
Effect of annealing on two different niobium-clad stainless steel PEMFC bipolar plate materials
Sung-Tae HONG1, Dae-Wook KIM2, Yong-Joo YOU2, K. Scott WEIL3
1. School of Mechanical and Automotive Engineering, University of Ulsan, Ulsan, Korea;
2. Department of Material Science and Engineering, University of Ulsan, Ulsan, Korea;
3. Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, P.O. Box 999, Richland, WA, USA
Received 2 March 2009; accepted 30 May 2009
Abstract: Niobium (Nb)-clad stainless steels(SS) produced via roll bonding are being considered for use in the bipolar plates of polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell(PEMFC) stacks. Because the roll bonding process induces substantial work hardening in the constituent materials, thermal annealing is used to restore ductility to the clad sheet so that it can be subsequently blanked, stamped and dimpled in forming the final plate component. Two roll bonded materials, niobium clad 340L stainless steel (Nb/340L SS) and niobium clad 434 stainless steel (Nb/434 SS) were annealed under optimized conditions prescribed by the cladding manufacturer. Comparative mechanical testing conducted on each material before and after annealing shows significant improvement in ductility in both cases. However, corresponding microstructural analyses indicate an obvious difference between the two heat treated materials. During annealing, an interlayer with thick less than 1 μm forms between the constituent layers in the Nb/340L SS, whereas no interlayer is found in the annealed Nb/434 SS material. Prior work suggests that internal defects potentially can be generated in such an interlayer during metal forming operations. Thus, Nb/434 SS may be the preferred candidate material for this application.
Key words: clad sheet; bipolar plate; proton exchange membrane fuel cell; annealing
1 Introduction
Despite significant technical progress made in recent years toward developing a commercially viable polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell(PEMFC) system, potential application of this device in the automobiles remains limited to prototypes[1]. The reasons for this are the high cost of PEMFC stack manufacture, the steady loss in power output during long-term continuous operation, and the larger than desired size and mass of the latest generation PEMFC systems[2-3]. The latter factor limits the specific power that can be generated, which then necessitates mass reduction in other parts of the vehicle (likely at a further increase in cost)[3]. For this technology is competitive in the automotive industry, cost reduction and performance improvement must come from all aspects of PEMFC system design and manufacture.
One of the most bulky components in the stack with respect to both mass and volume is the bipolar plate. It is also one of the most expensive to manufacture, accounting for about 45% of the total cost and 80% of the mass of the stack. This component not only serves as the electrical junction between serially connected cells in the stack, but also performs several other key functions in the overall device including uniform distribution of fuel and oxidant over the active areas of the cells[4], proper humidification of the electrochemical membrane while minimizing the potential for flooding, prevention of fuel and oxidant mixing (i.e. a chemically resistant, leak-proof barrier to both gas streams), structural support for the stack and heat removal from the cells. While various materials were considered for use in this component[5-10], metals offer a number of intriguing design advantages particularly for transportation applications, including low-cost, mass-production via stamping or embossing of sheet product, fabrication in thin form (<150 μm), to reduce mass and volume in the overall stack, impermeability to fuel, oxidant and water vapor, excellent thermal conduction properties and good mechanical robustness. Despite this material exhibits a higher density than alternative carbon-based bipolar plate materials, the reduction in thickness afforded by the strength of a typical candidate metal leads to an overall decrease in the mass of the plates required for the stack. Moreover, it is anticipated that a metal-based fuel cell stack will better endure the vibration stresses encountered during standard automotive use.
However, a potential show-stopper with any metal- based PEMFC stack component is corroded on surface, and the current drives to increase the operating temperature of the stack, which will only exacerbate this problem. Corrosion of the bipolar plate leads to a release of metal ions that can contaminate the electrolyte membrane and poison the electrode catalysts, thereby exaggerating the long-term degradation issues with PEMFC stacks. In addition, the formation of a passivating oxide or oxyhydroxide layer on the surface of the metal tends to increase the contact resistance between the bipolar plate and the adjacent carbon gas diffusion layer, often by many orders of magnitude, which limits the amount of power that can be generated by the stack and serves as an additional source of heat that must be removed during operation. A bipolar plate material incorporates the advantages of metal, but undergoes little or no corrosion.
