. Environment and Development, 2018, 30(8): 30, 32.
[32] 孙书晶. 矿山固体废弃物的处理与利用研究[J]. 科学技术创新, 2017(22): 49-50.
SUN Shu-jing. Research on the treatment and utilization of mine solid waste[J]. scientific and technical innovation, 2017(22): 49-50.
[33] 常前发. 矿山固体废物的处理与处置[J]. 矿产保护与利用, 2003(5): 38-42.
CHANG Qian-fa. Processing and disposition of solid wastes in mines[J]. Conservation and Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2003(05): 38-42.
[34] 王方汉, 缪建成, 曹维勤. 矿山固体废物综合利用的研究与实践[J]. 矿业快报, 2003(8): 12-14.
WANG Fang-han, MIAO Jian-cheng, CAO Wei-qin. Research and practice of comprehensive utilization of mine solid waste[J]. Express Information of Mining Industry, 2003(8): 12-14.
[35] 姜 楠. 金属矿山固体废弃物危害及资源再利用[J]. 农村科学实验, 2020(3): 117-118.
JIANG Nan. Metal mine solid waste hazards and resource reuse[J]. Rural Science Experiment, 2020(3): 117-118.
[36] 张利珍, 赵恒勤, 马化龙, 等. 我国矿山固体废物的资源化利用及处置[J]. 现代矿业, 2012, 27(10): 1-5.
ZHANG Li-zhen, ZHAO Heng-qin, MA Hua-long, et al. Resource utilization and disposal of mine solid waste in China[J]. Morden Mining, 2012, 27(10): 1-5.
[37] 孙秋君, 李 冰, 刘 欣. 固体废弃物的污染防治措施[J]. 科技创新与应用, 2013(12): 114.
SUN Qiu-jun, LI Bing, LIU Xin. Solid waste pollution prevention measures[J].Technology Innovation and Application, 2013(12): 114.
[38] 杨 林. 矿山固体废弃物的危害及其环保治理技术研究[J]. 中国资源综合利用, 2020, 38(1): 126-128.
YANG Lin. Research on the hazards of mine solid waste and its environmental protection technology[J]. Comprehensive Utilization of Resources in China, 2020, 38(1): 126-128.
[39] 李 莉. 矿产资源综合利用的研究与对策[J]. 现代矿业, 2009, 25(6): 5-9.
LI Li. Study and countermeasures of comprehensive utilization of mineral resources[J]. Morden Mining, 2009, 25(6): 5-9.
[40] 魏邦亿. 我国矿产资源综合利用的现状和对策[J]. 资源节约与环保, 2017(7): 88-91.
WEI Bang-yi. The current situation and countermeasures of comprehensive utilization of mineral resources in China[J]. Resources Economization & Environment Protection, 2017(7): 88-91.
[41] 唐 宇, 李瑞军, 王海军. 我国矿产资源综合利用现状分析及对策建议[J]. 中国矿业, 2013, 22(S1): 100-102.
TANG Yu, LI Rui-jun, WANG Hai-jun. Situation analysis and suggestions on comprehensive utilization of mineral resources in China[J]. China Mining Magazine, 2013, 22(S1): 100-102.
[42] 任世赢. 我国有色金属矿产资源综合利用的现状、问题及对策[J]. 中国资源综合利用, 2018, 36(1): 74-75.
REN Shi-ying. The current situation, problems and countermeasures of comprehensive utilization of nonferrous metal mineral resources in China[J]. Comprehensive Utilization of Resources in China, 2018, 36(1): 74-75.
[43] 周 正, 王恒峰, 杜 新, 等. 四川拉拉铜矿矿山废石综合利用新工艺研究[J]. 四川地质学报, 2012, 32(S2): 218-222.
ZHOU Zheng, WANG Heng-feng, DU Xin, et al. Study on the new technology of comprehensive utilization of waste rock in Sichuan Lala Copper Mine[J]. Acta Geologica Sichuan, 2012, 32(S2): 218-222.
[44] 邹 凯. 创新的低品位资源开发技术在紫金山矿的应用[J]. 采矿技术, 2011, 11(6): 1-3.
