DOI:10.19476/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2019.11.11
脉冲磁场对镁铜合金组织、力学性能及生物腐蚀行为的影响
张 磊,刘栩瑞,黄 浩,周 全
(南昌航空大学 航空制造工程学院,南昌 330063)
摘 要:在生物医用Mg-0.6Cu合金的凝固过程中施加脉冲磁场处理,研究脉冲电压对合金凝固组织、力学性能及生物腐蚀行为的影响。结果表明:随着放电电压的增加,在合金凝固组织逐渐细化的同时,第二相的数量也逐渐降低;当脉冲电压为300 V时,合金的屈服强度、抗拉强度和伸长率均逐渐提高,其较未处理合金分别提高了49.4%、45.7%和114.3%;试样在37 ℃的SBF溶液中的析氢速率、腐蚀速率和自腐蚀电流密度均逐渐降低,同时,其自腐蚀电位也逐渐向正向移动,这表明合金的耐腐蚀性能逐渐提高。
关键词:脉冲磁场;Mg-0.6Cu合金;组织;力学性能;生物腐蚀行为
文章编号:1004-0609(2019)-11-2540-09 中图分类号:TG146.22 文献标志码:A
作为一类可降解医用金属材料,镁合金由于具有生物安全性高、生物力学相容性好以及来源丰富、价格低廉等优点,备受人们关注,极富应用前景[1-3]。然而,镁合金的标准电极电位较负,表面极易腐蚀形成疏松多孔的氧化镁,耐腐蚀性能较差,这严重地限制了其在临床上的实际应用[4]。作为人体必须的微量元素之一,铜对于血液、中枢神经和免疫系统,头发、皮肤和骨骼组织以及脑、肝和心等内脏的发育和功能都有重要影响。铜还具有长效抑制细菌生长的作用[5-6]。大量研究结果表明,铜对大肠杆菌、金黄色葡萄球菌和白色念珠菌等多种细菌均具有较好的杀灭作用[7]。LIU等[8]设计并制备了3种成分可降解的Mg-Cu合金,并对其力学性能、耐腐蚀性能、生物相容性及抗菌性能进行了研究。结果发现:铸态Mg-Cu合金的力学性能在植入初期能够基本满足内植入材料的使用要求。Mg-Cu合金除具有良好的细胞相容性和血液相容性外,还表现出优异的抗细菌感染功能。然而,铜在镁中的固溶度很小,容易在α-Mg晶界处生成与基体有较大电位差的Mg2Cu第二相[9],其可以作为电偶腐蚀阴极加速基体的腐蚀,显著降低镁的耐蚀性。
近年来研究表明,在合金的凝固过程施加脉冲磁场,能够控制凝固过程,有效细化合金凝固组织,提高合金力学性能[10-14]。脉冲磁场处理技术除了能够避免对环境和合金本身的污染外,还具有瞬时高能、多参数可调、设备简单及细化效果显著等优点,具有极大的工业应用前景。杨院生等[10]研究发现脉冲磁场对AZ31、AZ80、AM60、AS31和 Mg-Gd-Y-Zr等镁合金均有显著的细化效果。施加脉冲磁场后,初生相由粗大、发达的枝晶变为细小的蔷薇状,溶质偏析显著降低。汪彬等[11]在Mg-Gd-Y-Zr镁合金凝固过程中施加脉冲磁场,发现脉冲磁场除了能够细化合金晶粒外,还能够提高Gd元素和Y元素在晶粒内部的溶质含量,使得晶界处第二相数量相应降低。本文作者课题组[12]在Mg-Zn-Y合金的凝固过程施加脉冲磁场,发现初生α-Mg相的显著细化,其形貌由树枝晶状转变为蔷薇状和多边形状共存,第二相的形貌由粗大骨骼状转变为不连续网状和孤岛状共存,其数量也显著降低,合金的力学性能得到显著提高。研究还发现,经脉冲磁场处理后,合金元素在合金晶内的固溶度显著增加,Zn元素和Y元素在晶内的溶质含量分别由2.6%和0.5%提高到6.0%和1.0%。
虽然脉冲磁场对于合金凝固组织和力学性能的影响已经得到广泛研究,但是对合金耐腐蚀性能的研究还鲜有文献报道。已有研究结果也表明,在镁合金的凝固过程中施加脉冲磁场,能够细化合金晶粒、降低第二相的数量以及增加晶内溶质元素含量,这些均有利于提高镁合金的耐腐蚀性能[15]。因此,本文作者在生物医用Mg-0.6Cu(质量分数,%)合金的凝固过程施加脉冲磁场,主要研究了脉冲电压对合金组织演变、力学性能以及生物腐蚀行为的影响。
