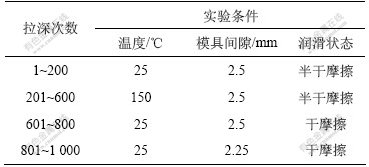
高强度钢板方盒形件拉深粘模行为
林启权1, 2,彭大暑1,王志刚3,薛德洲3
(1. 中南大学 材料科学与工程学院,湖南 长沙,410083;
2. 湘潭大学 机械工程学院,湖南 湘潭,411105;
3. 岐阜大学 工学部,岐阜 501-1193,日本)
摘 要:
摘 要:采用方盒形件拉深成形的方法,对高强度钢板SPFC590在干摩擦和半干摩擦条件下的拉深粘模行为进行研究。选用的模具材料分为2类:一类为无涂层模具SKD11,SLD和等温淬火球墨铸铁ADI;另一类为以SKD11为基体的涂层模具TiCN(PVD), TiCN(CVD), TiC(CVD)和DLC-Si (DC-PACVD)。采用无涂层模具时,在半干摩擦条件下仅少数几次拉深就出现宏观粘模现象,模具上粘模产生的位置位于凹模直边底部附近,而没有出现在凹模圆角处,并随着拉深次数的增加向上扩展;拉深工件中粘模产生的位置则位于工件顶部的直边和圆角部分连接处,并随着拉深的进行向下扩展;涂层模具经120次拉深后均未发生明显的粘模,但TiCN(PVD)和TiCN(CVD)涂层模具在凹模底部附近出现了微观粘着物;TiCN(CVD)和DLC-Si(DC-PACVD)涂层模具拉深1 000次后均未出现明显粘模现象,但TiCN(CVD)涂层模具上出现了微观粘着物,而DLC-Si(DC-PACVD)涂层模具上没有任何粘着物产生。
关键词:
中图分类号:TG131 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2009)06-1529-06
Galling behavior in square cup drawing of high tensile strength steel
LIN Qi-quan1, 2, PENG Da-xu1, WANG Zhi-gang3, XUE De-zhou3
(1. School of Materials Science and Technology, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. School of Mechanical Engineering, Xiangtan University, Xiantan 411105, China;
3. Department of Mechanical Engineering, Gifu University, Gifu 501-1193, Japan)
Abstract: The drawing galling behavior of a high tensile strength steel sheet SPFC590 was investigated under semi-dry and dry condition by the square cup drawing method. A cold alloy tool steel (SKD11, SLD) and ADI were used as the non-coated die. TiCN(PVD), TiCN(CVD), TiC(CVD) and DLC-Si (DC-PACVD) coated on SKD11 were used as the coated die. Using the non-coated dies in semi-dry, the macro-scale galling can clearly observed on die and drawn cup surface after a few drawing cycles. The galling on the die surface occurs at the bottom point of the straight boundary and not at the corner of the die, and grows upward with the drawing cycles. On the drawn cup, the galling starts at the top point of the boundary between the straight and corner edge, and grows downward. Using the coated dies, no remarkable galling is observed on die surface after 120 drawing cycles, but the micro-scale adhesion can be observed on TiCN(PVD) and TiCN(CVD) at the same boundary as the non-coated die. No conspicuous galling can be observed on TiC(CVD) and DLC-Si(DC-PACVD) ever after 1 000 cycles, but micro-scale adhesion can be recognized on TiC(CVD). No adhesion can be found on DLC-Si(DC-PACVD).
