Effect of nanotechnology on heavy metal removal from aqueous solution
来源期刊:中南大学学报(英文版)2016年第10期
论文作者:Hoda Kahrizi Ali Bafkar Masumeh Farasati
文章页码:2526 - 2535
Key words:cadmium; isotherm model; kinetic adsorption; zinc; nanotechnology
Abstract: The effect of nanotechnology on cadmium and zinc removal from aqueous solution was investigated. In order to characterize micro and nano phragmites australis adsorbent, we analyzed the data via FTIR, SEM, PSA, and EDX. The effect of various parameters such as pH, contact time, amount of adsorbent and initial concentration, was investigated. The optimum pH for the removal of cadmium for micro and nano phragmites australis adsorbent was 7, and for the removal of zinc by the micro adsorbent was 7 and by nano adsorbent was 6. The equilibrium time of zinc was 90 min and for the adsorption of cadmium by micro and nano adsorbent were 90 and 30 min, respectively. The optimum dose of micro adsorbent for the removal of cadmium was 0.7 g, and the other dose for the removal of zinc and cadmium was 0.5 g. The evaluation of adsorbent’s distribution coefficient showed that the highest rates of distribution coefficient with initial concentration of 5, 10, 30, and 50 mg/L were 394.83, 587.62, 759.39 and 1101.52 L/kg, respectively, which were observed in nano adsorbent. Desorption experiments for the nano adsorbent in three cycles were done. Among kinetics models, our experimental data were more consistent with Hoo kinetic model and for isotherm models, Freundlich isotherm was more consistent. The results show that nanotechnology could increase the performance of adsorbents and enhance the efficiency of the adsorption of cadmium and zinc ions.
J. Cent. South Univ. (2016) 23: 2526-2535
DOI: 10.1007/s11771-016-3313-8
Hoda Kahrizi1, Ali Bafkar1, Masumeh Farasati1, 2
1. Agricultural Faculty, Razi University, Kermanshah, Iran;
2. Agricultural Faculty, Gonbad Kavous University, Gonbad, Iran
 Central South University Press and Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 2016
Central South University Press and Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 2016
Abstract: The effect of nanotechnology on cadmium and zinc removal from aqueous solution was investigated. In order to characterize micro and nano phragmites australis adsorbent, we analyzed the data via FTIR, SEM, PSA, and EDX. The effect of various parameters such as pH, contact time, amount of adsorbent and initial concentration, was investigated. The optimum pH for the removal of cadmium for micro and nano phragmites australis adsorbent was 7, and for the removal of zinc by the micro adsorbent was 7 and by nano adsorbent was 6. The equilibrium time of zinc was 90 min and for the adsorption of cadmium by micro and nano adsorbent were 90 and 30 min, respectively. The optimum dose of micro adsorbent for the removal of cadmium was 0.7 g, and the other dose for the removal of zinc and cadmium was 0.5 g. The evaluation of adsorbent’s distribution coefficient showed that the highest rates of distribution coefficient with initial concentration of 5, 10, 30, and 50 mg/L were 394.83, 587.62, 759.39 and 1101.52 L/kg, respectively, which were observed in nano adsorbent. Desorption experiments for the nano adsorbent in three cycles were done. Among kinetics models, our experimental data were more consistent with Hoo kinetic model and for isotherm models, Freundlich isotherm was more consistent. The results show that nanotechnology could increase the performance of adsorbents and enhance the efficiency of the adsorption of cadmium and zinc ions.
Key words: cadmium; isotherm model; kinetic adsorption; zinc; nanotechnology
1 Introduction
The removal of heavy metal ions from industrial waste water is very important and has attracted the attention of many researchers. Different methods have been used to remove heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions, such as ion exchange, reverse osmosis, electrochemical deposition, ion exchange, membrane processes, evaporation, solvent extraction, and adsorption. Among these methods, in recent years, the adsorption method has been of interest to the soil and water researchers because it is a simple, inexpensive, and effective method for the removal of heavy metal ions [1-2]. Nano adsorbents, because of their high specific surface area, have many adsorption sites because of their high specific surface area. As one of the defining characteristics of nanomaterials, they behave differently from macro structure or microstructure materials. When the particle size of a material is less than a certain size, in addition to the composition and structure of that material, its size will be one of the factors which can affect its properties [3]. Nanotechnology can improve the quality of treated wastewater for reuse in agriculture, water cultivation, and industrial use, even drinking and washing [4]. Many researches have been done on the removal of heavy metals, including HEGAZI [5] using rice husk and ashes as adsorbent; SHAHEEN et al [6] using chitosan (CH), egg shell (ES), organic and mineral salts of potassium (HK), and sugar beets (SBFL) to remove cadmium (Cd), copper (Cu), lead (Pb) and zinc (Zn) from wastewater, the use of agricultural waste; SINGH and KUMAR [7] using low cost natural/ agricultural waste biomasses; EL-SADAAWY and ABDELWAHAB [8] using palm seed coat; MATOUQ et al [9] using isotherm and kinetics models for the removal of heavy metals by moringa pods; SINGHA and GULERIA [10] using modified agricultural waste for toxic heavy metal removal; SMOLYAKOV et al [11] using Humic-modified natural and synthetic carbon adsorbents for removal of Cd. Taking into consideration the above mentioned items, so far, there has been no study on the removal of cadmium and zinc through using phragmites australis nano adsorbents. Thus, in this work the effect of nanotechnology on the adsorption of cadmium and zinc from aqueous solutions was investigated.