1 实验
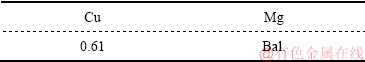
Mg-0.6Cu(质量分数,%)合金采用高纯镁锭(99.99%,质量分数)和高纯铜丝(99.99%,质量分数),按照名义成分配好后在坩埚电阻炉中熔炼,采用混合气体(99%CO2+1%SF6(体积分数))进行气体保护。
脉冲磁场处理试验采用自制的脉冲磁场发生装置,其具体设备参数见参考文献[12]。待合金熔清后,在760 ℃保温15 min,然后将金属液浇注到已预热至400 ℃的不锈钢坩埚后,立即施加脉冲磁场处理,直至合金凝固后取出。制备的铸锭尺寸均为d 48 mm×80 mm。实验时脉冲频率固定为10 Hz,脉冲电压分别为0、100、200和300 V。
在铸锭1/2高度的横截面的中心部位取样,经研磨、抛光后,采用3%(体积分数)硝酸乙醇溶液进行化学腐蚀。采用D/MAX-RC型X射线衍射仪测定合金的相组成。利用光学金相显微镜和QUANTA 200型环境扫描电镜(SEM)观察试样的显微组织,用扫描电镜自带的Inca-300型能谱能谱仪(EDS)对合金的成分进行分析。采用Image-Pro Plus 6.0软件统计第二相平均面积比。采用Metalscan2500光谱分析仪进行合金成分分析,其结果如表1所列。室温拉伸试验在E200D型电子万能试验机上进行,拉伸速率为0.5 mm/min。每组3个平行试样取平均值。采用SEM观察拉伸断口形貌。
腐蚀浸泡试验试样尺寸为10 mm×10 mm×3 mm。试样经研磨、抛光后,置于无水乙醇中超声清洗并吹干。腐蚀介质采用(37±0.5) ℃的SBF溶液[16],预先将溶液的pH值调控到7.4±0.1。SBF溶液每24 h更换1次。SBF体积与试样的表面积之比为60 mL/cm2。定时采用pH测试仪检测SBF溶液的pH值变化并记录。
表1 Mg-Cu合金的化学成分分析
Table 1 Chemical composition of Mg-Cu alloys used in this work (mass fraction, %).
采用失重法测试合金的腐蚀速率,每组4个平行试样取平均值。浸泡5 d后,使用铬酸(200 g/L CrO3+10 g/L AgNO3)清洗试样表面腐蚀产物,利用分析天平称量试样腐蚀浸泡前后质量。根据下式计算试样的质量损失腐蚀速率Pw[17]:
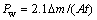 (1)
(1)
式中:Δm为损失质量,mg;A为试样表面积,cm2;t为浸泡时间,d。
采用SEM观察合金的腐蚀表面形貌。在CHE660B工作站上进行电化学腐蚀测试,测试采用三电极系统,即试样作为工作电极,饱和甘汞电极为参比电极,铂网为辅助电极,工作介质为(37±0.5) ℃的SBF溶液,扫描速率为0.5 mV/s。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 显微组织
图1所示为经不同脉冲电压的脉冲磁场处理后Mg-0.6Cu合金的XRD谱。由图1可见,施加脉冲磁场前后,Mg-0.6Cu合金的相组成并未发生变化,其均主要由初生α-Mg相和Mg2Cu两相组成。
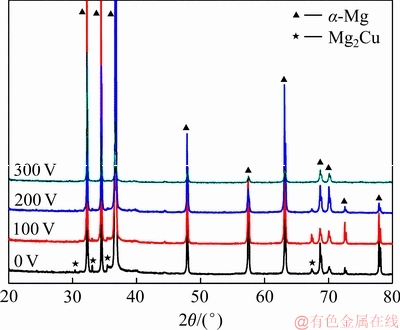
图1 经不同脉冲电压的脉冲磁场处理后Mg-0.6Cu合金的XRD谱
Fig. 1 XRD patterns of pure Mg-0.6Cu alloys under different discharging voltages
图2所示为经200 V脉冲磁场处理后Mg-0.6Cu合金第二相的SEM像。由图2可见,合金中的第二相主要呈现网络状和颗粒状两种形貌,分别对其进行EDS分析,其结果如表2所列。根据EDS分析结果可知,两种形貌的第二相均主要由Mg和Cu两种元素组成,结合X射线衍射图谱(见图1)可知,合金中的第二相为Mg2Cu相。
