采用铝热自蔓延法制备低氧高钛铁合金
豆志河,张廷安,张含博,张志琦,牛丽萍,姚永林,赫冀成
(东北大学 多金属共生矿生态化利用教育部重点实验室,辽宁 沈阳,110004)
摘要:以金红石、钛精矿和Al为原料采用铝热自蔓延法制备出低氧高钛铁合金。研究不同反应体系的相关热力学,考察配铝量对铝热自蔓延熔炼效果的影响,采用XRD,SEM以及化学分析等技术对高钛铁合金进行表征。研究结果表明:反应体系的绝热温度大于1 800 K,反应能自我维持进行;铝还原TiO2反应的单位质量热效应较低,铝还原铁氧化物反应的单位质量热效应较高;合金主要由TiFe2,Fe,TiO2和Al2O3等相组成,氧化物夹杂相的存在是合金中氧含量高以及合金微观缺陷存在的直接原因;合金中氧含量最低为2.62%;钛、铝、铁和硅质量分数分别为61.58~66.27%,4.05%~9.20%,16.15%~20.53%及2.78%~3.82%。
关键词:铝热自蔓延;低氧高钛铁;绝热温度;单位质量热效应;夹杂物
中图分类号:O665.2 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2012)06-2108-06
Preparation of high titanium ferrous with low oxygen content by thermit reduction-SHS
DOU Zhi-he, ZHANG Ting-an, ZHANG Han-bo, ZHANG Zhi-qi, NIU Li-ping, YAO Yong-lin, HE Ji-cheng
(Key Laboratory for Ecological Utilization of Multimetallic Mineral of Ministry of Education,
Northeast University, Shenyang 110004, China)
Abstract: Rutile, ilmenite and Al powder were used to prepare high titanium ferrous alloy by thermit reduction-SHS(self -propagating high-temperature synthesis). The thermodynamic of the relative reaction systems was studied, and the effects of the proportion of Al on the thermit reduction-SHS melting process were investigated. The high titanium ferrous alloys were characterized by XRD,SEM and chemical compositions analysis technologies. The results indicate that the adiabatic temperatures of all reaction systems are higher than 1 800 K, so that all the reactions can keep on carrying on by themselves. The unit reaction heat is low when Al reduces TiO2, but the unit reaction heat is higher when Al reduces iron oxides. The high titanium ferrous alloys mainly consist of TiFe2, Fe, TiO2 and Al2O3. The oxide inclusions exist in the alloy, which directly results in the high oxygen content and micro-structural defects in the alloys. The lowest oxygen content is 2.62% in the alloy, and the contents of titanium, aluminum, ferrous and silicon in the alloy are 61.58~66.27%, 4.05%~9.20%, 16.15%~20.53% and 2.78%~3.82%, respectively.