2 Methods
To reach the objectives of this work, the experiments were carried out at Faculty of Agriculture,Razi University of Kermanshah, Iran. To prepare the raw material, the phragmites australis plant was obtained from fields in Ahvaz. The phragmites australis were milled and converted to micro and nanometer particles using the Los Angeles mill device. The particles sieved by two sieves No. 30 and 60 (250-600 μm) were determined as micro adsorbent. Then, the samples were dried for 2 h using an oven with a temperature of 70 °C. Morphology specifications were determined by using of particle size analysis, FTIR test, SEM analysis, EDX test, and methylene blue test. All test solutions were artificially prepared using cadmium nitrate salt and zinc sulfate and deionized water.
Batch experiments were carried out at a temperature of (20±2) °C and in a 100 mL flask which was used as a conical flask, containing 40 mL of dissolved metal ions. The initial pH of the ions solutions was changed by adding 0.1 mol/L HCl or 0.1 mol/L NaOH solutions as required. The initial pH of metal solution is an important factor for the adsorption by various adsorbents [12]. The optimum adsorption of cadmium and zinc from aqueous solution was evaluated by using micro and nano adsorbent phragmites australis with dosage of 0.1, 0.3, 0.5, 0.7 and 1 g, with the initial concentration of 5, 10, 30, and 50 mg/L, and with optimum pH and time. During the reaction, the solution was put on a shaker at a speed of 150 r/min. After the reaction time, the solution was filtrated by using a filter paper and the remaining concentrations of cadmium and zinc ions in solution were measured using atomic adsorption devices: model VARIAN 220, made in Italy. Percentage of removal efficiency and the adsorption of cadmium and zinc were, respectively, calculated using
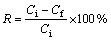 (1)
(1)
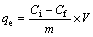 (2)
(2)
where qe is the capacity of equilibrium adsorption (mg/g); Ci is the initial concentration of solute (mg/L); Cf is the remaining concentration of solute (mg/L); m is the dosage of adsorbent (g); V is the volume of solution (L).
2.1 Desorption procedure
For carrying out desorption experiments, 40 mL of 0.1 mol/L hydrochloric acid was added to the optimum amounts of the adsorbent, and they were shaking with the speed of 120 r/min. After passing the optimum time, samples were centrifuged at the speed of 2000 r/min for 15 min and the final concentration of desorption samples was determined. Adsorbents remained from the first stage were reused in the next cycle. Desorption process was carried out over three cycles.
2.2 Isotherm equations
Adsorption isotherms are the equations that show the distribution of adsorbate between the adsorbed phase and the solution phase at equilibrium; adsorption isotherm is considered as a characteristic of a system at a certain temperature. In this work, to evaluate the adsorption of cadmium and zinc, Freundlich and Langmuir adsorption isotherm models were applied and their equations are presented [13-14]:
 (3)
(3)
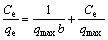 (4)
(4)
where qe is the capacity of equilibrium adsorption (mg/g); Ce is the concentration of ions in the liquid phase at equilibrium (mg/L); Kf is the constant related to the adsorption capacity of the adsorbent (mg/L); qmax is the maximum amount of metal ions adsorbed (mg/g); n is the heterogeneity index which varies between 0 and 1; b is the equilibrium constant of Freundlich isotherm (L/mg). Freundlich isotherm model is an empirical model to explain multilayer adsorption with heterogeneous distribution of energy of the active sites together with the reaction between the adsorbed molecules. Langmuir model explains the monolayer adsorption on the surface of a homogeneous adsorbent without interaction between adsorbed molecules and uniform adsorption energies on the surface. Freundlich distribution coefficient (Kd) is the ratio of the concentration of an element in the solid phase to its concentration in the solution after a given contact time. The distribution coefficient is defined as the concentration of the absorbent at the equilibrium to its concentration in the solution phase [15]. The distribution coefficient is determined as follows [6]:
Q=KdCn-1 (5)
Kd=KdCn-1 (6)
where Q is the adsorbed ion (mg/kg), C is the equilibrium concentration of the solution (mg/g), n is an experimental parameter demonstrating the density of adsorption, and Kd is the distribution coefficient (L/kg).
2.3 Adsorption kinetic equations
To study the control mechanisms for adsorption process, Pseudo 1st-order model [16], Pseudo 2nd-order model [17], the intra-particle diffusion model, and the exponential model were respectively used:
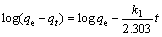 (7)
(7)
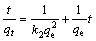 (8)
(8)
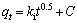 (9)
(9)
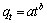 (10)
(10)
where qe is the capacity of equilibrium adsorption (mg/g); qt is the amount of adsorbed ion at time t (mg/g); k1 is the adsorption constant of Pseudo 1st-order model (min); k2 is the constant of Pseudo 2nd-order model (g/(mg·min)); ki is the constant of the intra-particle diffusion equation; C is the intercept of the intra-particle diffusion equation; a and b are the constants of exponential model.
WEBER and MORRIS [18] reported that when qt plot against t0.5 is linear and passes through the starting point, then intra-particle diffusion will be the only mechanism to control the adsorption rate. If intra-particle diffusion equation has a zero intercept, it will be the controller of the adsorption rate at the initial stage of adsorption. But a non-zero intercept shows that the pore diffusion cannot control the adsorption rate and it may be caused due to the difference between mass transfer rate at the early and final stages of adsorption [19].
3 Results and discussion
The results of phragmites australis nano-adsorbent particle size analysis (PSA) are presented in Fig. 1. As shown in Fig. 1, 18.5% of the phragmites australis adsorbent particles with a diameter of less than 51.47 nm were as nanoparticle, and 81.5% of particles with a diameter of less than 406 nm were as nanostructure. According to results, phragmites australis adsorbent was converted to nanostructure, but a percentage of the phragmites australis adsorbent changed into nanoparticle which is more effective in removal of ions.
