DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2016.07.033
片石挡墙支护煤矸石路堤现场试验研究
杨果林,段君义,宋淮
(中南大学 土木工程学院,湖南 长沙,410075)
摘要:为研究煤矸石路堤的结构特性,对湖南省安化—邵阳高速公路K127+700 km和K127+720 km 2个断面的煤矸石填筑路堤进行现场试验,测试路堤沉降、侧向变形、竖向土压力、水平土压力和基底不同方向土压力的分布规律。研究结果表明:煤矸石路堤在靠近挡墙处沉降较小,远离挡墙的位置沉降量逐渐增大;靠近挡墙的侧向位移的最大值发生在煤矸石路堤填土厚度较小处;2个试验断面的最大水平土压力均出现在煤矸石路堤和黏土路基的交界面处;在施工过程中,挡墙内侧基底土体存在应力主轴偏转现象;在施工结束后,煤矸石路堤与黏土地基交界面位置处挡墙内侧煤矸石的土压力从大至小依次为水平土压力、竖向土压力和45°方向土压力。
关键词:煤矸石路堤;包边土;土压力
中图分类号:TU471 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2016)07-2424-08
Field test study on coal gangue embankment supported by rubble bulkhead
YANG Guolin, DUAN Junyi, SONG Huai
(School of Civil Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410075, China)
Abstract: In order to study the structural characteristics of coal gangue embankment, a field test was conducted on the site of K127+700 km and K127+720 km of Anhua—Shaoyang expressway in Hunan Province, and its settlement of embankment, lateral deformation, vertical earth pressure, horizontal earth pressure and basal earth pressure in different directions were tested. The results show that the settlement of embankment near the retaining wall is small, and it increases with the increase of distance. The maximum lateral displacement of the retaining wall locates in the position where the thickness of embankment is relatively small. The maximum horizontal earth pressure of two embankments appears at the interface between coal gangue embankment and clay subgrade. In the construction process, the soil at this interface of inside retaining wall exhibits stress axis deflection, and after construction, and the horizontal soil pressure at this interface is larger than the vertical soil pressure, while the earth pressure in 45° direction is the smallest.
Key words: coal gangue embankment; covered clay; earth pressure
