文章编号:1004-0609(2010)07-1267-08
Al-Mg-Si合金中U1和U2相的原子成键与性能
高英俊,陈华宁,韦 娜,文春丽,黄创高
(广西大学 物理科学与工程技术学院,南宁530004)
摘 要:应用EET理论和改进的TFD理论对Al-Mg-Si合金时效过程中析出的U1与U2相的原子成键和结合能进行计算。结果表明:两相晶胞中最强键和次强键都是Al—Si键,其键络比基体Al晶胞中的最强键络都强得多;两析出相晶胞中都以较强的Al—Si键构成主要键络骨架结构,起到增强基体键络强度、强化合金的作用。由于析出相U1比析出相U2具有更强的Al—Si键络结构,且结合能较大,因此,相对U2相来说,U1相更稳定。计算结果还表明:(001)Al//(110)U1相界面处电荷保持连续且连续性较好,界面应变能较低,界面较稳定;界面(001)Al// (010)U2处的面电荷密度偏离连续条件,因此在此界面处,应力较大,界面原子键匹配较差,界面储能(应变能)较高,容易成为新相形核、长大和裂纹萌生的地方。
关键词:Al-Mg-Si 合金;U1和U2相;原子成键;力学性能
中图分类号:TG111.1 文献标志码:A
Atomic bondings and properties of U1 andU2 phases of Al-Mg-Si alloy
GAO Ying-jun, CHEN Hua-ning, WEI Na, WEN Chun-li, HUANG Chuang-gao
(College of Physics Science and Engineering, Guangxi University, Nanning 530004, China)
Abstract: Atomic bondings of U1 and U2 phases in Al-Mg-Si alloy during aging were calculated by using the EET theory and the improved TFD theory. The results show that the strongest bonding and the second strong bonding in two phases are both Al—Si bonds, which are stronger than those in Al matrix. The firm network structures of Al—Si bonds are formed in U1 and U2 phases to enhance the bond network and strengthen alloy, while the bonding networks of Al—Si in U1 phase are not only stronger than those in U2 phase, but also with greater combining energy, therefore the structure of U1 is more stable. The calculation results also show that the electron density on the interface (001)Al//(110)U1 between U1 and matrix of Al is continuous with lower strain energy so that the interface (0001)Al//(110)U1 is more stable, while that on the interface (001)Al//(010)U2 is not continuous with a greater stored energy, poor atom-matching and higher stored energy, which will lead to precipitate a new phase or form a creak to break the alloy.
