文章编号:1004-0609(2015)-05-1209-11
碳纳米管增强Cu和Al基复合材料的研究进展
易健宏1, 2,鲍 瑞1,李才巨1,沈 韬1,刘意春1,陶静梅1,谈松林1,游 昕1
(1. 昆明理工大学 材料科学与工程学院,昆明 650093;
2. 中南大学 粉末冶金国家重点实验室,长沙 410083)
摘 要:
碳纳米管(CNTs)增强Cu基或Al基复合材料是未来铜材或铝材方面最具潜力的发展方向之一。在本研究中,综述了近几年在CNTs增强Cu基和Al基复合材料研究方面取得的进展,论述CNTs的预处理、CNTs-金属复合粉末的制备、CNTs-金属复合块体材料的制备、界面结合机制以及CNTs的强化机理5个主要方面。
关键词:
碳纳米管;Cu基复合材料;Al基复合材料;制备方法;增强机理;
中图分类号:TB333 文献标志码:A
Research progress of CNTs reinforced Cu/Al matrix composites
YI Jian-hong1, 2, BAO Rui1, LI Cai-ju1, SHEN Tao1, LIU Yi-chun1, TAO Jing-mei1, TAN Song-lin1, YOU Xin1
(1. Faculty of Materials Science and Engineering,
Kunming University of Science and Technology, Kunming 650093, China;
2. State Key Laboratory of Powder Metallurgy, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: Carbon Nanotubes (CNTs) reinforced Cu or Al based composite material is one of the most potential developing direction in the copper or aluminum materials. In this work, research progress of the CNTs reinforced Cu and Al based composite materials in recent years was reviewed. Five main aspects including the pretreatment of CNTs, the preparation of CNTs-metal composite powder, the preparation of CNTs-metal composites, the interfacial bonding mechanism and the reinforcement mechanism of CNTs were discussed.
Key words: carbon nanotubes; copper-based composite; aluminum-based composite; preparation method; reinforced mechanism
有色金属材料是国民经济发展中至关重要的支柱性材料之一,其中铝和铜因具有导电导热性能良好、耐腐蚀、易于加工成形等优点而被广泛应用于航空航天、交通运输、电子电气、机械制造、建筑工业与国防军工等领域,成为用量仅次于钢铁的第二和第三金属。随着现代工业技术的快速发展,铜和铝的应用领域对铜材和铝材的强度、导电、导热、耐蚀、耐磨等性能提出了更高的要求[1-2],亟需开发出高综合性能的新材料。
碳纳米管(CNTs)具有独特的结构和优异的理化性能,其抗拉强度约为高强钢的100倍,密度仅为钢的1/6~1/7;同时,CNTs还具有优良的导电性、导热性、低的热膨胀系数、良好的热稳定性和耐蚀性而成为纳米科技领域的研究热点[3-8],相比碳纤维微米尺度下的增强作用,碳纳米管在微纳尺度下的增强作用更为显著,被认为是制备高性能复合材料的理想增强相之一,因此,CNTs增强复合材料成为全球材料学科中新材料开发的热点研究方向。目前,国内外已采用化学气相沉积法(CVD)大规模批量生产性能稳定的CNTs,且产品批次性能稳定、技术成熟、价格低廉,如YANG等[9]对可控生长碳纳米管结构的研究等,为CNTs的大规模工程应用奠定了坚实的原料基础。
由于CNTs增强Cu、Al基复合材料具有高强、高导、耐腐、耐磨、易加工等优良综合性能,具有非常广泛的应用前景。近年来,北美[10]、欧盟[11](欧盟第七框架计划-超级Cu-CNTs导线)、东南亚[12-13]等国家和地区都投入了大量的资金对CNTs增强Cu、Al基复合材料进行前期基础研究,国内也有多家科研院所从事相关研究开发工作。图1所示为2004~2013年发表的关于CNTs增强金属基复合材料的SCI文献数量。
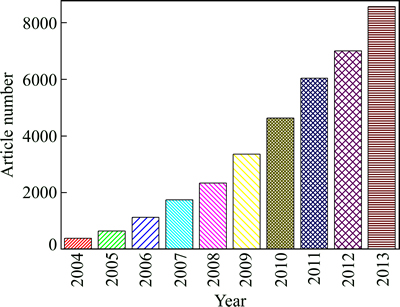
图1 2004~2013年发表的关于CNTs增强金属基复合材料的SCI文献数量
Fig. 1 SCI article numbers of CNTs reinforced metal matrix composite materials published in 2004-2013
但是由于存在一系列问题,如CNTs易团聚而难以均匀弥散分布及使组织均匀化、铜和铝金属基体与CNTs之间浸润性差而导致界面结合强度低、CNTs与金属基体多元体系中的组织和性能的关系缺乏研究等。因此,已有的CNTs增强Cu、Al基复合材料的相关研究成果大多还停留在实验室阶段[14]。本文作者对近几年国内外在CNTs增强Cu、Al基复合材料方面的研究进展进行了综述。
1 CNTs的预处理
1.1 CNTs的纯化
CNTs的制备方法包括电弧放电法、激光蒸发法、CVD法等,其中采用电弧放电法和激光蒸发法高温制备的CNTs具有较好的石墨化程度,但条件比较苛刻。而CVD法具有工艺简单、价格低廉等优点,是目前应用最广泛的生产方法。不管哪种方法制得的CNTs都会含有无定型碳、碳纤维、催化剂颗粒等杂质,这些杂质对CNTs增强金属基复合材料的应用均带来不利影响,因而需要对其进行纯化。现有的分离提纯方法有酸化法和空气氧化法,其主要是依据CNTs与杂质之间物理和化学性质的差异进行分离[14-19]。