Key words: thermit reduction-SHS; high titanium ferrous with low oxygen; adiabatic temperature; unit reaction heat; inclusion
高钛铁(含钛量65%~75%,质量分数,下同)合金具有熔点低、钛含量高[1]等优点,是冶炼高温合金和优质不锈钢不可缺少的材料。炼钢时添加高钛铁具有添加量少,钢水中成分易均匀化,偏析少,含铝、硅和氮等杂质少等优点[2-4],同时,钢的铸造组织变得致密,机械性能显著改善[5-7]。目前,高钛铁制备方法包括重熔法和铝热还原法。其中,重熔法是以废钛材加铁真空重熔,该法制备的高钛铁具有质量稳定和氧含量低等优点。该法已被广泛应用,尤其是在俄罗斯、西欧等发达国家。由于我国具有丰富的金红石资源,近年来一直在推广铝热法制备高钛铁新技术,但该法制备的高钛铁存在氧含量高(10%~12%)以及铝和硅成分含量不稳定等缺陷[7],严重限制了该方法的推广应用。为提高铝热法高钛铁的质量,国内外研究人员对铝热法工艺进行大量深入的研究工作[8]。四川峨眉铁合金厂以天然金红石为原料,采用炉外铝热还原法生产出含钛73.77%的高钛铁,但产品中Al含量较高,Mn,P,S和C等含量不稳定;北京有色金属研究总院通过控制原料质量,采用炉外铝热还原法制备的高钛铁合金尽管其他成分达标,但氧含量仍过高;南非Mintek公司在隔绝空气条件下采用等离子加热方式制备出低氮高钛铁[8],但氧含量仍无法有效去除。针对传统铝热法制备高钛铁氧含量高的原因和技术难 点[9-13],在系统分析铝热还原过程相关热力学基础上,本文作者提出采用铝热自蔓延法制备低氧高钛铁的新思路。即利用自蔓延反应局部温度高、能量密度大和反应热力学和动力学条件充分的特点,强化TiO2还原及金渣分离效果,制备低氧高钛铁。
1 热力学分析
1.1 绝热温度分析
绝热温度Tad是反应体系能达到的最高温度,是描述自蔓延合成反应特征最重要的热力学参数。Merzhanov等指出仅当Tad>1 800 K时,反应才能自我维持。比较Tad和Tm还可判断反应过程中产物的聚集状态。对于反应:
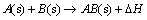 (1)
(1)
其放出的热量为:

式中: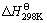 为298 K的标准焓变,kJ·mol-1;Q为非恒温条件下绝热反应的放热量,kJ;∑(vicpi)为各产物的比热容之和,J·K-1·mol-1。
为298 K的标准焓变,kJ·mol-1;Q为非恒温条件下绝热反应的放热量,kJ;∑(vicpi)为各产物的比热容之和,J·K-1·mol-1。
铝热法生产高钛铁采用的原料包括:金红石(或高钛渣)、钛铁矿及还原剂Al等。制备过程中涉及的主要反应为(2),(3)和(4)。通过计算可知:反应(2)和(3)和(4)的绝热温度分别为:1 805,3 135和2 327 K。其中:反应体系(2)中反应产物均以固态存在;反应体系(3)中反应产物以气、液两相存在(其中,13.04%的Fe为气态);反应体系(4)中反应产物以固、液两相存在,Fe和Ti以液态存在,而Al2O3有21.69%以液态存在。
4Al+3TiO2=3Ti+2Al2O3 (2)
2Al+Fe2O3=2Fe+Al2O3 (3)
2Al+TiO2·FeO=Fe+Ti+Al2O3 (4)
铝还原铁氧化物反应的绝热温度较高,而还原二氧化钛的绝热温度较低。因此,调控配料中金红石/钛铁矿的质量比不但可以调控合金中Ti和Fe的成分,还可以有效地调控反应的温度,进而调控还原熔炼过程及产品的质量。