煤矸石是在煤矿开采、洗煤过程中产生的一种副产品,因为其含煤量较低,导致工业价值低而成为一种废弃物。随着我国煤炭产量逐年增加,煤矸石的排放量也急剧增加,严重影响环境。目前,煤矸石在许多填筑工程得到运用且性能良好[1-2],其用作各种路基填筑材料已成为消耗煤矸石的主要途径[3]。随着我国高速公路的大规模建设,煤矸石在路用填料的应用中具有广阔的前景[4-5]。由于煤矸石具有不同于其他材料的自身特性,因此,对煤矸石路用性能进行研究具有重要意义。国内外研究者对煤矸石进行了大量的室内试验[6-8]。但现场试验是最佳的足尺试验,不仅避免了室内模型试验的相似性问题,而且不用考虑边界影响,能够反映煤矸石路堤结构的真实工作性态。BUTTLER等[9-12]利用不同煤矸石进行了现场模拟压密试验,认为煤矸石压密程度与颗粒级配密切相关,适当提高煤矸石中细小颗粒的密度可以显著增强煤矸石固结性能;赵鹏[13]开展了煤矸石路基现场碾压指标试验,对煤矸石路基的压碎值、级配及沉降随夯击次数进行分组测试,确定了煤矸石路基的强夯加固设计参数;王朝辉等[14]对煤矸石路堤开展了冲击压实试验,发现煤矸石填筑路基在普通振动压实的基础上进行10遍左右的冲击增强补压效果最好;刘松玉等[15]通过现场大型直剪试验对煤矸石的强度特性进行了系统研究,并绘制了煤矸石的强度包络曲线,得到了煤矸石的抗剪强度参数以及参数随粗颗粒含量的变化规律;贺建清等[16]对掺土煤矸石路堤进行了现场碾压与渗透试验,得出掺土煤矸石路堤经压实后的强度高于土路堤的强度,且具有良好的隔水效果。目前,人们针对煤矸石路堤本体结构工程特性的现场试验研究较少。本文以湖南省安化—邵阳高速公路K127+700 km与K127+ 720 km这2个断面为试验工点,对煤矸石路堤的整体结构工程特性进行现场试验研究。
1 工程概况与试验方案
煤矸石填筑路堤试验段K127+612.4~K127+863.0 km,位于安邵高速公路TJ2标施工段的起始处,全长250.6 m。在山坡位置选线,需要进行路堤填筑。本试验段利用当地沙坪煤矿废弃煤矸石作为路堤填料,边坡和封顶层采用黏土包边。鉴于路堤高度较小,采用M7.5片石砂浆坡脚矮墙进行边坡防护。现场填筑所用煤矸石基本物理性质:平均含水率(质量分数)为5.10%,最大干密度为2.14 g/cm3。图1所示为煤矸石路堤典型断面图。
现场试验分别在里程为K127+700 km和K127+ 720 km这 2个断面进行。其中,K127+700 km断面煤矸石路堤采用1 m厚黏土包边;K127+720 km没有进行黏土包边。本试验主要研究煤矸石填筑路堤和砂浆片石挡墙的力学特性,包括煤矸石填筑路堤的沉降、侧向变形、竖向土压力、挡墙的水平土压力以及基底不同方向土压力。监测元器件布置如图2所示,试验所选元器件如表1所示。其中,路堤填筑高度与施工时间关系如图3所示(注:若无说明,施工时间从挡墙顶部位置填筑起算,对应起算日期为2014-09-23)。

图1 煤矸石路堤典型断面图
Fig. 1 Typical profile of coal gangue embankment

图2 监测元器件布置图
Fig. 2 Arrangement of instrument on section
表1 试验所选元器件
Table 1 Corresponding components of test


图3 填筑高度与施工时间的关系曲线
Fig. 3 Relationship between filling height and time
2 测试结果与分析
2.1 沉降规律
为了测试煤矸石路堤的沉降情况,在每个试验断面埋设竖向应变计3个,编号为VY1,VY2和VY3,到墙趾水平距离分别为3,6和9 m,如图2所示。沉降随施工时间关系如图4所示,沉降沿路堤横向分布如图5所示。
从图4可以看出:沉降初期较快,后期较慢,且沉降曲线均有突变,这是进行了路堤碾压的结果;当施工过程结束时,沉降量基本趋于稳定;2个断面不同距离的沉降曲线具有相似规律性;有包边(无包边)断面距挡墙3 m位置处的沉降量为59.77 mm(54.99 mm),距挡墙6 m位置处的沉降量为69.37 mm(67.26 mm),距挡墙9 m处的沉降量为79.47 mm(73.11 mm);在离挡墙相同距离的位置,有包边土断面的沉降量比无包边土断面的沉降量大,这是由于包边断面覆盖1 m厚的黏土,增大了路堤的重力。