1.2 CNTs的表面修饰
通常大批量生产的CNTs存在着许多表面缺陷,容易团聚,与金属基体之间润湿性差,从而影响其电学、力学和光学等性能,使CNTs的优越性难以得到充分发挥。为了改善CNTs表面结构,采用表面修饰方法改善CNTs的分散性、稳定性以及与金属基之间的界面相容性,从而提高CNTs增强金属基复合材料的致密度和各项性能。表面修饰的方法很多,包括化学镀[20-21]、电化学镀[22]、气相沉积[23]等,其中尤以利用化学方法使溶液中的金属离子还原为金属并沉积在基体表面上,形成镀层的化学镀表面修饰方法最为常见。如通过化学镀方法对CNTs表面进行镀Cu[24-25]、Ni[26-27]、W[28]、Mo[29]等金属,得到连续、均匀、光滑、致密的镀层,优化了CNTs与基体的界面结合。
2 CNTs-金属复合粉末的制备
由于CNTs和金属基体之间存在较大的密度差,如多壁碳纳米管的密度(1.8~2.1 g/cm3)仅为铜粉密度(8.9 g/cm3)的1/4~1/5,因此,将CNTs均匀、有效地分散到金属基体中是制备性能优异的复合材料的前提,通常采用机械球磨法、原位合成法、分子水平混合法等制备出复合粉末。
其中球磨法的使用十分广泛,如CHOI等[30]用高能球磨的方法制备了不同类型碳纳米管的Al基复合粉末,其中碳纳米管包括单壁、双壁和多壁,结果发现多壁碳纳米管能够在Al基粉末中得到良好的分散。JEYASIMMAN等[31]采用机械合金化方法,通过高能球磨30 h制备了不同碳纳米管含量的6061Al纳米晶复合材料,发现在球磨最后2 h加入碳纳米管,可以有效避免球磨对碳纳米管结构的破坏。HANZEL等[32]采用冷冻干燥的方法制备了CNTs-Al复合粉末,将CNTs和Al粉的混合物球磨时添加一定量的粘结剂,然后将混合料在液氮条件下冷冻,进行干燥后得到复合粉体。PHAM等[33]在CNTs和Al粉的球磨过程中加入树脂,然后在400 ℃氩气气氛下保温2 h,将添加的树脂脱出后制备出复合粉体。
另外,原位合成方法也是一种重要的制备复合粉末的方法,许龙山等[34]将SnCl2·2H2O溶液敏化处理处理过的CNTs均匀地分散在水溶液中形成CNTs悬浮液。在这种CNTs悬浮液中加入五水硫酸铜,先后用葡萄糖和甲醛对铜进行还原,原位制备了CNTs分散均匀的CNTs-超细铜粉复合粉体,并且CNTs与铜颗粒形成较牢固的结合。XU等[35]采用超临界流体条件下的苯溶剂热反应,以无水三氯化铁为催化剂、六氯乙烷为碳源,在铝粉中成功原位合成了非晶CNTs,其长度为0.2~5 μm,直径为10~50 nm,与Al基体具有较好的润湿性。王伟等[36]利用明胶使CNTs分散在硫酸铜溶液中,和葡萄糖在碱性条件下还原得到内嵌CNTs的氧化亚铜复合颗粒,再利用氢气将其还原成为内嵌CNTs的铜复合颗粒,复合颗粒粒径在几百纳米到几微米之间。HE等[37]采用沉积-沉淀法在铝粉基体上获得均匀分散的活性Ni纳米颗粒,以该Ni-Al粉末为催化剂,利用化学气相沉积法原位合成形态好、纯度高、分散均匀的CNTs,获得CNTs(Ni)-Al复合粉末。
3 CNTs-金属复合块体材料的制备
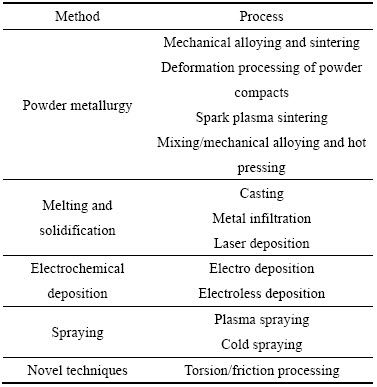
制备CNTs增强金属基复合材料首先应该考虑的问题是CNTs在金属基体中的分散性以及与基体的结合性。目前,通常采用的方法主要有粉末冶金烧结法[38-40]、熔炼法[41-42]以及喷涂法[43]等(见表1)。
表1 CNTs-金属复合材料的主要制备方法
Table 1 Main preparation methods of CNTs-metal composites
3.1 粉末冶金
SIM ES等[44]采用不用的超声分散方法制备出了复合粉末,然后通过粉末冶金方法制备了CNTs含量在0.25%~2.0%(质量分数)的CNTs-Al基复合材料。当CNTs含量在0.75%时,复合材料的抗拉强度和硬度分别为196 MPa和50 HV,分别比未添加碳纳米管试样的增加了200%和50%,CNTs增强效果十分显著。PHAM等[45]通过粉末冶金工艺制备了CNTs-Cu基复合材料,制备工艺如图2所示,研究了烧结工艺对复合材料显微组织和力学性能的影响,发现烧结温度为950 ℃时复合材料的致密度可以接近理论密度。
ES等[44]采用不用的超声分散方法制备出了复合粉末,然后通过粉末冶金方法制备了CNTs含量在0.25%~2.0%(质量分数)的CNTs-Al基复合材料。当CNTs含量在0.75%时,复合材料的抗拉强度和硬度分别为196 MPa和50 HV,分别比未添加碳纳米管试样的增加了200%和50%,CNTs增强效果十分显著。PHAM等[45]通过粉末冶金工艺制备了CNTs-Cu基复合材料,制备工艺如图2所示,研究了烧结工艺对复合材料显微组织和力学性能的影响,发现烧结温度为950 ℃时复合材料的致密度可以接近理论密度。
SHIN等[46]用微合金辅助致密化和热挤压相结合的方法制备了高致密度的CNTs-Al复合材料,当复合材料中含有4%CNTs(体积分数)时相对密度达到了约98%,抗压强度达到了约530 MPa;KWON等[47]用高能球磨和热挤压相结合的方法制备了CNTs-SiC-Al复合材料,SiC纳米粉末不仅有利于CNTs的分散,而且还能起到颗粒强化的作用,随着球磨时间的增加晶粒不断细化,细晶强化效果明显;通过球磨CNTs和Al粉得到复合粉末,然后通过粉末热挤压制备出接近全致密的1%CNTs-Al基复合材料(体积分数)[48];YOO等[49]将高能球磨后的CNTs-Cu复合粉末通过高异速比轧制方法制备出了CNTs分散均匀、定向分布并且Cu晶粒细小的CNTs-Cu基复合材料。图3所示为各种变形加工方式示意图[50]。
聂俊辉等[51]采用机械球磨和SPS工艺制备了CNTs/Cu复合材料。含量为1%(质量分数)的CNTs可在Cu基体中获得良好分散,CNTs与Cu基体界面结合良好,烧结压力和温度分别为40 MPa和850 ℃时,1%CNT-Cu(质量分数)复合材料的抗拉强度较纯铜提高了59.6%,导电率可以达到纯铜的75%。MAITI等[52]采用SPS方法制备了CNTs增强铝基复合材料,其显微组织的演变过程如图4所示。
