强磁场对电沉积镍铁合金膜显微组织的影响
温艳玲, 钟云波, 任忠鸣, 黄琦晟, 邓 康, 徐匡迪
(上海大学 上海市现代冶金与材料制备重点实验室, 上海 200072)
摘 要: 在电沉积镍铁合金膜过程中施加了不同强度的纵向强磁场, 研究了磁场强度对电沉积镍铁合金膜的微观形貌、 晶粒取向和成分的影响。 结果表明: 随着磁感应强度增加, 镀层表面晶粒先粗化, 然后细化为数百纳米的颗粒层; 同时样品截面组织经历了由层状生长转为树枝晶、 脊状晶和条状晶的一系列变化; 在12T强磁场下条状晶沿外磁场方向破碎为球状微晶组织; 强磁场使样品(111)晶面择优取向, 并进一步促进了Fe2+的优先沉积, 使样品中铁含量随外加磁场强度的增大而增加, 而膜的饱和磁化强度也线性提高。
关键词: 镍铁合金膜; 强磁场; 电沉积; 微观结构 中图分类号: TQ153.2
文献标识码: A
Effect of high static magnetic field on microstructure of electrodeposited NiFe film
WEN Yan-ling, ZHONG Yun-bo, REN Zhong-ming, HUANG Qi-sheng,DENG Kang, XU Kuang-di
(1. Shanghai Enhanced Laboratory of Modern Metallurgy and Material Processing,Shanghai University, Shanghai 200072, China)
Abstract: NiFe alloy films were electrodeposited in the high static magnetic fields with magnetic flux perpendicular to the electric current, and the effects of the magnetic flux density (MFD) on the micromorphology, preferential orientation, composition and saturation magnetization of the samples were studied. The results show that, with the increase of MFD, the crystal grains on the surface of the samples are coarsened firstly, then refined, and finally formed spherical crystal grains with several hundreds of nanometers in size, distributing uniformly. At the same time, the microstructure of across-section experiences a series of changes from lamellar crystal to fir-tree crystal to carinate crystal and finally to strip structure, and when MFD reaches 