Key words: steel; tool material; coating; high tensile strength; deep drawing; galling
近几年来,汽车使用量日益增多,燃油价格不断上涨,人们对汽车提出了越来越高的要求。既要降低能源消耗、防止环境恶化,又要保证汽车的安全性能。汽车轻量化是减少能源消耗及气体排放的最有效措施,汽车质量减少10%,汽油的消耗量就会减少3%~7%[1-4]。采用高强度钢板可以达到减薄车身用板的厚度和质量的目的,这样,既可减小汽车质量,在降低燃油消耗的同时降低排放,达到节能环保,又可提高汽车的安全性。这就使新型的高强度钢板在汽车行业中特别是在汽车车身的生产中得到越来越广泛的应用[5-8]。然而,随着高强度钢板强度的增加,其成形性变差,特别是在拉深成形过程中,容易引起模具和工件表面的粘合、磨损及划痕等系列缺陷,即产生拉深粘模现象,严重降低了模具的使用寿命和工件的表面质量。为了防止粘模,我国在拉深过程中常大量使用润滑剂,而这又容易造成资源浪费和环境污染。目前,世界发达国家正在采用半干摩擦和干摩擦条件下的拉深成形工艺[9-10],对模具材料的要求也越来越高。对高强度钢板在干摩擦和半干摩擦条件下的拉深粘模行为进行研究有着重要的现实意义。国内外研究者对拉深粘模问题已进行了一些研究。赵升吨等[11]对不锈钢弧焊环圆筒形冲压件拉深过程中划伤产生的机理进行研究,并提出了防止划伤出现的系列措施;田柱平等[12]研究了拉深模粘结瘤的形成过程,并分析了粘结瘤的特点及其粘着部位;张六玲[13]通过对不锈钢拉深件成形过程中的滑移状态及应力、应变分析,揭示了不锈钢拉深件成形时表面划痕出现的根源。Gaard 等[14-17]通过拉深等冲压成形试验,对粘模现象进行了宏观和微观观察,分析了粘模产生的位置和扩展情况。目前,对有关拉深粘模问题还缺乏系统的研究,无论是其产生机理还是控制和预防方面的研究都还不够全面和完善,为此,本文作者针对高强度钢板的方盒形工件拉深成形,研究半干摩擦和干摩擦条件下不同模具材料对粘模的影响。
1 实 验
方盒形件的拉深原理如图1所示。为便于实验观察和更换模具,凹模采用镶块结构。同时,为了研究温度对粘模的影响,该模具能在300 ℃内进行电加热。
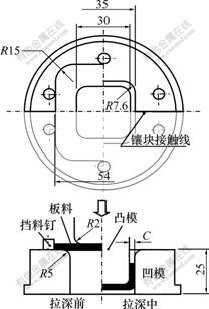
(单位:mm)
图1 盒形件拉深原理
Fig.1 Principle of square cup drawing
实验用工件材料为日产高强度钢板SPFC590,板厚为2.6 mm,形状如图1所示。为加速粘模的产生,拉深模具间隙取2.5 mm,即工件有4%的减薄量。本研究选用的拉深凹模材料分为无涂层模具和涂层模具两大类,无涂层模具的材料有冷作合金工具钢SKD11及其改良型SLD[18]、等温淬火球墨铸铁ADI。对于所选用的SLD钢,根据拉深方向与其材料切割方向的不同,分为SLD(P)和SLD(V) 2种:SLD(P)钢的拉深方向与切割方向平行;SLD(V)钢的拉深方向与切割方向垂直。涂层模具以SKD11为基体,表面通过化学气相沉积(CVD)、物理气相沉积沉积(PVD)和直流等离子化学气相沉积(DC-PACVD)的方法制备一层超硬涂层,涂层材料分别为:TiCN(PVD),TiCN(VVD),TiC(CVD)和DLC-Si(DC-PAVCD)。
拉深摩擦条件分为干摩擦和半干摩擦2种。坯料在不进行表面清洗时表面粘附一层防锈油,若在此状态进行拉深,防锈油则又充当润滑剂的作用,使得拉深为半干摩擦状态;利用丙酮对坯料表面的防锈油进行完全清洗后,拉深过程则处于干摩擦状态。拉深速度为3 mm/s,实验温度为室温。
2 结果与分析
2.1 粘模产生的位置和扩展