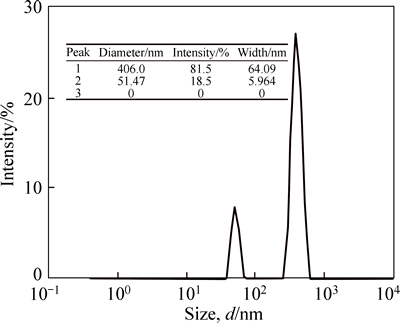
Fig. 1 PSA analysis result of nano particles
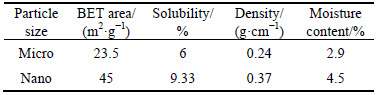
Table 1 shows the results of quantitative analysis of the studied adsorbents using EDX analysis. According to Table 1, micro-structure and nano-adsorbent contain chemical elements of magnesium, sodium, silicon, sulfur, chlorine, calcium, zinc and potassium.
Figure 2 presents the results of morphologic measurement of the micro and nano phragmites australis using SEM analysis. As shown, holes are created in the micro adsorbent that seems to be more coarse which is indicative of the increase in the specific surface area of the adsorbent, heterogeneous distribution of energy on the absorbent’s specific surface area, and better adsorption of ions. The surface of the nano phragmites australis adsorbent is softer and smoother, which indicates the removal of its impurity and a better ability to absorb ions. Based on Fig. 2, nanoparticles tend to form a lump. After the formation of a lump by the nanoparticles, their size is altered and this factor depends on the amount of adsorbent in the solution [20]. Taking into account the results of SEM analysis, nano phragmites australis adsorbent is expected to be more effective in the adsorption of cadmium and zinc.
Table 1 Selected properties of studied absorbent
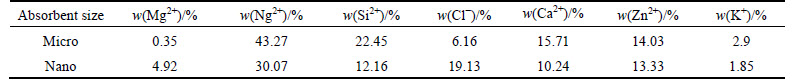
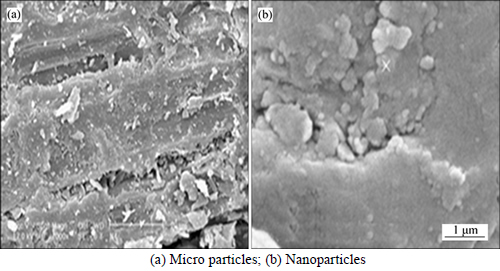
Fig. 2 SEM images of phragmites australis:
FTIR test was used to determine the functional groups in each type of the adsorbent (Fig. 3). Based on Fig. 3, the peak in the wave numbers 1069.93 and 1061.33 cm-1 related to (C—O) link are attributed to micro and nano phragmites australis adsorbent. In addition, the vibrational frequency of the wave numbers 2919.81 and 2921.28 cm-1 can be attributed to (C—H) link vibrations. Given the links shown in the spectrum of IR, FTIR analysis confirms the existence of functional groups in the structure of adsorbents links. Thus, considering the results of FTIR test, micro-phragmites australis adsorbent is expected to play an important role in the adsorption of cadmium and zinc.The specific surface areas of each adsorbent used in this work were calculated using methylene blue adsorption method and the results are presented in Table 2. As shown in Table 2, due to increased porosity and the smaller structures, the specific surface areas in nano scale were larger than those in the micro-adsorbents. By comparing the specific surface areas of micro and nano phragmites australis adsorbent (23.5 and 45 m2/g), nano-adsorbent had a more specific surface area, which increased the adsorption capacity of this adsorbent. Moreover, micro-phragmites australis adsorbent had smaller specific surface area than other studied adsorbents, because of its smaller porous structure and larger pores. Similar results have been obtained by other researchers [21].
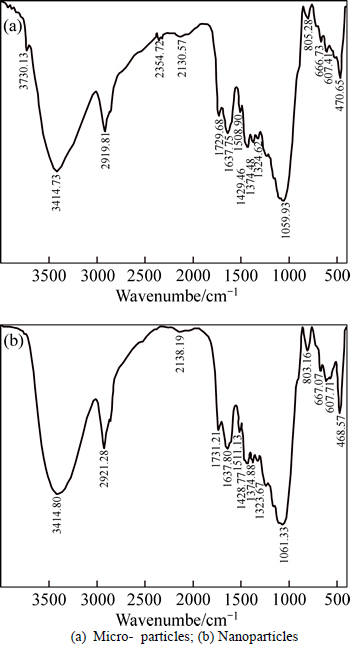
Fig. 3 FTIR spectra of raw phragmites australis:
Table 2 Basic physiochemical properties of phragmites australis
3.1 Effect of initial pH test
To find the optimum pH for the adsorption, 0.5 g of the adsorbent was poured in a flask containing 40 mL metal solution with a concentration of 10 mg/L. Then, its pH was set in the range of 3-7 (3, 4, 5, 6, and 7) and was put on a shaker for 120 min at a speed of 150 r/min (Fig. 4).