12T, the strip crystals are broken along the magnetic field direction and form spherical microcrystallites. With increase of MFD, the crystal plane(111) is oriented distinctly, and Fe2+ ion is preferential deposited with the increasing static magnetic field, which results in the increases of iron concentration and saturation magnetization of the samples.
Key words: NiFe alloy film; high static magnetic field; electrodeposition; microstructure
近年来, 电沉积由于具有廉价便利以及对镀层材料和基体形状适用性强的特点而成为一种重要的膜材料制备技术[1]。 但是如何提高电沉积膜层材料的结构和择优取向, 则一直是人们关注的问题。 考虑到磁场对晶体生长中的取向效应的影响, 人们自然想到在电沉积过程中施加磁场这一手段, 由此而形成了一个全新的研究领域——磁电化学, 并在这一领域展开了深入研究。
然而由于实验条件以及镀层体系不同, 磁场效应也不尽一致。 单金属研究方面, 大致有如下几种观点: 一是磁致对流效应, Aaboubi等[2]认为磁场引起溶液对流, 从而增大了其极限扩散电流, 他们通过对镍金属电沉积膜的研究证明了磁场使H+传质加快, 而延缓了镍的沉积, 从而导致表面形貌和择优取向改变; Hinds等[3]指出磁场引起溶液对流, 并且与旋转电极或搅拌溶液是等效的; Devos等[4]认为表面形貌的改变是由于磁场增加了抑制物向阴极的扩散量; Fahidy[5]认为沉积层表面粗糙度的减小是由于磁流体效应影响三维沉积薄片的结构。 二是Matsushima等[6]用蒙特卡罗模拟的研究方法发现晶体取向应归于结晶学各向异性的影响; 而Ito等[6]则发现磁场使样品晶粒细化, 表面平整化, 而晶体的择优取向随电流密度变化, 与磁场的强弱及施加方向无关。
磁场对于合金电沉积的影响更为复杂, 这方面的研究还很少。 近来, Ibro等[7]和Chopart等[8]各自在0.1T和0.1~0.9T的较弱磁场下电沉积出NiFe合金薄膜, 并分析了磁场对沉积过程和样品的影响, 发现磁场能够改变样品的表面形貌、 晶体取向等, 然而在磁场影响电流密度、 样品成分和磁性方面, 却得出了相反的结果。 由此可见, 由于实验条件和镀层体系的多样性, 磁场在电沉积中的作用规律和机理, 还有待于深入的研究和探索。
随着超导技术以及大功率Bitter磁体技术的发展, 人们可以长时间获得10T甚至45T以上的稳态超强磁场, 从而为研究高强磁场下电沉积过程及样品特性提供了条件[9-14]。 本文作者以磁感应强度为变量, 探讨了0~12T磁场对电沉积NiFe合金膜显微组织的影响。
1 实验