图1所示为不同金红石(以纯TiO2计)和钛铁矿(以纯TiO2·FeO计)质量配比时,反应体系绝热温度的变化曲线。由图1可知:金红石与钛铁矿配料比为1时,绝热温度为2 191 K;随着金红石配料量增大,反应绝热温度降低。当金红石与钛铁矿配料比增大到5时,绝热温度降低至1 933 K(金属钛的熔点)。当金红石与钛铁矿配料比为5和6时,理论上生成物钛液态质量分数分别为98.24%和16.06%,Al2O3均以固态存在,这是不利于金渣分离的。为保证高钛铁合金中65%~75%的钛含量,金红石与钛铁矿实际配料比多控制在5~6。考虑到反应过程中热量的损失,实际反应温度会更低,进而导致TiO2的还原程度和金渣分离效果不理想。为保证还原熔炼过程中TiO2的还原程度和金渣分离效果,配料中需加入发热剂KClO3等以提高反应体系的温度,同时,加入造渣剂组分降低熔渣的黏度可改善渣的流动性,强化金渣分离过程[14]。
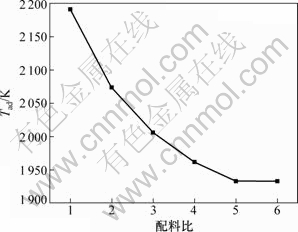
图1 不同配料比时的绝热温度
Fig.1 Adiabatic temperature with different mixture ratios
图2所示为金红石与钛铁矿配料比为6时,发热剂KClO3和造渣剂CaO对反应绝热温度的影响关系曲线。由图2可知:加入KClO3可使反应的绝热温度显著提高,而造渣剂CaO的加入则显著降低绝热温度。当KClO3添加量为金红石配料量的20%时,绝热温度为2 327 K(Al2O3熔点)。但随着CaO添加量的增大,液态Al2O3质量分数显著降低。当KClO3添加量为25%时,最高绝热温度为2 431 K。当CaO添加量增大到20%时,绝热温度下降为2 327 K,此时液态Al2O3质量分数为91.94%。当KClO3添加量为30%时,随着CaO添加量增加,绝热温度由2 635 K降至2 470 K。因此,合理的KClO3和CaO的配料量是提高和强化TiO2还原程度和金渣分离过程的有效手段和必要 保证。
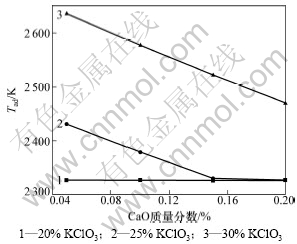
图2 KClO3和CaO添加量对绝热温度的影响
Fig.2 Effects of addition of KClO3 and CaO on adiabatic temperature
1.2 反应热效应分析
单位质量反应热(q)是另一个描述自蔓延反应的重要的热力学参量,它体现了燃烧反应体系释放化学能量的大小,也是表征能量释放速度与质量燃烧速度这2个热力学参量[7,10]。对于反应(5),
Me′O+Me=Me′+MeO (5)
单位质量反应热效应可按下式计算:
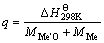
式中: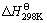 为298 K时标准焓变,kJ·mol-1;MMe′O为Me′O的相对摩尔质量,g·mol-1;MMe为Me的相对摩尔质量,g·mol-1。
为298 K时标准焓变,kJ·mol-1;MMe′O为Me′O的相对摩尔质量,g·mol-1;MMe为Me的相对摩尔质量,g·mol-1。
3/4SiO2+A1=3/4Si+1/2Al2O3 (6)
3/2FeO+A1=3/2Fe+1/2Al2O3 (7)
3/2MnO+Al=3/2Mn+1/2Al2O3 (8)
1/2KClO3+A1=1/2KCl+1/2Al2O3 (9)
计算结果表明:与铝热自蔓延反应制备高钛铁合金相关的反应(2)~(4)和(6)~(9)的单位质量反应热效应分别为1 484,3 971,2 135,2 172,3 182,1 949和9 772 J/g。由以上结果可知:矿石中SiO2和MnO等杂相的存在会显著降低反应的单位质量反应热效应,影响还原过程和金渣分离效果。因此,采用铝热自蔓延生产时应选择品位更高的原料来保证单位反应热效应。