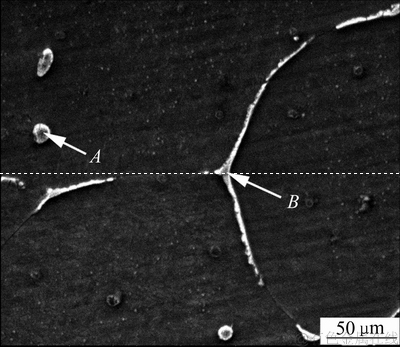
图2 经200 V脉冲磁场处理后Mg-0.6Cu合金的SEM像
Fig. 2 SEM image of Mg-0.6Cu alloy treated by 200 V PMF
表2 图2中各点的EDS分析结果
Table 2 EDS analysis of points marked in Fig. 2
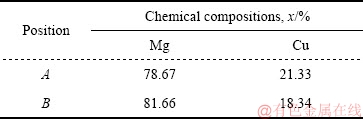
图3所示为脉冲电压对Mg-0.6Cu合金凝固组织中初生α-Mg相的影响。由图3(a)可见,未处理时,合金凝固组织中初生α-Mg相较粗大,其平均晶粒尺寸为520 μm。随着脉冲电压的增加,初生α-Mg相逐渐细化。当脉冲电压增加到300 V时,初生α-Mg相的平均晶粒尺寸减小到190 μm,相比未处理合金降低了63.5%。
图4所示为脉冲电压对Mg-0.6Cu合金凝固组织中第二相形貌的影响。由图4(a)可见,无磁场处理时,第二相主要呈连续网状沿初生α-Mg晶界分布。当脉冲电压为100 V时,连续网状分布的第二相有断开的趋势。当脉冲电压增加到200 V时,第二相演变为不连续网状、孤岛状和颗粒状共存。当脉冲电压继续增加到300 V时,第二相退化为孤岛状和颗粒状共存,其分布也变得更为均匀弥散。另外,由图4还可以看出,随着脉冲电压的增加,第二相的数量逐渐减低。经统计分析,无磁场处理时,第二相的平均面积比为12.4%。随着脉冲电压的增加,第二相的平均面积比逐渐降低。当放电电压为300 V时,第二相的平均面积比减小到6.3%,较无处理合金下降了49.2%。
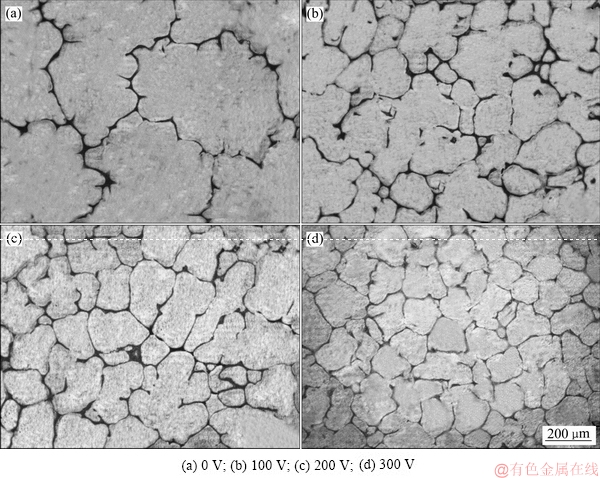
图3 不同脉冲电压时Mg-0.6Cu合金凝固组织中初生α-Mg相的形貌
Fig. 3 Morphologies of primary α-Mg phase in Mg-0.6Cu alloy under different discharging voltages
图4 不同脉冲电压时Mg-0.6Cu合金凝固组织中Mg2Cu相的形貌
Fig. 4 Morphologies of Mg2Cu phase in Mg-0.6Cu alloy under different discharging voltages
当脉冲磁场装置工作时,脉冲电流通过螺线管线圈就会在合金熔体中产生一个快速变化的脉冲磁场B,该快速变化的磁场又会在熔体中感应出感生电流J。脉冲磁场B和感生电流J之间发生作用将会产生洛伦兹力f。因为是f一个体积力,所以根据麦克斯韦方程可得
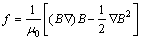 (2)
(2)
式中: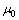 为真空磁导率;矢性微分算子
为真空磁导率;矢性微分算子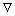 为哈米尔顿算子。
为哈米尔顿算子。
对式(2)进行体积分并结合高斯定理可得
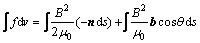 (3)
(3)
式中:b为磁场的单位矢量;n为积分面积元的外法向单位矢量;θ为矢量b和n的夹角。
由式(2)可见,f包含两项:第一项为垂直于试样侧表面的分力,第二项为沿磁场方向的作用力。因为本研究所采用的试样为圆柱体,并且θ角为90°,所以第二项分力可以忽略不计。由此可知,脉冲磁场对合金熔体的作用力为第一项分力,其方向沿圆柱体径向从试样表面指向试样中心。
电磁体力f在合金熔体中会产生磁压强P,其可表示为
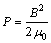 (4)
(4)