实验使用硫酸盐电镀液恒流电沉积制备镍铁合金膜。 主盐为200g/L的NiSO4·6H2O和20g/L的FeSO4·7H2O, 用NaCl溶液作为阳极活化剂, 用H3BO3作为稳定剂, 另外添加适当的缓冲剂、 光亮剂。 每次溶液总量为200mL。 为保证溶液浓度的一致性, 每沉积一个膜样品更换一次新溶液。 溶液的pH值为3.5, 电流密度为4.0A/dm2, 控制温度在55℃, 每个样品沉积时间为30min。 以分析纯镍片作阳极, 铜箔作阴极, 阴阳极间距为20mm。 实验中通入氮气搅拌, 一方面为反应体系创造惰性气体环境以防Fe2+的氧化, 另一方面可以保证镀液温度的均匀性。 实验装置如图1所示, 所加磁场与电流方向垂直。 强磁场由英国Oxford Instrument Co. Ltd. 生产的超导磁体提供, 其室温孔径98mm, 磁场方向竖直向上, 中心磁感应强度从0~12T连续可调, 在距磁场中心上下40mm范围内, 磁感应强度变化值不超过0.5T。

图1 强磁场下电沉积实验装置
Fig.1 Electrodeposited experimental equipment in high static magnetic field
采用配有能谱(EDS)的HITACHI S-570扫描电镜(SEM)观察样品的微观形貌并分析样品成分, D-MAX2550 X射线衍射仪分析膜样品的相结构, 振动样品磁强计(VSM)测试其室温下的磁性。
2 结果与分析
2.1 磁场对样品微观形貌的影响
在镍铁合金膜的电沉积过程中施加不同强度的外磁场, 样品表面微观形貌随磁感应强度变化情况如图2所示。 从图2可以看出, 电沉积样品晶粒大小均匀, 形状规则, 表面平整洁净; 无磁场样品结构疏松, 表面有气孔, 表面晶粒呈条状; 施加外磁场后, 气孔消失, 随磁感应强度增大, 晶粒逐渐增大, 形状也由条状逐渐转变为块状; 然而当磁感应强度增加到10T以上时, 镀层表面晶粒细化成小的圆形, 磁场增加到12T, 表面以直径约500nm的圆形晶粒均匀分布。
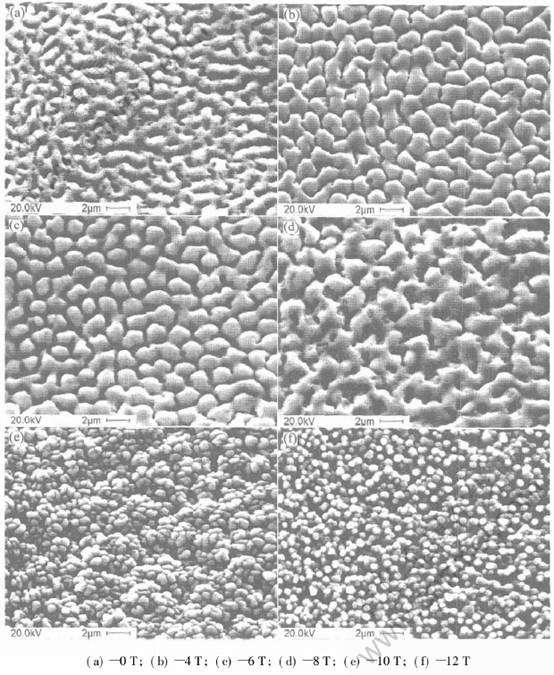
图2 不同磁场下电沉积NiFe膜的表面扫描电镜照片
Fig.2 SEM images of surface of NiFe films electrodeposited in various magnetic fields
对样品平行于外磁场方向的截面微观形貌(见图3)进行观察分析可以看出, 无磁场电沉积镍铁膜以小片层状生长, 略显主轴轮廓, 这与基体铜箔的结构类似, 因为铜箔经多次轧制变形后, 形成平行于膜面的织构; 4~6T磁场下样品转为树枝晶生长, 随外加磁场的增强, 主轴粗化, 主轴间距逐渐增大, 二次枝晶也逐渐变粗变长; 8T时, 转为脊状生长; 10T强磁场下, 从基片向外以大的条状晶生长, 并且靠近基片端晶粒大而粗糙, 而生长前端出现分裂, 晶粒排布紧密; 12T时, 条状晶沿外磁场方向破碎, 晶粒以球状堆积形式分布。
2.2 磁场对样品晶粒取向的影响
图4所示为不同强度磁场中电沉积薄膜样品表面的X射线衍射谱。 通过分析比较可知, 图谱中各峰的晶面间距值与标准PDF卡上Ni3Fe的晶面间距非常吻合, 并且没有其它衍射峰出现。 由此电沉积样品组分为单相置换固溶体Ni3Fe。
取向度计算公式[6]为:
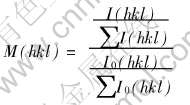
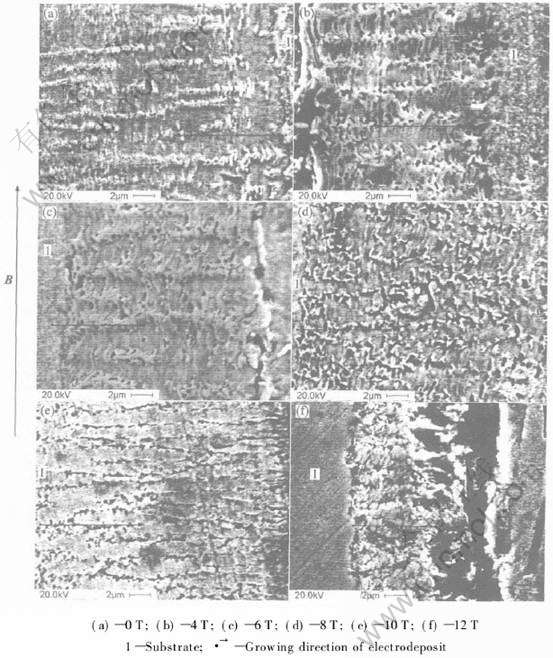
