Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 25(2015) 3747-3752
Effects of gallium on electrochemical discharge behavior of Al-Mg-Sn-In alloy anode for air cell or water-activated cell
Kun YU1,2, Shi-hai YANG1, Han-qing XIONG1, Li WEN1, Yi-long DAI1, Fei TENG1, Su-feng FAN1
1. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. State Key Laboratory of Powder Metallurgy, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China
Received 1 December 2014; accepted 19 May 2015
Abstract: In order to evaluate the electrochemical properties of aluminum alloy anode under high current densities in alkaline electrolyte, the galvanostatic discharge, potentiodynamic polarization and hydrogen evolution tests of three experimental Al-Mg-Sn-In-(Ga) alloys were performed. The results show that the alloying element gallium improves the working potentials of experimental Al-Mg-Sn-In alloys under different discharge current densities. The average working potentials of the alloys containing gallium can reach -1.3 V under current density ranging from 650 to 900 mA/cm2, while those of alloy without Ga are only -1.0 V. Such phenomenon is attributed to the solid solution which can form amalgam with aluminum matrix. Such an amalgam can form the hydrolyzed species during the discharge process and lead to the corrosion infiltrating into aluminum matrix.
Key words: aluminum anode; electrochemical property; discharge behavior; corrosion; dissolution-deposition
1 Introduction
Aluminum has a very negative thermodynamic potential of -2.4V (vs Hg/HgO) [1] in alkaline electrolyte and a high energetic capacity of 2980 A·h/kg. Such properties make aluminum a potential anode material used in air cell or water-activated battery system [2]. When aluminum is used as anode, the current-generating reaction can be described as Al+4OH--3e→Al(OH)4-. But when used in alkaline electrolyte, aluminum is consumed invalidly by a parasitic hydrogen evolution reaction, expressed as 2Al+ 6H2O+2OH-→2Al(OH)4+3H2↑ [3], and the discharge process of aluminum is consequently weakened. Therefore, it is necessary to solve such a problem while maintaining the active dissolution of aluminum. One of the resolutions is adding the alloying elements such as magnesium, tin, gallium, indium, zinc and thallium [4-6] in aluminum matrix. Among these elements, tin, indium and gallium can dissolve in aluminum matrix to form solid solution. Such elements can dissolve with aluminum matrix into electrolyte and form corresponding cations. Then, the cations can be plated out by aluminum and deposit on the surface of aluminum alloy, which benefits the discharge of aluminum anode for battery system. This process is called dissolution- deposition mechanism [7]. Some previous investigations have reported about aluminum used as the anode for battery systems with low current densities [8], but few works were done for battery systems yielding high current densities. Besides, few works were performed for aluminum anode used in alkaline brine electrolyte [7]. And it was reported that tin and indium obtained high hydrogen evolution overpotential and gallium can form amalgam with aluminum [9]. As a result, in the present study the experimental Al-Mg-based alloys containing tin, indium and gallium were prepared to investigate the electrochemical discharge behavior in alkaline brine electrolyte under high current densities.
2 Experimental
The chemical compositions of three experimental aluminum alloys in this work are listed in Table 1. The alloys were prepared by ingot metallurgy method with 99.99% aluminum and high purity magnesium (99.99%), tin (99.99%), indium (99.99%) and gallium (99.99%) in a furnace at 1023 K. The molten alloys were cast at 973 K, the water-cooled copper mold and as-cast alloy ingots were homogenized at 773 K for 8 h and then quenched in water. Then, the alloy ingots were cold rolled to a thickness of about 3 mm with a reduction of 82% to produce the experimental specimens.