图3所示为配料比为6时,KClO3和CaO添加量对单位质量反应热效应的影响关系曲线。由图3可知:实际反应体系的单位热效应在2 400~3 100 J/g之间变化,均满足铝热自蔓延反应自我维持的条件。实际生产中为保证还原反应和金渣有效分离,要求单位热效应在2 700 J/g左右。因此,要求KClO3的配料量要达到25%,才能达到理想的熔炼效果。
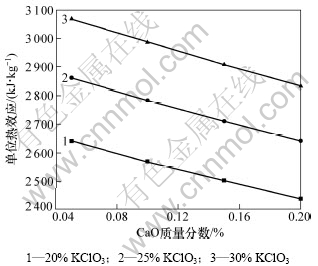
图3 KClO3和CaO添加量对单位热效应的影响
Fig.3 Effects of addition amount of KClO3 and CaO on unit thermal effect
由于铝热自蔓延采用的金红石和钛铁精矿原料中都存在SiO2和MnO等杂质相,铝还原该类氧化物的单位质量反应热效应较低,加上铝热自蔓延反应过程的热损失,实际反应热效应和反应温度会更低。除了配入大量的发热剂外,预热炉料也是提高单位热效应和反应温度的有效途径。原料预热温度每提高100 ℃,单位热效应可提高125 kJ/kg。
2 实验
2.1 实验原料
实验原料为:金红石(TiO2为89.2%(质量分数,下同),SiO2 5.4%,Al2O32.4%),钛铁精矿(TiO2 50.6%,TFe 32.3%,SiO2 4.1%),CaO(质量分数>98%),KClO3(质量分数>98%),Al粉(质量分数>99%)。
2.2 实验步骤
将金红石、钛铁精矿、CaO以及KClO3于400 ℃条件烘干10 h以上,然后与Al粉按比例称量。采用球磨机混合10~30 min,将混合好的反应物料放在有镁砂内衬的石墨反应器中,在反应物表层放适量镁粉,点燃镁粉引发自蔓延反应,冷却,除渣,起锭得合金,收集渣样。
2.3 表征
采用英国剑桥S300扫描电子显微镜观察合金的微观结构。合金试样制备步骤:先抛光,然后采用体积比V(HF):V(HNO3):V(H2O)=(1~3):(2~6):(91~97)腐蚀液腐蚀10~20 s,然后冲洗,酒精擦洗,烘干。采用PW3040/60型X’Pert Pro MPD分析合金和熔炼渣的物相,扫描速度为2°/min。采用德国布鲁克G8型氧氮分析仪测定合金中的氧含量。
3 结果与讨论
针对传统铝热法制备的高钛铁存在的氧含量高,夹杂物多等缺点,结合绝热温度和单位质量热效应等热力学分析结果,考查金红石与钛铁矿配料比为6,KClO3加入量为25%和CaO加入量为20%时,不同配铝量对铝热自蔓延熔炼效果的影响。
3.1 高钛铁合金的XRD分析
图4所示为不同配铝量时铝热自蔓延法制备的高钛铁合金的XRD图谱。由图4可知:所制备的高钛铁合金中都存在TiFe2,Fe,TiO2和Al2O3等相。随着配铝量的增加,合金中出现了Al3Ti相,如图(4)中铝过量2%时(图4(a))和化学剂量时的(图4(b))所示。当配铝量为理论量的90%时,合金中Al3Ti相消失,但有少量的Al2Fe相形成。合金中存在Al2O3相,说明金渣分离不够充分。而合金中存在TiO2相,说明TiO2还原不充分。对比(图4(a)~(c))可以发现:随着配铝量的减少,合金中氧化物相含量增加。当配铝量为理论量的90%时,合金中还出现了Ti4O7相,说明配铝量不足导致还原情况恶化。
3.2 高钛铁合金的SEM分析
图5所示为不同配铝量时铝热自蔓延法制备的高钛铁合金的SEM照片。由图5可看出:合金试样均存在a、b和c 3个明显不同的区域。能谱分析结果表明:a区为Al2O3夹杂相,b和c区域由Ti,Fe,Al和Si等元素组成,TiFe2和Fe相应该存在于这2个区域。其中,b区Al含量较低(5%左右),c区铝含量较高(13.8%左右),Al3Ti应该存在于c区。
