文章编号:1004-0609(2008)03-0483-06
强磁场下烧结MnZn铁氧体
傅小明,钟云波,任忠鸣,王 江,邓 康
(上海大学 上海市现代冶金与材料制备重点实验室,上海 200072)
摘 要:将Fe2O3、MnO和ZnO粉末按摩尔比为52.8?24.2?23.0混合后压制成30 mm×5 mm×5 mm的长方条,然后在无磁场和8 T强磁场下进行烧结,对两种情况下烧结的MnZn铁氧体进行XRD、SEM和VSM等检测。结果表明:与无磁场下烧结的MnZn铁氧体相比,8 T强磁场下烧结的MnZn铁氧体的(511)晶面沿平行于磁场方向发生明显取向,微观形貌也显示明显的取向织构,且致密化程度提高;其磁性能也明显提高,特别是其相对磁导率提高约130%;对于强磁场下烧结的MnZn铁氧体,平行磁场方向上的饱和磁化强度较垂直磁场方向上的饱和磁化强度提高7.56%,而剩余磁化强度降低48.19%。
关键词:MnZn铁氧体;强磁场;烧结;取向
中图分类号:O 511.1 文献标识码:A
Sintering of MnZn ferrite in high static magnetic field
FU Xiao-ming, ZHONG Yun-bo, REN Zhong-ming, WANG Jiang, DENG Kang
(Shanghai Key Laboratory of Modern Metallurgy and Material Processing, Shanghai University,
Shanghai 200072, China)
Abstract: The mixtures of Fe2O3, MnO and ZnO were sintered without or with 8 T static magnetic field, respectively. The sintered MnZn ferrite (MZF) samples in these two cases were characterized by XRD, SEM, VSM and etc. The results show that compared with MZF sintered without magnetic field, (511) plane of MZF sintered in 8 T static magnetic field is strongly oriented along the magnetic field direction. The oriented crystal texture appears in the sample sintered in 8 T static magnetic field, whose density is enhanced remarkably. The magnetic properties are increased. Especially, its relative magnetic permeability along the magnetic field direction is evaluated by about 130%. For MZF sintered in 8 T static magnetic field, the saturation magnetization along the magnetic field direction is increased by 7.56% compared with that along the vertical magnetic field direction, while its residual magnetization is reduced by 48.19%.
Key words: MnZn ferrite; high static magnetic field; sintering; orientation