Table 1 Designed chemical compositions of experimental alloys (mass fraction, %)
The electrochemical measurements of experimental alloy samples in cold-rolled state were performed by using the IM6ex electrochemical workstation containing a conventional three-electrode system with a platinum counter electrode and a Hg/HgO reference electrode. All potentials were measured referring to the Hg/HgO electrode. The Tafel polarization measurements of examined electrodes were conducted at a scan rate of 1 mV/s and the evolution of hydrogen test was also performed by the method of draining water out of a inverted sealed glass tube. All the measurements were carried out in a 20% NaOH + 3.5% NaCl solution. Three samples of the all these alloys were tested for the electrochemical properties and the minimum values were reported. The experimental temperature was maintained at (333±2) K and controlled by the use of a water-heated bath. The microstructures of the alloys were observed by using an FEI Quanta-200 fitted with an Edax-Genesis energy dispersive X-ray analyzer.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Electrochemical properties of experimental alloys
The discharge performance of aluminum anode can be reflected from its potential-time curve, which was measured by galvanostatic discharge at a certain impressed current density. The galvanostatic discharge behavior of three experimental aluminum alloys in rolled state in alkaline brine solution is shown in Fig. 1. The average discharge potentials of these alloys obtained from the potential-time curves are listed in Table 2. The impressed current densities of 650, 800 and 950 mA/cm2 were used in this work. The utilization of high current densities is aimed to investigate the discharge behavior of the anode for high-power applications [10].
As shown in Fig. 1, with the discharge current density increasing, the average potentials of three alloys shift to a more positive state. Such phenomenon is in accordance with the Tafel law. Because the open circuit potentials of the three alloys are different, the changes of the potentials at the initial phases of the three alloys are different. Among these three alloys, Alloy 3 obtains the most negative potential under all the three current densities (Table 2). This phenomenon is consistent with the relationship of corrosion current densities listed in Table 3. The potential of aluminum anode during the discharge process is important because the potential difference between the anode and cathode is the driving force for the anode to deliver electrons [11]. The aluminum anode with good discharge performance exhibits strong discharge activity and provides a negative discharge potential. Therefore, Alloy 2 and Alloy 3 are more suitable to be used as anodes for high power air cell or water-activated cell than Alloy 1. Furthermore, the discharge potentials of Alloy 2 and Alloy 3 remain steady during the whole discharge process under high current densities (Fig. 1). Such property is indispensable for being used as an anode material.
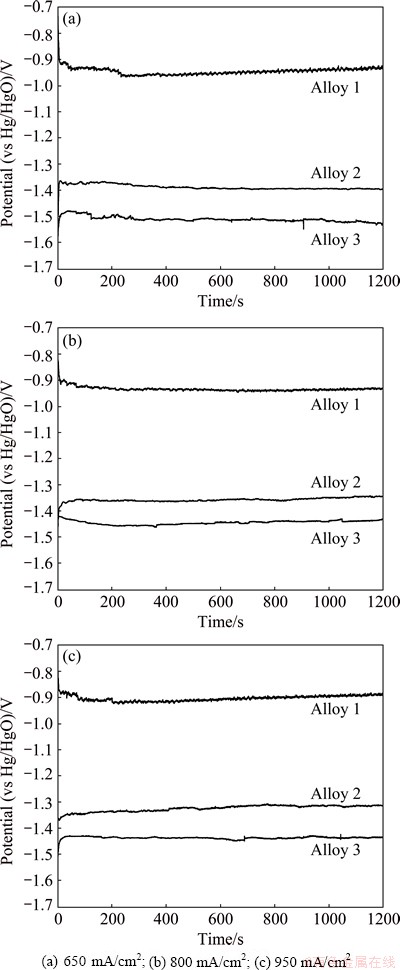
Fig. 1 Galvanostatic discharge curves of Alloys 1, 2 and 3 in rolled state under different current densities
Table 2 Average potential of three alloys in rolled state under different current densities
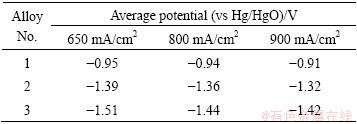
Table 3 Corrosion parameters of three aluminum alloys evaluated from polarization curves

Potentiodynamic polarization is an effective method for investigating the discharge behavior of aluminum anode over a wide potential range [12]. The representative polarization curves for three aluminum alloys in rolled state are shown in Fig. 2. It can be seen that the three alloys do not passivate but remain active in the whole potential range. In addition, the corrosion potentials of Alloy 2 and Alloy 3 shift more negative than that of Alloy 1. These polarization curves were used to measure the corrosion current density at the corrosion potential by Tafel extrapolation. It is clear that gallium increases the corrosion current density of aluminum alloys as seen in Table 3. Even though the corrosion current density cannot truly reflect the corrosion rate of aluminum alloy [13], it is an important parameter to judge the dissolution rate at the corrosion potential. Generally, the aluminum alloy with a large corrosion current density normally dissolves rapidly at its corrosion potential and consequently can be quickly activated during the discharge test [14]. Thus, Alloy 3 is more suitable to serve as the anode for air cell or water- activated cell due to its larger corrosion current density and more active polarization behavior compared with Alloy 2, while Alloy 1 is not suitable. Such results are in consistent with those of galvanostatic discharge.