Key Word: Al-Mg-Si alloy; U1 and U2 phases; atomic bonding; mechanical property
Al-Mg-Si 合金由于具有低密度、高强度和优良力学性能,现已被广泛应用于车辆和飞机结构件等领 域[1-2]。通常情况下,Al中添加少量的Mg和Cu,不改变合金时效过程的析出序列及析出相,即在一定时效条件下,从过饱和固溶体中依次析出GP区、β″、β′和β相[2]。最近研究[3-5]发现,在有过剩Si的Al-Mg-Si合金的时效过程中,存在新的析出相U1和U2相,合金微结构的演化顺序按以下方式进行[5]:SSSS→(Mg, Si)团簇→GPZ→β″→(β′+B′+U1+U2)→β(Mg2Si)。U1和U2相一般是在有过剩Si的Al-Mg-Si 合金中,在时效温度为200~300 ℃时才析出[4]。该合金在微结构演化过程中产生的析出相U1和U2对合金性能有不同影响[5-8]。目前,对U1和U2开展的研究还不多,主要是在实验上对该相晶体结构的测定和相稳定性的研究。在理论上,尽管有研究者采用第一原理计算其价电子结构[9-10],但有关其内部原子成键的计算,目前还没有相关报道。因此,研究和掌握这些析出相的内部原子键特征,对优化合金材料的性能有非常重要的意义。
基于价键理论[11]和能带理论建立的固体与分子经验电子理论(EET)[12]以及改进的界面TFD理论[13], 在处理复杂体系合金的电子结构方面提供一个简捷实用的经验方法,使得对该合金宏观性能的研究可以深入到原子成键的电子结构层次。本文作者将EET与改进的TFD方法用于对Al-Mg-Si合金析出相U1与U2内部原子间的价电子成键及其与基体界面间形成的界面键络特征进行计算,从原子成键方面分析这两种亚稳相的原子键络特点及其对合金性能的影响。
1 模型
1.1 亚稳相U1的晶胞结构
U1相[4]属三角晶系(属于Al2CaSi2,即La2O3型[14]),呈棒状,长为50~500 nm,宽为50 nm;分子式为Al2MgSi2,单位晶胞内有1个Mg原子,2个Al原子,2个Si原子;晶格常数:a=b=0.405 1 nm,c=0.674 1 nm;w(Mg)/w(Si)=0.66;空间群为 m1(No.164)。U1相的晶胞结构如图1所示,其与基体Al的取向关系为[7-8]:(001)A1//(110)U1,[310]A1//[001]U1,
m1(No.164)。U1相的晶胞结构如图1所示,其与基体Al的取向关系为[7-8]:(001)A1//(110)U1,[310]A1//[001]U1,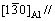
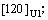 (001)A1//(110)U1,[100]A1// [0001]U1,
(001)A1//(110)U1,[100]A1// [0001]U1,
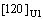 。
。
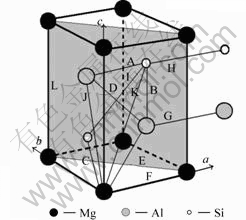
图1 U1晶胞结构
Fig.1 Microstructure of U1 cell
1.2 亚稳相U2的晶胞结构
亚稳相U2结构[5]中有12个原子,可以看作是由分子MgAlSi中各自排列4个原子而得到的(即其单位晶胞包含4个MgAlSi单元)。析出相U2可以由β"相中用Al原子来替代Mg原子和Si原子进行重新排列而生成。析出相 U1和U2与析出相β′′和β′都呈针状,在合金时效过程中形成时会沿着基体Al的á100?方向进行排列,属于正交晶系。U2单位晶胞与MgAlSi(Co2Si)单位晶胞[4, 14]相似,空间群是Pnma,晶格常数:a=0.675 2 nm,b=0.405 1 nm,c=0.794 nm。U2相的晶胞结构如图2所示,其与基体Al的位向关系[5]为: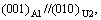