ZOU Kai. Application of innovative low-grade resource development technology in Zijinshan Mine[J]. Mining Technology, 2011, 11(6): 1-3.
[45] 李小文. 紫金山金矿低品位金矿资源的开发利用[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2005(5): 35-39.
LI Xiao-wen. Exploitation of low-grade gold mineral resources at Zijinshan Gold Mine[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2005(5): 35-39.
[46] 罗映南, 刘荣春, 邹 凯. 紫金山金矿低品位资源的开发利用技术[J]. 黄金科学技术, 2003(2): 27-31.
LUO Ying-nan, LIU Rong-chun, ZOU Kai. Technology of evaluation and exploration of lower grade gold resources Zijinshan Gold Mine[J]. Gold Science and Technology, 2003(2): 27-31.
[47] 万长峰. 德兴铜矿废石排放与堆浸筑堆相结合的探讨[J]. 有色矿山, 2000(2): 15-17.
WAN Chang-feng. Discussion on the discharge of waste stone and stack for heap leaching in Dexing Copper Mine[J]. Nonferrous Mines, 2000(2): 15-17.
[48] 刘维阁. 浅谈矿产资源的综合开发与科学合理利用[J]. 中国金属通报, 2008(44): 32-33.
LIU Wei-ge. On comprehensive development and scientific and reasonable utilization of mineral resources[J]. China Metal Bulletin, 2008(44): 32-33.
[49] 董 越. 多固废资源在金川矿山充填采矿中协同综合利用研究[D]. 北京: 北京科技大学, 2019: 3-7.
DONG Yue. Research on multi-solid waste collaborative comprehensive utilization of mining backfill in Jinchuan Mine[D]. Beijing: University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2019: 3-7.
[50] POTGIETER J H, POTGIETER S S. Mining backfill formulations from various cementitious and waste materials[C]//Proceedings of the 5th International Symposium on Cement and Concrete(Volume 2). Beijing: Cement Branch of China Silicate Society, 2002: 129-133.
[51] BAYRAM Ercikdi, FERDI Cihangir, AYHAN Kesimal, et al. Utilization of industrial waste products as pozzolanic material in cemented paste backfill of high sulphide mill tailings.[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2009, 168(2/3): 848-856.
[52] 张修香, 乔登攀, 孙宏生. 废石-尾砂高浓度料浆管道输送特性模拟[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2019, 29(5): 1092-1101.
ZHANG Xiu-xiang, QIAO Pan-deng, SUN Hong-sheng. Simulation on conveying characteristics in pipe about high-density slurry with waste rock-tailing[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2019, 29(5): 1092-1101.
[53] 李夕兵, 刘 冰, 姚金蕊, 等. 全磷废料绿色充填理论与实践[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2018, 28(9): 1845-1865.
LI Xi-bing, LIU Bing, YAO Jin-rui, et al. Theory and practice of green mine backfill with whole phosphate waste [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2018, 28(9): 1845-1865.
[54] 孙 勇. 凡口矿深部废石回填系统的建立及应用效果分析[J]. 冶金丛刊, 2016(3): 43-45.
SUN Yong. On the application effect of deep barren rock backfill system in Fankou Lead-zinc Mine[J]. Metallurgical Collections, 2016(3): 43-45.
[55] 许毓海. 凡口铅锌矿工业废弃物综合利用技术研究[J]. 矿冶, 2002(2): 74-76, 84.
XU Yu-hai. Research on comprehensive utilization technologies of industrial wastes at Fankou Lead-Zinc Mine[J]. Mining & Metallurgy, 2002(2): 74-76, 84.
[56] 何哲祥, 谢开维, 周爱民. 全尾砂胶结充填技术的研究与实践[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 1998, 8(4): 3-5.
HE Zhe-xiang, XIE Kai-wei, ZHOU Ai-min. Research and practice of total tailings backfilling[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 1998, 8(4): 3-5.
[57] 李欣远. 矿山地质环境恢复治理及综合利用探讨[J]. 中国金属通报, 2020(7): 295-296.
LI Xin-yuan. Discussion on the recovery and comprehensive utilization of mine geological environment[J]. China Metal Bulletin, 2020(7): 295-296.
