文章编号:1004-0609(2008)02-0254-06
Al2O3热压陶瓷激光辅助切削温度场分布与切削深度
鄢 锉,李力钧,金湘中,刘继常,陈 沛
(湖南大学 机械与汽车工程学院 汽车车身先进设计制造国家重点实验室,长沙 410082)
摘 要:建立Al2O3热压陶瓷激光辅助切削准稳态传热模型,采用有限差分方法,利用MATLAB软件,结合材料的受热软化特性,计算得到工件的温度场分布,并由此确定不同激光参数(激光功率、光束移动速度和光斑半径)下的切削深度。模拟计算发现工件表面等温线为卵圆形,横截面呈抛物线型,纵截面呈对称分布形式,而计算确定工件横、纵截面1 000 K等温线所对应的深度值为加工时合适的切削深度;通过对比分析发现:不同参数下温度场计算确定的切削深度值与实验值较吻合,采用较高的激光功率、较低的激光移动速度和工件表面受辐照激光光斑半径有利于切削区域材料的充分软化,从而获得较大的切削深度。
关键词:Al2O3热压陶瓷;激光辅助切削;温度场;切削深度
中图分类号:TG 506.4 文献标识码:A
Temperature field distribution and cutting depth during laser-assisted machining of hot-sintered Al2O3 ceramics
YAN Cuo, LI Li-jun, JIN Xiang-zhong, LIU Ji-chang, CHEN Pei
(College of Mechanical and Automobile Engineering, State Key Laboratory of Advanced Design and
Manufacturing for Vehicle Body, Hunan University, Changsha 410082, China)
Abstract: A quasi-steady heat conduction model for laser-assisted machining hot-sintered Al2O3 ceramics was established. Based on finite difference method(FDM), temperature field distribution of the workpiece was calculated by means of MATLAB. Considering the softened characteristic of material after being heated, cutting depths under different laser parameters (laser power, beam moving speed and spot radius) were obtained. The simulation results indicate that the isotherms are ovoid on the surface, parabolic in cross-section and symmetrical in longitudinal section. The corresponding softened depth to isotherm of 1 000 K is concerned as the proper cutting depth. The calculated cutting depths are in good agreement with the experimental ones under different parameters. The results show that the cutting depth and material removal rate can be increased by increasing the laser power, decreasing the beam spot radius and reducing the moving speed of laser beam.
Key words: hot-sintered Al2O3 ceramics; laser-assisted machining; temperature field; cutting depth