 [130]Al// [001]U2。
[130]Al// [001]U2。
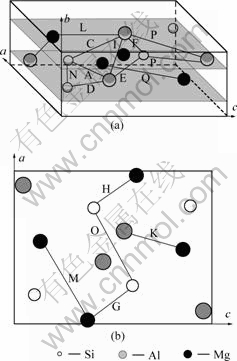
图2 U2晶胞结构
Fig.2 Microstructure of U2 cell: (a) Bond network structure in U2 cell; (b) Bond network structure along [010]
2 方法与结果
2.1 EET理论简介
固体中原子的价电子结构在本文是指该固体中原子所处的状态以及原子形成共价键的键络分布。按照EET[12-13]理论,原子的共价电子是分布在连接最近邻、次近邻以及s近邻原子的键上的。各键上共价电子对数(即键级na)由下列原子键距公式表示:
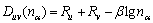 (1)
(1)
式中:Duv是共价键距;Ru和Rv是单键半距;β为参量,β的数值由文献[11-12]中的公式确定;u和v分别表示u原子和v原子;nα表示u和v原子形成的键。晶胞内的共价电子数满足下述方程关系:
 (2)
(2)
式中:k1、k2分别为晶胞中 u、v原子的个数; 、
、 分别为u、v原子的共价电子数;Iα为nα键级的等同键数,各等同键数的选取可依照文献[15]给出的方法来确定。
分别为u、v原子的共价电子数;Iα为nα键级的等同键数,各等同键数的选取可依照文献[15]给出的方法来确定。
由于各晶胞的结构已确定,实验晶格常数由文 献[4-5]给出,因此,运用键距差(BLD)方法[12]建立最强键nA方程,并参见文献[15-18]的求解步骤,联立式(1)和(2),逐个计算各晶胞中原子成键的价电子结构, 并依据BLD判据确定原子的杂阶状态ε。计算得到的各晶胞的共价键结果如表1~4所示,表中nc为共价电子数,ρα为单位键长的电子密度,EA为键结合能,?ρ为面电荷密度差, 为平均面电荷密度,S为界面参考单元的面积,σ为保持连续条件的原子状态数目,σ′为保持不连续条件的原子状态数目。
为平均面电荷密度,S为界面参考单元的面积,σ为保持连续条件的原子状态数目,σ′为保持不连续条件的原子状态数目。
表1 亚稳析出相U1的原子成键
Table 1 Atomic bonding of metastable phase U1
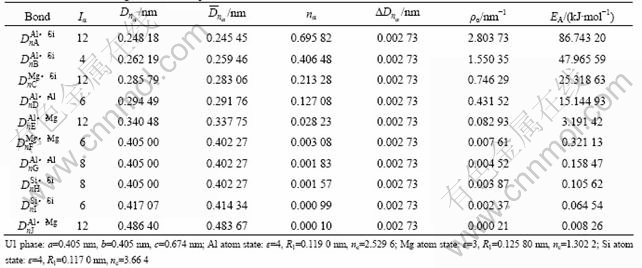
表2 析出相U2的原子成键
Table 2 Atomic bonding of metastable phase U2
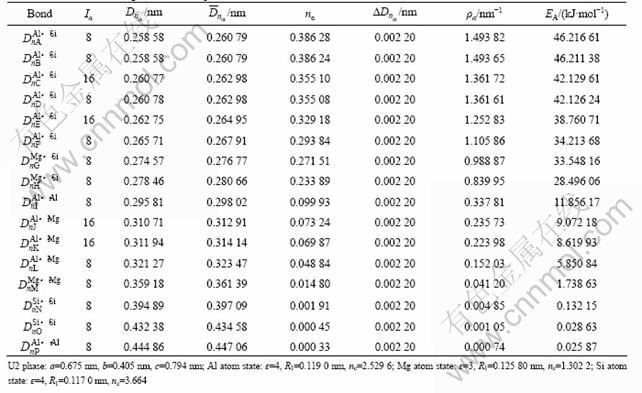
表3 (001)Al // (110)U1相界面的原子成键
Table 3 Atomic bonding of (001)Al // (110)U1 interphase boundary

2.2 改进的TFD理论简介
文献[13]定义了异相界面电子结构,指出异相界面电子结构除包括相界面两侧平面上的键络电子分布外,还包括相界面两侧平面上的平均共价电子密度ρ(hkl)、ρ(uvw)、电子密度的相对差值?ρ和使界面电子密度在一级近似下保持连续的原子状态组数σ(在一级近似下,以?ρ<10%来判断界面电子密度的连续性。当?ρ<10%时,把电子密度定义为连续或连续性较好;当?ρ>10%时,把界面电子密度定义为偏离连续或连续性较差)。相界面处电子密度ρ愈高,界面的原子键络就越密,界面结合得就越牢固;相界面处的电子密度差愈小,界面上的电子密度连续性就愈好,界面原子键络匹配得就越好,界面畸变能就越低,界面畸变应力也愈小;反之,界面畸变应力愈大,界面畸变能就越高,界面就越不稳定。当畸变应力大到一定值时,电子密度的连续性遭到破坏,将伴随新相的生成或在宏观上出现断裂。电子密度连续性的好坏实质上是点阵原子键络畸变而导致的结果,直接影响到材料的性能。
异相界面两侧平面(hkl)和(uvw)上的平均共价电子密度ρ(hkl)和ρ(uvw),界面处电子密度的相对差值?ρ,可分别依据改进的TFD理论[13]给出如下公式:
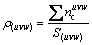 ,
,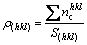 (3)
(3)
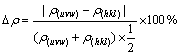 (4)
(4)
式中: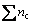 =nAIA+nBIB+nCIC+…,为面参考单元上的共价电子总数;S(uvw)和S(hkl)分别为(uvw)和(hkl)面参考单元的面积。
=nAIA+nBIB+nCIC+…,为面参考单元上的共价电子总数;S(uvw)和S(hkl)分别为(uvw)和(hkl)面参考单元的面积。
2.3 计算结果
2.3.1 U1和U2相的内部原子键强
在计算U1和U2相的键距差时,出现满足判据|?Duv(na)|≤0.005 nm的结果有多个解。按照BLD方法中对多解的处理方法[12, 16]:对于导体金属,要排除完全不含晶格电子的杂阶组合(εAl=6, εMg=4, εSi=6);按照文献[16]的分析,一般情况下,金属固溶体和金属间化合物中Al原子大多处在第3、4或5杂阶,且在第4、5杂阶可能性最大;而Mg是典型金属,处在无自由电子的第4杂阶的可能性很小,由于Mg的机械性能决定了Mg具有一定的结合强度和结合能,而 Mg原子处在第1、2杂阶时共价电子太少,不符合机械性能的要求。因此,最符合Mg的金属性能与机械性能要求的原子状态应处在第3杂阶。由于Si晶体的塑性很小,共价键结合很强,这一特性也决定Si原子通常处在价电子都为共价电子的第6杂阶。尽管合金中原子间的相互作用对原子杂阶的迁移有一定影响,使得合金中原子并不一定就处在最可能的杂阶,但经验也说明在通常原子间相互作用情况下,杂阶的迁移一般在最可能的杂阶附近变化,即Mg原子状态有时也会出现在第2、4杂阶。同样,Si原子状态有时也会出现在第4和5杂阶。
表4 (001)Al// (010)U2相界面的原子成键
Table 4 Atomic bonding of (001)Al// (010)U2 interphase boundary
原子杂阶状态的确定除了根据以上规则外,有时还需考虑晶体的结合能,可以利用文献[19]给出的计算结合能公式得到理论值,再根据结合能计算值与实验处理值[14]相符合的程度来判断结果是否合理。按照文献[19]的计算公式,结合已计算得到的原子键强结果。本研究计算得到U1和U2的结合能与实验值都吻合得很好,差异小于10%(U1相的结合能: 理论值EU1=-2.0327×103 kJ/mol,间接实验值[9, 20]E′U1= -1.7151×103 kJ/mol;U2相的结合能:理论值EU2= -4.073×103 kJ/mol,间接实验值[9, 20]E′U2=-3.6967×103 kJ/mol),而用第一原理计算得到的结合能[9]与实验值通常相差达15%。
2.3.2 U1和U2相的界面原子键强
根据文献[13]提出的界面电子结构理论,计算相界面价电子结构就是在相空间价电子结构基础上,考虑到既要满足相空间中的键距差判据|?Duv(na)|≤0.005 nm,同时又要满足计算的相与基体相间的相界面电子密度差?ρ最小的条件。依照此原则,计算了(001)Al// (110)U1和(001)Al// (010)U2相界面的电子结构,得到的结果如表3和4所列。
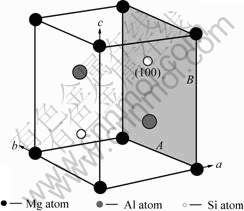
图3 U1晶胞(100)面的键结构
Fig.3 Bonding structure of plane (100) in U1 cell
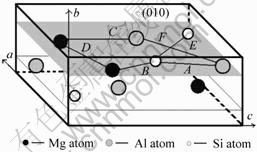
图4 U2晶胞(010)面的键结构
Fig.4 Bonding structure of plane (100) in U2 cell
3 讨论
3.1 U1和U2相的结构因子与合金性能