JAFARI等[53]采用热压的方法制备了纳米晶块体Al2024-MWCNT复合材料,发现最佳工艺:机械球磨时间为4 h,热压温度为500 ℃,压强为250 MPa,保温时间为0.5 h。当MWCNT添加2%(体积分数)时相对密度可以98%,硬度为245 HV。SHUKLA等[54]通过真空热压法制备了不同单壁和多壁CNTs含量的Cu基复合材料,发现单壁CNTs比多壁CNTs对提高复合材料力学性能的影响更为显著。
3.2 熔炼法
LI等[55]用熔体搅拌和高压压铸的方法制备了CNTs增强Al基复合材料,其实验过程示意图如图5所示,0.05% MWCNTs-Al(质量分数)复合材料的伸长率和抗拉强度比纯铝的分别提高了27%和8%。孙巍等[56]研究了区域熔炼法制备CNTs增强Cu基复合材料的工艺,该工艺使金属基体获得比粉末冶金更好的流动性,对组织有填补和焊合的作用,能消除基体中细小的弥散分布的孔洞,使材料更加致密,并且能改善碳管与铜基体的结合性。
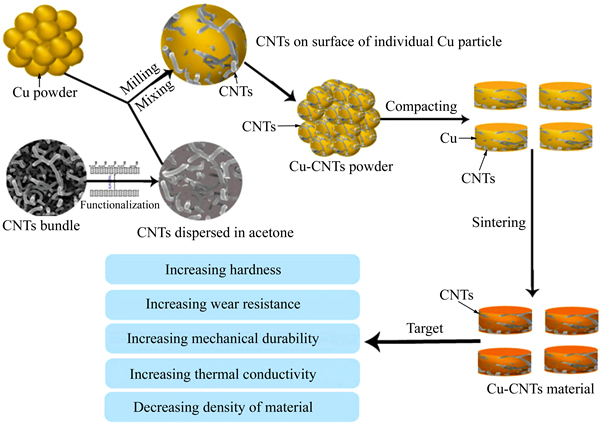
图2 粉末冶金方法制备CNTs-Cu基复合材料过程示意图[45]
Fig. 2 Schematic diagram of CNTs-Cu composite fabrication process based on powder metallurgy method[45]
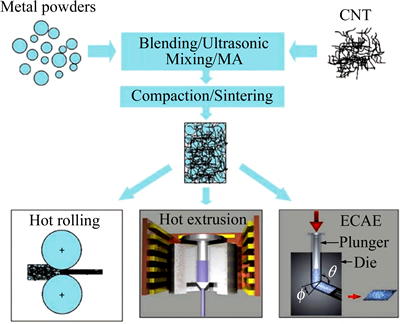
图3 各种变形加工方式示意图[50]
Fig. 3 Schematic diagrams of various deformation processes[50]
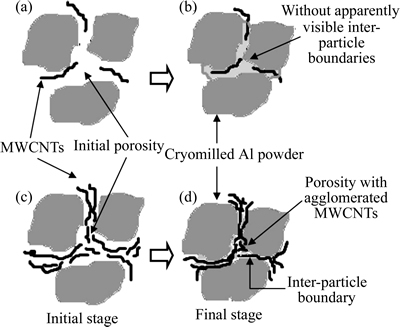
图4 SPS烧结过程中MWCNTs的演变示意图[52]
Fig. 4 Schematic diagram of evolution of MWCNTs during SPS sintering process[52]
KUCUKYILDIRIM等[57]采用真空辅助熔炼的方法,将6063Al合金熔渗到CNTs的多孔骨架中,发现CNTs分布均匀,但没有粉末冶金法制备的均匀。张科等[58]以CNTs微球作为多孔炭骨架,对其进行了铜粉熔渗,由于Cu对CNTs的浸润性较差,且液态铜具有较大的表面张力,熔渗效果并不理想。
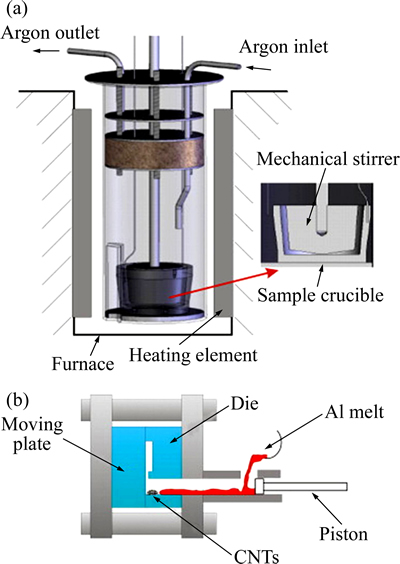
图5 搅拌熔炼和高压压铸法示意图[55]
Fig. 5 Schematic diagrams of melt stirring equipment (a) and high pressure die casting (b)[55]
ZHOU等[59]用激光诱导快速沉积的方法制备了CNTs和Fep增强铜基复合材料,当CNTs的含量为2.6%(质量分数)时,CNTs和Fep均匀的分散在Cu基体中,复合材料的显示出良好的综合性能,热导率为197 W·m-1·K-1,硬度为429 HV0.2,摩擦因数为0.11,磨损率为5.3×10-6 m3·N-1·m-1·lap-1。
3.3 沉积法
SUBRAMANIAM等[60-61]优先将碳纳米管原位生长定向排列的碳纳米管在基体上,然后在基底上面电镀Cu,得到CNTs-Cu基复合材料,其工艺制备过程如图6所示。所得复合材料的导电率(2.3×105~ 4.7×105 S/cm)和铜的(5.8×105 S/cm)接近,但是复合材料的载流量是Cu的100倍,达到6×108 A/cm2。赵海涛等[62]研究了不同辅助工艺对CNTs复合镀层质量的影响,发现使用超声波类辅助工艺时,镀液振动较大,镀层上的CNTs较少,基本无团聚。ARAI等[63]采用无电沉积法制备了多壁碳纳米管Cu基复合材料薄膜,其显微组织中CNTs分散均匀,且摩擦因数比纯铜的有了显著的降低。
3.4 喷涂法
BAKSHI等[64]采用等离子喷涂的方法制备了CNTs增强Al-Si复合涂层,当CNTs的含量为5%(质量分数)时弹性模型和抗压屈服强度分别增加17.5%和27%;而当CNTs增加到10%时,弹性模量和抗压强度分别增加39%和27%。
通过冷喷涂方法也可以制备CNTs增强金属基复合材料,工艺流程如图7所示[65]。CHO等[66]通过低压冷喷涂工艺制备了MWCNTs增强Cu基涂层,复合涂层具有较好的强度和较高的热导率。
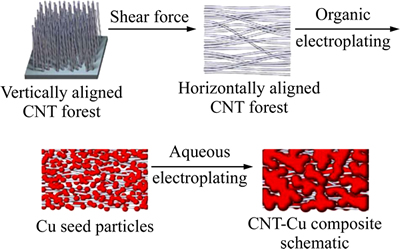
图6 CNTs-Cu基复合材料制备过程示意图[60]
Fig. 6 Schematic diagram of fabrication process of CNT-Cu composite[60]
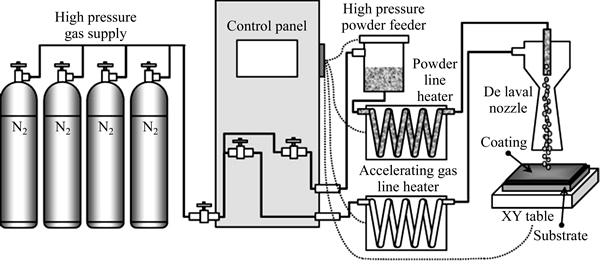
图7 冷喷涂装置示意图[65]
Fig. 7 Schematic diagram of cold gas dynamic spray (CGDS) system[65]
3.5 搅拌摩擦加工
搅拌摩擦加工法(FSP)是由搅拌摩擦焊技术演变而来的一种固态加工技术,是通过摩擦挤压产生的热和塑性变形来细化晶粒,均匀化显微组织,从而大幅提高合金力学性能[67-68]。LIU等[69]通过摩擦搅拌加工的方法制备了不同多壁碳纳米管含量的Al基复合材料(工艺示意图如图8所示),合金的抗拉强度和显微硬度都随着碳纳米管的增加而增加,而伸长率出现了下降。抗拉强度在碳纳米管含量为6.0%(质量分数)时达到了190.2 MPa,与纯铝基体相比提高了2倍。
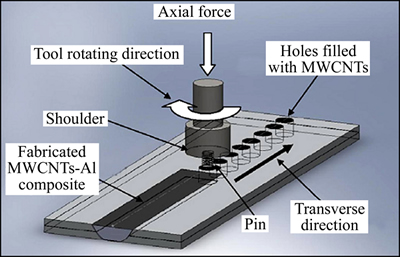
图8 搅拌摩擦制备MWCNTs-Al复合材料工艺示意图[69]
Fig. 8 Schematic diagram of FSP process of MWCNTs-Al composites[69]
4 CNT-金属的界面结合机制
对于CNTs-金属复合材料,CNTs的主要作用是形成能量传递通道,与之相接触的金属结构具有更大的尺寸,成为CNTs与外界通信的媒介。CNTs与金属在纳米尺度下的接触界面是影响复合材料理化性能和力学性能的重要因素,由于界面不仅仅是电阻或热阻的重要组成部分,而且是位错和应力较为集中的位置。因此,CNTs与金属之间界面结合的关键是形成CNTs与金属间的有效接触,从而保证界面具有可靠的连接性能和高效的能量传递机制[70-71]。