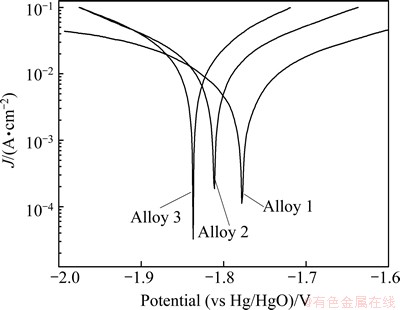
Fig. 2 Potentiodynamic polarization behaviors of three aluminum alloys in rolled state
Figure 3 shows the hydrogen evolution behavior of Alloys 1, 2 and 3 under different conditions immersed in alkaline brine aqueous solution for 20 min. The volume of hydrogen evolution shows a typical increasing sequence from Alloy 1 to Alloy 3 in both as-cast and rolled states. Even though aluminum alloys exhibit positive differential effect [15] in the working state, as-cast aluminum alloys are not suitable to be used as anode for air cell or water-activated cell because of their severe hydrogen evolution. Such a result is due to the reason that as-cast aluminum alloy would consume more aluminum invalidly compared with the rolled aluminum alloys. Hence, the rolled Al-Mg-Sn-In-Ga alloy is usually preferred to be used as an anode material for batteries [16].
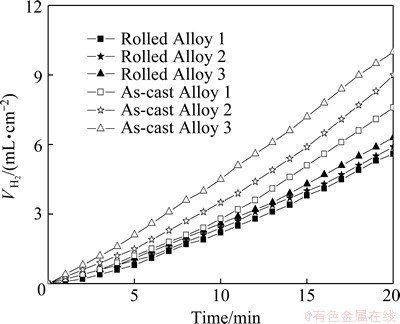
Fig. 3 Hydrogen evolution behavior of aluminum alloys in rolled and as-cast state in alkaline brine electrolyte
3.2 Effects of microstructure on experimental alloys
The effects of the element in activating aluminum are influenced by its concentration, existing state and electrochemistry property [7]. The alloy element magnesium can improve the electrochemical activity by making the oxide film of the aluminum matrix less compact [17]. The SEM images with EDAX analyses for the microstructures and corrosion behavior of the alloys were recorded to shed a relatively specific light on the effects of elements tin, gallium and indium. SEM images were recorded for polished specimen of Alloy 1 and Alloy 3 under the backscatter electron mode aiming to define the elements with higher atomic number in the alloy. As shown in Fig. 4, the microstructure of alloy consists of the matrix and the compound denoted by the white spots. The EDAX analyses (Table 4) manifest that gallium exists both in the matrix and the compound, while tin and indium are found only in the compound.