EET界面理论[13]中定义的相结构因子包括如下几个物理参量:σN 、nA 、ρA 、EA。其中:σN为相结构中可能存在的原子状态组数,σN愈大,相结构愈稳定。相结构因子nA为处于稳定状态(即是σN组可能的原子组态中最为可能的原子组态下最强键上的nA值)时最强共价键上的共用电子对数,用其代表相中诸原子所构成的共价键的强弱。nA值愈大,共价键愈强;反之,愈弱。显然,nA值的大小在一定程度上表征着相的瓦解或重构的难易程度,即nA愈大,析出相的键络拆散或重构愈困难。相结构因子ρA为最强共价键上的单位键长的电子密度(即ρA=nA/DA),其意义与因子nA相似。相结构因子EA为键结合能,其计算如下:
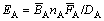 (5)
(5)
式中: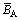 为A键上的异类原子的折合电荷屏蔽常数,数值上等于组成该结构的原子的电子对核电荷的屏蔽作用系数bu和bv的计权平均值;
为A键上的异类原子的折合电荷屏蔽常数,数值上等于组成该结构的原子的电子对核电荷的屏蔽作用系数bu和bv的计权平均值;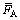 为结构单元的异类原子间的折合成键能力,数值上等于结构单元中各原子成键能力的计权平均值;nα/DnA为该结构中的最强共价键上的键电子密度,其值与
为结构单元的异类原子间的折合成键能力,数值上等于结构单元中各原子成键能力的计权平均值;nα/DnA为该结构中的最强共价键上的键电子密度,其值与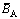 、
、 可依照文献[12]给出的参数求得。
可依照文献[12]给出的参数求得。
由表1~4子结构结果可以看出,析出相U1和U2中Al原子和Mg原子状态分别取与纯Al和Mg金属的原子处于同样的状态[16],即Al原子处于第4杂阶,Mg原子处于第3杂阶。而Si原子则取处于较低的第4杂阶(纯Si晶胞中处于第6杂阶,无晶格电子),其共价电子由纯Si晶胞的4减少到3.664,而晶格电子由0增加到0.336。
由表1~4还可见,析出相U1和U2的最强键为Al—Si键、次强键为Al—Si键,其上的共价电子数nA、nB、键密度ρA、ρB以及键能EA和EB都比基体金属Al的最强键的键强(如nA(Al)=0.208 57,ρα=0.728 39 nm-1,EA=25.563 9 kJ/mol)要大2~3倍。其中:U2相中计算得到主要的Al—Si键的键强比基体金属Al的最强键的键强都强。由此可见,析出相U1与U2由于具有较强的原子键络,其析出有可能增强合金的整体键强。
表1和2所列为EET定义的结构因子的计算结果。对于U1相,nA=0.695 82,ρA=2.803 73 nm-1,EA= 86.743 20 kJ/mol;对于U2相,nA=0.386 28,ρA=1.493 82 nm-1,EA=46.216 61 kJ/mol。显然,U1相的最强键的键强是U2相的近两倍,且由于U1和U2相的EA(U1)= 86.743 2 kJ/mol,EA(U2)=46.216 6 kJ/mol(EA(U1)>EA(U2)),说明Al和Si结合优先形成U1相,这与文献[9]中所述相符。计算结果还表明,无论是U1相还是U2相,最强键和次强键都是Al—Si键,其次为Mg—Si键,而且,Al—Si键比其它的Mg—Si、Al—Mg、Al—Al、Mg—Mg、Si—Si键都强很多,说明U1和U2相内形成了以Al—Si键为主的键络骨架结构,如图5所示。结合能计算结果表明:EU1=-2.032 7×103 kJ/mol,EU2=-4.073×103 kJ/mol,表明U2相比U1相的热稳定性更好。
3.2 U1和U2相的界面结合因子与合金性能
依据EET界面理论[13],界面结合因子的物理意义为?ρ,为相界面处的电子密度差;σ为使界面电子密度保持连续的原子状态总组数;σ′为偏离连续(即?ρ>10%)条件的可能原子状态组数;并且认为界面上的电子密度(ρ)愈大,界面结合愈强。当相界面处的电子密度差?ρ<10%时,?ρ愈小,界面上的电子密度连续性愈好,界面畸变应力愈小,使电子密度保持连续的可能原子状态组数σ愈多,界面结合越紧密越稳定;反之,界面畸变应力愈大,界面畸变能越高,界面就愈不稳定。当畸变应力达到一定值时,电子密度连续性遭到破坏,此时将伴随新相的生成或在宏观上出现断裂。