从图5可以看出:在填筑一段时间后,对于有包边断面,测点与挡墙水平距离增大3 m,沉降量随之增大约10 mm。无包边断面处的沉降也有类似特点。根据这一特征,在3~9 m区间内沉降量随着与挡墙距离的增加大致呈线性增加。这说明实际碾压要遵循由路肩逐渐向中心的碾压方式,防止路堤中心土体在碾压作用下往两边挤压,形成中间低、两边高的“盆地”现象。此外,当有碾压作用时,压实度增加,沉降量会明显增加,说明沉降与压实程度密切相关。

图4 沉降量时程曲线
Fig. 4 Time-history curves of settlement

图5 沉降沿路堤横向分布
Fig. 5 Lateral distribution of embankment settlement
2.2 侧向变形规律
为了测试煤矸石土体的水平变形情况,在每个试验断面布置水平应变计4个,编号为LY1~LY4,埋设深度分别为2.4,1.6,0.8和0 m,长度均为3.6 m,如图2所示。侧向位移随施工时间关系如图6所示,侧向位移随埋深的变化如图7所示(注:埋设深度是指从挡墙顶部垂直向下的埋设深度)。
从图6可以看出:侧向位移初期变化较大,后期较小,侧向位移曲线均有突变。这是因为在施工过程中进行路堤压实,当施工过程结束时,侧向位移基本趋于稳定。对比较浅埋深(小于1 m)位置和深埋深(大于1 m)位置的侧向位移发现,侧向位移主要发生在煤矸石路堤埋深较小位置。这是因为这一区域的煤矸石颗粒尚未压密振实,这使得一旦有压路机碾压,便会出现较大侧向位移。2个断面的不同埋设深度侧向位移曲线具有相似的规律。

图6 侧向位移时程曲线
Fig. 6 Time-history curves of lateral displacement
从图7可以看出:侧向位移与埋设深度呈非线性关系;侧向位移的最大值出现在埋设深度0.8 m附近,其原因是碾压使得填土产生按扩散角的侧向挤压作用,导致最大侧向位移出现在埋设深度0.8 m附近而非0 m附近;在相同埋置深度的位置,无包边土断面的侧向位移比有包边土断面的大。这说明包边后的煤矸石路堤刚度更好,有包边的煤矸石路堤整体性优于未包边的煤矸石路堤的整体性。
2.3 竖向土压力变化规律
按照现场试验方案,埋设到墙趾水平距离分别为2,4,6,8和10 m的竖向土压力盒,编号为VE3~VE7,埋设深度为2.4 m(从挡墙顶部往下算),如图2所示。图8所示为竖向土压力时程曲线,图9所示为竖向土压力沿路堤横向分布曲线。
从图8可以看出:在2个试验断面中,测点VE3,VE4,VE5,VE6和VE7的竖向土压力变化趋势大体一致,竖向土压力均随着填筑煤矸石高度的增加而有所增加;当填筑高度不再变化时,各位置处的竖向土压力也趋于稳定。

图7 侧向位移随埋深的变化
Fig. 7 Development of lateral displacement with depth
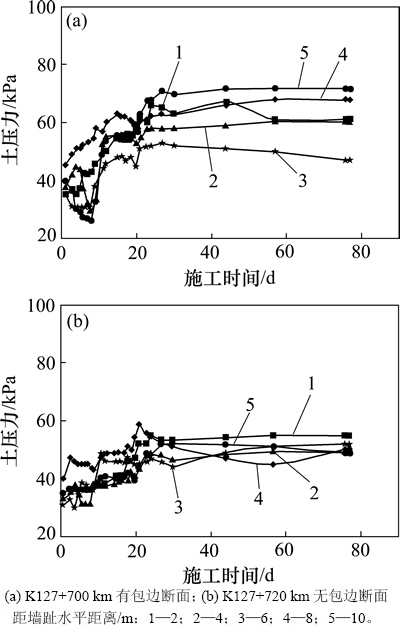
图8 竖向土压力时程曲线
Fig. 8 Time-history curves of vertical earth pressure
从图9可以看出:有包边土断面各位置处的竖向土压力相差较大,距挡土墙6 m处的竖向土压力最小,距挡土墙8 m和10 m处的竖向土压力要比2 m和4 m处的大,这是由于2 m和4 m处靠近挡墙,煤矸石在碾压时,在此位置受到挡墙约束作用较大而挤密,土压力增大,且在其上方存在1 m厚黏土包边,故其竖向土压力比6 m处的大;8 m和10 m处的填土厚度比其他位置的大,导致其竖向土压力比其他位置的大。无包边土断面各位置的竖向土压力相差不大,基本在区间40~55 kPa内变化,表明有包边断面路堤内的竖向土压力均匀性差。这主要是因为有包边断面路堤的包边土对路堤内土体变形有约束作用,导致竖向土压力的分布存在差异。此外,竖向土压力虽然逐渐趋于稳定,但各个位置的竖向土压力仍有变动,尤其是两边位置。其原因除有测试仪器测量的误差与碾压不均匀外,更重要的是煤矸石在压实过程中具有大颗粒破碎引起粒组重新分布的特点,这也使得煤矸石的自我结构得到改善,有利于路堤的填筑。

图9 竖向土压力沿路基横向分布
Fig. 9 Lateral distribution of vertical earth pressure
2.4 水平土压力变化规律
