文章编号:1004-0609(2010)S1-s0829-04
TC21钛合金电子束焊缝精细组织及其对硬度的影响
张秉刚1,王 廷1,陈国庆1,冯吉才1,李 东2
(1. 哈尔滨工业大学 现代焊接生产技术国家重点实验室,哈尔滨 150001;
2. 航天科工 哈尔滨风华有限公司,哈尔滨 150036)
摘 要:对TC21钛合金进行电子束焊接试验,通过光学显微镜和透射电子显微镜(TEM)对焊缝内不同特征区域的精细显微组织进行分析,并对各个区域的显微硬度进行测量。结果表明:TC21钛合金在焊接过程中,焊缝区和热影响区Ⅰ、Ⅱ区内发生了马氏体转变,由针状马氏体α′相和残余β相组成。热影响Ⅲ区只发生了α相向β相的转变。马氏体转变量与接头不同区域的降温速率有关,焊缝区内马氏体数量最大,尺寸最大,马氏体强化效果最明显,显微硬度最高。而在热影响Ⅲ区内无马氏体强化效果,且β相数量增多,硬度低于母材的,发生软化。
关键词:TC21钛合金;精细组织;马氏体转变;显微硬度
中图分类号:TG 456.3 文献标识码:A
Fine microstructure and its effect on hardness of electron beam welding joint of TC21 Ti alloy
ZHANG Bing-gang1, WANG Ting1, CHEN Guo-qing1, FENG Ji-cai1, LI Dong2
(1. State Key Laboratory of Advanced Welding Production Technology, Harbin Institute of Technology,
Harbin 150001, China;
2. Harbin Fenghua Limited Corporation, China Aerospace Science and Industry Corporation, Harbin 150036, China)
Abstract: The electron beam welding of TC21 titanium alloy was carried out. The fine microstructure in various feature regions of weld was analyzed by optical microscopy and transmission electron microscopy. As well, the microhardness of each region was measured. The results show that martensitic transformation occurs in weld zone and heat affected zone I and II which are characterized by acicular martensite α′ phase and retained β phase. The transformation of α to β phase is the only phase change process in heat affected zone Ⅲ. The extent of martensitic transformation is relevant to cooling rate in various region of the joint. The microhardness in weld zone is the highest for martensitic strengthening because there is the largest number of martensite with the biggest size in it. But the material in heat affected zone Ⅲ softened during welding with the increase of β phase and lack of martensitic strengthening effect.
Key words: TC21 Ti alloy; fine microstructure; martensitic transformation; microhardness
TC21钛合金具有良好的强度、塑性、断裂韧性和较低的裂纹扩展速率,是一种高强高韧损伤容限型钛合金,可用来制造飞机隔框、壁板等工作温度较高、受力较复杂的重要结构零件,有望成为飞机结构主要的钛合金用材[1]。
钛及其合金的连接主要通过熔化焊实现,主要包括钨极氩弧焊、等离子弧焊、电子束焊和激光焊等[2]。由于钛的化学活性强,随着温度的增高,在固态下能强烈地吸收各种气体,会使焊接接头的塑性和韧性急剧下降[3]。在各种熔化焊接方法中,真空电子束焊接具有电子束能量密度高、焊缝深宽比大、热影响区小、焊接变形小以及焊缝纯净度高等优点,在焊接钛合金时具有突出的优势[4-5],特别适合于航空航天领域中钛合金构件的高精度焊接[6]。
本文作者对56 mm厚TC21进行了电子束焊接试验,对接头不同特征区域的精细显微组织以及显微硬度值进行分析。揭示不同区域的组织演变过程以及显微硬度变化原因,为大厚度TC21钛合金电子束焊接工艺参数的制订提供理论依据。
1 试验