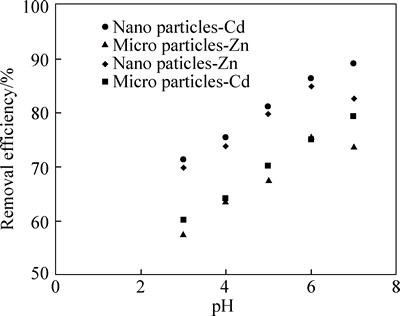
Fig. 4 Effect of pH on adsorption of Cd and Zn ion by micro and nano phragmites australis (Cd and Zn initial concentration: 10 mg/L; adsorbent loading: 0.5 g; adsorption time: 90 min)
As shown in Fig. 4, with increasing pH of the solution from 3 to 6 in micro-phragmites australis adsorbent, zinc removal efficiency increased from 57.86% to 75.53%, but at pH=7 the removal efficiency reduced to 73.95%. With increasing pH of the solution from 3 to 6 in phragmites australis nano adsorbent, zinc removal efficiency increased from 69.86% to 84.95%, however at pH=7 the removal efficiency decreased to 82.53%. With increasing pH, cadmium adsorption efficiency by micro and nano adsorbent showed a continuous and gradual increase. For cadmium, with increasing pH of the solution from 3 to 7, cadmium removal efficiency increased from 60.24% to 71.24%, 79.33%, and 89.10%, respectively. The maximum zinc removal efficiency by nano-adsorbent was 84.95 at pH=6 and the maximum cadmium removal efficiency by nano-adsorbent was 89.10 at pH=7. At low pH, the increase of H+ increases the competition between H+ and dissolved cations and H+ will be adsorbed instead of cadmium and zinc, which consequently declines the absorption of ions [22]. With the increase in pH, due to the increased amount of OH-, the adsorption of zinc and cadmium increases and with a reduction in the concentration of H+, negative charge on the surface of the adsorbent increases, resulting in increased adsorption of zinc and cadmium [8].
At pH greater than 6, zinc was sediment on the surface of the adsorbent and its adsorption slightly decreased. At acidic pH, the adsorption capacity of the adsorbents was low and with increasing pH values adsorption increased; similar results have been obtained by other researchers [3, 23-24]. Hence, the optimum pH for the adsorption of zinc and cadmium are 6 and 7, respectively. Among the studied scales for the phragmites australis adsorbent, nano-adsorbent, due to its large specific surface area, had more capacity to remove cadmium and zinc. To determine the pH at zero charge, the range of pH was determined to be between 2 and 8 (Fig. 5).
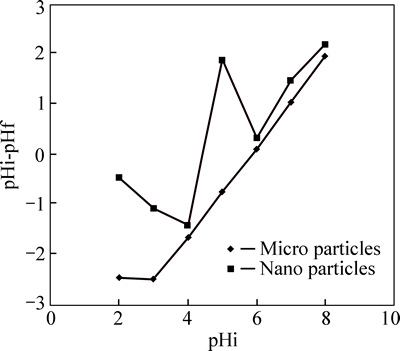
Fig. 5 Point of zero charge (PZC)
The pHpzc was 5.9 in micro adsorbent. The pHpzc value is approximately equal with optimum pH, indicating the increase in the interaction between the adsorbent and adsorbate. The pHpzc for nano adsorbent was 4.42. Hence, at pH 5 and 6, the surface of the nano adsorbents was negative and because of the interaction between negative charges and the positively charged surface of zinc, zinc adsorption was negative, while for cadmium adsorption at pH 5, 6 and 7, the surface of adsorbent was negatively charged. Since the pH of nano adsorbent used in experiments was larger than the pH value at zero charge, the optimum level of pH for the adsorption was satisfactory and the adsorbent surface tended to adsorb cations. Therefore, with increasing the pH, the electrostatic interactions between positive charge of ions and negative charge of adsorbent’s surface increased and thereby increased the adsorption of cadmium and zinc.
3.2 Effect of contact time
Figure 6 shows the changes in the cadmium and zinc adsorption efficiency over the time, in the optimum pH of 6 and 7, with an initial concentration of 10 mg/L in metal solution, 0.5 g of micro and nano adsorbent. In order to determine the equilibrium time, experiments were carried out in different contact times of 10, 30, 60, 90 and 120 min. As shown in Fig. 5, in micro and nano adsorbent, with increasing the contact time from 10 to 90 min, zinc adsorption efficiency increased from 70.50% and 79.56% to 78.32% and 91.67%, respectively; however, with the passing of time, the rate of adsorption become almost fixed. As a result, the equilibrium time for the optimum removal of zinc using phragmites australis adsorbent was 90 min. In micro adsorbent, with increasing the contact time from 10 to 90 min, cadmium adsorption efficiency increased from 71.78% to 84.33%, and then, with the passing of time, adsorption efficiency become almost fixed. In nano adsorbent, with increasing the contact time from 10 to 30 min, cadmium adsorption efficiency increased from 84.79% to 94.54%, and when the timed passed 120 min, adsorption efficiency become too low. Thus, the equilibrium time for the removal of zinc by micro and nano adsorbent was 90 min, while for the removal of cadmium by micro adsorbent, it was 90 min and by nano adsorbent, it was 30 min. Putting zinc and cadmium in contact with the studied adsorbents after the equilibrium time had a little effect on the rate of adsorption. This phenomenon can be attributed to the completion of the capacity of the studied adsorbents. After the saturation of absorption, the rate of cadmium and zinc adsorption from the solution declined, the solid and liquid phases almost reached equilibrium, and the cadmium and zinc absorption rate become equal to the rate of adsorbents’ ions that returned into the solution. These findings are in line with the results of a study by FARASATI et al [23]. According to the results, cadmium absorption efficiency is more than zinc adsorption efficiency. The results of this work are consistent with the findings of other researchers [25]. In addition, among the studied adsorbents, the nano adsorbent was more efficient for the removal of cadmium and zinc; it is probably due to the presence of larger specific surface area and more adsorption sites on the surface of the nano absorbent than micro adsorbent.