水平土压力盒主要是测试煤矸石路堤对起护坡作用的砂浆片石挡墙的作用力。按照试验方案,分别从挡墙顶垂直向下依次埋设水平向土压力盒,埋设深度依次为0,0.8,1.6,2.4,3.2和4.0 m(从挡墙顶部往下算),编号为LE1~LE6,如图2所示。图10所示为不同深度水平土压力时程曲线,图11所示为水平土压力随埋深的变化。
从图10可以看出:水平土压力随填筑高度的增加而增大,当填筑高度不再增加或碾压过程结束时,水平土压力也趋于稳定;在填筑过程中,相比于有包边断面,无包边断面不同深度水平土压力有一定的变化幅度,这是由于其边坡没有黏土包边的约束作用。

图10 不同深度水平土压力时程曲线
Fig. 10 Time-history curves of lateral earth pressure in different depths
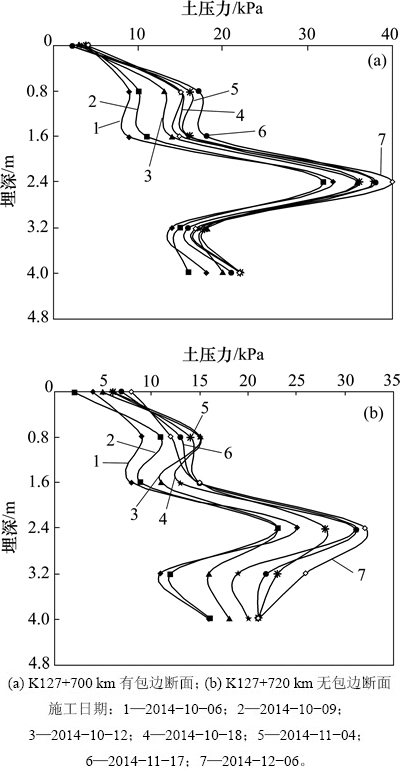
图11 水平土压力随埋深的变化
Fig. 11 Development of lateral earth pressure with depth
从图11可以看出:2个断面的最大水平土压力均出现在埋深2.4 m处,即煤矸石路堤和黏土路基的交界面处,该处的水平土压力有明显突变,远比其他各位置的大。其主要原因是挡墙朝路堤倾斜,挡墙与天然黏土地基在交界面处构成夹角,土体在碾压过程中往夹角处不断挤压密实而导致其水平土压力比其他埋深处的大;此外,由于天然黏土地基面以下的土体是天然密实状态,故碾压作用对天然黏土地基面以下的土体水平土压力影响较小。除了埋深2.4 m的突变点外,水平土压力大体随深度增加而呈变大趋势;在施工过程结束后,无包边土断面的水平土压力总体上小于有包边土断面的水平土压力。
2.5 基底不同方向土压力变化规律
为了测试同一埋深位置处(煤矸石路堤与天然地基土交界面)各个方向土压力的关系,在路堤开始填筑前,预先在天然地基面下紧贴挡墙处埋设3个受力面不同朝向的土压力盒:1个受力面向上(LE3垂直),测量竖向土压力(90°);1个竖直放置(LE3),测量水平土压力(0°);还有1个土压力盒的受力面与水平面呈45°。测量45°方向的土压力(如图2所示)。3个土压力沿路堤纵向间隔为0.5 m。图12所示为基底不同方向土压力变化(注:图12中施工时间从基底位置填筑起计算)。

图12 基底不同方向土压力变化
Fig. 12 Change of earth pressure along different directions of base
从图12可以看出:路堤刚开始填筑时,竖向土压力迅速增大,其数值为煤矸石填料容重与填筑厚度的乘积,且大于水平土压力,45°方向的土压力增加缓慢;随着填筑高度继续增加,45°方向的土压力仍然缓慢增加,而水平土压力增加速度增大,甚至比竖向土压力的增大速度大。当填筑过程结束后,3个方向土压力从大至小依次为水平土压力、竖向土压力、45°方向土压力。水平土压力与竖向土压力相差不大,45°方向土压力远比其他2个方向土压力小很多。从摩尔应力圆角度分析可知,水平土压力与竖向土压力在应力圆上对应点的连线与应力坐标轴趋近垂直,两者作用面均存在较大的剪应力,45°方向土压力朝着最小主应力靠近。可见,在煤矸石路堤填筑过程中,墙趾附近基底处的土体应力状态发生了明显的应力主轴偏转现象。此位置的土压力主要是水平土压力和竖向土压力,特别是水平土压力对挡墙的作用较大。对于边坡的稳定性,边坡的潜在滑裂面可能会穿过基底的表层,然后在坡脚前方溢出,坡脚后方的土体会受到较大的水平推力[17-18],致使坡脚前方的土体可能发生向上隆起的现象。本试验结果与理论研究结果具有一致性,所以,在进行煤矸石路堤的设计与施工时,要注意煤矸石路堤压实和挡墙防护设计,尤其是要注意考虑水平土压力对挡墙的作用。
3 结论
1) 煤矸石路堤随着与挡墙距离的增大,沉降量大致呈线性增大;包边断面在相同位置的沉降量比无包边断面的大。侧向位移沿挡墙高度呈非线性分布,最大值在埋深0.8 m处;包边断面在同一埋深处的侧向位移比无包边断面的小,表明包边后的煤矸石路堤刚度和整体性更好。
2) 基底的竖向土压力均随着填筑高度的增加而增加,沿路堤横向呈非线性分布;包边断面路堤在距挡墙水平距离为6 m处的竖向土压力最小;无包边断面各位置处的竖向土压力规律不明显。
3) 2个断面最大水平土压力均出现在煤矸石路堤与黏土路基的交界面处,该处水平土压力有显著突变,远比其他埋深处的大;除突变点外,其他各处水平土压力随深度增加而大致呈线性增大。相比包边断面,无包边断面的水平土压力总体偏小,且其变化幅度较大。