[58] 陈永贵, 张可能. 中国矿山固体废物综合治理现状与对 策[J]. 资源环境与工程, 2005(4): 311-313.
CHEN Yong-gui, ZHANG Ke-neng. Comprehensive treatment and application of solid waste of mines[J]. Resources Environment & Engineering, 2005(4): 311-313.
[59] 高韩锋, 姚 乐. 钢铁企业固体废弃物资源化利用[J]. 知识经济, 2015(20): 125-126.
GAO Han-feng, YAO le. Utilization of solid waste resources in iron and steel enterprises[J]. Knowledge Economy, 2015(20): 125-126.
[60] 王湖坤, 龚文琪, 刘友章. 有色金属矿山固体废物综合回收和利用分析[J]. 金属矿山, 2005(12): 70-72.
WANG Hu-kun, GONG Wen-qi, LIU You-zhang. Analysis of Comprehensive Recovery and Utilization of Solid Waste in Nonferrous Metallic Mines[J]. Metal Mine, 2005(12): 70-72.
[61] 陈希廉. 矿山废石和尾矿的50种可能应用领域[C]// 第五届中国矿山地质学术会议暨振兴东北生产矿山资源高层论坛论文集. 北京: 中国有色金属工业协会, 2005: 40-49.
CHEN Xi-lian. 50 possible applications for mine waste rock and tailings[C]// Proceedings of the 5th China Mining Geology Academic Conference and High-level Forum on Revitalizing Northeast Production and Mine Resources. Beijing: China Nonferrous Metals Industry Association, 2005: 40-49.
[62] 潘德安, 逯海洋, 刘晓敏, 等. 铁尾矿建材化利用的研究进展与展望[J]. 硅酸盐通报, 2019, 38(10): 3162-3169, 3214.
PAN De-an, LU Hai-yang, LIU Xiao-min, et al. Research progress and prospect on utilization of iron tailings for building materials[J]. Bulletin of The Chinese Ceramic Society, 2019, 38(10): 3162-3169, 3214.
[63] 郑 科. 机制砂在高速公路桥梁高标号混凝土结构中的应用研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2019: 1-4.
ZHENG Ke, Application research of machine-made sand in high-grade concrete structure of expressway bridge[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2019: 1-4.
[64] 孙超铨. 废石利用的新途径[J]. 采矿技术, 2005(1): 11-12.
SUN Chao-quan. New ways of using waste rock[J]. Mining Technology, 2005(1): 11-12.
[65] 宋少民, 程 成, 杨 楠. 机制砂岩性对胶砂和混凝土性能影响的研究[J]. 混凝土, 2019(9): 67-70.
SONG Shao-ming, CHENG Cheng, YANG Nan. Influence of manufactured sand lithology on mortar and concrete performance[J]. Concrete, 2019(9): 67-70.
[66] GONCALVES J P, TAVARES L M, TOLEDO FILHO R D, et al. Comparison of natural and manufactured fine aggregates in cement mortars[J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 2007, 37(6): 924-932.
[67] LI Bei-xing, WANG Ji-liang, ZHOU Ming-kai. Effect of limestone fines content in manufactured sand on durability of low- and high-strength concretes[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2009, 23(8): 2846-2850.
[68] GORI U, MARI M. The correlation between the fractal dimension and internal friction angle of different granular materials[J]. Soils and Foundations, 2001, 41(6): 17-23
[69] 刘 智, 吕 明, 杨和平. 机制砂颗粒粒形特征及其对砂浆性能的影响[J]. 城市建筑, 2020, 17(8): 127-129.
LIU Zhi, LU Ming, YANG Hei-ping. Particle shape characteristics of machine-made sand and its influence on mortar performance[J]. Urbanism and Architecture, 2020, 17(8): 127-129.
[70] 杨华山, 方坤河, 涂胜金, 等. 石灰石粉在水泥基材料中的作用及其机理[J]. 混凝土, 2006(6): 32-35.
YANG Hua-shan, FANG Kun-he, TU Sheng-jin, et al. The effect and its mechanism of calcium carbonate on the cement based materials[J]. Concrete, 2006(6): 32-35.