图2所示为凹模采用ADI模具材料、半干摩擦条件下,当拉深次数为1时,在模具和拉深件表面产生粘模时的照片。从图2(a)可以看出,粘模并非发生在凹模圆角部位,而是离凹模圆角部位有一段距离才产生粘模,粘模主要出现在模具直边底部至中心的区域内,凹模圆角部位和直边上部基本上没有划痕。这与文献[11-13, 19]中作者认为粘模发生在凹模圆角附近区域的观点不一致。从图2(b)可以看出,由于出现粘模,在拉深件表面产生了明显的划痕,划痕主要分布在工件的直边部分,而圆角部分则很少有划痕,在圆角和直边的连接处划痕最严重。工件表面的划痕分布情况也同样反映了粘模现象的存在。
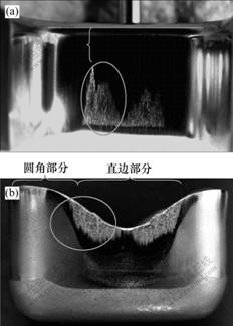
(a) 凹模表面粘模产生的位置;(b) 拉深件表面划痕的位置
图2 粘模产生的位置
Fig.2 Position of galling
采用SLD(P)模具材料,在半干摩擦下进行连续拉深,研究粘模在工件表面的产生和扩展,拉深工件表面的粘模现象如图3所示(N为拉深次数)。可见,随着拉深次数的增加,拉深件上的粘模越来越多,划痕产生并随着拉深的继续而扩展。前几次拉深中工件表面质量非常好,当拉深进行到第7次时工件表面出现划痕(图3(c)),随着拉深的继续进行,后续工件上的划痕越来越多,划痕朝凸耳谷部及直边中心扩展,使得面积和长度均增加,同时,划痕的深度也不断增加,变得越来越明显(图3(d))。
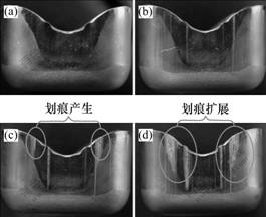
拉深次数N:(a) 1; (b) 4; (c) 7; (d) 15
图3 SLD(P) 模具拉深时拉深件表面划痕形貌
Fig.3 Surface appearance of SLD(P) drawn cup
据文献[12]报道,粘模最先出现在图4中阴影所示的位置,即凹模圆角下方的颈部,随加工次数的增加向下扩展。本研究所观察到的粘模的产生和扩展如图5所示。粘模最先出现在凹模直边底部稍上的位置,随着加工次数的增加,向上方和中心扩展;工件上的粘模则出现于工件顶部凸耳圆角与直边相交的区域内,随着加工次数的增加向中心和下方扩展。由于问题的复杂性及影响因素的多样性,拉深粘模形成机理至今尚未有统一的认识,有待以后进一步研究。
图4 传统粘模位置示意图
Fig.4 Schematic map of traditional galling position
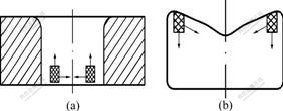
(a) 模具;(b) 工件
图5 粘模的产生及扩展示意图
Fig.5 Schematic map of galling position and growth
2.2 模具材料对粘模现象的影响
模具材料的性能是保证模具寿命的一个最基本也是最重要的条件,同时,也影响着其所成形的产品质量。为探讨模具材料对粘模现象的影响,选用凸凹模间隙为2.5 mm,材料为SKD11,SLD和ADI的非涂层模具在半干摩擦条件下进行拉深实验。图6所示为不同的非涂层模具拉深时凹模和工件表面的宏观形貌。从图6中可以看出,3种材料的凹模表面在拉深中都迅速出现了明显的粘模现象。从图中划痕的分布可以看出,粘模主要出现在模具直边底部至中心的区域内,并随着拉深过程的进行,逐渐向上方及中心方向扩展,凹模圆角部位和直边上部基本没有划痕。ADI和SKD11的抗粘模能力相近,在第1次拉深时就出现了大面积划痕;SLD材料特别是SLD(P)表现出较强的抗粘模能力,SLD(P)模具表面划痕的长度和面积都明显小很多,且在第15次拉深时才产生明显的粘模现象。
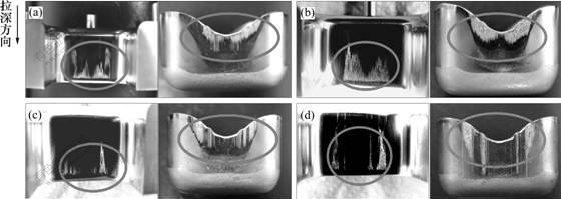