图3 不同磁场下电沉积NiFe膜的截面扫描电镜照片
Fig.3 SEM images of across-section of NiFe films electrodeposited in various magnetic fields
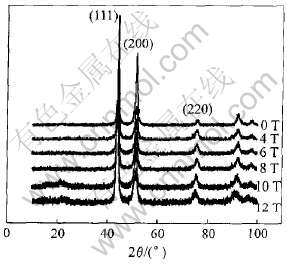
图4 不同磁场中电沉积样品的X射线衍射图谱
Fig.4 XRD patterns of samples electrodeposited in various magnetic fields
式中 M为取向度; I(hkl), I0(hkl)分别为沉积层试样和标准JCPDF卡上粉末样品(hkl)晶面的衍射强度。 样品各晶面的取向度与外磁场强度的关系如图5所示。 可以看出, 与无磁场下的电沉积膜样品相比, 强磁场下电沉积样品的(200)面的衍射峰强度明显减弱, (111)及(220)面的衍射峰相对增强; 当外加磁场强度增大到12T时, 又出现一个峰值强度的突变, 此时(111)面的衍射峰很强, 其余各峰很弱, 样品已具有良好的〈111〉择优取向。
2.3 磁场对样品微区成分及磁性的影响
对镍铁合金膜样品进行低倍(500倍)面扫描,其成分测试结果如图6所示。 从图6可以看出, 薄
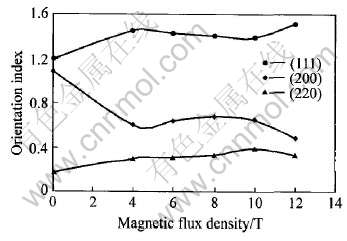
图5 样品取向度与外加磁场强度的关系曲线
Fig.5 Relation between electrodeposit texture and external magnetic flux density
膜样品中铁含量随外加磁场强度增大而增大。 12T强磁场下电沉积的镍铁合金薄膜样品中铁含量由无磁场的12.71%增大到26.10%, 增加了一倍以上。 这与Choport等[8]的报导结果是一致的。
镍铁合金的电沉积受传质控制, Fe2+的质量小于Ni2+的质量, 而二者带电荷数相等。 由力学计算可知, 电场力相同的情况下, Fe2+的传质速度大于Ni2+的传质速度而优先到达阴极表面并穿过氢氧化亚铁胶体膜放电[15], 且前者的放电对后者起抑制作用, 从而形成了镍铁合金的异常共沉积过程。 施加外磁场后, 磁致对流与氮气搅拌共同作用, 影响了扩散层内带电粒子向阴极表面的传质, 使Fe2+的传质速度相对于Ni2+更大, 并且磁场越强, 差值越大, 从而镀层中铁含量越高。 Ibro等[7]也曾指出搅拌速率和电流密度不同, 可以导致铁含量的增加或减小。 其实质也是指传质的影响。
图7所示为电沉积样品中铁含量及饱和磁化强度与制备磁场的关系曲线。 从图7可以看出, 随制备磁场的增强, 样品的铁含量线性增大, 同时饱和磁化强度也线性增加。 因为饱和磁化强度只与样品成分有关, 测试结果与磁化理论相一致[16]。 另外, 膜样品的铁含量与饱和磁化强度随磁场的同步线性递增关系以及饱和磁化强度较高的数值(例如: 12T外磁场下样品的饱和磁化强度约1.2T), 也证明了电沉积样品的高纯度及其组织的均匀性。
3 讨论
图8所示为溶液传质过程中带电粒子的运动轨迹俯视图。 在图8中, 电场力FE=E×q, 方向指向阴极表面; 洛伦兹力FL=q×(v×B), 方向始终与
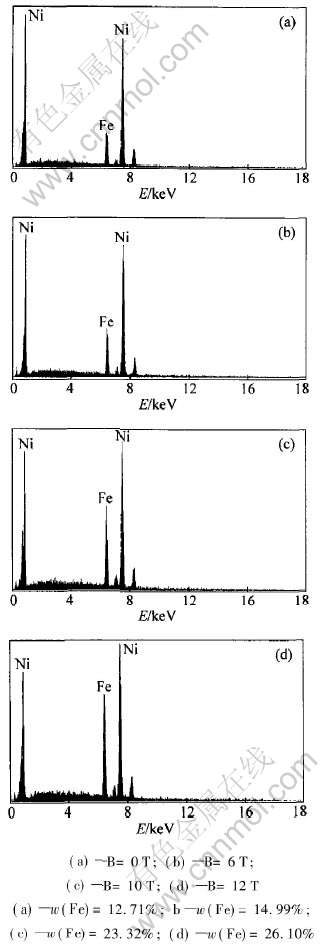
图6 不同磁场下电沉积样品表面成分分析