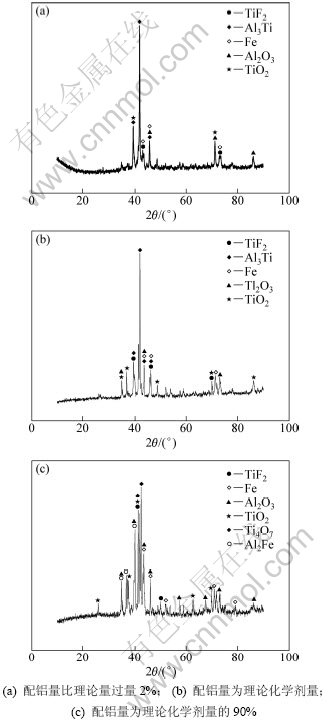
图4 铝热自蔓延制备的高钛铁合金的XRD图谱
Fig.4 XRD patterns of high titanium prepared by thermit-SHS
对比图5(a)~(c)试样的SEM照片,随着配铝量的减少,图5(c)中出现了纯钛区域d。因为随着配铝量的降低,铝与钛结合机会减少,从而使得还原出来的钛一部分以单质形式析出,从而形成了纯钛相区域,这与XRD分析结果相吻合。随着反应物料中配铝量的降低,合金中出现了大块的夹杂物Al2O3相区域。因为配铝量不足,会造成熔炼过程中还原反应进行不完全以及反应温度下降,进一步导致Al2O3渣不能够有效地从合金融体中分离出来,从而导致高钛铁合金的微观结构缺陷增多。而氧化物夹杂相的存在是导致氧含量的直接原因之一,若要降低合金中的氧含量,则必须有效去除合金中的氧化物夹杂。

图5 铝热自蔓延制备的高钛铁合金的SEM照片
Fig.5 SEM photos of high titanium prepared by thermite-SHS
3.3 高钛铁合金的化学分析
表1所示为高钛铁合金的化学成分分析结果。
表1 高钛铁合金的化学成分(质量分数)
Table 1 Chemical compositions of high-titanium ferrous alloy %
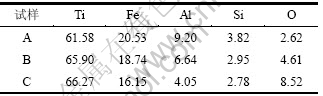
由表1可看出:铝热自蔓延法制备的高钛铁合金中钛的质量分数在61.58%~66.27%间变化,相应的铁的质量分数在20.53%~16.15%间变化,硅的质量分数为3.82%~2.78%,均符合优质高钛铁的标准。与传统的炉外铝热法制备的高钛铁相比,铝热自蔓延法制备的高钛铁合金中氧含量显著降低(最低只有2.62%,采用传统炉外铝热法时为12.2%[9])。随着物料中配铝量的增加,合金中的氧含量显著降低,但铝含量显著增高。因为随着配铝量增加,还原熔炼效果得以保证,但过量的铝与还原生成的钛结合生成钛铝化合物的几率显著增加。为了控制合金中氧含量和铝残留量,必须合理调控原料中的配铝量。
另外,分析发现:随着物料中配铝量的增加,合金中钛含量显著降低,但铁含量增高。因为随着物料中配铝量的增加,实际反应温度升高,因此,熔炼过程中TiO2和氧化铁还原率提高。但随着反应温度的升高,金属的高温挥发损失增加。金属钛回收率只有71.5%左右,铁的回收率较高,为83.5%左右。
4 结论
(1) 采用铝热自蔓延方法制备高钛铁合金是可行的。
(2) 高钛铁合金主要由TiFe2,Fe,TiO2和Al2O3等相组成,微观结构上存在Al2O3夹杂相区,钛铁共溶体区和钛基体区等区域。氧化物夹杂相的存在是造成合金中氧含量高以及微观缺陷存在的直接原因。
(3) 高钛铁合金中钛的质量分数在61.58%~ 66.27%间变化,铁的质量分数在20.53%~16.15%间变化,硅质量分数为3.82%~2.78%,均符合优质高钛铁的标准。合金中氧被有效去除,最低为2.62%,远低于传统铝热法的12.2%。
参考文献:
[1] 莫畏. 钛[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2008: 1-12.
MO Wei. Titanium[M]. Beijing: Metallurgy Industry Press, 2008: 1-12.
[2] 王方, 高敬. 世界非航空钛市场现状及发展趋势[J]. 钛工业进展, 2009, 26(6): 9-26.