(a) SKD11(拉深次数N=1);(b) ADI(N=1);(c) SLD(V)(N=1);(d) SLD(P)(N=15)
图6 半干摩擦条件下非涂层模具拉深时凹模和工件表面的宏观形貌
Fig.6 Surface appearance of non-coated die and drawn cup after deep drawing under semi-dry condition
2.3 超硬涂层对拉深粘模的影响
采用不同涂层的模具,在半干摩擦条件下拉深120次后凹模和工件表面的宏观及微观形态如图7所示。由图7可知,所有涂层模具和拉深件上均没有出现明显的粘模现象,表明超硬涂层具有良好的抗粘模能力。但通过显微观察发现,TiCN(PVD)和TiCN(CVD)涂层表面已经出现了粘着现象,而TiC(CVD)和DLC-Si (DC-PACVD)涂层没有出现任何粘着现象。从工件表面来看,除DLC-Si(DC-PACVD) 涂层模具成形的工件外,均出现了微观划痕或微观粘着现象。
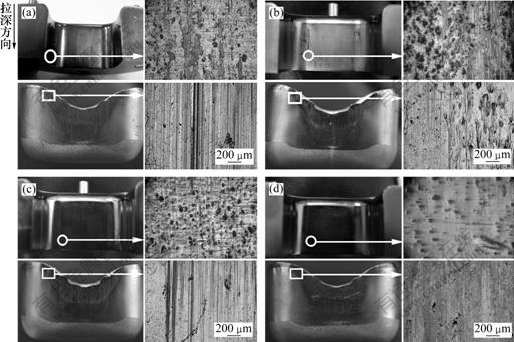
(a) TiCN(PVD); (b) TiCN(CVD); (c) TiC(CVD); (d) DLC-Si(DC-PACVD)
图7 拉深120次时不同涂层的模具拉深后凹模和工件表面的宏观及微观形态
Fig.7 Surface appearance of coated die and drawn cup after deep drawing under semi-dry condition (N=120)
使用扫描电镜(SEM)对拉深120次后的TiCN (PVD)涂层模具的各个位置进行观察,涂层观察区域的划分及观察结果如图8所示。由图8(b)可见,轻微的粘结现象遍布整个涂层,越靠近凹模的底部,粘着现象越严重,如图8(c)和8(d)所示。由此可见,模具上粘模产生的位置均为直边底部稍上,粘模位置与模具是否有涂层无关。
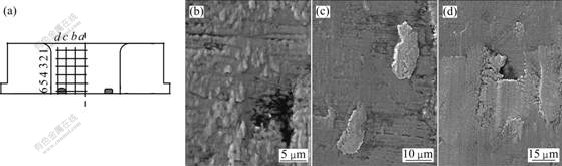
(a) SEM 观察区域; (b) b-1; (c) d-3; (d) d-6
图8 TiCN(PVD)涂层模具上各位置的粘着现象
Fig.8 Surface texture of coated die TiCN(PVD) after deep drawing (N=120)
TiC (CVD) 和 DLC-Si (DC-PACVD)在拉深中表现出来的抗粘模能力比其他几种材料的强。为进一步了解这2种材料的抗粘模性,本研究中设计了新的实验方案来对其进行继续拉深,实验条件如表1所示。
表1 TiC (CVD) 和 DLC-Si (DC -PACVD)的拉深条件
Table 1 Experimental conditions for TiC(CVD) and DLC-Si(DC-PACVD)
经过1 000次拉深后,凹模及拉深工件的表面形貌如图9所示。从图中可看出,在拉深进行1 000 次以后,涂层和工件表面仍没有明显的粘模出现。
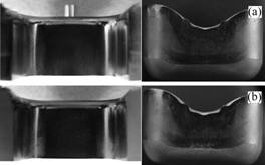
(a) TiC(CVD); (b) DLC-Si(DC-PACVD)
图9 凹模及拉深工件的表面形貌
Fig.9 Surface appearance of coated die and drawn cup after deep drawing (N=1 000)
TiC(CVD)和DLC-Si(DC-PACVD)优良的抗粘模能力得到了充分体现。