范德华力是由分子间距小于一定的距离范围(1 nm)时相互吸引形成的力场。从比表面积来说,CNTs的比表面积为40~300 m2/g,表面的尺度越细化就会引入接触面积越多,为范德华力的产生提供更大的可能。化学键主要是由两相间通过化学官能团相互起化学反应实现有效的黏结,结合力主要为主价键力,结合强度取决于反应结合数目和结合类型。如果复合材料各组分本身不存在化学键,CNTs与金属界面之间不能直接进行化学反应,也可以通过媒介作用实现化学键结合。机械啮合作用是依靠纯粹的粗糙表面相互嵌入(或互锁)作用进行连接,而CNTs表面的粗糙程度及与基体的嵌合情况决定界面的好坏。从微观角度看,提高界面摩擦力以及有效地传递应力可以使复合材料有较高的粘结强度。
CNTs经过表面处理后,能减缓由于复合材料成形时基体和增强体的膨胀系数相差较大而产生的附加应力。对CNTs-金属界面的形成及其作用有两种理论:变形层理论认为表面处理能在界面形成一层塑性层,能松弛界面的应力,起到减少界面应力集中的作用;而抑制层理论认为表面处理层是界面区的组成部分,是介于高模量增强体和低模量基体之间的中等模量物质,能够均匀地传递应力从而减弱界面应力的作用。如在制备CNTs增强铝基复合材料时,经常会在显微组织中发现Al4C3相(见图9),其可以减缓界面应力的集中,对复合材料的力学性能起到一定的促进作用。
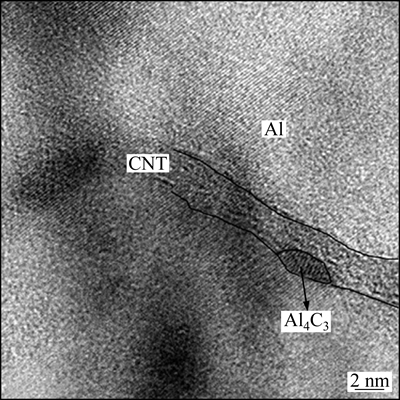
图9 CNTs-Al复合材料中Al4C3的HRTEM像[44]
Fig. 9 HRTEM image of Al4C3 phase in CNTs-Al composite[44]
SILVESTRE等[72]采用分子动力学模型,研究了CNTs-Al复合材料在受外力情况下的强化机理在研究过程中采用了两种假设:假设A(自由CNTs边界)和(假设B(固定CNTs边界)。和纯铝比较发现,在假设A和假设B两种情况下,复合材料的弹性模量分别增加了50%和100%,这是由于CNTs固定的轴向刚度和不可忽略的表面滑移应力造成的。通过对刚度的结算,发现CNTs可以有效地增强铝基复合材料。
5 强化机理
CNTs-金属复合材料的强化机制比较复杂,一般认为是由两种或者两种以上的机理组成的多元强化机制,其中主要为基体和增强体之间的载荷传递、位错强化、细晶强化和弥散强化等[73-77]。
通过界面剪切从基体向CNTs传递载荷而使CNFs承载,是金属基复合材料的主要强化机制之一。载荷传递过程中CNTs与基体的有效界面结合是实现CNTs载荷传递强化的关键[78]。对于CNTs-Cu基复合材料界面之间没有化学反应不能直接形成化学键,在发生塑变过程中,由于CNTs本身具有较高的强度和韧性而不易发生折断,从而发生协同变形并最终从基体中拔出[79]。
细小的CNTs增强体决定了复合材料的晶粒尺寸较小,当CNTs体积分数越高,弥散分布的密度越大,形核的核心越多,对金属基体晶粒生长的阻碍作用增大,从而晶粒尺寸较小。如果制备工艺为粉末冶金过程,由于合金粉末的起始晶粒尺寸已定,在复合材料的制备过程中,CNTs只能阻碍其晶粒的长大,并非铸造过程中CNTs成为形核核心。因此,CNTs引起的细晶强化作用对强度的贡献要小。BRADBURY等[80]测量了不同多壁碳纳米管含量(质量分数为1%~9%)的Al基复合材料的显微硬度,通过XRD分析方法研究Hall-Petch关系中晶粒尺寸对复合材料硬度的影响。
在Cu、Al基复合材料中,由于CNTs的热膨胀系数和弹性模量与金属基体之间存在很大的差异,因此,将导致复合材料内产生很大的热应力和相变力。这种应力引发的塑性变形,使复合材料中的位错密度显著增加,从而使材料发生加工硬化,这使得位错对复合材料强度的提高作了很大的贡献[81]。
在外力作用下,Cu、Al基体晶粒内的位错源被激发,产出的位错以滑移等方式运动从而释放内应力,当位错运动到CNTs周围时,由于CNTs具有极高的强度,不易在较高应力下发生切变断裂现象,从而阻碍了位错运动并导致在弥散分布的CNTs周围出现位错缠结现象,这抑制了塑性变形过程,并在CNTs周围产生新的应力场,当CNTs周围的位错群对晶界产出足够大应力时,可激发启动临近晶粒的位错源从而导致位错增值,上述位错以Orowan机制绕过CNTs的过程又进一步提高了基体中的位错密度,抑制了复合塑性变形过程的进行,从而提高了复合材料的强度[82]。
综上所述,对于CNTs增强Cu、Al金属基复合材料,需要采用综合强化模型,即把各种强化因素引起的强化效果叠加在一起,这样预测的强度值才能更接近于测量值。
6 展望
1) CNTs具有高的长径比和高的比强度、高的电导率和热导率、低的热膨胀系数、耐强酸强碱和耐高温氧化等特性,而成为极具应用潜力的一维纳米材料,随着CNTs批量化生产技术的成熟和制备成本的下降,使其在Cu、Al基复合材料作为增强体具有广阔的研究空间和良好的应用前景。
2) 在CNTs增强Cu、Al基复合材料的研究中还有一些问题有待解决:从研究层面来看,CNTs有效均匀分散到金属基体是制备高性能复合材料的基础,而CNTs增强体与金属基体的有效结合与结合界面的稳定性,是该类材料实际应用的前提,深入研究微纳尺度下CNTs增强Cu、Al基复合材料的多元强化机制可为高致密度、高均匀度和高强度的CNTs-Cu、CNTs-Al基复合材料制备提高指导。
3) 从应用层面来讲,由于CNTs-Cu、CNTs-Al基复合材料的制备还存在着技术的问题,如何实现应用上的突破,也是加快该类材料的发展的重要方面。从现有的研究来看,发展高强CNTs-Al基复合材料构件,尤其尺寸不大的结构零件和高导、减磨耐磨的粉末冶金CNTs-Cu基复合材料有望更快获得实际应用。
REFERENCES
[1] SRIVASTAVA A, DIXIT A R, TIWARI S. A Review on fabrication and characterization of aluminium metal matrix composite (AMMC)[J]. International Journal, 2014, 2(2): 516-521.