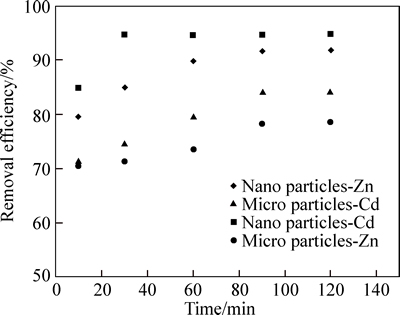
Fig. 6 Effect of contact time on adsorption of Cd and Zn ion by micro and nano phragmites australis (Cd and Zn initial concentration: 10 mg/L; adsorbent dosage: 0.5 g; pH=7, 6)
3.3 Effect of adsorbent dosage on cadmium and zinc removal
In the experiment, different amounts of micro and nano adsorbents (0.1, 0.3, 0.5, 0.7, and 1 g in 40 mL of solution) with an initial concentration of 10 mg/L in solution phase were used at equilibrium time of 90 min, and at pH=6 for the adsorption of zinc; moreover, they were also used at an equilibrium time of 30 min, and at pH=6 and pH=7 for the adsorption of zinc and cadmium so as to evaluate the efficiency of adsorption. Figure 7 shows the effect of adsorbent dosage on the removal of zinc and cadmium by micro and nano adsorbent straw. As shown in Fig. 7, in micro and nano adsorbent with a mass of 0.5 g, the maximum adsorption of zinc was 78.32% and 88.10%; with increasing adsorbent mass from 0.5 to 1 g, adsorption efficiency increased from 78.48% to 88.42%. In micro adsorbent, with an increase in adsorbent from 0.1 to 0.7 g, the efficiency of cadmium adsorption increased from 72.66% to 83.33%, and with further incase in adsorbent dosage, a little change in adsorption was observed. With an increase of nano-adsorbent from 0.1 to 0.5 g, cadmium adsorption efficiency increased from 80.62% to 90.54%, which was due to its larger specific surface area available for the adsorption of cadmium with fixed initial concentration. However, with an increase of adsorbent mass from 0.5 to 1 g, the removal efficiency became almost fixed. Thus, 0.5 g of nano-adsorbent is enough to remove cadmium and zinc with the concentration of 10 mg/L. With the increase of adsorbent dosage, the adsorption efficiency was increased because it led to an increase in specific surface area and the number of adsorption locations. When nano adsorbent dosage exceeded 0.5 g, the removal of zinc and cadmium was too low, thus increasing the mass of adsorbent did not increase the rate of cadmium and zinc removal. Moreover, the highest zinc adsorption efficiency was obtained when the mass of adsorbent micro was 0.7 g. Thus, the increase in the adsorbent mass did not have a significant effect on the zinc adsorption efficiency; this finding might be attributed to the saturation of the adsorption sites of phragmites australis. With increasing adsorbent mass, the percentage of zinc and cadmium removal did not increase because the concentration of zinc and cadmium in adsorbent was equal to their concentration in the solution and equilibrium was reached. THAVAMANI and RAJKUMAR [26] also reported the increase in the adsorption per unit of increase in adsorbent dosage; it could be due to two reasons: firstly, too much adsorbent effectively reduces unsaturated adsorption sites and consequently the number of sites per unit of mass decreases; it leads to lower rates of adsorption at the presence of large quantities of adsorbent. Secondly, high amounts of adsorbent form lumps of particles, which reduces the total surface area and increases the length of the diffusion path, both of which reduce the absorption rate per unit of adsorbent mass. According to the results, with an increase in the amount of absorbent, the absorption of cadmium increased more than zinc adsorption. As a result, nano adsorbent phragmites australis has a high potential for the removal of cadmium. Moreover, when comparing micro and nano adsorbent, it was found that nano adsorbent had a greater capacity for the adsorption of cadmium and zinc.
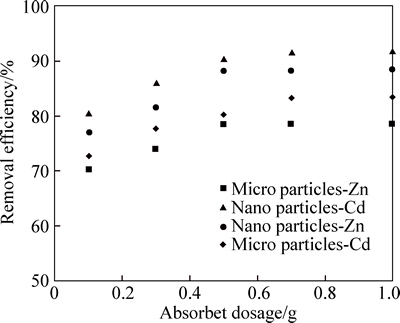
Fig. 7 Effect of adsorbent dosage on removal of Cd and Zn by micro and nano phragmites australis (Cd and Zn initial concentration: 10 mg/L; pH=7, 6; agitation time: 90 min)
Figure 8 shows the changes in the initial concentration of cadmium and zinc which were caused by micro and nano phragmites australis adsorbent with initial concentrations of 5, 10, 30 and 50 mg/L, 0.5 and 0.7 g of adsorbent, and at pH=6 and pH=7. In the initial concentration of 5 mg/L, the adsorption efficiency of micro and nano adsorbent, respectively, were 80.51% and 91%, but with an increase in initial concentration from 5 to 10, 30 and 50 mg/L, the efficiency of zinc adsorption by micro adsorbent changed to 72.84%, 66.12% and 55.48%, respectively, and using nano- adsorbent it deceased to 85.48%, 80.1% and 72.46%, respectively. The cadmium absorption efficiency in concentrations of 5, 10, 30 and 50 mg/L using micro adsorbent straw was 84.51%, 78.84%, 71.12% and 65.48%, respectively, while using nano adsorbent, it was 94.92%, 88.53%, 84.23% and 75.78%, respectively. With the increase in initial concentrations, the efficiency of cadmium and zinc removal was decreased, which might be due to the fill of adsorbent sites which are required for the adsorption of cadmium and zinc; consequently, it can lead to the reduction of adsorption in high concentrations. According to Fig. 8, the reduction of the efficiency of zinc adsorption was faster than the reduction in cadmium adsorption efficiency. When testing the effects of initial concentrations of zinc and cadmium on the adsorption, it was found that due to use of fixed amount of the adsorbent, there is a large specific surface area and many adsorption sites, hence the metal ions are able to utilize the available adsorption sites and interact with the adsorbent surface and consequently increase adsorption efficiency. In higher concentrations, due to the saturation of adsorption sites, the adsorption efficiency decreases [26]. The results of this work also confirm this finding; with increasing the initial concentration of zinc and cadmium, adsorption efficiency decreased.