试验所用的TC21钛合金厚度56 mm,其化学成分如表1所列。钛合金TC21的β相稳定系数Kβ为0.619,属于α+β双相钛合金,β稳定元素的添加量为6.69%,介于2%~10%之间。铝的物质的量为6%~8%之间,为高铝含量钛合金。
表1 TC21的化学成分
Table 1 Chemical composition of TC21 (mass fraction, %)

焊接试验在KL-110大型真空电子束焊机上进行,焊接工艺参数为:加速电压60 kV,束流400 mA,聚焦电流2.06 A,焊接速度500 mm/min。
焊后在焊缝位置切取试样进行分析。对焊缝横截面进行打磨和抛光,然后采用混合酸(HF+HCl+ HNO3+H2O,体积比为1:1.5:2.5:95)浸蚀。光学金相观察在OLYMPUS光学显微镜下进行,采用HV-100型显微硬度计对接头横截面水平方向显微硬度分布进行了测量,载荷为1 N,加载时间为10 s。在不同区域沿焊缝纵向切取0.4 mm薄片,然后将其研磨至100 μm,再进行双喷剪薄以进行TEM分析。TEM分析在Philips CM12透射电子显微镜下完成。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 接头特征区域划分
选取接头中部位置分析了接头的横截面形貌特征,如图1所示。从图1中可以看出,根据焊接过程中经历的冶金过程和组织特征的不同,焊缝在宽度方向可以明显分为4个区域,焊缝区(WZ)、熔合区(FZ)、热影响区(HAZ)和母材区(BM)。
热影响区进一步观察,其微观形貌如图2所示。由图2可见,在热影响区内,存在3个不同组织特征的区域,分别标识为Ⅰ、Ⅱ和Ⅲ区,其中Ⅰ区与熔合区毗邻,为热影响区内受热温度最高的区域,温度达到β相变温度以上,冷却过程中发生了再结晶过程,生成等轴晶;Ⅲ区靠近母材,为热影响区内受热温度最低的区域,其形貌与母材相似;而在Ⅱ区内,晶粒则为长条状。
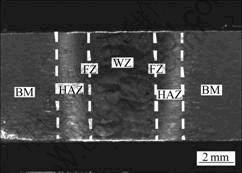
图1 焊缝横截面形貌
Fig.1 Macrostructure in cross section of weld

图2 热影响区微观组织
Fig.2 Microstructure of HAZ
2.2 不同区域精细微观组织
对各个区域进行TEM分析以观察其内部精细微观结构,其中由于熔合区的范围很窄,且为热影响区与焊缝区的结合部位,因此没有单独对该区域进行分析。各个区域的TEM图像如图3所示。
母材组织由板条状的初生α相与次生α相和β相的混合组织构成,初生α相板条的宽度约为1 μm。在热影响区的Ⅰ区和Ⅱ区,组织为细小的白色针状相和颜色较深的β相组成。从形态上判断,该针状组织为

图3 不同区域的TEM像
Fig.3 TEM images of various regions of weld: (a) BM; (b) HAZ(Ⅲ); (c) HAZ(Ⅱ); (d) HAZ(Ⅰ); (e) WZ; (f) Diffraction pattern of α′ phase
马氏体相,不同方向的马氏体针交叉排列。Ⅲ区组织仍然为α+β,只是α相已经开始发生向β的转变,因而相界变得模糊。而在焊缝区内,柱状晶内部亦为针状马氏体组织,其分布形态也与热影响区Ⅰ区和Ⅱ区中相同。图3(f)的电子衍射结果显示,热影响区和焊缝中形成的马氏体相与α相的晶体结构类似,同样为密排六方结构。
2.3 马氏体相变过程
从上面的分析可知,在TC21焊接过程中,在热影响区和焊缝区内主要发生了马氏体相变,该区域内性能的改变也跟这一过程有关,因此有必要对其进行讨论。
马氏体由β相在快速冷却过程中形成,是含过饱和合金元素的固溶体组织。钛合金中的马氏体主要有两种:具有密排六方结构的针状马氏体α′相,主要在β稳定元素含量较少的合金中出现;另一种为斜方结构马氏体α″相,其形态更加细小,内部含有孪晶,在含β稳定元素含量较多的合金中出现[7]。从形态、晶体结构以及合金成分可看出,本试验中出现的马氏体为α′相。
对比热影响区中Ⅰ区和Ⅱ区内和焊缝区内的马氏体形态可以发现,Ⅱ区内的马氏体针更加细小,而焊缝区的马氏体则更粗大,Ⅰ区介于二者之间。各区内马氏体的这种尺寸对比关系与对应区域在焊接过程中经受的焊缝峰值温度相对应,而峰值温度又对应于不同的降温速率,即峰值温度越高,降温速率越快。焊接过程中的马氏体相变属于变温转变过程,其转变量与时间无关,具有动态奥氏体热稳定化,即转变量随冷却速度的加大而增加。而马氏体长大是马氏体加厚的过程,而马氏体变长是马氏体加厚过程的几何结 果[8]。由此,越靠近焊缝中心的金属,降温速度越 快,因此,Ⅱ区的马氏体针更加细小,而焊缝内则比较粗大。
马氏体相变要经历形核和长大过程,而在各个区域中,马氏体的分布形态能够说明这一过程。从上面的分析不难看出,尺寸较大的马氏体最先形核,而尺寸较小的马氏体则随后在其周围形核。先形核马氏体和后形核马氏体可以看成一套结晶系统,而先形核马氏体决定着长大方向,这样的形核过程在β基体多个位置同时进行。这样,在马氏体形核长大的过程中就将β基体分割开来,从而在最终组织中残余部分β相。显然,冷却速度最快的区域,即马氏体长大最充分的区域,残余β相含量最少。在本试验中,从接头不同区域的TEM图像中各相的颜色对比来看,Ⅱ区中残余β相的含量也最高,这与上述分析结果一致。
2.4 接头不同区域的显微硬度