Fig.6 EDS analysis of samples electrodeposited in different magnetic fields
离子的运动方向相垂直。 不施加磁场时, 带电粒子在电场力FE作用下, 以近似直线运动到达阴极表面(如图8(a))。 施加外磁场后, 镀液中的带电粒子在正交
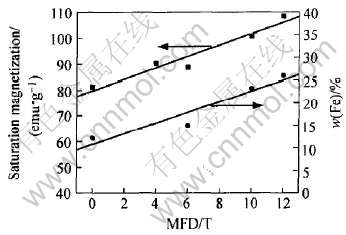
图7 样品铁含量及饱和磁化强度与制备磁场的关系曲线
Fig.7 Relation between iron concentration and saturation magnetization of samples and preparation magnetic field
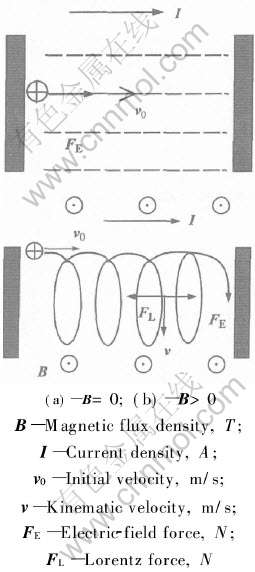
图8 溶液中阳离子的运动轨迹示意图
Fig.8 Diagrammatic sketch of trajectory of positive ions in electrolyte
阴极表面(如图8(b))。 阴极附近离子的切向运动使扩散层减薄, 金属离子传质增快。 顺磁性的金属阳离子形成金属原子, 进入晶格形成亚铁磁性的Ni3Fe晶体, 正的磁化率依次增大[17]。 根据物质相变时磁自由能变化计算公式

可知, 从溶液中的金属离子到金属原子, 最后转变为Ni3Fe晶体, 是磁自由能逐步降低的过程, 因而强磁场能量引入降低晶核的临界形成功, 促进形核, 使晶粒细化。 然而, 在磁场强度不高时(4~8T), 由于洛仑兹力的作用导致镀液本体的流动加剧, 冲刷阴极表面, 使镀层晶粒生长前端断裂, 呈侧向生长趋势, 因而晶粒粗化。 当磁场强度达到10T以上时, 磁化能影响形核率效果加剧, 洛仑兹力在阴极界面附近引起的微小涡流也将导致晶粒尖端分裂, 因此晶粒细化, 以小的球状形式生长。
外磁场作用下, 阴极表面吸附金属原子进入晶格形成面心立方结构的Ni3Fe晶体[18], 必然遵循吉布斯自由能最低原理, 使其易磁化轴〈111〉指向磁场方向, 而难磁化轴〈100〉远离磁场方向, 又由于{111}面的表面自由能最低, 使易磁化轴〈111〉轴同时成为晶粒的择优生长方向, 因而磁场下电沉积样品晶粒的〈111〉轴取向程度增大, 并且晶粒沿平行于磁场方向择优生长。 4T到8T样品的晶体取向程度稍有降低可能与二次枝晶的粗化有关。 处于12T超强磁场中时, 样品铁含量提高, 因而Ni3Fe晶体易磁化轴方向的磁化率提高, 这有利于晶体的进一步取向, 所以样品具有更好的〈111〉轴向织构(见图4)。
4 结论
1) 强磁场对电沉积镍铁镀层的微观形貌产生显著影响。 随着磁感应强度增加, 镀层表面晶粒先粗化, 然后细化为数百纳米的颗粒层。
2) 随外磁场的增强, 样品由层状生长转为树枝晶生长, 且主轴粗化, 二次枝晶逐渐发达且互相连结而形成脊状与粗大的条状晶生长; 12T强磁场下样品晶粒分裂为无数球状微晶组织。
3) 强的磁化力使电沉积镍铁膜的晶粒择优取向, (111)面织构增强。
4) 外加垂直磁场进一步促进Fe2+的优先沉积, 从而使镍铁镀层的铁含量与饱和磁化强度随磁场强度的增大而线性提高。
REFERENCES
[1]温艳玲, 钟云波, 任忠鸣, 等. 巨磁电阻薄膜材料的研究进展[J]. 上海金属, 2005, 27(2): 56-60.