[2] 张敬国, 汪礼敏, 张少明, 王林山, 张景怀. 铜及铜合金粉末应用及研究现状[J]. 粉末冶金工业, 2013(1): 52-57.
ZHANG Jing-guo, WANG Li-min, ZHANG Shao-ming, WANG Lin-shan, ZHANG Jing-huai. The copper and copper alloy powders application and research status[J]. Powder Metallurgy Industry, 2013(1): 52-57.
[3] CAI An-hui, XIONG Xiang, LIU Yong, AN Wei-ke, ZHOU Guo-jun, LUO Yun, LI Tie-lin, LI Xiao-song. A Cu-based bulk amorphous alloy composite reinforced by carbon nanotube[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2012, 22(9): 2191-2197.
[4] LI Hai-peng, FAN Jia-wei, KANG JIAN-li, ZHAO Nai-qin. In-situ homogeneous synthesis of carbon nanotubes on aluminum matrix and properties of their composites[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2014, 24(7): 2331-2336.
[5] HAO Xiao-ning, ZHANG Hai-ping, ZHENG Rui-xiao, ZHANG Yi-tan, AMEYAMA K, MA Chao-li. Effect of mechanical alloying time and rotation speed on evolution of CNTs/Al-2024 composite powders[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2014, 24(7): 2380-2386.
[6] 孟振强, 刘如铁, 熊拥军, 赵福安,李溪滨. 球磨方式对多壁碳纳米管形貌和结构的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2012, 22(12): 3421-3427.
MENG Zhen-qiang, LIU Ru-tie, XIONG Yong-jun, ZHAO Fu-an, LI Xi-bin. Effect of ball milling on morphology and structure of multi-walled carbon nanotubes[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2012, 22(12): 3421-3427.
[7] 许世娇, 肖伯律, 刘振宇, 王文广,马宗义. 高能球磨法制备的碳纳米管增强铝基复合材料的微观组织和力学性能[J]. 金属学报, 2012, 48(7): 882-888.
XU Shi-jiao, XIAO Bo-lü, LIU Zhen-yu, WANG Wen-guang, MA Zong-yi. Microstructures and mechanical properties of CNT/Al composites fabricated by high energy ball-milling method[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2012, 48(7): 882-888.
[8] CIAMBELLI P, ARURAULT L, SARNO M, LEONE C, DATAS L, SANNINO D, LENORMAND P, PLOUY S L B D. Controlled growth of CNT in mesoporous AAO through optimized conditions for membrane preparation and CVD operation[J]. Nanotechnology, 2011, 22(26): 265613.
[9] YANG Feng, WANG Xiao, ZHANG Da-qi, YANG Juan, LUO Da, XU Zi-wei, WEI Jia-ke, WANG Jian-qiang, XU Zhi, PENG Fei, LI Xue-mei, LI Ruo-ming, LI Yi-lun, LI Mei-hui, BAI Xue-dong, DING Feng, LI Yan. Chirality-specific growth of single-walled carbon nanotubes on solid alloy catalysts[J]. Nature, 2014, 510: 522-524.
[10] MAZLOUMI M, SHADMEHR S, RANGOM Y, NAZAR L F, TANG X W. Fabrication of three-dimensional carbon nanotube and metal oxide hybrid mesoporous architectures[J]. ACS Nano, 2013, 7(5): 4281-4288.
[11] SUNDARAM R M, KOZIOL K K, WINDLE A H. Continuous direct spinning of fibers of single-walled carbon nanotubes with metallic chirality[J]. Advanced Materials, 2011, 23(43): 5064-5068.
[12] LUKASZ K, AGNIESZKA L R, JEFF P, KRZYSZTOF K. Replacing copper wires with carbon nanotube wires in electrical transformers[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2014, 24: 619-624.
[13] CHO W, SCHULZ M, SHANOV V. Growth and characterization of vertically aligned centimeter long CNT arrays[J]. Carbon, 2014, 72: 264-273.
[14] BAKSHI S R, LAHIRI D, AGARWAL A. Carbon nanotube reinforced metal matrix composites-a review[J]. International Materials Reviews, 2010, 55(1): 41-64.
[15] KRUUSENBERG I, ALEXEYEVA N, TAMMEVESKI K, KOZLOVA J, MATISEN L, SAMMELSELG V, SOLLA-GULL N J, FELIU J M. Effect of purification of carbon nanotubes on their electrocatalytic properties for oxygen reduction in acid solution[J]. Carbon, 2011, 49(12): 4031-4039.
N J, FELIU J M. Effect of purification of carbon nanotubes on their electrocatalytic properties for oxygen reduction in acid solution[J]. Carbon, 2011, 49(12): 4031-4039.
[16] WEPASNICK K A, SMITH B A, SCHROTE K E, WILSON H K, DIEGELMANN S R, FAIRBROTHER D H. Surface and structural characterization of multi-walled carbon nanotubes following different oxidative treatments[J]. Carbon, 2011, 49(1): 24-36.
[17] SURI A, COLEMAN K S. The superiority of air oxidation over liquid-phase oxidative treatment in the purification of carbon nanotubes[J]. Carbon, 2011, 49(9): 3031-3038.
[18] SHIRAZI Y, TOFIGHY M A, MOHAMMADI T, PAK A. Effects of different carbon precursors on synthesis of multiwall carbon nanotubes: Purification and functionalization[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2011, 257(16): 7359-7367.
[19] 张 翼, 齐暑华, 王 洲, 段国晨. 碳纳米管纯化处理的研究进展[J]. 材料导报, 2011, 25(9): 6-9.
ZHANG Yi, QI Shu-hua, WANG Zhou, DUAN Guo-chen. Research progress on purification methods of carbon nanotubes[J]. Materials Review, 2011, 25(9): 6-9.
[20] KAROUSIS N, TAGMATARCHIS N, TASIS D. Current progress on the chemical modification of carbon nanotubes[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2010, 110(9): 5366-5397.
[21] SITKO R, ZAWISZA B, MALICKA E. Modification of carbon nanotubes for preconcentration, separation and determination of trace-metal ions[J]. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 2012, 37: 22-31.
[22] SO K P, LEE I H, DUONG D L, KIM T H, LIM S C, AN K H, LEE Y H. Improving the wettability of aluminum on carbon nanotubes[J]. Acta Materialia, 2011, 59(9): 3313-3320.
[23] ADAMS T, DUONG B, SERAPHIN S. Effects of catalyst components on carbon nanotubes grown by chemical vapor deposition[J]. Journal of Undergraduate Research in Physics, 2012(1): 1-8.
