Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 27(2017) 227-233
Comparison of dendrite and dispersive structure in rapidly solidified Cu-Co immiscible alloy with different heat flow modes
Sheng LI1, Feng LIU1, Wei YANG2
1. State Key Laboratory of Solidification Processing, Northwestern Polytechnical University, Xi’an 710072, China;
2. School of Aeronautic Manufacturing Engineering, Nanchang Hangkong University, Nanchang 330063, China
Received 13 January 2016; accepted 7 July 2016
Abstract: Rapid solidification of Cu-Co immiscible alloy was investigated by glass-fluxing, spray casting and melt-spinning techniques. Both the transition from dendrite to dispersive structure and corresponding scale evolution were revealed and further elucidated in terms of the heat flow mode, nucleation and growth processes under different solidification conditions. With the increase of undercooling, columnar dendrite is replaced by dispersive structure due to the immiscible effect. In contrast, equiaxed dendrite forms in spray cast alloy due to multiple nucleation events and becomes thinner for the case of higher cooling rate. Ascribed to the enhanced non-equilibrium effect and insufficient period for collision and coagulation processes between separated droplets, fine globular dispersion appears upon the diameter of spray casting reaching 4 mm. As for the melt-spun ribbon with the highest cooling rate, a single-phase solid solution microstructure with refined grain of cellular morphology can be obtained, which is attributed to the suppression of liquid phase separation by instant solidification.
Key words: rapid solidification; immiscible alloy; microstructure; nucleation; growth
1 Introduction
Rapid solidification belongs to a field of condensed-matter physics and has aroused extensive research in material science [1]. With the significant increase of undercooling or cooling rate phase transformation takes place far from the equilibrium condition [2-4]. Then, it is possible to explore new nucleation and grain growth mechanisms, which in turn influences the type and morphology of as-obtained phases [5-7].
Cu-Co alloy has a metastable liquid miscibility gap due to the large mixing enthalpy [8]. Because of the unique thermodynamic feature of this system, continuous attempts have been made by adopting rapid solidification technique to synthesize high performance materials [9-12]. ELDER et al [9] investigated the miscibility gap of Cu–Co alloy and further constructed the phase diagram for both stable and metastable equilibrium. PALUMBO et al [10] optimized this binary system and further extended it to ternary Cu-Co-Fe system. The dependence of the radius of Co-rich droplet on undercooling and its solidification behavior were revealed by CAO et al [11] and KOLBER and GAO [12]. Recently, ZHANG et al [13] have discussed the nucleation transition in the undercooled Cu70Co30 alloy. In this direction, core-shell composite or dispersive material with fine globule can be fabricated successfully, whereas the abovementioned structures are not obtainable by conventional processing routes [14,15].
In terms of the heat flow mode during the phase transformation process, rapid solidification can be achieved by high undercooling or melt quenching technique [16,17]. For the first case, the released latent heat is absorbed by the undercooled melt itself [18], while in the second case, it is withdrawn by the attached substrate [19]. So far, it is generally agreed that the heat flow condition prior to and during solidification has the most pronounced influence on interface migration as well as the resulting microstructure [20,21]. However, a systematic comparison for the microstructure transition for immiscible alloy, especially the scale variation under different solidification condition is not fully understood. Moreover, the occurrence of nucleation and subsequent growth arising from the actual non-equilibrium effect is still ambiguous. So, it is necessary to do more work on these aspects.
In this work, we report the preparation of rapidly solidified Cu-Co alloy by high undercooling and melt quenching techniques separately. The former is achieved by glass fluxing method and the latter is performed by spray casting and melt-spinning. Then, the transition from dendrite to dispersive structure, as well as the morphology and scale evolution for corresponding solidification mode is compared and further elucidated from the specific nucleation and growth processes.
2 Experimental
The nominal composition for the studied alloy is chosen as Cu70Co30 in terms of its excellent liquid separation ability [22]. High purity Cu (99.98%, mass fraction) block and Co (99.8%, mass fraction) powder with a mass of 5-10 g were mixed in a quartz crucible, which was placed at the middle position of high frequency induction coil located in a vacuum chamber. In glass fluxing experiment, the boron oxide purifier (A.P.) was employed to protect the melt from oxidation and remove the inclusions from the sample, which had been dehydrated in an alumina crucible at 1073 K for 6 h in advance. After heating the sample to desired temperature for 5 min, the electric power was switched off and the thermal behavior was recorded by an infrared temperature measuring meter. As for quenching experiment, the apparatus was firstly vacuumed to 5 Pa and then backfilled with high-purity argon to protect the melts from oxidation. The spray casting was achieved by injecting the melt into a multi-step copper mould with the inner diameter of 4, 6, 8 and 10 mm separately, while the melt-spun ribbon was fabricated by injecting the melt onto the surface of copper roller with a diameter of 200 mm. The rotation speed of the roller was chosen to be 30 m/s and the ejection pressure was 100 kPa.