[71] 李金朋, 张成龙, 王浩明, 等. 研山铁矿排岩废石生产砂石骨料研究[J]. 现代矿业, 2019, 35(6): 278-279.
LI Jin-peng, ZHANG Cheng-long, WANG Hao-ming, et al. Research on the production of sand and gravel aggregates from the waste rock of Yanshan Iron Mine[J]. Modern Mining, 2019, 35(6): 278-279.
[72] 李建政, 王安理, 范尚立, 等. 小秦岭金矿区废石资源综合利用试验研究[J]. 矿冶工程, 2010, 30(6): 51-53, 56.
LI Jian-zheng, WANG An-li, FAN Shang-li, et al. Experimental study on comprehensive utilization of waste rock resources from Xiaoqinling Gold Mine[J]. Mine and Metallurgical Engineering, 2010, 30(6): 51-53, 56.
[73] 郭学益, 田庆华, 刘 咏, 等. 有色金属资源循环研究应用进展[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2019, 29(9): 1859-1901.
GUO Xue-yi, TIAN Qing-hua, LIU Yong, et al. Progress in research and application of non-ferrous metal resources recycling[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2019, 29(9): 1859-1901.
[74] 陈思思. 国外废旧汽车环境押金制度的实践及对我国的启示[J]. 西安建筑科技大学学报(社会科学版), 2013, 32(5): 23-27.
CHENG Si-si. The practice of the environmental deposit system of scrap automobile aboard and its enlightenment to China[J]. Journal of Xi’an University of Architecture & Technology (Social Science Edition), 2013, 32(5): 23-27.
[75] 王李管, 陈 鑫. 数字矿山技术进展[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2016, 26(8): 1693-1710.
WANG Li-guan, CHENG Xin. Advancing technologies for digital mine[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2016, 26(8): 1693-1710.
Current status and development of comprehensive utilization of waste rock in metal mines in China
YAO Hua-hui1, 2, CAI Lian-bing1, 3, LIU Wei1, 2, QIN Wen-qing1, 2, JIAO Fen1, 2, YANG Cong-ren1, 2
1.School of Minerals Processing & Bioengineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2.Hunan Key Laboratory for clean and efficient utilization of strategic calcium bearing mineral resources, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
3.Jin Gui Non-ferrous Metal (Group) Co., Ltd., Chenzhou 423038, China )
Abstract: With the development of society, China’s demand for mineral resources is increasing. The accumulation of large amounts of waste rock in mines not only causes a serious waste of mineral resources, but also occupies a large amount of land, and it also brings serious safety problems and environmental pollution. In view of the characteristics of large mine waste rock piles, rapid growth, complicated waste rock types and compositions, and low comprehensive utilization rate of waste rock resources in china, this paper summarizes the hazards and the current treatment and utilization methods of waste rock, describe the characteristics, development and application of the main treatment methods of mine waste rock for recycling valuable metals and further waste rock backfilling, covering soil and making fields, manufacturing building materials, and summarize the key directions of possible research and development of mine waste rock and put forward the mine Feasibility suggestions for the utilization of waste rock resources. It is pointed out that the cross-regional agglomeration processing, multi-field multi-industry collaborative processing and classification and segmentation processing of the comprehensive utilization of waste rock resources in the mine are the key points for future research. It is an important prerequisite for comprehensive utilization of mine waste rock to determine the mine waste rock stock, composition, particle size, and content of valuable metals. It is an important step to improve the comprehensive utilization rate of mine waste rock by adopting a reasonable plan to classify and treat mine waste rock.