[24] MAQBOOL A, HUSSAIN M A, KHALID F A, BAKHSH N, HUSSAIN A, KIM M H. Mechanical characterization of copper coated carbon nanotubes reinforced aluminum matrix composites[J]. Materials Characterization, 2013, 86: 39-48.
[25] 王 伟, 陈小华, 刘云泉, 易 斌, 颜海梅. 内嵌碳纳米管铜复合颗粒的制备[J]. 机械工程材料, 2011, 35(4): 38-41.
WANG Wei, CHEN Xiao-hua, LIU Yun-quan, YI Bin, YAN Hai-mei. Preparation of copper composite particles inner-embedded with carbon nanotubes[J]. Materials for Mechanical Engineering, 2011, 35(4): 38-41.
[26] CHU Ke, JIA Cheng-chang, JIANG Li-kun, LI Wen-sheng. Improvement of interface and mechanical properties in carbon nanotube reinforced Cu-Cr matrix composites[J]. Materials and Design, 2013, 45: 407-411.
[27] CHU Ke, WU Qing-ying, JIA Cheng-chang, LIANG Xue-bing, NIE Jun-hui, TIAN Wen-huai, GAI Guo-sheng, GUO Hong. Fabrication and effective thermal conductivity of multi-walled carbon nanotubes reinforced Cu matrix composites for heat sink applications[J]. Composites Science and Technology, 2010, 70(2): 298-304.
[28] NIE Jun-hui, JIA Cheng-chang, JIA Xian, LI Yi, ZHANG Ya-feng, LIANG Xue-bing. Fabrication and thermal conductivity of copper matrix composites reinforced by tungsten-coated carbon nanotubes[J]. International Journal of Minerals, Metallurgy, and Materials, 2012, 19(5): 446-452.
[29] NIE Jun-hui, JIA Cheng-chang, JIA Xian, ZHANG Ya-feng, SHI Na, LI Yi. Fabrication, microstructures, and properties of copper matrix composites reinforced by molybdenum-coated carbon nanotubes[J]. Rare Metals, 2011, 30(4): 401-407.
[30] CHOI H, WANG L, CHEON D, LEE W. Preparation by mechanical alloying of Al powders with single-, double-, and multi-walled carbon nanotubes for carbon/metal nanocomposites[J]. Composites Science and Technology, 2013, 74: 91-98.
[31] JEYASIMMAN D, SIVAPRASAD K, SIVASANKARAN S, NARAYANASAMY R. Fabrication and consolidation behavior of Al 6061 nanocomposite powders reinforced by multi-walled carbon nanotubes[J]. Powder Technology, 2014, 258: 189-197.
[32] HANZEL O,  P. New approach for distribution of carbon nanotubes in alumina matrix[J]. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2014, 34(7): 1845-1851.
P. New approach for distribution of carbon nanotubes in alumina matrix[J]. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2014, 34(7): 1845-1851.
[33] PHAM V T, NGUYEN V A, BUI H T, LE D C, NGUYEN V C, NGUYEN V L, DOAN D P, PHAN N M. A method to obtain homogeneously dispersed carbon nanotubes in Al powders for preparing Al/CNTs nanocomposite[J]. Advances in Natural Sciences: Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, 2013, 4(2): 025015.
[34] 许龙山, 陈小华, 吴玉蓉, 潘伟英, 徐海洋, 张 华. 碳纳米管铜基复合材料的制备[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2006, 16(3): 406-411.
XU Long-shan, CHEN Xiao-hua, WU Yu-rong, PAN Wei-ying, XU Hai-yang, ZHANG Hua. Preparation of CNTs/Cu composite[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2006, 16(3): 406-411.
[35] XU Xin, LI Zhi-qiang, ZHANG Di, CHEN Zhi-xin. In situ synthesis of nanostructured carbon reinforcement in aluminum powders[J]. Materials Letters, 2010, 64(10): 1154-1156.
[36] 王 伟, 陈小华, 熊伊那, 易 斌, 陈传盛, 刘云泉, 颜海梅. 碳纳米管铜基复合颗粒的制备[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2011, 21(6): 1929-1935.
WANG Wei, CHEN Xiao-hua, XIONG Yi-na, YI Bin, CHEN Chuan-sheng, LIU Yun-quan, YAN Hai-mei. Preparation of carbon nanotube embedded in copper composites particles[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2011, 21(6): 1929-1935.
[37] HE C, ZHAO N, SHI C, DU X, LI J, LI H, CUI Q. An approach to obtaining homogeneously dispersed carbon nanotubes in Al powders for preparing reinforced Al-matrix composites[J]. Advanced Materials, 2007, 19(8): 1128-1132.
[38] STEIN J, LENCZOWASKI B, FR TY N, ANGLARET E. Mechanical reinforcement of a high-performance aluminium alloy AA5083 with homogeneously dispersed multi-walled carbon nanotubes[J]. Carbon, 2012, 50(6): 2264-2272.
TY N, ANGLARET E. Mechanical reinforcement of a high-performance aluminium alloy AA5083 with homogeneously dispersed multi-walled carbon nanotubes[J]. Carbon, 2012, 50(6): 2264-2272.
[39] SHUKLA A K, NAYAN N, MURTY S V S N, MONDAL K, SHARMA S C, GEORGE K M, BAKSHI S R. Processing copper-carbon nanotube composite powders by high energy milling[J]. Materials Characterization, 2013, 84: 58-66.
[40] 易健宏, 鲍瑞. 粉末冶金在CNTs增强金属基复合材料中的应用[J]. 粉末冶金工业,2015, 25(1): 1-7.
YI Jian-hong, BAO Rui. Application of powder metallurgy in CNTs reinforced metal-based composites[J]. Powder Metallurgy Industry, 2015, 25(1): 1-7.
[41] XU Wu, HU Rui, LI Jin-shan, FU Heng-zhi. Effect of electrical current on tribological property of Cu matrix composite reinforced by carbon nanotubes[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2011, 21(10): 2237-2241.
[42] KIM J D, KIM J H, ZHANG X H, PARK J H, CHA J H, JUNG S I. Control of mechanical properties according to content ratio of copper coated carbon nanotubes in alumimum composites[J]. J Chem, 2012, 6: 455-461.
[43] 韩晓东, 李志强, 范根莲, 江 林, 张 荻. 碳纳米管增强铝基复合材料制备技术进展[J]. 材料导报, 2012, 26(11): 40-46.
HAN Xiao-dong, LI Zhi-qiang, FAN Gen-lian, JIANG Lin, ZHANG Di. Progress in fabrication technique of carbon nanotubes reinforced Al matrix composites[J]. Material Review, 2012, 26(11): 40-46.
[44] SIM ES S, VIANA F, REIS M A L, VIEIRA M F. Improved dispersion of carbon nanotubes in aluminum nanocomposites[J]. Composite Structures, 2014, 108: 992-1000.
ES S, VIANA F, REIS M A L, VIEIRA M F. Improved dispersion of carbon nanotubes in aluminum nanocomposites[J]. Composite Structures, 2014, 108: 992-1000.