The fabricated samples were mounted, polished and etched according to standard metallographic procedures. Microstructure analysis was performed by an optical microscope (VHX-600, KEYENCE) and scanning electron microscope (SEM, Quantan 200) equipped with energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS, INCA 6650). The higher magnification for melt-spun ribbon was characterized by field-emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM, Nova Nano SEM450) with energy dispersive spectroscopy (INCA 250X-MAX50).
3 Results
3.1 Transition from dendrite to dispersive structure for undercooled alloys
Figure 1 shows the representative micrographs for Cu70Co30 alloy with the undercooling of 31 K. Well-developed dendrites with the trunk length larger than 400 μm can be observed, accompanied by the preferred-growth morphology and partly fragmented segments (Fig. 1(a)). According to the EDS results given in Fig. 1(b), the primary dendrite can be determined as α-Co phase with the Co content of 83.17% (molar fraction). It should be noted that this value is very close to that deduced from the phase diagram [23], indicating the weak non-equilibrium effect herein. As expected, the matrix phase is finally solidified Cu phase with the Co content of 13.41% (molar fraction).
With the further increase of undercooling, liquid separation takes place because of the enhanced non-equilibrium effect. Figure 2 presents the micrographs taken from the sample with ΔT=132 K, which is much different from the previous one. As can be seen clearly, the Co-rich phase forms with the spherical morphology and its size distribution is rather uneven (Fig. 2(a)). From the enlarged SEM image (Fig. 2(b)), the largest radius for Co-rich droplet can reach 500 μm. According to the EDS measurement, the Co content in the Co-rich droplet is 87.35% (molar fraction), which is slightly larger than that in the preceding dendrite morphology. Inspection of Fig. 1(a) and Fig. 2(a) reveals that the volume fraction of Co-rich phase has increased significantly after liquid separation. As a result, the Co content in the finally solidified Cu matrix is merely 2.9% (molar fraction), revealing a significant reduction in comparison with that of smaller undercooling.
3.2 Transition from dendrite to dispersive structure for spray casted alloys
The microstructure examination of spray cast Cu70Co30 alloy is revealed in Fig. 3, where the diameters for corresponding sample are 10 mm, 8 mm and 6 mm, respectively. Obviously, the primary α-Co appears with flower-like dendrite and distributes randomly in the matrix. It should be noted that the equiaxed dendrite observed herein is different from the radial-like morphology formed in undercooling condition (Fig. 1). Moreover, the length of dendrite truck is about 100 μm, which is much less than the previous case. In addition, the secondary dendrite arm becomes thinner gradually with the reduction of sample diameters.
With the further decrease of the sample diameter to 4 mm, the cooling rate is increased and the non-equilibrium effect is strengthened. Figure 4 shows the corresponding structural morphology of the spray cast alloy. Besides the as-mentioned refinement trend of primary α-Co phase (Fig. 4(a)), local liquid separation occurs obviously, as revealed by the existence of Co-rich sphere dispersed in the Cu matrix (Fig. 4(b)). However, the largest size of these Co-rich spheres is merely 8 μm, which is much less than that formed in the undercooling condition.