We recently investigated the electrochemical[11] and mechanical[12] properties of niobium-clad 304L stainless steel manufactured via roll bonding for potential use in a new clad PEMFC bipolar plate material concept. Linear voltammetry and potentiostatic test results demonstrate that the material is electrochemically viable, i.e., it affords excellent corrosion stability under an accelerated version of simulated stack conditions, while material costs is allowed to be minimized by incorporating the passivating Nb as a thin layer roll clad to a more robust steel sheet. Measurements of contact resistance between TorayTM carbon paper and Nb-side of the clad sheet in the as-received or passivated conditions were comparable to previously reported values for graphite[11]. The results from mechanical testing indicate that annealing is required to restore sufficient ductility in the Nb-clad SS so that metal can be formed into the PEMFC bipolar plate configuration[12]. However, when microstructural analyses are conducted on a series of roll bonded Nb/304 L SS specimens annealed under various conditions, it is found that an interfacial layer typically forms between the Nb cladding and the SS substrate during the post-roll heat treatment[12-13].
Because this micron thick interlayer is brittle, it fractures into a series of periodically spaced cracks during initial deformation. These eventually form internal pores that initiate necking and through-thickness failure in the Nb cladding layer at larger material strains. In addition to the Nb/304L SS material investigated previously, Nb/434 SS was also elected as a candidate for the PEMFC bipolar plate application. Since Nb/304L SS forms a potentially disadvantageous interfacial layer during annealing, heat treatment effects on the microstructure of Nb/434 SS need to be investigated to determine if a similar phenomenon occurs. The results are presented from a follow-up study to compare the microstructures of Nb/434 SS and Nb/304L SS in the annealed condition.
2 Experimental
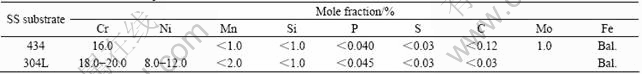
The study was conducted on Nb/434 SS sheets fabricated via roll bonding by Engineered Materials Solutions Inc. (EMS; Waltham, MA). The M/434 and Nb/340L SS materials are listed in Table 1. The nominal chemical compositions of the 434 SS and 304L SS substrates are listed in Table 2. The niobium sheet employed in both cases was 99.8% (with impurity Ta less than 0.2%). Nb/434 SS was annealed in high vacuum at 816 ℃ for 30 min to regain the ductility compatible with the ductility of the annealed Nb/304L SS annealed in high vacuum at 982 ℃ for 15 min[12]. These conditions were determined by the manufacturer from a series of annealing tests conducted on each roll bonded material. The annealing conditions for the two clad materials are different because of the two different stainless substrates. In general, the austenitic 300 series stainless steels require a higher annealing temperature than the ferritic 400 series stainless steels. One reasons for this is that the cold work structure of FCC-structured (austenitic) materials inherently exhibits a higher activation energy for recrystallization (i.e. the nucleation and growth of strain-free grains, the primary mechanism in annealing) than BCC-structured (ferritic) steels. Prior to heat treatment, the sheets were degreased by ultrasonically cleaning in acetone and methanol followed by rinsing with distilled water.
Table 1 Thicknesses of Nb and SS used in cold roll bonding
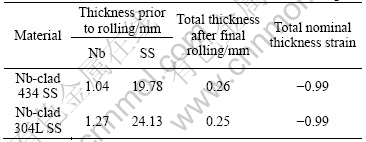
Table 2 Nominal chemical compositions of 434 SS and 304L SS substrates
The effect of annealing on the mechanical properties of the Nb-clad 434SS was evaluated by quasi-static tensile tests. The specimens used in these tests were cut from the clad metal sheets along the direction of roll bonding as schematically shown in Fig.1. The tests were performed according to the ASTM E8-04[13] using an Instron universal test machine. During testing, the specimens were loaded in tension at a constant strain rate of 0.1 min (under a strain controlled condition) to the point of rupture. A calibrated load cell and extensometer were used, respectively, to record changes in the applied tensile force and the length of the specimen during each test.
Fig.1 Schematic diagram of specimen preparation direction with rolling direction
Microstructural analysis of the Nb-clad 434 SS specimens in as-rolled and annealed conditions was conducted on planar and polished cross-sectioned samples using a JEOL JSM-6100LV scanning electron microscope(SEM) equipped with an Oxford energy dispersive X-ray analysis (EDX) system that employs a windowless detector for quantitative detection of both light and heavy elements. In order to avoid electrical charging on the samples, they were gold coated and grounded. Elemental profiles were determined across the joint interfaces in the line-scan mode.