MnZn铁氧体是一种重要的软磁材料,它要求具有高磁导率、高饱和磁化强度、高电阻、低损耗和稳定性好等特性,其中高磁导率和低损耗是最重要的性能指标[1]。MnZn铁氧体的这些性能取决于它自身的化学成分和组织结构,而其组织结构又与制备技术(工艺)密切相关。
通常制备的MnZn铁氧体,其晶粒的择优取向较混乱,呈各向同性,因此,其性能远不如单晶铁氧体。为了有效利用晶体的各向异性,常常希望制备出具有晶粒取向的多晶织构材料。取向的多晶织构MnZn铁氧体材料兼有单晶和多晶材料的优点,其性能类似单晶[2]。普通的烧结方法一般无法达到上述要求。
随着现代科学技术的发展,磁性材料的制备技术(工艺)取得显著的进步,出现一大批新方法和新工艺。磁场烧结就是其中之一。所谓磁场烧结就是在材料的烧结过程中引入外部磁场来强化烧结过程(活化烧结)、控制和改变组织的一种烧结方法[3]。目前国内外学者对磁场中烧结金属磁粉进行了较多的研究,譬如,TUSREKAWA等[4]研究发现:磁场能提高烧结铁粉的致密化程度,促进晶粒长大;而对钴粉而言,磁场对其致密化起着抑制的作用。但是,对于磁场中烧结MnZn铁氧体磁性材料,国内外尚未见文献报道。
近年来,随着超导技术的发展,人们可以得到长时间稳定的强磁场(0~20 T)。在强磁场中,MOGI[5]和ASAI[6]研究发现,非铁磁性物质如木头、水滴、塑料、铝、铋等可以在强磁场中悬浮,这表明磁力已达到与重力场相当的程度。因此,利用强磁场这种显著的磁力作用,有望对材料制备过程产生显著的促进或控制作用,从而制备出性能独特的新材料。因此,本文作者探讨了强磁场对烧结MnZn铁氧体的组织、结构和性能影响。
1 实验
1.1 实验设备
1) XMT型数字控温仪;2) 铂铑铂热电偶;3) 本实验所用的强磁场是由超导磁体提供,该磁体由英国牛津仪器(Oxford Instrument Co. Ltd.)公司生产。强磁场下烧结实验装置的示意图如图1所示。
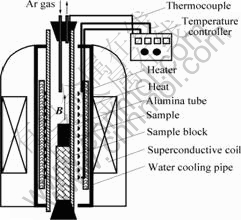
图1 强磁场下烧结实验装置示意图
Fig.1 Sketch map of sintering device in high static magnetic field
1.2 试样的制备
用液压万能实验机将摩尔比分别为52.8?24.2?23.0的Fe2O3、MnO和ZnO混合物压制成30 mm×5 mm×5 mm的压坯,压力为60 kN。
1.3 烧结工艺
Fe2O3、MnO和ZnO混合物压坯在无磁场和8 T强磁场中的烧结工艺如图2所示。在1 250 ℃保温结束前20 min通入惰性气体,随炉冷却至室温为止。
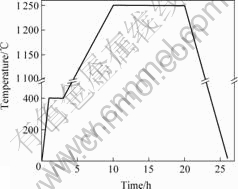
图2 无磁场和8 T强磁场下混合物压坯的烧结温度曲线
Fig.2 Sintering temperature curve of mixture without or with high static magnetic field of 8 T
1.4 检测设备
1) 利用D/max-ⅡB型X射线衍射仪对试样进行取向分析;2) 利用JXA-840A电子探针扫描仪对试样进行形貌分析;3) 利用JDM-13型振动样品磁强计对试样进行磁性能分析;4) 采用闭合磁路法和LCR仪测试电感的方法测试试样的磁导率。
2 结果与分析
2.1 XRD分析
无磁场和8 T强磁场下烧结试样的XRD分析结果分别如图3和图4所示。
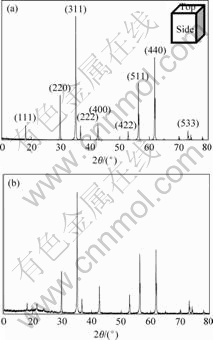
图3 无磁场下烧结MnZn铁氧体的XRD谱
Fig.3 XRD patterns of MnZn ferrite sintered without magnetic field: (a) Side; (b) Top
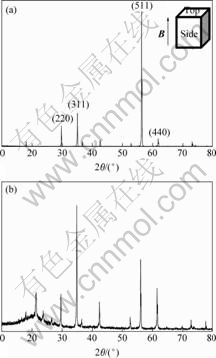
图4 8 T强磁场下烧结MnZn铁氧体的XRD谱
Fig.4 XRD patterns of MnZn ferrite sintered with 8 T static magnetic field: (a) Side; (b) Top