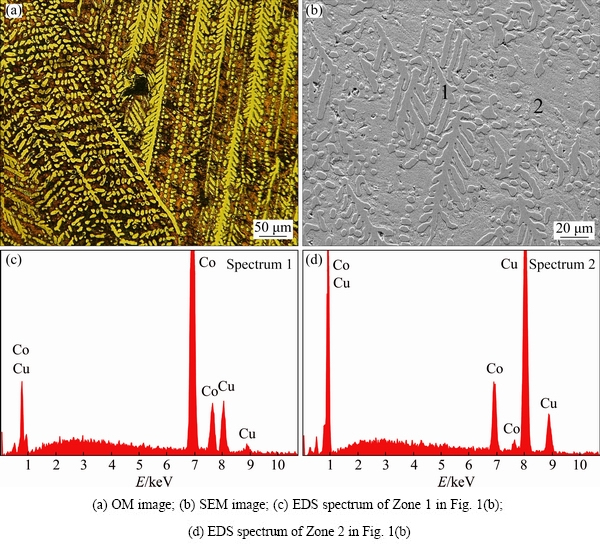
Fig. 1 Microstructures of Cu70Co30 alloy with ΔT=31 K
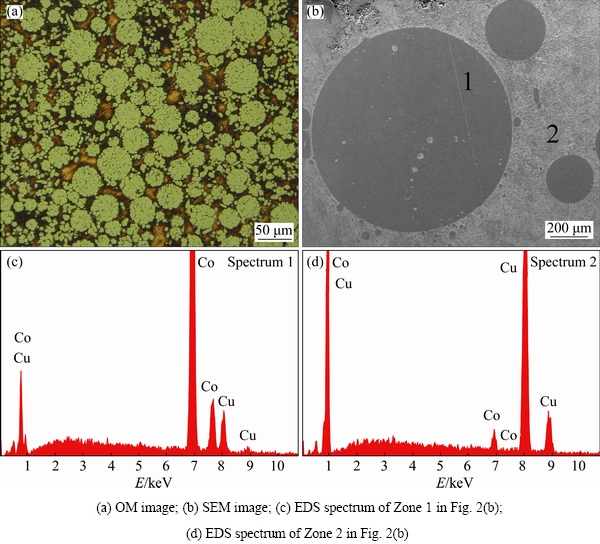
Fig. 2 Microstructures of Cu70Co30 alloy with ΔT=132 K
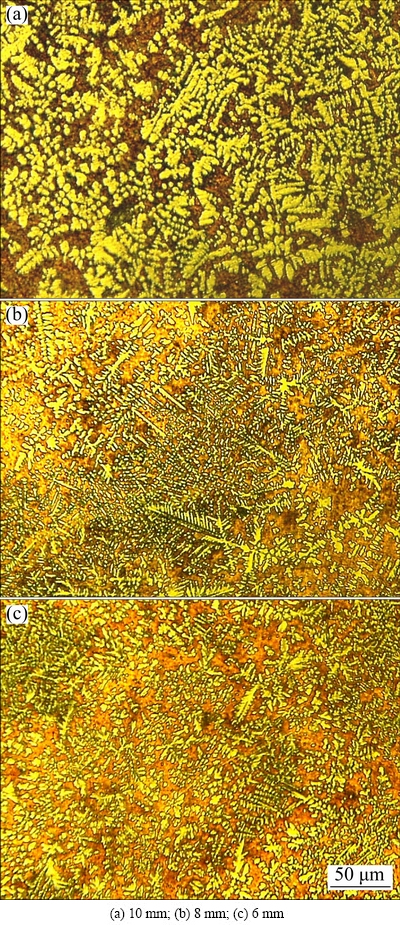
Fig. 3 Optical microstructures of spray cast Cu70Co30 alloys with different diameters
3.3 Formation of single phase solid solution structure for melt-spun alloy
The optical micrograph of the melt-spun ribbon for Cu70Co30 alloy is displayed in Fig. 5. It can be seen that the thickness of ribbon is about 50 μm and a homogenous microstructure forms herein. As reported in Ref. [10], solid solution is the existing phase in binary Cu-Co alloy without any intermetallics because of positive mixing enthalpy. In contrast to the previous dendrite or dispersive structure, a single phase microstructure is observed in the melt-spun alloy, as indicated by the SEM image shown in Fig. 6(a). Moreover, fine cellular grains without any branch of dendrite morphology are detected in the higher magnification (Fig. 6(b)). According to the EDS measurement, the Co content of the fabricated solid solution is 26.51% (molar fraction), which is very close to the initial alloy composition, indicating serious solute trapping effect to form free micro-segregation microstructure.