3 Results and analysis
3.1 Effect of annealing on tensile properties
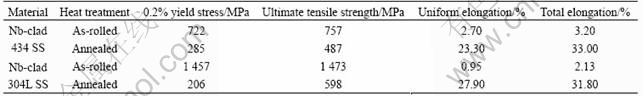
The tensile properties of the as-rolled and annealed the Nb/434 SS as tested along the direction of rolling in comparison with those of the as-rolled and annealed Nb/304L SS are listed in Table 3[12]. The data listed in Table 3 are average values of three tests for each thermomechanical condition. As anticipated, the results indicate that annealing significantly improves ductility and softens the Nb/434 SS by allowing it to recrystallize from the cold worked state of the as-rolled condition. Comparison with the previously reported data for the Nb/304L SS[12] shows that the yield strength of the annealed ferritic-based material is higher than that of the annealed austenitic based material, while the ultimate tensile strength(UTS) exhibits the opposite relationship. This indicates that the work hardening is more pronounced for the annealed Nb/304L SS than for the annealed Nb/434 SS, primarily due to the difference in hardening behavior between austenitic and ferritic stainless steel substrates. In the as-rolled condition, both materials display that the elongation are too low for practical use in the PEMFC bipolar plate application.
Table 3 Effective mechanical properties of Nb-clad 434 SS in as-rolled and annealed conditions
3.2 Microstructure analysis
The cross-sectional back scattered electron images of the as-rolled and annealed the Nb/434 SS are shown in Figs.2(a) and (b), respectively. Similar images of the as-rolled and annealed Nb/304L SS material are shown in Figs.2(c) and (d), respectively. It is apparent from Figs.2(a) and (c) that roll bonding yields a metallurgical bond between the cladding and underlying core for both sets of materials, as evidenced by a non- diffuse interface and the lack of interfacial porosity and/or interfacial de-bond flaws. In the case of the as- rolled Nb/304L SS, a few intermetallic phase inclusions were observed along the interface. It should be noted that the roll bonding process does lead to a transient rise in temperature within the material that can cause interdiffusion and/or generate interfacial phases. This is likely the source of the infrequent, discrete interfacial phases found in the Nb/304L SS material.
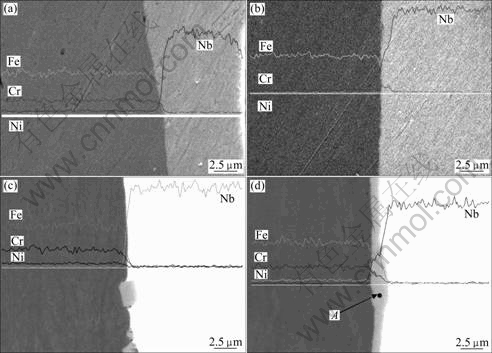
Fig.2 Cross-sectional secondary electron images with result of elemental line scans for as-rolled Nb-clad 434 SS (a), annealed Nb- clad 434 SS (b), as-rolled Nb-clad 304L SS (c) and annealed Nb-clad 304L SS (d)
No such phases are observed in the Nb/434 material. The reason for this may be the lack of nickel in the 434 SS or the higher thermal conductivity of the ferritic substrate relative to that of the austenitic one (thus leading to a higher temperature rise during the cladding process). The results from EDS analysis indicate only a minor amount of interdiffusion into each constituent for both materials in the as-rolled condition. Diffusion is limited to region with thick of less than 1 μm on either side of the bondline for both materials as shown in Figs.2(a) and (c).
Comparison of Figs.2(b) and (d) shows that the type of interfacial layer found in the annealed Nb/304L material is not observed in the annealed Nb/434 SS. The likely reason for this is the lower annealing temperature used for Nb/434 SS. Based on prior analysis of the annealed Nb/304L SS under extreme bending conditions, the interfacial layer is suspected to be a brittle intermetallic phase[12]. The chemical composition of point A in the interfacial layer (see Fig.2(d)) is listed in Table 4, suggesting possibly the-FeNb phase (with some iron site substitution). As discussed in our previous study[12], the failure of annealed Nb304L SS during folding originated in this interfacial layer via the formation of a series of periodically spaced cracks. With excessive bending (i.e. around a bend radius approaching zero), these flaws form pores that eventually lead to necking and through-thickness failure in the Nb layer [12]. This would negate the effectiveness of the protective cladding in the PEMFC bipolar plate application. The presence of this type of brittle interfacial layer can limit the forming parameters for a clad bipolar plate material.