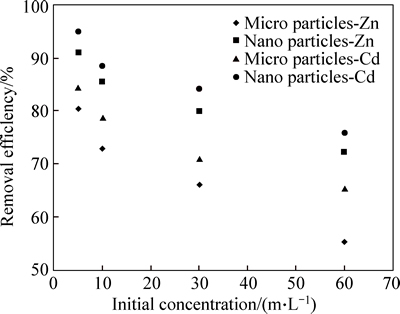
Fig. 8 Effect of initial concentration on removal of Cd and Zn by micro and nano phragmites australis (adsorbent dosage: 0.5 g; pH:7, 6; contact time: 90 min)
3.4 Desorption time
Figure 9 shows the changes in desorption of cadmium and zinc in the three desorption cycles. In the first stage of desorption, the cadmium and zinc desorption efficiencies, respectively, were 58.23% and 62.67%, in the second stage of desorption they were 4% and 3.3%, respectively, and in the third cycle they were 0.3% and 2.2%, respectively. The results have shown that the speed of the cadmium and zinc desorption in the first stage was very high and the largest amounts of cadmium and zinc were removed from the adsorbent. Desorption efficiency was reduced a lot in the second and third stages. Desorption efficiency of zinc was more than the desorption efficiency of cadmium.
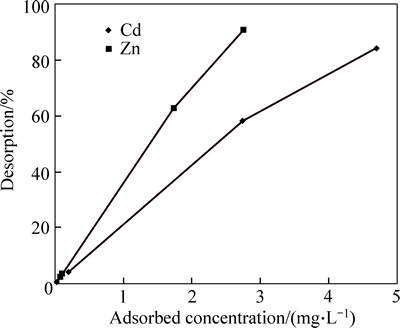
Fig. 9 Desorption of Cd and Zn ions by using nanoparticles
3.5 Evaluation of cadmium and zinc adsorption isotherms
We determined the relationship between final concentration of the solution and adsorption capacity of micro and nano adsorbent at initial concentrations of 5, 10, 30 and 50 mg/L, with a mass of 0.5 and 0.7 g. Figure 10 shows the results of nano adsorbent, as an example. Considering the coefficient values of 0.97 and 0.85 for cadmium and zinc, respectively, which are shown in Fig. 8, it can be concluded that nano adsorbent removed more cadmium than zinc. Langmuir isotherms for the adsorbents under the study were determined, and the results for nano adsorbent are shown in Fig. 10.
Langmuir isotherm equation for cadmium was Ce/qe=-0.3374Ce+1.8797 and for zinc was Ce/qe= -3.3387Ce+13.44 (Fig. 11). Maximum exchange capacities for cadmium and zinc, respectively, were 8 and 6.3 mg/g, which indicated the high capacity of nano absorbent for cadmium removal. Moreover, b values for cadmium and zinc, respectively, were 0.07 and 0.25 L/mg, and due to the positive values of b parameter in all the results, this coefficient was always between zero and one. The values of R2 for cadmium and zinc ions, respectively, were 0.69 and 0.63, which were very low. According to the results, Langmuir isotherm was not much consistent with the adsorption data; thus it was not a suitable isotherm.
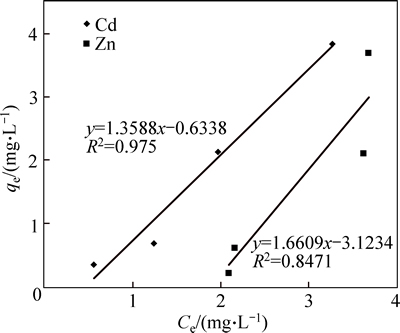
Fig. 10 Relationship between final concentration values and adsorption capacity
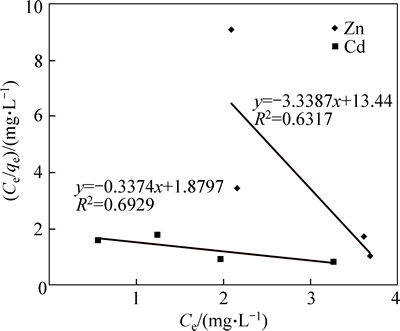
Fig. 11 Langmuire isotherm of Cd and Zn
Figure 12 shows the results of Freundlich isotherm for the nano adsorbents. As shown, the values of R2 for cadmium and zinc, respectively, were 0.96 and 0.86, which indicated a high correlation between the data for both metals, particularly cadmium. The values of Freundlich coefficient n for cadmium and zinc, respectively, were 0.70 and 0.26. The values of n were less than one, which indicated a desirable level of adsorption. In Freundlich model, with increasing Kf, the adsorption capacity increased. The values of Kf were 2.71 and 1.33. High value of Kf represents an increase in the capacity of nano adsorbent for the adsorption of cadmium, which was more than that for the adsorption of zinc. According to the results, Freundlich isotherm was more consistent with the adsorption data. Freundlich isotherm indicated that the surface of the adsorbent was heterogeneous and the adsorption was multi-layered. Considering the coefficients of determination in Langmuir isotherm and Freundlich model, the adsorption data were consistent with Freundlich model; this finding is in line with the results of a study by ANIRUDHAN and SREEKUMARI [27].