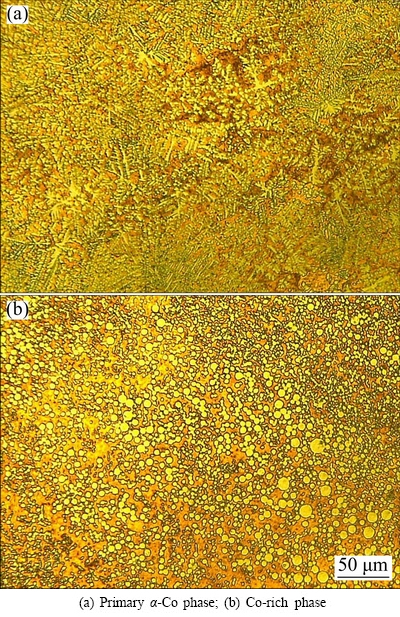

Fig. 4 Optical microstructures of spray cast Cu70Co30 alloy with diameter of 4 mm
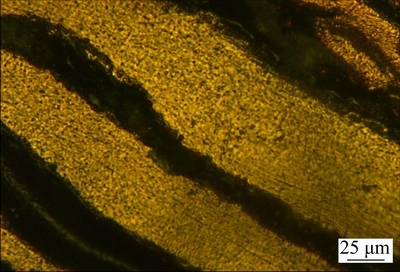
Fig. 5 Optical microstructure of melt-spun Cu70Co30 alloy
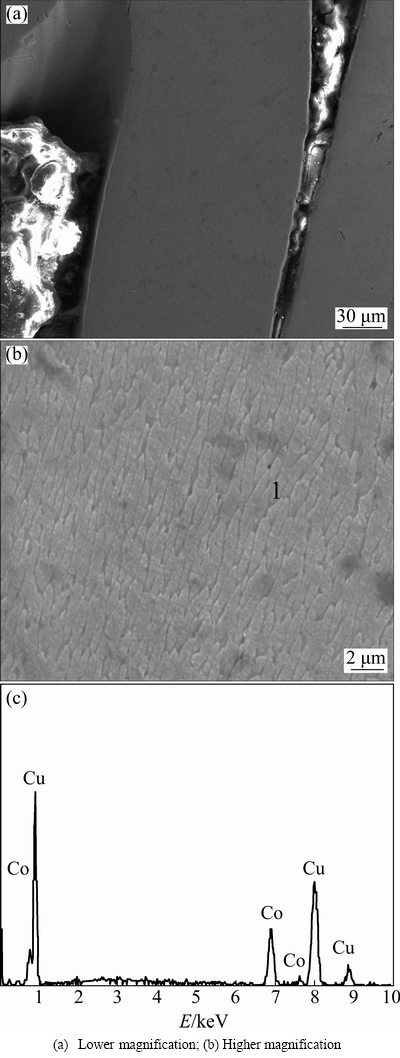
Fig. 6 SEM images (a, b) and EDS spectrum of spot 1 in Fig. 6(b) (c) for melt-spun Cu70Co30 alloy
4 Discussion
A systematic comparison of above rapidly solidified microstructures reveals distinctive features which depend on the processing conditions. Understanding the origin of these features is vital for the control of microstructures. As for smaller undercooling of 31 K, solidification begins with the formation of one nucleation event and then, rapid growth of primary phase is expected due to larger thermal undercooling in front of the liquid-solid interface. Consequently, the radial-like dendrite forms because of the oriented growth direction (Fig. 1). In contrast, multiple nucleation events are promoted simultaneously in as-quenched condition and immediate extraction of heat from the melt restricts the subsequent growth of primary phase. It was previously reported that the cooling rate of spray casting is inversely proportional to its diameter and the magnitude is on the order of about 102 K/s [24]. Consequently, the whole solidification period is shortened, thus leading to the refinement of dendrite gradually (Fig. 3).
Moreover, rapid cooling is also effective for the generation of large undercooling. Figure 7 presents the calculated Gibbs free energy curves for the liquid Cu-Co alloy with ΔT=31 K and 132 K separately, where the optimized thermodynamic parameters are adopted from Ref. [10]. Owing to the immiscible effect arising from positive mixing enthalpy, a saddle-shaped curve forms for larger undercooling. In such a case, liquid separation is expected according to the thermodynamic interpretation.