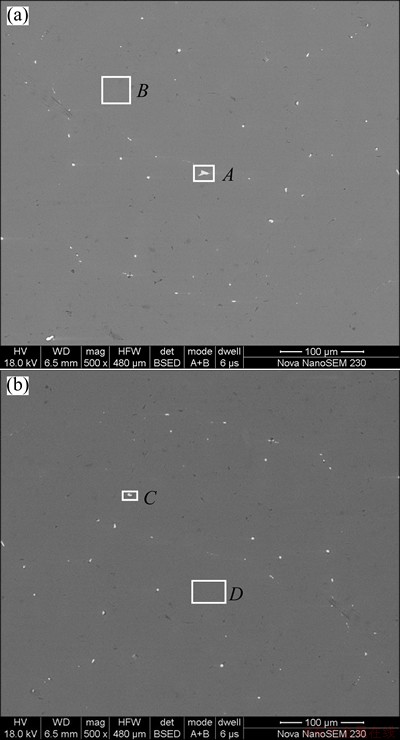
Fig. 4 SEM images of surface of Alloy 1 (a) and Alloy 3 (b)
Table 4 EDAX analysis in certain region in Fig. 4 (mass fraction, %)

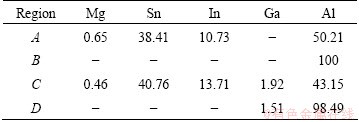
Figure 5 shows the corrosion morphologies of Alloy 1 and Alloy 3 after discharging under the current density of 800 mA/cm2 for 10 s. As these compounds possess more positive potential than aluminum matrix, they cannot dissolve anodically along with aluminum and instead act as the dissolution centers of the pits. The pits consequently first initiate from these spots. Then, with the growth of these pits, some of the spots shed physically when the spots are large enough as seen in Fig. 5(b) [18]. The EDAX results of Figs. 5(b) and (d) listed in Table 5 manifest that the compounds mainly contain tin and indium among the alloy elements, which corresponds to the result shown in Table 4.
It can be seen from Fig. 5 that the corrosion pits exist on the surfaces of both Alloy 1 and Alloy 3. However, as seen in Figs. 5(a) and (c), stripe-like corrosion morphology presents on the surface of Alloy 3 compared with the surface of Alloy 1.
Gallium produces an obvious different corrosion morphology compared with tin and indium to aluminum through a different mechanism. It is mentioned that alloying elements with melting point dissolve with the aluminum matrix, producing the corresponding cations when they are contained in the solid solution among the aluminum matrix. Then, these cations can plate back onto the aluminum surface [18]. This process is called the dissolution-deposition mechanism. As discussed before, there is only gallium presented in solid solution among the alloying elements. It can also be seen in Fig. 5(d) that there is gallium surrounded by aluminum oxide. For gallium, the alkaline environment is in favor of the formation of hydrolysed species of [GaO2]-, [HGaO3]2- and [GaO3]3- [19]. According to the Pourbaix diagram for pure gallium [1], the reversible potentials corresponding to Ga|[GaO2]-, Ga|[HGaO3]2- and Ga|[GaO3]3- are given by the following equations:
φ0=-0.144-0.0788 pH+0.0197 lg c(GaO2-) (1)
φ0=0.088-0.0985 pH+0.0197 lg c(HGaO3)2- (2)
φ0=0.319-0.118 pH+0.0197 lg c(GaO3)3- (3)
As the pH of the electrolyte during the experiment changes little, the potentials needed to oxidize these hydrolysed species to gallium shift positively with the increase of [GaO2]-, [HGaO3]2- and [GaO3]3- concentrations. So, a critical gallium is necessary to make these species deposit onto the specimen surface under the working potential of the alloys. The oxidized gallium deposits on the specimen surface and then forms amalgam with aluminum. The aluminum atoms diffusing through the amalgam electrochemically react with the electrolyte, yielding the needed potential. Gallium would however diffuse back into the bulk from the specimen surface [20], it needs time to produce enough [GaO2]-, [HGaO3]2- and [GaO3]3- species in the electrolyte. Once gallium deposits, the aluminum atoms diffuse through the amalgam and the alloy is activated. Hence, that is the reason why at the beginning of the galvanostatic discharge test of Alloy 2 and Alloy 3, the potential is not as negative as that in the latter part as demonstrated in Fig. 1. As the potential of Alloy 3 is more negative than that of Alloy 2 under the same condition, a concentration of alloy element gallium higher than 0.1% is needed to activate the aluminum matrix.