高强度、高硬度、耐高温、耐腐蚀的陶瓷材料在现代制造业中得到广泛应用,然而对于这类材料,采用传统的机械方法加工时,由于切削力大、温升高,刀具磨损严重,难以保证工件的加工精度和表面质量,且加工效率低,成本高。利用激光辅助切削工件,被切削材料局部受热软化,大大改善了硬质脆性陶瓷材料的切削加工性能,因而激光辅助切削是解决这些问题的有效方法之一[1]。
激光辅助切削是一个多因素综合作用的过程,国内外学者对此开展了相关研究。美国帕杜大学ROZZI等[2-6]通过改变激光参数和切削用量工艺参数,借助在线的温度和切削力测量实验,研究了激光辅助切削Si3N4、ZrO2陶瓷材料过程中工件表面温度、切削力和刀具磨损的变化情况。然而,由于激光与材料作用的特殊性,其测量的温度并不准确。国内的学者也做了很多有益的研究,如王慧艺等[7]运用有限元分析的方法,对激光加热辅助铣削45号钢的三维温度场进行了仿真研究;王扬等[8-11]运用位错理论阐述了激光辅助切削的作用机理,并用有限元分析法建立了陶瓷材料加热表面温度场数学模型,对高温合金、冷硬铸铁、Si3N4、ZrO2陶瓷、Al2O3颗粒增强铝基复合材料等难加工材料的激光辅助车削开展了研究;陈沛等[12]采用有限元法对激光辅助切削氮化硅的温度场进行了研究;CHANG等[13-14]利用低于80 W激光辅助加热,并计算了温度场。但以上的研究均假设激光束垂直辐射到工件上,很少考虑入射角度对温度场的影响,因此计算温度值偏高,瞬间即远远超过材料的升华温度,与实际辅助切削情况显然不太吻合。
由于切削深度是激光辅助切削过程中的一个重要的加工参数,其大小的选取取决于热源对材料的热作用程度。为此,本文作者建立了Al2O3热压陶瓷激光辅助切削准稳态传热模型,基于实验测定的非垂直入射角,采用有限差分方法,利用MATLAB软件,结合材料的受热软化特性,计算得到工件的温度场分布,并由此确定不同激光参数下的切削深度值,与实验结果进行了比较。
1 准稳态传热模型的建立
1.1 Al2O3热压陶瓷激光辅助切削原理
激光辅助切削是利用激光器产生的激光束经透镜聚焦后,对被夹持在车床头架的Al2O3热压陶瓷试件表面进行加热,使表层材料被软化,同时利用刀具对其进行切削,其工作原理如图1所示,其中:n为工件转速,f为进给量,β为刀尖中心与光束中心在工件横截面内夹角。
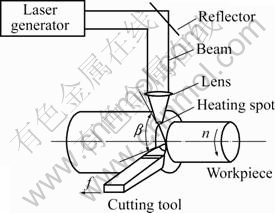
图1 激光辅助切削示意图
Fig.1 Schematic of LAM
1.2 传热模型的基本假设
为建立Al2O3热压陶瓷激光辅助切削的热传导模型,进行如下假设:
1) 被加工材料为各向同性,热物理性质(如比热容、密度、热传导系数以及热扩散系数)均不随温度变化;
2) 表面对流和辐射换热相对于传导很小,忽略不计;不受激光辐射的表面视为绝热边界;
3) 加工过程激光束为基模高斯分布;
4) 加工过程不含内热源;
5) 因进给速度与工件线速度相比很小,忽略不计;
6) 由于切削点至加热点位置短,切削点从加热位置运动到切削位置时间很短,热量传递深度远小于工作截面厚度,工件截面可看成半无限大平面;
7) 为研究问题的方便,建立移动的直角坐标系,选择激光光束的移动方向为x轴正方向,把坐标原点建立在激光光斑的中心处,并随着激光光斑一起移动,模型简化为激光束以一恒定速度U(U=πdn/1 000,d为工件直径)在工件表面进行匀速直线加热,在这样的移动坐标系内,只要激光加热持续了一段时间,激光光斑周围的温度场就处于准稳定状态。
1.3 准稳态传热模型的建立
在直角坐标系中,传热模型的一般形式为[14-15]

根据假设,可将式(1)变换为
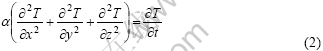
且:

代入式(2),得到准稳定状态下的传热模型为
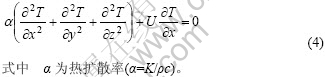
1.4 边界条件与模型求解条件
为求解准稳定状态下的传热模型,对边界条件作如下分析:
1) 工件内各点的初始温度保持为室温,且在距离激光光斑中心无限远处,工件的温度维持室温不变;
2) 激光光束的功率密度分布为

对于本研究,由图1可知,由于考虑光束并非垂直入射工件表面,而以入射角θ照射到工件,光束-刀尖周向距离小。因此,光束被拉长,光束投射到工件表面上可视为椭圆,其半长轴为rb/cos θ,半短轴为rb,如图2所示,所以激光功率密度为
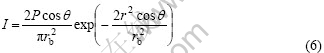
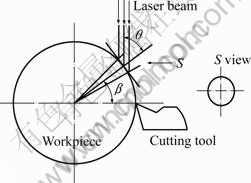