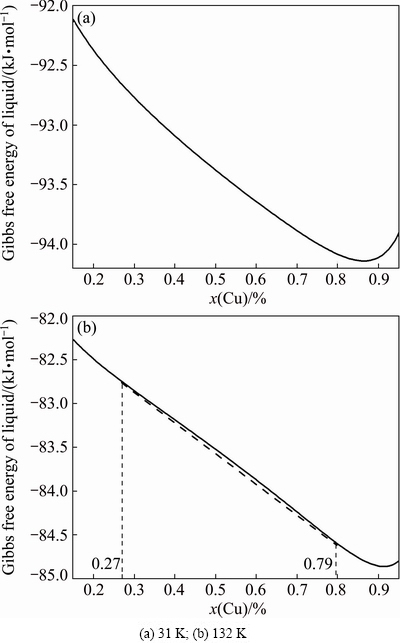
Fig. 7 Gibbs free energy curves for Cu-Co alloy with different undercoolings
As is well known, small droplets nucleate firstly due to immiscible effect and grow continuously by diffusion. During the moving process, each droplet is in collision with another and becomes larger in size. Consequently, the finally formed microstructure depends upon the competition between the relative kinetics of liquid phase separation and the actual solidification time. In undercooling experiment, the moving time before solidification is long and thus gives sufficient coalescence process to form larger droplets, as indicated by the present observation in Fig. 2. As for spray cast specimen with diameter of 4 mm, the reduced solidification time weakens this coalescence effect and most second-phase liquid droplets are captured by the as-transformed solid matrix. Consequently, relatively fine and homogeneously dispersed second-phase morphology can be observed (Fig. 4(b)). According to Ref. [25], the melt-spinning experiment is associated with extremely high cooling rate with the order of 106 K/s, indicating a significant undercooling for the fabricated ribbons. In such a case, it would be difficult to achieve necessary transportation and diffusion for liquid separation because of the extremely short time for massive solidification herein. This will suppress the nucleation of liquid droplets and favor the formation of super-saturation solid solution with very fine grain morphologies.
5 Conclusions
1) With the increase of undercooling from 31 to 132 K for Cu70Co30 alloy, preferred-growth columnar dendrite is replaced by the liquid separation structure, which can be interpreted by the presentation of Gibbs free energy curve with a saddle shape.
2) Fine equiaxed dendrite forms in spray casting due to the coupled effects of multiple nucleation events and growth restriction of primary phase by immediate extraction of heat from the melt.
3) As for the spray casting with a diameter of 4 mm, finer globules appear because of local liquid separation, which is caused by the competition between the kinetics of liquid phase separation and the actual solidification process.
4) In the melt-spun ribbon with the highest cooling rate, a single-phase supersaturated microstructure with fine cellular grain forms because of the suppression of liquid phase separation by instant solidification.
References
[1] LIU F, YANG G C. Rapid solidification of highly undercooled bulk liquid superalloy: Recent developments, future directions [J]. International Materials Reviews, 2006, 51: 145-170.
[2] LIU N, YANG G C, YANG W. Microstructure evolution of undercooled Fe-Co-Cu alloys [J]. Physica B, 2011, 406: 957-962.
[3] LUO S B, WANG W L, CHANG J, XIA Z C, WEI B. A comparative study of dendritic growth within undercooled liquid pure Fe and Fe50Cu50 alloy [J]. Acta Materialia, 2014, 49: 355-364.
[4] WANG Li-dong, LI Xue-song, WANG Chao, WANG Li-min, CAO Zhan-yi. Effects of cooling rate on bio-corrosion resistance and mechanical properties of Mg-1Zn-0.5Ca casting alloy [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2016, 26: 704-711.
[5] JANOVSZKY D, TOMOLYA K, SYCHEVA A, PEKKER P, ROOSZ A. Liquid separation in Cu-Zr-Ag ternary alloys [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2014, 586 : 194-198.
[6] TIAN Ze-an, ZHOU Li-li, MO Yun-fei, LIANG Yong-chao, LIU Rang-su. Cooling rate dependence of polymorph selection during rapid solidification of liquid metal zinc [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2015, 25: 4072-4079.
[7] WANG H F, GALENKO P K, ZHANG X, KUANG W W, LIU F, HERLACH D M. Phase-field modeling of an abrupt disappearance of solute drag in rapid solidification [J]. Acta Materialia, 2015, 90: 282-291.
[8] YANG W, XU Z F, LI W J, CAI C C, LI S, LIU F, YANG G C. Comparisons of grain refinement and recalescence behavior during the rapid solidification of undercooled Cu-Co and Cu-Ni alloys [J]. Physica B, 2011, 406: 3710-3714.
[9] ELDER S P, MUNITZ A, ABBASCHIAN G J. Metastable liquid immiscibility in Fe-Cu and Co-Cu alloys [J]. Materials Science Forum, 1989, 50: 137-150.
[10] PALUMBO M, CURIOTTO S, BATTEZZATI L. Thermodynamic analysis of the stable and metastable Co-Cu and Co-Cu-Fe phase diagrams [J]. Computer Coupling of Phase Diagrams and Thermochemistry, 2006, 30: 171-178.
[11] CAO C D, HERLACH D M, KOLBE M. Rapid solidification of Cu84Co16 alloy undercooled into metastable miscibility gap [J]. Scripta Materialia, 2003, 48: 5-9.