2种涂层的扫描电镜像如图10所示。从图10可以看出,经过1 000次拉深后,在图8所示的d-6部位,TiC(CVD)出现了微观的粘着物,但DLC-Si (DC-PACVD)上没有出现任何的粘着现象。通过观察可发现,在DLC-Si(DC-PACVD)涂层的凹坑中留有少量坯料掉落下来的颗粒。大量的拉深试验结果表明,DLC-Si(PACVD)涂层显示出了其超强的抗粘模能力。
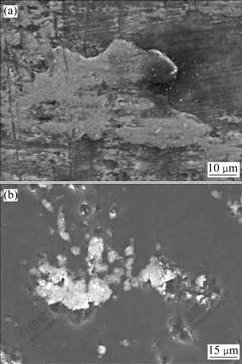
(a) TiC(CVD); (b) DLC-Si(DC-PACVD)
图10 经过1 000次拉深后TiC(CVD)和DLC-Si(DC-PACVD)在d-6处的显微形貌
Fig.10 Surface texture of TiC(CVD) and DLC-Si(DC-PACVD) at position d-6 after deep drawing when N=1 000
3 结 论
a. 粘模最先出现在凹模直边底部稍上的位置,而并非传统上认为的粘模发生在凹模圆角处附近;随着加工次数的增加,粘模区域逐渐向上扩展,直至凹模圆角的下方;工件上的粘着现象最先出现在凸耳圆角与直边相交处的较小区域内,随着加工次数的增加,粘着现象朝下方扩展直至直边的中心。
b. 无涂层模具(SKD11,ADI和SLD)仅经过少数几次拉深后,模具和工件表面均出现明显的粘模,ADI和SLD的抗粘模能力比SKD11的抗粘模能力稍强。
c. 采用涂层模具(TiCN(PVD),TiCN(CVD),TiC(CVD)和DLC-Si (DC-PACVD))时,半干摩擦状态下经过120次拉深后,模具和工件表面均无明显的粘模出现。但是TiCN(PVD) 和TiCN(CVD) 涂层中出现微观的磨损和粘着;经过1 000次拉深后,TiC(CVD)和DLC-Si(DC-PACVD)仍无明显的粘模出现,但在模具直边底部附近,TiC(CVD)涂层的表面出现了微观粘着现象,DLC-Si(PACVD)涂层显示出了超强的抗粘模能力。
参考文献:
[1] Senuma T. Physical metallurgy of modern high strength steel sheets[J]. ISIJ International, 2001, 41(6): 520-532
[2] Kuriyama Y, Takahashi M, Ohashi H. Trend of car weight reduction using high-strength steel[J]. Journal of Society of Automotive Engineers of Japan, 2001, 55(4): 51-57.
[3] 王 利, 朱晓东, 张丕军, 等. 汽车轻量化与先进的高强度钢板[J]. 宝钢技术, 2003(5): 53-59.
WANG Li, ZHU Xiao-dong, ZHANG Pi-jun, et al. Lightweighting of automobiles and advanced high strength steel[J]. Baosteel Technology, 2003(5): 53-59.
[4] 于忠奇, 赵亦希, 林忠钦. 汽车用铝合金板拉深性能评估参数[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2004, 14(10): 1689-1693.
YU Zhong-qi, ZHAO Yi-xi, LIN Zhong-qin. Evaluation parameter of drawability of automotive aluminum alloy sheets[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2004, 14(10): 1689-1693.