图5 U1和U2析出相的键络
Fig.5 Bonding networks of U1 (a) and U2 (b) phases
由表3和4可见,(001)Al//(110)U1相界面处平均面电子密度ρU1=11.906 9 nm-2,比(001)Al//(010)U2相界面处的平均面电子密度ρU2=8.385 5 nm-2要大,说明界面(001)Al//(110)U1结合较强;U1界面处的电子密度差?ρmin=0.082 4%(<10%),故U1相界面电荷保持连续且连续性较好,这说明U1相与基体界面畸变应力较小,界面原子键匹配得较好,界面较稳定,界面应变能较低,有利于基体的晶粒长大。但界面(001)Al// (010)U2处的面电荷密度?ρmin=47.856%(>10%),偏离连续条件,因此,在此界面处应力较大,界面原子键匹配得较差,界面储能(应变能)较高,此时界面容易成为新相形核析出、长大和裂纹萌生的地方。
4 结论
1) 在相空间价电子结构中,析出相U1和U2中的组成原子Al和Mg都处在与纯元素晶体中的原子相同的杂阶,即Al都处于第4杂阶,Mg都处于第3杂阶,而Si原子状态发生改变,迁移到第4杂阶状态。
2) 析出相U1和U2的最强键都为Al—Si键,次强键为Al—Si键,都比基体Al晶胞中的最强键要强2~3倍,说明U1与U2相的析出可增强合金的整体键强。析出相U1的最强共价键比析出相U2的最强共价键要强近2倍,其次强键也比U2相的最强键强。由于U1相的Al原子与Si原子具有更强的结合能力,因此,U1相比U2相更易先析出。
3) (001)Al// (110)U1相界面处电荷保持连续且连续性较好,界面应变能较低,界面较稳定。界面(001)Al// (010)U2处的面电荷密度偏离连续条件,因此,在此界面处应力较大,界面原子键匹配得较差,界面储能较高,容易成为新相形核、长大和裂纹萌生的地方。
REFERENCES
[1] HIROSAWA S, SATO T. Nano-scale clusters formed in the early state of phase decomposition[J]. Mater Sci Forum, 2005, 475/479: 357-360.
[2] FUKUI K, TAKEDA M. The metastable phase responsible for peak hardness and its morphology in an Al-Mg-Si alloy[J]. Mater Sci Forum, 2005, 475/479: 361-364.
[3] VISSERS R, van HUIS M A, ZANDBERGEN H W, MARIOARA C D. The crystal structure of the β'phase in Al-Mg-Si alloys[J]. Acta Mater, 2007, 55: 3815-3823.
[4] ANDERS G F, RAGNVALD H. Bonding in MgSi and Al-Mg-Si compounds relevant to Al-Mg-Si alloys[J]. Phys Rev B, 2003, 67: 224106.
[5] ANDERSEN S J, MARIOARA C D, FR?SETH A, VISSERS R, ZANDBERGEN H W. Crystal structure of the orthorhombic U2 precipitate in the Al-Mg-Si alloy system and its relation to the β'and β" phases[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2005, 390: 127-138.