磁压强P会使得熔体沿径向收缩,即产生箍缩效应[16]。由于脉冲磁场B是快速变化的,因此,磁压强P也是剧烈变化的,在其作用下,合金熔体内将会产生强烈的电磁振荡。这种电磁振荡不仅影响了晶体的形核,还会影响晶体的长大。首先,由于型壁的激冷作用,合金溶液浇入铸型后首先在型壁处形成大量的晶核。电磁振荡效应将促使型壁处形成的晶核快速脱落,并将其带入熔体的中心部位,增加熔体中心的晶核数量,提高形核率。其次,电磁振荡效应能够使得二次枝晶臂的颈缩部分发生折断,即产生枝晶破碎。这些枝晶碎片成为合金凝固新的晶核,显著提高形核率[16-17]。再者,电磁振荡效应还使得铸型边缘的低温熔体和中心的高温熔体发生快速的热量交换,降低熔体内温度梯度,大大增加晶核的存活率。另外,在合金熔体中施加脉冲磁场还会产生焦耳热效应。在凝固过程中,由于焦耳热主要集中在枝晶尖端,而这些枝晶尖端非常细小,因此焦耳热很容易使其熔化,从而增加枝晶尖端曲率半径,降低枝晶的生长速度,最终使得枝晶发生球化[10]。
在合金熔体中,溶质原子将会失去价电子成为带电离子了[11]。未施加脉冲磁场时,这些带电离子热运动是随机和任意的。但在磁场的作用下,运动的带电离子会受到洛伦兹力的作用而沿磁力线方向做螺旋运动[12],这使得溶质粒子对基体镁产生相对运动,增强了溶质元素在镁中的扩散,导致溶质元素在α-Mg晶粒内固溶度的增加,从而显著降低第二相的数量。
2.2 力学性能
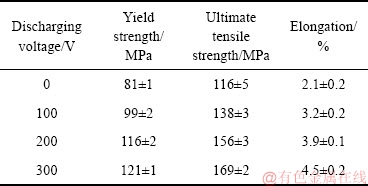
表3所列为不同脉冲电压下Mg-0.6Cu合金的室温拉伸性能。由表3可见,随着脉冲电压的增加,合金的屈服强度、抗拉强度和伸长率均逐渐提高。当脉冲电压为300 V时,合金的屈服强度、抗拉强度和伸长率分别为121 MPa、169 MPa和4.5%,相比未处理合金提高了49.4%、45.7%和114.3%。
表3 Mg-0.6Cu合金室温拉伸性能
Table 3 Tensile properties of Mg-0.6Cu alloys tested at room temperature
施加脉冲磁场后,合金力学性能的提高可以主要归因于凝固组织的细化。合金材料的强度和晶粒尺寸的关系可以用的Hall-Petch公式表示:
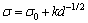 (5)
(5)
式中: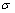 为金属材料的强度;
为金属材料的强度;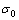 与k为材料有关常数;d为晶粒平均直径。
与k为材料有关常数;d为晶粒平均直径。
由式(5)可见,合金材料的强度将随晶粒的细化而提高。细化晶粒不仅能提高合金强度,还能提高其塑性。因为晶粒越细,则在同样的塑性变形量下,变形分散在更多的晶粒内而更趋于均匀,晶内和晶间的应力集中及引起的开裂倾向较小,因此,断裂前能够承受较大的塑性变形。
图5所示为施加脉冲磁场前后Mg-0.6Cu合金拉伸试样断口的SEM像。由图5(a)可见,未施加脉冲磁场时,合金的断口处可以观察到明显的解理台阶和解理面,呈典型的解理断裂特征。而在施加300 V脉冲磁场条件下,合金断口处的解理台阶和解理面基本消失,取而代之的是大量的撕裂棱,表现为典型的准解理断裂特征,如图5(b)所示。合金拉伸断口的断裂特征和拉伸实验数据相一致,在施加300 V脉冲磁场条件下,合金由解理断裂特征转变为准解理断裂特征,其塑性得到显著提高。
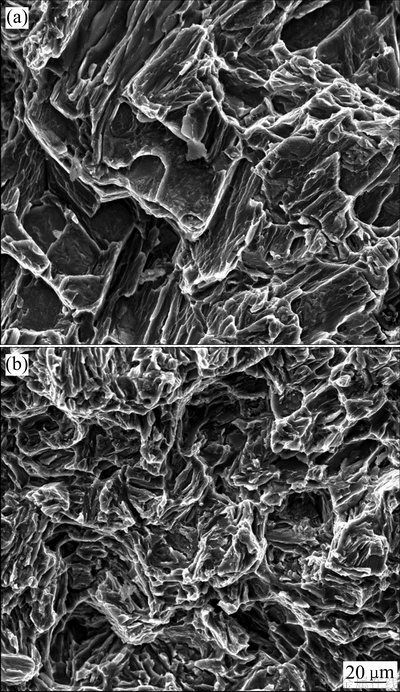
图5 Mg-0.6Cu合金室温拉伸试样的断口形貌
Fig. 5 Typical tensile fracture surface morphologies of Mg-0.6Cu alloy treated by PMF at 0 V(a) and 300 V(b)
2.3 耐腐蚀性能