WANG Fang, GAO Jing. Present status and development trend of world titanium market in non-aviation field[J]. Titanium Industry Progress, 2009, 26(6): 9-26.
[3] 汪汉臣. 用残钛料真空试炼高钛钛铁[J]. 铁合金, 1996(1): 36-38.
WANG Han-chen. The vacuum melting of high titanium ferroalloy with waste titanium[J]. Ferroalloys, 1996(1): 36-38.
[4] 夏冬冬, 吴晓东. 铝热法冶炼高钛铁合金的试验研究[J]. 上海金属, 2008, 30(2): 28-31.
XIA Dong-dong, WANG Xiao-dong. Melting high titanium ferroalloy by thermite method[J]. Shanghai Metals, 2008, 30(2): 28-31.
[5] 邓国珠. 钛冶金工业中的三个高端产品[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2005(12): 60-63.
DENG Guo-zhu. Three high quality products in titanium metallurgy[J]. Iron Steel, Vanadium and Titanium, 2005(12): 60-63.
[6] Benjamin J S. Dispersion strengthened super-alloys by mechanical alloying[J]. Metallurgical Transactions, 1970, 1(10): 2943-2951.
[7] 肖翔鸿, 刘名扬, 罗发应. 铝热法冶炼高钛铁工艺试验[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2001, 22(4): 47-51.
XIAO Xiang-hong, LIU Ming-yang, LUO Fa-ying. Technology of ferrotitanium by Aluminum thermal[J]. Iron Steel, Vanadium and Titanium, 2001, 22(4): 47-51.
[8] Jones R T, Barcza N A, Curr T R. Plasma developments in Africa[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 1993, 8(11): 2819.
[9] 宋雪静, 魏莉, 张廷安, 等. 高钛铁中氧形成机理分析及脱氧实验[J]. 过程工程学报, 2008, 8(S1): 176-179.
SONG Xue-jing, WEI Li, ZHANG Ting-an, et al. Analysis of forming mechanism of oxygen in high ferrotitanium and deoxidizing oxygen experiment[J]. The Chinese Journal of Process Engineering, 2008, 8(S1): 176-179.
[10] 许磊, 竺培显, 袁宜耀. 高品位钛铁生产新工艺的研究与探讨[J]. 南方金属, 2008(4): 4-7.
XU Lei, ZHU Pei-xian, YUAN Yi-yao. A new process of making high titanium ferroalloy[J]. Southern Metals, 2008(4): 4-7.
[11] 夏文堂, 张启修. 有衬电渣炉冶炼高品位钛铁的研究[J]. 铁合金, 2004(4): 36-39.
XIA Wen-tang, ZHANG Qi-xiu. Research on melting high titanium ferroalloy by electroslags crucible remelting[J]. Ferroalloys, 2004(4): 36-39.
[12] Paton B E, Medovar B L, Benz M G. ESR for titanium: Yesterday, today, tomorrow[C]//Processing of the Ninth World Conference on Titanium.2000. Saint-Petersburg, Russia, 1999: 1385-1398.
[13] Chen G Z, Fray D J, Farthing T W. Direct electrochemical reduction of titanium dioxide to titanium in molten calcium chloride[J]. Nature, 2000, 407(9): 361.
[14] 李宗强. 铝酸钙预熔渣及其在转炉渣洗脱硫中的应用[D]. 武汉: 武汉科技大学材料与冶金学院, 2006: 7-20.
LI Zong-qian. Calcium aluminate premelted slagand its application on converter wash heat[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University of Technology. School of Materials and Metallurgy, 2006: 7-20.
(编辑 何运斌)
收稿日期:2011-03-05;修回日期:2011-06-02
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(50874027,50644016,50704011);国家重点基础研究发展计划项目(2007CB613504);中央高校基本科研业务费资助项目(N090402015)
通信作者:张廷安(1960-),男,河南周口人,博士,教授,从事反应工程学,高附加值冶金产品和自蔓延冶金研究;电话:024-83686283;E-mail:zta2000@163.net