Table 4 Chemical analysis at point A indicated in Fig.2(d) (mole fraction, %)

In the case of the annealed Nb/434 SS material, only a thin diffusion zone is present between the niobium and stainless steel layers as shown in Fig.2(c). Thus, the forming conditions for this material are less constrained than those for Nb/304L SS, which may prove to be a significant benefit in designing stamped bipolar plates from these types of Nb-clad materials. It should be noted that the conditions for the failure in the annealed Nb-clad 304L SS occur under fairly extreme conditions and may be avoidable in practice. An additional advantage currently is the lower cost of common ferritic stainless steel grades in comparison with many austenitic alloys due to the high price of nickel. Depending on whether the final clad bipolar plate design contains internal water cooling channels or not (i.e. whether the non-Nb side of each plate truly requires some form of corrosion resistance), it may be possible to further reduce the cost of this concept by employing a low-cost microalloyed ferritic steel.
4 Conclusions
1) The two different niobium-clad stainless steels, Nb/434 SS and Nb/304L SS, exhibit similar degrees of ductility under separate sets of optimized annealing conditions.
2) The thin interfacial iron/niobium rich layer forms within the Nb/304 SS during the vacuum annealing treatment.
3) The layer places constraint on the extent to the Nb/304L SS material, which can be subsequently formed during the manufacture of PEMFC bipolar plates.
4) The annealed Nb/434 SS material suggests at least one possible benefit to selecting a ferritic steel substrate for this niobium cladding application.
Acknowledgement
The authors thank Steve Chang at Engineered Materials Solutions, Inc. for providing the clad materials and for his technical assistance on the study. This work was supported by 2008 research fund by TP, Ulsan, Korea. The Pacific Northwest National Laboratory is operated by Battelle Memorial Institute for the United States Department of Energy (U.S. DOE) under Contract DE-AC06-76RLO 1830.
References
[1] LIN M, CHENG Y, LIN M, YEN S. Evaluation of PEMFC power systems for UPS base station applications [J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2005, 140(2): 346-349.
[2] Department of materials science and metallurgy, university of cambridge. DoITPoMS TLP-fuel cells-proton exchange membrane fuel cells [EB/OL]. http://www.msm.cam.ac.uk/doitpoms/tlplib/fuel- cells/low_temp_pem.php (2009 April 8th).
[3] LI X, SABIR I. Review of bipolar plates in PEM fuel cells: Flow-field designs [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2005, 30(4): 359-371.
[4] HERMANN A, CHAUDHURI T, SPAGNOL P. Bipolar plates for PEM fuel cells: A review [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2005, 30(12): 1297-1302.
[5] HORNUNG R, KAPPELT G. Bipolar plate materials development using Fe-based alloys for solid polymer fuel cells [J]. Journal of Power Sources, 1998, 72(1): 20-21.
[6] SCHOLTA J, ROHLAND B, TRAPP V, FOCKEN U. Investigations on novel low-cost graphite composite bipolar plates [J]. Journal of Power Sources, 1999, 84(2): 231-234.
[7] CUNNINGHAM N, GUAY D, DODELET J P, MENG Y, HLIL A R, HAY A S. New materials and procedures to protect metallic PEM fuel cell bipolar plates [J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2002, 149(7): A905-A911.
[8] DAVIES D P, ADCOCK P L, TURPIN M, ROWEN S J. Bipolar plate materials for solid polymer fuel cells [J]. Journal of Applied Electrochemistry, 2000, 30(1): 101-105.
[9] WANG H, SWEIKART M A, TURNER J A. Stainless steel as bipolar plate material for polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells [J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2003, 115(2): 243-251.
[10] NIKAM V V, REDDY R G. Corrosion studies of a copper–beryllium alloy in a simulated polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell environment [J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2005, 152(1): 146-155.
[11] WEIL K S, XIA G, YANG Z G, KIM J Y. Development of a niobium clad PEM fuel cell bipolar plate material [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2007, 32(16): 3724-3733.
[12] HONG S T, WEIL K S. Niobium-clad 304L stainless steel PEMFC bipolar plate material: Tensile and bend properties [J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2007, 168(2): 408-417.
[13] ASTM E8-04 [S].
Corresponding author: Sung-Tae HONG; Tel: +82-52-2592129; E-mail: sthong@ulsan.ac.kr
(Edited by LI Yan-hong)