[45] PHAM V T, BUI H T, TRAN B T, NGUYEN V T, LE D Q, THAN X T, NGUYEN V C, DOAN D P, PHAN N M. The effect of sintering temperature on the mechanical properties of a Cu/CNT nanocomposite prepared via a powder metallurgy method[J]. Advances in Natural Sciences: Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, 2011, 2(1): 015006.
[46] SHIN S E, CHOI H J, BAE D H. Micro-alloying assisted consolidation of aluminum/carbon nanotubes powder[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2014, 599: 46-50.
[47] KWON H, SAARNA M, YOON S, WEIDENKAFF A, LEPAROUX M. Effect of milling time on dual-nanoparticulate- reinforced aluminum alloy matrix composite materials[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2014, 590: 338-345.
[48] KWON H, LEPAROUX M. Hot extruded carbon nanotube reinforced aluminum matrix composite materials[J]. Nanotechnology, 2012, 23(41): 415701.
[49] YOO S J, HAN S H, KIM W J. A combination of ball milling and high-ratio differential speed rolling for synthesizing carbon nanotube/copper composites[J]. Carbon, 2013, 61: 487-500.
[50] AGARWAL A, BAKSHI S R, LAHIRI D. Carbon nanotubes: Reinforced metal matrix composites[M]. U.S.: CRC Press, 2010.
[51] 聂俊辉, 贾成厂, 张亚丰, 史 娜, 李 一. 机械球磨与放电等离子体烧结制备碳纳米管/铜复合材料[J]. 粉末冶金工业, 2011, 21(5): 44-50.
NIE Jun-hui, JIA Cheng-chang, SHI Na, ZHANG Ya-feng, LI Yi. Fabrication of carbon nanotubes/copper composites using mechanical milling and spark plasma sintering[J]. Powder Metallurgy Industry, 2011, 21(5): 44-50.
[52] MAITI A, REDDY L, CHEN F, ZHANG L, SCHOENUNG J M, LAVERNIA E J, LAHA T. Carbon nanotube-reinforced Al alloy-based nanocomposites via spark plasma sintering[J]. Journal of Composite Materials, 2014: 0021998314541304.
[53] JAFARI M, ABBASI M H, ENAYARI M H, KARIMZADEH F. Mechanical properties of nanostructured Al2024–MWCNT composite prepared by optimized mechanical milling and hot pressing methods[J]. Advanced Powder Technology, 2012, 23(2): 205-210.
[54] SHUKLA A K, NAYAN N, MURTY S, SCHARMA S C, CHANDRAN P, BAKSHI S R, GEORGE K M. Processing of copper-carbon nanotube composites by vacuum hot pressing technique[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2013, 560: 365-371.
[55] LI Qian-qian, ROTTMAIR C A, SINGER R F. CNT reinforced light metal composites produced by melt stirring and by high pressure die casting[J]. Composites Science and Technology, 2010, 70(16): 2242-2247.
[56] 孙 巍, 李文珍. 碳纳米管增强铜基复合材料的制备技术研究[J]. 铸造技术, 2008, 29(1): 29-32.
SUN Wei, LI Wen-zhen. Progress of CNTs reinforced copper-based composite preparation[J]. Foundry Technology, 2008, 29(1): 29-32.
[57] KUCUKYILDIRIM B O, EKER A A. A novel technique for carbon nanotube reinforced metal matrix composite fabrication[J]. Conference of the International Journal of Arts and Science, 2012, 1(2): 171-181.
[58] 张 科, 陈小华, 刘云泉, 周灵平, 许龙山, 易 斌, 王 伟. 网络互穿结构的碳纳米管铜基复合材料研究[J]. 湖南大学学报(自然科学版), 2009, 36(12): 59-63.
ZHANG Ke, CHEN Xiao-hua, LIU Yun-quan, ZHOU Ling-ping, XU Long-shan, YI Bin, WANG Wei. Research of carbon nanotubes-Cu composite with interpenetrating networks[J]. Journal of Hunan University (Natural Sciences), 2009, 36(12): 59-63.
[59] ZHOU Sheng-feng, WU Chao, ZHANG Tian-you, ZHANG Ze-zhong. Carbon nanotube-and Fep-reinforced copper–matrix composites by laser induction hybrid rapid cladding[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2014, 76: 25-28.
[60] SUBRAMANIAM C, YASUDA Y, TAKYA S, ATA S, NISHIZAWA A, FUTABA D, YAMADA T, HATA K. Carbon nanotube-copper exhibiting metal-like thermal conductivity and silicon-like thermal expansion for efficient cooling of electronics[J]. Nanoscale, 2014, 6(5): 2669-2674.
[61] SUBRAMANIAM C, YAMADA T, KOBASHI K, SEKIGUCHI A, FUTABA D N, YUMURA M, HATA K. One hundred fold increase in current carrying capacity in a carbon nanotube-copper composite[J]. Nature Communications, 2013, 4: 1-7.
[62] 赵海涛, 陈吉安, 范振民, 王全保. 铜基碳纳米管复合电镀辅助工艺的对比研究[J]. 电镀与环保, 2012, 32(1): 12-14.
ZHAO Hai-tao, CHEN Ji-an, FAN Zhen-min, WANG Quan-bao. A comparative research on auxiliary processes for copper based carbon nanotube composite electroplating[J]. Electroplating and Pollution Control, 2012, 32(1): 12-14.
[63] ARAI S, KANAZAWA T. Electroless deposition of cu/multiwalled carbon nanotube composite films with improved frictional properties[J]. ECS Journal of Solid State Science and Technology, 2014, 3(6): 201-206.
[64] BAKSHI S R, KESHRI A K, AGARWAL A. A comparison of mechanical and wear properties of plasma sprayed carbon nanotube reinforced aluminum composites at nano and macro scale[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2011, 528(9): 3375-3384.
[65] PIALAGO E J T, PARK C W. Cold spray deposition characteristics of mechanically alloyed Cu-CNT composite powders[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2014, 308: 63-74.
[66] CHO S, TAKAGI K, KWON H, SEO D, OGAWA K, KIKUCHI K, KAWASAKI A. Multi-walled carbon nanotube-reinforced copper nanocomposite coating fabricated by low-pressure cold spray process[J]. Surface and coatings Technology, 2012, 206(16): 3488-3494.
[67] 赵 霞, 柯黎明, 徐卫平, 刘鸽平. 搅拌摩擦加工法制备碳纳米管增强铝基复合材料[J]. 复合材料学报, 2011, 28(2): 185-190.
ZHAO Xia, KE Li-ming, XU Wei-ping, LIU Ge-ping. Carbon nanotubes reinforced aluminum matrix composites by friction stir processing[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2011, 28(2): 185-190.
[68] LIU Z Y, XIAO B L, WANG W G, MA Z Y. Singly dispersed carbon nanotube/aluminum composites fabricated by powder metallurgy combined with friction stir processing[J]. Carbon, 2012, 50(5): 1843-1852.
[69] LIU Qiang, KE Li-ming, LIU Fen-cheng, HUANG Chun-ping, XING Li. Microstructure and mechanical property of multi-walled carbon nanotubes reinforced aluminum matrix composites fabricated by friction stir processing[J]. Materials and Design, 2013, 45: 343-348.
[70] SONG Xiao-hui, GAN Zhi-yin, LIU Sheng, YAN Nan, L Qiang. Computational study of thermocompression bonding of carbon nanotubes to metallic substrates[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2009, 106(10): 104308.