4) 挡墙内侧煤矸石路堤与黏土地基交界面处的土压力从大至小依次为水平土压力、竖向土压力、45°方向土压力;在煤矸石路堤填筑过程中,该处的土体应力状态出现主轴偏转现象。
5) 煤矸石路堤与黏土地基交界面处的土压力主要是水平和竖向土压力,表明设计和施工时必须要注意煤矸石路堤压实和挡墙防护设计,特别是要考虑水平土压力对挡墙的作用。
参考文献:
[1] SUN Y Z, FAN J S, QIN P, et al. Pollution extents of organics from a coal gangue dump of Jiulong Coal Mine[J]. Environment Geochemistry and Health, 2009, 31(1): 81-89.
[2] FALLMAN A M, AURELL B. Leaching tests for environmental assessment of inorganic substances in wastes, Sweden[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 1996, 178(1): 71-84.
[3] 姜振泉, 赵道辉, 隋旺辉, 等. 煤矸石固结压密性与颗粒级配缺陷关系研究[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 1999, 28(3): 212-216.
JIANG Zhenquan, ZHAO Daohui, SUI Wanghui, et al.Study on relationship between consolidation compactness and size grade shortage of coal gangue[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 1999, 28(3): 212-216.
[4] 刘松玉, 童立元, 邱钰, 等. 煤矸石颗粒破碎及其对工程力学特性影响研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2005, 27(5): 505-510.
LIU Songyu, TONG Liyuan, QIU Yu, et al. Crushable effects on engineering mechanical properties of colliery wastes[J]. Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2005, 27(5): 505-510.
[5] 邱钰, 缪林昌, 刘松玉. 煤矸石在道路建设中的应用研究现状及实例[J]. 公路交通科技, 2002, 19(2): 1-5.
QIU Yu, MIAO Linchang, LIU Songyu. Application study and practice of coal gangue applied to road construction[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2002, 19(2): 1-5.
[6] ZHANG Yapeng, MENG Wenqing, ZHANG Zhifei. Experimental study of indirect tensile strength of calcareous coal gangue mixture[J]. World Journal of Engineering, 2013, 10(5): 457-462.
[7] 王凤江. 颗粒破碎对煤矸石渗透性能的影响[J]. 岩土工程技术, 2007, 20(3): 147-150.
WANG Fengjiang. The impact of granule crash on infiltration capability of coal wastes[J]. Geotechnical Engineering Technology, 2007, 20(3): 147-150.