图6所示为经不同脉冲电压的脉冲磁场处理后Mg-0.6Cu合金在(37±0.5) ℃的SBF溶液中浸泡120 h内溶液pH值的变化。由图6可见,所有浸泡试样的SBF溶液的pH值均呈现了相同的变化趋势。开始阶段,pH值迅速增加,当浸泡时间为24 h时,pH值达到峰值,然后缓慢下降;当浸泡时间超过72 h后,pH值逐渐趋于平稳。这是因为在浸泡实验的开始阶段,试样表面与SBF溶液直接接触,溶液中的C1-、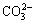 和
和 等离子会与镁基体发生反应,从而在试样表面生成大量Mg(OH)2,造成溶液中OH-的增多,从而使得溶液的pH值迅速增加。随着浸泡时间的延长,试样表面会生成类羟基磷灰石等腐蚀产物,这些腐蚀产物阻碍了试样表面与SBF溶液的直接接触,从而使得pH值逐渐下降,并趋于平稳。对比4条pH变化曲线可知,在相同时间内,浸泡脉冲磁场处理后试样的溶液的pH值均低于未处理试样,且随着脉冲电压的增加,pH值逐渐降低。由此可知,施加脉冲磁场后,Mg-0.6Cu合金的耐腐蚀性能显著提高,且随着脉冲电压的增加,合金的耐腐蚀性能逐渐提高。
等离子会与镁基体发生反应,从而在试样表面生成大量Mg(OH)2,造成溶液中OH-的增多,从而使得溶液的pH值迅速增加。随着浸泡时间的延长,试样表面会生成类羟基磷灰石等腐蚀产物,这些腐蚀产物阻碍了试样表面与SBF溶液的直接接触,从而使得pH值逐渐下降,并趋于平稳。对比4条pH变化曲线可知,在相同时间内,浸泡脉冲磁场处理后试样的溶液的pH值均低于未处理试样,且随着脉冲电压的增加,pH值逐渐降低。由此可知,施加脉冲磁场后,Mg-0.6Cu合金的耐腐蚀性能显著提高,且随着脉冲电压的增加,合金的耐腐蚀性能逐渐提高。
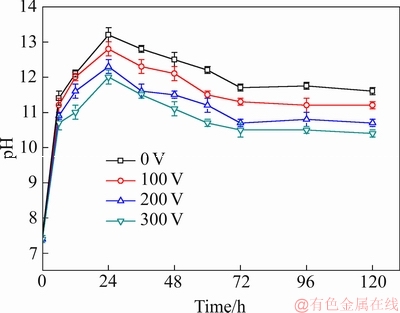
图6 Mg-0.6Cu合金在(37±0.5) ℃的SBF溶液中浸泡120 h内溶液的pH值变化
Fig. 6 Change of pH value when Mg-0.6Cu alloy immersed in SBF solution at (37±0.5) ℃ for 120 h
图7所示为经不同脉冲电压的脉冲磁场处理后Mg-0.6Cu合金在(37±0.5) ℃的SBF溶液中浸泡120 h后由质量损失结果计算的腐蚀速率。由图7可见,无磁场处理时,合金的腐蚀速率为62.57 mm/a。随着脉冲电压的增加,合金的腐蚀速率逐渐降低。当放电电压为300 V时,合金的腐蚀速率降低到28.19 mm/a,较未处理合金下降了54.9%,表现出较好的耐腐蚀性能。
图8所示为经不同脉冲电压的脉冲磁场处理后Mg-0.6Cu合金在(37±0.5) ℃的SBF溶液中浸泡24 h后去除腐蚀产物的表面形貌。由图8(a)可见,无磁场处理时,合金腐蚀表面出现了大且深的腐蚀坑。随着脉冲电压的增加,腐蚀坑的面积逐渐变小,其深度也逐渐变浅,表明合金的耐腐性能得到逐步提高。
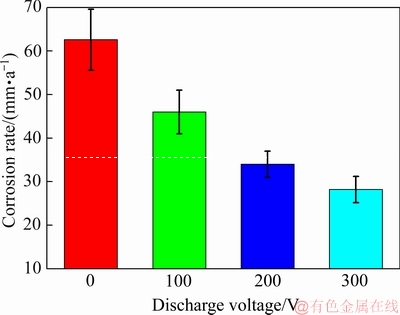
图7 Mg-0.6Cu合金在(37±0.5) ℃的SBF溶液中浸泡120 h后由质量损失结果计算的腐蚀速率
Fig. 7 Corrosion rate evaluated from mass loss change rate of Mg-0.6Cu alloys immersed in SBF solution at (37±0.5) ℃ for 120 h
图9所示为经不同脉冲电压的脉冲磁场处理后Mg-0.6Cu合金在(37±0.5) ℃的SBF溶液中测得的电化学极化曲线。根据极化曲线拟合得到的腐蚀电位(φcorr)和腐蚀电流密度(Jcorr)在图9中也一并给出。由图9可见,无磁场处理时,合金的腐蚀电位最低(-1.571 V),同时具有最大的腐蚀电流密度(263.4 μA/cm2),表明其耐腐蚀性能最差。随着脉冲电压的增加,合金的腐蚀电流密度逐渐降低,腐蚀电位也逐渐向正向移动。当脉冲电压为300 V时,合金具有最低的腐蚀电流密度(97.5 μA/cm2)和最高的腐蚀电位(-1.523 V),表现出最佳的耐腐蚀性能。上述电化学测试结果与腐蚀浸泡实验结果相一致。