Key words: mine waste rock; environmental pollution; recycling; comprehensive utilization
Foundation item: Project(2020YFC1909203) supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China; Project(2018TP1002) supported by Key Laboratory of Hunan Province for Clean and Efficient Utilization of Strategic Calcium-containing Mineral Resources, China; Project supported by the Collaborative Innovation Centre for Clean and Efficient Utilization of Strategic Metal Mineral Resources (2011 Program of Hunan), China
Received date: 2020-08-03; Accepted date: 2020-12-14
Corresponding author: YANG Cong-ren; Tel: +86-13874962836; E-mail: yangcongren@csu.edu.cn
(编辑 何学锋)
基金项目:国家重点研发计划资助项目(2020YFC1909203);战略含钙矿物资源清洁高效利用湖南省重点实验室资助项目(2018TP1002);战略金属矿产资源清洁高效利用协同创新中心资助项目(湖南省2011计划)
收稿日期:2020-08-03;修订日期:2020-12-14
通信作者:杨聪仁,副教授,博士;电话:13874962836;E-mail:yangcongren@csu.edu.cn
摘 要:随着社会的发展,我国对矿产资源的需求日益增加,矿山废石的大量堆积不仅造成矿产资源的严重浪费,而且占据大量土地,还会带来严重的安全问题和环境污染。针对我国矿山废石堆存量大、增长快、废石种类及成分复杂、废石资源化综合利用率低等特点,本文总结了矿山废石的危害和现行的处理及利用方式,详述矿山废石用于回收有价金属及进一步的废石回填、覆土造田、制造建筑材料等主要处理方式的特点、发展及应用情况,并归纳展望矿山废石未来可能研究发展的重点方向,提出矿山废石资源化利用的可行性建议。指出矿山废石的资源化综合利用的跨区域集聚处理、多领域多产业协同处理和分类分段处理是日后研究的关键。确定矿山废石堆存量以及成分、粒度、有价金属的含量是矿山废石综合利用的重要前提。制定合理方案对矿山废石进行分类分段处理是提高矿山废石综合利用率的重要步骤。
[1] 余国合. 地下铁矿工业品位优化决策研究[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学, 2013: 1-5.
[2] 于崇波. 某铜矿床工业品位探讨[J]. 有色矿冶, 2020, 36(1): 54-57, 15.
[3] 何 瑜. 采矿废弃资源综合利用对策与措施[J]. 建材与装饰, 2018(24): 215.
[4] 赵满云, 马 斌, 欧 浩. 矿山固废物主要处理方式及发展前景[J]. 中外企业家, 2019(24): 129.
[5] 杨小聪, 郭利杰. 尾矿和废石综合利用技术[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社,2018: 187-191.
[6] 冯安生, 吕振福, 武秋杰, 等. 矿业固体废弃物大数据研究[J]. 矿产保护与利用, 2018(2): 40-43, 51.
[7] 冯安生, 许大纯, 吕振福. 重要矿产开发利用技术与指标[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2018: 412-473.
[8] 王琼杰. 《重要矿产资源开发利用水平通报》解析[N]. 中国建材报, 2018-02-22(003).
[9] 范继涛. 矿产资源综合利用效益对福利影响研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2015: 1-5.
[10] 王海军, 薛亚洲. 我国矿产资源节约与综合利用现状分析[J]. 矿产保护与利用, 2017(2): 1-5, 12.
[11] 柴寿军. 废弃矿山生态环境保护与恢复治理问题研究[J]. 世界有色金属, 2020(3): 225-226.
[12] 余 斌, 徐 慧. 矿山固体废弃物综合利用技术现状与发展趋势[J]. 矿冶, 2002, 11(Z1): 236-240.
[13] 简 荣, 赵常伟. 山东省装饰石材矿山现状及可持续发展几个亟待解决问题探讨[J]. 石材, 2018(4): 39-43.
[14] 刘淑鹏, 张小伟, 魏 芳. 金属矿山固体废弃物危害及资源再利用[J]. 现代矿业, 2017, 33(2): 122-125.
[15] 薛亚洲, 王海军, 汤家轩, 等. 中国矿产资源节约与综合利用报告2015[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2014: 137-169.
[16] 李福来, 胡 克, 冯 军, 等. 我国矿山固体废弃物现状与对策分析[J]. 国土资源科技管理, 2005(3): 66-70.
[17] 齐文涛, 陈智伟. 海南岛矿山废石资源特征及综合利用研究[J]. 中国矿业, 2019, 28(2): 40-44.
[18] 程学斌. 露天矿山废石综合利用探讨[J]. 硅谷, 2011(9): 146, 112.
[19] 朱能武. 固体废物处理与利用[M]. 北京: 北京大学出版社, 2006: 6-20.