图2 工件表面光斑形状
Fig.2 Laser spot on surface of workpiece
3) 加热热源为激光束,且其输入能量转换为热流密度,为第二类边界条件,即:

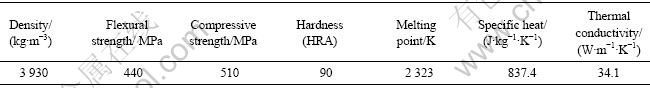
为求解准稳定状态下的传热模型,本研究采用桁架式折叠准封离型CO2激光器PCH-1500,其主要技术参数见表1所列。试件为冷水江某刀具制造公司提供的Al2O3热压陶瓷,其性能参数见表2,其对激光的吸收系数为实验确定70?入射角时的0.95;试件表面聚焦光斑直径为0.5~1.5 mm,激光束移动速度按CQ6232型机床的转速选取。
表1 激光器技术参数
Table 1 Specifications of laser generator

表2 Al2O3热压陶瓷的性能
Table 2 Properties of hot-sintered Al2O3 ceramics
2 工件加热区域温度场分布的计算结果
图3所示为P=250 W,rb=0.5 mm,U=0.23 m/s(n=147 r/min)条件下求得的工件加热区域温度场分布。从图3 (a)可以看出,工件表面的等温线呈卵圆形,位于激光束后方的区域,温度变化比较缓慢,温度梯度小;位于激光束前方的区域,温度梯度大。从图3 (b)可看出,平行于光束移动方向的截面(横截面)内等温线呈抛物线型。随着时间的推移,热量逐渐传递到工件内部,当激光束移动到工件中部时,在其左端(即加热起始处),热量已经传递到工件深处;而在激光束正在作用的区域内,工件内部的热量传递才开始;在靠近激光作用点的区域,温度较高,材料性能受热影响程度较大。从图3 (c)可以看出,垂直于光束移动方向的截面(纵截面)内,温度场对称分布,这是由激光束能量分布的对称性以及工件在空间上的对称性引起的。在靠近工件表面的区域,等温线比较密集,温度梯度大;而在较远的区域,等温线稀疏,温度梯度小;在靠近激光作用点的区域,温度较高,材料性能受热影响较大。
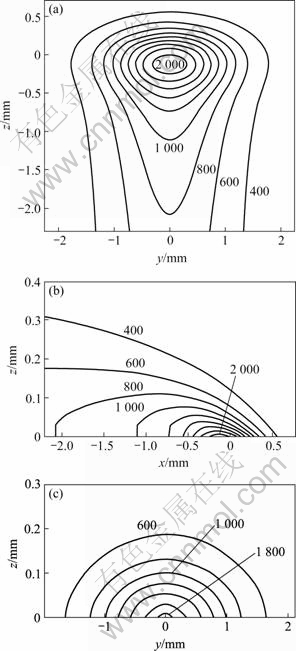
图3 工件加热区域的温度场分布
Fig.3 Calculated temperature field distribution of workpiece (K): (a) On surface; (b) In plane along laser beam moving; (c) In cross-section perpendicular to laser beam moving
当温度升高到1 000 K以上时,陶瓷材料出现较均匀的软化,其硬度低于刀具材料的硬度值,此时,适合进行切削加工[16]。根据图3(b)与图3(c)截面的温度场的计算结果,1 000 K等温线所对应z坐标值0.08 mm即为合适的切削深度。由图3(a)~(c)和图4还可以看出,处于光束加热中心位置的试件最高温度达2 000 K,远远低于相同工艺参数下激光垂直入射时的温度(6 000 K),且此时材料软化区域大,更有利于刀具高效率去除。
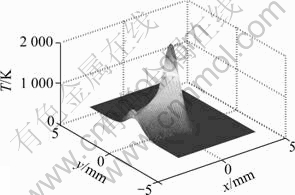
图4 工件表面的三维温度场分布
Fig.4 3D temperature field distribution on surface of workpiece
3 切削深度的计算值与实验值的对比与分析
3.1 不同参数下温度场计算得到的切削深度
分别改变激光功率、光束移动速度(改变工件转速)和工件表面的激光束光斑半径,通过求解温度场分布,获得的切削深度值如表3~5所列。
表3 不同激光功率下的切削深度
Table 3 Cutting depths calculated for different laser powers (n=147 r/min, rb=0.5 mm)
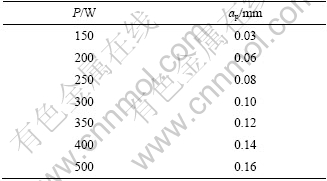
表4 不同转速下的切削深度
Table 4 Cutting depths calculated at different rotational speeds (P=250 W, rb=0.5 mm)
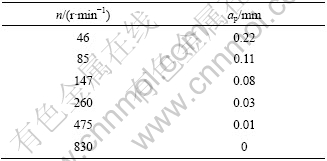
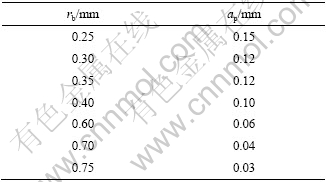
表5 不同激光光斑半径下的切削深度