根据文献[7],晶粒取向度计算公式为:

根据式(1),对无磁场和8 T强磁场下烧结MnZn铁氧体的晶粒取向度M(hkl)进行计算,其结果分别如图5和图6所示。
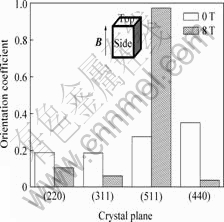
图5 无磁场和8 T强磁场下烧结的MnZn铁氧体沿平行于磁场方向上的晶粒取向度
Fig.5 Orientation coefficient of crystal grains of MnZn ferrite sintered without or with 8 T static magnetic field along magnetic field direction (side plane)
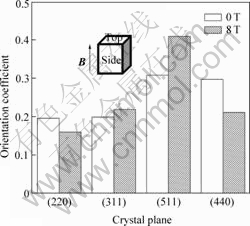
图6 无磁场和8 T强磁场下烧结的MnZn铁氧体沿垂直于磁场方向上的晶粒取向度
Fig.6 Orientation coefficient of crystal grain of MnZn ferrite sintered without or with 8 T static magnetic field along vertical magnetic field direction (top plane)
由图5可知,8 T强磁场下烧结的MnZn铁氧体,平行于磁场方向上(511)晶面的取向度增加得最多。因此,强磁场下烧结MnZn铁氧体时,MnZn铁氧体沿平行于磁场方向发生了明显地取向。
由图6可知,8 T强磁场下烧结的MnZn铁氧体,垂直于磁场方向上(511)晶面的取向度降低较多,而(440)晶面和(311)晶面的取向度则有较大程度的增加,从另一个侧面表明(511)晶面沿平行磁场方向发生了取向。
此外,由于MnZn铁氧体属于立方晶系,因此,其晶面间距与点阵参数的关系式为

根据式(2),对无磁场和8 T强磁场下烧结MnZn铁氧体的的点阵参数进行计算,其结果如表1所列。
表1 无磁场和8 T强磁场下烧结MnZn铁氧体的点阵参数
Table 1 Lattice constants of MnZn ferrite sintered without or with 8 T static magnetic field
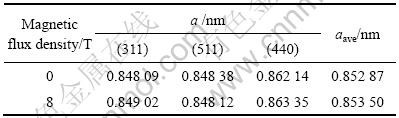
比较无磁场与8 T强磁场下烧结的MnZn铁氧体的点阵参数a值(表1),8 T强磁场下烧结的MnZn铁氧体的点阵参数a值变大,这也说明8 T强磁场下烧结的MnZn铁氧体发生取向。
2.2 SEM分析
图7(a)和图8(a)表明,无磁场下烧结的MnZn铁氧体平行于磁场方向没有明显的取向织构,而8 T强磁场下烧结的MnZn铁氧体平行于磁场方向出现明显的取向织构。并且,8 T强磁场下烧结的MnZn铁氧体孔洞减少,其致密化程度有较大程度提高(图7(b)和图8(b))。
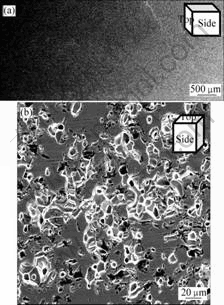
图7 无磁场下烧结MnZn铁氧体的SEM像
Fig.7 SEM images of MnZn ferrite sintered without magnetic field: (a) Side; (b) Top
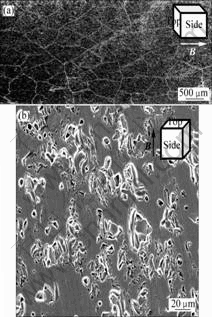
图8 8 T强磁场下烧结MnZn铁氧体的SEM像
Fig.8 SEM images of MnZn ferrite sintered with 8 T static magnetic field: (a) Side; (b) Top
2.3 VSM分析
无磁场和8 T强磁场下烧结的MnZn铁氧体磁性能如表2所列。
表2 无磁场和8T强磁场下烧结MnZn铁氧体的磁性能
Table 2 Magnetic properties of MnZn ferrite sintered without or with 8 T high magnetic field