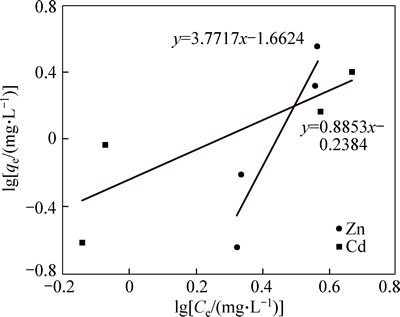
Fig. 12 Freundlich isotherm of Cd and Zn
Figure 13 shows the effects of the initial concentration of cadmium and zinc on the distribution coefficient. According to Fig. 12, the highest values of the distribution coefficients were obtained at initial concentrations of 5, 10, 30 and 50 mg/L and they were equal to 394.83, 587.62, 759.39 and 1101.52 L/kg which were observed in nano adsorbent. According to the results, at the initial concentrations of 5, 10, 30 and 50 mg/L, the distribution coefficient of cadmium was more than that in zinc; it shows that cadmium was more adsorbed by micro and nano adsorbent; moreover, its final concentration in the solution was reduced. Furthermore, the distribution coefficient of cadmium adsorption by nano adsorbent was more than that by micro adsorbent, which indicated higher adsorption of cadmium by nano adsorbent.
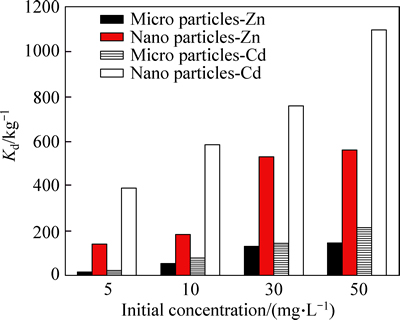
Fig. 13 Relationship between initial concentration values and distribution coefficient
3.6 Fitting of cadmium and zinc adsorption kinetics models by micro and nano adsorbent
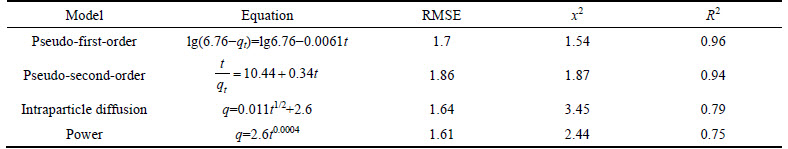
The cadmium and zinc ions adsorption kinetics experiments were carried out using micro and nano adsorbent; the results of experiments using nano adsorbent are presented in Table 3 and 4.
According to Tables 3 and 4, the adsorption capacities of cadmium and zinc calculated by Pseudo- first-order model were 2.34 and 6.76 mg/g and they were more than the adsorption capacities obtained from the experiments which were 8.42 and 10.62 mg/g. The adsorption capacities calculated by Pseudo-second-order model to remove cadmium and zinc using nano- adsorbent straw were 9.76 and 11.96 mg/g, respectively, which were closer to the capacities obtained from the experiments. According to Table 3 and 4, for both adsorbents, the regression equation derived from the intra particle diffusion model had a non-zero intercept (q plot against t0.5 was not linear), hence the intra-particle diffusion model alone did not control the initial adsorption velocity mechanism, and the mass adsorption mechanism and intra-particle diffusion occurred simultaneously. Comparison of R2 and RMSE of the models showed that the exponential model (R2 was equal to 0.74 and 0.74, RMSE was equal to 1.92 and 1.62, and x2 was equal to 2.04 and 2.42) had the highest error among the studied models, and Pseudo-second-order model with the highest coefficient of determination and the lowest error (R2 was 0.92 and 0.96, RMSE was 0.51 and 1.71, and x2 was 1.61 and 1.54) was the best model and the adsorption data were consistent with Pseudo- second-order model. The results of this work are in line with the results of ANIRUDHAN and SREEKUMARI [27].
Table 3 Different kinetic models for Zn adsorption by micro particles (Concentration: 50 mg/L; dosage: 0.5 g/40 mL; pH=6)
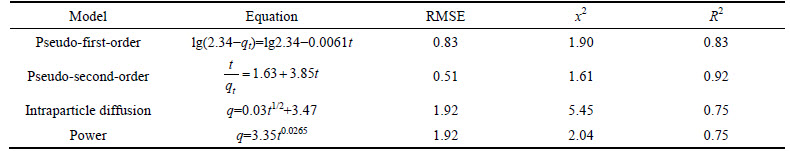
Table 4 Different kinetic models for Cd adsorption by nano particles (Concentration: 50 mg/L; dosage: 0.5 g/40 mL; pH=7)
4 Conclusions
1) The maximum cadmium adsorption was obtained at pH=7, and the maximum zinc adsorption using micro- and nano-adsorbents, respectively, were obtained at pH=7 and pH=6.
2) The optimum contact time for cadmium adsorption using micro- and nano-absorbents, respectively, were 90 and 30 min, while for zinc adsorption using micro and nano absorbents it was 90 min.
3) The optimum dosage of micro absorbent for the removal of cadmium was 0.7 g while for other adsorbents used for the removal of zinc and cadmium it was 0.5 g.
4) With increasing the initial concentrations of cadmium and zinc, the adsorption efficiency was reduced.
5) The maximum efficiency of cadmium and zinc desorption using nano adsorbent phragmites australis was observed in the first cycle.
6) The adsorption process was consistent with the results of Freundlich isotherm and Pseudo-second-order kinetic model.
7) According to the results, the use of adsorbent phragmites australis to remove cadmium and zinc from aqueous solution is a low cost technology and is promising for the treatment of wastewater and reuse of waste products.
8) The use of nanotechnology has been able to increase the performance of adsorbents and enhance the efficiency of the removal of cadmium and zinc ions.
References
[1] OZCAN A, TUNALI S, AKAR T, KIRAN I. Determination of the equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic parameters of adsorption of copper(II) ions onto seeds of Capsicum annuum [J]. Journal of Hazard Mater, 2005, 124: 200-208.
[2] PRASAD M, SAXENA S. Sorption mechanism of some divalent metal ions onto low-cost mineral adsorbent [J]. J Ind Eng Chem Res, 2004, 43: 1512-1522.