Qiang. Computational study of thermocompression bonding of carbon nanotubes to metallic substrates[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2009, 106(10): 104308.
[71] MEI Lei, HE Xiao-dong, LI Yi-bin, WANG Rong-guo, WANG Chao, PENG Qing-yu. Grafting carbon nanotubes onto carbon fiber by use of dendrimers[J]. Materials Letters, 2010, 64(22): 2505-2508.
[72] SILVESTRE N, FARIA B, LOPES J N C. Compressive behavior of CNT-reinforced aluminum composites using molecular dynamics[J]. Composites Science and Technology, 2014, 90: 16-24.
[73] 邓春锋. 碳纳米管增强铝基复合材料的制备及组织性能研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2007.
DENG Chun-feng. Investigation of fabrication, structure and properties of carbon nanotube reinforced aluminum matrix composites[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2007.
[74] 夏 春, 许 冬, 柯黎明, 邢 丽, 刘奋成. 碳纳米管增强铝基复合材料的热轧强化研究[J]. 南昌航空大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 27(4): 6-10.
XIA Chun, XU Dong, KE Li-ming, XING Li, LIU Fen-cheng. Study on hot-rolled strengthening of carbon nanotubes reinforced aluminum composites[J]. Journal of Nanchang Hangkong University (Natural Sciences), 2013, 27(4): 6-10.
[75] 郭忠全. 高性能铜基电接触复合材料的研制及强化机理研究[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2011.
GUO Zhong-quan. The production and reinforcement of high-performace copper-based electrical contact composite[D]. Jinan: Shandong University, 2011.
[76] BARAI P, WENG G J. A theory of plasticity for carbon nanotube reinforced composites[J]. International Journal of Plasticity, 2011, 27(4): 539-559.
[77] NOURI N, ZIAEI-RAD S, ADIBI S, KARIMZADEH F. Fabrication and mechanical property prediction of carbon nanotube reinforced Aluminum nanocomposites[J]. Materials and Design, 2012, 34: 1-14.
[78] BAKSHI S R, AGARWAL A. An analysis of the factors affecting strengthening in carbon nanotube reinforced aluminum composites[J]. Carbon, 2011, 49(2): 533-544.
[79] NAM D H, CHA S I, LIM B K, PARK H M, HAN D S, HONG S H. Synergistic strengthening by load transfer mechanism and grain refinement of CNT/Al-Cu composites[J]. Carbon, 2012, 50(7): 2417-2423.
[80] BRADBURY C R, GOMON J K, KOLLO L, KWON H, LEPAROUX M. Hardness of Multi Wall Carbon Nanotubes reinforced aluminium matrix composites[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2014, 585: 362-367.
[81] LI H, MISRA A, HORITA Z, KOCH C C, MARA N A, DICKERSON P O, ZHU Y. Strong and ductile nanostructured Cu-carbon nanotube composite[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2009, 95(7): 071907.
[82] NAM D H, KIM Y K, CHA S I, HONG S H. Effect of CNTs on precipitation hardening behavior of CNT/Al-Cu composites[J]. Carbon, 2012, 50(13): 4809-4814.
(编辑 王 超)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金面上项目(51274107);云南省科技厅重大项目(KKSB201451004);云南铜业有限公司校企基金资助项目(4201351007);粉末冶金国家重点实验室开放基金资助项目(KKZ6201451021);云南省人才培养项目(KKSY201451070);左铁镛院士工作站项目(KKKP201451016)
收稿日期:2014-09-24;修订日期:2015-01-10
通信作者:鲍 瑞,博士;电话:13888480327;E-mail:baorui@kmust.edu.cn
摘 要:碳纳米管(CNTs)增强Cu基或Al基复合材料是未来铜材或铝材方面最具潜力的发展方向之一。在本研究中,综述了近几年在CNTs增强Cu基和Al基复合材料研究方面取得的进展,论述CNTs的预处理、CNTs-金属复合粉末的制备、CNTs-金属复合块体材料的制备、界面结合机制以及CNTs的强化机理5个主要方面。
[2] 张敬国, 汪礼敏, 张少明, 王林山, 张景怀. 铜及铜合金粉末应用及研究现状[J]. 粉末冶金工业, 2013(1): 52-57.
[6] 孟振强, 刘如铁, 熊拥军, 赵福安,李溪滨. 球磨方式对多壁碳纳米管形貌和结构的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2012, 22(12): 3421-3427.
[7] 许世娇, 肖伯律, 刘振宇, 王文广,马宗义. 高能球磨法制备的碳纳米管增强铝基复合材料的微观组织和力学性能[J]. 金属学报, 2012, 48(7): 882-888.
[19] 张 翼, 齐暑华, 王 洲, 段国晨. 碳纳米管纯化处理的研究进展[J]. 材料导报, 2011, 25(9): 6-9.
[25] 王 伟, 陈小华, 刘云泉, 易 斌, 颜海梅. 内嵌碳纳米管铜复合颗粒的制备[J]. 机械工程材料, 2011, 35(4): 38-41.
[34] 许龙山, 陈小华, 吴玉蓉, 潘伟英, 徐海洋, 张 华. 碳纳米管铜基复合材料的制备[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2006, 16(3): 406-411.
[36] 王 伟, 陈小华, 熊伊那, 易 斌, 陈传盛, 刘云泉, 颜海梅. 碳纳米管铜基复合颗粒的制备[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2011, 21(6): 1929-1935.
[40] 易健宏, 鲍瑞. 粉末冶金在CNTs增强金属基复合材料中的应用[J]. 粉末冶金工业,2015, 25(1): 1-7.
[43] 韩晓东, 李志强, 范根莲, 江 林, 张 荻. 碳纳米管增强铝基复合材料制备技术进展[J]. 材料导报, 2012, 26(11): 40-46.
[51] 聂俊辉, 贾成厂, 张亚丰, 史 娜, 李 一. 机械球磨与放电等离子体烧结制备碳纳米管/铜复合材料[J]. 粉末冶金工业, 2011, 21(5): 44-50.
[56] 孙 巍, 李文珍. 碳纳米管增强铜基复合材料的制备技术研究[J]. 铸造技术, 2008, 29(1): 29-32.
[58] 张 科, 陈小华, 刘云泉, 周灵平, 许龙山, 易 斌, 王 伟. 网络互穿结构的碳纳米管铜基复合材料研究[J]. 湖南大学学报(自然科学版), 2009, 36(12): 59-63.
[62] 赵海涛, 陈吉安, 范振民, 王全保. 铜基碳纳米管复合电镀辅助工艺的对比研究[J]. 电镀与环保, 2012, 32(1): 12-14.
[67] 赵 霞, 柯黎明, 徐卫平, 刘鸽平. 搅拌摩擦加工法制备碳纳米管增强铝基复合材料[J]. 复合材料学报, 2011, 28(2): 185-190.
[73] 邓春锋. 碳纳米管增强铝基复合材料的制备及组织性能研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2007.
[74] 夏 春, 许 冬, 柯黎明, 邢 丽, 刘奋成. 碳纳米管增强铝基复合材料的热轧强化研究[J]. 南昌航空大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 27(4): 6-10.