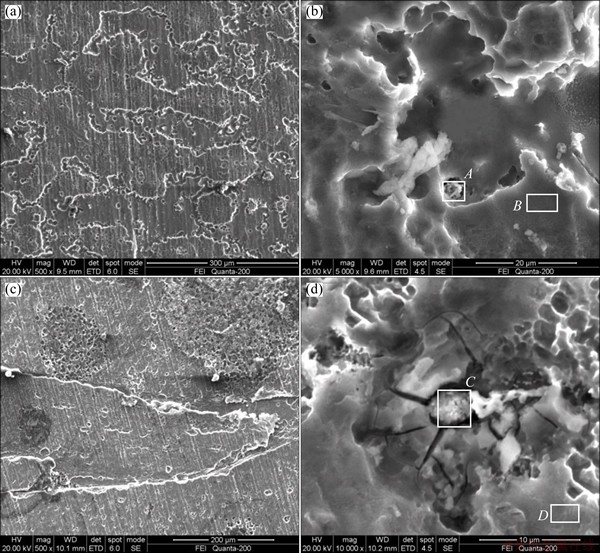
Fig. 5 Overall surface corrosion morphology (a) and local corrosion morphology (b) of Alloy 1, overall surface corrosion morphology (c) and local corrosion morphology (d) of Alloy 3 after discharging under current density of 800 mA/cm2 for 10 s
Table 5 EDAX analysis in certain regions in Fig. 5 (mass fraction, %)
4 Conclusions
1) Gallium provides high electrochemical activity and working potential as negative as -1.51 V for aluminum alloy anode used for air cell or water-activated cell. The addition of gallium should exceed 0.1% to obtain a good electrochemical activity for aluminum matrix.
2) The hydrogen evolution of aluminum alloy in alkaline brine electrolyte decreases after rolling process, which benefits to improve the discharge efficiency of aluminum.
3) Gallium activates aluminum matrix by the dissolution-deposition mechanism as a typical solute atom. Gallium can form amalgam with aluminum matrix, through which aluminum atom reacts with the electrolyte.
References
[1] POURBAIX M. Atlas of electrochemical equilibria in aqueous solutions [M]. Huston: Pergamon Press, 1966.
[2]  S, SMOLJKO I,
S, SMOLJKO I,  M. Electrochemical behaviour of aluminium alloys containing indium and tin in NaCl solution [J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2010, 121(3): 561-566.
M. Electrochemical behaviour of aluminium alloys containing indium and tin in NaCl solution [J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2010, 121(3): 561-566.
[3] ZHUK A Z, SHEINDLIN A E, KLEYMENOV B V, SHKOLNIKOV E I, LOPATIN M Y. Use of low-cost aluminum in electric energy production [J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2006, 157(2): 921-926.
[4] NESTORIDI M, PLETCHER D, WOOD R J K, WANG S, JONES R L, STOKES K R, WILCOCK I. The study of aluminium anodes for high power density Al/air batteries with brine electrolytes [J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2008, 178(1): 445-455.
[5]  W. The influence of electrolyte additives on the anodic dissolution of aluminum in alkaline solutions [J]. Journal of Power Sources, 1980, 5(3): 245-253.
W. The influence of electrolyte additives on the anodic dissolution of aluminum in alkaline solutions [J]. Journal of Power Sources, 1980, 5(3): 245-253.
[6] WILHELMSEN W, ARNESEN T, HASVOLD O, STORKERSEN N J. The electrochemical behaviour of Al in alloys in alkaline electrolytes [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 1991, 36(1): 79-85.
[7] EGAN D R,  C P D, WOOD R J K, JONES R L, STOKES K R, WALSH F C. Developments in electrode materials and electrolytes for aluminium–air batteries [J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2013, 236: 293-310.
C P D, WOOD R J K, JONES R L, STOKES K R, WALSH F C. Developments in electrode materials and electrolytes for aluminium–air batteries [J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2013, 236: 293-310.
[8] NESTORIDI M, PLETCHER D, WHARTON J A, WOOD R J K. Further studies of the anodic dissolution in sodium chloride electrolyte of aluminium alloys containing tin and gallium [J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2009, 193(2): 895-898.
[9] FLAMINI D O, SAIDMAN S B. Polarisation behaviour of Al-Zn-Ga alloy in chloride medium [J]. Journal of Applied Electrochemistry, 2008, 38(5): 663-668.