ZHU Neng-wu. Solid waste treatment and utilization[M]. Beijing: Peking University Press, 2006: 6-20.
[20] 李 畅, 陈云嫩, 何彩庆, 等. 特色产业固体废物环境影响与资源化技术研究进展[J]. 中国资源综合利用, 2019, 37(6): 96-100.
[21] 龙 涛, 余 斌. 露采剥离废石资源化节约综合利用研究综述[J]. 有色金属(矿山部分), 2007(2): 14-16, 34.
[22] 陈建平, 宁建民, 范立民, 等. 陕西省矿山固体废弃物综合利用与治理技术探讨[C]// 2014年陕西省地质灾害防治学术研讨会论文集. 西安: 陕西省地质学会等, 2014: 56-60.
[23] 陈明莲. 矿山固体废物综合利用的几种途径[J]. 南方金属, 2011(4): 1-4.
[24] 牛莎莎, 徐明德. 矿山固体废弃物的综合利用及其环保治理分析[J]. 资源节约与环保, 2016(1): 192.
[25] 荆曼黎, 敖海龙. 矿山固体废弃物的危害及其环保治理技术[J]. 资源节约与环保, 2018(7): 146.
[26] 李明立, 原振雷, 朱嘉伟. 矿山固体废物对环境的影响及综合利用探讨[J]. 矿产保护与利用, 2005(4): 38-41.
[27] 武俊杰, 孙 阳, 刘 强. 我国尾矿库溃坝原因及防治措施[C]//高强度采矿区地质灾害与防控学术研讨会论文集. 西安: 陕西省地质调查院, 2016: 114-119.
[28] 薛 亮. 数百亿吨“废石”, 成灾还是成金?[J]. 国土资源, 2016(2): 21-24.
[29] 刘永强. 我国县级政府应急管理能力的影响因素及提升对策[D]. 西安: 西北大学, 2016: 9-10.
[30] 邱加州. 突发事件中地方政府网络舆情应对与舆论引导研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉大学, 2017: 10-11.
[31] 陈 森, 周晓明, 李 靖, 等. 固体废物填埋场对环境的影响及治理对策[J]. 环境与发展, 2018, 30(8): 30, 32.
[32] 孙书晶. 矿山固体废弃物的处理与利用研究[J]. 科学技术创新, 2017(22): 49-50.
[33] 常前发. 矿山固体废物的处理与处置[J]. 矿产保护与利用, 2003(5): 38-42.
[34] 王方汉, 缪建成, 曹维勤. 矿山固体废物综合利用的研究与实践[J]. 矿业快报, 2003(8): 12-14.
[35] 姜 楠. 金属矿山固体废弃物危害及资源再利用[J]. 农村科学实验, 2020(3): 117-118.
[36] 张利珍, 赵恒勤, 马化龙, 等. 我国矿山固体废物的资源化利用及处置[J]. 现代矿业, 2012, 27(10): 1-5.
[37] 孙秋君, 李 冰, 刘 欣. 固体废弃物的污染防治措施[J]. 科技创新与应用, 2013(12): 114.
[38] 杨 林. 矿山固体废弃物的危害及其环保治理技术研究[J]. 中国资源综合利用, 2020, 38(1): 126-128.
[39] 李 莉. 矿产资源综合利用的研究与对策[J]. 现代矿业, 2009, 25(6): 5-9.
[40] 魏邦亿. 我国矿产资源综合利用的现状和对策[J]. 资源节约与环保, 2017(7): 88-91.
[41] 唐 宇, 李瑞军, 王海军. 我国矿产资源综合利用现状分析及对策建议[J]. 中国矿业, 2013, 22(S1): 100-102.
[42] 任世赢. 我国有色金属矿产资源综合利用的现状、问题及对策[J]. 中国资源综合利用, 2018, 36(1): 74-75.
[43] 周 正, 王恒峰, 杜 新, 等. 四川拉拉铜矿矿山废石综合利用新工艺研究[J]. 四川地质学报, 2012, 32(S2): 218-222.
[44] 邹 凯. 创新的低品位资源开发技术在紫金山矿的应用[J]. 采矿技术, 2011, 11(6): 1-3.