Table 5 Cutting depths calculated for different laser spot radius (P=250 W, n=147 r/min)
3.2 切削深度的实验值
采用直径30 mm,长70 mm的Al2O3热压陶瓷圆棒,夹持在CQ6232型车床头架,通过调整激光器、机床和聚焦透镜离焦量实现功率、光束移动速度和光斑尺寸的改变,刀具牌号为YW1的硬质合金。实验时,进给量相同,光斑对准切削点;取β为20?,光束中心与刀尖在周向的距离为5 mm,保证激光加热软化深度与刀具切削深度一致,同时避免光束烧伤刀尖;采用喷嘴出口压力为0.05 MPa的压缩空气以保护透镜。为便于对比分析,将实验选取与理论确定的切削深度值与激光功率、机床转速和光斑半径参数间关系分别绘于图5(a)~(c)中。
3.3 实验值与计算值的对比与分析
图5所示为不同参数下切削深度的实验值与计算值的比较。分析发现,3种条件下得到的切削深度实验值与计算值接近,且变化趋势一致,表明理论计算与实验吻合较好,但实验值比计算值略有增高,其主要是进行数值计算时,将工件假设为半无限大平板,激光光束在平板上做匀速直线运动,仅考虑光束对切削区域材料的一次加热。而实际实验中工件为有限大的圆柱体,光束沿工件螺旋运动(转动和进给运动的合成),切削区域材料在被切除之前实际被激光光束重复加热多次,因而存在着热量的积累,导致切削区域实际温度偏高,如果考虑上述因素的影响,模拟计算应该与实验结果完全相符。
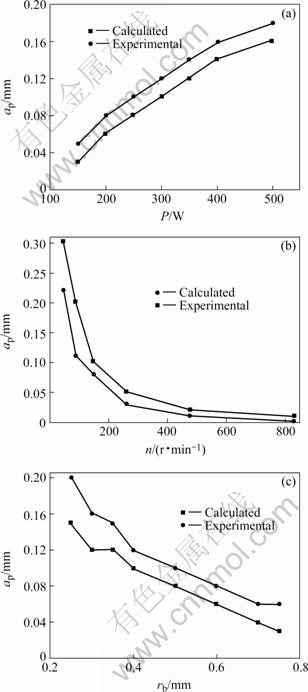
图5 不同参数下切削深度实验值与计算值的对比
Fig.5 Comparison of experimental and calculated cutting depth under different parameters
进一步分析图5(a)发现:随着激光功率的增加,切削深度值近似成线性增加,但到达400 W以后,增加趋势变得平缓。其主要原因是随着激光功率的增加,工件受辐照部分材料吸热量增加,材料软化区的范围扩大,导致这部分材料的强度和硬度降低,从而切削变得容易。但激光功率超过400 W以后,由于本身激光加热区域小,材料吸收热量区域近饱和状态,材料软化扩散趋势相对变缓,则有很大一部分激光能量被浪费。因此,适当地提高激光功率,可以扩大热影响区的范围,有利于切削区域材料的充分软化,使其切削性能得到提高,也有利于采取较大的切削深度,提高切削加工效率,但从节约能量的角度,激光功率不宜太高;从图5(b)易知:随着激光移动速度(机床转速)的增加,可选择切削深度值降低,在达到机床的最大转速时,已不能进行正常切削。这主要是由于随着激光移动速度的增加,激光与材料间相对运动速度加快,工件受光束辐照时间缩短,工件吸热量减少,热量传递到工件的深度低,工件温升变缓,其加热软化区范围窄。因此,适当的降低激光移动速度,有利于采取较大的切削深度,提高材料的切除率。但如果激光移动速度过低,由于激光对材料局部区域的瞬时累计加热,会导致工件加热区组织结构的改变,严重时会烧毁工件,反而不利于切削加工;分析图5(c)发现:随着激光光斑半径的增加,可选择的切削深度值近似线性降低。其主要在于,随着激光光斑半径的增加,虽然工件表面辐照面增大,工件等温线分布范围扩大,但由于激光功率密度降低,工件受辐照单位面积能量减少,材料吸收热少,加热软化区的范围相对减小,此时也不适合选取较大的切削深度。
REFRENCES
[1] 叶邦彦. 加热切削及其发展[J]. 机械开发, 1995, 4: 10-12.
YE Bang-yan. The heat-aided machining and it’s development[J]. Machinery Development, 1995, 4: 10-12.
[2] ROZZI J C, PFEFFERKORN F E, INCROPERA F P, SHIN Y C. Transient thermal response of a rotating cylindrical silicon nitride workpiece subjected to a translating laser heat source, part Ⅰ: Comparison of surface temperature measurement with theoretical results[J]. Journal of Heat Transfer, 1998, 120(4): 899-906.