WEN Yan-ling, ZHONG Yun-bo, REN Zhong-ming, et al. Researching progress on giant magnetoresistive thin films[J]. Shanghai Metals, 2005, 27(2): 56-60.
[2]Aaboubi O, Chopart J P, Douglade J, et al. Magnetic field effects on mass transport[J]. J Electrochem Soc, 1990, 137: 1796-1783.
[3]Hinds G, Coey J M D, Lyons M E G. Influence of magnetic forces on electrochemical mass transport[J]. Electrochemistry Communications, 2001(3): 215-218.
[4]Deveos O, Aaboubi O, Chopart J P, et al. Magnetic field effects on Nickel electrodeposition Ⅱ. A steady-state and dynamic electrochemical study[J]. J Electrochem Soc, 1998, 145: 4135-4139.
[5]Fahidy T Z. Characteristics of surfaces produced via magnetoelectrolytic deposition[J]. Progress in Surface Science, 2001, 68: 155-188.
[6]Matsushima H, Nohira T, Mogi I, et al. Effects of magnetic fields on iron electrodeposition[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2004, 179: 245-251.
[7]Ibro T, Steve R. Effect of magnetic field on electrode reactions and properties of electrodeposited NiFe films[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2003, 150: 635-640.
[8]Msellak K, Chopart J P, Jbara O, et al. Magnetic field effects on Ni-Fe alloys codeposition[J]. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 2004, 281: 295-304.
[9]Waskaas M, Kharkats Y I. Effect of magnetic fields on convection in solutions containing paramagnetic ions[J]. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 2001, 502: 51-57.
[10][CM(22*2]Asai S. Special work of the material science in the[CM)]static high magnetic field[J]. Transaction of Japanese Metal, 1997, 61(12): 1271.
[11]Coey J M D, Hinds G. Magnetic electrodeposition[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2001, 326: 238-245.
[12]Devos O, Aabonubi O, Chopart J P, et al. Is there a magnetic field effect on electrochemical kinetics?[J]. J Phys Chem A, 2000, 104: 1544-1548.
[13]OReilly C, Hinds G, Coey J M D. Effect of a magnetic field on electrodeposition chronoamperometry of Ag, Cu, Zn, and Bi[J]. J Elect Soc, 2001, 148: C674-C678.
[14]LU Zhan-peng, HUANG De-lun, WU Yang, et al. Effects of an applied magnetic field on the dissolution and passivation of iron in sulphuric acid[J]. Corrosion Science, 2003, 45: 2233-2249.
[15]Breener A. Electrodeposition of Alloys[M]. New York: Acadmio Press, 1963. 175-178.
[16]陈树川, 陈凌冰. 材料物理性能[M]. 上海: 上海交通大学出版社, 1999. 154.
CHEN Shu-chuan, CHEN Ling-bing. Physical Property of the Materials[M]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiaotong University Press, 1999. 154.
[17]姜寿亭, 李卫. 凝聚态磁性物理[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2003, 10: 31-34, 52.
JIANG Shou-ting, LI Wei. Condensational Magnetic Physics[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2003, 10: 31-34, 52.
[18]Ispas A, Bund A. Influence of a magnetic field on the electrodeposition of nickel-iron alloys[A]. Proceedings of the 2nd German-Sino Workshop on Electromagnetic Processing of Materials (EPM)[C]. Dresden, Germany: Rossordorf Safety Research Institute, 2005. 95.
(编辑何学锋)
基金项目: 上海市科学技术委员会重点基础研究计划资助项目(03JC14029); 国家自然科学基金资助项目(50574055)
收稿日期: 2005-08-09; 修订日期: 2005-12-16
通讯作者: 钟云波, 副研究员; 电话: 021-56336048; E-mail: yunboz@mail.shu.edu.cn