[45] 李小文. 紫金山金矿低品位金矿资源的开发利用[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2005(5): 35-39.
[46] 罗映南, 刘荣春, 邹 凯. 紫金山金矿低品位资源的开发利用技术[J]. 黄金科学技术, 2003(2): 27-31.
[47] 万长峰. 德兴铜矿废石排放与堆浸筑堆相结合的探讨[J]. 有色矿山, 2000(2): 15-17.
[48] 刘维阁. 浅谈矿产资源的综合开发与科学合理利用[J]. 中国金属通报, 2008(44): 32-33.
[49] 董 越. 多固废资源在金川矿山充填采矿中协同综合利用研究[D]. 北京: 北京科技大学, 2019: 3-7.
[52] 张修香, 乔登攀, 孙宏生. 废石-尾砂高浓度料浆管道输送特性模拟[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2019, 29(5): 1092-1101.
[53] 李夕兵, 刘 冰, 姚金蕊, 等. 全磷废料绿色充填理论与实践[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2018, 28(9): 1845-1865.
[54] 孙 勇. 凡口矿深部废石回填系统的建立及应用效果分析[J]. 冶金丛刊, 2016(3): 43-45.
[55] 许毓海. 凡口铅锌矿工业废弃物综合利用技术研究[J]. 矿冶, 2002(2): 74-76, 84.
[56] 何哲祥, 谢开维, 周爱民. 全尾砂胶结充填技术的研究与实践[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 1998, 8(4): 3-5.
[57] 李欣远. 矿山地质环境恢复治理及综合利用探讨[J]. 中国金属通报, 2020(7): 295-296.
[58] 陈永贵, 张可能. 中国矿山固体废物综合治理现状与对 策[J]. 资源环境与工程, 2005(4): 311-313.
[59] 高韩锋, 姚 乐. 钢铁企业固体废弃物资源化利用[J]. 知识经济, 2015(20): 125-126.
[60] 王湖坤, 龚文琪, 刘友章. 有色金属矿山固体废物综合回收和利用分析[J]. 金属矿山, 2005(12): 70-72.
[61] 陈希廉. 矿山废石和尾矿的50种可能应用领域[C]// 第五届中国矿山地质学术会议暨振兴东北生产矿山资源高层论坛论文集. 北京: 中国有色金属工业协会, 2005: 40-49.
[62] 潘德安, 逯海洋, 刘晓敏, 等. 铁尾矿建材化利用的研究进展与展望[J]. 硅酸盐通报, 2019, 38(10): 3162-3169, 3214.
[63] 郑 科. 机制砂在高速公路桥梁高标号混凝土结构中的应用研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2019: 1-4.
[64] 孙超铨. 废石利用的新途径[J]. 采矿技术, 2005(1): 11-12.
SUN Chao-quan. New ways of using waste rock[J]. Mining Technology, 2005(1): 11-12.
[65] 宋少民, 程 成, 杨 楠. 机制砂岩性对胶砂和混凝土性能影响的研究[J]. 混凝土, 2019(9): 67-70.
[69] 刘 智, 吕 明, 杨和平. 机制砂颗粒粒形特征及其对砂浆性能的影响[J]. 城市建筑, 2020, 17(8): 127-129.
[70] 杨华山, 方坤河, 涂胜金, 等. 石灰石粉在水泥基材料中的作用及其机理[J]. 混凝土, 2006(6): 32-35.
[71] 李金朋, 张成龙, 王浩明, 等. 研山铁矿排岩废石生产砂石骨料研究[J]. 现代矿业, 2019, 35(6): 278-279.
[72] 李建政, 王安理, 范尚立, 等. 小秦岭金矿区废石资源综合利用试验研究[J]. 矿冶工程, 2010, 30(6): 51-53, 56.
[73] 郭学益, 田庆华, 刘 咏, 等. 有色金属资源循环研究应用进展[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2019, 29(9): 1859-1901.
[74] 陈思思. 国外废旧汽车环境押金制度的实践及对我国的启示[J]. 西安建筑科技大学学报(社会科学版), 2013, 32(5): 23-27.
[75] 王李管, 陈 鑫. 数字矿山技术进展[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2016, 26(8): 1693-1710.