[3] ROZZI J C, INCROPERA F P, SHIN Y C. Transient thermalresponse of a rotating cylindrical silicon nitride workpiece subjected to a translating laser heat source, part Ⅱ: Parametric effects and assessment of a simplified model[J]. Journal of Heat Transfer, 1998, 120(4): 907-915.
[4] ROZZI J C, PFEFFERKORN F E, SHIN Y C. Experimental evaluation of the laser assisted machining of silicon nitride ceramics[J]. Journal of Heat Transfer, 2000, 122(4): 666-670.
[5] PFEFFERKORN F E, INCROPERA F P, SHIN Y C. Surface temperature measurement of semi-transparent ceramics by long-wavelength pyrometry[J]. Journal of Heat Transfer, 2003, 125(1): 48-56.
[6] PFEFFERKORN F E, SHIN Y C, TIAN Y G, INCROPERA F P. Laser-assisted machining of magnesia-partially-stabilized zirconia[J]. Journal of Heat Transfer, 2004, 126(1): 42-51.
[7] 王慧艺, 李从心, 阮雪榆. 激光辅助切削温度场的三维有限元仿真[J]. 上海交通大学学报, 2001, 35(1): 98-101.
WANG Hui-yi, LI Cong-xin, RUAN Xue-yu. 3D simulation of the temperature field of laser-assisted machining with FEM[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiaotong University, 2001, 35(1): 98-101.
[8] 王 扬, 马丽心, 谢大纲, 韦随心. 陶瓷材料激光加热辅助切削温度场分析[J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报, 2001, 33(6): 785-788.
WANG Yang, MA Li-xin, XIE Da-gang, WEI Sui-xin. Distribution of temperature fields for laser heating assisted cutting of ceramics[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2001, 33(6): 785-788.
[9] 马丽心, 王 杨, 谢大纲, 杨立军, 刘 璇. 冷硬铸铁激光加热辅助切削实验研究[J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报, 2002, 34(2): 228-231.
MA Li-xin, WANG Yang, XIE Da-gang, YANG Li-jun, LIU Xuan. Experimental investigation on laser assisted hot machining of cold hard cast iron[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2002, 34(2): 228-231.
[10] 王 扬, 杨立军, 齐立涛. Al2O3颗粒增强铝基复合材料激光加热辅助切削的切削特性[J]. 中国机械工程, 2003, 14(4): 344-346.
WANG Yang, YANG Li-jun, QI Li-tao. Laser-assisted hot cutting characteristics of particle reinforced Al-matrix composite[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2003, 14(4): 344-346.
[11] 高 霁, 曹国强. 利用CO2高能激光辅助干式切削GH761实验研究[J]. 辽宁工程技术大学学报, 2005, 24(5): 739-741.
GAO Ji, CAO Guo-qiang. Study on dry cutting GH761with high-power CO2 lasers[J]. Journal of Liaoning Technical University, 2005, 24(5): 739-741.
[12] 陈 沛, 金湘中. 激光辅助切削温度场的数值模拟[J].机械制造, 2005, 43(12): 32-34.
CHEN Pei, JIN Xiang-zhong. Numerical simulation on temperature histories of laser aided machining[J]. Machinery Manufacturing, 2005, 43(12): 32-34.
[13] CHANG C W, KUO C P. An investigation of laser-assisted machining of Al2O3 ceramics planning[J]. International Journal of Machine Tools & Manufacture, 2007, 47: 452-461.
[14] CHANG C W, KUO C P. Evaluation of surface roughness in laser-assisted machining of aluminum oxide ceramics with Taguchi method[J]. International Journal of Machine Tools & Manufacture, 2007, 47: 141-147.
[15] 李力钧. 现代激光加工及其装备[M]. 北京: 北京理工大学出版社, 1993: 130-135.
LI Li-jun. Modern laser processing and it’s equipment[M]. Beijing: Beijing Institute of Technology Press, 1993: 130-135.
[16] 李建保, 黄 勇. 新型陶瓷刀具材料的研究与开发[J].现代技术陶瓷, 1993, 1: 7-13.
LI Jian-bao, HUANG Yong. Investigation and developing on newer ceramic tool materials[J]. Modern Technology Ceramic, 1993, 1: 7-13.
基金项目:湖南省骨干青年教师和湖南大学重点科研基金资助项目
收稿日期:2007-07-27;修订日期:2007-11-09
通讯作者:鄢 锉,副教授;电话:0731-8821772; E-mail: cuoyan@yahoo.com.cn
(编辑 陈爱华)