[3] WANG F Y, WANG H, MA J W. Adsorption of cadmium(II) ions from aqueous solution by a new low-cost adsorbent Bamboo charcoal [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2010, 177: 300-306.
[4] AYATI B, DELNAVAZ M, FARTOOS S. Evaluation of nanoparticle technology in environmental engineering [D]. Tehran: University of Amirkabeer, 2006.
[5] HEGAZI H A. Removal of heavy metals from wastewater using agricultural and industrial wastes as adsorbents [J]. HBRC Journal, 2013, 9: 276-282.
[6] SHAHEEN M S, FAWZY I E, KHALED M G H, HALA M G. Heavy metals removal from aqueous solutions and wastewaters by using various byproducts [J]. Journal of Environmental Management 2013, 128: 514-521.
[7] SINGHA B, KUMAR DAS S. Adsorptive removal of Cu(II) from aqueous solution and industrial effluent using natural/agricultural wastes [J]. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 2013, 107: 97-106.
[8] EL-SADAAWY M, ABDELWAHAB O. Adsorptive removal of nickel from aqueous solutions by activated carbons from doum seed (Hyphaenethebaica) coat [J]. Alexandria Engineering Journal, 2014, 53: 399-408.
[9] MATOUQ M, JILDEH N, QTAISHAT M, HINDEYEH M, AL SYOUF M Q. The adsorption kinetics and modeling for heavy metals removal from wastewater by Moringa pods [J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2015, 608: 1-10.
[10] SINGHA A S, GULERIA A. Utility of chemically modified agricultural waste okra biomass for removal of toxic heavy metal ions from aqueous solution [J]. Engineering in Agriculture, Environment and Food, 2015, 8(1): 52-60.
[11] SMOLYAKOV B S, SAGIDULLIN A K, BYCHKOVB A L, LOMOVSKY I O, LOMOVSKY O I. Humic-modified natural and synthetic carbon adsorbents for the removal of Cd(II) from aqueous solutions [J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2015, 3: 1939-1946.
[12] SEN T K, GOMEZ D. Adsorption of zinc (Zn2+) from aqueous solution on natural bentonite [J]. Desalination, 2011, 267: 286-294.
[13] LANGMUIR I. The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum [J]. J Am Chem Soc, 1918, 40: 1361-1368.
[14] FREUNDLICH H. Adsorption in solution [J]. Phys Chem Soc, 1906, 40: 1361-1368.
[15] SHAHEEN S M, TSADILAS C D, MITSIBONAS T, TZOUVALEKAS M. Distribution coefficient of copper in different soils from egypt and Greece [J]. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 2009, 40: 214-226.
[16] LAGERGREN S. Zur theorie der sogenannten adsorption geloster stoffe [J]. Kungliga Svenska Vetenskapsakademiens Handlingar, 1898, 24: 1-39. (in German)
[17] HO Y S, MCKAY G, WASE D A J, FOSTER C F. Study of the sorption of divalent metal on to peat [J]. Adsorpt Sci Technol, 2000, 18: 639-650.
[18] WEBER W J, MORRIS J C. Kinetics of adsorption on carbon from solution [J]. J Sanit Eng Div Am Soc Civ Eng, 1963, 89: 31-60.
[19] HAMEED B H, EL-KHAIARY M I. Equilibrium, kinetics and mechanism of malachite green adsorption on activated carbon prepared from bamboo by K2CO3 activation and subsequent gasification with CO2 [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2008, 157: 344-351.
[20] JAGUARIBE E F, MEDEIROS L L, BARRETO M C S, ARAUJO L P. The performance of activated carbons from sugarcane bagasse, and coconut shells in removing residual chlorine [J]. Brazilian Jowrnal of Chemical Engineering, 2005, 22(1): 41-47.
[21] AFKHAMI A, TEHRANI M S, BAGHERI H. Simultaneous removal of heavy-metal ions in wastewater samples using nano-alumina modified with 2, 4-dinitrophenylhydrazine [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2010, 181: 836-844.
[22] BESTANI B, BENDERDOUCHE N, BENSTAALI B, BELHAKEM M, ADDOU A. Methylene blue and iodine adsorption onto an activated desert plan [J]. Bio Resource Technology, 2008, 99: 8441-8444.
[23] FARASATI M, SEYEDIAN M, BOROOMANDNASAB S, JAAFARZADEH N, MOAZED H, GHAMARNIA H. Batch and column studies on the evaluation of micrometer and nanometer Phragmites australis for nitrate removal [J]. Desalination and Water Treatment, 2013, 51: 28-30.
[24] GUPTA S S, BHATTACHARYA K G. Immobilization of Pb (II), Cd (II) and Ni (II) ions on kaolinite and montmorillonite surfaces from aqueous medium [J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2008, 87: 46-58.
[25] KUMAR U, BANDYOPADHYAY M. Sorption of cadmium from aqueous solution using pretreated rice husk [J]. Bio Resource Technology, 2006, 97(1): 104-109.
[26] THAVAMANI S H, RAJKUMAR S R. Removal of Cr(VI), Cu(II), Pb(II) and Ni(II) from aqueous solutions by adsorption on alumina [J]. Research Journal of Chemical Sciences, 2013, 3(8): 44-48.
[27] ANIRUDHAN T S, SREEKUMARI S. Adsorptive removal of heavy metal ions from industrial effluents using activated carbon derived from waste coconut buttons [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2011, 23(12): 1989-1998.
(Edited by YANG Bing)
Received date: 2015-08-18; Accepted date: 2015-12-19
Corresponding author: Masumeh Farasati; Tel: +98-33581712; E-mail: farasati2760@gmail.com