在纯镁中添加Cu元素,会在基体中析出Mg2Cu相。由于Mg2Cu相对于镁基体具有较高的腐蚀电位,因此其会与镁基体形成原电池,发生电偶腐蚀。而Mg2Cu将作为腐蚀电偶的阴极加速镁基体的腐蚀。前边的凝固组织分析表明,施加脉冲磁场后,能够细化化Mg-0.6Cu合金的晶粒和降低Mg2Cu相的数量。一方面,晶粒细化能够提高晶界的数量,从而提高抗腐蚀壁垒的数量[15, 18];另一方面,Mg2Cu相数量的降低,使得与镁基体形成腐蚀原电池的数量减少,腐蚀电流密度降低,因此,在Mg-0.6Cu合金的凝固过程施加脉冲磁场处理能够提高合金的耐腐蚀性能。随着脉冲电压的增加,合金晶粒尺寸逐渐减小的同时,第二相的数量逐渐降低,因此,当脉冲电压为300 V时,合金表现出最佳的耐腐蚀性能。
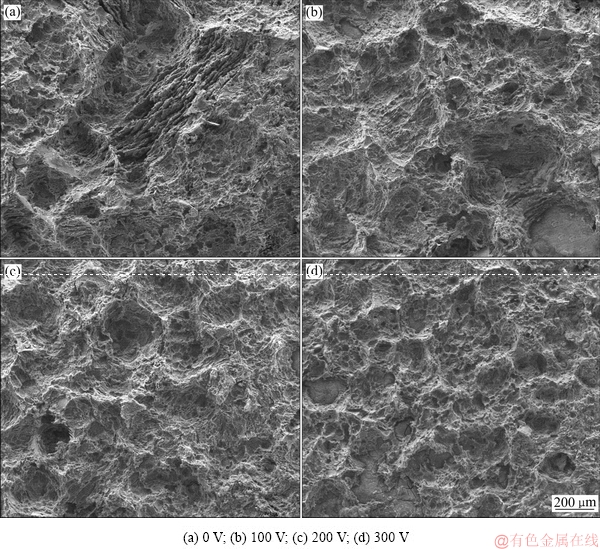
图8 Mg-0.6Cu合金在(37±0.5) ℃的SBF溶液中浸泡24 h后去除表面腐蚀产物的表面形貌
Fig. 8 Surface morphologies of Mg-0.6Cu alloys after removing corrosion products immersed in SBF at (37±0.5) ℃ for 24 h
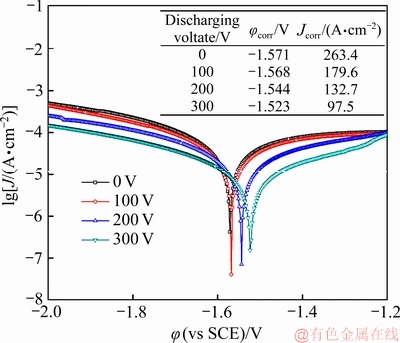
图9 Mg-0.6Cu合金在(37±0.5) ℃的SBF溶液中的电化学极化曲线
Fig. 9 Electrochemical polarization curves of Mg-0.6Cu alloys in SBF at (37±0.5) ℃
3 结论
1) 脉冲磁场处理能够显著细化Mg-0.6Cu合金的凝固组织。随放电电压的增加,合金的晶粒尺寸逐渐减小,Mg2Cu相的形貌由连续网状逐渐退化为孤岛状和颗粒状共存,其数量也逐渐降低。
2) 脉冲磁场处理可以显著提高Mg-0.6Cu合金的力学性能。随着放电电压的增加,合金的屈服强度、抗拉强度和伸长率均逐渐提高,当脉冲电压为300 V时,其分别为121 MPa、169 MPa和4.5%,相比未处理合金提高了49.4%、45.7%和114.3%。
3) 腐蚀浸泡实验和电化学实验结果均表明,脉冲磁场处理能够提高Mg-0.6Cu合金在37 ℃的SBF溶液中的耐腐蚀性能。随着放电电压的增加,合金的析氢速率、腐蚀速率和自腐蚀电流密度均逐渐降低,同时,其自腐蚀电位也逐渐向正向移动,表明合金的耐腐蚀性能得到逐渐提高。
REFERENCES
[1] WITTE F. The history of biodegradable magnesium implants: A review[J]. Acta Biomaterialia, 2010, 6(5): 1680-1692.
[2] WITTE F, KAESE V, HAFERKAMP H, SWITER E, MERYER-LINDENBERG A, WIRTH C J, WINDHAGEN H. In vivo corrosion of four magnesium alloys and the associated bone response[J]. Biomaterials, 2005, 26(17): 3557-3563.
[3] ZHENG Y F, GU X N, WITTE F. Biodegradable metals[J]. Materials Science and Engineering R, 2014, 77: 1-34.