[5] 陈 亮, 陈 军, 张贵宝, 等. 高强度钢板拉深模具结构有限元分析与试验研究[J]. 塑性工程学报, 2008, 15(2): 42-45.
CHEN Liang, CHEN Jun, ZHANG Gui-bao, et al. Research of finite element modeling & experiment of the die structure for high-strength steel sheet metal stamping[J]. Journal of Plasticity Engineering, 2008, 15(2): 42-45.
[6] 朱 铮. 汽车用高强度钢板的开发应用和发展前景[J]. 钢铁, 2000, 35(11): 66-70.
ZHU Zheng. Development, application and perspective of high strength steel sheets for automobiles[J]. Iron and Steel, 2000, 35(11): 66-70.
[7] Takashi S, Shuji K, Sadao H, el al. Materials and technology for automotive use[J]. JFE Technical Report, 2004, 3(2): 1-18.
[8] Takita M, Ohashi H. Application of high strength steel sheets for automobiles in Japan[J]. Revue de Metallurgie—Cahiers D’Informations Techniques, 2001, 98(10): 899-909.
[9] Kataoka S, Motoi A, Tamaoki K, et al. Improvement in DLC thin film adhesion and its application to dry deep[J]. Journal of the Japan Society for Technology of Plasticity, 2005, 46(32): 412-416.
[10] Kataoka S, Murakawa M, Aizawa T, et al. Tribology of dry deep-drawing of various metal sheets with use of ceramics tools[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2004, 177/178: 582-590.
[11] 赵升吨, 王 骥, 崔晓勇, 等. 弧焊环拉深划伤机理及其防止技术的研究[J]. 锻压技术, 2003(5): 15-18
ZHAO Sheng-dun, WANG Ji, CUI Xiao-yong, et al. Investigation on scratching mechanism of arc-welding ring and technology preventing from its scratching[J]. Forging & Stamping Technology, 2003(5): 15-18.
[12] 田柱平, 卫雅文. 拉深模粘结瘤的形成及有效预防[J]. 模具技术, 1999(2): 69-72.
TIAN Zhu-ping, WEI Ya-wen. Forming and effective prevention of seizing tumour on a drawing die[J]. Die and Mould Technology, 1999(2): 69-72.
[13] 张六玲. 浅谈不锈钢拉深件成形时的表面保护方式[J]. 金属成形工艺, 2000, 18(5): 54-56.
ZHANG Liu-ling. The simple discusses about the surface protecting way of the stainless steel to form the extension piece[J]. Metal Forming Technology, 2000, 18(5): 54-56.
[14] Gaard A, Krakhmalev P V, Bergstrom J, et al. Galling resistance and wear mechanisms—Cold work tool materials sliding against carbon steel sheets[J]. Tribology Letters, 2007, 26(1): 67-72.
[15] Podgornik B, Hogmark S, Sandberg O. Proper coating selection for improved galling performance of forming tool steel[J]. Wear, 2006, 261(1): 15-21.
[16] Panjana P, Bonina I, Bevk J, et al. PVD hard coatings applied for the wear protection of drawing dies[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2005, 200: 133-136.
[17] Moura G C R, Aguilar M T P, Pertence A E M, et al. The failure analysis of a deep drawing die in the manufacturing of an automotive shock absorber cap[J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2004, 11(6): 943-950.
[18] Kubota K, Komatsubara S, Ogihara T, et al. Development of new cold working die steel “SLD-MAGIC”[J]. Hitachi Metals Technical Review, 2005, 21: 45-52.
[19] 陈筱俊. 筒形拉伸件拉痕的成因与消除[J]. 模具工业, 1993(7): 22-25.
CHEN Xiao-jun. Cause and elimination of scratching for tube-shaped parts in sheet drawing process[J]. Die & Mould Industry, 1993(7): 22-25.
收稿日期:2009-01-25;修回日期:2009-04-09
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(50874083)
通信作者:林启权(1965-),男,湖南浏阳人,博士,教授,从事金属材料加工研究;电话:0731-58293706;E-mail: xtulqq@126.com