[8] 杨果林, 高礼, 杜勇立. 不同掺土量格宾网加筋煤矸石的残余强度试验研究[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 44(12): 5060-5067.
YANG Guolin, GAO Li, DU Yongli. Test study on residual strength characteristics between coal gangue and gabion mesh mixed with different qualities of soil[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2013, 44(12): 5060-5067.
[9] BUTTLER P E. Utilization of coal mine refuse in the construction of highway embankments[C]// The 1st Symposium on Mine and Preparation Plant Refuse Disposal. Louisvill, Kentucky, USA, 1974: 238-255.
[10] MICHALS P, SKARZYNSKA K M. Compactability of coal mining wastes as a fill material[C]// Treatment and Utilization of Coal Mining Wastes. Durham, England, 1984: 283-288.
[11] SOLESBURY F W. Coal wastes in civil engineering works: two case histories from South Africa[C]// The 2nd Symposium on the Reclamation, Treatment and Utilization of Coal Mining Wastes. Nottingham, England: British Coal Corporation, 1987: 207-218.
[12] RAINBOW A K M, SKARZYNSKA K M. Mine stone impoundment dams for fluid fly ash storage[C]// The 2nd Symposium on the Reclamation, Treatment and Utilization of Coal Mining Wastes. Nottingham, England: British Coal Corporation, 1987: 219-238.
[13] 赵鹏. 邢汾高速煤矸石填筑路基关键技术研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学公路学院, 2012: 41-57.
ZHAO Peng. Research on key technology of Xingfen highway gangue subgrade[D]. Xi’an: Chang’an University. Institute of Highway, 2012: 41-57.
[14] 王朝辉, 王选仓, 申文胜, 等. 冲击压实技术在高速公路煤矸石路基中的应用及效果分析[J]. 河北工业大学学报, 2010, 39(4): 96-100.
WANG Chaohui, WANG Xuancang, SHEN Wensheng, et al. Application and effect analysis of impact compaction technology to coal gangue subgrade of expressway[J]. Journal of Hebei University of Technology, 2010, 39(4): 96-100.
[15] 刘松玉, 邱钰, 童立元, 等. 煤矸石的强度特征试验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2006, 25(1): 199-205.
LIU Songyu, QIU Yu, TONG Liyuan, et al. Experimental study on strength properties of coal wastes[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2006, 25(1): 199-205.
[16] 贺建清, 靳明, 阳军生. 掺土煤矸石的路用工程力学特性及其填筑技术研究[J]. 土木工程学报, 2008, 41(5): 87-93.
HE Jianqing, JIN Ming, YANG Junsheng. A study on the road engineering mechanical properties of coal gangue mixed with clay and the filling techniques[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2008, 41(5): 87-93.
[17] 李凯, 陈国荣. 基于滑移线场理论的边坡稳定性有限元分析[J]. 河海大学学报(自然科学版), 2010, 38(2): 191-195.
LI Kai, CHEN Guorong. Finite element analysis of slope stability based on theory of slip line field[J]. Journal of Hehai University (Natural Science), 2010, 38(2): 191-195.
[18] 宋雅坤, 郑颖人, 赵尚毅, 等. 有限元强度折减法在三维边坡中的应用研究[J]. 地下空间与工程学报, 2006, 2(5): 822-827.
SONG Yakun, ZHENG Yingren, ZHAO Shangyi, et al. Application of three-dimensional strength reduction FEM in slope[J]. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering, 2006, 2(5): 822-827.
(编辑 陈灿华)
收稿日期:2015-07-07;修回日期:2015-09-12
基金项目(Foundation item):国家自然科学基金资助项目(51478484,51278499);交通运输部联合攻关项目(2010 353 343 290);中南大学中央高校基本科研业务费专项资金资助项目(2016zzts401) (Projects(51478484, 51278499) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(2010 353 343 290) supported by the Ministry of Transport of China; Project(2016zzts401) supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities of Central South University)
通信作者:杨果林,教授,博士生导师,从事岩土工程、道路与铁道工程和结构工程研究;E mail: guoling@csu.edu.cn