[4] 袁广银, 章晓波, 牛佳林, 陶海荣, 陈道运, 何耀华, 蒋 垚, 丁文江. 新型可降解生物医用镁合金 JDBM 的研究进展[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2011, 21(10): 2476-2488.
YUAN Guang-yin, ZHANG Xiao-bo, NIU Jia-lin, TAO Hai-rong, CHEN Dao-yun, HE Yao-hua, JIANG Yao, DING Wen-jiang. Research progress of new type of degradable biomedical magnesium alloys JDBM[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2011, 21(10): 2476-2488.
[5] WANG S, YANG C, REN L, SHEN M, YANG K. Study on antibacterial performance of Cu-bearing cobalt-based alloy[J]. Materials Letters, 2014, 129: 88-90.
[6] HONG I T, KOO C H. Antibacterial properties, corrosion resistance and mechanical properties of Cu-modified SUS 304 stainless steel[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2005, 393(1/2): 213-222.
[7] REN L, YANG K, GUO L, CHAI H W. Preliminary study of anti-infective function of a copper-bearing stainless steel[J]. Materials Science and Engineering C, 2012, 32(5): 1204-1209.
[8] LIU C, FU X K, PAN H B, WAN P, WANG L, TAN L L, WANG K H, ZHAO Y, YANG K, CHU P K. Biodegradable Mg-Cu alloys with enhanced osteogenesis, angiogenesis, and long-lasting antibacterial effects[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 27374.
[9] 李爱文, 刘江文, 伍翠兰, 罗承萍, 焦东玲, 朱红梅. Cu含量对铸造Mg-3Zn-xCu-0.6Zr镁合金时效析出行为的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2010, 20(8): 1477-1494.
LI Ai-wen, LIU Jiang-wen, WU Cui-lan, LUO Cheng-ping, JIAO Dong-ling, ZHU Hong-mei. Effects of Cu addition on aging precipitation behavior of cast Mg-3Zn-xCu-0.6Zr magnesium alloys[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2010, 20(8): 1477-1494.
[10] 杨院生, 付俊伟, 罗天骄, 汪 彬, 冯小辉, 童文辉, 李应举. 镁合金低压脉冲磁场晶粒细化[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2011, 21(10): 2639-2649.