[10] ZHAO Jun, YU Kun, HU Ya-nan, LI Shao-jun, TAN Xin, CHEN Fu-wen, YU Zhi-ming. Discharge behavior of Mg-4wt%Ca- 2wt%Hg alloy as anode for seawater activated battery [J]. Electro Chimica Acta, 2011, 56(24): 8224-8231.
[11] RASHID K T. Effect of mixing speed and solution temperature on cathodic protection current density of carbon steel using magnesium as sacrificial anode [J]. Eng Technol J, 2009, 27(8): 1640-1653.
[12] WANG Nai-guang, WANG Ri-chu, PENG Chao-qun, FENG Yan, ZHANG Xiang-yu. Corrosion behavior of Mg-Al-Pb and Mg-Al-Pb-Zn-Mn alloys in 3.5% NaCl solution [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2010, 20(10): 1936-1943.
[13] SHI Z M, LIU M, ATRENS A. Measurement of the corrosion rate of magnesium alloys using Tafel extrapolation [J]. Corrosion Science, 2010, 52(2): 579-588.
[14] YU Kun, XIONG Han-qing, WEN Li, DAI Yi-hong, YANG Shi-hai, FAN Su-feng, TENG Fei, QIAO Xue-yan. Discharge behavior and electrochemical properties of Mg-Al-Sn alloy anode for seawater activated battery [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2015, 25(4): 1234-1240.
[15] SHI Peng-fei, YIN Ge-ping, XIA Bao-jia, LU Guo-qi. Studies on the anodic behavior of aluminum electrodes in alkaline solution [J]. Journal of Power Sources, 1993, 45(1): 105-109.
[16] LIANG Shu-quan, ZHANG Yong, GUAN Di-kai, TANG Yan, MAO Zhi-wei. Effect of rolling processing on microstructure and electrochemical properties of high active aluminum alloy anode [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2010, 20(6): 942-949.
[17] MA Jing-ling, WEN Jiu-ba, GAO Jun-wei, LI Qua-nan. Performance of Al-1Mg-1Zn-0.1Ga-0.1Sn as anode for Al-air battery [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2014, 129: 69-75.
[18] REBOUL M C, GIMENEZ P H, RAMEAU J J. A proposed activation mechanism for Al anodes [J]. Corrosion, 1984, 40(7): 366-371.
[19] BRESLIN CARMEL B, CARROLL WILLIAM M. The electrochemical behaviour of aluminium activated by gallium in aqueous electrolytes [J]. Corrosion Science, 1992, 33(11): 1735-1746.
[20] TUCK C D S. The electrochemical behavior of Al-Ga alloys in alkaline and neutral electrolytes [J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 1987, 134(12): 2970-2981.
镓对空气电池或水激活电池阳极用Al-Mg-Sn-In合金电化学性能的影响
余 琨1,2,杨士海1,熊汉青1,文 利1,戴翌龙1,滕 飞1,范素峰1
1. 中南大学 材料科学与工程学院,长沙 410083;
2. 中南大学 粉末冶金国家重点实验室,长沙 410083
摘 要:采用恒电流放电、动电位极化和析氢方法测试待测Al-Mg-Sn-In-Ga合金在碱性介质中、高放电电流密度下的电化学性能。结果表明,合金元素镓能够使Al-Mg-Sn-In合金在不同电流密度下的工作电位变负,含镓的铝合金在电流密度为650~900 mA/cm2时的放电电位可达-1.3 V,而不含镓的Al-Mg-Sn-In合金的放电电位大于-1.0 V。这是由于镓与铝基体形成固溶体,并在放电过程中形成汞齐,使腐蚀深入到铝基体内部。
关键词:铝阳极;电化学性能;放电行为;腐蚀;溶解再沉积
(Edited by Xiang-qun LI)
Foundation item: Project supported by the Open Fund of the State Key Laboratory of Powder Metallurgy, China
Corresponding author: Kun YU; Tel: +86-731-88879341; Fax: +86-731-88876692; E-mail: yukun2010@csu.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(15)64018-3