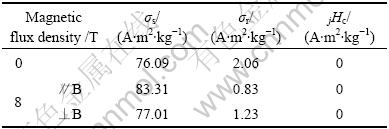
表2表明,8 T强磁场下烧结的MnZn铁氧体的饱和磁化强度有所增大,剩余磁化强度明显地降低。对于8 T强磁场下烧结的MnZn铁氧体,平行磁场方向的饱和磁化强度较垂直磁场方向的饱和磁化强度提高7.56%;平行磁场方向的剩余磁化强度较垂直磁场方向的剩余磁化强度降低48.19%。因此,在强磁场中烧结MnZn铁氧体时,其磁性能均得到提高。
2.4 磁导率分析
采用闭合磁路和电感法,对无磁场和8 T强磁场下烧结MnZn铁氧体的磁导率进行测试。结果表明,无磁场下烧结MnZn铁氧体的相对磁导率为3 921.4,而8 T强磁场下烧结MnZn铁氧体的相对磁导率为 9 006.5,较无磁场下烧结MnZn铁氧体的相对磁导率提高约130%。因此,强磁场下烧结MnZn铁氧体可以显著提高其相对磁导率。
3 机理讨论
无磁场下烧结MnZn铁氧体,由于压坯是将MnO、ZnO和Fe2O3按一定比例混合压制而成的,所以,首先MnO、ZnO和Fe2O3在其接触点发生反应,分别生成MnFe2O4和ZnFe2O4。一旦MnO、ZnO和Fe2O3在接触生成MnFe2O4和ZnFe2O4,MnO、ZnO和Fe2O3的接触点则被中断。后续反应则主要通MnO、ZnO和Fe2O3向生成的铁氧体层继续扩散而得以持续,铁氧体层逐渐变厚,直到全部生成MnFe2O4和ZnFe2O4,同时这两者互相固溶形成MnZn铁氧体[8]。
在磁场下烧结粉末压坯时,图8(b)所示的试验结果表明,压坯的致密度明显提高,孔洞减少,说明强磁场能促进烧结体致密化。上述磁场效应的机理有可能是强磁场极强的磁场能促进了晶界迁移,加速MnO、ZnO或者Fe2O3的扩散,从而促进压坯的致密化。文献[4,9-11]在研究磁场中低温烧结粉末材料时,也发现磁场对晶界的迁移具有重要促进作用。
此外,SOLIN等[12-18]指出:强磁场可以使具有磁各向异性的顺磁性和铁磁性晶体中磁化率绝对值最大的晶轴沿平行磁场方向取向。由于MnZn铁氧体为亚铁磁性磁性材料,因此,在磁场中烧结,磁场也会使得MnZn铁氧体晶粒沿着平行于磁场方向进行取向。这两者都能使得MnZn铁氧体的磁性能提高。
4 结论
1) 强磁场下烧结MnZn铁氧体可促进(511)晶面沿磁场方向发生明显取向。并且强磁场下烧结的MnZn铁氧体形成明显的取向织构,同时,其致密化程度也得到了提高。
2) 与无磁场下烧结MnZn铁氧体的磁性能比较,强磁场下烧结的MnZn铁氧体具有更高的饱和磁化强度和更低的剩余磁化强度,其相对磁导率也提高约130%,表明强磁场下烧结MnZn铁氧体有利于提高其磁性能。
3) 对于强磁场下烧结的MnZn铁氧体,平行磁场方向上的饱和磁化强度较垂直磁场方向上的饱和磁化强度提高7.56%,而剩余磁化强度降低48.19%。
REFERENCES
[1] 荆玉兰, 张怀武. 预烧温度对高磁导率MnZn铁氧体性能的影响[J]. 电子科技大学学报, 2005, 34(6): 836-838.
JING Yu-lan, ZHANG Huai-wu. Effects of anneal temperature on properties of high permeability MnZn ferrite[J]. Journal of UEST of China, 2005, 34(6): 836-838.
[2] HANDLEY R C. 现代磁性材料原理和应用[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2002.
HANDLEY R C. Modern magnetic materials principles and applications[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2002.
[3] 杨四新, 黄继华. 磁场烧结在材料制备中的应用[J]. 材料导报, 2002, 16(2): 19-21.