[12] KOLBER M, GAO J R. Liquid phase separation of Co-Cu alloys in the metastable miscibility gap [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2005,413: 509-513.
[13] ZHANG Y K, SIMON C, VOLKMANN T, KOLBE M, HERLACH D, WILDE G. Nucleation transitions in undercooled Cu70Co30 immiscible alloy [J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2014, 105: 041908.
[14] LU X Y, CAO C D, KOLBE M, WEI B, HERLACH D M. Microstructure analysis of Co-Cu alloys undercooled prior to solidification [J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2004, 375: 1101-1108.
[15] YANG W, CHEN S H, YU H, LI S, LIU F, YANG G C. Effects of liquid separation on the microstructure formation and hardness behavior of undercooled Cu-Co alloy [J]. Applied Physics A, 2012, 109: 665-672.
[16] ZHOU J K, LI J G. Grain refinement in bulk undercooled Fe81Ga19 magnetostrictive alloy [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2007, 461: 113-116.
[17] YANG Chang-lin, LI Yuan-bing, DANG Bo, LV He-bin, LIU Feng. Effects of cooling rate on solution heat treatment of as-cast A356 alloy [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2015, 25: 3189-3196.
[18] RATHZ T J, ROBINSON M B, LI D. Study of the containerless undercooling of Ti-Ce immiscible alloys [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2001, 36: 1183-1188.
[19] LI J F, ZHOU Y H, YANG G C. Solidification behavior of undercooled Cu70Ni30 alloy [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2000, 277: 161-168.
[20] ROBINSON M B, LI D, RATHZ T J, WILLIAMS G. Undercooling, liquid separation and solidification of Cu-Co alloys [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 1999, 34: 3747-3753.
[21] LU Y P, LIU N, SHI T, LUO D W, XU W P, LI T J. Microstructure and hardness of undercooled Ni78.6Si21.4 eutectic alloy [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2010, 490: L1-L5.
[22] YANG W, ZHANG Y L, HE W, XU Z F. Effects of copper content and liquid separation on the microstructure formation of Co-Cu immiscible alloys [J]. International Journal of Materials Research, 2014, 105: 861-868.
[23] SUBRAMANIAN P R, CHAKRABARTI D J. Phase diagrams of binary copper alloys [M]. Materials Park, OH, USA: ASM International, 1994.
[24] YAMASAKI M, IZUMI S, KAWAMURA Y, HABAZAKI H. Corrosion and passivation behavior of Mg-Zn-Y-Al alloys prepared by cooling rate-controlled solidification [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2011, 257: 8258-8267.
[25] CHRISTIAN J W. The theory of transformation in metals and alloys [M]. Oxford: Pergamon Press, 2002.
不同热流模式下快速凝固Cu-Co不混溶合金枝晶-分相结构的转变
李 圣1,刘 峰1,杨 伟2
1. 西北工业大学 凝固技术国家重点实验室,西安 710072;
2. 南昌航空大学 航空制造工程学院,南昌 330063
摘 要:综合采用熔融玻璃净化、铜模喷铸及单辊旋淬技术,对比研究不同过冷度、不同冷速作用下Cu-Co不混溶合金的快速凝固行为。通过对凝固发生时的热流方式、形核及生长过程的分析,阐述合金非平衡组织由枝晶到分相结构的转变及其相应尺寸的变化规律。随过冷度增加,不混溶效应的增强导致柱状枝晶向分相结构转变。由于铜模喷铸时发生多点形核,凝固组织呈现为等轴枝晶并随冷速增加而不断细化。当喷铸试棒直径为4 mm时,不混溶效应形成的液滴由于长大不充分最终形成细小粒状分相组织。单辊旋淬薄带由于冷速最高,凝固过程瞬间完成,可有效抑制液相分离的发生,有利于胞状单相固溶体组织的形成。
关键词:快速凝固;不混溶合金;显微组织;形核;生长
(Edited by Sai-qian YUAN)
Foundation item: Project (SKLSP201118) supported by the State Key Laboratory of Solidification Processing in Northwestern Polytechnical University, China; Projects (51431008, 51461032) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project (51125002) supported by the China National Natural Science Foundation for Distinguished Young Scholars; Project (GJJ14504) supported by the Education Department of Jiangxi Province, China
Corresponding author: Feng LIU; Tel: +86-29-88460374; E-mail: liufeng@nwpu.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(17)60026-8