图4所示为接头横截面水平中心线上的显微硬度分布。由于接头两侧组织沿焊缝中心线对称,因此只对一侧进行了测量。从图4中可以看出,焊缝区内硬度最高,其次是热影响区Ⅰ区和Ⅱ区,而在接头热影响区,Ⅲ区出现硬度最低点,这与接头各区域中显微组织相对应。马氏体强化是双相钛合金中重要的强化方式,其强化效果取决于析出针状马氏体的数量、尺寸以及分布。焊缝区内α′马氏体数量最多且尺寸较大,因此硬度最高。而在热影响区Ⅲ区内,没有马氏体相析出,且出现α相向β相的转变,因而出现硬度最低点,该区域材料在焊接过程中发生软化。
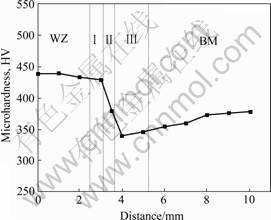
图4 接头横截面显微硬度分布
Fig.4 Microhardness distribution of cross section of joint
3 结论
1) TC21钛合金在焊接过程中,焊缝区和热影响Ⅰ区、Ⅱ区内发生了马氏体转变,由针状马氏体α′相和残余β相组成。而在热影响Ⅲ区则没有马氏体相形成,只发生了α相向β相的转变。
2) 马氏体转变量与接头不同区域的降温速率有关,焊缝区内马氏体数量最多,尺寸最大,残余β相最少。
3) 接头不同区域的显微硬度决定于马氏体强化的效果,焊缝区内强化效果最明显,硬度最高,而在热影响Ⅲ区内,无马氏体强化效果,且β相数量增多,硬度最低。
REFERENCES
[1] 马少俊, 吴学仁, 刘建中, 王利发. TC21钛合金的微观组织对力学性能的影响[J]. 航空材料学报, 2006, 26(5): 31-34.
MA Shao-jun, WU Xue-ren, LIU Jian-zhong, WANG Li-fa. Influence of microstructures on mechanical properties for TC21 titanium alloy[J]. Journal of Aeronautical Materials, 2006, 26(5): 31-34.
[2] 赵红凯, 王春亮, 任 飞, 刘兰霄. 钛合金焊接的研究进展[J]. 材料导报, 2007, 21(5A): 342-348.
ZHAO Hong-kai, WANG Chun-liang, REN Fei, LIU Lan-xiao. Progress in research on titanium alloy welding[J]. Materials Review, 2007, 21(5A): 342-348.
[3] HARWIG D D, FOUNTAIN C, ITTIWATTANA W, CASTNER H. Oxygen equivalent effects on the mechanical properties of titanium welds[J]. Welding Research, 2000(11): 305-316.
[4] MLADENOV G, VUTOVA K, WOJCICKI S. Experimental investigation of the weld depth and thermal efficiency during electron beam welding[J]. Vacuum, 1998, 51(2): 231-233.
[5] SARESH N, PILLAI M G, MATHEW J. Investigations into the effects of electron beam welding on thick Ti-6Al-4V titanium alloy[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2007, 192/193(1): 83-88.
[6] 周广德, 陶守林. 电子束焊接技术在航天领域中应用[J]. 电工电能新技术, 1999(1): 52-55.
ZHOU Guang-de, TAO Shou-lin. Application of electron beam welding technique in the space flight[J]. Advanced Technology of Electrical Engineering and Energy, 1999(1): 52-55.
[7] 邓安华. 钛合金的马氏体相变[J]. 上海有色金属, 1999, 20(4): 193-199.
DENG An-hua. Martensitic transformation of titanium alloys[J]. Shanghai Nonferrous Metals, 1999, 20(4): 193-199.
[8] 徐祖耀. 马氏体相变与马氏体[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1980.
XU Zu-yao. Martensitic transformation and Martensite[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1980.
(编辑 杨幼平)
基金项目:国家重点基础研究发展计划资助项目(2010CB731704)
通信作者:张秉刚;电话:0451-86412911;E-mail: zhangbg@hit.edu.cn