YANG Yuan-sheng, FU Jun-wei, LUO Tian-jiao, WANG Bin, FENG Xiao-hui, TONG Wen-hui, LI Ying-ju. Grain refinement of magnesium alloys under low-voltage pulsed magnetic field[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2011, 21(10): 2639-2649.
[11] 汪 彬, 沈燕青, 朱天宇. 脉冲磁场对 Mg-Gd-Y-Zr合金组织中溶质含量的影响[J]. 特种铸造及有色合金, 2012, 32(5): 407-409.
WANG Bin, SHEN Yan-qing, ZHU Tian-yu. Effect of the pulsed magnetic field on the solute content in Mg-Gd-Y-Zr magnesium alloy[J]. Special-cast and Non-ferrous Alloys, 2012, 32(5): 407-409.
[12] ZHANG L, ZHOU W, HU P H, ZHOU Q. Microstructural characteristics and mechanical properties of Mg-Zn-Y alloy containing icosahedral quasicrystals phase treated by pulsed magnetic field[J]. Journal ofAlloysandCompounds, 2016, 688: 868-874.
[13] 腾跃飞, 李应举, 冯小辉, 杨院生. 脉冲磁场作用下矩形截面宽厚比对K4169高温合金晶粒细化的影响[J]. 金属学报, 2015, 51(7): 844-852.
TENG Yue-fei, LI Ying-ju, FENG Xiao-hui, YANG Yuan-sheng. Effect of rectangle aspect ratio on grain refinement of superalloy K4169 under pulsed magnetic field[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2015, 51(7): 844-852.
[14] ZHANG L, LI W, YAO, QIU H. Effects of pulsed magnetic field on microstructures and morphology of the primary phase in semisolid A356 Al slurry[J]. Materials Letters, 2012, 66: 190-192.
[15] CAO F F, DENG K K, NIE K B, KANG J W, NIU H Y. Microstructure and corrosion properties of Mg-4Zn- 2Gd-0.5Ca alloy influenced by multidirectional forging[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2019, 770: 1208-1220.
[16] GU X N, ZHENG W, CHENG Y, ZHENG Y F. A study on alkaline heat treated Mg-Ca alloy for the control of the biocorrosion rate[J]. Acta Biomaterialia, 2009, 5(7): 2790-2799.
[17] SHI Z M, ATRENS A. An innovative specimen configuration for the study of Mg corrosion[J]. Corrosion Science, 2011, 53(1): 226-246.
[18] ANTENS A, SONG G L, GAO F Y, SHI Z M, BOWEN P K. Advances in Mg corrosion and research suggestions[J]. Journal of Magnesium and Alloys, 2013, 1(3): 177-200.
Effects of pulsed magnetic field on microstructure, mechanical properties and bio-corrosion behavior of Mg-0.6Cu alloy
ZHANG Lei, LIU Xu-rui, HUANG Hao, ZHOU Quan
(School of Aeronautical Manufacture Engineering, Nanchang Hangkong University, Nanchang 330063, China)
Abstract: The pulsed magnetic field (PMF) has been imposed during solidification of biodegradable Mg-0.6Cu alloy. The effects of discharging voltage on the solidification microstructure, mechanical properties and bio-corrosion behavior of Mg-0.6Cu alloy were studied. The results show that the solidification microstructure of Mg-0.6Cu alloy is further refined with the increase of the discharging voltage. Moreover, the volume fraction of second phase in the alloy is reduced by PMF. The mechanical properties of Mg-0.6Cu alloy are enhanced. The yield strength, ultimate tensile strength and elongation of the alloy treated by PMF at discharging voltage of 300 V are increased by 49.4%, 45.7% and 114.3%, respectively, compared to those of the alloy untreated by PMF. The PMF treatment is beneficial to the bio-corrosion resistance improvement of Mg-0.6Cu alloy. With the increase of the discharging voltage, the hydrogen evolution rate, corrosion rate and corrosion current density of the alloys gradually decrease, and the corrosion potential of the alloys, meanwhile, gradually move towards positive direction.
Key words: pulsed magnetic field; Mg-0.6Cu alloy; microstructure; mechanical property; bio-corrosion behavior
Foundation item: Project(51401102) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project (20181BAB206005) supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangxi Province, China
Received date: 2018-10-22; Accepted date: 2019-05-20
Corresponding author: ZHANG Lei; Tel: +86-13576062172; E-mail: LZhang@nchu.edu.cn
(编辑 李艳红)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(51401102);江西省自然科学基金资助项目(20181BAB206005)
收稿日期:2018-10-22;修订日期:2019-05-20
通信作者:张 磊,副教授,博士;电话:13576062172;E-mail:LZhang@nchu.edu.cn