YANG Si-xin, HUANG Ji-hua. Application of magnetic field sintering in preparation of materials[J]. Materials Review, 2002, 16(2): 19-21.
[4] TSUREKAWA S, HARADA K, SASAKI T, MATSUZAKI T, WATANABE T. Magnetic sintering of ferromagnetic metal powder compacts[J]. Mater Trans, JIM, 2000, 41(8): 991-999.
[5] MOGI I. Magneto-electrochemical processing of material[J]. CAMP-ISIJ, 1998, 11: 124-129.
[6] ASAI S. Now, how interesting magnetization force is[J]. CAMP-ISIJ, 1997, 10: 817-911.
[7] MATSUSHIMA H, NOHIRA T, MOGI I, ITO Y. Effects of magnetic fields on iron electrodeposition[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2004, 179: 245-251.
[8] 聂建华. 高性能MnZn铁氧体材料的制备及机理研究[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2004.
NIE Jian-hua. Study on preparation and mechanism of high properties MnZn ferrites[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2004.
[9] MOLODV D A, GOTTSTEIN G, HERINGHAUS F, SHVINDLERMAN L S. Motion of planar grain boundaries in bismuth bicrystals driven by a magnetic field[J]. Scripta Mater, 1997, 37 (8): 1207-1213.
[10] MOLODV D A, GOTTSTEIN G, HERINGHAUS F, SHVINDLERMAN L S. True absolute grain boundary mobility: Motion of specific planar boundaries in Bi-bicrystals under magnetic driving forces[J]. Acta Matter, 1998, 46(16): 5627-5632.
[11] MA Y W, XU A X, LI X H, ZHANG X P, AWAJI S, WATANABE K. Enhanced critical current density MgB2 superconductor synthesized in high magnetic fields[J]. Jpn J Appl Phys, 2006, 45(19): 493-496.
[12] SOLIN S A, GARCIA N, VIERA S, HORTAL M. Field-induced orientation of nonlevitated microcrystals of superconducting YBa2Cu3O7-x[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 1988, 60(8): 744-747.
[13] MORIKAWA H, SASSA K, ASAI S. Control of precipitating phase alignment and crystal orientation by imposition of a high magnetic field[J]. Mater Trans, JIM, 1998, 39(8): 814-818.
[14] De RANGO P, LEES M, LEJAY P, SULPICE A, TOURNIER R, INGOLD M, GERMI P, PERNET M. Texturing of magnetic materials at high temperature by solidification in a magnetic field[J]. Nature, 1991, 25: 4232-4234.
[15] SUGIYAMA J, CHANZY H, MARET G. Orientation of cellulose microcrystals by strong magnetic fields[J]. Macromolecules, 1992, 25: 4232-4234.
[16] LEES M R, BOURGAULT D, BRAITHWAITE D, RANGO P D, LEJAY P, SULPICE A, TOURNIER R. Transport properties of magnetically textured YBa2Cu3O7-d[J]. Physica C, 1992, 191: 414-418.
[17] LEES M R, RANGO P D, BOURGAULT D, BARBUT J M, BRAITHWAITE D, LEJAY P, SULPICE A, TOURNIER R. Bulk textured rare earth-Ba2Cu3O7-delta prepared by solidification in a magnetic field[J]. Supercond Sci Technol, 1992, 5: 362-367.
[18] TOKUNAGA R K, WATANABE S I. The effect of high magnetic field on the crystal growth of benzophenone[J]. Chem Lett, 1996, 8: 607-608.
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(50404018);全国优秀博士学位论文基金资助项目(200235);上海市科委纳米专项基金资助项目(0252nm048);上海市科委基金资助项目(05JC14065)
收稿日期:2007-07-02;修订日期:2007-12-02
通讯作者:傅小明,博士研究生;电话:021-56333843;E-mail: 05810015@shu.edu.cn
(编辑 龙怀中)