[6] TSAO C S, CHEN C Y. Precipitation kinetics and transformation of metastable phases in Al-Mg-Si alloys[J]. Acta Mater, 2006, 54: 4621-4631.
[7] ANDERSEN S J, MARIOARA C D, VISSERS R, FROSETH A, ZANDBERGEN H W. The structural relation between precipitates in Al-Mg-Si alloys[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2007, 444: 157-169.
[8] MATSUDA K, SAKAGUCHI Y, MIYATA Y. Precipitation sequence of various kinds of metastable phases in Al-Mg-Si alloy[J]. J Mater Sci, 2000, 35: 179-189.
[9] RAVI C, WOLVERTON C. First-principles study of crystal structure and stability of Al-Mg-Si-(Cu) precipitates[J]. Acta Mater, 2004, 52: 4213-4227.
[10] VAN M A, CHEN J H. Phase stability and structural relations of nanometer-sized, matrix-embedded precipitate phases in Al-Mg-Si alloys in the late stages of evolution[J]. Acta Mater, 2006, 54: 2945-2955.
[11] 鲍林L. 化学键本质[M]. 卢嘉锡, 等译. 上海: 上海科学技术出版社, 1996: 393.
PAULING L. The nature of chemical bonds[M]. LU Jia-xi, et al, transl. Shanghai: Shanghai Science and Technology Press, 1996: 393.
[12] 张瑞林. 固体与分子经验电子理论[M]. 长春: 吉林科学技术出版社,1993.
ZHANG Rui-lin. Empirical electron theory in solids and molecules[M]. Changchun: Jilin Science and Technology Press, 1993.
[13] 刘志林, 李志林, 刘伟东. 界面电子结构与界面性能[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2002: 23.
LIU Zhi-lin, LI Zhi-lin, LIU Wei-dong. Electron structure and properties of interface[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2002: 23.
[14] GREGORY A L, ROALD H. The TiNiSi family of compounds: Structure and bonding[J]. Inorg Chem, 1998, 37: 5754-5763.
[15] GAO Ying-jun, HUANG Chuang-gao, HOU Xian-hua. Atomic bonding and property of Al-Mg-Sc alloy[J]. Materials Transaction, 2005, 46: 1148-1153.
[16] 余瑞璜. 铝-镁二元金相图α, δ相以及γ-Al12Mg17相的价电子结构分析[J]. 吉林大学学报, 1979, 4(4): 54-66.
YU Rui-huang. Analysis of valence electron structure about α, δ phase and γ-Al12Mg17 phase in Al-Mg binary phase diagram[J]. Journal of Jilin University, 1979, 4(4): 54-66.
[17] GAO Ying-jun, HOU Xian-hua, MO Qi-feng. Atomic bonding of precipitate and phase transformation of Al-Cu-Mg alloy[J]. J Alloy & Compounds, 2007, 441: 241-245.
[18] GAO Ying-jun, MO Qi-feng, CHEN Hua-ning. Atomic bonding and mechanical properties of Al-Li-Zr alloy [J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2009, 499: 299-303.
[19] 徐万东, 张瑞林, 余瑞璜. 过渡金属化合物晶体结合能计算[J]. 中国科学 A, 1988, 18(3): 323-327.
XU Wan-dong, ZHANG Rui-lin, YU Rui-huang. Calculation of crystal binding energy in transition metal compounds[J]. Science in China (Series A), 1988, 18(3): 323-327.
[20] 饭田修一, 等. 物理学常用数表[M]. 张质贤, 等译. 北京: 科学出版社, 1979: 85.
Shuichi Iida , et al. Mathematical tables of physics[M]. ZHANG Zhi-xian, et al, transl. Beijing: Science Press, 1979: 85.
(编辑 杨 华)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(50661001, 50061001); 广西省自然科学基金资助项目(0991026, 0832029, 0639004)
收稿日期:2009-10-09;修订日期:2010-01-22
通信作者:高英俊,教授; 电话: 0771-3232666; E-mail: gaoyj@gxu.edu.cn